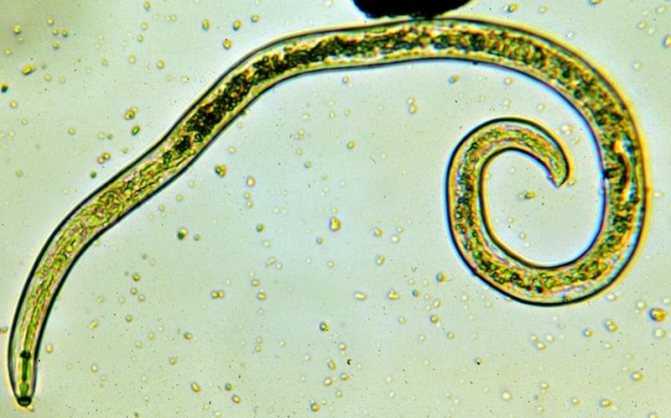
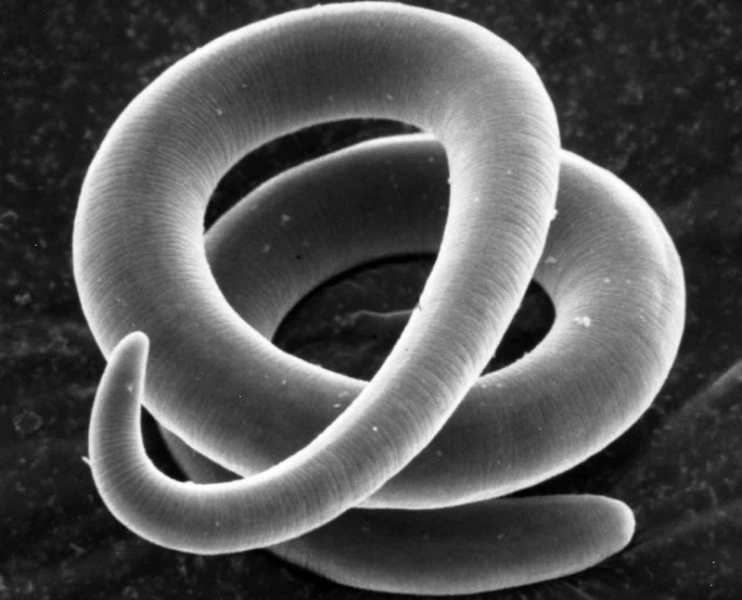
Parasites are divided into a number of categories, they are more or less dangerous, some of them inhabit the intestines, others settle under the skin, and others in the organs of the visual system.
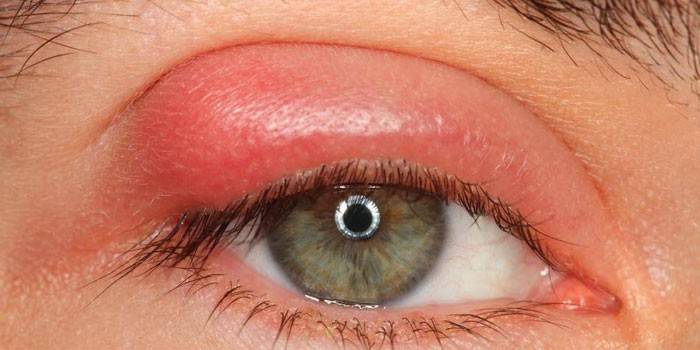
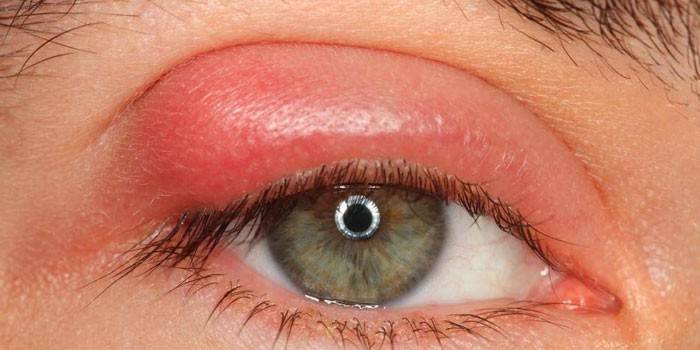
Worms in the eyes are very dangerous because they cause metabolic disturbances, destroy soft tissues, reduce immunity, trigger inflammation and ultimately impair vision. Pathology affects both eyes, measures must be taken so as not to go blind.
Worms settle mainly in the digestive tract, but they can take a fancy to the liver, lungs, blood, eyes. Since the parasites multiply quickly, the invasion is quite dangerous, it is the cause of serious health problems in general.
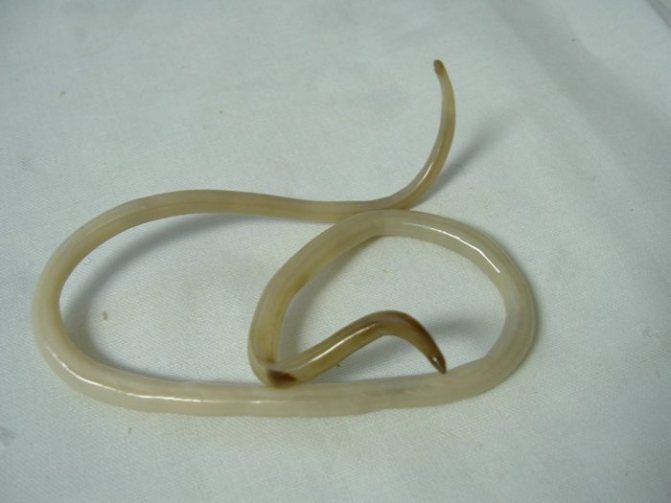
It is impossible to see the worms in the eyes, corresponding doubts arise in patients with subcutaneous invasions - in this case, you can see how the worm moves in the dermis.
It is imperative to carry out treatment, since parasites knock down the metabolism, quickly develop and multiply, can cause the formation of cysts, compression of the surrounding tissues. All this causes organ dysfunction, up to and including loss of vision.
Trichinella and roundworm

