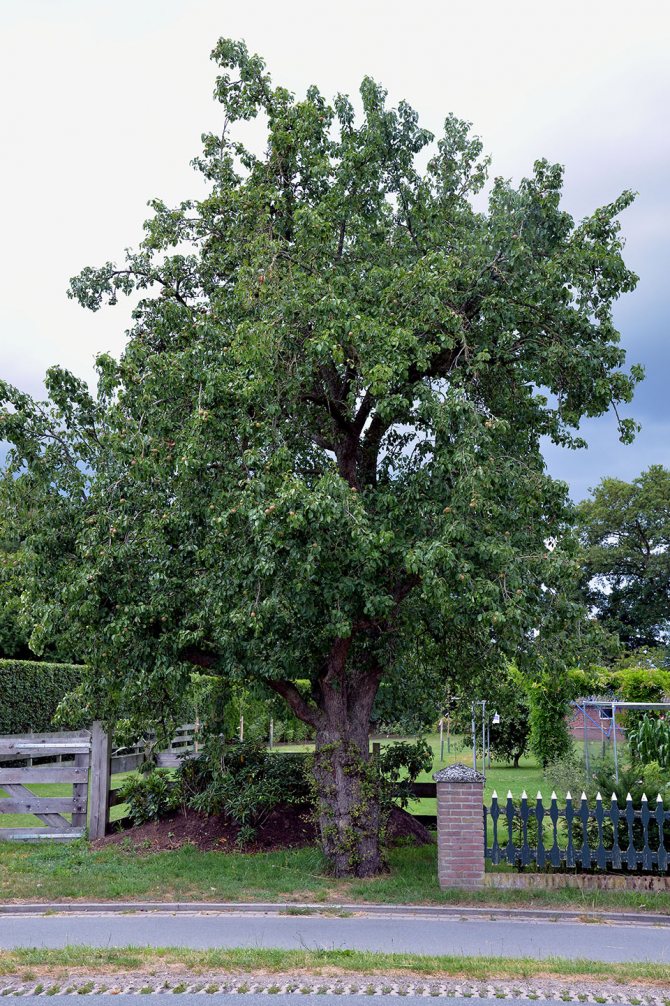
Common or domestic pear (Pyrus communis or Pyrus domestica) is classified botanically as a species of the genus Pear and belongs to the Rosaceae family. It originally appeared in Asia and Eastern Europe. A tree needs sufficient sunlight and a cultivated and fertile soil to grow well. The trees reach a height of no more than thirty meters. They live an average of fifty years. Breeding a tree is done by planting cuttings, seedlings or seeds.
Description and characteristics of the pear
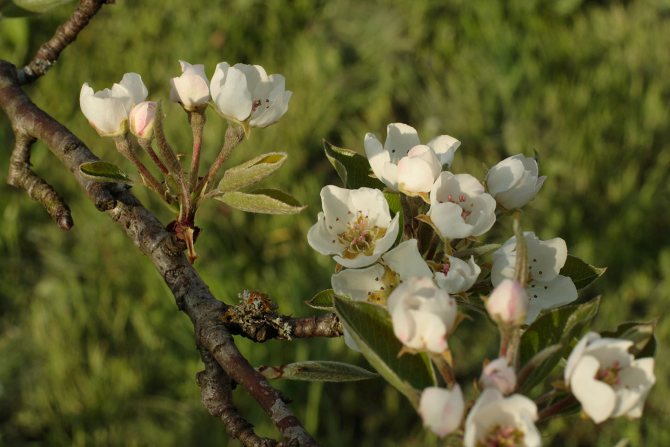
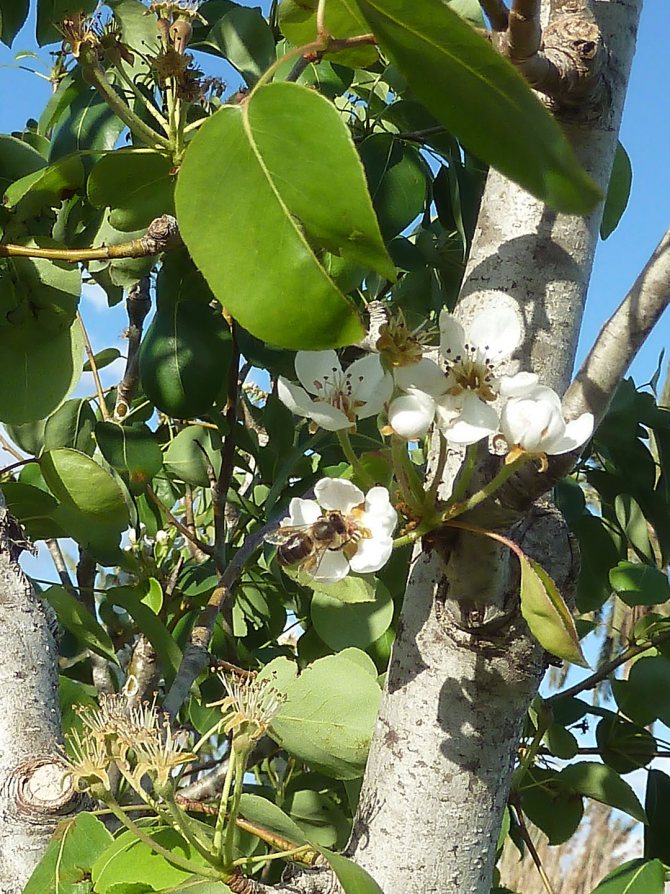
This fruit tree from the Pink family grows up to 25 meters, blooms from April to May with large white 5-petal flowers up to 3 cm in diameter.The pyramidal or rounded crown reaches 5 meters in diameter, and branches grow by 30-40 cm per year. green leaves are oblong, sharp at the end, 2.5-10 cm in length, depending on the variety, on a branch they are arranged in a spiral in 5 rows, in autumn they turn golden orange, and fall off with the onset of frost.
Pear fruits are elongated or spherical. The pulp contains stony cells, so it has a characteristic granularity.

Pear leaves.
Experienced gardening tips
Here are some helpful tips for breeding pears:
- Before grafting the plant, you need to water the young seedlings and loosen the near-stem circle.
- When connecting the scion to the stock, make sure that the bark and cambial layer of both parts match.
- The cut of the cutting should always be treated with fungicides or charcoal.
- In greenhouses, seedlings are grown under diffused lighting.
