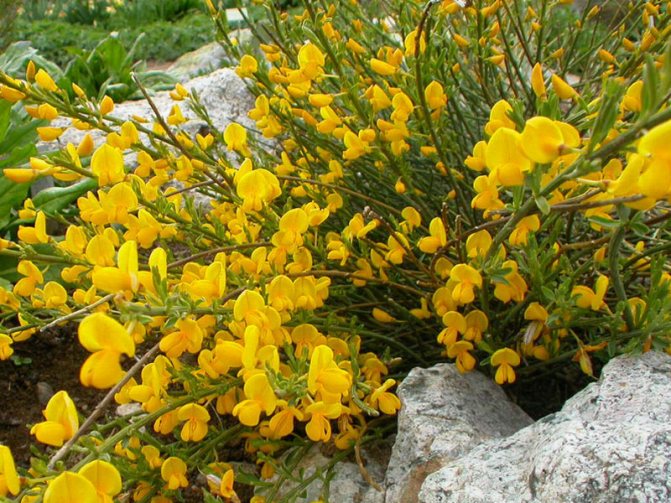
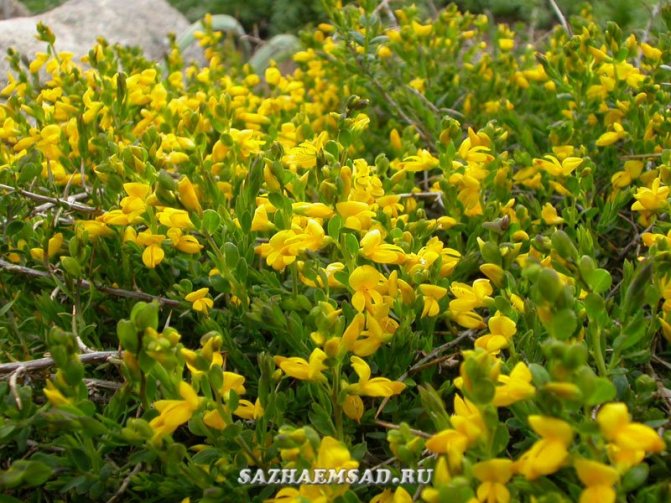
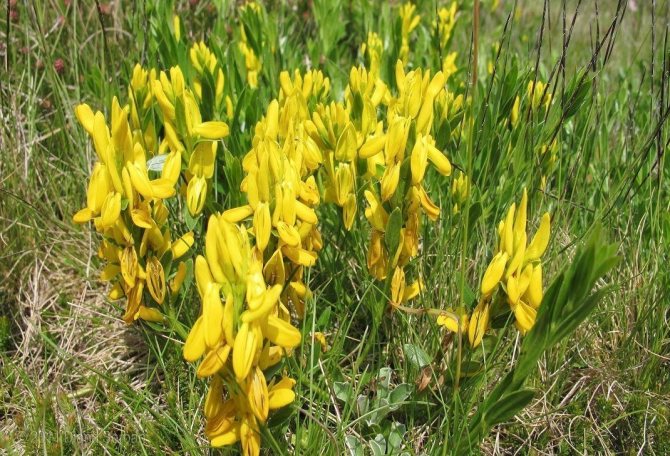
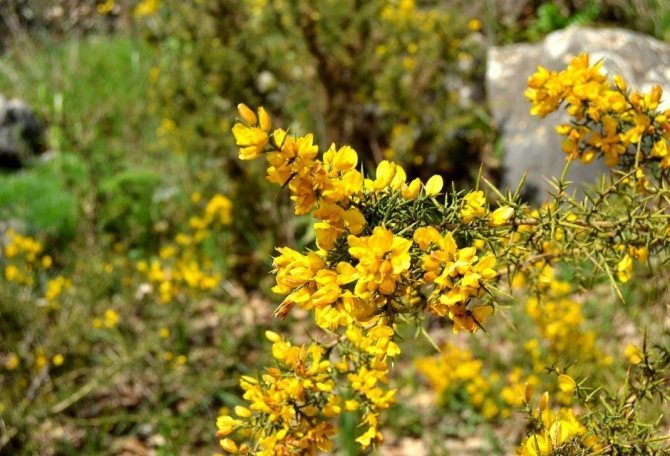
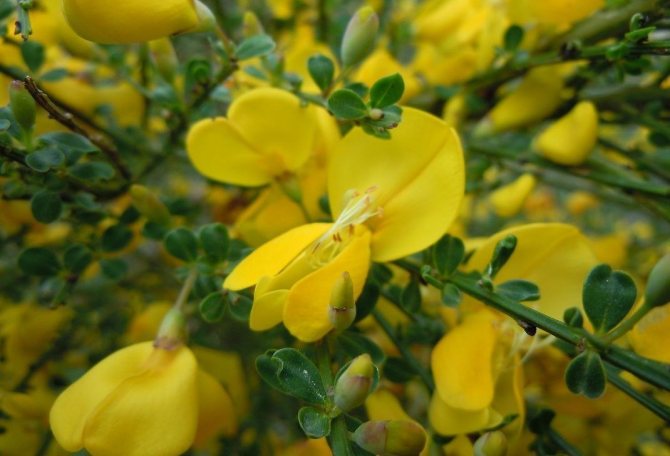
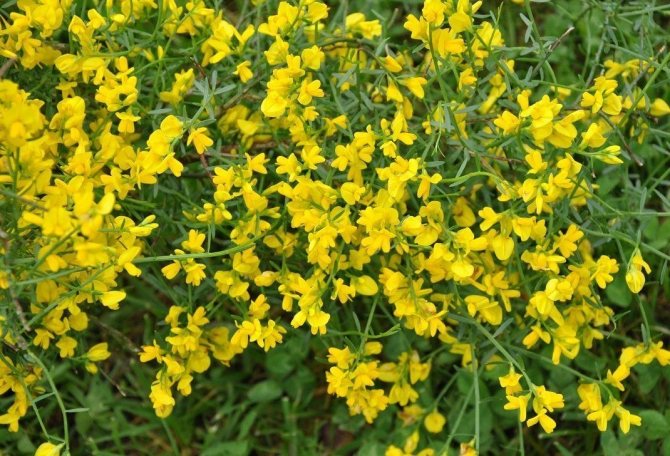
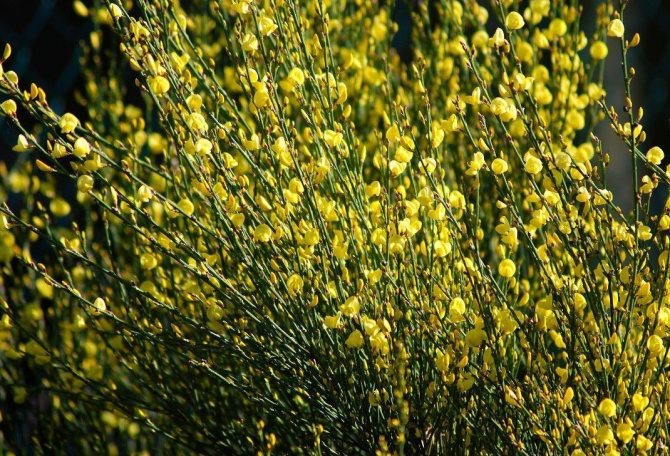
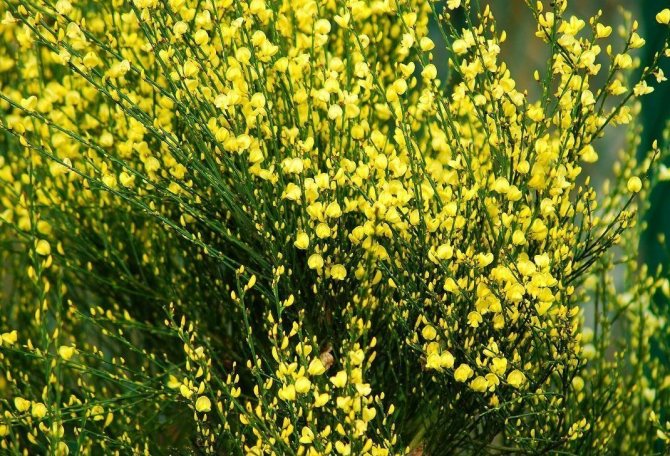
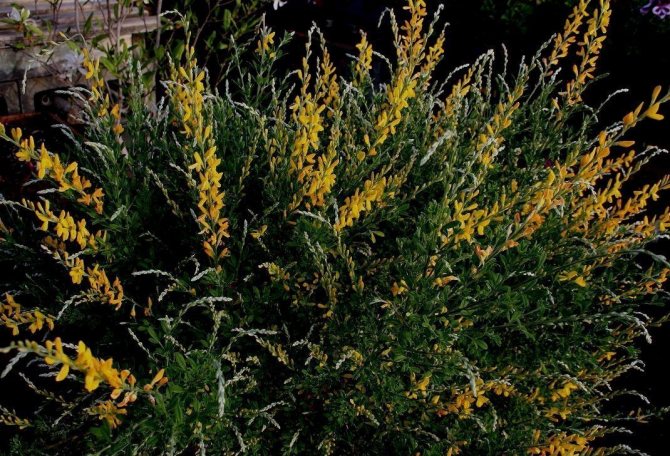
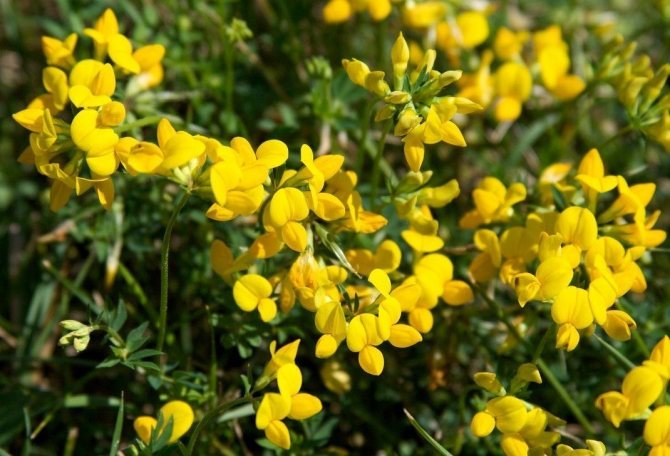
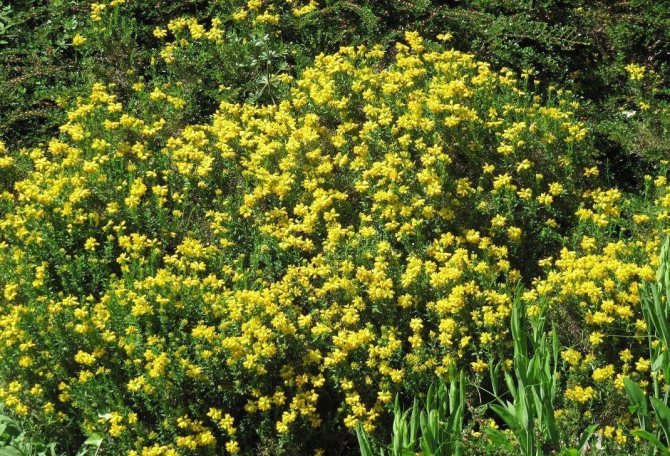
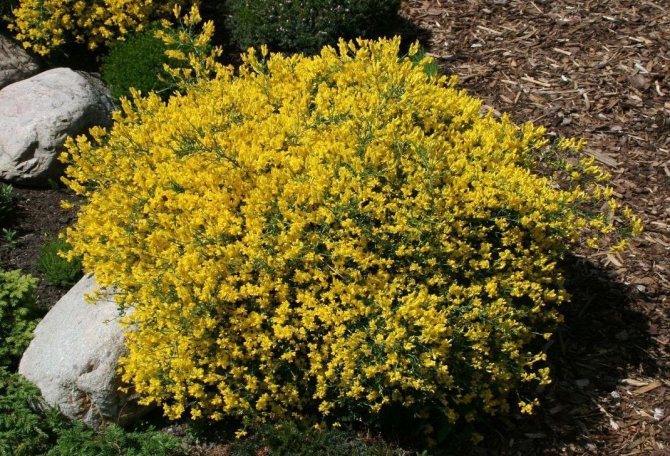
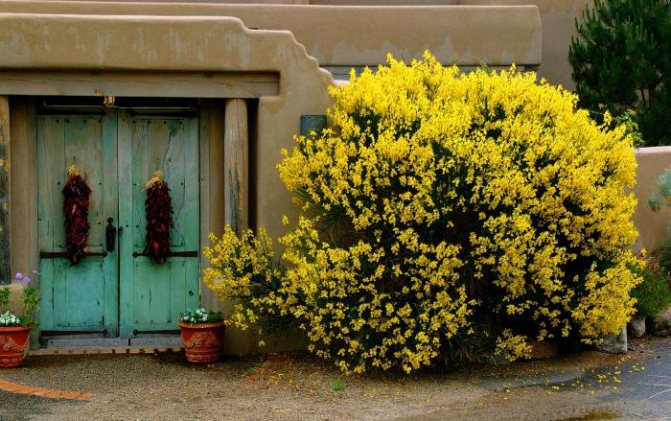
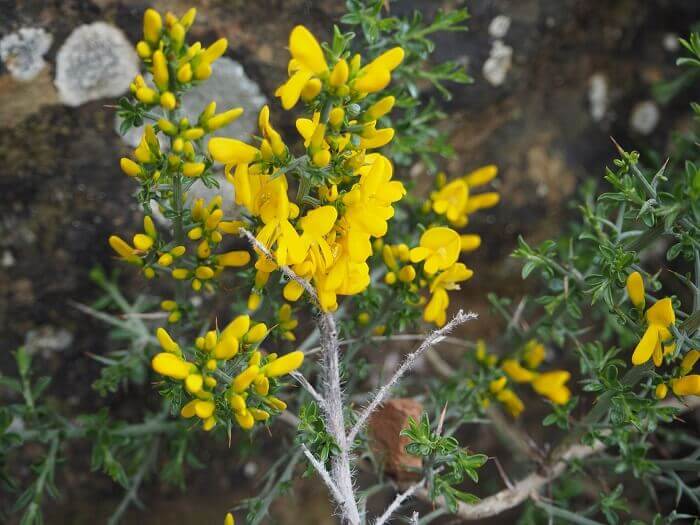
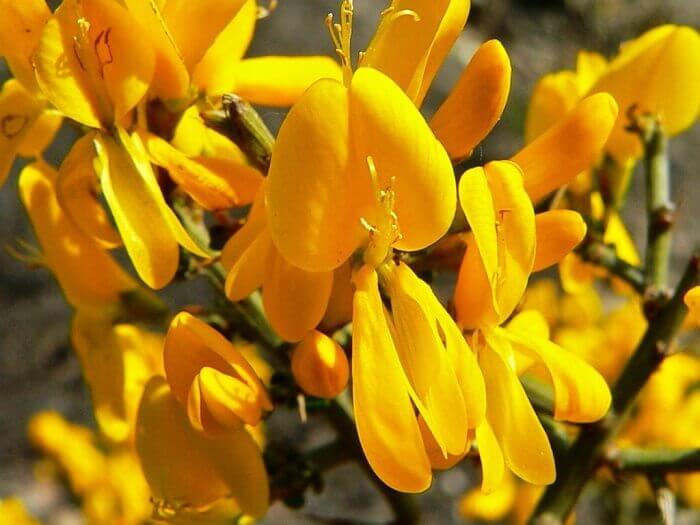
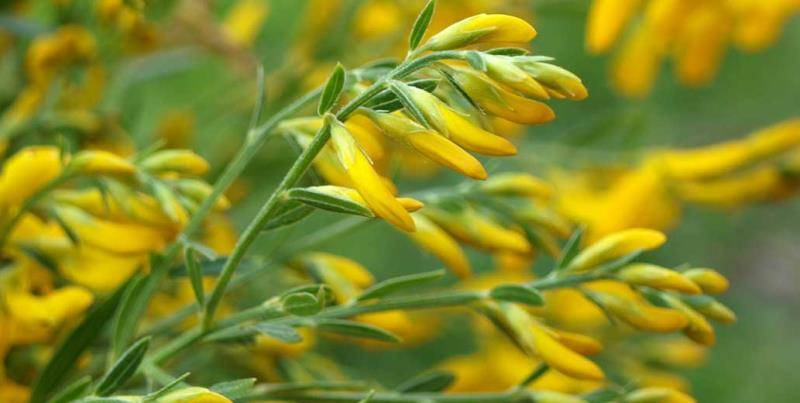
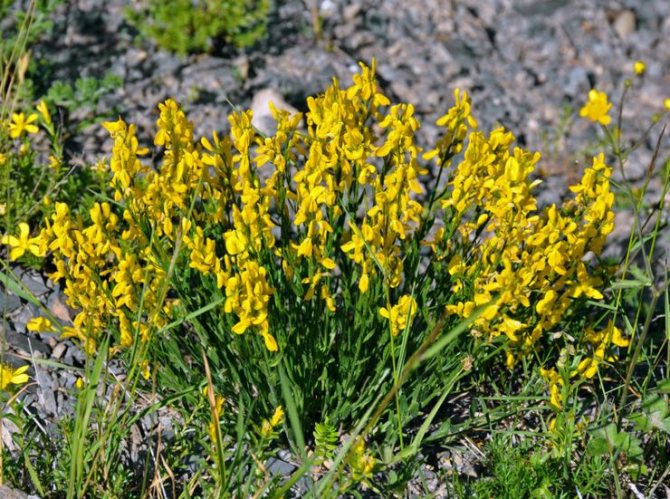
Gorse are perennial shrubs and liana-like plants from the legume family. They can be found in Western Europe and Northwest Africa. The dense green crown is abundantly covered with golden flowers during the flowering period. Photophilous gorse is planted on the slopes and along the perimeter of the lawn. He ennobles the garden and saturates it with bright colors. In addition, gorse is a medicinal plant, therefore not only pleasing to the eye, but also takes care of the health of its owners.
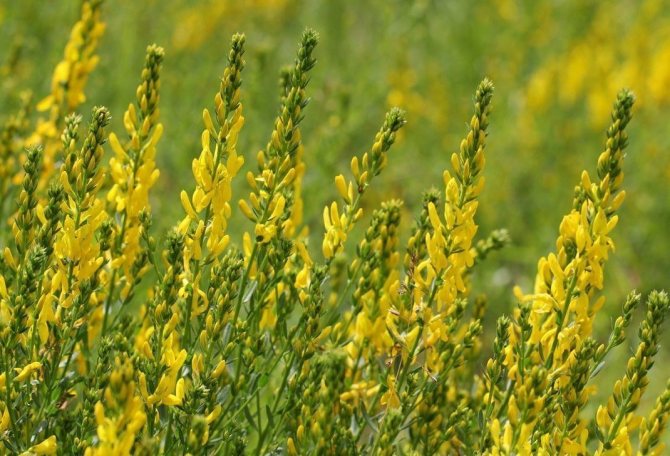

General information