The symptoms of the appearance of worms in the eyes in this case are as follows:
- Muscle pain
- Eye swelling (sometimes the face is affected)
- Fever,
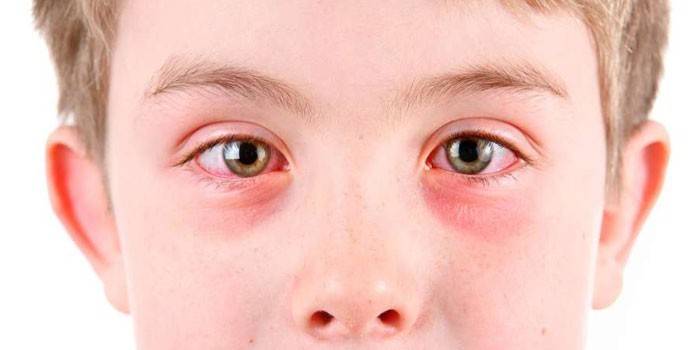
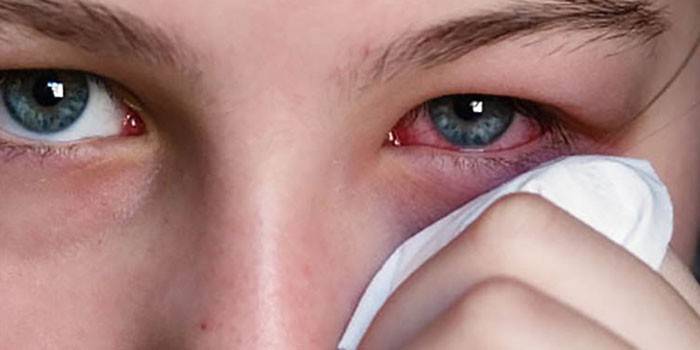
- Persistent conjunctivitis.
Ascaris in the eyes are much less common, but this still happens. Worms enter the body through the consumption of unwashed plant foods. Worms like Baylisascaris procyonis can settle inside humans, but in general, parasites found in the organisms of dogs, cats and raccoons are adopted.
Roundworms are unable to continue their development in the human body, they are carried to various organs through the bloodstream. So the worms end up in the eyes, where they are simply covered with a membrane and seem to go into hibernation. In this case, in addition to conjunctivitis, the list of symptoms will be replenished with iridocyclitis, as well as the risk of strabismus and blindness.
Helminthic invasion of the organs of vision
For example, opisthorchis is often found in fish meat, if the product is improperly processed, then infection occurs, the eggs of the worms, along with blood, can linger in the eyes, where they will begin to develop. At the initial stage of opisthorchiasis, the usual symptoms of irritation occur, and nothing bodes well. But over time, vascular tissues are affected, vision is impaired, if timely treatment is not carried out, then this threatens the onset of blindness.
Often, opisthorchiasis infection occurs through the fault of the patient himself, who could not follow simple rules of hygiene in an unfamiliar area.
Eye damage can be both internal and external, depending on the type of helminths. In any case, any helminthic infection is dangerous for the eyes, the parasite inflicts a complex lesion, regardless of the type of development. As medical practice shows, parasites prefer to settle in an organism that is greatly weakened.


Eye worm and Onchocerca
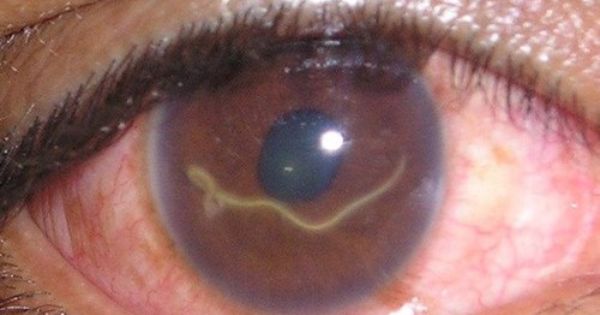

Loaloa is one of two worms that colonize the eye according to their nature, and not by coincidence. They are capable of damaging the tissues of the organs of vision both as adults and at the larval stage. Parasites enter a person through the bite of a horsefly.Once under the epithelium, they go straight to the eyeballs.
Loalosis is most often found in Africa, and in forests. The people living there are asymptomatic. The only moment when you can suspect something was wrong is if the infected person begins to have conjunctivitis. Quite differently, the symptoms of loaloa worms in the eyes are manifested in tourists.
They are observed:
- Pain syndrome at the points of localization of the worm,
- Inflammation,
- Allergy,
- Quincke's edema.
Onchocerca Are parasites that lead to the so-called river blindness. They are also common in sub-Saharan Africa, but they are also found in other countries such as Turkey, Hungary, the United States and Albania. Cases of infection have been registered in Crimea. If these worms get into the eyes, then the person will suffer from itching, bumps will appear under the skin, the corneas become inflamed, which can ultimately lead to glaucoma and blindness.
Thelazia callipaeda and rat lungworm
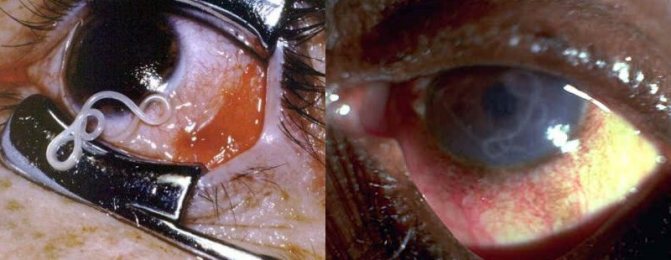

Thelazia callipaeda larvae enter the organs of vision through flies. If they bring parasites onto the cornea, a pathology called theleiosis will develop. Mature individuals of worms live not only directly in the eye, but also in the surrounding tissues. Males reach the largest size - they grow up to 20 mm in length, and their diameter can be about 800 microns. Females, as a rule, are somewhat smaller, but the minimum length is 5 mm and the diameter is 250 microns.
Despite the fact that the worm colonizes directly in the eye area, humans are not among its final hosts. Such worms in the eyes in the photo resemble white threads.
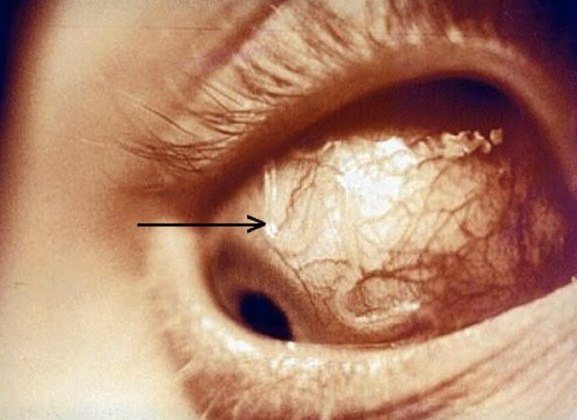

In this case, the sick develop a number of symptoms:
- Sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
- Increased discharge of tears.
- Light sensitivity.
- Follicular hypertrophy of the mucous membranes.
The rat lungworm is found in the Pacific Ocean, USA and Southeast Asia. It enters the human body through a variety of intermediate hosts. For example, people can eat sick slugs or snails. Also, these snails could have been eaten by some other animal, and a person would have been infected from it.
In the photo, such worms in the eyes are especially clearly visible, since in size they can reach more than a centimeter in length. Symptoms directly depend on the severity of the lesion. Some patients only complain of blurry vision, while others may develop neuritis or even meningitis.
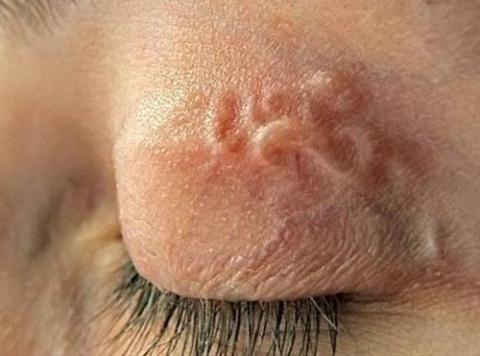