- It is advisable to harvest cuttings in the morning on a fine day.
- Columnar pear is propagated by grafting (cutting on stock).
Did you know? Reproduction by cuttings depends on the size of the pear fruits. The smaller they are, the more successful the cuttings are.
So, pear trees reproduce well in vegetative ways. All of them are quite simple and do not require special knowledge and skills. Strict adherence to the recommendations will allow even a beginner to grow a good tree in his area.
How to plant a pear
Autumn planting and care are different from spring.
In the south, autumn is warm and winter is very mild. When planting in spring, the seedlings will not have time to get stronger and will burn out during the dry hot summer. A tree planted in the fall will have time to adapt, to put down new roots for winter. In Siberia, autumn planting is carried out in September. If the seedlings are bought in late autumn, they are dropped into the ground at an angle, covered with peat, leaves and non-woven cloth on top so that they do not freeze until spring.
In the fall, planting holes are prepared for trees, which will be planted in spring. In a pit 70 by 70 cm, the top layer with turf is laid, about 20 cm, with the grass down. A support stake for a seedling with a height of 1.5-2 meters is stuck into the center, the pit is filled in three stages with 2 buckets of 3-year manure, 2 buckets of peat or humus, 200 g of ash and fertile soil from the pit. They take a third of each component, mix it in the pit with a shovel, trample it down, repeat it two more times, as a result, a hill with a height of 20 cm should turn out in place of the pit.
