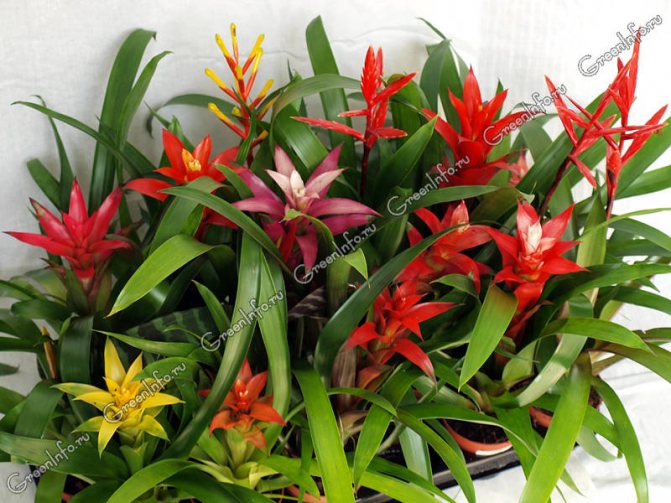
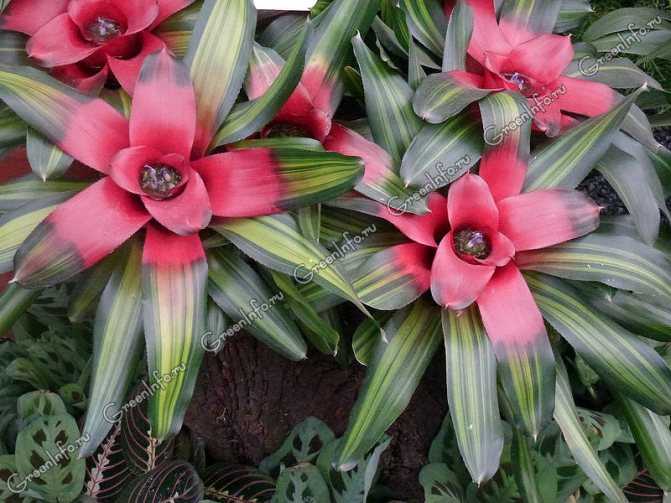
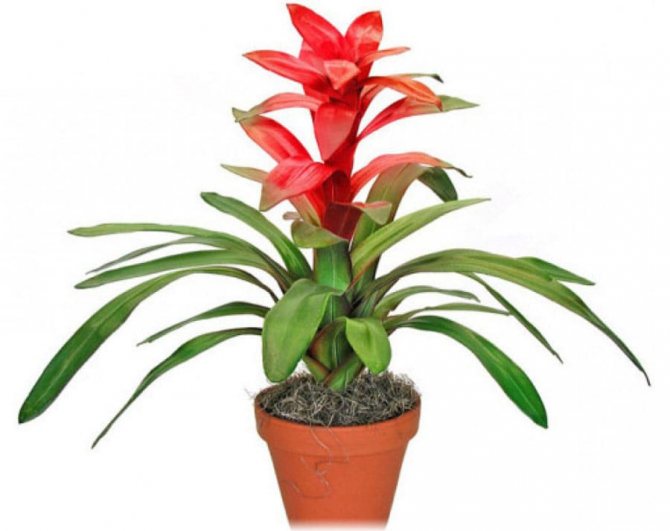
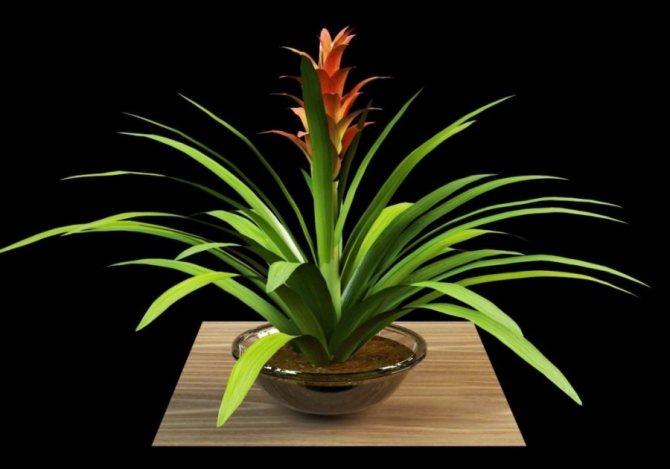
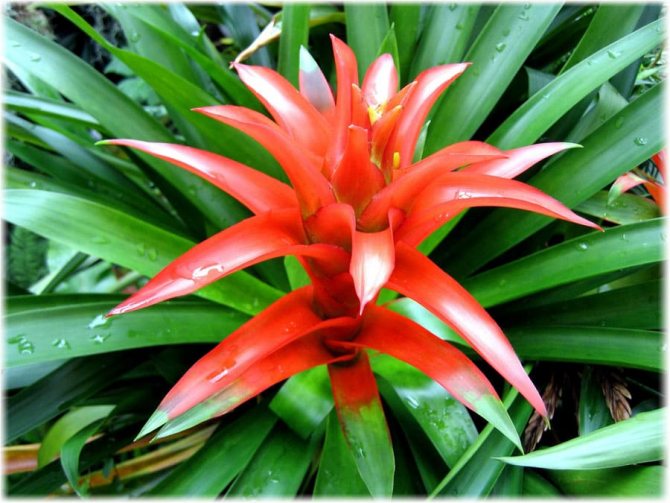
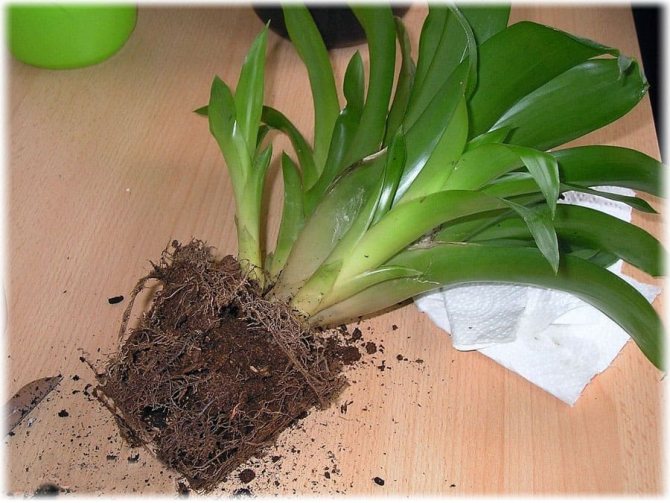
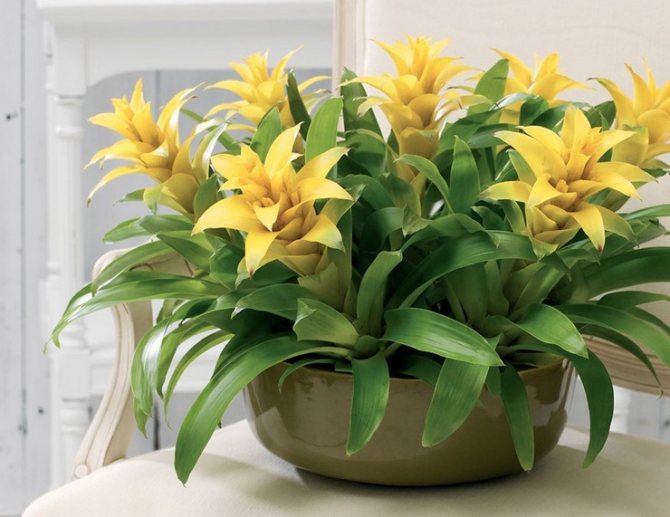
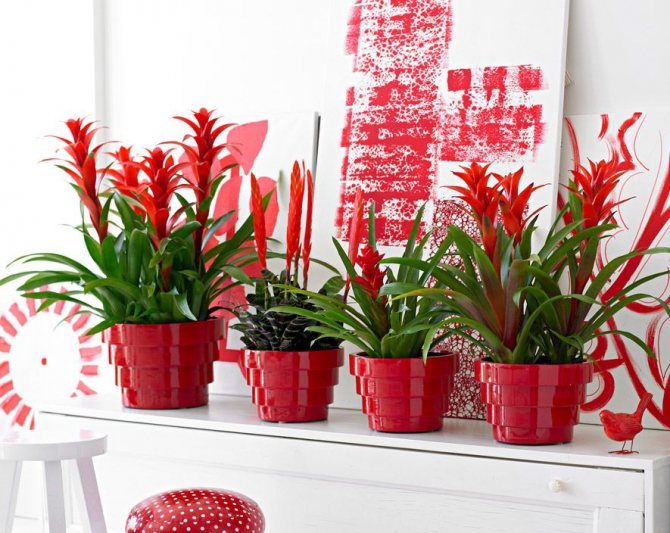
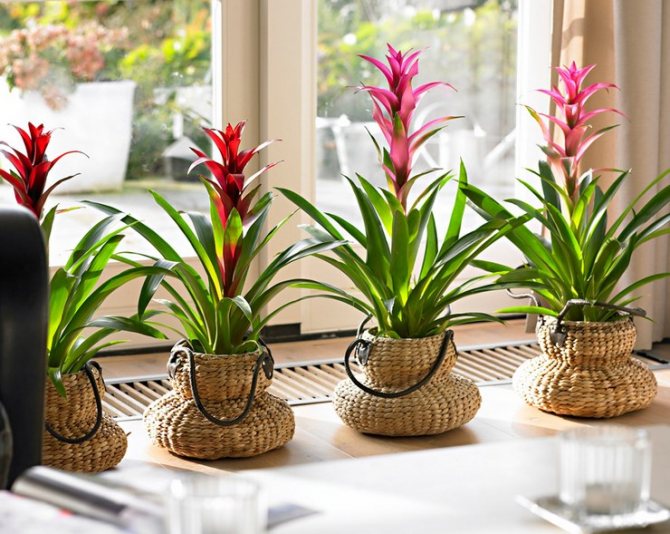
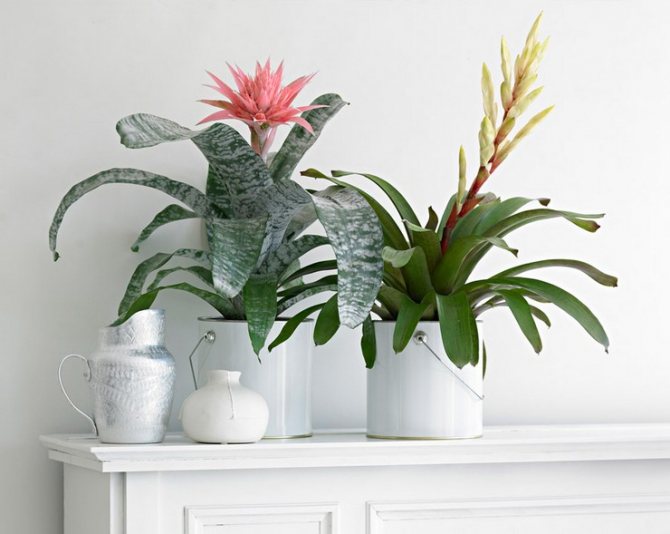
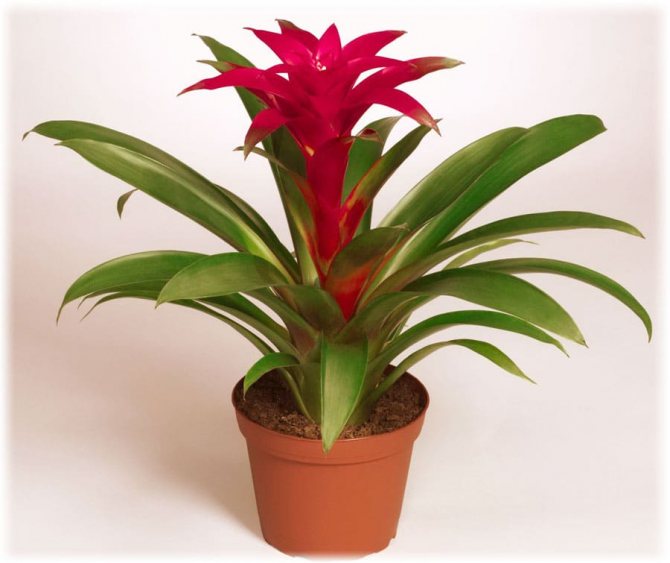
Often, very little is known about the plants that have settled in our home, especially if they were presented as a gift. A very large group of indoor flowers is sometimes mistakenly called one word "bromeliad". Taking care of them at home is extremely simple, which is why guests from the South American tropics are highly popular. Let's learn in more detail about bromeliads, as well as some of the intricacies of their cultivation.