Dirofilaria and Gnathostoma
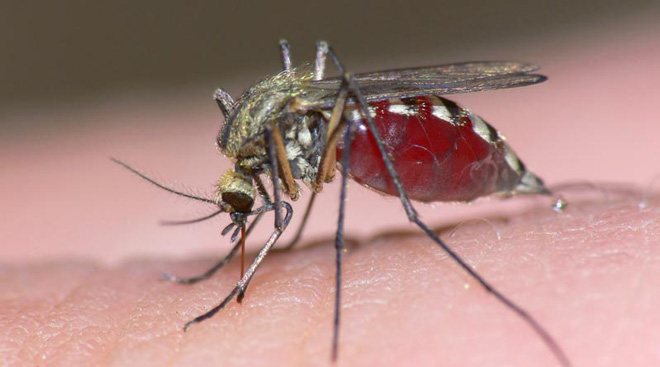
Dirofilariasis is a disease that develops due to a mosquito bite. Because of this, a parasite enters the human body, which accumulates in the skin of the eyelids. It can also enter the conjunctiva, the thin tissue that covers the eyes and the back of the eyelids. If dirofilariae settle in the anterior chamber of the eye, then they can create a granuloma, leading to double vision.
However, the following symptoms are most often observed:
- Sensation of a foreign body.
- Swelling.
- Discharge of tears.
- Itching.
- Peeling of the skin.
- Problems with the mobility of the eyelids.
- The appearance of seals under the skin.
- Pain syndrome both on palpation and at rest.
If the human body becomes infected with a parasite called Gnathostoma, then patients develop gnatostomosis. This happens if an infected bird, snake, fish, or frog is eaten. Once inside, the parasite can reach the eyes, but is unable to return to the digestive tract. In general, this interferes with the development of the worm, a person for him is a random host.
Tapeworm hit
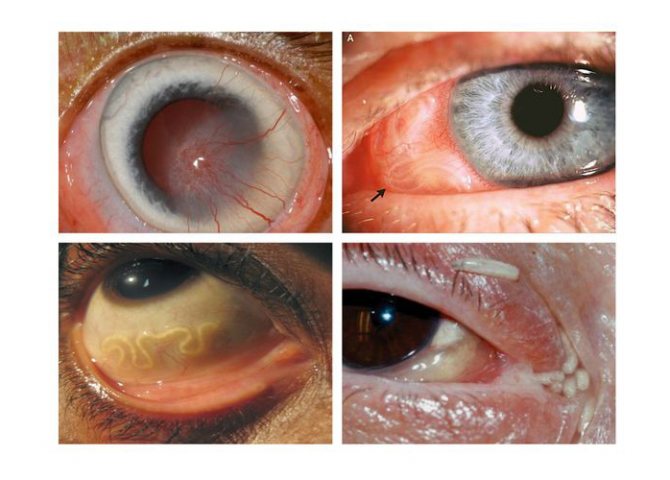

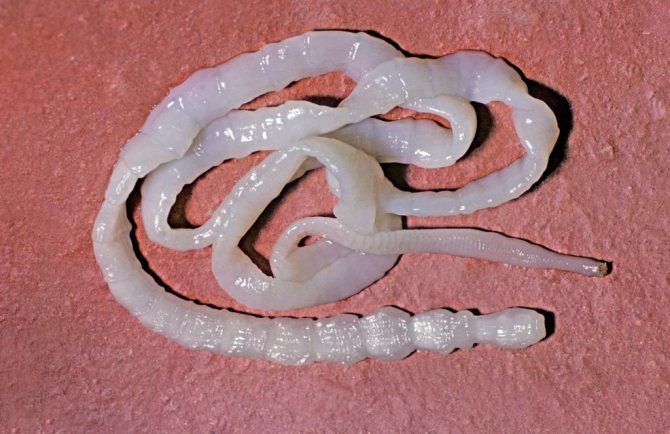
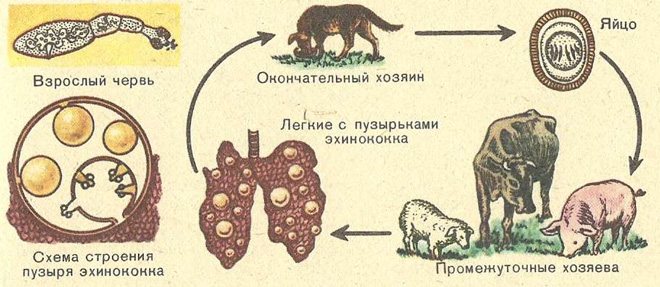
Tapeworms appear in a person's eyes in a random way, by being spread throughout the body along with the bloodstream. For example, this is how echinococcus can get there. These worms tend to form cysts, since they have no other way of existence in a person, a biological dead end.
Note.If the cyst grows too much, it will begin to squeeze out the eyeball, and the person will develop bulging eyes.
The appearance of the mass leads to pain when blinking or trying to close the eyes. As a result of the latter, the mucous membranes begin to dry, which, in turn, damages the cornea and causes conjunctivitis. Gradually, the skin of the eyelids becomes thinner, they swell, and the patient feels a foreign body, he has double vision. If the worms enter the lacrimal canals, then increased lacrimation will begin.
Pork tapeworm enters a person through contaminated food. In this case, they talk about the development of cysticercosis. The disease proceeds either in an acute form, or does not lead to the appearance of any symptoms. Much less often, but still sometimes worms called Sheep's Brain get into the eyes. In general, the disease is in many ways similar to echinococcosis, but in this case, retinal fibrosis sometimes develops.
Characteristics of the disease
Opisthorchiasis
This disease is provoked by a helminth called a cat fluke. People become infected with it when eating fish raw, or if this product has not been properly prepared. The onset of the disease is an allergy, after which the parasite affects the digestive system.
He is able to move around the human body, so it can be in different organs, including the eyes. The result of his damage to the visual system can be keratitis or optic neuritis. If left untreated, the patient may go blind.
Opisthorchiasis
Echinococcosis
This pathology is considered the most dangerous. It is caused by echinococci, which are among the tapeworms. At the initial stage, the disease is asymptomatic, only after a while urticaria may occur.
Dirofilariasis
Infection with dirofilariae occurs with insect bites. Pathology develops very slowly, often of a chronic nature. After a bite, it can take about six months before an egg that has entered the human body develops into an adult.
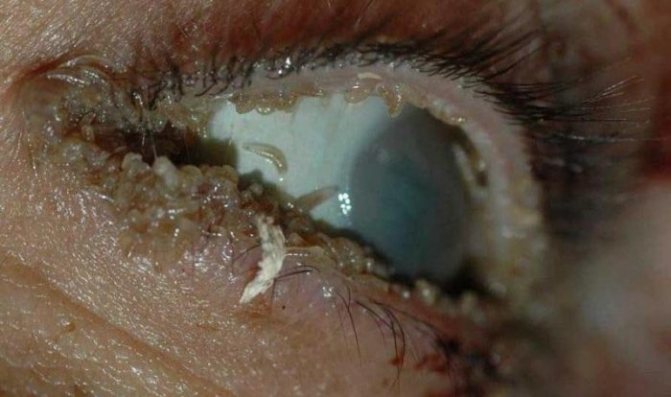
Ophthalmomyasis
Ophthalmomyasis
The disease occurs due to infection with fly larvae, which get onto the mucous membrane from the skin of the hands. This disease causes chronic conjunctivitis, sharp pains, suppuration. If left untreated, ophthalmomyasis leads to blindness.
In addition to the listed diseases, which cause discomfort to the patient, dangerous complications can develop due to eye parasites. The main one is blindness. In the absence of therapy, the patient may even lose an eye.

