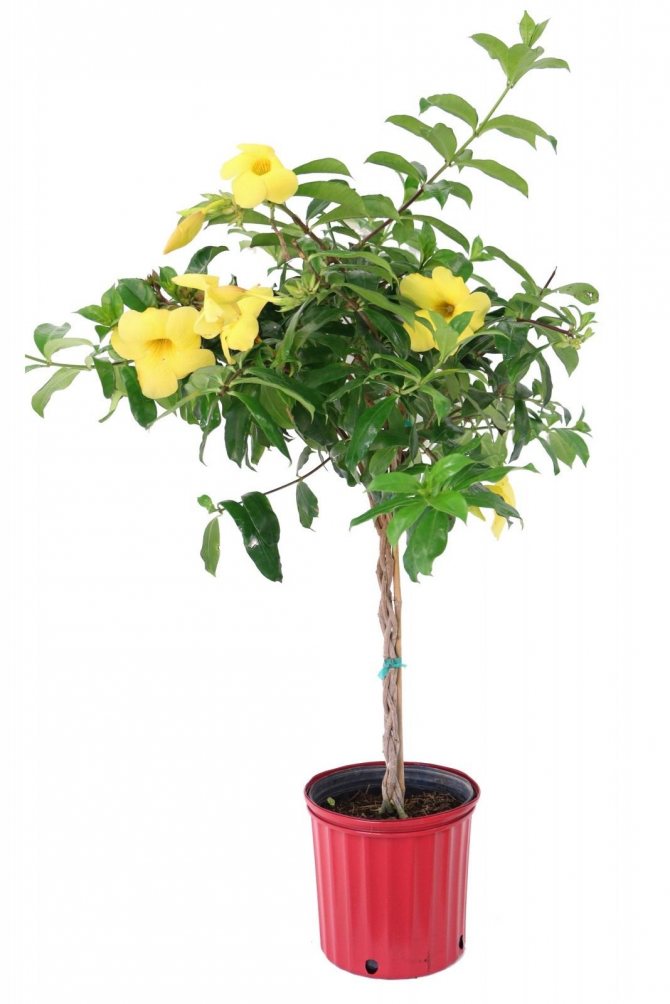
The allamanda flower is a liana, sometimes a shrub that has year-round green foliage. The family to which the culture belongs, kutrovye. The plant is found in the humid tropics of America.
Allamanda at home is unlikely to be able to bloom. Comfortable conditions for growing crops will only be in the greenhouse. In such places, the plant will be given enough attention, there will be a certain comfortable humidity and temperature.
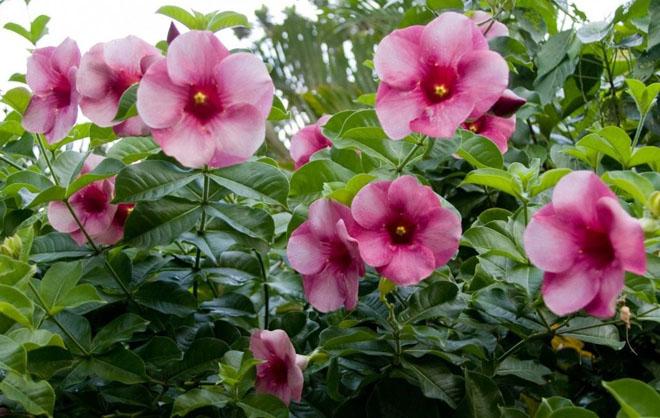