Family bromelet
For the first time, Columbus's associates encountered its representatives. The bromeliad flower is native to the tropical forests of South America. In 1805, all the data available at that time were summarized by Saint-Hilaire (a French biologist). Now the family has about 2.5 thousand species. An impressive part of them are epiphytes, they grow on trees and have a sufficient supply of moisture in the axils of the leaves.
If we regard representatives of bromeliads as home flowers, then they are not too demanding on the conditions of detention. The only subtlety is proper watering and maintaining the right humidity and air temperature.
Calling plants bromeliad, as a rule, means one of the representatives of the genus of the same name. In total, it includes about 50 species. All of them are grasses growing on the ground, with a rosette of hard leathery leaves and flowers, collected in an inflorescence panicle or head. A family includes a certain number of genera. We will learn in more detail about the most common in our houses and apartments. All of them are sometimes called simply "bromeliads" by mistake.
Growing problems
Bromeliad will grow well if all of the above rules and conditions of detention are observed. Unfortunately, if gardeners do not pay enough attention, it comes to serious problems.
- Excessive sun exposure leads to burns in the form of gray spots on the leaves.
- With high humidity, or low temperatures, the leaves of the flower darken and dry.
Pests
If the rules are not followed, the plant gets sick and weakens, which leads to an attack by such pests as: spider mites, thrips, scale insects, mealybugs.
