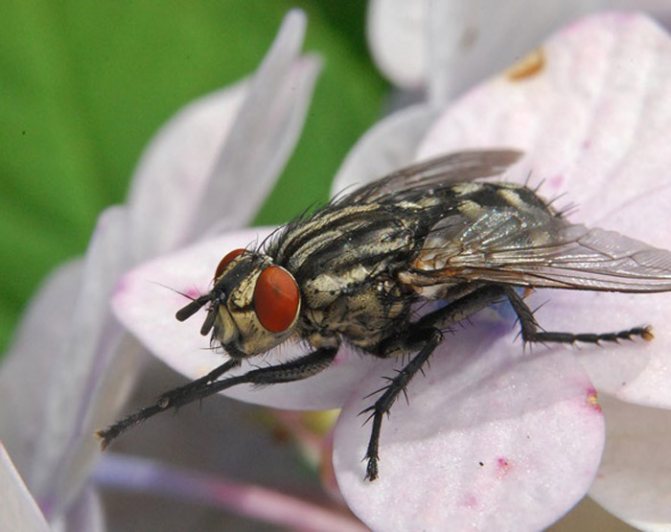
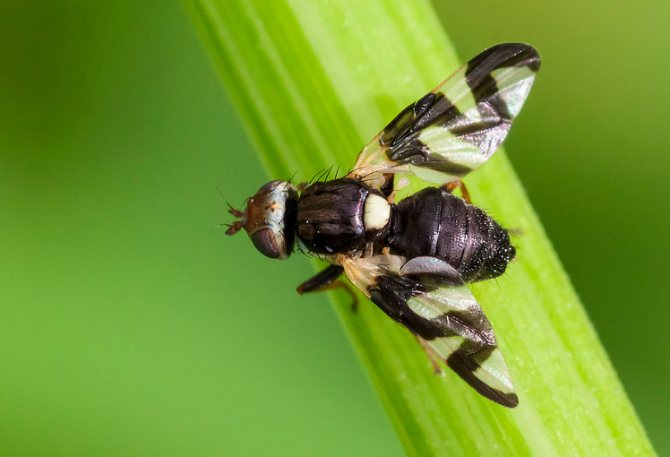
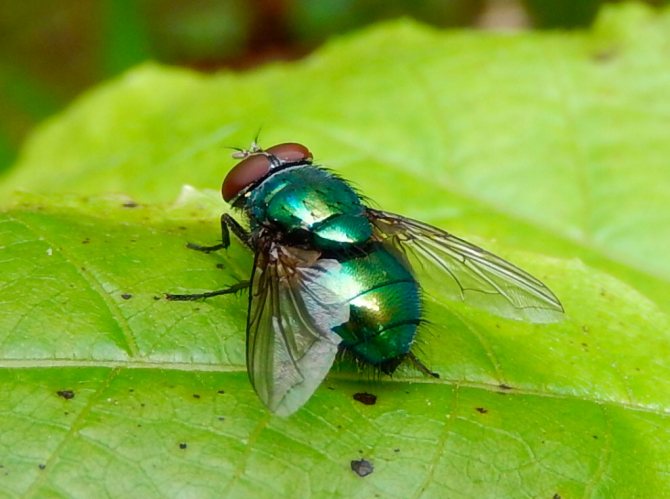
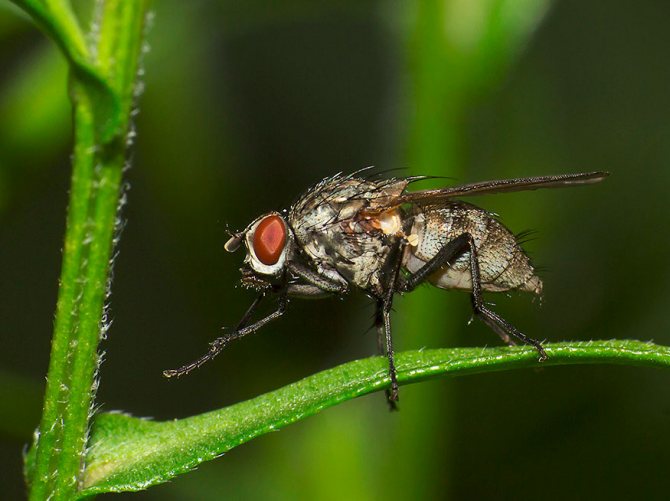
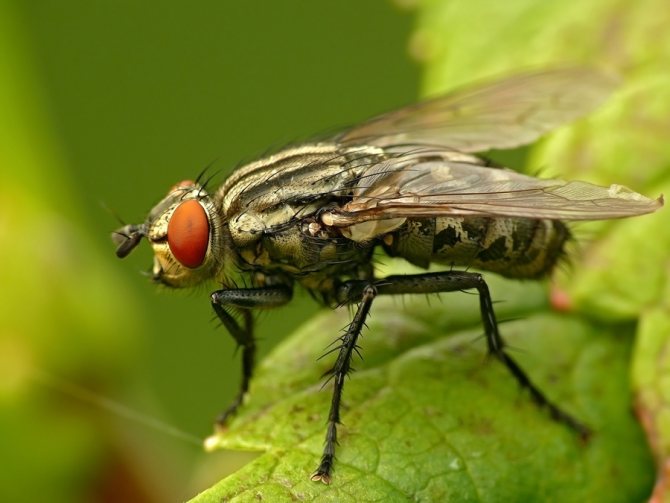
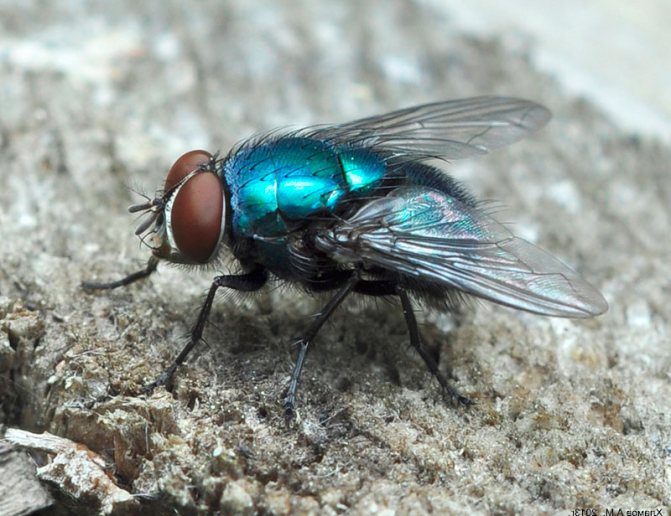
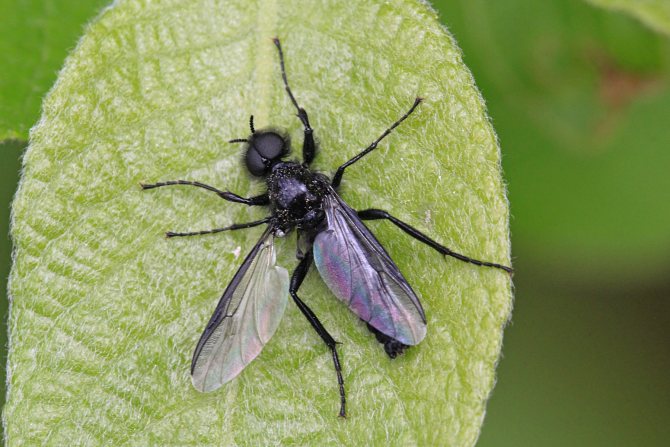
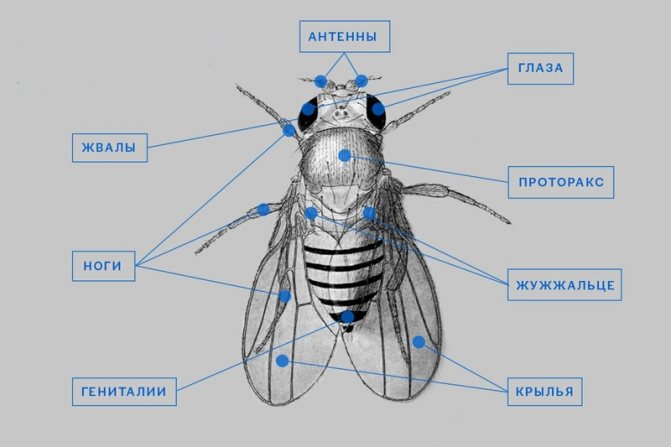
Diptera detachment of insects. In a fossil state, Diptera have been known since the Late Triassic. Diptera is a progressive group with a fast evolutionary rate. They have only a front pair of wings (hence the name). The hind wings are transformed into flask-shaped organs - halteres, presumably the sense organs of balance and direction; in a few wingless forms, they are sometimes reduced. The head is rounded, with large faceted eyes on the sides. Oral apparatus - piercing-sucking or licking. Breast segments are fused together. The abdomen consists of 4-10 visible segments, the last of them are transformed in females into a telescopically retractable ovipositor, in males - into a copulatory apparatus, the structure of which is a systematic (specific) character. Suborders; long-wattled (or mosquitoes), short-wattled (or flies) straight-seam and short-wattled round-seam; division is based on the structure of the antennae, head, features of hatching of adults from the pupa shell. Diptera have over 150 modern families. About 100 thousand species, widespread, over 10 thousand species are known in Russia. Most adult Diptera fly well; can hover, hang motionless in the air.