This plant belongs to the genus Gorse, to the Legumes family and to the Moth subfamily. It is attributed to the Beans because of the shape of its fruits, and to the Moths because of the shape of its flowers, which resemble the wings of a miniature butterfly. The peculiarity of the dyeing gorse is its unique polymorphism. This means that depending on environmental conditions, weather and climatic conditions, as well as the growing area, its leaf shape, size, pubescence, bush shape may differ, although all these variations will be the same species. Of its invariable qualities, one can name the flowering period, which falls on the beginning of summer and lasts until the last days of July. The fruits also ripen at the same time, about 30-45 days after the flowers wilt.
Botanical description
Dyeing gorse (lat. Genista tinctoria, English Dyer's greenweed) is a plant of the legume family, a branched shrub reaching a height of one and a half meters. Gorse leaves are simple, alternate, axially elongated with lateral veins on the blades.
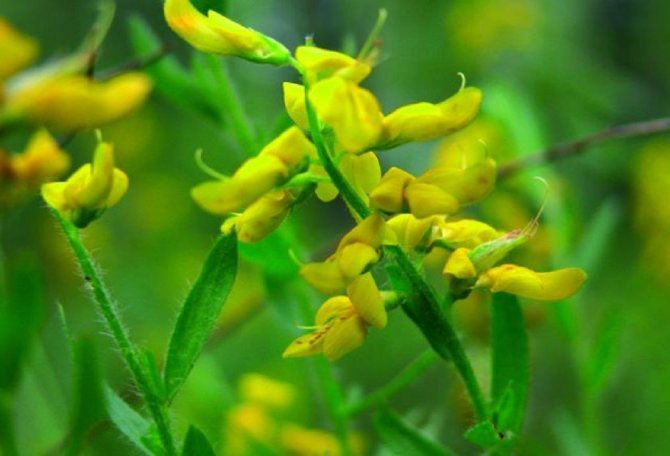
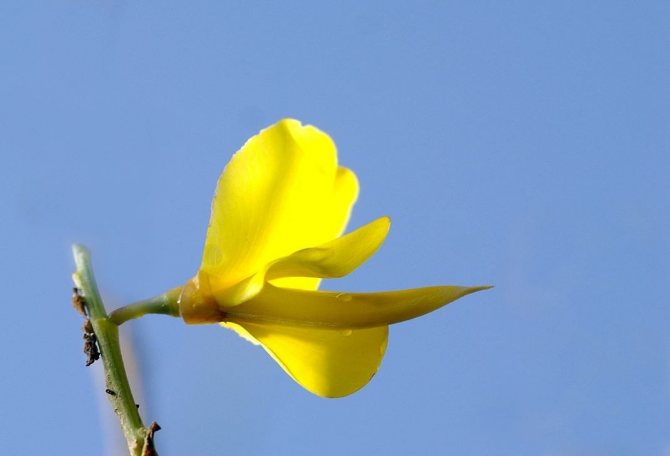
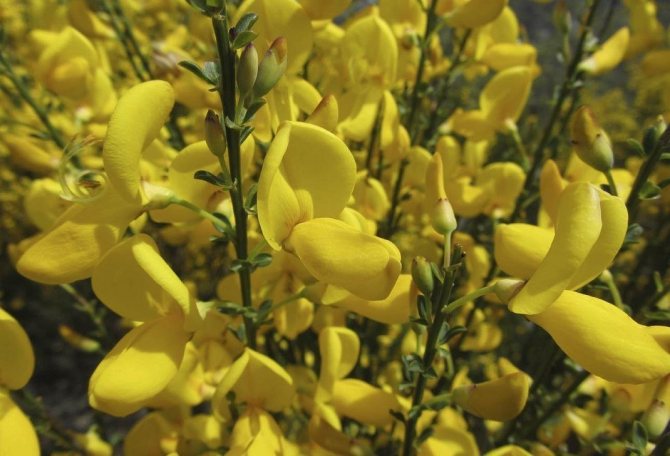
Gorse blooms in June-July with yellow flowers. Flowers are five-membered, irregular, clustered in a raceme at the top of the stem. After flowering, in August-September, the fruits ripen - oblong-linear, flattened beans. Bean seeds are poisonous to humans and cause severe poisoning.