Rod bilbergia
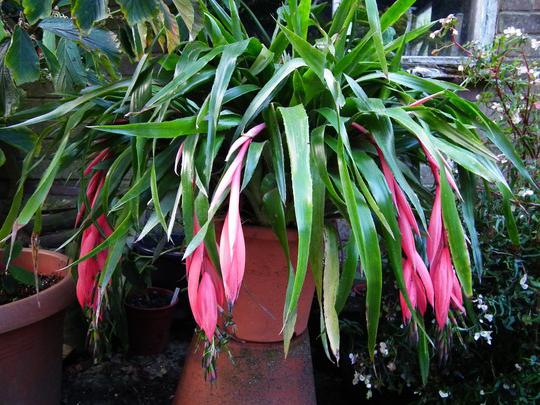

The group of plants received its generic name in honor of the Swedish botanist, in total there are about 60 species. In the culture of indoor floriculture, the most common bilbergia drooping, which also served as the source material for breeding many hybrids and varieties. Leathery leaves reach 70 cm in length and form a dense rosette, like other bromelets. Also in stores you can often find Winda bilbergia, pale-flowered, pyramidal (pictured above), Brazilian, etc.
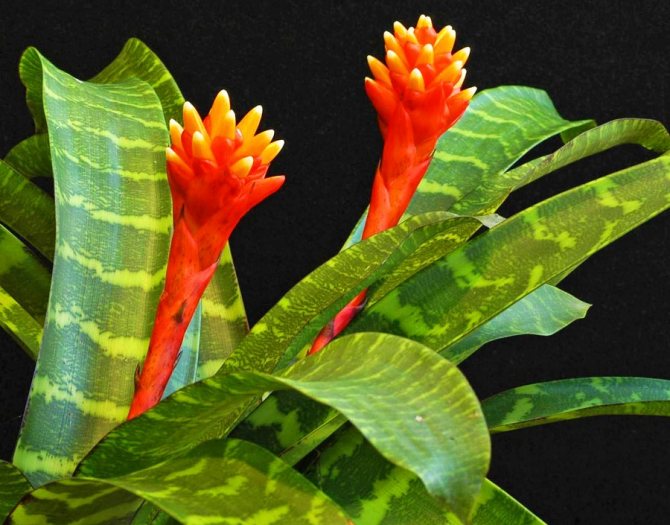
Guzmania (guzmania): description of the plant and flower
What is Guzmania? Bromelia Guzmania is an epiphytic flower. Like other relatives, root nutrition is obtained from the air. The main differences from them:
- colorful bracts. They are red, orange, yellow, purple;
- a characteristic feature - after flowering, the plant dies.
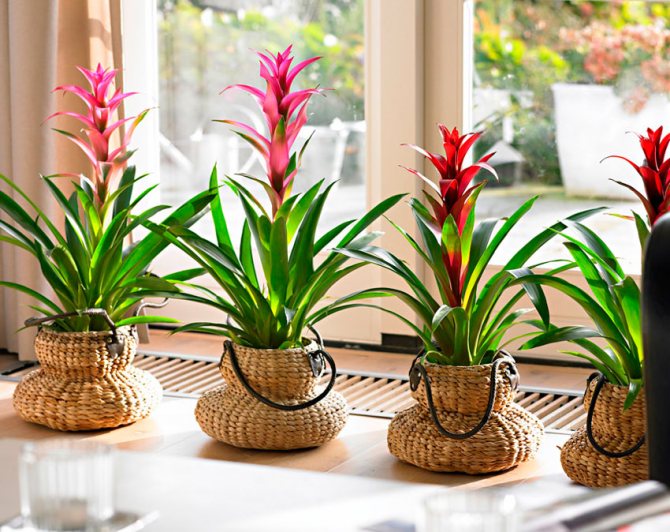


Guzmania
Description of popular types of guzmania, adapted for indoor breeding
For home content, they try to choose compact varieties of guzmania. The most demanded ones:
- reed guzmania is a large flower with half-meter leaves. The rosette of the plant is dense.Peduncle red or orange, small white flowers;
- Minor is a hybrid of reed Guzmania. The plant is compact, blooms from late winter to early autumn. Its bracts are red, flowers are white and few;
- hybrid Tempo. It differs from Minor only in size, it is larger;
- hybrids Mix. A lot of them. They differ in the colors of the panicles;
- Guzmania Nicaraguan. Compact version. The rosette consists of long, densely folded leaves. Spike inflorescence is light red. The flowers are bright yellow;
- Guzmania Konifer. Large-sized flower with a high red-yellow inflorescence;
- Donell-Smith's guzmania. The inflorescence is dense, paniculate. The flowers are bright yellow. Sepals are bright red;
- one-headed. Very decorative rosette. Its long leaves from bottom to top change their shade from light green to green-yellow. The peduncle also changes color from green to red (scarlet, orange). The flowers themselves are white;
- Ostara is a hybrid of Reed Guzmania and Guzmania Witmackii. Long blooming epiphyte with burgundy bracts;
- Tricolor. It is distinguished by the beauty of the striped leaves. There are clear red and white stripes on a green background. Flowers are yellowish, inconspicuous.