Diptera
Diptera feed on nectar and pollen of plants, other insects, blood of vertebrates (gnat). Diptera have complete transformation. The larvae live in water, soil, in rotting remains of plants, living plants and animals, in corpses; few, mostly. predatory, live openly, most of them - inside a nutritious substrate, possessing extraintestinal digestion. The pupa in higher (round-seam) flies, as well as lionesses and gall midges, is enclosed in a lagging and hardened shell of the larva of the last (3rd) instar - the so-called. puparium, or pseudococone. A number of Diptera species are carriers of causative agents of human diseases (housefly, mosquitoes, blood-sucking mosquitoes, etc.) and domestic animals (horseflies, flies, etc.). Larvae pl. D. - plant pests, as well as agricultural parasites. animals and occasionally humans. Some are Diptera. useful as pollinators of plants and soil formers, others, such as tahini, destroy agricultural pests.
Latin name Diptera - Diptera
A very large order of Diptera includes over 85,000 species of highly organized and specialized insects.
Diptera are insects with only a pair of membranous front wings. Diptera are the best flyers among insects.
The rear pair of wings is reduced. Its rudiments are transformed into halteres, inside which are placed chordotonal organs, which are very important in the flight of dipterans. The wings are usually widened in the middle part, and at the very base they are strongly narrowed, sometimes forming a small projection - a winglet.
Diptera are characterized by a mobile head with very large faceted eyes, a powerful chest, where the mesothorax reaches its greatest development, to which the wings are attached, and small anterior and metathorax; sessile, rarely pedunculated abdomen. The larvae are legless, with or without a head. Pupae are mobile or in a false cocoon - puparia.
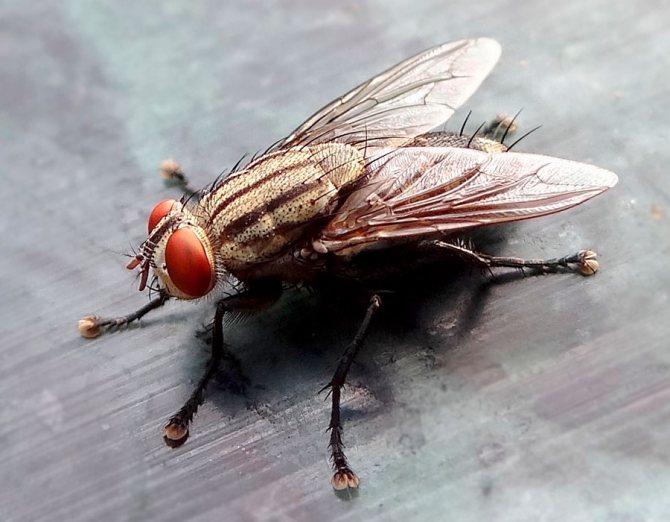
Distinctive features of house flies
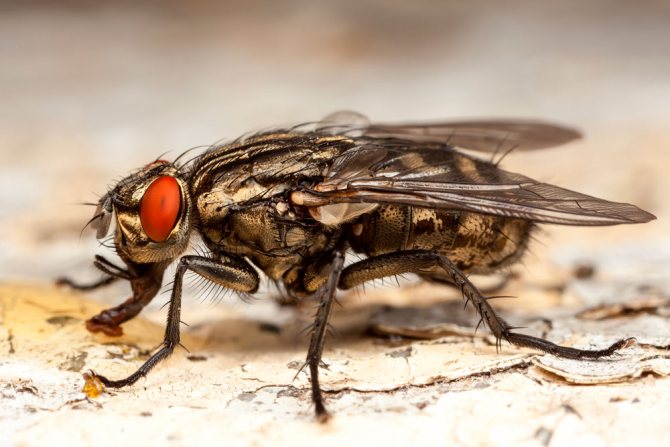
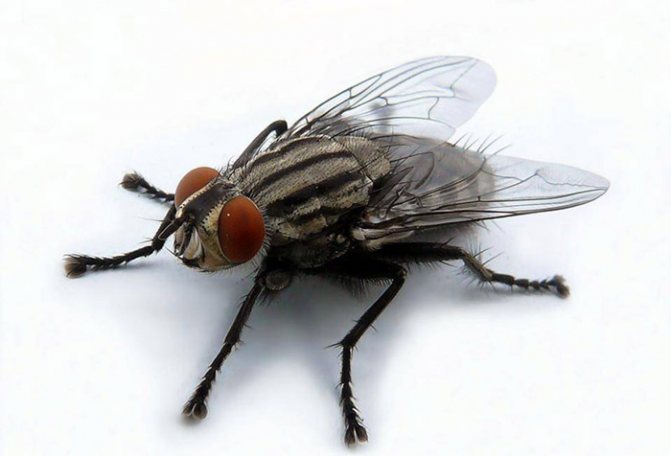
House flies have several distinctive characteristics that make them recognizable from other subspecies.
