Each of us has seen a butterfly at least once in our life. These cute creatures, like sun bunnies, love to flutter in the meadows and parks of our country. In this regard, it is not surprising that many people often have certain questions about the life of moths. For example, who knows how butterflies eat? What do they eat and where do they get it?
Let's try to find answers to these questions. However, it will be necessary to understand not only the very diet of these creatures, but also how exactly they eat. Looking ahead, we note: much depends on their species and the place where, in fact, butterflies live.
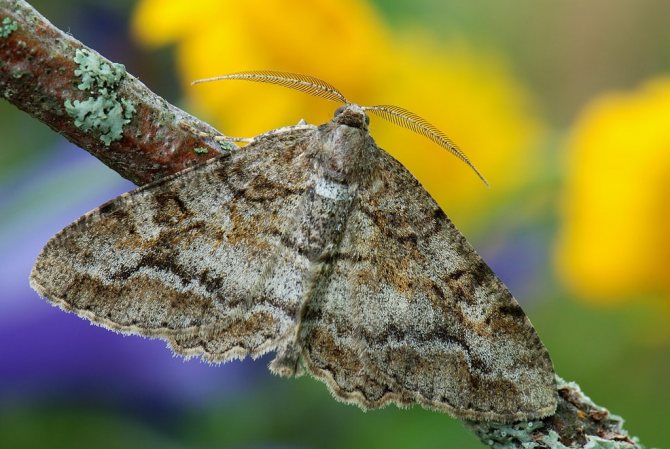
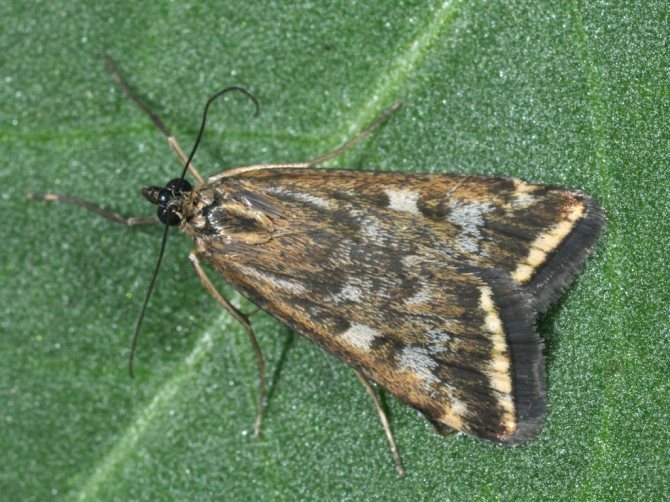
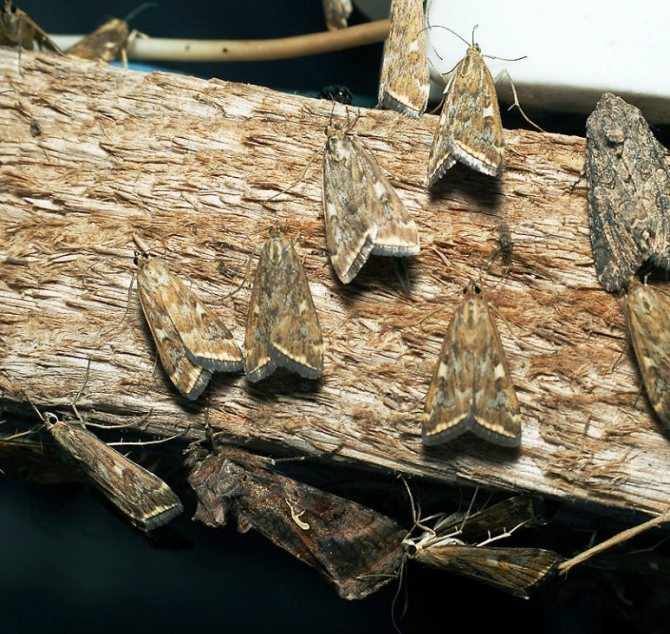
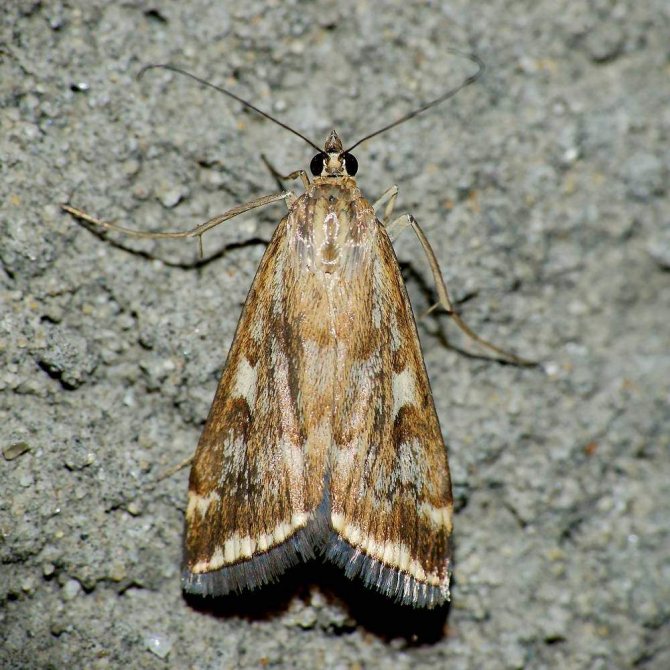
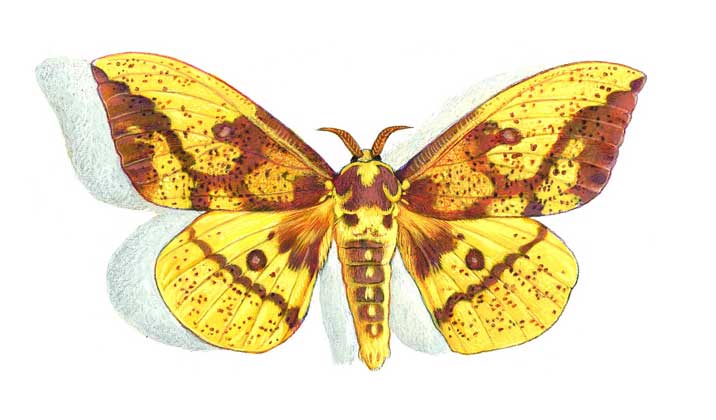
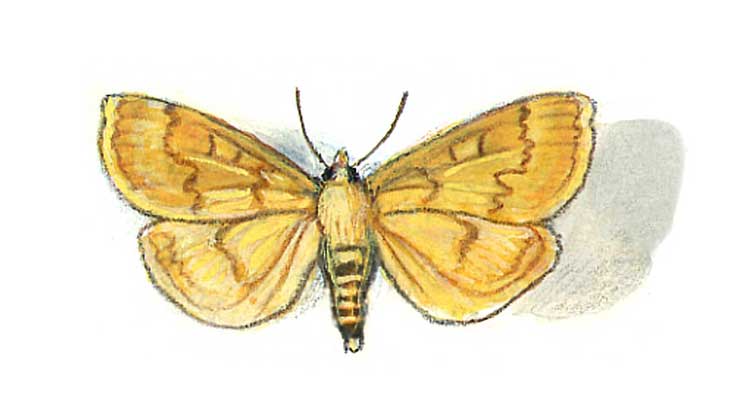
What does a meadow moth look like?