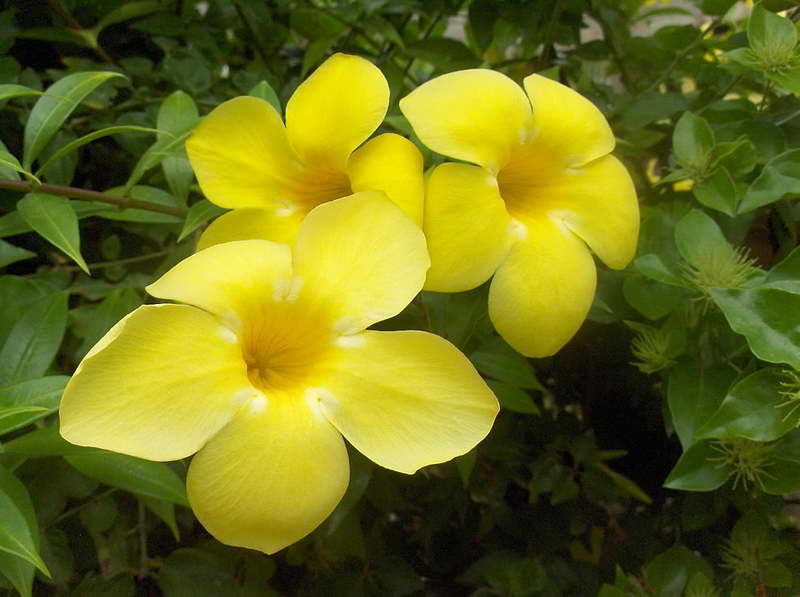
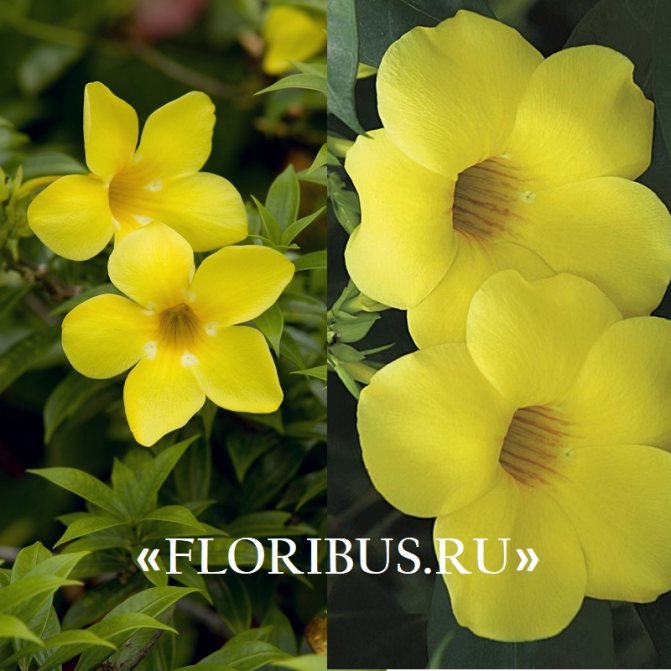
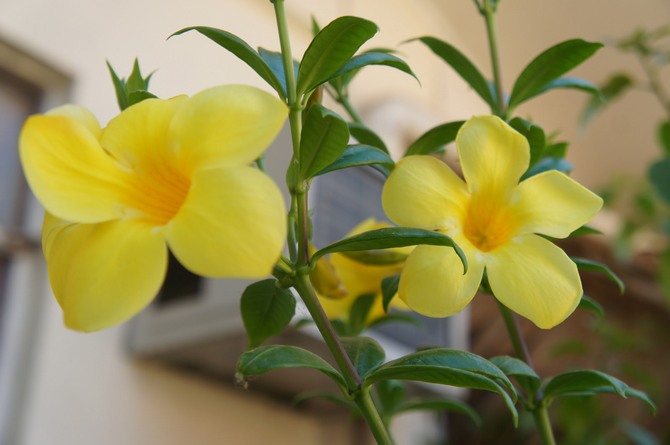
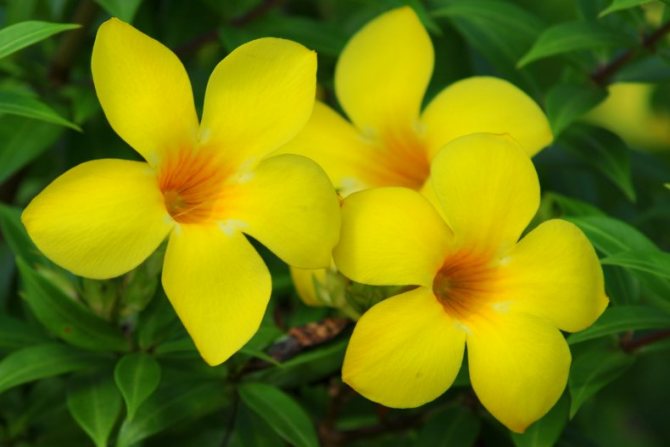
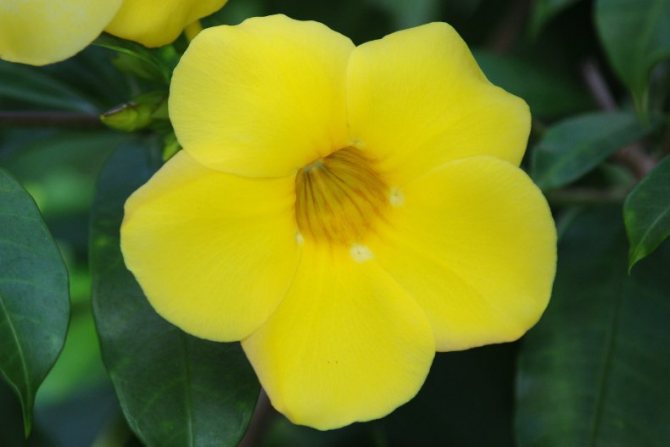
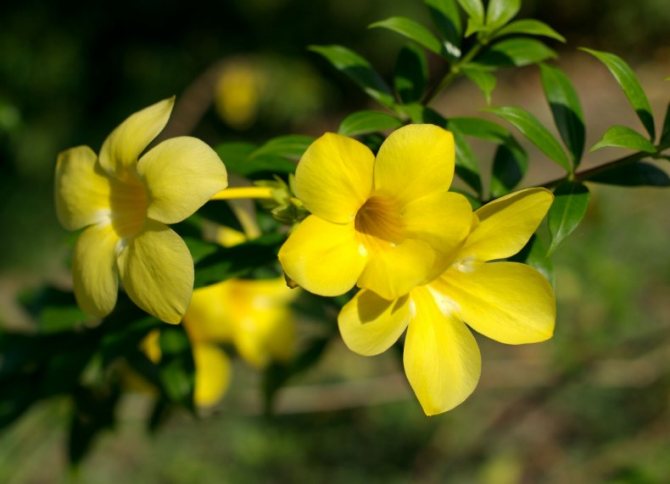
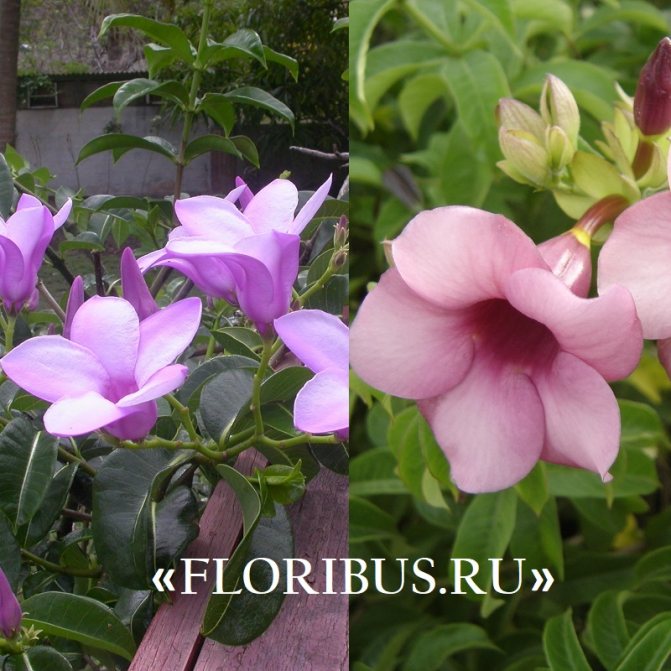
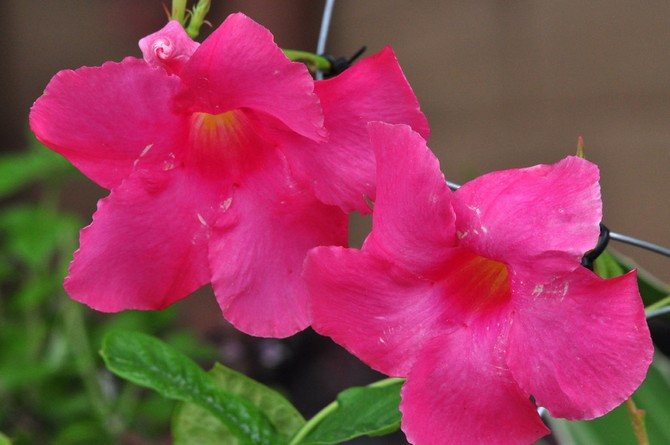
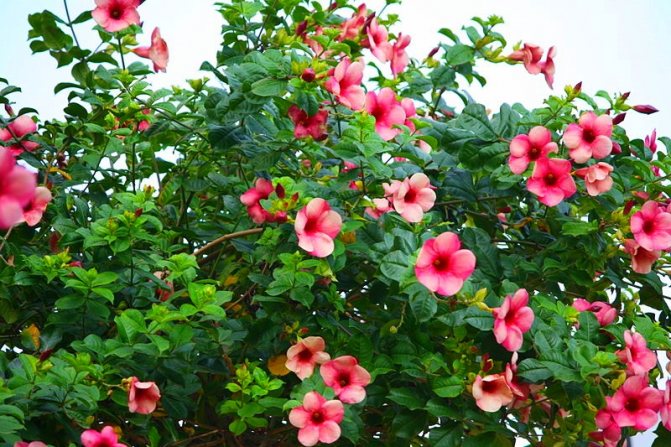
The flowers of the shrub can reach twelve centimeters in size. The shade of the inflorescences is bright, which attracts the attention of others.
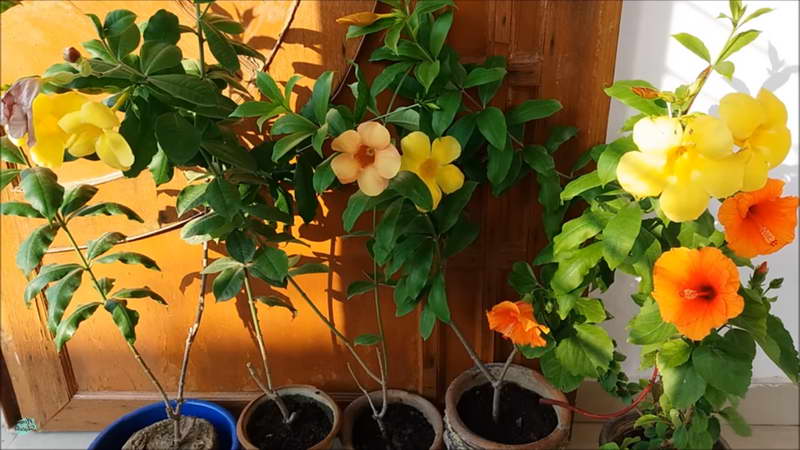
Indoor plants allamanda yellow terry and laxative
The genus Allamanda includes about fifteen subspecies of evergreen artisanal plants and vines.
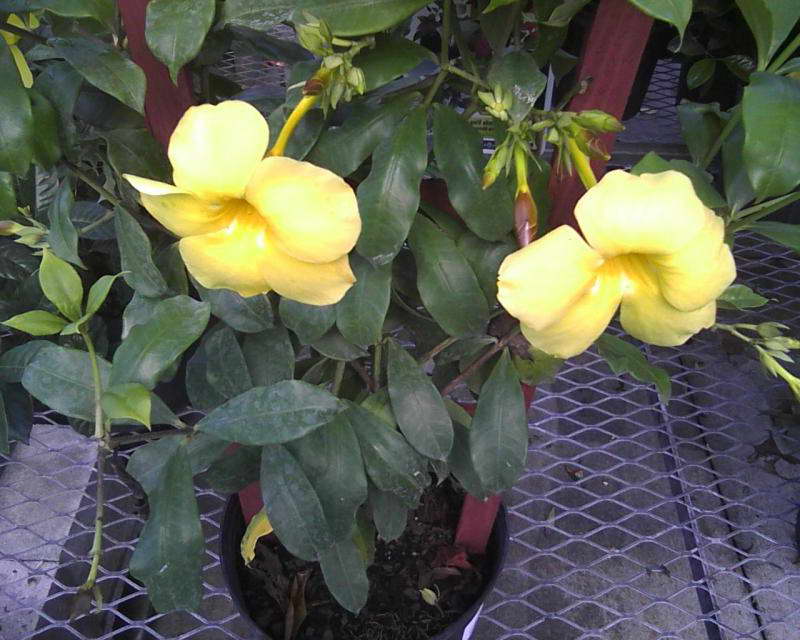
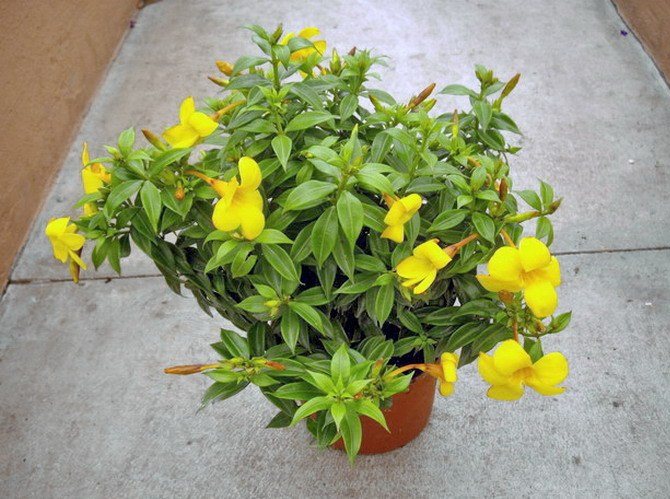
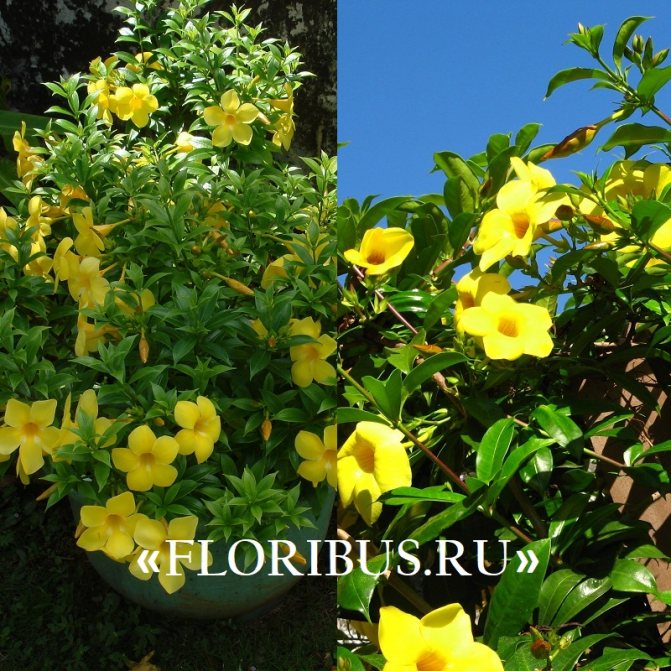
Allamanda yellow is the most common species of this plant. The shrub reaches a height of 90 cm, characterized by drooping climbing shoots.
The plant is also known as allamanda yellow terry, which is due to the velvety surface of the flowers. The leaves are short-petiolate, pointed, have an elliptical shape, their length reaches 12 cm. They are dark green above, and a few tones lighter below. The flowers of the yellow terry allamanda are located on long pedicels.
See what the allamanda indoor flowering plant looks like in the photo below:
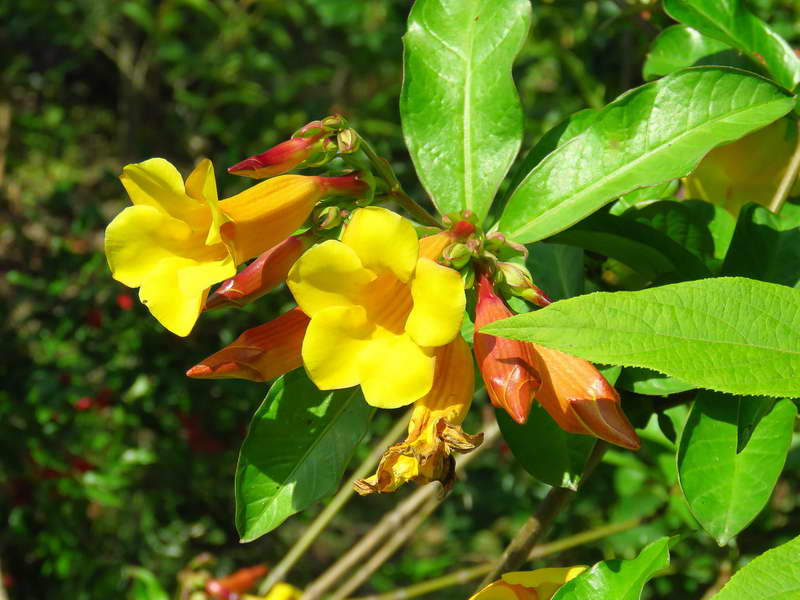
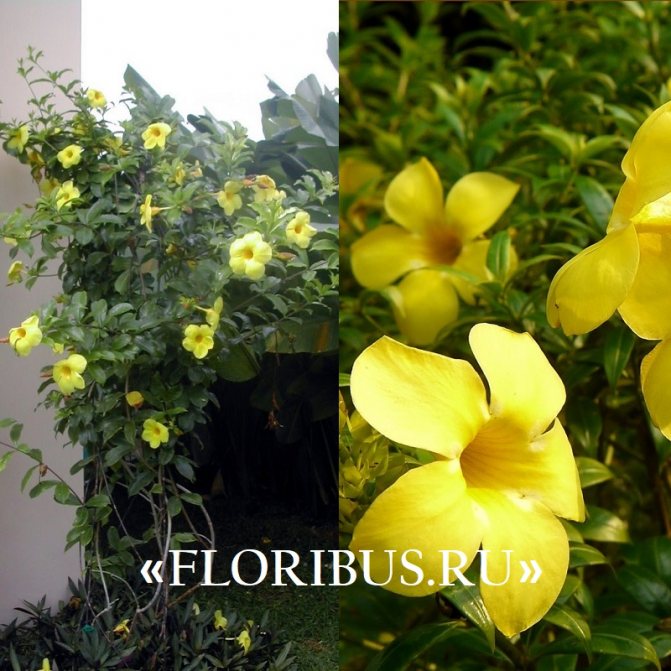
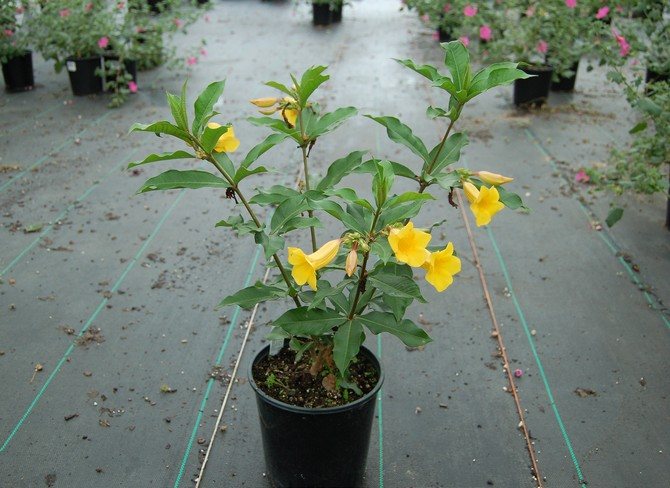
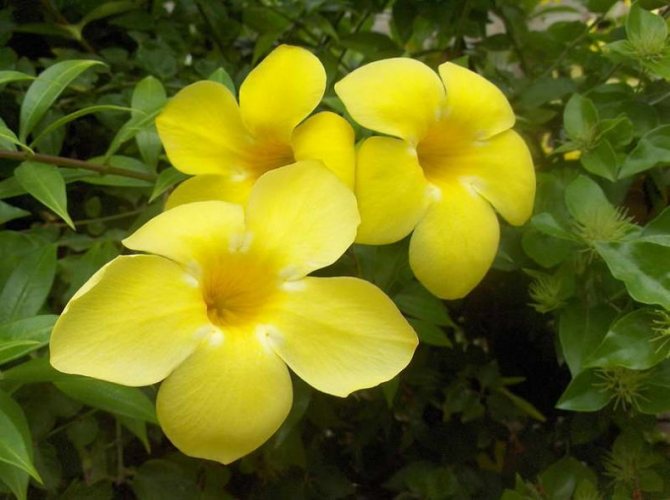
Another popular houseplant is allamanda laxative. Perhaps this is the most common species in this family. It is a climbing plant up to 6 m high. Flowers of the laxative of allamanda are yellow-golden in color with a white base, collected in the apical part of the shoot. Its leaves are rather large, ovate-elongated, can reach up to 14 cm in length and 2-4 cm in width.
In indoor floriculture, other types are also used, such as:
Allamanda noble
(A. nobilis)
.
Allamanda grandiflorum
(A. grandiflora)
.
Allamanda oleandroliferous
(A. neriifolia)
.
Allamanda purple
(A.violacea)
.
Allamanda Henderson
(A. Hendersonii)
.
Allamanda Shott
(A. schottii)
.
General information about Allamand
Allamanda
- lat. Allamanda
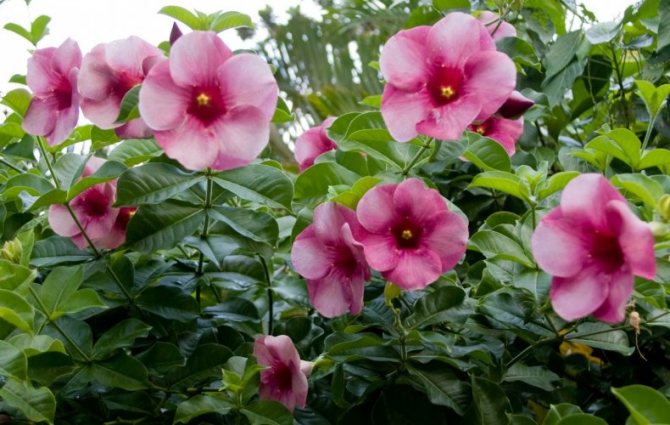
The graceful Allamanda grows naturally only in tropical rainforests. In total, there are 15 plant species, of which only a few are cultivated. Liana is prized for its simple but large, showy bright flowers in yellow, pink and lilac colors.
Leaves of medium size - 6-10 cm in length. The color of leaves and young shoots is dark green with an emerald tint. Over time, the stems turn wood and turn brown.
Shoots can grow up to 3-4 meters in length. Cultivated species should be pruned 1-2 times a year. Curly stems are ideal for ampel cultivation. When placing allamanda in floor pots, it is necessary to put supports for the vines.
With regard to the complexity of cultivation, the plant is recommended for experienced growers who already have an acquaintance with exotic crops.
Important! The stems and leaves of allamada contain poisonous sap. It is advisable to work with a flower with gloves. It is not recommended to keep the vine where there are small children and pets.
Allamanda plant care at home
Allamanda is quite demanding on the conditions of the habitat, only in this way will it delight flower growers with exuberant flowering and lush greenery. She needs bright sunlight, the plant is not afraid even of direct sunlight. It is thermophilic, in winter it must be kept at a temperature not lower than 14-18 ° С, and in summer the air temperature in the room should not be higher than 22 ° С. The ideal place for the location of the indoor flower will be windows facing south, southeast and southwest. Allamanda is afraid of drafts, so it is important to protect the plant from them.
High humidity is required, 60-70% is optimal, it will create good conditions for the growth and development of a vine or shrub. To increase the humidity, it is advisable to often spray the plant with settled water. At the same time, it is strictly forbidden to get water on the flowers. For a longer time, peat or drainage will help to maintain the optimal level of soil moisture if you put a pot with a flower on them. The substrate should be loose, from leafy soil, humus, peat and sand in a ratio of 2: 2: 1: 1.
When caring for an allamanda plant at home, it is important to provide it with abundant watering in the warm season, and reduce it in winter. In winter, allamanda should be watered so that the topsoil has time to dry out between waterings. The soil should never dry out. For good growth and development, fertilizing in spring and summer is required twice a month with organic and mineral fertilizers.
Be sure to carry out pruning, which is needed so that allamanda grows well and blooms. This must be done in November, always using gloves, since the plant sap is poisonous. Shoots are cut to half their length above the leaf nodes. Vine stems are not strong enough, so it is better to tie them to a support.
At a young age, Allamanda care also consists of an annual transplant, it is carried out in the spring. During this period, adult plants can also be transplanted, but this should not be done annually, it is enough to transplant once every two to three years.
Growing conditions
Illumination
Set aside a place with good lighting for the plant. Liana is very fond of bright sunlight, place it on windowsills or close to windows, do not keep it in the depths of rooms where it will lack sunlight. However, try to avoid drafts.
Air temperature
During the autumn-summer period, the room temperature regime is quite comfortable for the allamanda plant. With the onset of autumn, the indicators should be gradually reduced to 18 ° C, and in winter, a temperature of 15 ° C will be required.
Allamanda breeding methods
Plant propagation is carried out in two ways - stem cuttings using phytohormones at a temperature of 25 ° C, and seeds. When choosing the second method of plant propagation, the seeds are treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate before planting in the ground. After the seeds are sown in a wet substrate, they should be covered with foil on top, creating a greenhouse effect. It is important that the temperature does not drop below 25 degrees, so the seeds should be kept for 6 weeks before the first shoots appear. The greenhouse needs to be ventilated and moistened every day.
Propagating allamanda by cuttings, it is necessary to choose the right shoots. They must be covered with lignified bark. The ideal length of stem cuttings for reproduction of allamanda is 8-10 cm. Before planting, the cut is treated with succinic acid or zircon. The cuttings are planted in a greenhouse for rooting, when the plant takes root, it can be transplanted to a permanent place.
Growing allamand from seeds
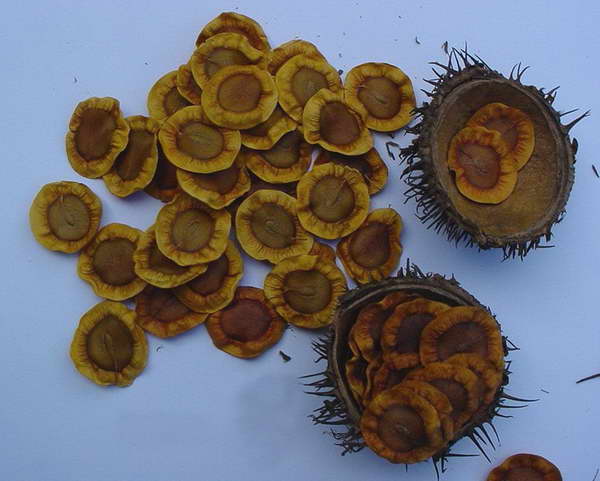