Another danger is that the eyes are located near the brain, and worms can penetrate there. This leads to severe and sometimes irreversible changes in the functioning of the brain. Sometimes the outcome can be fatal.
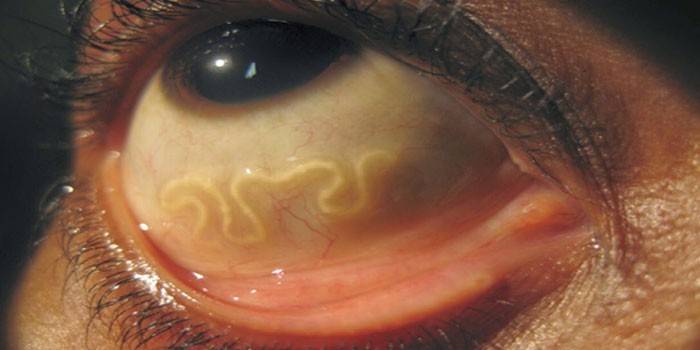
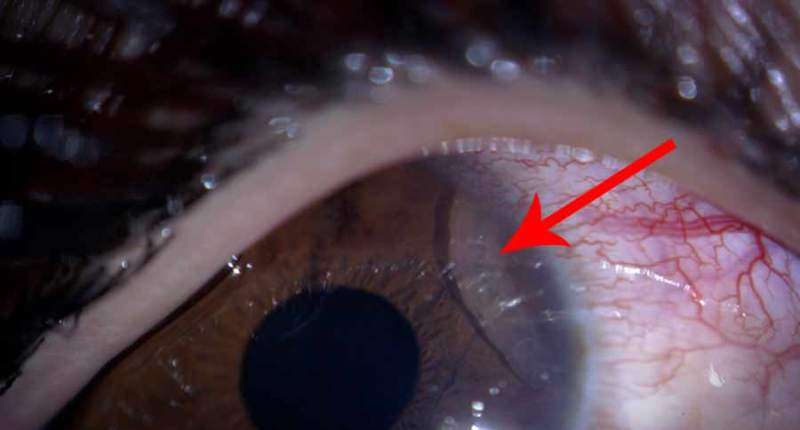
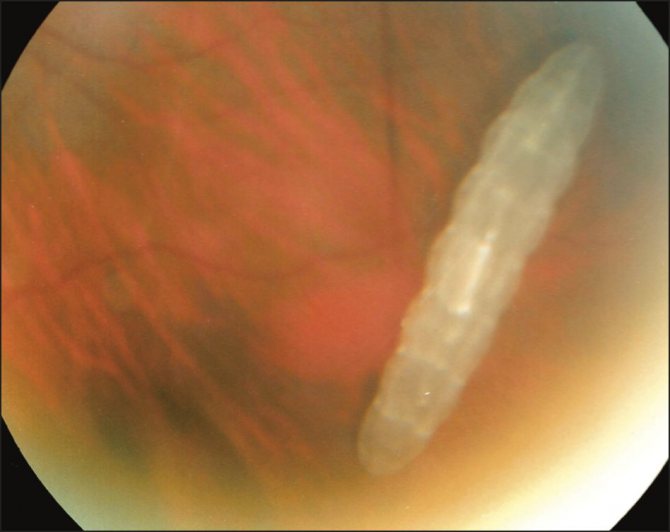
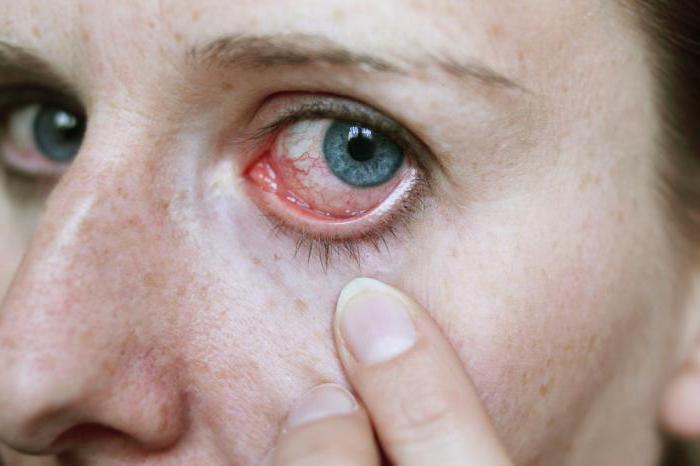
The presence of helminths in the eyes of a person in most cases is clearly visible, some types of parasites can be immediately seen in the eye. At the same time, the patient feels the movement of worms in the eyes.
If the parasites have penetrated under the mucous membrane, then a granuloma develops in the affected area, which looks like an inflamed node.
The most serious form of eye helminthiasis is ophthalmomyasis. This disease is characterized by extensive damage to the larvae of the mucous membrane, orbit, and lacrimal sac. In the infected eye, soft tissue begins to break down.
The disease occurs in two stages.
- At the first stage, the parasites adapt in the organ. After a couple of days, itching begins in the eyes, a burning sensation, which passes after a while. Over time, the person's condition worsens.
- The next step is the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Removal of eye parasites from the organ of vision occurs only by a surgical method.
Treatment for worms in the eye
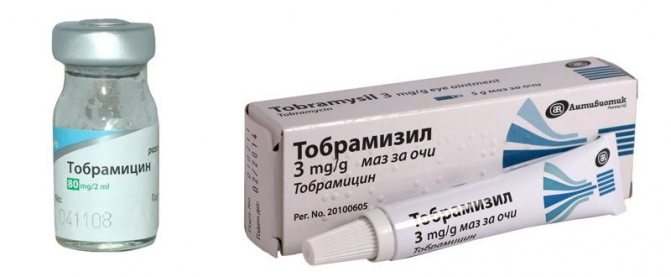