The body of the insect is mostly gray in color. The lower segment of the head has received a yellow coloring.
The upper part of the rib cage is decorated with four black stripes. On the abdomen, black spots of a regular quadrangular shape are visible.
Its lower part has a slight yellowish tint. The size of the insect's body reaches six to eight millimeters.
Benefit

Most people are used to thinking that flies only cause harm. In fact this is not true. There are flies that pollinate plants like bees. Such dipterans do not live in apartments and do not feed on animal or human blood.
Scientists studied flies and found that the insect is endowed with a rare gene code that recognizes and eliminates harmful cells. Thanks to the discovery, there is a chance for the treatment of serious diseases.
Features of the structure of house flies
The main difference between the housefly and other relatives is the presence of only one pair of wings.
The second back pair, in the process of evolution of the insect, turned into halteres used to maintain balance.
In addition, the insect, despite the complex structure of the eye, is blind. The limit of visibility is limited by a distance of 40 - 70 cm.
External structure
The skeletal structure of the house fly is no different from other classes of insects.
Represented by the head, chest and abdomen. The head is equipped with a mouth apparatus, eyes and antennae.
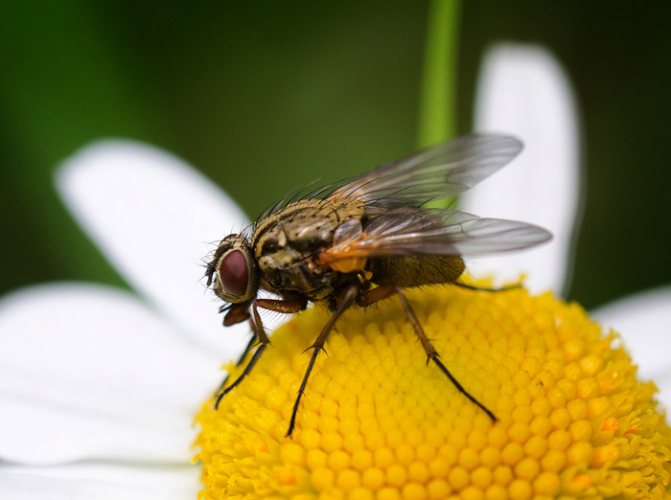


House fly appearance
The chest has a segmental structure - there are three in total. There are two wings, they are completely transparent. Legs - three pairs.
Well-developed musculature is located in the chest cavity. The main part of the digestive organs and the entire reproductive system is located inside the abdomen.
Chest
The chest is represented by three interconnected segments. Allocate the anterior, middle and metathorax.
The insect gets the ability to fly due to its powerful muscles, therefore, the middle segment is the most developed.
The body is equipped with three pairs of legs, each of which is divided into five interconnected particles. The paws are well muscled.
At the tips of the paws, there are smaller claws and suckers, with the help of which the insect gets the opportunity to attach and hold on to any surface.