Care features
Guzmania prefers temperatures between 18 ° C and 25 ° C and lacy shade.
Watering is carried out as the soil dries up. Warm water is needed. Spraying is encouraged. Desired air humidity 60-85%.
The soil is loose, lightweight. A mixture for orchids will be optimal. A third of the pot's volume should be filled with drainage material. A ceramic shallow pot will do.
Does not need constant feeding.
Note! Can be fertilized to speed up flowering. Fertilizers are suitable for orchids. The dosage should be halved.
Genus vriese
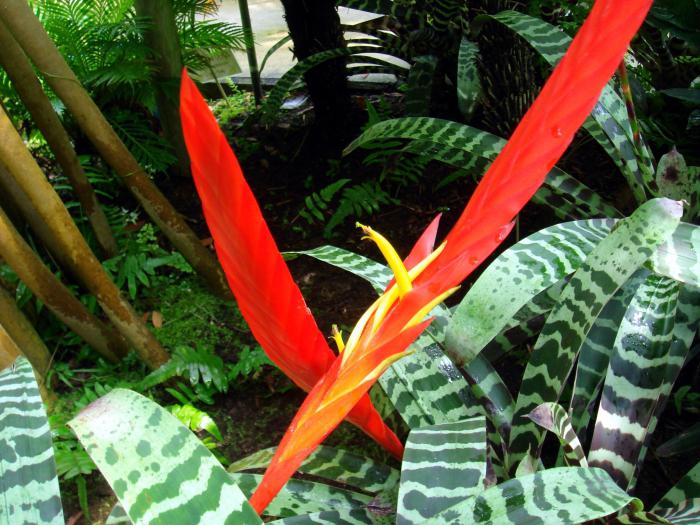


It includes a fairly large number of species - about 250 terrestrial and epiphytic plants, and 150 of them are cultivated in indoor conditions. They are known as the most thermophilic house flowers in the bromelet family, and sometimes you even have to provide additional heating for the pot. The leaves form a dense funnel, the color can be any - from monochromatic to variegated. In culture, the most famous vriezia brilliant (pictured), the height of which, together with the peduncle, can reach up to one meter.
Species and varieties of bromeliads
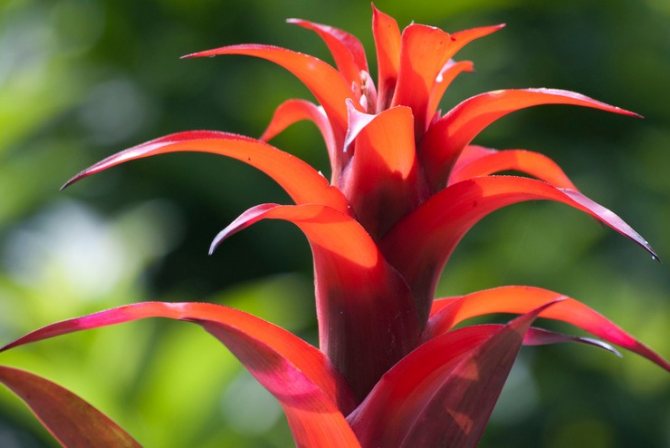


Bromelia penguin - can grow in natural and indoor conditions. This is the only bromeliad that is grown in culture.
Ehmeya - an epiphyte, which is widespread in the USA and differs from other species by leaves with a serrated edge, a thick and long peduncle, and inflorescences of bright color shades. Popular indoor types - Matte red, Sparkling, Holostebelnaya, Curved, Two-row, Striped, Bearded, Shaggy.
Neoregelia - a perennial species with a racemose inflorescence emerging from a rosette of light purple leaves. The best types for the house: Tiger, Blue, Bubble, Beautiful, Gloomy, Few flowers, Marble, Offspring.
Guzmania - stemless epiphyte with leathery belt-like leaf plates and bright bracts of different color shades. The inflorescence consists of small and unsightly flowers. As an indoor flower, Nicaraguan gusmania, Yazychkovaya, Mosaic, One-spiked, Blood-red, Konifera, Tricolor are grown. The best varieties of reed gusmania are Tempo, Minor.
Tillandsia - a species that unites in its family about 500 species of herbaceous crops, some of which are very famous in indoor floriculture - Medusa Head, Blue, Silver, Violet, Sitnikovaya.
Vriezia - Plants of tropical origin, characterized by dense and long leaves, collected in a decorative rosette and large inflorescences in the form of an ear or panicle.Popular indoor types are Sanders, Beautiful, Royal, Perforated, Giant, Hieroglyphic, Keel.