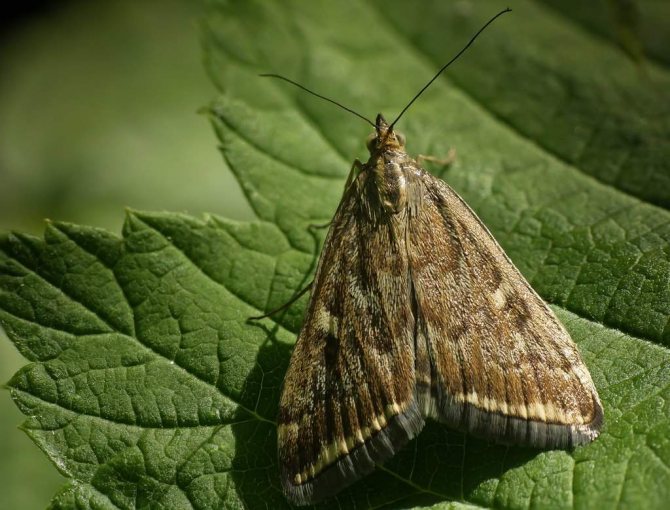
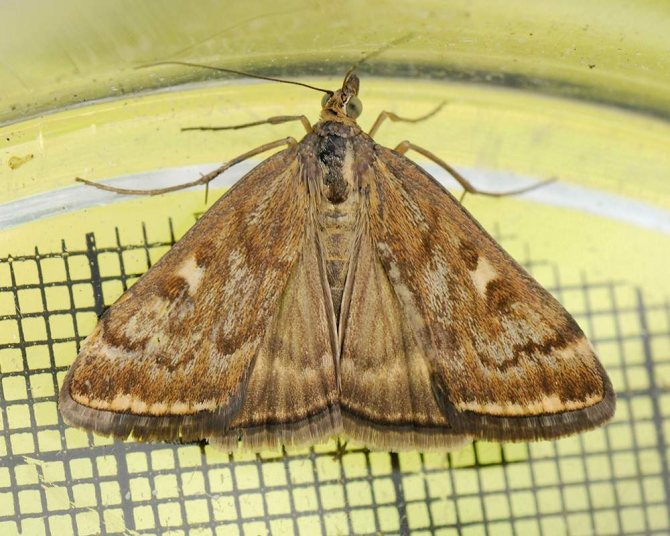
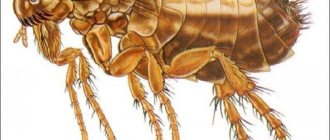
The meadow moth is a typical representative of the herb moth family. The habitat covers almost the entire forest-steppe zone of the post-Soviet space. The most favorable regions for development are with a temperate warm climate, where precipitation is stable.
Appearance
The description of the meadow moth has a lot in common with the relatives of the moths:
- nondescript color of light brown or yellow shades;
- wingspan from 17 to 27 mm, when folded, they represent the shape of a triangle;
- the front wings are gray-brown with a yellow pattern;
- darker hind winglets bordered by parallel stripes;
- forehead with conical protrusion;
- thin filiform antennae in females and serrate in males.
In the meadow moth butterflies, sexual dimorphism is expressed. Females are larger than males and have a thick belly. In the latter, the body is thinner and longer, when pressing on the abdomen, a brush of hair appears at the end, while in the female it looks like a fan.