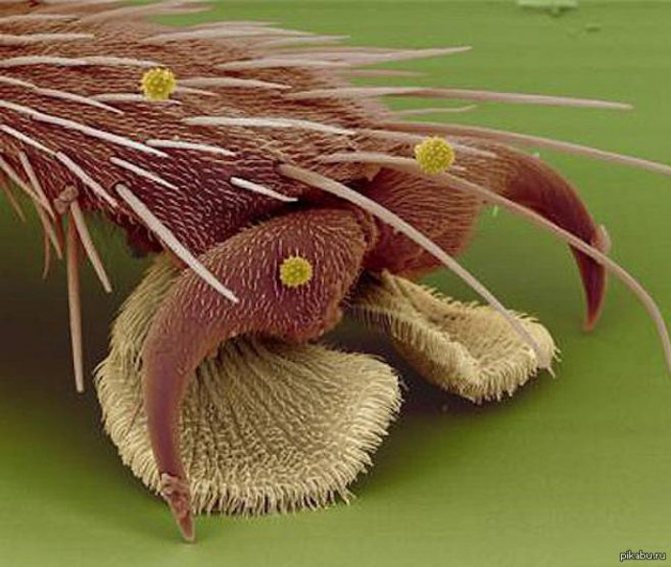

Housefly foot under a microscope
Thanks to this, houseflies have the ability to move upward with their belly. During movement, a sticky secretion is released from the pads as a result of compression.
This feature helps the fly stay firmly on the glass and absolutely smooth surface.
The paws of the housefly perform the duties of the olfactory organs. Thanks to the villous receptors located on them, the insect will be determined by the edibility - inedibleness of food.
Head
The structure of the fly's head is simple. The organs of sight, hearing and nutrition are located on its surface.
The mouth apparatus of a fly - the structure depends on the type of insect feeding - is represented by a proboscis of a licking or sucking format.
The lips, represented by the lower and upper lobes, come into direct contact with the food mass.
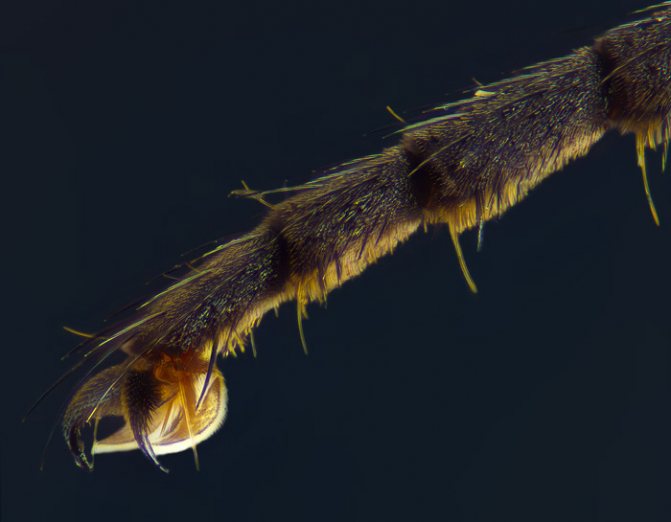


Housefly oral apparatus
A large number of channels converge into the fly's food proboscis through which food enters the digestive system.
The fly has a powerful jaw apparatus. The mouth apparatus of a fly, whose diet is based on blood, has sharp and hard scales.
This is a kind of imitation of teeth that help the fly damage the surface of the human skin. The pump located in the throat is responsible for drawing in liquid and liquefied food.
You can also read our article: What flies eat at home
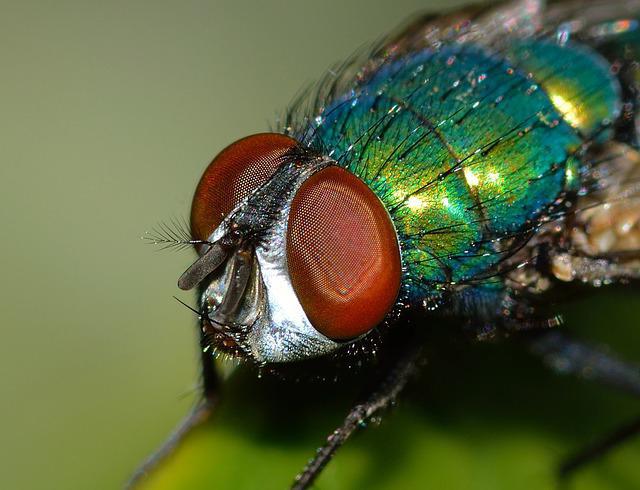
Most of the surface of the head is occupied by eyes, which have a very complex structure. They are composed of a large number of simple eyes.
Visually - when zoomed in - it looks like a faceted mesh.