Genus gusmania
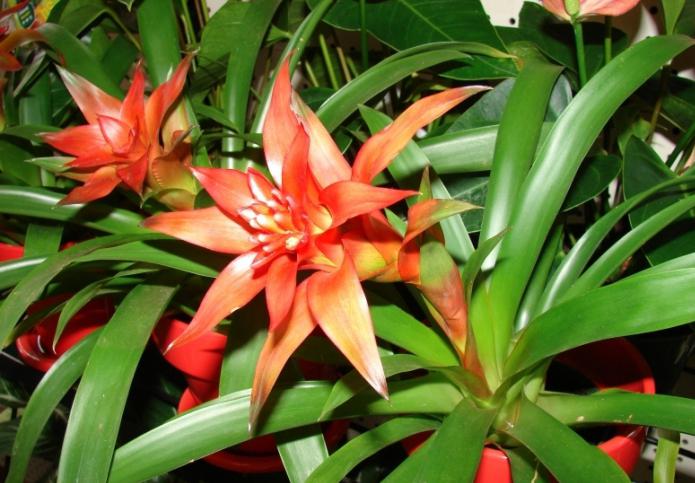


All representatives are epiphytes, there are about 120 species. On sale is found mainly reed gusmania and its varieties. The leaves form a flat rosette up to 30-45 cm long. Flowering lasts up to two months, after which the plant dies, like any other bromeliad. Home care is quite simple and will not cause any particular difficulties even for beginners. Gusmania minor (up to 30 cm tall), mosaic (with decorative striped leaves), Tsana, one-spiked, blood-red, etc. are also popular and known.
How to choose a healthy plant in the store


Examine the plant carefully and do not hesitate to ask all your questions regarding the flower from the seller.
When you come to the flower market for a new pet, pay attention to the general appearance. Conduct a thorough examination of the leaves, rosettes, peduncles. A healthy representative has elastic, fleshy, rich green foliage. There should be no damage, dry ends or yellowing. Any damage is a serious reason to refuse to purchase. Bacteria can enter your pet through wounds.
A root system with an unpleasant odor or visible defects is a sure sign that you will not be able to grow a seedling at home.
Ehmey's clan
Includes about 180 species. Lovers of indoor floriculture are most famous for one - striped ehmeya (pictured). The beautiful leaves have striking silvery stripes formed by scales that disappear when there is a lack of light or touch. The plant grows up to 50 cm in height. The flowers are small and inconspicuous, large pink bracts are striking. Ehmeya Chantini is also popular, pubescent, sky blue, sparkling.


Bromeliads
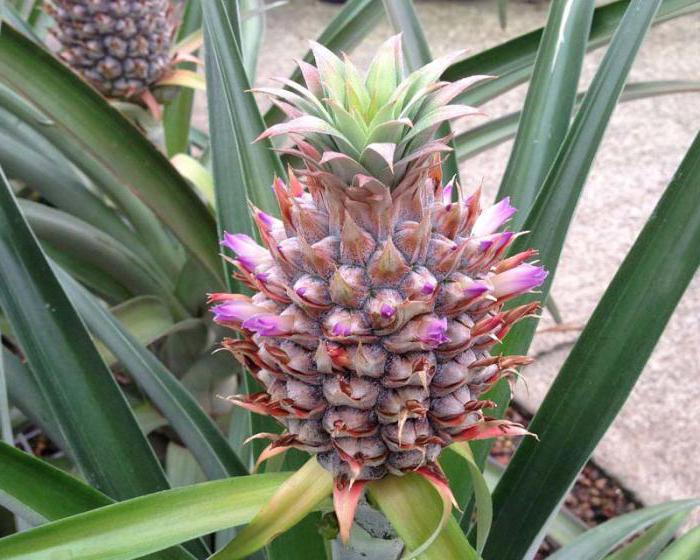
Bromeliad plants are among the plants about which the first information appeared in Europe during the great geographical discoveries. When Columbus visited America in 1493 and landed in Guadeloupe, he was the first of the Europeans to see pineapple plantations, then he did not yet know that this is a plant of the bromeliad family. It attracted the attention of the discoverer not only for its exotic appearance, but also for its special taste.
A little later, it turned out that the homeland of pineapple is Guiana and Brazil, from where the pineapple was resettled by the local population, who ate pineapples not only for food, but also as a raw material for obtaining fiber, as well as for medical purposes. The first description of pineapple was made by botanists in 1741. An interesting fact is that two centuries earlier, in 1535, rumors about this plant had already reached the Europeans.
Pineapples were introduced to Holland in the 16th century. Then they spread to France, Germany and England. In the middle of the last century, pineapples began to be grown in Russia.
Botanical research encompassed ever larger scales, enriching the understanding of scientists about the diversity of tropical plant species, including bromeliads. Some facts are known that indicate significant dates for the introduction of bromeliads into culture.
Interesting! In Europe in 1753, only fourteen species of bromeliads were known.