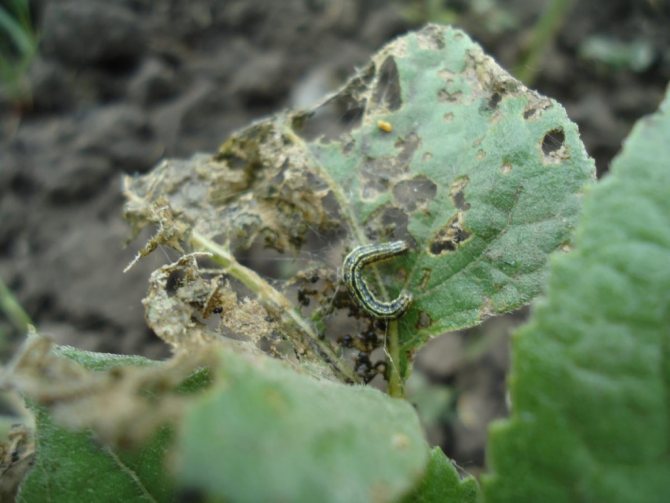
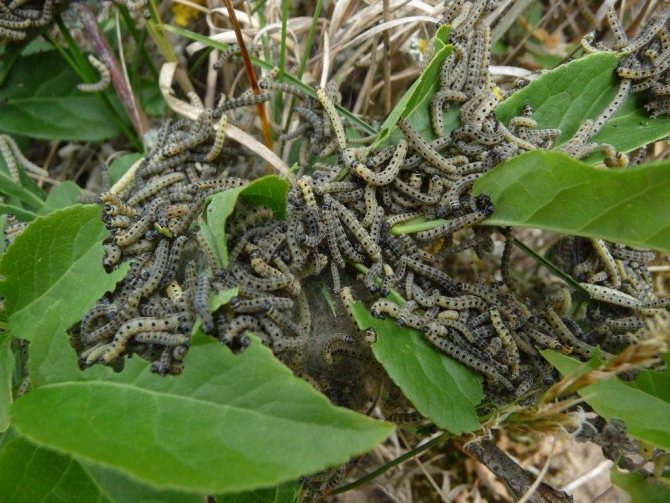
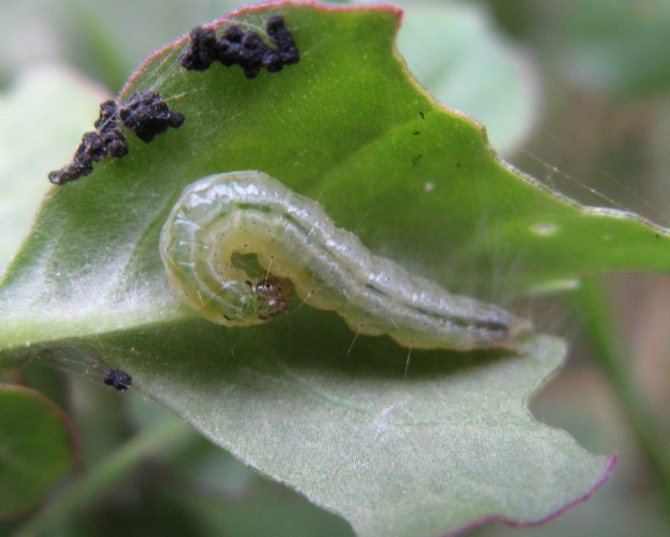
The length of the eggs does not exceed 1 mm. The shape is elongated. The color is yellowish with nacre. The hatched larva is transparent yellow or greenish. As they grow older, the color becomes more intense and almost black. The adult caterpillar of the meadow moth grows up to 3.5 cm. Two stripes can be distinguished on the back, and elongated shiny lines on the sides. 8 pairs of legs provide the larva with good mobility.
The length of the pupa is 12 m. The color is light brown, on the eve of the release of the butterfly it becomes gray. The cocoon is usually found in the soil and covered with lumps of dirt. On the upper part there is a special hole, slightly tightened with cobwebs, from which a young moth will fly out.
Dangers of Lepidoptera Insects
Because butterflies are still small insects, many dangers lie in wait for them. These are mainly birds - that's who can eat Lepidoptera. For example, titmouses. They can become insect killers when their larvae are taken out.
They should also be afraid of insectivorous insects, some types of flies, etc. But most of all, caterpillars should be afraid of them.
Despite all of the above, it should be noted that the best habitat for all Lepidoptera species is wildlife. That is, they should not be kept at home for a long time. Therefore, after the insect is hatched at home, it is better to release it after a while.
Subtleties of life
In the photo, the meadow moth is a cute creature, looking at which the thought does not even come that it is a malicious pest and a thunderstorm of farmers. In principle, it is not the butterfly itself that is harmful, but its offspring. But first things first.Insects hibernate in the caterpillar stage in a cocoon, which reliably protects them from the negative influences of the external environment.