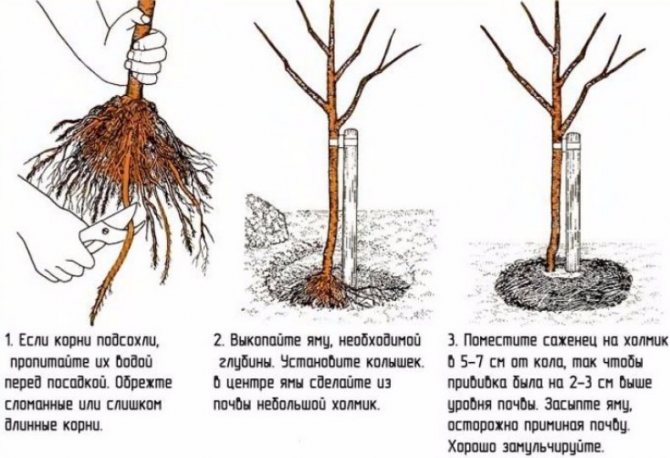

The order of planting pears.
Interesting facts about the fruit


Pear puree - perfect for babies
- Before the appearance of tobacco in Europe, people smoked dry and crushed leaves of this fruit;
- In the seventeenth century, its fruit was also called the "butter fruit" due to the fact that its soft texture resembled this product;
- In ancient Greece, its fragrant fruits were used as a cure for nausea;
- Pear wood is famous for its amazing resistance to deformation - therefore, rulers for professional architects are made from it;
- Its fruits are recommended for feeding babies who are weaned by mothers: this is due to their low allergenicity and minimal acidity.
Pear care
Young plants for the winter are wrapped in straw with herbs that scare off mice: mint, wormwood, tansy and burlap treated with an anti-mouse drug - birch tar, dust, diesel fuel. The watering circle is cleared of weeds. The first year after planting, pears are watered at the root once a week, 1-2 buckets per seedling. From the second year, the amount of water is gradually increased, and watering is reduced to 1-2 per month. Mature trees are watered with sprinkling, then the soil is loosened and mulched so that the crust of the earth does not block the access of oxygen to the plant.
In the first 2-4 years, the trees are fed with nitrogen during the leaf blooming period. Then - if necessary, if the tree is growing slowly, and the foliage becomes atypically light. Organic matter is applied once every 3-5 years, mineral fertilizer - every autumn.
Classification [edit | edit code]
The genus includes 69 species [8], which are distributed in two sections Pashia
and
Pyrus
[9] .
- Pyrus armeniacifoliaT.T.Yu
- Pyrus betulifoliaBunge
- Pyrus calleryanaDecne.
- Pyrus cossoniiRehder
- Pyrus dimorphophyllaMakino
- Pyrus fauriei C.K. Schneid.
- Pyrus hondoensis Nakai & Kikuchi
- Pyrus koehnei C. K. Schneid.
- Pyrus pashiaBuch.-Ham. ex D.Don
- Pyrus pseudopashiaT.T.Yu
- Pyrus pyrifolia (Burm.f.) Nakai - Pear-leaved pear
- Pyrus taiwanensis Iketani & H. Ohashi
- Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim. - Ussuri pear
- Pyrus xerophilaT.T.Yu
- Pyrus boissierianaBuhse
- Pyrus communisL.typus [2] - Common pear
- Pyrus communis L. subsp. caucasica (Fed.) Browicz [syn. Pyrus caucasica Fed. - Caucasian pear] basionym
- Pyrus communis L. subsp. pyraster (L.) Ehrh. [syn. Pyrus pyraster (L.) Burgsd. - Forest pear]
- Pyrus cordataDesv.
- Pyrus elaeagrifoliaPall. - Shaggy pear
- Pyrus gharbianaTrab.
- Pyrus glabraBoiss.
- Pyrus korshinskyiLitv.
- Pyrus mamorensisTrab.
- Pyrus regeliiRehder
- Pyrus sachokianaKuth.
- Pyrus salicifoliaPall. - Willow pear
- Pyrus spinosaForssk.
- Pyrus syriacaBoiss.