Pyramidal bilbergia, popular in Brazil, was described in a botanical journal in 1815, where a detailed description of the bromeliad plant and its color illustration were given. This multivolume edition is considered a classic today. Two other species of Bilbergia zebra and B. attractive at the same time were mentioned in the botanical literature of England.
In Italy, thornless bromeliad was cultivated in 1824. And in 1826 in England, the Kew botanical garden collected more than a hundred species of the bromeliad family. A little later, in 1827, in England, the striped ehmeya is known.Thanks to the famous botanist and artist Glazivi, who worked in Brazil for about thirteen years, in the fifties of the nineteenth century, interest in these original bromeliads increased significantly in European countries. The increasing interest can be attributed to two reasons:
- First, the natural sciences developed rapidly, which opened up wide opportunities for travel to overseas countries.
- Secondly, gardening began to develop rapidly, and many collectors wished to have more different exotic, such as bromeliads.
A huge role in this was played by the commercial interests of the owners of private gardens and farms, for whom rare subtropical and tropical plants brought huge profits. But, the main circumstance that determined the widespread introduction of bromeliad plants into culture was the achievements of construction technology. It was they who made it possible to build greenhouses, greenhouses and other structures that were able to protect plants from low temperatures.
The first collection of bromeliad plants in Russia, of decorative value was collected in the botanical garden of St. Petersburg by the botanist E. Regel.
Interesting! In 1890, a botanist's book was published, which was called "The maintenance and education of plants in rooms." The book focused on how to grow exotic plants at home. The famous botanist concluded in his book that in the future, bromeliads will also gain their importance in indoor floriculture.
At the turn of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, bromeliads were cultivated in European countries both in botanical gardens and in many trading companies. However, at this time, the interest of gardeners is mainly given to traditional indoor plants: palm trees, tradescantia, hibiscus, ficus. Only in the postwar years did bromeliad plants begin to acquire wide horizons in crop production. They began to quickly gain popularity among amateur flower growers, and this was facilitated by the activities of botanical gardens, both domestic and foreign.
Conditions for bromeliads
Representatives of the family are typical inhabitants of the rainforest, therefore, appropriate lighting is required for them. The bromeliad flower prefers a location with intense light, but not in direct sunlight. The second important condition for growing is the relative constancy of the temperature regime, without sudden changes and fluctuations. In summer, at 18-25 ° С, and in winter, at least 14-16 ° С. Add to all this the high humidity. Any bromeliad (species are very numerous) requires daily spraying with soft settled water. From this it follows that the most unfortunate location for a flower will be the space near heating radiators. Try to keep a small amount of moisture in the leaf funnel during summer.
Origin
The Bromeliad family, which includes more than 2000 plant species, grows in the tropical rainforests of South and Central (Mexico) America. Among the representatives of the family, there are herbaceous aboveground plants and epiphytes that parasitize on tree trunks.
Interesting... The world famous and favorite tropical fruit - pineapple, also belongs to the bromeliad family. Even in the appearance of a growing pineapple, there is a resemblance to the indoor flower bromeliad.
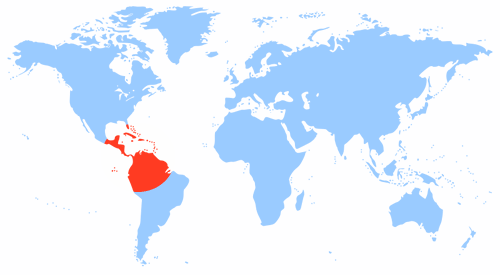

Homeland of the plant
Bromelia: home care
It mainly consists of two points. Firstly, compliance with the conditions listed above, and secondly, correct watering and soil selection. We recommend buying the soil in specialized stores. If you prefer to cook it yourself, then keep in mind a few important points. Many bromeliads are epiphytes, and their root system is rather poorly developed, therefore, a large pot is not required.Provide maximum air flow to the roots. To do this, use ordinary garden soil (previously disinfected), peat, sphagnum moss (it is possible to replace it with fern roots, previously crushed) in equal parts. Also add some charcoal. After planting the plant, cover the top layer of the substrate with moss, this will help to retain moisture and prevent drying out, which bromeliad does not tolerate at all. The transplant is carried out once every two years in case of emergency. The roots will tell you about its need, which will stick out to the surface and into the drainage holes. Choose a new plant pot 2-3 cm in diameter larger than the previous one. After transplantation, care for bromeliads remains the same.


The soil
Bromeliads grow well in a loose and light substrate with an acidic reaction. For a pet, you can buy ready-made orchid soil in the store or prepare a suitable soil with your own hands. There is a proven recipe for bromeliads:
- leafy sod soil 2 parts;
- river sand 0.5 parts;
- peat 1 part;
- humus 1 part.
It is useful to add to this mixture: sphagnum moss, chopped coniferous bark, pieces of charcoal, perlite. Additives should be no more than 20% of the soil volume.