The method of treating worms in the eyes depends on what kind of parasites have settled on the organs of vision. For example, in the case of opisthorchiasis, a five-day course of Chloxil is usually prescribed in conjunction with antihelminthic drugs.
To influence the symptoms that appear with worms in the eyes, the following drugs are prescribed to patients:
- Antihistamines,
- Sulfanilamide,
- Detoxification.
If the infection has just begun, then sometimes it is permissible to limit yourself to rinsing the eyes with agents like Tobramycin, while the situation is also affected by the type of parasite. However, all of the above methods are used only for external localization of worms. If the worms have developed inside the eyeball, then the only way out of the situation will be surgery.
In such cases, refer to:
Sometimes, even after treatment, patients develop the infection again. In this case, corticosteroids are added to the course of therapy. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to observe all hygiene rules, subject meat and other similar products to heat treatment, and thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables.
Parasites can infect any organ of the human body, and the organs of vision are no exception. The larvae develop only at the initial stages of the pathological process, but sometimes they persist in the eyes until they fully mature, provoking the development of a serious illness. What is the danger of ocular invasions?
Worms can migrate from the organs of vision to other parts of the body, choosing a more suitable place for themselves. They cause disruptions in metabolic processes, the work of the immune system, and can also lead to the development of an allergic reaction and mechanical damage to soft tissues.
Sometimes patients even feel the movement of worms, in some cases this is visible visually. A photo of an eyeball affected by parasites is frightening, and the possible consequences can be sad. Miasis can cause the appearance of cysts that squeeze the surrounding tissues, and this is ultimately fraught with complete loss of vision.
Could there be bruises under the eyes from parasites? Yes, the appearance of dark circles in the periorbital region is a sign of chronic intoxication caused by parasites. Although this symptom may indicate overwork or lack of sleep.
Next, let's talk about the most common worms that can enter the eyes. To begin with, consider a disease such as cysticercosis.
ethnoscience
Alternative medicine includes many gentle methods, which are mainly prescribed for pregnant women, children and people with chronic diseases.
List of the most effective anthelmintic drugs in traditional medicine:
- linseed and pumpkin oil;
- vegetable crops - garlic, onion, horseradish;
- a variety of spices based on pepper and ginger (see also - what is the use of ginger);
- pumpkin seeds;
- Walnut;
- treatment with meadow herbs - wormwood, St. John's wort, eucalyptus, immortelle, mint.
You can use the above types of recipes, starting from the type of parasitic worms:
- Tapeworms.
- A mixture of fennel and chamomile is combined in equal proportions for 1 tsp. and 500 ml of boiled water is poured. Take every day instead of tea with honey.
- Infusion on dry pomegranate peel. The finished peel is poured with boiling water and taken in 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day.
- Ascaris.
Fill a liter dish to half with chopped onions, add vodka and take 50 ml before meals.
- Pinworms.
Wormwood decoction. Pour 10 grams of wormwood with 1 liter of boiling water, insist, strain. Add honey before taking. Consume on an empty stomach and before meals, 30 ml.
Taking pumpkin seeds on an empty stomach will have an effective anthelmintic effect, but to get rid of dead individuals of helminthiasis, it is recommended to take laxatives.
In this video, experts will tell you in detail about food products that affect parasites and help remove them from the body.
Cysticercosis
To activate the process, it is necessary that the eggs of the helminths penetrate into the stomach. Under the influence of hydrochloric acid, the shell of the worms dissolves. Further, the released embryos penetrate into the circulatory system and are carried through the tissues and organs of the human body. As a result, the larvae can reach the organs of the visual apparatus.
The causative agent of the disease is the larvae of the pork tapeworm. You can get infected with a tapeworm in several ways, namely:
- the use of pork meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment;
- swimming in dirty waters;
- the use of agricultural products grown on organic fertilizers;
- as a result of the ingress of eggs from the intestines into the stomach.
The danger of helminthic invasions is that they can disrupt the functional activity of any organ. Parasites can cause deterioration of the skin and even trigger oncological processes.
Consider the main symptoms of parasites in the eyes:
- chronic inflammation of the eyes;
- deterioration of vision;
- headaches;
- tearing;
- hemorrhage;
- constipation followed by diarrhea;
- bloating;
- change of mood.
Important! It is quite difficult to preserve vision with cysticercosis.
Treatment of flatworms is carried out in a stationary environment under the supervision of medical personnel. A modern drug for the treatment of cysticercosis is Praziquantel. It contains a broad-spectrum antihelminthic agent.
Deworming leads to massive destruction of worms in the eyes. This is fraught with the development of an allergic reaction or even anaphylactic shock. In order to prevent the development of complications, antihistamines, anticonvulsants and non-steroidal drugs are prescribed.
How to get rid of parasites from your eyes
Diptera larvae, protozoa, ticks and other pathogens of parasitic diseases are capable of rapidly destroying the eye structures. Therefore, treatment is carried out immediately after the diagnosis is made. When choosing therapeutic tactics, doctors take into account the type of infectious agents, the severity of the course of the disease and the severity of symptoms.
If an infected person turns to doctors with advanced helminthic invasion, then often conservative treatment does not work.
Parasitic worms must be removed surgically - by opening and draining abscesses according to generally accepted rules.
And then a long period of rehabilitation follows with the use of anthelmintic drugs.
Folk remedies
Even long-term use of powerful modern anthelmintic drugs is often ineffective for such diseases. Urgent surgical removal of larvae, eggs and sexually mature individuals is required.
And traditional medicine is completely powerless when the eyes are affected by helminths. Neither tansy, nor centaury, nor bitter wormwood are able to cope with ocular invasion.
The use of decoctions and infusions slightly alleviates the symptoms, so the patient postpones the visit to the doctor. And at this time, inflammatory and destructive processes intensify and spread in his eyeballs. They predispose to retinal detachment, complete or partial blindness.
Medicines
Various treatment regimens for ophthalmic diseases caused by worms have been developed. Individual therapy is carried out only by specially trained parasitologists. The fact is that after the death of helminths and their decomposition, intraocular toxic-allergic reactions can develop. Only an experienced doctor can minimize their consequences. To destroy parasitic worms, the following drugs are used:
- antinematode - Albendazole, Levamisole, Befenia hydroxynaphthoate, Piperazine, Pirantel;
- anticestodal - Niclosamide, Albendazole;
- antitrematode - Tetrachlorethylene, Hexachloroparaxylene, Bithionol;
- broad-spectrum drugs - Mebendazole, Albendazole.
From external agents, a solution of furacilin is used to wash the eyes. Antihistamines must be included in therapeutic regimens, and, if necessary, antibiotics and antimycotics.
Ophthalmomyasis
Specialists call a specific parasitic disease ophthalmomyasis. Ophthalmomyasis is external and intraocular. With external myiasis, the larvae are located in the lacrimal sac, lacrimal ducts and under the conjunctiva. With internal damage, the worm makes its way into the eyeball itself. Worms can penetrate the organ of vision through dirty hands, contaminated food, an insect bite or fly carriers.
The larvae are able to drill tissue, making a move under the mucous membrane. If the larva gets into the anterior chamber of the eye, there is a deterioration in vision up to absolute blindness. In this case, to eliminate miosis, photocoagulation is performed (a gentle method in which helminths are burned out by a laser) or vitrectomy (removal of the vitreous body of the eye).
The following signs may indicate the development of ophthalmomyosis:
- sharp cutting pain in the eyes;
- profuse tearing;
- deterioration of vision;
- pain and itching;
- inflammatory response;
- temperature increase;
- suppuration;
- bags under the eyes;
- headache;
- chills and nausea occur when the parasite dies.
Myiasis symptoms
Ophthalmomyiasis can manifest itself in completely different ways. Basically, there are two types of ophthalmomyiasis:
- Extrabulbar (external, subconjunctival, palpebral, inhabited).
- Intraocular (intrabulbar, internal).
According to the clinical course, external ophthalmomyasis can be represented by myiasis of the eyelids (furuncle-like), larval conjunctivitis, destructive ophthalmyiasis, as well as larval conjunctival granuloma. Internal ophthalmomyasis is much less common and is subdivided into posterior and anterior.
Miasis of the eyelids often manifests itself in the form of a furuncle-like tumor of the skin. It is usually associated with parasitizing the larvae of Hypoderma bovis and Oestrus ovis. The larva initially penetrates the skin and then continues its development. Most often this occurs in the upper eyelid area. Often, a patient with such a disease feels the movements of the larvae, in some cases, their movements are even noticeable