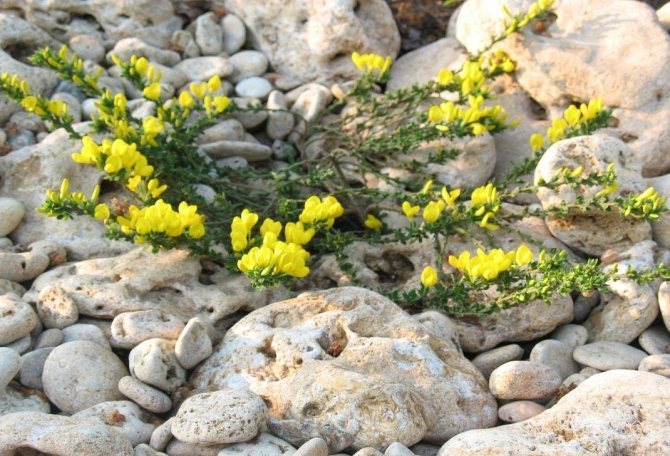
The plant is widespread in dry, light forests of the Baltic States, the Volga region, Western Siberia, etc. It prefers to grow among other shrubs on the slopes of hills and forest edges. Loves sandy and calcareous soil.
Description of gorse dyeing
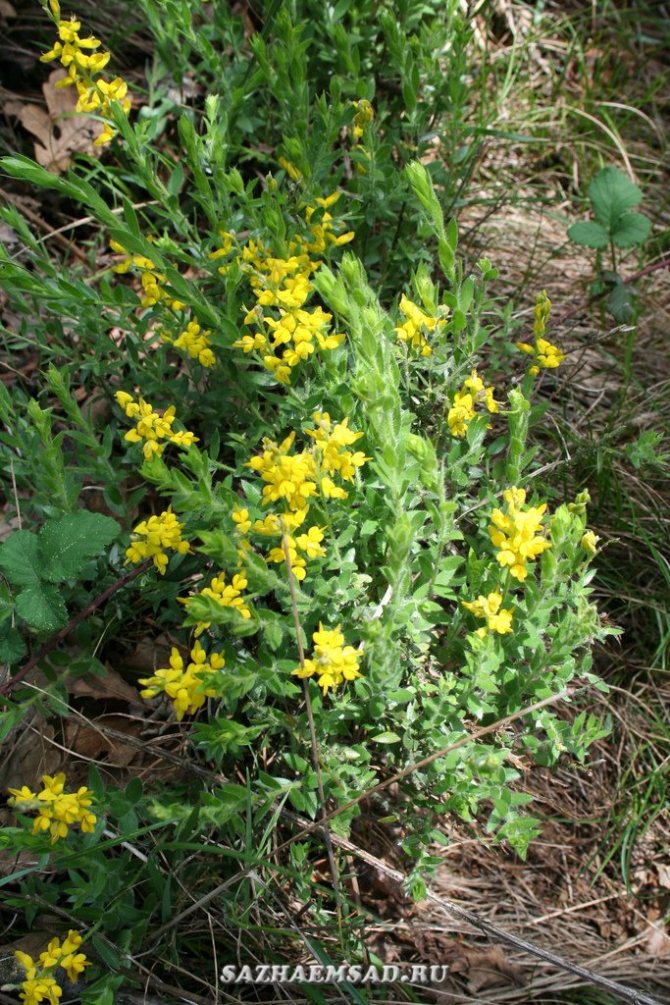
Regardless of growing conditions, this plant is a herbaceous shrub with thin long stems of rich green color. Their length varies from 60 to 170 cm. The gorse stems can be erect or inclined to the ground, glabrous or slightly pubescent. Its leaves are also bright green, not large, thin, up to 25 mm long, lanceolate, alternate, growing on very short petioles or directly on the stem.
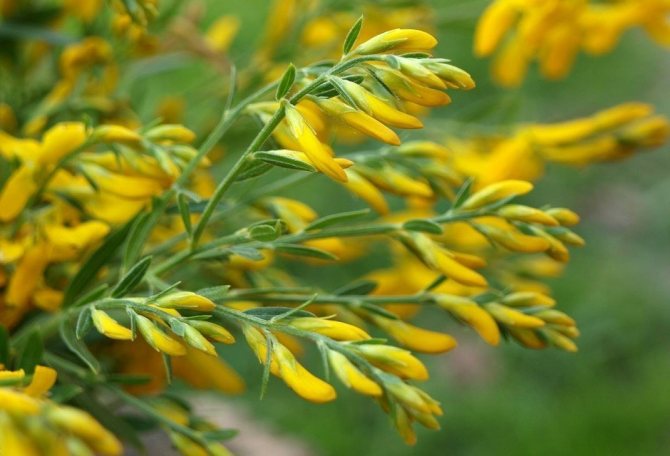
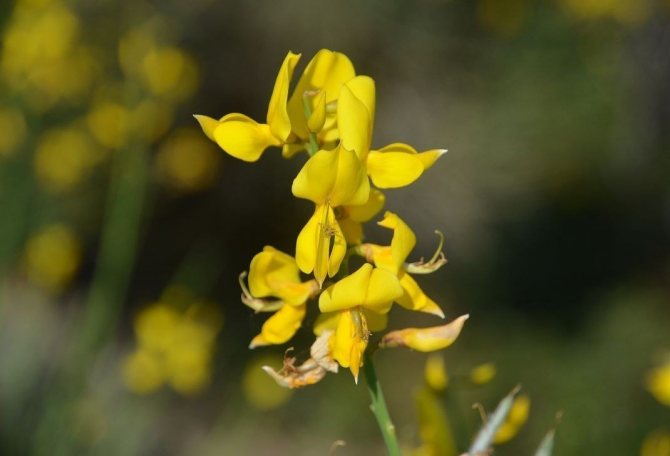
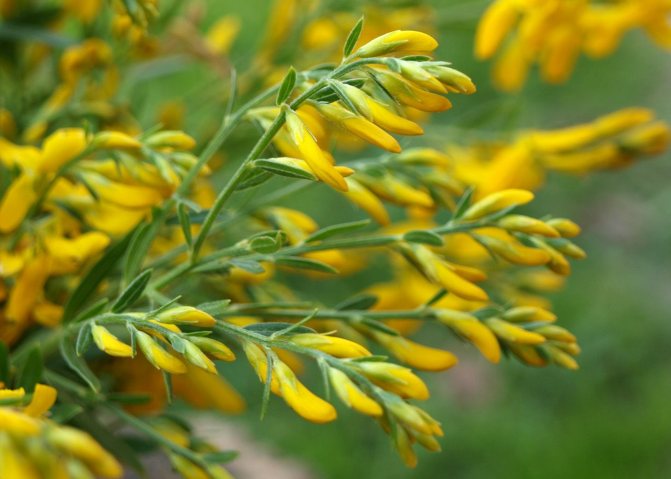
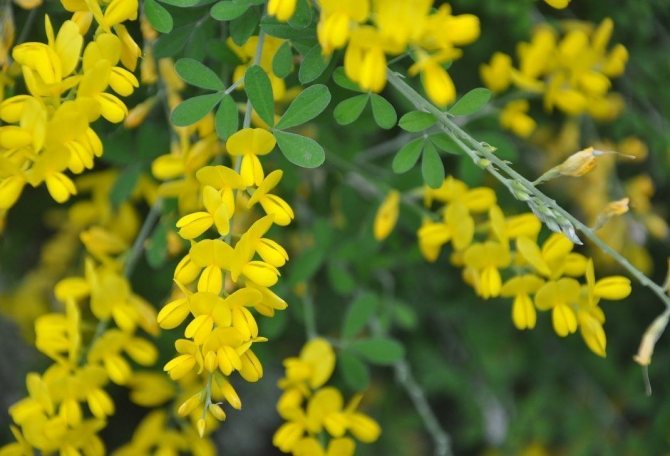
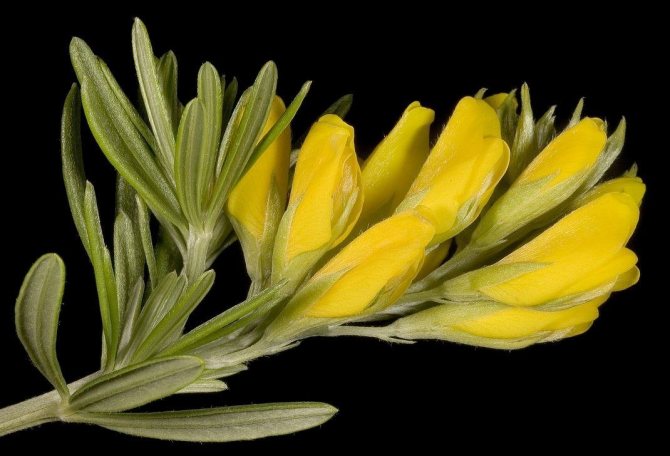
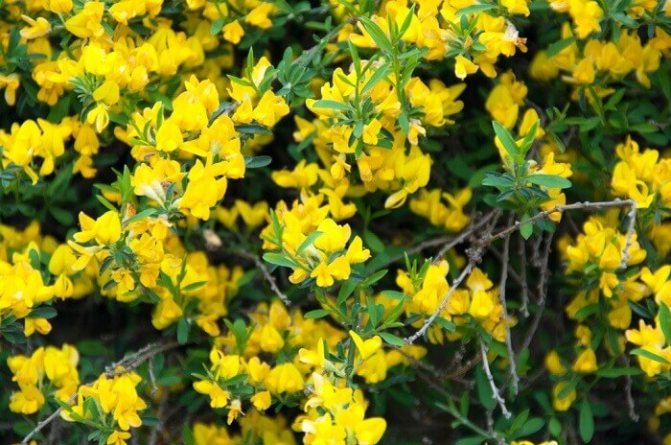
The bright yellow flowers of the dyeing gorse always look very original and impressive. They, as mentioned above, resemble a small moth with folded wings. Flowers are located in the upper part of the stems, forming multiple loose brushes. Like all members of the legume family, the fruit of the gorse is a bean. It is slightly curved in shape, linear, not pubescent, bivalve. People call it a pod. Inside are shiny, dark, almost black seeds.
Botanical characteristics
Gorse is a perennial shrub, semi-shrub or woody liana. It can have smooth or thorny shoots. Many thin branches are covered with bright green smooth bark. Plant height can range from 30 cm to 1.7 m. Stems are erect or creeping.Lateral processes are located along their entire length. The branches are densely covered with small oblong-lanceolate leaves. Dark green leaf plates are smooth, but sometimes they are covered with a short nap. Trifoliate or simple leaves on short petioles are arranged alternately.