Allamanda seeds photo
- Seeds should be sown in late February - early March.
- Before sowing, it is advisable to treat the seeds with a low-borne solution of potassium permanganate and rinse.
- Then dry them slightly and sow them in a light soil mixture at a distance of 3-5 cm, sprinkle on top with a layer of sand or loose soil with a layer of 0.5 cm.
- Spray with a fine spray and cover with cling film or clear glass to create a greenhouse effect.
- Lighting is required bright diffused, and the temperature is within 22-25 ° C, also raise the shelter daily for ventilation, periodically moisten the soil.
- Under such conditions, the emergence of seedlings should be expected 3-6 weeks.
- After that, gradually accustom the nursery to life without shelter.
- At the stage of appearance of 3-4 true leaves, we transplant into separate containers and grow to transplant into permanent pots.
Possible problems when growing allamanda
In the absence of proper care, the plant can become sick. Often, novice flower growers complain that allamanda has turned yellow, its leaves are twisted or have acquired a brown color. Such changes in appearance indicate that the flower has been overly hydrated or has been exposed to hypothermia.
In the case when the leaves become too pale, and the shoots are elongated, the plant grows slowly and does not bloom very abundantly, most likely, it lacks light and nutrients.
Another possible problem when growing allamanda is the blackening of the base of the stem, this disease is known as "black leg", which also indicates abundant watering and insufficient light.
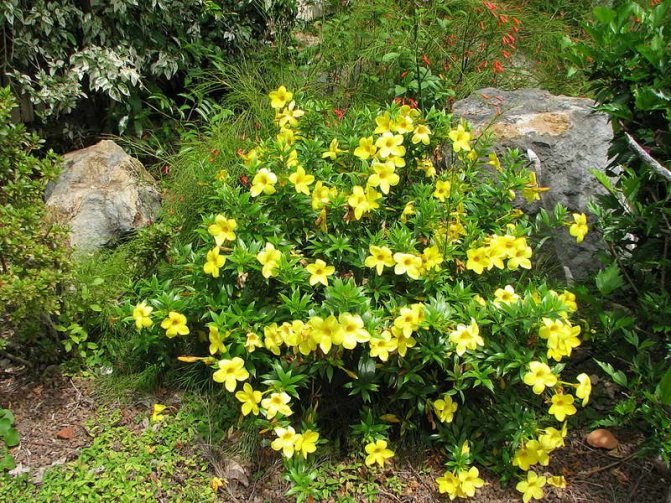
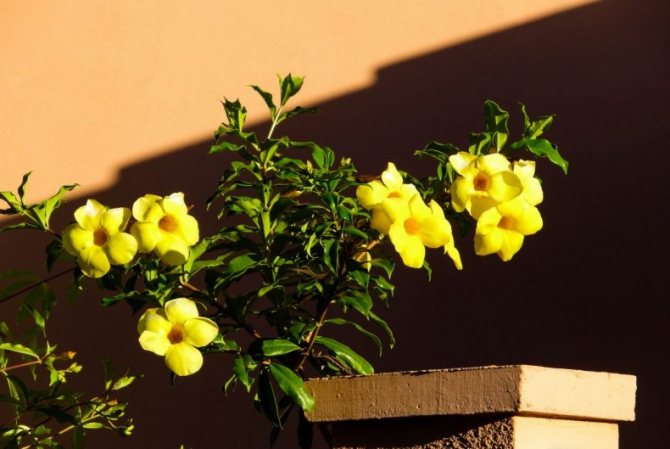
This graceful flowering ornamental plant is often used in vertical landscaping. It is mainly grown in conservatories and greenhouses.
Given that the allamanda houseplant is quite capricious and fastidious, it is not recommended for growing for beginners in floriculture. Only experienced flower growers can grow a beautiful and healthier plant.
Origin. Brazil
Description.
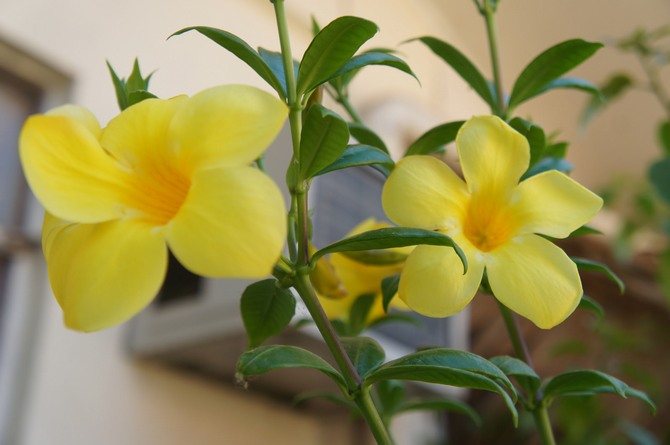
Allamanda is a laxative - this tropical evergreen plant has long stems densely covered with glossy, dark green oval leaves, 3-4 leaves in a whorl. Inflorescence is an apical brush. The buds appear in the summer at the ends of the stems, open with yellow tubular flowers up to 10 cm in diameter. Support the plant as its flexible stems grab onto it and easily twist around the trellis. This plant requires a lot of heat, moisture and light.
Allamanda Terry
differs in a large number of petals in flowers, which makes the flowering look more lush.
An evergreen shrub with shiny dark green leaves, about 12 cm long. Flowers with a long flower tube and 5 rounded petals, yellow, up to 15 cm in diameter.
Height
... Up to 2.4 m if not trimmed. There are dwarf varieties with a height of about 38 cm.
Description
Allamanda is a tropical flower with long branches and shiny leaves in a rich green color. Allamanda's homeland is South America, in particular Brazil. The plant belongs to the kutrovy family. The stems are very elongated; at home, their length can reach 4 meters. They easily cling to the supports and pull upwards. Allamanda loves a lot of heat, moisture and sunlight.
With proper care, the plant produces flower stalks. They have a pleasant aroma and a varied color palette: yellow, pink, purple, coral. The shape is a drop-down bud, consisting of 5 petals.
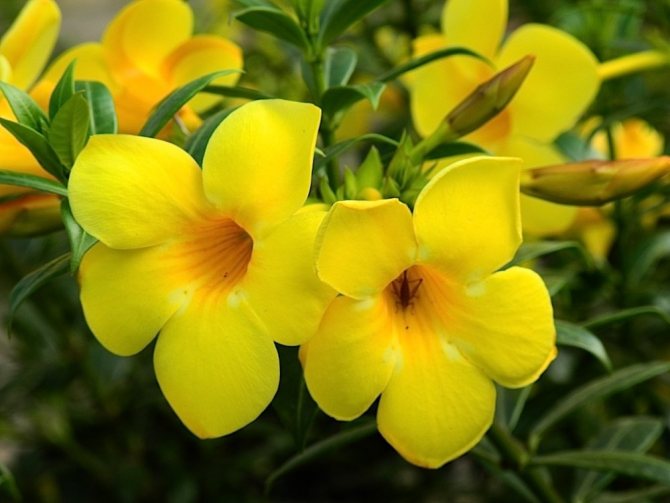