This symptom is of great diagnostic value. In a different clinical course, sinuous lines may appear inside the skin of the eyelids, which gradually lengthen.
This form is called creeping myiasis.
Larval conjunctivitis is usually acute and develops immediately after the larvae enter the area of the conjunctival sac. Usually the female gadfly releases these larvae on the fly. After removal of the larvae, the symptoms of conjunctivitis quickly regress. The development of larval conjunctivitis is sometimes accompanied by the appearance of a marginal ulcer of the cornea.
Larval conjunctival granuloma can form if the larva penetrates under the mucous membrane of the eye. A node of inflammation is formed around the larva. After cutting the mucous membrane, the larva can be easily removed.
Destructive ophthalmomyasis is commonly diagnosed in tropical countries. In this case, a large number of larvae penetrate under the mucous membrane, skin, orbit, lacrimal sac, and even into the surrounding tissues. In the future, tissue destruction occurs, and in some cases the bones of the orbit.
Dirofilariasis
Eye disease develops slowly and is chronic. A person can become infected through mosquito bites. At risk are fishermen, gardeners, dog and cat owners, and hikers.
After a mosquito bite, the skin becomes thickened and reddened. The place begins to itch, but usually it is attributed to the bite itself.After a few days, the seal disappears, but after a while it reappears. This time, the itching takes on an intolerable form, soreness arises.
After about six months, the parasites begin to migrate. In the old place, the swelling and induration disappear, but they appear in a new place. Sometimes the capsule can rupture spontaneously, and as a result, the worm comes out.
Parasites in human eyes most often affect the conjunctiva and subcutaneous tissue of the eyelid, less often the sclera and vitreous body. Eyes watery, redden, an inflammatory reaction occurs. Often people say that they feel the parasites living in the eyes, feel their movement. Worms in the eyes can also cause other symptoms:
- blepharospasm;
- bulging of the eye;
- drooping of the eyelid;
- headache;
- nausea and weakness;
- increased body temperature.
Given the fact that one immature individual parasitizes, antitoxic treatment is not required. Most often, the helminth is removed surgically. In order to avoid further migration of the parasite, the patient is prescribed a drug such as Ditrazin. Also, after the operation, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs are prescribed. Dexamethasone eye drops will help reduce the inflammatory response.
Sacks (edema), papillomas and worms
There is a point of view that bags under the eyes, papillomas on the eyelids indicate the presence of parasites in the body. This is partly true - yes, helminths can cause the formation of edema, but the presence of sacs in itself does not indicate an invasion.
After recovery, if the bags were caused by worms, the symptom goes away along with intoxication.
Papillomas in the eyes indicate the presence of human papillomavirus. Formations grow on the skin or do not change size for a long time, they do not create anxiety for a person.
There are studies confirming that with the active growth of papillomas, there were worms in the human body.
It is not at all necessary that the invasion is diagnosed in you, but it is better to play it safe.
Opisthorchiasis
This is fish helminthiasis, which occurs in a chronic form. You can get infected by eating fish that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. There is a hypothesis, but it has not been scientifically proven that infection can occur when cleaning river fish infected with helminths. But many experts consider this unlikely, since the eggs live in the muscles.
When the parasite migrates from the liver to the eyes, inflammation of the iris of the eye and eyelids occurs. The adhesion process threatens with loss of vision. The pathological process, as a rule, is bilateral in nature. It manifests itself in the form of neuritis and keratitis of the optic nerve, damage to the choroid of the eye, as well as hemorrhage. Patients are prescribed Chloxil, as well as choleretic (Tsikvalon, Olimetin, Cholagol) and allergic drugs.
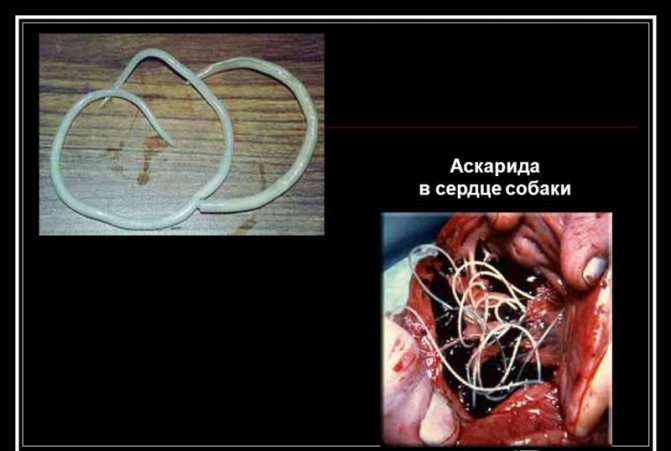
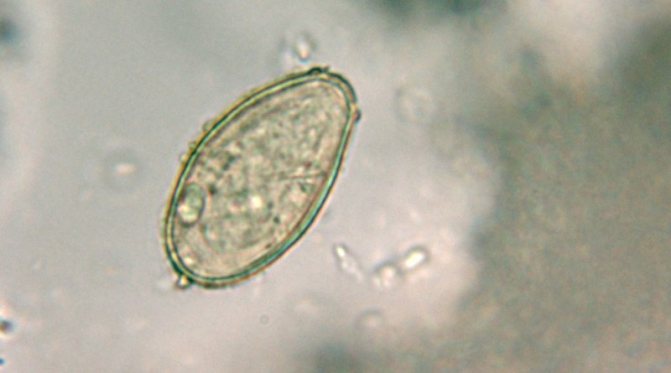
Ascariasis
The eggs go into the intestines, but they don't stay there. They drill through the intestinal wall, enter the bloodstream, and migrate to the lungs. There, the larva matures and turns into an adult. The worm irritates the nerve endings, which leads to coughing and the release of the parasite down the throat.
Usually the worm is swallowed and reintroduced into the intestines, but sometimes the young form is not swallowed up the esophagus or spit out. Then the worm can accidentally crawl into the middle ear, and then into the eye. As you can see, the worm makes a very difficult path.
Ascariasis causes a number of serious symptoms, including:
- edema;
- inflammation of the cornea;
- hemorrhage;
- drooping of the eyelid;
- bruising under the eyes;
- tearing;
- strabismus;
- glaucoma.
Other parasites
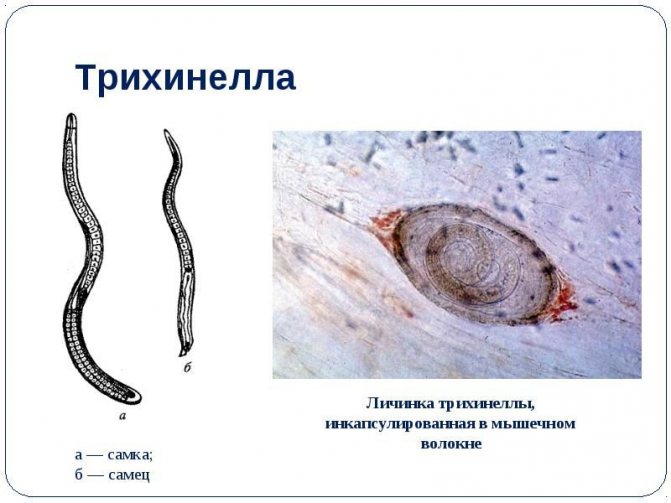
Trichinosis occurs when eating meat from infected animals. The larvae enter the intestines, and then through the circulatory system they reach the organs of vision.The disease causes an inflammatory reaction, muscle pain, conjunctivitis, swelling of the eyelids and even the entire face.
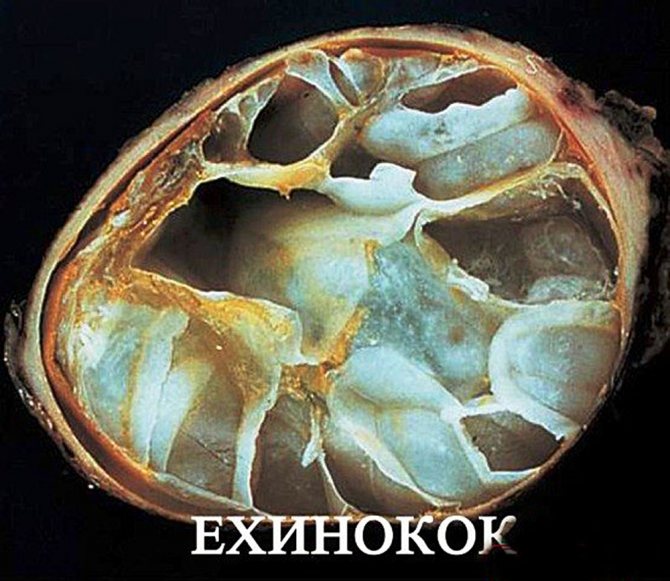
It is impossible not to mention echinococcosis of the eye. Most often, parasites settle in the liver, and only later migrate to the visual apparatus. Echinococcus builds itself a house in the form of a cyst, which causes protrusion of the eyeball, difficulty in blinking, drying out of the mucous membrane. Echinococcosis leads to destruction of the cornea, atrophy of the eyelid skin and constant tearing.
In the end, let's talk about trematodes. Immature liver flukes can accidentally get into the blood and internal organs, but it is also possible for the parasite to enter the anterior chamber of the eye. The cause of the disease in the recorded cases was the consumption of poorly prepared frog legs.
Echinococcal eye damage
It is caused by echinococcus, which is initially localized in the intestines, and then enters the liver, muscles, bones, lungs and eyes through the blood.
Symptoms
As the disease progresses, the cyst in which the parasite exists increases in size, pushing the eye outward and thereby causing bulging. In this case, it becomes difficult for a person to blink and close their eyes.
The skin on the eyelids becomes thin and swollen. Due to the inability to fully blink, the mucous membrane dries up, which can lead to conjunctivitis and complete damage to the cornea. The patient may experience a feeling of double vision in the eye, as well as the presence of a foreign body. When helminths are localized in the lacrimal glands, constant lacrimation occurs.
Treatment
For the purpose of therapy, synthetic anthelmintics are prescribed: Dekaris and Pirantel, which prevent the development and reproduction of the parasite. Chemotherapy drugs: Ditrazin, Chloxil. They are injected directly into the cyst cavity. An operation is performed to remove worms.
Treatment features
First of all, a specialist conducts an examination to identify the causative agent of an ophthalmic disease. Before direct treatment, a preparatory stage is carried out, which includes the fight against the symptoms of the disease and reduces the harm from taking antiparasitic drugs, which will then be prescribed.
The main goal of the treatment process for ophthalmomyasis is to remove worms and its larvae from the eye. The process of eliminating a foreign organism is carried out as follows:
- a solution of dicain is dripped into the eyes to provide local anesthesia;
- the larva is removed with tweezers. In some cases, you will need to make an incision at the site of inflammation;
- the eyes are washed with a weak solution of soda;
- antibiotic therapy;
- applying ointment to the wound.
Treatment for parasites also includes the use of antihistamines, detoxification and sulfa drugs. Traditional medicine will also help to cope with miosis. Brew dried birch leaves in a glass of boiling water. The remedy should be infused overnight. You must drink the received medicine three times.
Pumpkin seed oil is renowned for its anti-parasitic properties, especially when combined with extracts of clove, fennel and wormwood. It is also beneficial to consume pumpkin seeds.
Alcohol tincture of black walnut is also made against parasites. A decoction of green walnuts based on honey is sent to a water bath for thirty minutes. The resulting product is added only one teaspoon to the tea.
The following recommendations will help to avoid the appearance of miosis:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- control of insects that can be carriers of parasite larvae;
- the use of special barrier ointments and creams. This will prevent the penetration of worms under the skin;
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after using the restroom, contact with animals, going outside and before eating;
- watch your nails, they should be cut regularly so that dirt does not accumulate under them;
- do not buy fish and meat in questionable places or at spontaneous markets;
- do not drink raw water from a tap or spring;
- do not swim in polluted water bodies near pastures and watering holes;
- wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly before eating;
- if you experience alarming symptoms, see a qualified doctor.
Prevention of ocular helminthiasis