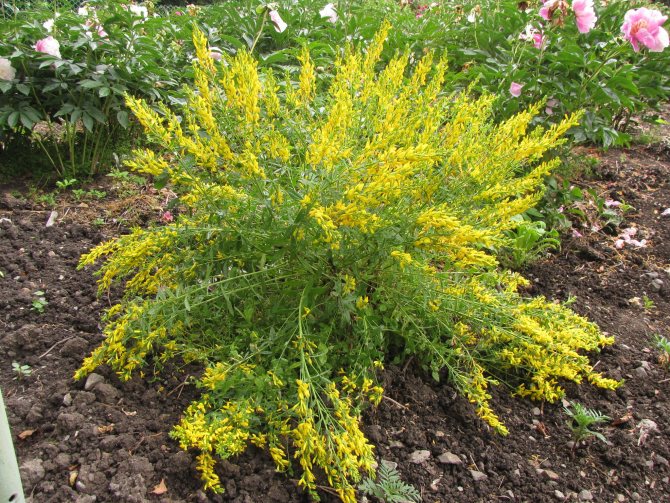
At the age of 3-6 years, gorse begins to bloom. Bright yellow racemose inflorescences bloom in early June. They remain on the branches for 15-60 days. Axillary flowers are grouped at the ends of young branches. During the flowering period, the gorse is covered with a dense yellow blanket, which hides all the green vegetation underneath. Fruit ripening begins in August. The branches are decorated with long narrow beans with shiny oblong seeds of brown-black color.
Growing area
A wonderful plant gorse is rather unpretentious. It feels good in hot and temperate climates, does not suffer from the sun and soil infertility. The only thing that he does not like is the swampy area, so he cannot be found on the banks of the rivers. The gorse is quite widespread. It is found, one might say, throughout Europe, from the Mediterranean to Scandinavia. It can be seen in Transcaucasia and Central Asia, Turkey and the Caucasus. In Russia, gorse grows in the temperate zone of the European part, in the Urals and in Western Siberia. He likes to settle on the edges of the forest, on the slopes of hills, in clearings, among dense bushes, preferring sandy or limestone soils.
Gorse care
Grooming outdoors is easy. The plant is very unpretentious and develops on its own. For planting, you should choose a place on a slope or hill. Gorse prefers loose, well-drained soils with a high content of sand and limestone. Only young plants can be transplanted. After the age of three, the roots grow so much that a painless transplant becomes impossible.
Gorse's lifespan is not that long. A decade later, it stretches and exposes the branches, which negatively affects the decorative effect. To avoid this, old bushes are replaced with young plants.
The gorse needs intense lighting and is not afraid of direct sunlight. It should be planted in an open area. Under the shade of other trees, the branches become bare faster, and flowering becomes scarce.
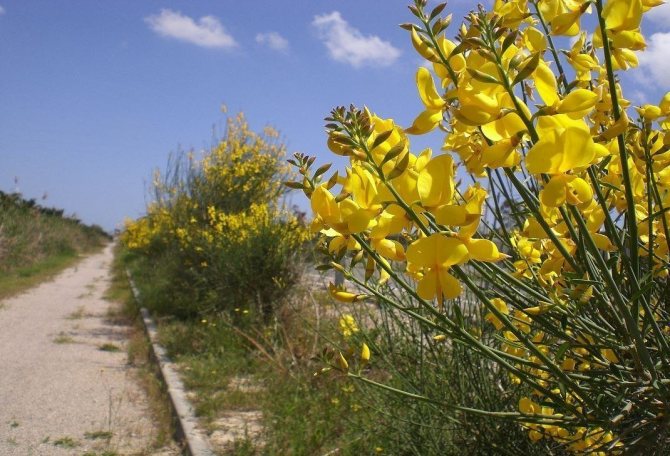


High temperatures are also okay for gorse, but they can suffer from frost. In central Russia, the bushes are covered with spruce branches and non-woven material for the winter. In snowy, mild winters, undersized varieties hibernate without shelter, but the upper branches often freeze slightly.
Gorse is drought tolerant but can suffer from excessive soil moisture. Usually it has enough natural precipitation. Watering is carried out only in case of a long absence of rain.
To form the crown, you can prune the shoots. The beginning of spring is best suited for this procedure. Dense thickets can be given any shape. Care should be taken when handling thorny varieties to avoid injury.
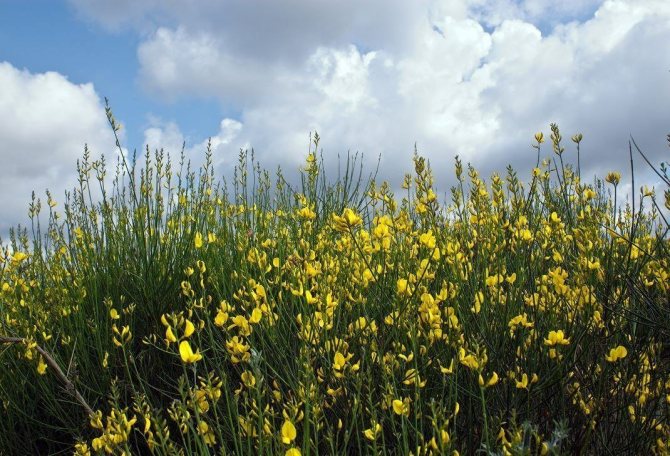


Chemical composition
The medicinal properties of gorse dye are based on those substances that are contained in its root and ground parts. The plant contains:
- flavonoids;
- resin;
- methylcytisine;
- cytisine;
- thyroxine;
- saponins;
- tannins;
- essential oil (though a little, only from 0.02% to 0.04%);
- organic acids;
- pigments genistein and luteolin;
- ascorbic acid;
- trace elements (phosphorus, barium, potassium, manganese, silicon, calcium).
It is important to remember that all parts of the gorse, especially the seeds, are poisonous.
Prescriptions for various diseases
Decoction of gorse dye shoots
100 g of dry crushed raw materials (shoots, leaves and flowers) are poured with 10 liters of water and boiled for 5 minutes, insisted in a warm vengeance for 30 minutes. Strain into a bath (temperature 37 ° C) and take it for 12 - 14 minutes.The course of treatment is 12 baths for diabetic polyneuritis.
Insist 1 tablespoon of chopped flowers and fruits in 100 ml of vodka for 5 - 7 days, moisten a tampon with tincture and put on the wart overnight. Pre-seal the skin around the wart with a plaster.
Useful properties for people
The use of gorse dyeing in decoctions and infusions can have the following therapeutic effects:
- vasodilator;
- antibacterial;
- fortifying;
- choleretic;
- hemostatic;
- laxative.
Folk healers use gorse to treat malaria, asthma, hepatitis, rheumatism, constipation, uterine bleeding, lichen, scrofula, hypotension, gout, and externally to remove warts and calluses.
In America, in official medicine, this miraculous plant is used to treat cancer. We still have such techniques unpopular, but the gorse is widely used for hypothyroidism. Reviews of the treatment with this herb are very good. People note that their well-being noticeably improves, and the effectiveness of the treatment is confirmed by analyzes.
Growing
Growing a gorse in a garden is not that difficult. The plant is unpretentious, so it is quite easy to care for it. It is important to land correctly.
It is best to plant shrubs in open ground in spring or early September.
You need to decide in advance on the landing site. To maintain a high decorative effect and abundant flowering, the shrub must be planted in well-lit areas.
With respect to the soil, the gorse reacts poorly only to acidic soils. There are no restrictions on fertility. Under natural conditions, the plant thrives on poor soils. Therefore, infertile areas are an ideal place for planting this shrub, which, unlike other garden plants, will not only grow well, but will also delight you with abundant flowering. As a fertilizer, it is recommended to add a little dry lime to the planting pit before planting the gorse, thereby reducing the acidity of the soil. Also, the bottom of the pit must be covered with a drainage layer, about ten centimeters thick, made of stones and river sand. The size of the planting pit directly depends on the root system of the seedling. After planting the gorse, you need to water and mulch the root circle with humus or peat.
Some recipes
For constipation. Pour 1 cup of boiling water over 1 desserts without a slide of beans (seeds) and leave for at least 5 hours, then gently strain. Take the resulting product in small doses throughout the day.
With obesity. Dried stems and leaves (you can also grind flowers), take 3 tablespoons without a slide, put them in an enamel mug, pour boiling water and place in a water bath, where to stand for at least a quarter of an hour. Cool down. Strain. Add a little honey (about 2 spoons) and use this remedy three times a day, no more than a tablespoon about half an hour before the start of the meal.
With hypothyroidism. Gorse is widely used to treat this condition. Here are two recipes.
- Tea. Take dry crushed raw materials prepared from the ground parts of the plant in the amount of a teaspoon without a slide. Pour cold water (glass) and place on the stove. As the water with the grass boils, turn it off, let it stand for a while and strain. Drink two very small sips during the day.
- Broth (patients advise). Pour a teaspoon completely without a slide with 100 ml of boiling water and leave to infuse for 2 hours. Strain. Drink two dessert spoons three times a day.
Outwardly (to get rid of corns). An alcoholic tincture is prepared, for which they take fresh stems, flowers, green pods of gorse dyeing, pour vodka and insist for a week. Before applying the prepared product to the corn, you need to glue the nearby parts of the body with a plaster so as not to injure them.
Outwardly (for compresses with sore joints). Three tablespoons or four dessert spoons of dry gorse herb pour 500 ml of water and put on the stove. Boil. Reduce heat and simmer for half an hour. Insist for another 60 minutes. Strain. In the resulting product, you need to moisten a rag or gauze, squeeze it a little, attach it to the joint, cover it with polyethylene and something woolen on top. Keep for no more than an hour.
The most decorative varieties and forms of gorse:
Virgata (‘Virgata‘) With dense shoots;
Royal Gold (‘Royal Gold‘) With orange flowers;
Humilior (‘Humilior‘) Is a dwarf bush with red flowers and silk-shaggy beans;
Angusta (‘Augusta‘) With elliptical leaves;
Latifolia (‘Latifolia‘) With wide leaves;
Prostate (‘Prostata') - a spreading plant with small foliage and flowers;
Golden Plate (‘Golden plate‘) - a bush with yellow flowers;
Captivity (‘Plena‘) - undersized shrub, with delicate twigs; bloom in June, with bright yellow flowers;
Alpestris (‘Alpestris‘) - undersized shrub with open shoots;
Contraindications
No matter how miraculous dyeing gorse may be, not everyone can use it to get rid of ailments. It is forbidden to use drugs from it to the following categories of people:
- pregnant women (regardless of the term);
- children;
- those suffering from hyperthyroidism should not be used without consulting a specialist;
- hypertensive patients;
- suffering from arterial hypertension and heart failure.
Absolutely all categories of patients need to remember that gorse is poisonous, therefore, when preparing drugs from it, the indicated dosages cannot be exceeded, and it is advisable to take drugs from it after consulting a doctor.