Popular Allamanda varieties suitable for home growing:
- Oleandroliferous - a small bush, up to 1 meter high. With large (up to 12 cm) leaves that have a transition from rich green at the top to a lighter shade at the base. Flowers are yellow, up to 4 cm in diameter;
- Yellow terry. Height - up to 1 meter. The leaves are elliptical with sharp tips. Flowers are yellow with a velvet surface;
- Laxative. The name of the species corresponds to its effect on the human body.Climbing plant, up to 4 meters long. The leaves are large, more often in the form of an ellipse. This species includes many separate varieties: Noble. The shoots are reddish. The leaves are large (up to 20cm) with a sharp tip. The flowers are bright yellow, with white dots and a pleasant aroma;
- Henderson. Fast growing specimen. Leaves are collected in a knot of 3-4 pieces. Flowers are bright yellow or orange with chaotic white spots;
- Large-flowered. Climbing, slow-growing plant. Leaves in the shape of an ellipse, lemon-colored flowers up to 10 cm in diameter;
- Schott. Shoots are directed downward, numerous tubercles are visible on them. Leaves grow in nodes of 3-4 pieces. Flowers are yellow with an orange center;
- Purple. A plant with long shoots, a slow-growing plant. Lanceolate leaves. Flowers are located on the tops of the shoots, can be of all shades of purple: from pale to rich.
Allamanda - home care
Temperature conditions
... A fairly wide range of temperatures from 18 to 27 ° C is suitable for growing allamanda at home. It does not tolerate frost, the minimum temperature in winter is 16 ° C. A winter period of dormancy is desirable, when the growth of the shrub slows down.
Allamanda lighting
... Prefers bright light. Give at least 4 hours of direct sunlight every day.
How to care
... Keeping the plant outdoors in summer will give you more abundant flowering. As soon as night temperatures approach 16 ° C, return the plant to the house. It is advisable to radically prune the plant in early spring to maintain a compact shape, if necessary, up to half the length of the stems.
Growing allamanda - soil
... Sufficiently moisture-permeable - with the addition of peat and sand.
Top dressing
... Allamanda in a pot has a limited feeding area and needs additional feeding. Every 2 weeks of spring to autumn with a fertilizer with a high phosphorus content, diluted by half.
Appointment
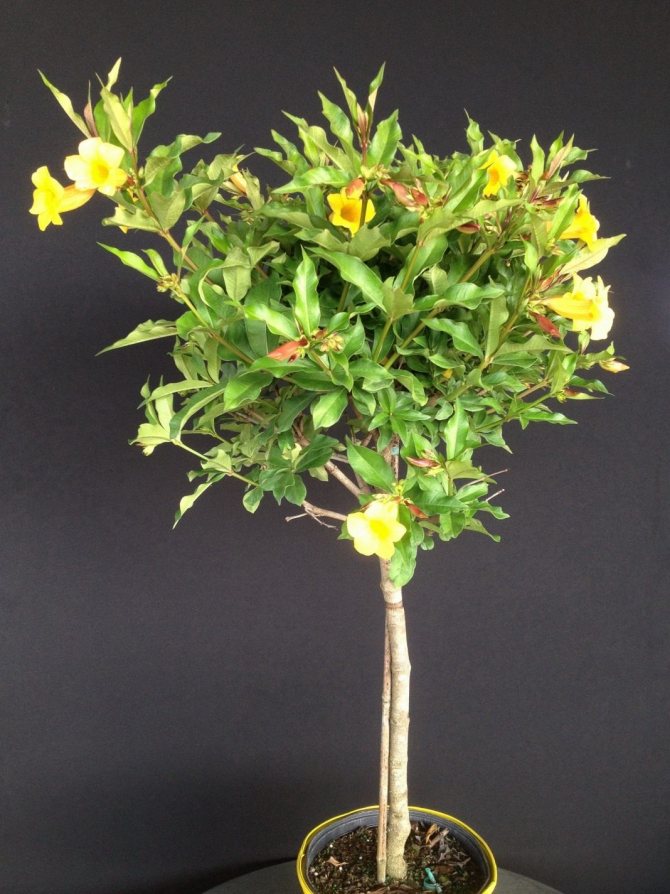
... Allamanda is sometimes grown as an attractive flowering bonsai.
Flowering time
... Large, funnel-shaped yellow flowers appear all summer and all fall.
Air humidity
... Moderate to high (50% relative humidity or higher). Use a damp pebble tray or a room humidifier to increase the moisture in the air around the plant.
Watering allamanda
... In winter, watering is very economical, feeding is stopped, but never let the soil dry out completely. The top 5 cm of soil should dry out between waterings. Good drainage is essential.
Transfer
... It is one of the few flowering plants that grows well in a large pot. Use a pot with drainage holes to prevent soil dampness as the plant is prone to root rot.
- Growing temperature
: throughout the year from 18 to 27 ° C. - Lighting
: at least 4 hours of direct sunlight daily - morning and evening. - Watering and humidity
: dry the soil a few centimeters deep between waterings, it is advisable to increase the air humidity. - Pruning
: formative, held in spring. - Priming
: nutritious with good drainage. - Top dressing
: during spring and summer with mineral fertilizers every 2 weeks. - Reproduction
: Apical cuttings in spring and summer.
You may also be interested in:
The genus Allamanda has about 15 evergreen lianas and shrubs, which are successfully grown at home and are not too capricious in their care, they are part of the kutrovy family. In the wild, it is most often found in the rainforests of Central, South and North America.
And in cultural cultivation, it is most often used in vertical gardening, as a beautifully flowering plant.
Transplant features