Prevention of diseases in which the development of worms in the organs of vision is possible is not too difficult.
It is enough to follow a number of simple rules:
- compliance with the rules of cooking, sufficient heat and salt treatment. Attentive attitude to river fish (source of opisthorchis) and pork (source of pork tapeworm);
- do not eat unwashed vegetables and fruits, but especially wild plants and mushrooms;
- do not drink water without boiling from open natural sources;
- observance of personal hygiene, washing hands after playing and communicating with animals, working in the garden, vegetable garden, after visiting the streets, parks, forests;
- do not touch your eyes with your hands, especially unwashed ones;
- get rid of insects at home in time, keep the house clean in order to avoid the spread of flies and their larvae, use repellents to protect against bites on vacation or during a long stay in the open air during a period of high activity of blood-sucking insects.
Clinical manifestations
The worm does not start immediately in the eyeball, it moves from other human organs. And the eye is the most favorable area for worms to live. As they move through the body, parasites infect the parenchymal organs, thereby causing inflammatory reactions. The most common diseases in which the organs of vision are affected are:
- Toxocariasis.
- River blindness.
- Keratitis.
- Cysticercosis.
- Telyaziosis.
- Opisthorchiasis and others.
Doctors say that the cause of helminthic invasion in the eyeball can be the wearing of contact lenses. Before putting on the lenses, the patient must thoroughly wash his hands with soap and water.
Depending on the disease, the symptoms of the presence of parasites in the eye in a person will be different. However, each pathology proceeds with pronounced symptoms.
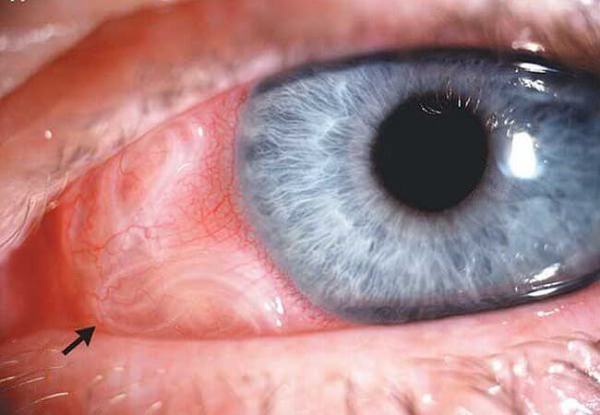