Some common types
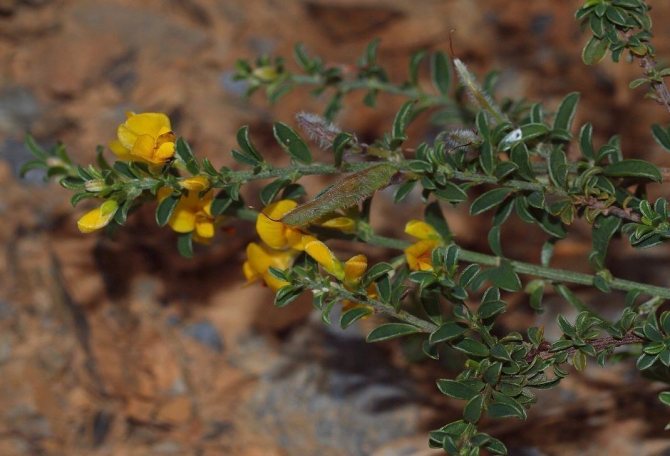
English gorse photo 1 - Genista anglica. This plant can grow up to 1 meter in height, but often its growth does not exceed half a meter. Prefers acidic, peaty soils.
The flowering period begins at the end of May and lasts about a month. It has long spines. It does not have a high winter hardiness.
Propagated by cuttings and seeds. Rooting of summer cuttings is good enough. Growth rates are average.
German gorse photo 2 - Genista germanica. Deciduous shrub up to 0.6 m in height and up to 120 cm in diameter. It has pubescent straight branches with small thorns at the base. The shoots of the shrub end in beautiful golden inflorescences. Very unpretentious. Blooms from June to July.
Care consists of periodical pruning of the bush. She needs shelter for the winter. Perfect for growing in rocky gardens and rock gardens.
Grows on light (sandy) to medium (loamy) well-drained soils, but can tolerate nutrient-poor soil. Prefers sunny locations and dry or slightly damp soil and can tolerate drought well.
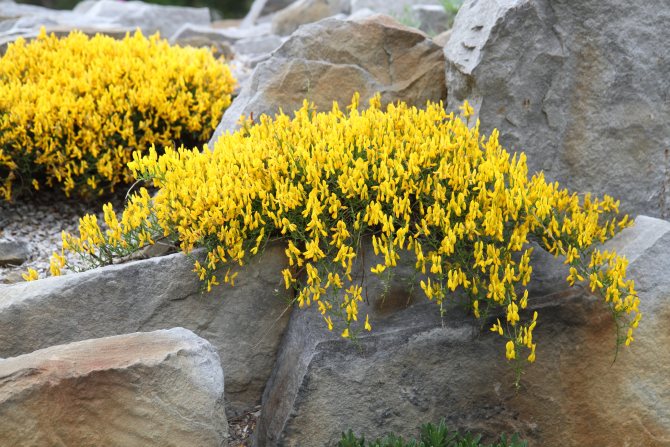
Lydian gorse photo 3- Genista lydia. The most popular undersized species, forming compact round half-meter bushes with light green foliage. Spreads up to 150 cm wide. In spring it is covered with small bright yellow flowers. Blooms until early June. Stems are erect, thin.
It grows naturally on dry, sunny hillsides in southern France and northern Spain, responding to more fertile soils by reducing the number of flowers. It grows at a slow pace and, under ideal conditions, a life expectancy of 20 years can be expected.
This shrub should only be grown in bright, sunny locations. Prefers dry to medium moisture and very well-drained soil - plants often die in stagnant water. It is considered drought tolerant, making it an ideal choice for rockeries and alpine slides.
Unpretentious in leaving. Pruning will keep your shrubs beautiful and rejuvenated. Winter resistant.
Furry gorse photo 4- Genista pilosa. Very popular in landscape design, a fast-growing dwarf shrub with creeping stems that form a beautiful carpet no higher than 40 cm. Spread 61-90 cm. Bright yellow fragrant flowers appear in May. Drought-resistant, loves sandy, rocky soils and full sun.
Looks great on slopes, in stone gardens next to low-growing blue spruce, weigela or in group planting.Withstands temperatures in winter up to - 7 degrees. Therefore, shelter or high snow cover is needed.
Lancet gorse - Genista sagittalis. Forms a green covering of evergreen creeping stems of 30 cm, which grow until the very frost. Leaves are elliptical, 5-20 mm long, flowers of a rich yellow hue are collected at the ends of the shoots in short dense brushes. Widely distributed in Central Europe (southern Belgium, southern Spain, Greece). Reproduces very easily by cuttings of summer shoots.
Very unpretentious and easy to grow on dry sandy soils.
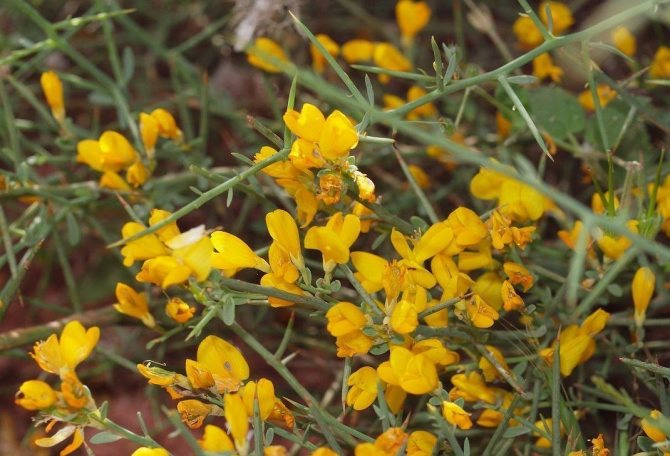
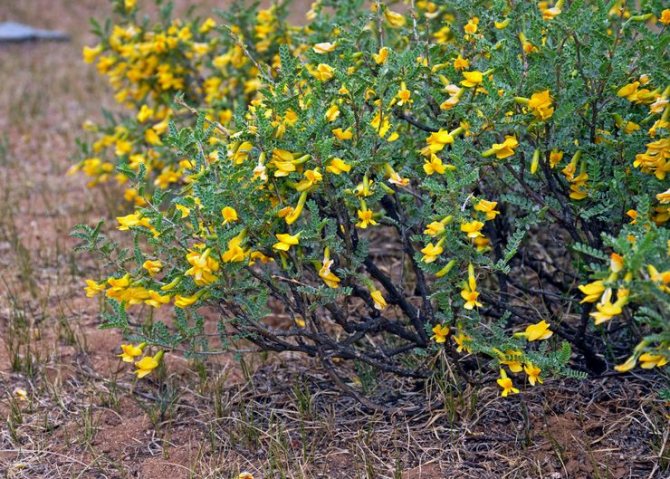
Bloodthirsty gorse or dye photo 5 - Genista tincioria. Not a thorny, fast-growing shrub that grows in the region from central Europe to Siberia. The height of the plant is from 30 to 100 cm, the width of the bush is about a meter. Slightly branched shoots, thin with smooth green leaves. Beautiful yellow flowers are collected in carpal inflorescences located at the tops of the branches. Flowering time June-July.
Gorse is propagated by seeds that ripen in bean-like pods. Sow them in the fall. Coloring gorse can propagate by cuttings, but rooting is problematic without stimulants.
Easily grown on relatively poor, dry, sandy or calcareous permeable soils. Prefers sunny locations. Drought-resistant, but can tolerate temporary excess moisture. Withstands temperature drop down to about -35 ° С.
The gorse blooms in June in large, bright yellow fragrant flowers that appear on the leafless tops of the stems.
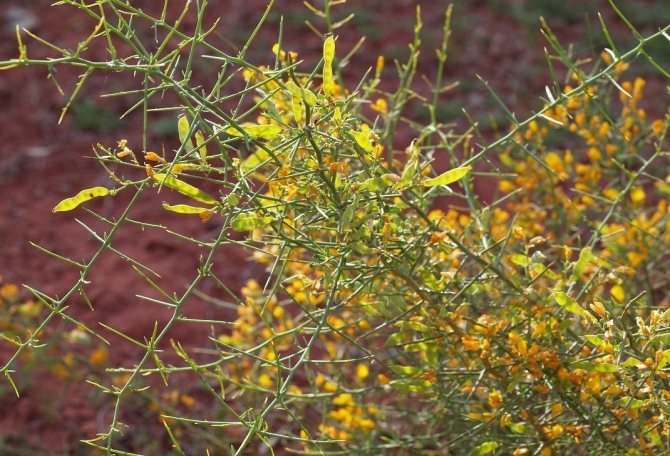
Most often, Spanish gorse is used as a soil-fixing ornamental plant. On the Black Sea coast, it is used especially widely - for landscaping slopes and railway embankments, since in these places, besides the gorse, only very few plants normally exist. It is also suitable for creating low, but impassable hedges.
- Height: 1 m
- Width: 1 m
- Foliage classification: deciduous shrub
- Frost resistance: thermophilic, tolerates frosts down to -10 ° С
- Soil: sandy, dry
- Usage: in hedges, in groups with other shrubs, on slopes, in tubs
- Pruning Period: After the end of flowering (in September)
Procurement rules
The timing of harvesting depends on which part of the plant is planned to be used. So, the ground part (stems, leaves) can be harvested throughout the growing season, while the gorse is green, fresh and juicy. Flowers are harvested from mid-June until the end of flowering. The roots and fruits are harvested in the fall.
The collected parts (except for the roots) are placed in a ventilated place, where the sun's rays do not fall, and dried until tender. The roots are pre-washed. The finished raw materials are put in glass or cardboard containers with a lid and stored for no more than one year.
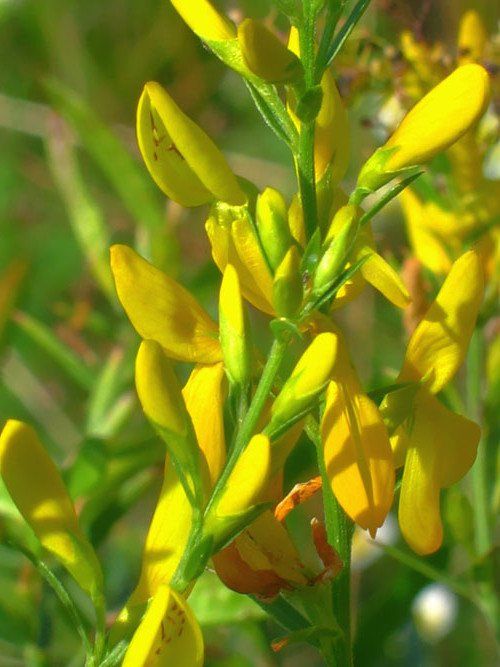


Dyeing gorse - Latin name Genista tinctoria L. This plant belongs to the legume family. It is also called dill, green, yellow dyed flower, bloodthirsty gorse, other.
Features Characteristic of appearance. Gorse is a semi-shrub or shrub, reaching a height of 30-60 cm, with furrowed, erect, branched stems of bright green color. There are compressed hairs at the top. A plant without thorns.
The leaves of the plant are sessile, alternate, lanceolate or elliptical. The underside of the leaves is ciliate, lighter; the upper side is glabrous and dark green; curved stipules; the lateral veins stand out strongly.
Flowers are arranged in multi-flowered terminal racemes, the length of which can reach 60 mm. Flowers are moth-shaped, on stalks, golden-yellow in color; the calyx is two-lipped, naked, falling; the rim has an egg-shaped flag, the rim is hollow. Pedicels have two bracts, the length of which is equal to the calyx.