The drainage layer (expanded clay, perlite, bark) in the pot where the bromeliad is planted should occupy about a third of the volume of the dishes. The plant is very sensitive to moisture stagnation at the roots.
How to water?
This is one of the main points of care for bromeliads. Observance of all the subtleties will help you grow a beautiful healthy plant. It is worth noting immediately that the flower is not one of the moisture-loving ones, and an excess of water will lead to decay. Therefore, even at the planting stage, it is worth thinking about a good drainage layer (expanded clay, brick chips). Many members of the family also do well in hydroponics.
Use only soft, room temperature water for watering. Water not the substrate and roots, but the very rosette of leaves. Moisture should linger in the leaf axils, which is what bromeliad loves. Home care involves frequent and abundant watering in spring and summer and more moderate watering in winter. Fertilization is encouraged, fertilize at intervals of two times a month, starting from March-April until autumn. Use special preparations for bromeliads or regular ones. Strictly follow the instructions, in this case it is better to dilute it more than to overfeed the plant.
Care
A flower, whose homeland is a humid tropical forest, needs to create similar conditions of high humidity in the apartment.
- The most "advanced" option used by professional growers is to put a household humidifier near the plants, which will increase the humidity to 60 - 65%.
- A less effective, but inexpensive option is a container with expanded clay filled with plain water. Expanded clay absorbs moisture well, and then evaporates it into the air. It is better to choose wide dishes so that the evaporation area is larger. Some growers put the bromeliad pot directly in this container on a small stand.
- It is appropriate to install a decorative fountain in the flower corner. It will create the necessary humidity in the air, and its quiet murmur has a calming effect.
Watering bromeliads is different from the traditional watering of indoor flowers. The root system of a plant cannot absorb moisture from the soil. The flower absorbs water through the aerial part. Watering is carried out by directing a stream of water directly to the center of the outlet.
Important! The socket and leaf plates of the flower must be regularly cleaned of debris and wiped from dust.
Bromeliads should only be watered with soft water. Melt water or rainwater will do. Tap water is defended for three days and only the top layer without sediment is taken for irrigation. You can soften the water with peat: 1 teaspoon of peat is poured into a liter of water and insisted for several hours.
The plant is fed once a month by adding fertilizer to the water for irrigation. The fertilizer is used for orchids; all the substances necessary for bromeliads are present.
On a note. To speed up the onset of the bromeliad bloom, the flower pot is placed in a large plastic bag along with a few apples or a couple of banana fruits. Ripening fruits release ethylene gas into the atmosphere, which acts as a stimulant and stimulates flower formation in bromeliads.
After the end of flowering, the bromeliad rosette, from which the peduncle grew, dies off. The bush continues its life at the expense of young shoots - kick.
The plant does not like a transplant. Without extreme need, the root system of the flower should not be disturbed. If it is necessary to transplant bromeliads, it is very carefully transferred from the pot to another container, without destroying the earthen lump.
Bromeliad: reproduction


At home, the vegetative method is optimal. From an old plant, a new one is obtained with the help of new processes called kiki. As a rule, they are visible even before the beginning of flowering, however, for rooting, you must wait until it ends. In time, this falls around September. Carefully cut off the shoots with a sharp knife and plant in small containers filled with a mixture of sand and peat. Rooting takes place in the bulk successfully and quickly, while no special conditions are required, the main thing is timely watering. Young plants already next year in the summer can delight you with beautiful flowering.
Pests, diseases
Bromeliad is a fairly disease-resistant crop, but due to excessive soil moisture, it can be affected by rot. The leaves of the flower can dry out from dry air.
Bromeliads are annoyed by mealybugs and scale insects. They get rid of the pest by removing it from the leaves with a cotton pad dipped in soapy water. Sometimes, with a large number of parasites, they resort to the biological preparation Fitoverm.


Vriezia
Vriezia Astrid: description of the plant and features of care
Vriezia Astrid (Bromelia Vriesea) has about 100 varieties. They are all tall. Depending on the variety, the color of the leaves can be different (green, striped, purple, crimson).
For your information! At the age of 3-4 years it begins to bloom. The spikelet can be monochromatic and multi-colored. The plant dies after flowering.
Vriezia brilliant
Vriesea brilliant, or royal (Vriesea regina) - a variety that is distinguished by shiny long leaves. With a peduncle height of 2 m, the leaves grow up to 1 m and longer. Paniculate inflorescence with light yellow fragrant flowers. Bracts are pink.
Vriezia Slendens
Vriesia Splenriet is the most beautiful representative of the Bromeliads. The funnel-shaped rosette of leaves grows to almost 0.8 m. The leaf blade itself can be cross-striped. Its edges are bent. The peduncle is long, the inflorescence is spike-shaped, large, bright red. The yellow flowers open gradually.















