- Pyrus turcomanicaMaleev
Reproduction of pear
There are several options:
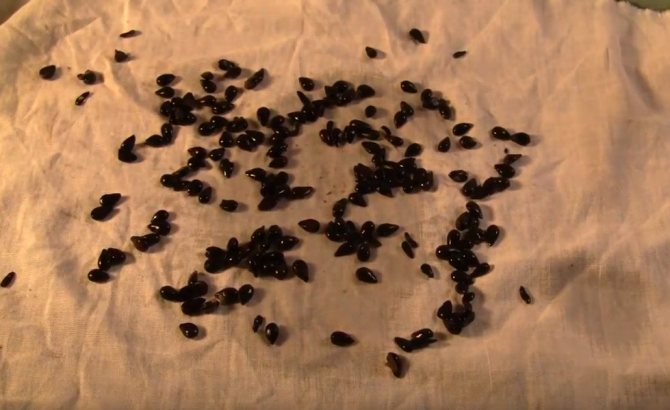
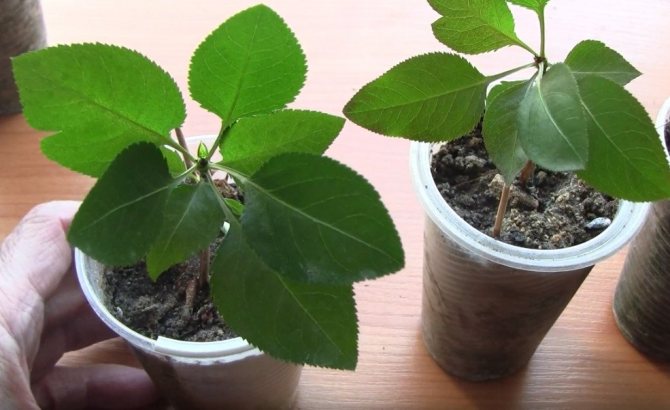
- The seeds are planted in a pot of fertile soil. For several years, the tree is transplanted two or three times in larger containers, then planted in the ground. This rather lengthy process does not guarantee high yields.


Pear seeds.
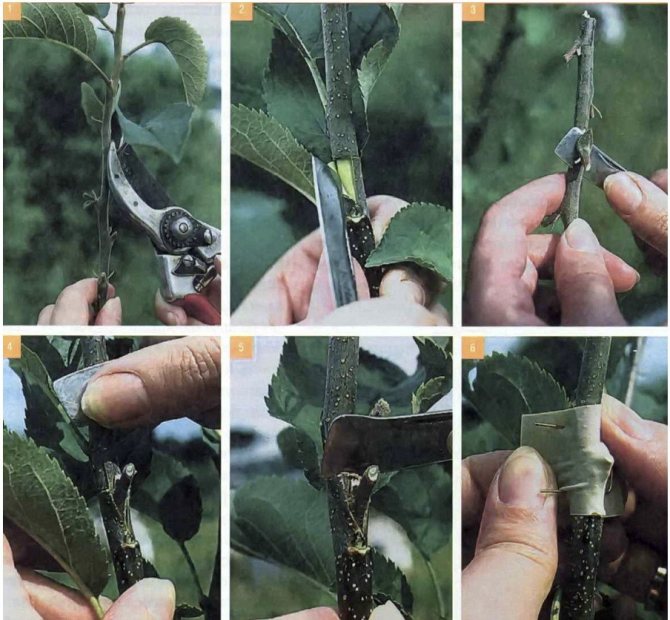
- Vegetative propagation is the best way to accelerate the onset of fruiting: a stalk or part of a stalk with a bud of the variety you like is grafted to a well-rooted fruit crop - the stock. As a rootstock for a pear, quince, pear, apple tree are suitable, a good rootstock is the basis of the future harvest.