The large fruit is a pod with 6-10 seeds.
The plant blooms from June to August, and the fruit ripens in August-September.
Habitat
You can find dill in pine forests and mixed forests, dry sparse forests, on the tops of hills, between shrubs, along the edges, in sunny glades, since the plant is light-loving.
The plant prefers sandy, calcareous soils. It grows in Western Siberia and in the European part of Russia, does not require care.
Chemical composition The chemical composition of gorse dyeing has not been sufficiently studied. The plant contains alkaloids such as sparteine, cytisine, methylcytisine. Bloodthirsty gorse contains: tannins, essential oil, vitamin C, flavonoids. The flowers also contain essential oil, and yellow pigments (genistein and luteolin) give the yellow color.
Medicinal and beneficial properties
The gorse has choleretic, laxative, diaphoretic, diuretic, homeostatic, soothing and tonic properties. Medicinal infusion made from the aerial part of the plant has an active antibacterial and vasodilating effect on the body. Also, preparations from this plant have anesthetic and blood-purifying effects, therefore they are used in folk medicine.
Decoction and infusion of gorse reduce the muscle of the uterus, stimulate the function of the thyroid gland, are distinguished by vasodilating, laxative, diuretic, choleretic and lactogonic action.
The herbal infusion of the green parts of the yellow dye flower is distinguished by a noticeable vasoconstrictor effect, stimulates respiration, and is also capable of stimulating the function of the thyroid gland. The fruits of the plant have an anthelmintic effect.
Application
The roots of the plant are used in medicine as a diuretic for nephritis and cardiac edema, malaria, jaundice, heart weakness, thyroid diseases, and uterine bleeding. Also, the roots are used as a means of promoting the removal of chlorides from the human body. The roots are used in the treatment of salt diathesis and constipation; they are often taken for the manufacture of mixtures for the treatment of arthritis, gout, nephritis, rheumatism.
The aerial part of the plant is also regularly used in folk medicine. For homeopathy, the aerial part is suitable for fresh application. The essence is used as an antibacterial agent.
Infusion and decoction in folk medicine is necessary for cystitis, gout, rheumatism, edema of renal and cardiac origin, dermatomycosis, furunculosis, migraine, scrofula, allergic dermatitis, asthenia, ascites, salt deposition, hypotension, rickets, bone fractures, venereal diseases of thyroid glands.
Fruits and leaves are needed to remove corns and warts.
Seeds and flowers in America are prescribed for the treatment of malignant tumors.
Collection and procurement The aboveground part is harvested during flowering and loosely placed in baskets. Dry in rooms that are well ventilated or under awnings, or in dryers. Raw materials are stored for a year.
Contraindications The plant should be used under the supervision of specialists and with caution, since it is classified as poisonous. Seeds are especially poisonous. It is required to strictly observe the dosage.
Healing recipes To prepare a decoction of gorse, which is prescribed for cardiac edema, it is required to take a crushed plant in the amount of 1 tbsp. l., and also add 1 tbsp. water and boil. It is necessary that as a result of boiling, a third remains. Consume 2 tbsp. l. every 2 hours until urination is frequent. Take every other day.
A decoction of gorse, together with the fruits of hawthorn and motherwort fruits, is taken for hypothyroidism, hypotension.
Ingredient ratio: 1: 2: 2. At 1 st. water take 2 tbsp. l. mixtures. The mixture is boiled over low heat for 10 minutes, insisted for half an hour. Drink 4 times a day for 1 tbsp. l. half an hour before eating.
Reproduction
The gorse is propagated by seeds and cuttings.Seeds should be harvested in August, immediately after ripening. The ripe bean turns brown and cracks on its own. The seeds are dried and, without preliminary preparation, are planted in open ground to a depth of 2.5-3 cm. The plantings are sprinkled with earth and watered moderately. The first shoots appear in spring. Flowering is expected no earlier than two years of age.
Some species reproduce better by cuttings. In June, the apical cuttings are cut with a length of 12-15 cm. They are rooted without preliminary processing on wet sandy-peat soil. While the roots are forming, it is necessary to keep the seedlings under a hood or in a greenhouse. Only 30-40% of plants take root.
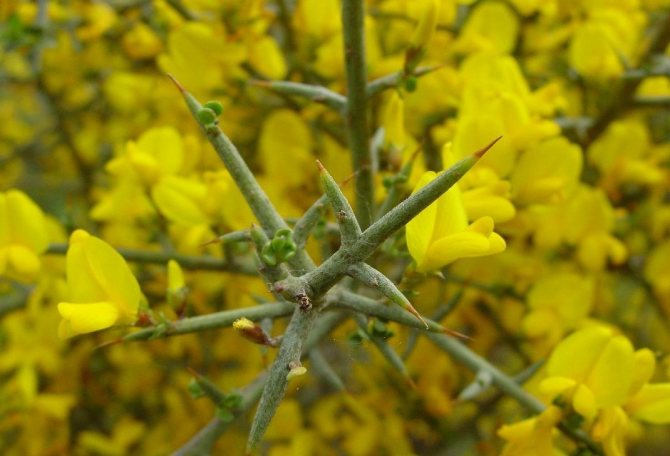


The most famous types of gorse
There are over 100 known plant species. However, some of them are the most numerous:
- aristocratic or English gorse;
- Germanic, which is a small shrub with a sessile type of leaves and straight branches slightly drooping downward;
- hairy gorse refers to semi-shrubs with creeping stems on which small yellow flowers are located;
- Lydian or evergreen;
- gorse radiant, which has bright yellow flowers. It belongs to straight shrubs;
- lancet - decorative species, which is an evergreen shrub;
- gorse dyeing. This species has some medicinal properties that are widely used in medicine.
Plant in the garden
In landscape design, gorse is prized for its bright and abundant flowering. Bushes or small trees can be planted singly at the entrance to the house or along the fence. Creeping and undersized forms are suitable for decorating rocky slopes and hillocks in a southern or southeastern orientation. The branched rhizome strengthens the soil well and can be used to prevent soil shattering.
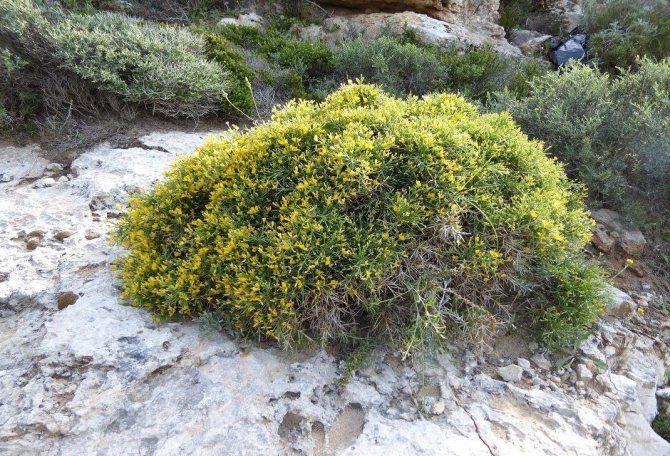


The plant is suitable for decorating rock gardens, rockeries and sometimes mixborders. When composing compositions, gorse is better combined with woody and shrubby plants. It can be juniper, cotoneaster, euonymus, yew, barberry, elecampane or buzulnik.
A source
What does gorse treat?
Dyeing gorse is taken in the form of infusions and herbal decoctions. The infusion must be prepared from the following calculation: for 2 cups of boiling water, there is one tablespoon of the herb. The remedy is infused for a couple of hours and taken in an exact dosage, one tablespoon 3 times a day. Its use for medicinal purposes is widespread enough.
The aerial part of the plant is used to treat many diseases. Among them:
- severe furunculosis;
- rheumatism;
- frequent cystitis;
- hepatitis;
- allergic dermatitis;
- children's rickets.
Infusions and decoctions from this shrub have some tonic properties. The essential oils and tannins it contains have a very good and relaxing effect on the body. That is why such infusions are often used for aromatherapy sessions.
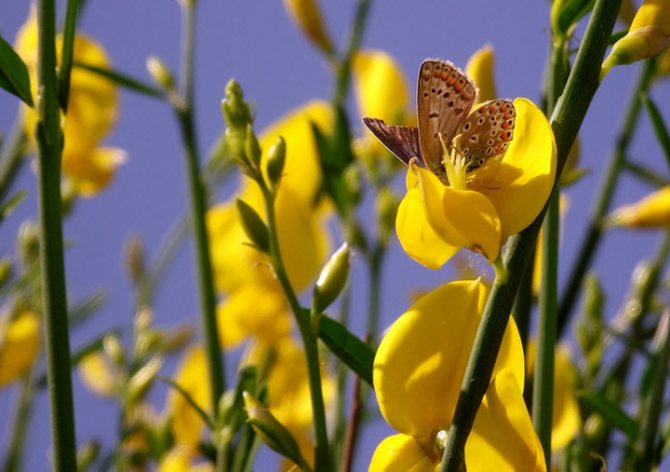


The plant is widely used to treat edema of various origins, with fractures, strong salt deposits. This infusion helps with certain diseases related to the thyroid gland, as well as with bronchial asthma. In some countries, yellow flowers and specific gorse seeds are even used for the complex treatment of sexually transmitted diseases and malignant tumors. Their use is quite justified.
Dyeing gorse is often used in dermatology. Fresh leaves are good for quickly getting rid of corns and all kinds of warts. The plant is even used in the treatment of diseases such as jaundice and malaria. Its roots help well with salt diathesis and constipation. However, you should always remember that no matter what additional funds are used to treat certain diseases, you should always consult your doctor.After self-medication, you may not help yourself, but rather cause irreparable harm to the body. Then it will already be a question of eliminating complications from taking decoctions from gorse.
German gorse
Grows in the forests of the European part of Russia and Europe. Grows in birch and pine forests on gravelly and sandy soils.
A low shrub with straight branches and sessile leaves, densely pubescent below. The edges of the leaves have ciliate pubescence. Almost every shoot ends with a golden inflorescence.


Bloom from June to July. German gorse fruits ripen in October, their ripening occurs with the growth of shoots, which lasts until frost; from this, the shoots are lignified by 25-75% and every year they freeze over, but the bush is restored and blooms.
German gorse seeds practically do not germinate. The shrub is propagated by green cuttings. This species is photophilous, grows on sandy loam soils. Requires protection for the winter.
The main contraindications for use
Dorke has several direct contraindications for the complex treatment of certain diseases. This plant is considered poisonous, therefore, when taking it, the indicated dosage must be strictly observed. The categorical contraindications are:
- pregnancy;
- high blood pressure;
- coronary artery disease;
- chronic kidney and liver diseases. In such cases, herbs can cause irreparable harm to the body. After all, such infusions are a supportive factor in treatment, but not the main drug.
If an overdose of gorse occurs, the following signs of poisoning may appear:
- dizziness;
- Strong headache;
- nausea;
- indomitable vomiting.
With the manifestation of such symptoms, the use of the plant is strictly prohibited. After all, if you do not stop taking it on time, then the consequences can be dire. Therefore, it is necessary to observe the exact dosage of the decoction for each individual case.