How to transplant allamanda at home
As usual for all crops, transplanting young plants should be carried out annually, and after reaching the age of three years - with a frequency of 2-3 years. Repotting should be done in the spring to stimulate growth.
The soil requires nutritious, loose. It is advisable to cook it yourself: we take 2 parts of leaf and humus soil, add 1 part of sod land and peat, mix 0.5 parts of sand for looseness. Mix all the ingredients well and proceed with the transplant procedure.
- Take a container with a slightly larger diameter than the previous one, put a layer of drainage on the bottom, then pour a little substrate.
- Remove the flower from the pot, carefully remove about a third of the soil from the roots (you can use any garden tool) and move it to a new container, placing it in the center.
- Fill the voids with the substrate, and press the soil around the stem with your palms and water.
Varieties and types
It is a shrub, reaching up to 90 centimeters in height, quite often found with climbing, drooping shoots. Leaves are elliptical short-petiolate, pointed-elongated, with a dark green color on the upper side, and with a lighter shade on the lower side, reaching up to 12 centimeters in length. The flowers have a yellowish tint and are located on long pedicels, reaching up to 4 centimeters in width, with a swollen corolla tube.
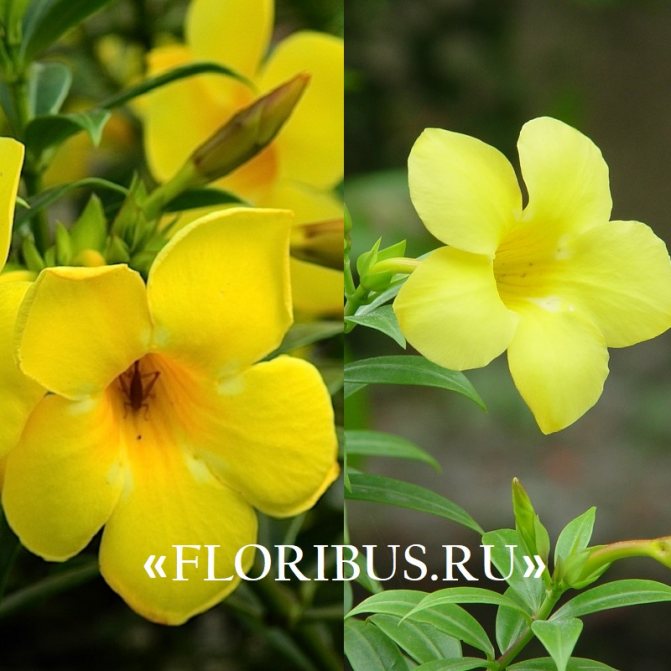
One of the most popular cultivated species. It is a climbing plant, reaching up to 6 meters in length. The leaves are ovate-elongated, opposite, often glabrous, have pubescence only in the lower part of the shoot, rather large, reaching about 14 centimeters in length and 2-4 centimeters in width. The flowers are golden yellowish with a whitish base, which are collected in the apical part of the shoot, tubular-funnel-shaped, rather large, up to 5-6 centimeters wide. There are also many forms in cultivation, but a number of authors evaluate them as independent species.
differs from laxative in large elongated lanceolate sessile leaves and reddish shoots, foliage reaches up to 20 centimeters in length. The tops of the leaf cover are pointed, pubescent from the bottom. There are 2-3 leaves in internodes. The flowers are golden yellow in color with a light speck in the throat, reach up to 12 centimeters in diameter, the aroma is very pleasant, somewhat reminiscent of magnolias.
It stands out from all varieties for its rapid growth. The leaf cover is thick, leathery, collected in 3-4 pieces. Flowers are orange-yellow in color with light spotting, reaching up to 12 centimeters in diameter.
Due to its thin climbing shoots, it can be grown as an ampelous plant; rather slow growth is noticed. The leaf cover is ovate-lanceolate, rather small. The flowers are lemon yellow in color, reaching up to 10 centimeters in diameter.
It is a fast-growing vine with pubescent shoots and warty branches. The leaf cover is lanceolate and wide, collected in 3-4 leaves. The flowers are yellow with brown stripes and a dark yellow throat.
A rather slowly growing liana with densely pubescent, elliptical leaves, reaching up to 10-15 centimeters in length, collected in 4 pieces. The flowers are light purple in color, they are concentrated on the tops of the shoots in 2-3 pieces.
Allamanda: varieties
Before we move on to the rules of home care for the Allamanda, consider those types of tropical guests that are adapted to growing in an artificial environment.
- Allamanda nobilis.
It has large lanceolate leaves (up to 20 cm in length), pubescent on the back. Flowers of deep golden color with light specks in the pharynx area. In diameter, they can reach 12-14 cm. - Allamanda laxative (Allamanda cathartica).
The most popular domesticated species, suitable for indoor cultivation. Vines are strong, they can grow up to 5-6 m in length.Leaves are oval, pointed at the ends. Funnel-shaped flowers are located on the tops of the shoots, have a yellow color and 5-6 cm in diameter. - Allamanda oleandrolist (Allamanda neriifolia).
The bush can reach a height of 1 meter. Shoots are weak, drooping. Ovoid leaves are dark green in color, slightly pubescent on the back. Bright yellow flowers 5-7 cm in diameter are located on a long peduncle. - Allamanda violet (Allamanda violacea).
Vine leaves are pubescent, have an elongated shape, reach 13-15 cm in length. The flowers are funnel-shaped and light purple or lilac in color. The species is characterized by a rather slow growth. - It grows too slowly. Stems are weak, leaves are medium (5-8 cm in length) lanceolate-ovate, collected in 4 pieces. The color of the flowers is from light lemon to dark yellow.
- Allamanda Henderson.
Differs in dense leaves and accelerated growth. If the vines are not cut, they can reach about 2 m in a year. The flowers are large (up to 13 cm in diameter), yellow or orange. - Allamanda schottii.
Leaves are oval with pointed tips. The shoots are pubescent and grow quickly. Flowers are yellow, medium-sized, funnel-shaped.
Consider what kind of care is needed for Allamanda at home.
Location selection, lighting
Direct sunlight is a must for a tropical vine. In hot climates in the summer during the midday period (from 12.00 to 16.00) it is better to avoid direct sun exposure. The right choice for a flower would be the southeast or southwest side. It is better not to place allamand on the north side.
From a lack of light, it will develop poorly and you will not wait for flowering from it.
In winter, on cloudy and short days, it is necessary to use artificial lighting.
Temperature
In summer, the optimum temperature for keeping lianas will be + 20-25 ° C. In winter, the plant "falls asleep" and can live peacefully at a temperature of + 15-18 ° C. The culture will tolerate a short-term heat calmly, but a drop in temperature below + 10 ° C is fraught with the fact that the roots and stems will begin to freeze.
Allamanda is especially sensitive to drafts - they greatly harm the delicate beauty, especially during the flowering period. When caught in a strong wind, the vine can quickly shed all the flowers. But she also needs fresh air, the room should be well ventilated.
Avoid sudden temperature fluctuations in the room. It is desirable to maintain a stable microclimate.
Humidity
Allamanda likes high humidity (70-80%). If the air in the area where it grows is dry, it must be humidified. To do this, use containers with water, automatic humidifiers, fine-dispenser systems that spray water.
In summer, the flower can be sprayed with a spray bottle. The main thing is that the water for spraying is at room temperature, and not cold.
In no case should a tropical liana be placed near heating appliances.
Watering
Water the plant abundantly in summer and moderately in winter. There are no clear instructions for the intervals between watering - it is necessary to monitor the soil and prevent it from drying out by more than 50%. In the warm season, irrigation is done about every other day or every two days.
With the onset of cold weather, watering 2 times a week or even 10 days is enough. But it is important to ensure that there is no waterlogging. Water should not stagnate on the surface of the substrate or in the sump.
Fertilizer
Caring for Allamanda at home involves feeding without fail. The plant is suitable for complex universal mineral fertilizers for flowering home crops.
They begin to feed the liana in the spring with a frequency of once every 20-25 days. In autumn, the interval is slightly reduced, and in winter it is completely stopped.
Pests, diseases
The flower is sick, mainly from improper care: drafts, cold, excessive nailing under the scorching sun.
Transplant, soil
For the first 3-4 years, Allamand needs to be replanted every spring. Each time she will need an ever larger flowerpot.
When the plant becomes an adult, it is transplanted every 3-4 years.
Liana is suitable for ready-made store-bought slightly acidic substrate for tropical plants.
You can prepare the soil mixture yourself:
- Deciduous land - 2 parts.
- Sod land - 1 part.
- Humus - 4 parts.
- Peat - 1 part.
- Sand - 1 part.
A good drainage layer must be laid at the bottom of the flowerpot. After transplanting, the substrate is immediately moistened.
Reproduction
Allamanda is propagated by cuttings and seeds in late spring, when stable warm weather is established.
- The seeds are first soaked in water for 2 days.
- Then for a short time (an hour or two) they are placed in a solution with an antiseptic.
- After that, they are sown into a substrate of sand and peat to a depth of 1-2 cm.
- The containers are covered with plastic wrap and removed to a warm place.
All this time, the seeds should be at a temperature of + 22-25 ° C. Every day it is tedious to open the film and irrigate the soil.
As soon as the shoots appear, the film is completely removed, and the containers are placed in a bright place. When the sprouts are 5-7 cm high, they can be planted in separate pots.
The situation is much simpler with cuttings: a cut twig is also immediately placed in a soil of sand and peat, irrigated every other day, kept warm and in the light. The cutting takes root quickly enough and after a month it can be transplanted into a flowerpot.
Pruning
In order for the vine to retain its decorative appearance, it must be cut off after flowering. Weak shoots are removed completely, long ones are shortened in half. Sometimes pruning is carried out 2 times a year - in spring and autumn.
Allamanda home care
Allamanda is a light-loving plant that tolerates not much direct sunlight. It is best to place the plant on the windows of the south, south-east and south-west orientation. The plant is well suited for landscaping bright conservatories and greenhouses.
In the summer, the plant needs to provide a temperature limit of 20 to 24 degrees. And in the period from November to February, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for a dormant period, reduce watering and the temperature of the content to 15-18 degrees. Draft is bad for plant development.
Watering and water humidity
In summer, the Allamanda vine needs abundant watering, but you should not allow strong waterlogging or drying out of the soil. In winter, moderate watering is provided, after the top layer of the soil has dried.
When keeping allamanda, it is necessary to ensure a favorable air humidity in the range of 60-70 percent. For this reason, the plant needs frequent spraying during the growing season, while water should be avoided on the flowers, this can worsen their decorative effect. Also, dishes with a plant can be placed on wet expanded clay or pebbles, but so that the dishes do not touch the water.
Allamanda pruning
At the end of November, to improve the flowering period of the allamand, pruning is done. At the same time, they are cut to half the height of the shoots, above the leaf internodes, or pinching is used for young shoots.
It is also necessary to carry out cleansing pruning from thickening and weak shoots during the entire growing season. The stem part of the plant must be tied to supports, since they are not strong enough.
Be careful and use gloves, as the milky sap of the plant is poisonous!
Transplanting soil and fertilizers
Allamanda needs to be fed with mineral and organic fertilizers, which are applied every three weeks in normal concentrations, during the period of active growth.
In the spring, after flowering, allamands require transplanting, young specimens annually, and older ones as needed, approximately once every two to three years.
The ground mix can be composed of:
- 2 parts of leaf and 1 part of sod land, 2 parts of peat and 1 part of humus, with the addition of 1/3 part of sand.
- 1 part of sod land and 2 parts of deciduous land, 5 parts of humus, 1 part of sand and 1 part of peat.
Botanical description and beneficial properties
Allamanda is a perennial evergreen of the Kutrov family. It is a shrub or liana, the shoots are thin and flexible. The leaf plates are arranged in pairs, they are oblong in shape with a sharp top, the color of the leaves is deep green, they shine, as if oiled.
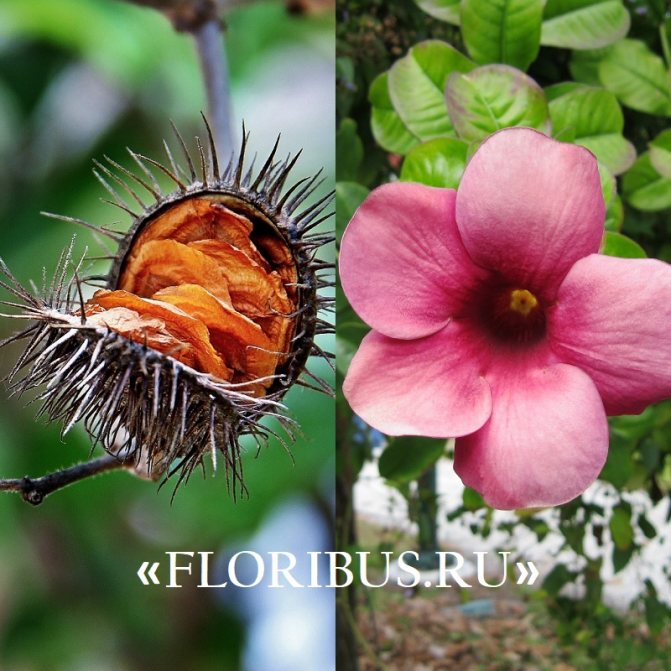
The inflorescences are in the form of tubes with five petals, the diameter is 8-12 cm, and the shades of the corollas are the brightest (sunny yellow, pink, there are snow-white and cream). When twigs or leaves are broken off, milk juice flows out, all parts of the plant are poisonous.
The plant is medicinal, acting as an antibiotic against microorganisms of the genus Staphylococcus. It is used as a medicine against complications of malaria, against enlargement of the spleen, and helps against jaundice. It is an excellent laxative.
Unfortunately, the plant does not tolerate frost at all, it can only withstand a short-term drop in temperature to 1-2 ° C, and dies during frost. That is why allamanda is grown here exclusively as a greenhouse or indoor plant. At home, it is widely used to decorate facades, garden recreation areas and park areas.
Bloom
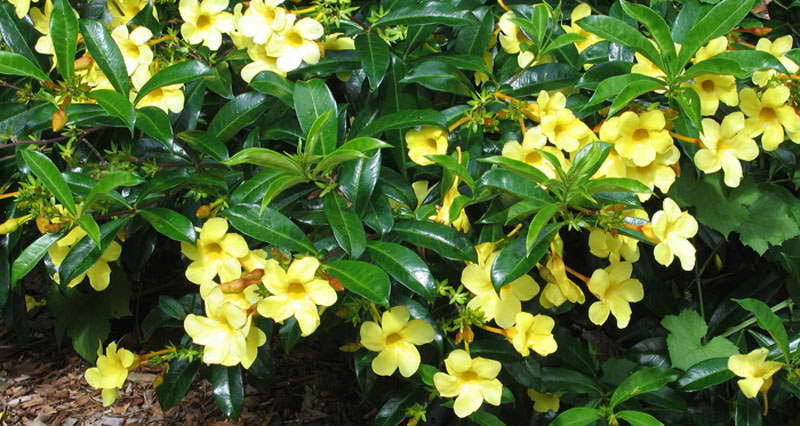