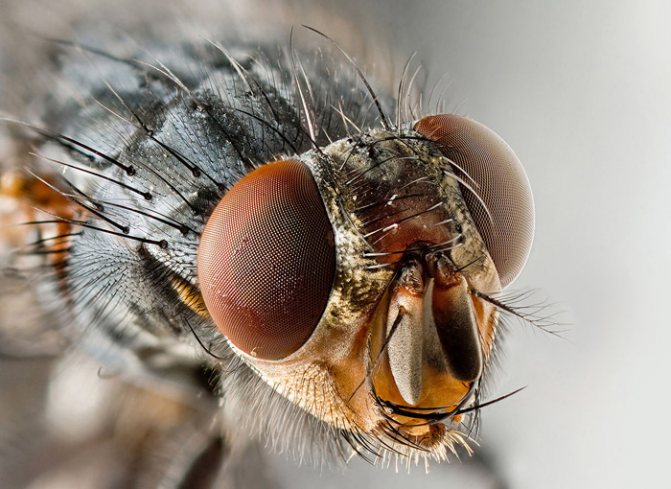


Fly eyes
Such a structure provides the house fly with a comprehensive image of objects, but the overall picture is perceived as a mosaic.
In a housefly, the total number of simple eyes reaches 4 thousand pieces. The insect is able to instantly react to any movement, but it does not receive a full-fledged volumetric image.
Antenna antennae are used by insects as landmarks. They help in the perception of various odors and in determining the direction of flight and movement. They have characteristic differences between females and males.
Wings
The wing structure of a fly is simple. The insect has one pair of wings. They are well developed, completely transparent, and have membranes.
The strength of the wing is provided by the cylindrical veins piercing it. The back pair in the course of evolution was transformed into halteres. The wings help the fly maintain balance during flight.
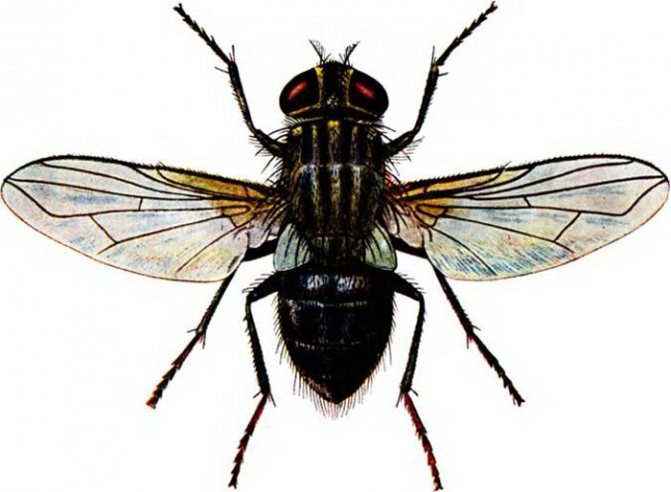


House fly wings
It also allows you to hover in the air if needed. During the flight, they emit a characteristic buzz.
In flight, the housefly can turn off one of the wings, which helps it to sharply change the flight trajectory, perform complex maneuvers, and start from a place without a preliminary run.
Belly
The abdomen of a housefly has the shape of an elongated cylinder.
Segmental, represented by ten interconnected particles-segments.
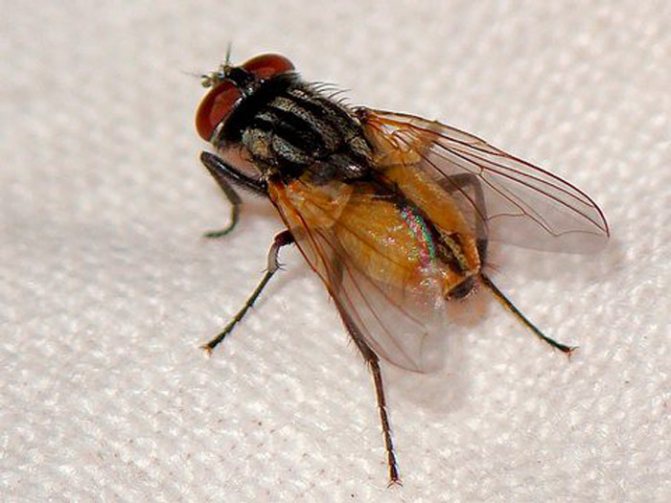


Fly body
The organs of the reproductive, respiratory, digestive and other vital systems are located inside the abdominal cavity.