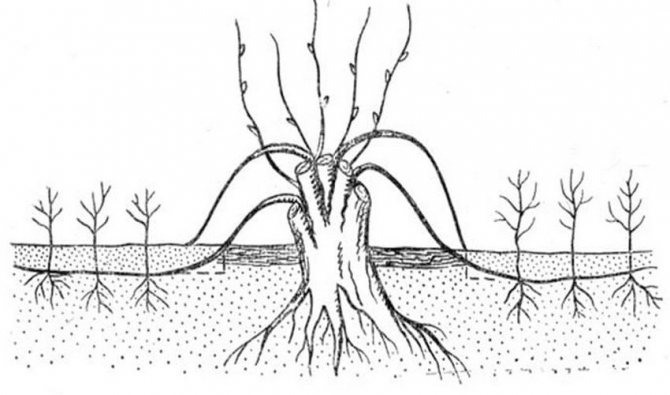
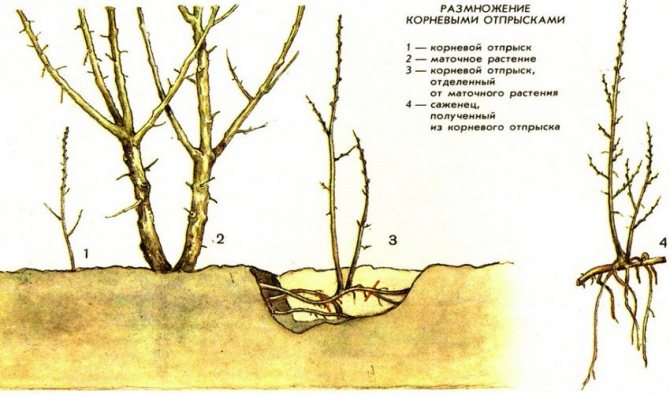
- The root shoots, which appear near the fruit tree, are carefully buried in, separated from the mother plant in order to transplant from it. Such shoots have a developed root system, grow well and, with proper care, give an excellent harvest in the future.
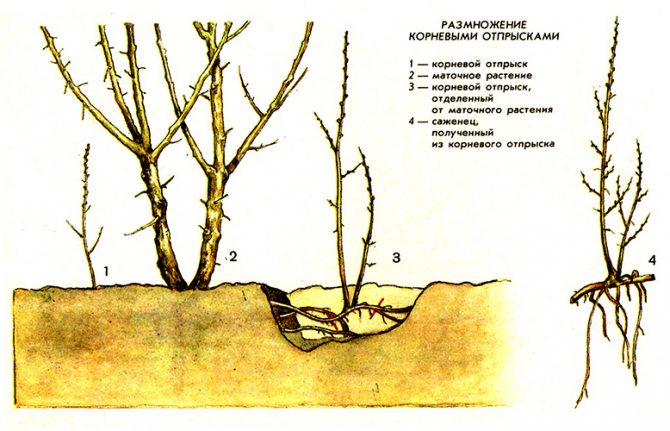

Root growth.
- When propagating by layering, gently tilt one of the branches to the box with the ground, attach to it so that part of the branch is in the ground. When roots appear on the branch, this part is separated from the tree and rooted in a new place. Such layers take root well.
- For propagation by cuttings, in the morning, young lateral shoots are pruned, treated with growth activators and planted in fertile soil. The seedlings are intensively watered, fed with mineral fertilizers for 3-4 months, and after six months they are transplanted into open ground.
Distribution in Russia
On the territory of modern Russia, the pear tree began to be cultivated since ancient times. Most likely, it first came here from Byzantium and was first bred in the gardens of various monasteries.In the annals there are open references to the cultivation of a tree in the gardens of Kievan Rus, dating back to the eleventh century. The ancient Russian tsar Alexei Romanov also grew pears in his grandiose gardens near Moscow. In the Izmailovsky Tsar's Garden, up to sixteen varieties of wood were grown. Romanov was not the only pear lover - Peter the Great also took care of their assortment. On his orders, seedlings of new varieties of wood were brought from Western Europe.
The pear was brought to America from Europe no earlier than the fifteenth century, and its large-scale cultivation as a fruit crop began only in the eighteenth century (it is curious that to obtain cold-resistant varieties, American breeders at the end of the nineteenth century imported about 80 Russian pear varieties into the country). It was around this time that European colonists began growing trees in Africa, South America, and Australia.
Pests, diseases and pear treatment
To preserve the harvest of fruit trees, pests are fought with folk or special means strictly according to the instructions:
- Green aphids infect young branches and leaves, another dangerous parasite develops in the secretions of the pest - a sooty mold fungus. Before the buds begin to bloom, the pests are eliminated with Kinmix, the second time the flower buds are sprayed with Agravertin, the third time with Iskra when fruit ovaries appear. Solutions of dandelion, chamomile or garlic infusion are effective.
- Gall mite infects young leaves. Colloidal sulfur is effective against it.
- The larvae of the pear moth devour ripe fruits. Against the pest, Agravertine solutions are used before and after the flowering period, Kinmix is used 3 weeks after flowering, and a week later - Iskra solution.