Allamanda yellow flower photo
Alas, it is not so easy to achieve flowering of allamanda in indoor conditions. The fact is that in the natural environment, Allamanda lives in the humid tropical forests of North and South America. The plant needs warmth, high air humidity - in a greenhouse, this is not difficult to do, but more effort will be required for indoor cultivation. Do not despair, because even whimsical orchids bloom regularly with proper care.
Propagation by cuttings
When propagated by cuttings, the semi-lignified shoots are cut off about 8-10 centimeters in length, which are rooted in wet sand. If faster rooting is required, the cuttings are treated with growth stimulants and provide lower heating of the soil. Newly planted cuttings need constant ventilation and spraying and are kept within a temperature range of 22 to 25 degrees.
After the cuttings take root, they are dived into the soil, made up of equal parts of humus earth, sod land, with the addition of sand. And after about 1-1.5 months, the plant is provided with the usual care, as for an adult Allamand.
Planting and leaving
This houseplant feels equally well in the apartment, and in the winter garden or greenhouse. However, for its maintenance, a sufficient volume of premises will be required, since Allamanda reaches impressive dimensions.
When growing a flower, it is necessary to maintain a temperature not lower than +17 and high air humidity. Only if these conditions are met will the plant bloom regularly.
Important! Allamanda has poisonous juice. Its contact with the skin and mucous membranes causes irritation and burns. All manipulations with the flower must be carried out only with gloves.
Transplanting and soil selection
For planting, nutritious, loose soil with a slightly acidic or neutral reaction is suitable. You can buy it ready-made, or make it yourself. The mixture includes equal parts of leafy earth, humus and sand.


For planting, it is better to choose a spacious pot, the plant loves a large amount of land. The faster a particular variety develops, the more land it needs. It is worth making additional drainage holes, or increasing the existing ones. Allamanda roots are very sensitive to overflow and rot easily.
The frequency of transplants depends on the age of the plant:
- young - once a year;
- over 3 years old - once every 2-3 years;
- freshly purchased plant - no earlier than two weeks after purchase.
The optimal time for the procedure is early spring, March. The transplant is carried out by the transshipment method, without injuring the root system.
Attention! If the diameter of the pot is equal to or greater than 1 meter, then the transplant can be omitted. It is enough to cut off the roots at the edges and add new soil.
Light mode
Light is an important condition for the correct keeping of this plant. There should be a lot of it, so it is better to stir the pots on the south side. In winter, additional lighting is required. The duration of daylight hours should be at least 12 hours in all seasons.
When direct sunlight hits the foliage, it is worth creating an artificial shade. Otherwise, burns will appear on the leaves and peduncles.


Temperature regime
The temperature of the content varies, depending on the season:
- in autumn and winter - from +17 to + 19;
- in spring and summer - from +20 to +25.
If the temperature drops below + 16 ... + 17, the plant may die. Allamanda does not tolerate even short-term frosts and freezing temperatures. Drafts are also contraindicated; when ventilating the room, the plant must be protected from the movement of cold air.
Humidity
The moisture content in the air must be high, at least 60%. To do this, it is necessary to carry out regular spraying from a spray bottle. And also, place the pot in a tray with wet expanded clay or install a humidifier.


Watering
Allamanda loves moisture very much, its irrigation regime changes, depending on the season:
- in summer - daily or every other day until the earthen coma is completely moistened;
- when the temperature drops - only after the top layer of the soil has completely dried. The dry soil must be at least 5 cm thick.
Important! For irrigation, you can use only soft, settled and lukewarm water.
Top dressing
Fertilization is carried out during spring and summer, as well as during the flowering period. Frequency - no more than twice a month. Complex mineral fertilizers intended for indoor plants are suitable as fertilizers. Organic fertilizers should be applied no more than 1 time in 2 months.
Trimming and shaping
Cropping is required in the following cases:
- with excessive growth of vines;
- to increase the number of peduncles.
The time for pruning is in February, before the onset of abundant flowering, or in November, after the completion of the ejection of the peduncles.
1/2 of the longest branches should be pruned. The slice should be a few centimeters above the node with the growth point. All dried shoots are subject to mandatory removal.
Reference! To form a lush bush, you need to regularly pinch young shoots.
Possible difficulties
- Rotting or blackening of the base of the stem and root collar, possible reasons may be excessive soil moisture, high seeding density or lack of lighting. This can lead to Black Leg disease of the plant. It is necessary to ensure proper watering and good illumination.
- The leaves are pale and turn yellow, the growth of the plant has slowed down, the stems are elongated, and the flowering is not stable, this may be due to a lack of nutrients or a lack of lighting.
- The leaves turn brown and curl, due to excessively moist soil and a supercooled plant.
- Allamanda can be damaged by pests such as spider mites, nematodes, aphids, whiteflies if proper home care is not provided.
Latin name
:
AllamandaFamily
:
ApocynaceaeHomeland
:
Tropics of South AmericaGrowing
:
medium difficultyLocation
:
bright lightTemperature
:
not lower than 15 ° СWatering
:
moderate from spring to autumn, in winter - limitedBloom
:
in summerHeight
:
up to 3 m for climbing species, 1-1.5 m for shrubsTransfer
:
annually in springCare
:
removal of wilted flowers and damaged parts
On a note
Allamanda is not very widespread.This plant can only be purchased from specialist stores and garden centers. It is best to buy allamanda in spring or autumn.
Allamanda Photos