In any case, before starting treatment with such a plant, it is better to consult with your doctor who will help you choose the right dosage. Only then can the broth be taken without worrying about possible side reactions. But it should also be remembered that folk remedies are not a panacea in the treatment of most diseases. They can only be considered as additional supportive agents, but not as the basis of the entire treatment process.
Dyeing gorse (bloodthirsty) is a shrub of the legume family.
It is sometimes called:
- guillemot;
- Theresa.
Description
This shrub grows on average to a height of 0.5-1.5 meters. The stem is erect or lying, strongly branched at the base. There are no thorns. The leaves are elliptical. Flowers are collected in loose clusters at the tops of the stems. The color of flowers in wild gorse is yellow, in varietal plants there are other colors (pale red, orange). Flowering occurs from May to mid-summer. The fruit is a bare or slightly pubescent pod with several seeds.
In the wild, it is found in the European part of the Russian Federation, the Caucasus, and Western Siberia. Grows among other shrubs or in light forests. Planting gorse for decorative purposes is gaining popularity. Since the plant belongs to the legume family, it enriches the soil with nitrogenous compounds. The gorse buds are pickled, they taste like capers. Italian and French agriculture was engaged in the cultivation of dyeing gorse, since it was used to make burlap. Flowers and leaves are raw materials for yellow paint, which is why this type of gorse is called dyeing. Previously, wool was dyed with shrub pigments, but today they are used to create natural hair dyes (for example, under the TM Kydranature).
Gorse dyeing photo
Structure
The gorse dye contains alkaloids of the quinolizidine group (cytisine, N-methylcytin, anagirin and others), flavonoids (genistein, genistin, luteolin, diadzein), tannins, saponins. Leaves and flowers contain some essential oil. All parts of the gorse are poisonous, the maximum concentration of hazardous substances is in the fruits of the bush.
Healing properties
The main properties of the plant are diuretic and laxative. In addition, a decoction of gorse dyeing improves conditions caused by a decrease in the function of the thyroid gland. Experiments have proven the vasodilating effect of the plant's preparations. In folk medicine, they are used to eliminate urinary retention in heart failure, to treat kidney stones, stones in the bladder. The laxative and diuretic effect of gorse is due to the content of the flavonoid glycoside luteolin in it. Cytisine increases blood pressure and stimulates respiration. Gorse is also sometimes used to treat the liver and to stop uterine bleeding.
Shoots with leaves and flowers are raw materials for folk remedies against rickets, migraine headaches, hypertension, edema, thyroid diseases, narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, bacterial infections. The roots are used to treat jaundice, uterine bleeding, nephritis, cardiac edema, constipation, and joint diseases. The fruits were used to expel helminths, but the high toxicity of the shrub beans makes such use impractical.
Externally, plant preparations are used against:
- fungus;
- blistering acne;
- depriving;
- warts;
- dry calluses;
- psoriasis;
- itchy dermatosis due to hypothyroidism.
The tincture is used in the fight against atopic and allergic dermatitis, dermatomycosis. Infusion rinse sore throat. Homeopaths use the essence of young bush shoots as a herbal antibiotic. There are recommendations for the treatment of intestinal oncology with plant preparations (as an adjunct to chemotherapy).
Dye stimulates the production of thyroid hormones, its active substances act similarly to thyroidin, but they give fewer side effects and a longer lasting result. It can be used with both decreased and increased thyroid function, goiter, autoimmune thyroiditis. A decoction of the plant fights hardening of thyroid tissue. Topically relieves itching in hypothyroid patients.
Medicinal use
For medicinal purposes, flowering aerial parts are used, separately flowers and roots. The roots are dug up in the fall. Dry in the shade. If a dryer is used, the mode should be up to 50 ° C. Raw materials retain their useful properties for 12 months from the date of procurement. You need to store it in canvas bags or a cardboard box.
Recipes
Diuretic, laxative, choleretic decoction:
Pour 15 g of raw materials with 300 ml of warm water, keep on low heat until 2/3 of the liquid has evaporated. Take 1-2 tbsp. every 2 hours. For the treatment of thyroid gland, take a course of 1-2 tablespoons. three times a day, every other day.
Decoction of gorse dye, general recipe:
1 tbsp boil dry crushed aerial parts in 500 ml of water for 20 minutes, then leave for 45 minutes, filter. Take a third of a glass two or three times a day.
Infusion:
2 tbsp overground part, brew 250 ml of boiling water. Insist under the lid for half an hour. Filter out. Take 1 tbsp. three times a day.
Tincture of flowers and beans for warts and dry corns:
beans and fresh / dry flowers are poured with vodka in a ratio of 1 to 10. Insist for a week, filtered. The place around the problem area is pasted over with a plaster. A cotton swab soaked in tincture of gorse dye is applied to a wart or corn, and fixed with a plaster. They keep it all night. The procedure is repeated for 7-10 days.
Juice for warts and dry calluses:
fresh juice treat problem areas in the same way as tincture.
Tea for thyroid diseases:
1 tsp pour 250 ml of cold water, slowly bring to a boil, turn off immediately.After cooling, the mixture is filtered. Drink the resulting volume of tea during the day in small sips.
Collection for hypothyroidism:
1 part of the dry aerial part of the dyeing gorse, 2 parts of the hawthorn fruit, 2 parts of the motherwort herb are mixed and crushed. 1 tbsp collection is poured into 0.5 liters of water, boiled over low heat for 10 minutes. Refrigerate for half an hour. Take 1 tbsp. decoction 4 times a day, 30 minutes before meals.
Wine root tincture (general tonic):
Pour 10 g of finely chopped roots with a bottle of red wine, keep in a dark place for 10 days, filter, squeeze the raw material into a tincture. Children were given 1 tbsp. such a tool, adults - 2-3 tbsp. tinctures once a day.
Lotion for joint pain, skin problems:
4 tablespoons boil the dry aerial part in 500 ml of water for half an hour. Insist for another 1 hour. Filter out. Make compresses for an hour. Apply 1-3 times a day
Baths against psoriasis, dermatitis, joint pain:
add the broth prepared according to the previous recipe to the evening bath. It is recommended to take such a bath for 20 minutes, repeat the procedure three times a week.
Contraindications
Overdose and frequent use of gorse dye can lead to toxic poisoning of the body, similar to nicotine poisoning (due to the presence of cytisine in the composition). Preparations based on parts of the bush are contraindicated for pregnant women (cause uterine contractions) and lactating patients, persons with arterial hypertension and ischemia.
Other plants
Gorse radiant
The homeland of the gorse is the Northern Alps, where it settled on clay-rocky hills. Grows on dry, loose soils.
Radiant gorse is a straight shrub, up to 80 cm tall, with ribbed shoots without thorns. Young shoots of radiant green gorse. The dark green foliage consists of oblong leaves. Radiant gorse blooms in June for 3 weeks. Yellow flowers are collected in short inflorescences, appearing at the end of May, at the top of the shoot. The fruits of gorse radiant are pointed beans. Seeds are dark brown, shiny, ripen in September.
The gorse is propagated by radiant green cuttings and seeds. It's a shame that radiant gorse does not find a place in rock gardens and rocky gardens in central Russia.
Pruning
Formative pruning
When planting, cut off all shoots in half before placing the plant in the ground. This will help him to quickly settle down on your site and will have a beneficial effect on the formation of new shoots. In the future, you do not have to cut the bush.
Sanitary pruning
It is produced every 4-5 years, not more often. To rejuvenate the bush, shorten all the shoots to a length of 15-20 cm. Such an operation will avoid the formation of voids "in the legs" of the plant.
Pharmacological properties
The composition of terza is unique, therefore it is used in the treatment of various ailments. The use of the plant in alternative medicine can provide the following therapeutic effects:
- vasodilation;
- elimination of bacteria;
- general strengthening;
- separation of bile;
- stopping blood;
- relaxation.
Healers use the plant to supplement therapy:
- malaria;
- asthma;
- jaundice;
- rheumatic pains;
- constipation;
- bleeding of the uterus;
- lichen lesion;
- scrofula;
- low blood pressure;
- gout;
- elimination of wart and callus formations.
Plant species
According to the international classification, the gorse genus includes 125 plant species. Some of them are suitable for growing in central Russia.
The plant is found in Western Siberia, Kazakhstan and the Middle East. The undersized, spreading shrub has no thorns and grows up to 1 m in height. Weakly branched, creeping shoots are covered with oblong, almost bare leaves. The length of narrow dark green leaves does not exceed 2.5 cm. Yellow flowers are collected in racemose inflorescences at the tops of young shoots. Flowering begins in June and lasts up to 65 days. After pollination, the narrow, flattened beans mature.A few decades ago, leaves and flowers were used to produce yellow paint, for which the variety got its name.
A heat-loving plant does not tolerate frost well. Straight pubescent branches form a shrub up to 60 cm high and up to 1.2 m wide. On the shoots there are sessile lanceolate leaves with tomentose pubescence on the reverse side. There is a long green thorn where the leaf is attached. At the beginning of June, golden spike-shaped inflorescences bloom at the ends of the branches. They persist until August, and fruits ripen in October. Seeds of this species germinate very poorly.
The plant forms a spherical thorny bush up to 50 cm high. Its dense bright green crown consists of lanceolate shiny leaves up to 1 cm long. Flowering occurs in 2 stages. For the first time, dense bright yellow inflorescences bloom in early June. Repeated and less abundant flowering occurs at the end of August. This species can withstand frosts down to -20 ° C.
This variety is common in southern Europe, although it can withstand cold snaps down to -15 ° C. Creeping shoots are located near the ground or fall beautifully from mountain slopes. The branches are densely covered with small dark green oval leaves. A bright and abundant bloom occurs in April-June.
1.Gorse - planting and care
1.1 When it blooms
The end of spring is the beginning of summer.
1.2 Reproduction, growing from seeds
Seeds can be sown in early spring. Stem cuttings.
Up in the menu
1.3 Transplant
Only when needed. The gorse takes a long time to handle when the root system is damaged - try to transship along with a lump of earth.
1.4 Growing conditions - temperature
From spring to autumn, the usual room temperature of 18 - 22 ° C is well suited. In winter, the plant must be given a dormant period in a cool place with a temperature of about 10 ° C. It tolerates short frosts.
Up in the menu
1.5 Lighting
Well lit area with direct sunlight in the evening or morning.
1.6 Home content
This hardy plant is ideal for budding flower growers. Prune gorse shoots every year to maintain a compact, bushy shape. Try not to prune old branches - they take a long time to recover. Remove wilted flowers. The gorse will appreciate being outdoors during the warmer months.
Up in the menu
1.7 Watering
During the growing season, watering is abundant and quite frequent. Reduce watering in winter.
Up in the menu
1.8 Soil
It adapts well to almost any type of soil, but prefers nutrient-poor soils with good drainage.
1.9 Fertilizer
During the period of active growth, monthly fertilizers with a high potassium content.
Up in the menu
1.10 Spraying
It is advisable to spray periodically.
1.11 Pests and diseases of gorse
Appointment.
Note.
Hydroponics.
Water infusion
An infusion is made from a dessert spoon of dry branches and flowers, as well as a glass of boiling water. The medicinal liquid is infused in a thermos or other sealed container for two hours. Then it is filtered out. Drink 15 grams 15 minutes before meals three times a day.