On a note! Overwintering larvae are very resistant to low temperatures and retain their vital activity at minus 30 ° C. However, in the spring, they become susceptible to even minor frosts, which can destroy them.
Individuals that survived the winter pupate. The first generation of meadow moths begins at the end of April. In the northern regions, the time of departure of butterflies is celebrated in early June. Insects are active during twilight and night hours. The daytime is spent in the grass, under the foliage. Meadow moths are very shy. At the slightest rustle, they show a feeling of anxiety and take off.
To reproduce offspring, females need food. Nectar serves as a fodder base for them. But there is one more nuance that affects the development of the population. If during the life of the caterpillar of the meadow moth there was not enough liquid in the diet, then the female may be sterile or give a small number of offspring. Drought can provoke insects to migrate.
Meadow moths cover long distances in search of food or moisture. Such migrations are called active. But there are also passive migrations, when moths move through air masses. The migratory capacity of butterflies reaches 300-900 km.
Diet of domestic butterflies
They are often kept as pets. Moreover, keeping butterflies is not such a difficult task if you grow an omnivorous insect. Certain species of butterflies are very picky about their food and feed on certain nectar from certain plants. These pets are not suitable for home keeping.
In summer, insects can be fed with flower leaves, pollen, etc. But in the winter they will have to prepare nectar for them. To do this, you need the following ingredients:
- 2 tsp water;
- 1/5 tsp honey.
We take a container and pour water into it. Add honey and stir everything thoroughly. We serve this solution to insects.

Also, you can make gruel from fruits such as bananas, apples, oranges, pears, etc.
Reproduction nuances
Under the accompanying optimal conditions: the presence of food, moisture, temperature from 20 ° C, sexually mature individuals begin to mate. As a rule, oviposition begins 5-7 days after the butterfly leaves its cocoon. The female places eggs on the inner side of leaves, on weeds, stems, less often on dry residues or soil, 5-20 eggs each, superimposing them on top of each other, like shingles. The process of laying offspring lasts 1-2 weeks.
Fertility of the female meadow moth reaches 600 eggs and is due to the quality of the caterpillar's diet. It was noticed that under the same meteorological conditions, those individuals that ate beets are more fertile.
At a temperature of 27 ° C and a humidity of 75%, embryonic development lasts from 2 to 15 days. In hot weather, when the thermometer is above 30 ° C and the humidity does not exceed 45%, almost half of the eggs die. The young larva of the first instar feeds on leaf tissues from the underside, forming peculiar "windows" on them.
Young individuals of the first instar do not touch cereals. If any caterpillar is tempted by corn, it will lead to its death. Older individuals, starting from the third age, consume cereals without harm to their health and these crops no longer pose a threat to their life.
Adult caterpillars unceremoniously eat a variety of crops, the list of which includes 200 different types of vegetation. After their invasion, skeletonized leaves with visible veins and braided with cobwebs remain. During mass invasions, cuttings are also eaten. Root crops, shoots, fruits are damaged.
The development and life of the meadow moth caterpillar depends on many factors.For the larvae of the first instars, moisture is very important; at an older age, the need for nutrition increases. The larvae are distinguished by their mobility. In search of a food base, they easily overcome 50 meters, in forced situations they migrate to longer distances.
The larvae feed for about 15-30 days. Then they burrow into the ground, weave a cocoon and pupate. After 14-0 days, new butterflies appear, ready to mate and increase the population size. From 1 to 4 generations of generations are possible per year. The larvae of the last generation go to the ground for wintering.
Citrus joy: growing sunny lemons from seed to tree
Although citrus fruits are subtropical plants, our gardeners can also grow lemons in containers or pots to enjoy the fresh citrus fruits. And if you work a little, then you can grow a lemon tree ...
16 October 2020, 21:10
• verbena of Buenos Aires; • scabiosa • ivy (flowers are an excellent source of nectar in autumn); • thyme; • red valerian; • mint; • lavender; • buddley; • annual lunar; • primrose; • jaundice.