The genus Allamanda includes 15 species of graceful shrubs and climbing evergreens. Of greatest interest is the curly species of Allamanda laxative (A. catharnica), whose representatives in the wild reach 3.5 m in height. The Grandiflora variety has light yellow flowers, reaching 10 cm in length, while the Hendersonii variety has a yellow-orange color. Plants of the A. neriifolia species have spear-shaped leaves, grouped into groups of 3-4 leaves, and yellow tubular flowers reaching 4-5 cm in length. The height of this bush is about 1-1.5 m. Growers also grow A. Violacea, a plant with sufficient resistance to low temperatures, with pink-purple flowers blooming in autumn, and A. Nobilis with fragrant yellow flowers.
Features of growing at home
The best place for allamanda would be a window that is located on the south side of the house, or in the southwest, or southeast, since this beauty loves sunlight.
However, with a great love for the sun's rays, allamanda is very sensitive to air humidity. The optimum humidity for it will be 60-70%. To maintain such humidity, the flower pot can be placed on a tray with damp pebbles or in a bowl with damp peat; you can also use frequent spraying, but try to avoid getting water on the flowers so as not to spoil their decorative effect.
Pruning in late fall will allow for a better flowering process. Pruning is best done at half the height of the shoots above the leaf nodes, while observing safety precautions, since the plant sap is poisonous.
The soil is neutral or slightly acidic, watered regularly, but not poured.
Attention!
Allamanda does not tolerate drafts, and also does not like waterlogging or drying out of the soil. Observance of the correct temperature regime (in winter, the temperature should not fall below 18 ° C) will help you keep a flower that will never cease to amaze and delight you.
Care
Caring for allamanda consists in removing wilted flowers and yellowed or damaged parts of the plant, as well as in constant spraying.
Reproduction
In spring, allamands use stem cuttings for reproduction. Taken from branches without flowers. They are rooted in a substrate of peat and sand, taken in equal parts at a minimum temperature of 21 ° C. For better rooting, phytohormones and bottom heating are used.
Difficulties you may face when caring for Alamanda at home
There are no flowers for a long time.
The reason that the allamanda does not have flowers may be a lack of light and a lack of nutrients, but, as a rule, the plant in this situation just needs a rejuvenating haircut. Cut it: young shoots will go, and the old ones will just see the light. This method is the best "stimulator" for flowering. It is best to cut the plant in late autumn, then next year it will bloom.
The plant wilts
... This can be caused by overdrying the soil (in summer) or keeping it in the cold with damp soil.
Allamanda leaves curl, turn brown
... The reason for this is cold, put the pot in a warm place.
Leaves turn yellow, stems are strongly elongated
... Again: not enough light, possible nutritional deficiencies.
The plant stretches strongly, becomes rare and unattractive
... Most likely, there is not enough light, in addition, the vine needs pruning.
The leaves turn black, the stems begin to rot.
I think you already understand everything: too much water, plus keeping it in the cold.
Move the pot to a warm place, treat the plant with a fungicide, if it does not help, transplant. If the transplant also did not help save the flower, cut and re-root the young shoots.
Based on materials from the magazine "Indoor and garden plants from A to Z"
| Adenium Adeniums stand out in the large group of "domestic" plants for their exoticism - small trees or shrubs, with thick trunks, shiny or velvety leaves and large flowers from white to dark crimson. |
| Tabernemontana: Growing and Care They say that everyone on Earth has their own counterpart. So Tabernemontana looks like a double of a gardenia (they are very similar), but not so capricious in their care. Tabernemontana is also called Indian carnation or Indian oleander - for the splendor of flowering, during which it becomes similar to these plants ... |
Correct and timely pruning is the key to the flowering of allamanda. It should be carried out at the very end of autumn. All shoots are cut in half.
Note. The plant needs support. Its shoots are weak and fragile, so they need to be tied up.
Reproduction of allamanda
The flower can be propagated both by seeds and cuttings. The seed propagation technology is nothing special and is similar to. Unless it is necessary to constantly maintain the temperature not lower than +22 degrees. Seedlings may appear in three weeks, but you may have to wait up to 6 weeks.
It is much easier and safer to propagate allamanda by cuttings (if there is a mother plant). Young semi-lignified cuttings from 7 to 10 centimeters long are suitable for reproduction. They can be pretreated in a solution of any stimulant (Kornevin, Heteroauxin, etc.). Warm and humid conditions should also be created for cuttings. Ideally, if a mini-plate will be used.
The most favorable time for the breeding of Allamand is the end of winter - the beginning of spring.
Diseases and pests
Allamanda is quite resistant to diseases and pests.
Let's consider problem cases:
- Although the plant needs high humidity, the root collar can rot under such conditions. Treat the plant urgently with a fungicidal preparation;
- Stems and shoots become long, thin, and leaves turn pale with insufficient light or lack of nutrients - move the plant closer to light or feed;
- Waterlogging of the soil, hypothermia, as well as a draft provokes leaf discharge;
- Allamanda can suffer from pests such as spider mites, aphids, whiteflies. If you find them, treat the plant with an insecticide, but first bathe the bush in a warm shower.
Difficulties in growing allamanda
Does not bloom for a long time. Despite the fact that the reason that allamanda does not bloom can be both a lack of light and depleted soil (lack of necessary ones), the most likely reason is ignoring the obligatory annual pruning. If allamanda is not cut off, then even if all the other rules of care are followed, flowering may never come.
Allamand leaves begin to curl and turn brown. Obvious non-observance of the temperature regime. The flower is cold.
The stems are elongated, the foliage is thinning. There can be two reasons: the flower has not been cut for a long time and insufficient feeding.
Allamanda droops. Improper watering. Equally, this can be both overdrying and waterlogging of the soil.
Blackening of leaves and stem decay. Most often, this phenomenon is associated with improper watering during the wintering of the plant. Excessive watering when kept cool can kill any plant! In the initial stage, fungicide treatment and moving to a warmer place can help. But it is also advisable to play it safe and immediately transplant the plant. If the process has gone too far, then before it's too late, take cuttings and start growing a new plant.
Have you noticed a mistake in the text?
Select it with the mouse and press Ctrl + Enter
Site search
Sections of the site
Recent articles
Popular types of allamanda


Allamanda laxative is an evergreen climbing plant that can reach a length of 5-6 m.Leaves are ovoid, opposite each other, smooth, slightly pubescent only at the base of the attachment to the stem. Yellow large flowers are located at the top of the shoots, tubular in shape.
- As an independent unit, the noble ammalanda is distinguished, which has slightly red shoots, growing in the form of a liana with smooth elongated leaves. Flowers of a yellow shade with a white center, 11-12 cm in diameter, have a unique aroma.
- Allamanda Henderson has thick leaves, grows quickly and develops in the shape of a vine. The diameter of the flowers is about 12 cm, the color is orange-yellow with white specks on the petals.
- The large-flowered allamanda is a slow-growing evergreen that has thin, curly shoots. The leaves are elongated, ovoid, small. The diameter of the flowers reaches 10 cm, the bloom is strong. The shade of the flowers is lemon yellow, bright and rich.
- Allamanda Shota is a fast-growing evergreen vine with pubescent shoots. Broad leaves are collected in 3-4 pieces. Large dark yellow flowers have brown stripes.
Allamanda deer-leaved - grows in the form of an evergreen shrub, climbing stems, drooping. In length, the shoot can reach 1 meter. The leaves are pointed, 10-12 cm long, dark green above and light green underneath. The flowers grow on long legs, yellow, the diameter relative to other species is small - about 4-5 cm.
Allamanda purple - is a slow-growing evergreen vine with oval leaves arranged in 4 pieces. Flowering is noted only on the tops of the stems, flowers are pale purple, 2-3 pieces each.
The striking exterior of the jungle bell
Allamanda's popular nicknames vividly describe her appearance. "Jungle bell", "golden pipe" - these epithets really convey the main features of the plant better than others. After all, simplicity, laconism of forms and showiness, minimalism and catchiness are the best in allamands.
Allamanda is a genus of plants in the Apocynaceae family, named after Leiden University professor Frederic Allamanda. The genus has 15 species.
The most widespread in room culture received allamanda laxative (Allamanda cathartica). It is difficult to guess that this allamanda belongs to evergreen vines. Indeed, in a room culture, the plant develops rather in the form of evergreen shrubs and rarely shows all its abilities in vertical gardening. But if you give allamanda laxative will, then curly shoots can reach 5-6 m in length. A beautiful cushion of greenery in a plant is formed due to large, up to 14 cm long leaves of a narrow, elongated-ovoid shape, sitting oppositely on the shoots. The cold, emerald color seems to have been created to contrast with the bloom. And allamanda's laxative is really outstanding. Large funnel-shaped flowers reach 5-6 cm in diameter, stand out with a bright, yellow-lemon-golden color with an almost imperceptible whitish base. Flowers bloom at the tops of the shoots, the corolla lobes are a bit like lilies. Bright "tubes" seem to crown the bushes, and the rich and even color makes an unforgettable impression.
The charming representative of the Kutrov family, when we first met on the shelves of flower shops, seems to be a remarkably compact plant. But you should not be mistaken about the size of the Allamanda: this is a large, constantly growing plant that will quickly "throw off" the influence of growth inhibitors and show all its true power. At the same time, the growth rate is average, but the very nature of the plant does not allow it to be ranked among compact indoor accent crops. Allamanda needs to be given a lot of space, this plant loves solo parties and does not tolerate competitors nearby: when placing it in the interior, it should be borne in mind that in splendid isolation Allamanda is able to outshine even a whole group of the brightest smaller cultures.
Allamanda blooms throughout the summer, from May to September. But the terms are often shifted, stretched, changed.
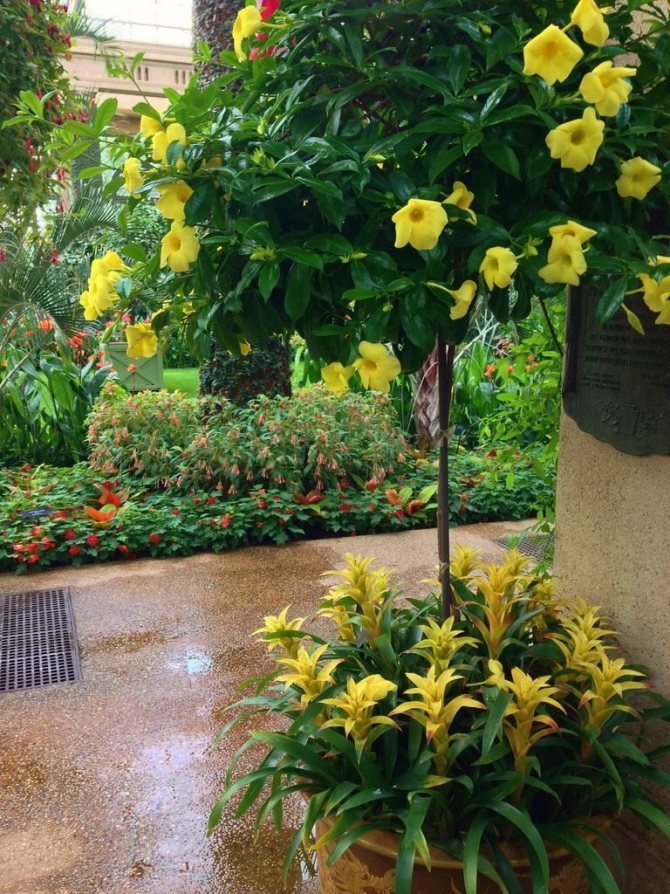


Allamanda laxative in a pot of gusmania.
In addition to the basic type, the plant has a number of decorative forms:
- noble nobilis with a reddish tone of shoots, lanceolate, sessile, very long twenty-centimeter leaves and golden flowers up to 12 cm in diameter with an unusual light spot in the throat and a delicate aroma of magnolias;
- hendersonii variety with accelerated growth, very thick, leathery leaves, collected in nodes of 4 pieces and orangey, with light spots on the petals, large flowers up to 12 cm in diameter;
- a large-flowered form of grandiflora with a diameter of only 10 cm, but very numerous lemon flowers, small lanceolate leaves and curly shoots, which is more suitable for the role of an ampel.
In addition to allamand laxative, there are about 15 species of plants in the genus Allamand, half of which are used as indoor plants. The best decorative types of jungle bells, in addition to the most popular type, include:
- Allamanda Shott (Allamanda schottii, formerly known as allamanda oleandroliferous - allamanda neriifolia) is a naturally shrub form with climbing, arcuate drooping shoots up to 90 cm long, long pointed-elliptical, very dark leaves and flowers up to 4 cm in diameter with a swollen corolla tube base;
- Allamanda Blanchet (Allamanda blanchetii, formerly known as allamanda purple - allamanda violacea) is a slowly growing liana with pubescent, grayish-gray leaves up to 15 cm in length, collected in nodes of 4 pieces, with unusual light lilac-pink flowers arranged in pairs at the tops of the shoots.