Echinococcosis
The defeat of echinococcus begins in the human intestine, over time, parasites move through the body and enter the liver, lungs, muscles. If the worms have reached the eyes of a person, the following clinical manifestations of echinococcus are noted:
- Painful sensations when blinking.
- Swelling.
- Split eyes.
- The skin on the eyelids is thin.
- The mucous membrane of the eye is dry.
- Sensation of a foreign substance in the eye.
Also, doctors note additional symptoms of echinococcus:
- Heat.
- General weakness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Migraine headaches and dizziness.
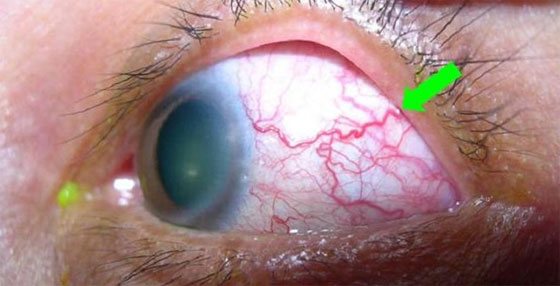

Opisthorchiasis
With opisthorchiasis, the body is poisoned. In case of damage to the eyes of the patient, the following clinical manifestations are disturbed:
- Red eyes.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Optic neuritis.
- Swelling.
- Soreness on pressure, blinking.
- The presence of white threads that the doctor can see visually.
- Hemorrhage.
Dirofilariasis
Dirofilariasis is a disease caused by parasites of the nematode class. Infection occurs from a single parasite that grows and develops, is transported through the human body under the skin. The most common cause of helminthic infestation is a mosquito bite. After 30 days, the worm multiplies, affecting various organs and tissues. The most common eyeball symptoms include:
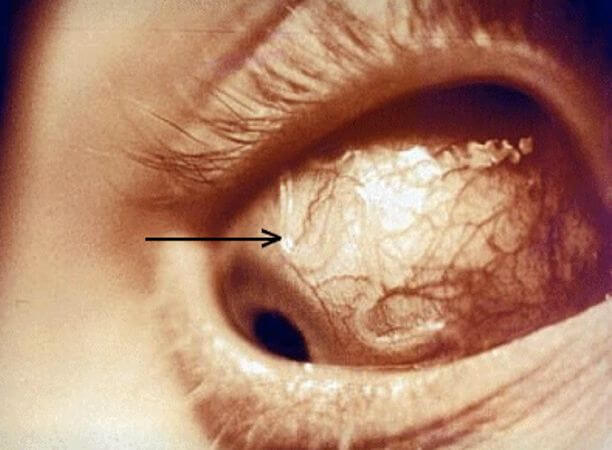

- The appearance of nodules, when pressed, the patient feels a sharp pain.
- Painful sensations when blinking.
- Swelling.
- Redness of the eyes.
- Fear of bright light.
The causative agent of dirofilariasis lays the larvae, which the physician can visually notice. The larva resembles a pimple.
Ophthalmomaz
Ophthalmomaz can be internal or external. Insects that lay the larvae are considered the main causes of the invasion.Signs of eye damage caused by ophthalmatosis that live in the eye:
- Conjunctivitis of various etiologies, edema of the eyes.
- Burning sensation.
- The patient feels the movement of the worm over the eyeball.
- Reduced pressure.
- Exfoliation of fiber.
This disease is considered the most dangerous, since the symptoms are often mild, and a person is diagnosed by doctors only after blindness. Doctors call the invasion creeping miass due to the movement of the worm.


Onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis or helminthic invasion, in which eye damage is noted with the following symptoms:
- Itching and burning in the eye area.
- Short-term blindness.
- Beauty.
- Migraine.
In rare cases, onchocerciasis develops in patients who live in the territory of the Russian Federation. In most cases, it affects the inhabitants of tropical countries, since the pathogen living in this strip is the most dangerous.
How to treat
Before starting treatment, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination, pass tests - so the doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the type of pathogen, since there are many of them, and each requires a specific approach. The course is designed for several weeks, after completing it, the state of health improves significantly.
Side effects are possible, but the harm from worms to the body is much greater. Do not waste time - folk remedies in the fight against helminthic invasions in the eyes are powerless.


Opisthorchis therapy
Opisthorchis is a helminthic worm from the family of flukes that affects the digestive tract. Hemorrhages often provoke hemophthalmos - the eyeball is completely filled with blood. It is very dangerous to eat contaminated fish as it is the main source of the disease.
The iris of the eye and the surrounding tissues are regularly inflamed, adhesions are formed, and in the future, vision can also deteriorate.
Treatment is carried out with the use of chloxyl, choleretic agents, enzymes, antihistamines. The doctor prescribes the exact scheme of therapy based on the tests.
Echinococcus
The parasite on the mucous membranes is attached with suckers-hooks, initially settles in the intestine, but then it can migrate. It is also possible to damage several organs at once. Subsequently, echinococci form cysts, where they multiply and live.
The defeat manifests itself, like any neoplasm - the apple begins to bulge outward, discomfort appears when the eyelids close, during blinking, the eyelids stretch, swell, become very thin, and the mucous membrane dries up.
This provokes secondary infections, conjunctivitis, corneal manifestations appear. The cyst begins to be felt as it grows in size.

The first thing that needs to be done is to relieve symptoms of intoxication, headache, and normalize sleep. The second stage is specific therapy. If the cyst is less than 0.5 cm in diameter, the doctor will not find it. The main research method is ultrasound.
It is obligatory to take anthelmintic agents, which start active processes of development of young individuals. Chemicals are injected directly into the cyst (this is done with a special needle). Radical treatment is operative, one puncture is enough.
Diroflariasis
With this type of invasion, the parasite migrates through the implants under the skin. One individual is enough for infection; it can enter the bloodstream even as a result of one insect bite. The incubation period is 4 weeks, after its completion the worm begins to move through the body.
Crawling under the skin is distinct, if the parasite penetrates deeply, you can lose your sight. The method of treatment is an operation (the helminth must be removed from the eye).

Ophthalmomyasis
A group of diseases caused by the fly larva. Ophthalmomyasis is external and internal (if the parasite enters the mucous membrane, this is the internal form, if it lives near the eye, it is external).
The fly larva in many ways resembles a worm, when it moves in the organ, characteristic unpleasant sensations arise, a feeling of sand appears in the eyes.Over time, the parasite destroys tissue, causing necrosis.
If the pathology progresses, you can completely lose your vision. The method of treatment is surgery.
The danger
If parasites enter the eyeball, the disease is considered serious, as the patient may lose sight. If a therapy regimen is not prescribed in a timely manner, then a complete loss of the eyeball is possible. Doctors say that in advanced cases, the worm enters the brain, causing irreversible consequences, which already threatens human life. If the patient notes the presence of a helminthic invasion, which is localized in the eye, then an urgent need to contact a medical institution to start therapy.
Why are worms dangerous in the human body outside the intestines?
Parasites of this kind:
- violate metabolism;
- suppress the immune system;
- contributing to the allergization of the body;
- damage tissues at the site of their penetration.
As a result, inflammation occurs.
Worms that develop rapidly (echinococcus and cysticercus) form cysts that compress the surrounding tissue. Such neoplasms disrupt the function of the affected organ - liver, brain, eye.
For example, symptoms can manifest itself in decreased vision, liver failure, etc. Parasites can mimic tumor damage to an organ. This situation makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
Diagnostics
It is possible to diagnose the presence of a worm in the eyeball by passing tests and using hardware diagnostic methods. The doctor can see the worms in the eyeball visually, while pathological changes are noticeable. There are filamentous bulges on the eye, these are the worms. If the parasite grows and develops intensively, then in the blood test the number of eosinophils increases.