Photo:
Moth Traps:
1. Buy a moth trap consisting of a wooden box, perspex sheets, and a light bulb. You can make such a device yourself, but if you have no experience with an electrician, it is better to purchase a kit in a specialized store. There are two types of light bulbs: mercury discharge lamps, which are very bright and are best used away from neighbors so as not to irritate them; and actinic, which give less light.
2. Place the trap on an old white sheet to attract moths.
3. Collect egg boxes and place near traps so moths can settle somewhere.
4. Use the moth study guide to identify pests.
5. Check the forecast to make sure it is not raining, set up a trap at dusk, and return to the unit the next morning.
6. Do not catch moths every night, as this will repel other insects and they will not be able to get food.
7. Release the caught moths into the undergrowth away from the garden. Keep moths out in open areas so they don't become tasty food for flying birds.
8. Try a homemade trap: at dusk, place a white sheet on a clothesline or between tree branches. Place a bright torch in the back. Wait a couple of hours, then check which moths were attracted to the light.
Photo:
Perhaps you still know how to rid your garden of harmful moths, then share your ideas in the comments, and our article on social networks.
Alternatively, if you want to attract birds and butterflies to your garden for beauty, read our early article.
Liked? Be sure to subscribe to us at,, Zen and
For garden moth traps
Kristina Volkova 2 years ago 11 months ago
To comment, log in via social networks or enter your name
Harmfulness
In the case of mass dispersal, both adults and caterpillars are harmful. Numerous flocks of meadow moths become competitors to honey bees, which no beekeeper can rejoice in. The amount of honey in the hives is significantly reduced.
Caterpillars of the first generation eat weeds along roadsides, in beams, in forest belts. The gluttonous larvae of the second generation of the meadow moth infect sunflowers, alfalfa, buckwheat, sugar beets and other agricultural and forest crops. Depending on the amount of the pest, the crop can be reduced by 50%, or even completely destroyed.
On a note! The threshold of harmfulness of the meadow moth on sunflower is 10 caterpillars per 1 sq. m in the germination phase of up to 6 leaves. During the flowering period, the indicator increases to 20 caterpillars per sq. m. A similar threshold of harmfulness is typical for sugar beet.Only the flowering is not taken into account, but the closing of the leaves.
The larvae with an irrepressible appetite destroy all vegetation in their path. They are not inferior to locusts in their gluttony. It is also noteworthy that, like the latter, an outbreak of mass reproduction is characteristic of the meadow moth, which occurs cyclically with an interval of 10-12 years. It has not yet been possible to unravel the reasons for this phenomenon. It is possible that some of the main factors are climatic conditions, mass migrations of the meadow moth, and solar activity. Interestingly, the ability to migrate helps butterflies avoid natural enemies and parasitic individuals.
What do they eat in winter?
In the cold season, the basis of the diet of moths is honey nectar, which is easy to prepare yourself. It is enough to take boiled water without impurities and natural honey or granulated sugar in a ratio of 1x10. An overly concentrated solution has a detrimental effect on the butterfly's digestive system due to the crystallization of sugar.
Such food should not be left for longer than a day, as it tends to sour. If necessary, it is allowed to replace honey with pear, apricot or peach puree for baby food.
Chestnut moth
It is an insect that parasitizes chestnut and maple leaves. The caterpillars of the moth gnaw passages in them, which leads to the fall of the leaves, the weakening and death of the plant.
Butterflies have bright and even attractive coloring. They have orange wings with bright white and black stripes and fringes around the edges. This moth belongs to the small species - it has only 1 cm in wingspan. The danger is not butterflies, but voracious larvae. In just one summer, breeding caterpillars can completely destroy the crown of a tree.