Allamanda schottii.
Decorative forms
Allamanda laxative in floriculture is represented by several decorative forms that differ in the size and color of the flowers.
Basically they are all fast growing.
- Large-flowered is an evergreen shrub with a height of 40 to 2.5 m with slender stems, latent leaves and large yellow gramophone flowers.
- Schotta is a liana with wide lancental leaves and yellow flowers that have a darker coloration of the throat and characteristic brown stripes on the petals.
- Henderson - differs in large flowers of an orange-yellow shade with lighter specks on the petals.
- Purple - unlike yellow allamanda, the bush has red flowers.
- Purple is a shrub with long ellipsoidal leaves and gorgeous lilac flowers.
- Oleand-leaved is a short bush with drooping stems, pointed elongated leaves and relatively small pale yellow flowers.


In addition to varieties with simple flowers, terry allamanda looks very gorgeous, which has a large number of golden yellow petals in each flower.
Important! All parts of the plant secrete milky latex, which can cause irritation, so it is best to wear protective gloves when in contact with allamanda. Plants also contain a laxative.
Allamanda care and cultivation
For young plants of fast-growing species of allamand, transplanting will require frequent, perhaps even several times during the growing season, and adult plants are not transplanted every year, about once every 2-3 seasons, they are guided by the state of an earthen coma in a pot, add fresh soil and periodically loosen ...
Allamanda is planted in a mixture of leafy and soddy soil, peat, humus and sand in the following proportions: 2: 1: 2: 1: 1, or use ready-made universal store soils for planting with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. Ampel species are placed on elevations in a very bright corner of a room with windows facing south, southeast, or southwest; vines will need devices that support the branches.
The plant does not like drafts and temperature changes, where allamanda grows, temperature conditions are observed from 16 to 20 degrees Celsius, in winter - at least 15 degrees above zero. High humidity is desirable, watering is abundant during the growing season, and moderate during dormancy from November to February. In the summer, spraying will be required, but without droplets of moisture falling on the flowers. A pot with a flower is placed in wet peat in hot weather. It is possible to grow the plant in hydroponics.
During the growing season, they are fed with universal fertilizers for indoor plants every 20-25 days at the concentration recommended in the instructions for use.
In October-November, after flowering and before the dormant period, the plant needs pruning.
Possible growing difficulties
Allamanda must be provided with support in the form of a lattice. The lashes bend well and you can create an interesting decorative composition from them.
If the plant does not develop well, the color of the leaf blades fades, and the flowering is poor, then the reason for this may be a lack of light and a lack of nutrients. If the flowers are kept in too cold conditions or are constantly exposed to drafts, the leaves begin to turn brown and curl. Too thickened crown can be the reason for poor bud formation.
Of the pests, flowers can attack aphids or mealybugs. In this case, it is better to treat the plant with insecticidal preparations. Of the fungal diseases, the most common root rot, which occurs when waterlogged and is treated with fungicides.
Although it is very problematic to grow and care for an exotic beauty at home, if you make some effort and try, then Allamanda will definitely reward with a chic appearance and wonderful flowering.
Allamanda: the nature of growth and flowering
Allamanda laxative, which is grown in a pot, regularly forms growths that lengthen by about 1 meter in one year. It can be grown like a liana, but for this allamanda requires a reliable support.
The first flowers appear on the plant around the beginning of summer. They will remain there until mid-autumn. Flowers appear at the tips of the shoots, so they can be pinched, which in the future will give a positive result - in the next season, flowering will be more abundant.
Reproduction
Allamanda reproduces by seed and vegetative means.
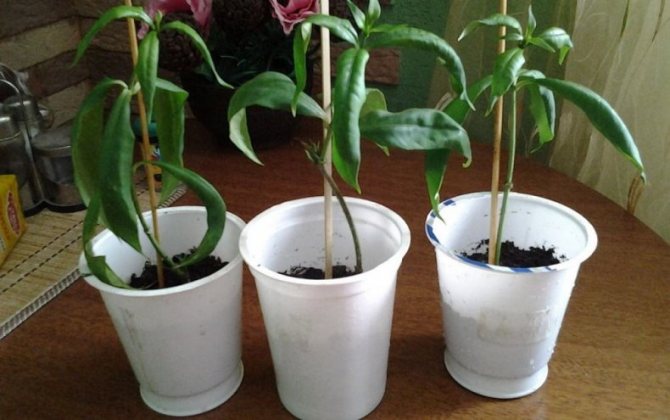


Reproduction by cuttings occurs in several stages:
- At the end of winter - with the arrival of spring, half lignified cuttings are cut, the length of which is from 8 to 10 cm.
- From below, the formed sections will not be superfluous to treat with a growth stimulator ("Zircon", "Kornevin", "Heteroauxin", succinic acid solution).
- The cuttings are planted in moistened sand, which is better to be slightly heated from below.
- Cover the seedlings with plastic wrap or other transparent device that provides diffused lighting.
- Carry out regular airing and spraying, maintaining an optimal level of humidity and temperature at +23. +25 degrees.
- When the first leaves appear, indicating that rooting has been successful, the cutting can be transplanted into nutrient soil.
- In one or two months, the full development of young Allamands will take place.
Features of seed reproduction:
- At the end of February or with the onset of March, allamanda seeds can be sown.
- The seed is preliminarily treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, washed and dried.
- Seeds are sown in moist soil, consisting of sand and peat in equal proportions, at a distance of 3 to 5 cm, sprinkled with a layer of soil 0.5 cm.
- Covering with polyethylene or other transparent material is provided.
- Ventilate and spray periodically.
- Maintain the temperature regime at +22. +25 degrees.
- The first shoots should appear in 4-6 weeks.
- Next, you should gradually accustom the seedlings to existence without shelter.
- After the appearance of several leaves, the seedlings are dived and gradually transplanted into separate containers with a more nutritious soil mixture.
Irrigation mode and air humidity
Allamanda does not like drought and can suffer greatly from the drying out of the earthen coma. In the spring-summer period of vegetative growth, observe the regime of abundant watering. But, with water procedures, you should not get too carried away. It is better to wait until the upper earthen lump dries up. In the autumn-winter season, watering is reduced to moderate. When the soil is swamped, rot begins to develop in the root system. For irrigation, use soft melt water without heavy impurities, especially lime. It is best to purchase bottled moisture for water procedures.
The humidity of the air in the room where allamanda is kept is of great importance. The humidity indicator is recommended in the range of 60-70%. In the wild, the perennial grows along the banks of streams and spreads its seeds with streams of rain. In no case should the air humidity at home content drop to 30-40 percent, as the leaves begin to turn yellow and dry.
In the spring-summer season, nutrients are added at intervals of 7-9 days. For this, mineral fertilizers are used for flowering plants.
Growing problems
- If allamanda does not bloom or blooms poorly, then the reasons may be too warm and dry wintering, lack of lighting, lack of nutrients in the soil, or overfeeding with nitrogenous fertilizers.
- Leaves curl, turn brown and fall off if the ambient temperature is too low, especially in wet soil. Those. if it is below 12 ° C in winter and below 18 ° C in summer, you need to dry the soil very well.
- Shoots and leaves wilted - if this happened in summer, then due to the drying out of the earthy coma, in winter - it is more likely that it is too cold and humid.
- If the leaves turn yellow, interveinal chlorosis appears - check the soil, remember that Allamanda prefers acidic soils, measure the acidity, replace the soil.
The genus Allamanda has about 15 evergreen lianas and shrubs, which are successfully grown at home and are not too capricious in their care, they are part of the kutrovy family. In the wild, it is most often found in the rainforests of Central, South and North America.
And in cultural cultivation, it is most often used in vertical gardening, as a beautifully flowering plant.
Crown formation and flowering of alamanda at home:
This liana has a phenomenal long flowering, which, if you use supplementary lighting, can be stretched throughout the fall.
Alamanda can be grown not only as a full-fledged vine and ampel culture, but also in the form of a bush. If you decide to grow this plant as a vine, pruning is not worth it, but it is worth providing it with support and tying branches. In other cases, formative pruning is indispensable.
The formation of the alamanda is carried out only after the beginning of the dormant period, most often at the end of November. All old, weak, thin, dying shoots are cut off, and young ones are pinched. Pinching young twigs allows you to stimulate the density and control the growth rate of the alamanda. If it is necessary to radically update and reduce the size of the vine, the shoots can be cut by a third or half the height. Trimming is done over the leaf nodes.


Allamanda Blanchetii. <>
Botanical description of the plant
The culture is named after Leiden University professor Frederic Allamand. The natural habitat for her is the tropics of South America, mainly Brazilian lands. It is a perennial evergreen culture of the Kutrov family.
Allamanda grows in the form of trees, shrubs, lianas. It reaches a height of 2 to 10 meters. Thin shoots are flexible.Most of the species representatives have aromatic flowers of yellow, purple, crimson, coral shades of significant size in a tubular shape. Each of the flowers has the shape of an opening bud, consists of five petals slightly protruding with a wider area.


All of them are collected in large inflorescences. When opened, their size is up to 12 cm. After flowering, in place of flowers, thorny fruits are located in the form of bolls filled with a large number of seeds. The oval leaves of the plants are arranged in pairs, have a pointed top, are distinguished by the smoothness and juiciness of a luxurious green color with a shiny oily effect.
Allamanda blooms all summer and autumn. With proper care, abundant flowering is repeated from year to year. The culture is excellent for growing conditions of conservatories and greenhouses with enormous spatial possibilities and significant air humidity. It is not so easy to grow Allamanda in residential premises.
Allamanda pests and diseases
Allamanda is a fairly persistent culture under comfortable conditions. When the air is too dry or in a weakened state, it is vulnerable to spider mites, whiteflies and nematodes. It is better to fight pests with comprehensive measures.
Common growing problems:
- curling leaves with excessive watering or hypothermia;
- browning of leaves at low temperatures or dampness;
- stretching shoots and pallor of greenery with poor lighting or insufficient feeding;
- the appearance of black spots at the base of the shoots - waterlogging or an urgent need to increase lighting.
Temporary pot and transplant
You can transplant a perennial immediately after purchase. A temporary pot is not suitable for permanent growing allamanda. This is best done in the spring. Some varieties are vigorous and quickly develop roots from drainage holes. For such specimens, an unscheduled transplant will be required. There are flowers that have to be replanted several times during the growing season.
Also, a transplant is necessary if you constantly use running water for irrigation. Due to hard, non-melt water, the soil can begin to saline. And this often becomes the cause of the death of an indoor flower. When choosing a soil, it is best to give preference to formulations specialized for azaleas or conifers.


During the transplant, you need to prune. This is necessary to stimulate the active formation of new flowers. Most of the soil should be shards and sand, as allamanda prefers moist, but not swampy soil. The plant will have to be watered very often, so there is a risk of waterlogging the soil. In warm weather, the soil near the room allamanda should dry out in no more than 4-5 days.