The surface of the abdomen is covered with a chitinous layer with good elasticity. If necessary - after eating and during the period of bearing offspring - the cover is able to expand.
Internal structure
The internal structure of a fly is represented by the digestive system, reproductive system and other organs important for the vital activity of the insect.
Digestive system
In the abdominal cavity of the insect, there is the main part of the organs responsible for and ensuring the assimilation of food.
It:
- goiter;
- intestines;
- malpighian vessels;
- excretory tubules.
The digestive system in its direct sense does not exist in the housefly. Food is digested before the insect enters the digestive tract, i.e. food enters the goiter cavity in a form completely ready for assimilation. Before starting to absorb food, the fly processes it with a special secret that ensures its digestion.
Reproductive and reproductive system
The internal genital organs are also located in the abdominal cavity. In males, these are testes, in females, eggs, accessory glands and ducts.
The external genital organs of the house fly subspecies have their own characteristic features.
Males are distinguished by a special structure of grips, with the help of which they hold the female in the process of mating.
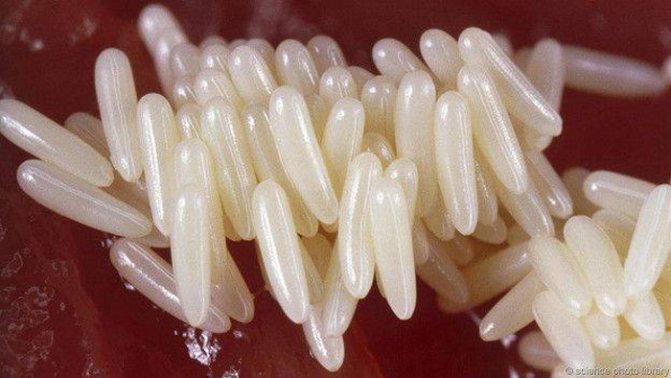

Clutch of fly eggs
The number of eggs in a clutch of a housefly is variable and can reach 70 - 150 pieces. The number depends on the subspecies of the insect.
Other systems of the insect body
The brain consists of numerous nerve nodes that are located in different parts of the insect's body. The complex brain system inherent in humans is absent in insects.
The main task of the brain is to help coordinate movements. Another organ is responsible for reflexes - the reflex arc.
The brain is tiny, but composed of several hundred thousand neurons. This helps the insect to perform incredibly difficult maneuvers during flight.
The circulatory system is represented by the following organs:
- aorta;
- pterygoid muscle;
- dorsal vessel;
- a heart.
The heart has the simplest structure. The organ does not perform the functions familiar to a person.
The circulatory system is filled with blood - a completely colorless or slightly yellowish liquid.
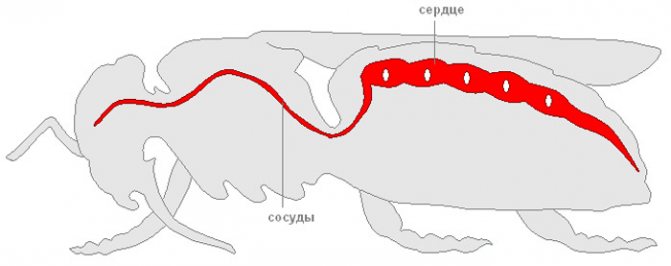

Diagram of the circulatory system of a fly
The main function of this biological fluid is to transport the nutrients necessary for the insect. It does not take part in the transfer of oxygen, does not contain erythrocytes in the composition.
The respiratory system is represented by a large number of tracheas, which are located throughout the body. The flow of oxygen into the respiratory canals is provided by the opening spiracles.
Tracheas, in turn, are highly branched, representing a rather complex capillary system. Thanks to this, oxygen is delivered directly to the vital organs.
In total, the insect has 10 pairs of spiracles: two are on the surface of the chest, the other eight pairs are on the lower surface of the abdomen.
Conclusion
The housefly, despite its external primitiveness, is a flying dipteran insect with a rather complex internal and external structure.
Ktyr


Fly ktyr
A representative of this species can be found everywhere, with the exception of the territory of Antarctica. The ktyr fly is a predator-exterminator of various insects (flies, beetles, wasps, butterflies, grasshoppers, beetles), which sometimes renders a great service to humans.