During the breeding season, the chestnut moth hovers around the trees. One butterfly lays up to 65 eggs on the leaves. A few days later, pale green spindle-shaped larvae emerge from them, which immediately penetrate into the thickness of the leaf. At first, they feed on juice. After they develop powerful jaws, the caterpillars begin to actively gnaw through the passages in the leaves. They grow rapidly and gain weight. Ripe insects pupate, and by the time the chestnuts bloom, a new generation of butterflies has appeared. In one season, the chestnut moth produces several generations of larvae, which weaken the tree so that sometimes it does not survive the winter.
Other signs
- In Ireland and Scotland, a moth hovering over a dying person is considered a sign that a place in paradise has already been prepared for him.
- If an insect is circling over a candle or a light bulb in an airy dance, it no longer predicts the wedding, but has practically begun to celebrate it! It remains only to wait for the marriage proposal.
- Some tend to panic when they notice a moth crouching on an icon. Do not worry: there are no signs on this score. And if the worm of doubt still gnaws at the soul, remember that butterflies were often depicted on icons as a symbol of rebirth. Maybe it's time for you to stop being tormented by doubts and put in order some part of your life that has recently fallen into decay?
Over time, beliefs change. Those that frightened our ancestors evoke delight and joyful expectations among contemporaries. Why don't you learn to interpret for the better any incomprehensible sign? Life will become more fun, and good events will begin to happen more often.
Classification.
The most common classification scheme for the order Lepidoptera divides it into two suborders - Palaeolepidoptera and Neolepidoptera. Their representatives differ from each other in many ways, including larval structures, mouth apparatus, wing venation, and the structure of the reproductive system. Few species belong to Palaeolepidoptera, but they are represented by a wide evolutionary spectrum of mainly very small forms with miner caterpillars, while the suborder Neolepidoptera unites the vast majority of modern butterflies.In total, the order of Lepidoptera has more than 100 families, some of them (only for moths) are listed below.
Glassworms (Sesiidae): slender forms with transparent wings without scales; outwardly resemble bees; fly during the day.
Moths (Pyralidae): small butterflies of various shapes; the wings at rest are folded in a triangle: many species are pests.
Fingerwing (Pterophoridae): small forms with longitudinally dissected wings, the edges of which bear a fringe of scales.
True moths (Tineidae): very small butterflies with fringed scales along the edges of the wings.
Pronged moths (Gelechiidae): small, often brightly colored butterflies; many, for example, a grain moth (barley), are malicious pests.
Sphingidae: Usually large species, resembling hummingbirds in appearance.
Sachets (Psychidae): winged males, small, dark colored; wingless females and caterpillars live in silk sacks.
Peacock eyes (Saturniidae): very large, wide-winged butterflies with a massive body; many have “eye” spots on their wings.
Moths (Geometridae): small, slender, wide-winged forms, the caterpillars of which "walk", bending in a loop in a vertical plane.
Leaf rollers (Tortricidae): small to medium sized species; folded wings often resemble a bell in outline; many are dangerous pests, such as the spruce budworm and apple moth.
Coconut moths (Lasiocampidae): medium-sized shaggy butterflies with a massive body; caterpillars are dangerous pests.
Dipper (Arctiidae): Medium-sized furry butterflies with brightly colored wings.
Moths (Noctuidae): Forms with nondescript gray or brown wings and filamentous antennae.
Volnanki (Lymantriidae): males with gray or brown wings and feathery antennae; females are sometimes wingless; caterpillars are brightly colored.
Parallel civilization
Caterpillars of all kinds eat a lot, and they only eat certain types of leaves. This is how they store protein for the development of the pupa and butterfly. When the protein accumulated by the caterpillar runs out, the butterfly is forced to feed. For this they have a proboscis. In butterflies, the proboscis is very elastic and mobile. The length of the proboscis usually corresponds to the depth at which the nectar is in the flower. When the butterfly is not eating, it folds its proboscis into a spiral and holds it above its head.
Most often, butterflies feed on liquid flower nectar, fruit juice. In some cases, the source of liquid food for butterflies may be tree sap or liquid excrement from aphids. Some butterflies do not eat anything at all, and their proboscis is either underdeveloped or not.