- The buds and fruits are deformed from the influence of the pear beetle (leaf beetle), the leaves fall off, the drug Karbofos will destroy the parasites, the second time the plant is sprayed after the flowering period with Iskra or Agravertin. Decoctions of yarrow, chamomile, dandelion also help.
- Leafworm larvae roll the leaves into a tube and devour them. To combat them, the tree is sprayed with the "Cymbush" preparation until the buds open.
Diseases of pear trees
In case of a disease, you need to get rid of the infected parts of the tree as soon as possible and start treatment.
- Cytosporosis or stem rot from sun or cold burns is removed with a garden knife, the wound is treated with copper sulfate with water or garden varnish.
- Moniliosis manifests itself as small brown spots on the fruits, from which the fungus is carried by the wind throughout the tree, the tree is sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or copper chloride in the spring and autumn periods.
- Rust (bright orange spots) on foliage is caused by a pathogenic fungus, it can be transferred from juniper. The tree is treated with colloidal sulfur and Bordeaux liquid, in the spring - when buds appear, in the fall - after the leaves fall.
- A milky sheen appears from sunburn or from exposure to a wood-destroying fungus, the leaves become fragile when infected and acquire a metallic hue. For prevention, all the necessary agrotechnical measures are carried out: soil cultivation, timely and sufficient watering, fertilization.
- Black cancer manifests itself as red spots on the leaves, wounds on the bark, black spots on the fruits, the bark is cut off with a garden knife along with a two-centimeter layer of healthy wood to prevent the spread of the fungus. Wounds are disinfected with copper sulfate, and mullein mixed with clay is used for quick healing.
- Scab on foliage and fruits completely affects the tree with spots up to 3 cm in size, if it is not immediately treated. The reason may be the close planting of pears to each other, in the spring a tree with near-stem soil is treated with a 7% urea solution and Bordeaux liquid.
- Powdery mildew deforms young shoots with leaves, the plant is sprayed with colloidal sulfur in autumn and spring, all measures for the care of fruit crops are strictly observed.
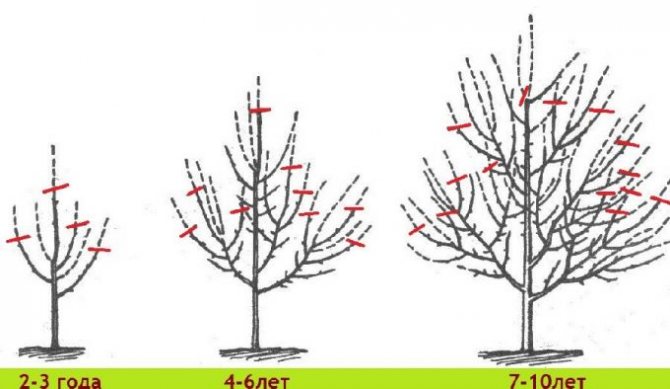
Pruning old trees
To trim an old tall tree you will need:
- saw;
- secateurs;
- ladder;
- composition for processing the place of cutting branches.
Pollination of pears
Large tree-like plants are pruned in two ways. The first involves removing all fragile and dry branches. Remove those branches that are not able to withstand the weight of the fruit.
Following the second scheme, only those branches are left on the tree that grow horizontally to the surface of the earth. Cutting fruit trees allows you to get rid of unnecessary growth and direct all the forces of the plant to the formation of a high-quality and high yield.
Important! Fertilizers with a high nitrogen content should not be applied after spring pruning.
Popular message topics
- Cromwell Oliver
A statesman and an outstanding English commander, Oliver Cromwell, was born on May 5, 1599 into a poor family. Working modestly for the good of the family, Oliver showed little hope for a successful future. Throwing out the institute, - Animal kingdom
The animal kingdom is rich in animal species, they are all different, they all live and eat in their own way. Each family has its own specific task that they perform. For example, insect predators cleanse the world of pests, - Murmansk
Murmansk is located in North-Eastern Europe and is the largest city in terms of population in the polar region. The city was founded in 1916, and until 1917 it bore the name Romanov-on-Murman.