Differs in large size (5-8 cm), strong body, strong spiked limbs, rigid proboscis. A characteristic feature of the structure of the imago is a large mesothorax and an elongated abdomen. The predator is black in color, sometimes there are species with brown, reddish or red sclerites. The entire body of an individual is covered with gray pollen; there are also specimens with a pattern of light stripes or spots. On the large head are the faceted structure of the eye, three simple eyes and short antennae.
On a note!
The caught victim ktyr destroys poison. With the help of the proboscis, the predator wounds the prey, and from the salivary glands it throws out a potent poison, which contains substances that break down the insides of the insect.
Species and habitat
Some species of Diptera living next to humans are among the most ancient insects. This is exactly what the common common housefly is, which, according to scientists, has been living on the planet for 145 million years.
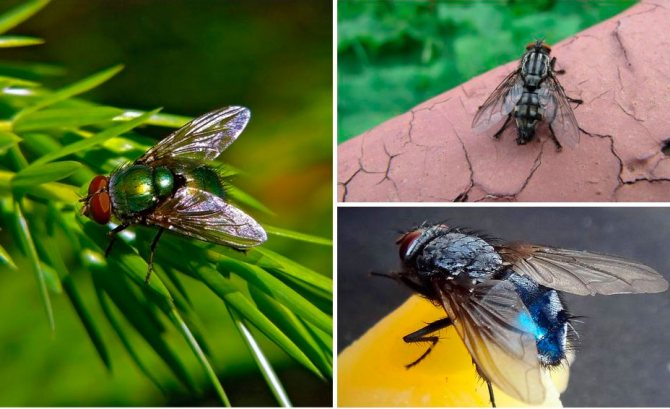
Diptera are widespread on the planet, numbering more than 5 thousand species, of which a fifth live in Russia. The most famous: domestic (indoor), meat, etc. They all have a similar body structure, differ only in size, color and habitat.
The smallest flies in the world are Megaphragma caribea (0.17 mm long) and representatives of the Myrmaridae family (2.1 mm), the largest are the South American Mydas hero (grow up to 6 cm in length with a wingspan of up to 12 cm) and the New Zealand species Egsul up to 5 cm long.
Getting rid of flies with insect repellents
With the help of insect control products, you can not only get rid of the annoying neighborhood with flies, but also scare them away from your home or summer cottage.


Flies stick to the glue trap
A proven fly repellent is adhesive tapes and plates. They must be hung from the ceiling, in a doorway, or not far from a window. Insects adhere securely to the glue trap and die. Valbrenta's assortment includes adhesive tape from Kleelov flies and a sticky plate of Kleelov "Fruit". The funds have proved to be highly effective.
In the end, to avoid the appearance of these annoying and potentially dangerous insects in the house, it is enough to install mosquito nets on the vents or windows. With just a little effort, your family will be provided with a comfortable pastime and fresh air at any time of the day.
Diptera squad: reproduction
The larvae and adult representatives of this order have striking differences in the field of anatomical and physiological structure. The period of aggravated reproduction for a number of Diptera insects is not easy. Often, the males, ready to reproduce, create a kind of swarm, the noise of which can lure many females.
The majority of Diptera are oviparous.But in nature there are flies, which are characterized by egg production. In this case, the insect lays an egg, in which the finally formed dipteran larvae are located. After hatching, they immediately begin such a life process as food.
There are also flies capable of live birth. In this case, there are two options for the outcome of events. In the first, an older larva is born, which requires a certain amount of time to feed; in the second, the larva is born in full readiness for pupation.
Also, Diptera breeding can occur at the larva stage. This phenomenon is called pedogenesis. It is based on the maturation of about sixty daughter larvae in the body of pedogenetic ones. Daughter larvae emerge through breaks in the mother's integument. Reproduction in favorable conditions allows insects belonging to the Diptera order to give up to 10 new generations per year.


Great gray horsefly Tabanus autumnalis Linnaeus


Great gray horsefly Tabanus autumnalis Linnaeus
A large, well-recognized fly, the body length of which reaches 16-23 mm. Quite often, such gadflies are mistaken for gadflies, although the latter are representatives of the superfamily Oestroidea. The insect has a dark gray color, the abdomen is black with a well-recognizable pattern.
Females suck the blood of mammals, they are capable of attacking humans. Before landing on their victim, they circle over it for a long time. Males of the big fly lead a vegetarian way of life, feeding exclusively on flower nectar. The insect carries very dangerous infections such as anthrax.
You can meet such a fly in Europe, North Africa, Western Siberia, Asia, the Caucasus and Kazakhstan.