Many butterflies feed on rotting fruits and vegetables, even animal and bird droppings, and decay products from animal corpses. In the tropics, there are moths that suck the tears of animals. Many butterflies gather near puddles, where they drink water with sodium salts. Butterflies can drink a sugar solution in an amount that is twice their own weight. Some species of butterflies do not eat anything at all - they live off the reserves that they have accumulated as caterpillars.
Insect feeding
This question is especially relevant for beginners who will definitely need expert advice:
- The butterfly should be calm. You need to very carefully bring it to the food, taking the folded wings at the very base.
- If the insect is hungry, it will quickly unfold its proboscis and start eating. When the butterfly is full, it will start to escape.


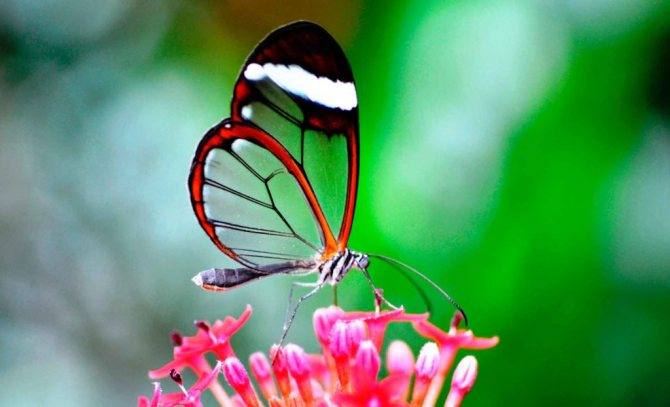
Glass butterfly
Sometimes the animal refuses to eat for a long time, in which case you will have to help him. You should carefully release the proboscis with a toothpick and lower it into the nectar or plant the moth in the feeder with its paws. By touching the syrup with its front legs, where the taste buds are located, the insect immediately recognizes the contents of the feeder.
It is not necessary to keep the pet by force.If she refuses to eat, offer food later.
The best feeder can be organized from an artificial flower by making a corolla from bright, attractive plastic or thick paper. The size is determined by the volume of homemade nectar. A piece of foam rubber will keep the moth's legs from getting bogged down. The flower is placed in a well-lit place, convenient for approaching. It is not forbidden to use a saucer or a cork from a plastic bottle.
Feeding frequency: once a day. Some Lepidoptera require more frequent meals, others less.
Daytime breeds feed in the daytime, nighttime - at dusk. Food is absorbed in 2-15 minutes.
No need to feed red and pear saturnia, hawk moths, large harpy, peacock eye. Breeds lacking a proboscis survive on the energy accumulated during the caterpillar stage.
Divination by color
Superstitious people are prejudiced against moths. As, however, to many creatures leading a nocturnal lifestyle. You often hear a categorical opinion: they say, by hook or by crook, you need to try to prevent the appearance of an insect in the house, and if it has already broken through into an unattended crack, get ready for the worst. The least that a winged guest can call on the heads of the careless inhabitants of the apartment is a serious illness, or even death. One of the legends even claims that three night moths together are capable of taking a human soul with them.
However, most will not be so ruthlessly disposed. In order not to torment yourself with empty fears, heed the advice of "seasoned" lovers of mysticism and try to consider the wings of an insect that has visited you. What color prevails on them?
- Black is really a bad sign, foreshadowing danger. And the larger the size of the "Goth" butterfly, the more serious the problems it predicts.
- Gray and brown are also not the best options. Nothing bad will happen to the owners of the house, but minor health problems are possible.
- White is another matter. It is associated exclusively with positive predictions. A lonely white-winged moth portends a meeting with love. For those who have already found their soul mate, but did not have time to formalize the relationship - a walk to the registry office. A married white moth promises pregnancy.
- Pink and red shades are a sign of a whirlwind romance.
- Orange and yellow talk about money.