This infusion helps to relieve inflammatory processes in the body, normalizes digestion, has a laxative and diuretic effect. They rinse the mouth and throat, apply compresses for fungal, infectious and viral skin diseases.
Description
The plant belongs to the legume family. The bush can grow up to 50-150 centimeters in height. Its branches are green, ribbed and almost always point upwards. The leaves are narrow and long (4 cm long, 1 cm wide), often pointed at the end, dark green in color. They grow on short petioles and have two awl-shaped hairpins. At the end of each stem (shoot) a multicolor tassel. The flowers are large, with a green calyx and a bright yellow wreath. The fruit (pod) is linear, slightly curved.The seed is black-brown in color, elliptical in shape, slightly shiny. It grows mainly in pine and mixed forests, in clearings.
Harvesting and storage of dyestuffs
As a medicinal herb, the ground upper part of the branches of the dyeing moth is used and harvested, as well as its flowers. Roots are also used to make natural medicines for the treatment of various diseases.
Medicinal raw materials are harvested exclusively during the flowering period. The collected medicinal material is dried in the shade, avoiding direct sunlight, or under a canopy, in the open air (draft is possible), in dry, well-ventilated rooms, or in special dryers. But in this case, you should carefully monitor that the temperature in the dryer does not exceed 45-50 degrees.
The storage term for the medicinal material of the dyecake is 12 months. Store well-dried leaves, as well as plant flowers, in clean cardboard boxes with lids, or bags made of natural fabrics, in dry, well-ventilated rooms where there are no strong third-party odors.
Household use
Back in the Middle Ages, in Italy and France, peasants used gorse to make fabrics similar to modern burlap. Today, this plant is often used in agriculture as a natural remedy for enriching the soil of fields with nitrogen.
Gorse is used as a beautiful ornamental shrub for landscaping household plots, for decorating flower beds and borders in gardens, and also as a plant material for strengthening hillsides. And in Transcaucasia, young buds and shoots of gorse are pickled, and then used in traditional cooking as capers.
Content
- Types and varieties
- Gorse planting care in the open field
- Watering gorse
- Gorse soil
- Fertilizer for gorse
- Gorse flowering
- Trimming gorse
- Gorse transplant
- Preparing gorse for winter
- Gorse propagation by cuttings
- Gorse growing from seeds
- Diseases and pests
- Gorse: Medicinal properties and contraindications
- Gorse: Signs and superstitions
- Conclusion


Care
At first, the shrub must be watered regularly. As it grows, watering is reduced, it is carried out only on hot dry summer days. The rest of the time, an adult bush completely independently provides itself with moisture from the soil.
With regard to fertilizers, the shrub needs spring feeding with phosphate and potassium fertilizers.
In the spring, pruning of the shrub is carried out. It consists in removing damaged, dried shoots and cutting out old branches in order to rejuvenate the gorse.
In the fall, wilted inflorescences are removed and the shoots are slightly shortened. This will stimulate abundant flowering in the next season.
Dyeing gorse, although considered frost-resistant, still needs shelter for the winter, especially young specimens. It is necessary to huddle the roots with earth mixed with peat or humus, tie up the branches and wrap them in burlap or agrofibre.
We also note that if the shelter for the winter was not carried out and the stems were damaged, you should not immediately panic. The plant is quite capable of restoring them on its own and will even delight you with flowering, only its abundance can be somewhat reduced, because part of the effort will be spent on building up young shoots and restoring stems.


Alcohol solution
Helps to establish the digestive tract, improve appetite, strengthen the defenses and invigorate. To do this, you need to take a weak red wine in the amount of a liter and a large spoonful of dry roots (grind). Combine the two components, leave for ten days. The drug can be given to children from three years old to 10 g.
Undoubtedly, dyeing gorse grass is fraught with a lot of advantages. However, you should know that taking folk remedies can only be done under the strict guidance of a doctor.The plant is considered poisonous, if used improperly, it can seriously harm: cause intoxication, gag reflex, nausea, pain in the abdomen, dizziness, migraine. Hallucinations, an increase in pressure to a critical level, convulsions and respiratory arrest are not excluded.
Gorse growing from seeds
The gorse is propagated with the help of seeds. They can be purchased at a flower shop or harvested from the plant's bushes in September.
You need to plant seed immediately in open ground in mid-May. After planting the seeds, the garden must be watered regularly. And when shoots appear and the plants grow a little, the soil should be loosened and mulched with peat. Young plants bloom only in the second year after planting.


Gorse transplant
Only young plants up to three years old can be transplanted. After the expiration of this period, the root system grows so much that it will not be possible to transplant the gorse without damaging it.
However, he does not need a transplant, since after ten years the plant begins to stretch, lose leaf mass, and with it decorativeness. Therefore, instead of transplanting, gardeners use the rejuvenation of the bushes by replanting new seedlings.


Composition and medicinal properties
In the official medicine of the CIS countries, drugs are not used, which are made on the basis of dyeing gorse. But in the United States, such drugs are used in the complex therapy for the treatment of malignant tumors. Most often these are tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.
Traditional healers use this medicinal plant as the main component of medicines for the treatment of a wide range of ailments. They have proven themselves well in the treatment of thyroid diseases, as prophylactic agents for endocrinological diseases.
Aqueous preparations based on an extract of a medicinal plant are used as a means of promoting vasodilation, a preparation with a powerful antibacterial effect.
As an external remedy, alcoholic tinctures and water decoctions of gorse are used in dermatology. The crushed fresh leaves along with the green fruits of the medicinal plant are used to treat calluses and warts. The essence from fresh shoots of this medicinal plant is used as a natural herbal antibiotic. Infusions and decoctions based on gorse have strong diuretic and laxative properties, reduce the uterus. Therefore, in gynecology, such drugs are used in the treatment of uterine bleeding. And also the sphere of application of gorse dyeing is the treatment of diseases of the kidneys and liver, inflammatory processes in these organs. They treat chronic respiratory diseases. Most often it is chronic bronchitis and bronchial asthma.
The use of gorse in traditional medicine
For aching joint pain (external use only)
3 tbsp Pour 500 g of water into crushed dry leaves of gorse dyeing, bring to a boil and then leave on low heat, preferably in an enamel bowl, for 30 minutes. After the required time has elapsed, turn off the fire completely, and leave the broth for another 1 hour. After that, the finished broth should be filtered. Gauze, or a piece of cloth made of natural fibers, must be moistened in the prepared broth, not squeezed much and applied to the aching joint for a period of no more than 1 hour. Such compresses on sore aching joints can be done no more than 3 times in 24 hours.
Laxative
1 tbsp gorse seeds dyeing (without top!) Pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave for about 5 hours in a closed enamel (glass) container. After this time has elapsed, the infusion should be thoroughly filtered. The medicinal infusion prepared in this way should be drunk during the day. But at one time you should drink no more than 3 tablespoons. infusion!
With uterine bleeding
3 tbspPour 200 ml of boiling water over finely chopped leaves and flowers of gorse dyeing and leave in a water bath for another 15 minutes. Then strain the broth, squeeze the leaves and bring to the original volume (200 ml) with boiled water. You should take a decoction of 1 tablespoon. 3 times a day.
Read also: Sinningia - care, cultivation and reproduction
With hypotension, depression and obesity
Prepare a decoction from the ground part of this medicinal plant - 3 tbsp. pour 200 ml of dry medicinal raw materials without top. boiling water and soak in a constantly boiling water bath for about 15 minutes. Allow to cool, and then strain thoroughly. Add 2 tsp to the cooked broth. natural liquid fresh honey and take 1 tbsp. 3 times a day 20-30 minutes before meals.
For dermatological diseases (lichen, scrofula)
4 tablespoons Pour chopped leaves and flowers of gorse dyeing with 1 liter of boiled hot water and leave for about 1 hour. After that, the infusion should be filtered through several layers of natural fabric and poured into a bath with warm water. The water temperature in the medicinal bath should not exceed 37 degrees. The duration of taking such a therapeutic bath becomes 20 minutes, no more than 1 time per week.
Tea for thyroid diseases
1 tsp pour 250 ml of dry medicinal raw materials of the ground part of the gorse dyeing (without top!). cold water, bring to a boil and strain. Drink for 1 day in small, slow sips. No more than 2 small sips at a time.
Diuretic, laxative, choleretic
1 tbsp Pour 500 ml of cold water with crushed dry leaves of gorse dyeing. Bring to a boil and cook over low heat in a tightly sealed enamel bowl for 20 minutes. Let cool (about 40 minutes) and only then drain. Take 65-70 g (1/3 cup) 2 times a day, regardless of food intake.
With gout
Mix in equal parts such herbs as: tricolor violet grass, gorse leaves and flowers, dioecious nettle leaves, and birch buds. 1 tbsp chopped herbal collection pour 200 ml of boiling water, insist in a tightly sealed glass container for 15 minutes and then strain. On the day, take the infusion prepared in this way 2 glasses a day. They should be divided into 3 doses before meals (about 130 ml each). The course of treatment is 1 month.
For the removal of calluses and warts
50 g of chopped dried flowers and fresh fruits of gorse dyeing are poured into 0.5 liters of vodka or moonshine and insisted in a tightly sealed container for 7 days. Alcoholic infusion is used for lotions on sore spots. But before use, healthy areas of the skin must be sealed with adhesive plaster in order to prevent this infusion from getting on healthy areas of the skin. The course of treatment is 7 days. For external use only!
Brief description of the plant
The description of the gorse dye goes like this:
- the plant is deciduous, semi-evergreen;
- it has erect or creeping branches that are covered with small thorns;
- foliage is small, with a simple or trifoliate shape, glabrous or heavily pubescent;
- blooms with a bright golden shade with a white color;
- sometimes blooming with red shades;
- flowering occurs in spring or summer;
- bears fruit in small, flat, polyspermous pods.
The gorse plant can grow on dry, sandy loam, rocky, or calcareous soil. Due to its compact root system, the flower is often grown in pots with indoor conditions.
Shrub varieties
There are these types of shrubs:
- Dyeing gorse. The low thornless shrub has thin shoots, bright green leaves, yellow flowers. Blooms for 50 days. The plant grows very quickly. This variety has the following forms: Virgata, Angusta, Golden Plate, Alpestris and others.
- The yellow plant species grows up to one meter in height. It has thin shoots covered with long leaves.It blooms with yellow flowers for 40 days.
- The Spanish cultivar has straight, thorny branches that can grow up to two meters. It blooms with bright yellow flowers, which are collected in inflorescences.
- A forest type of shrub blooms in mid-summer. It has drooping shoots with bright yellow flowers.
- Humilior blooms with light red flowers, which later form shaggy silky beans.
- A radiant shrub variety grows up to 80 centimeters. It has silvery shoots, without thorns. Oblong leaves are located on dark green shoots. The plant blooms in mid-summer and lasts for three weeks. Fruiting in pointed beans with dark brown seeds, ripening in early fall.
In addition to the listed species of gorse, there are other types of shrubs.
The usefulness of the plant
To create medicinal products, flowers, rhizomes, and herb are collected. The aboveground part of the gorse is harvested during the flowering period, and the roots - in the fall. Raw materials are dried outdoors in the shade or in a room with constant ventilation. The collected fee is kept for no longer than one year.
The plant stops blood, strengthens the immune system, dilates blood vessels, destroys bacteria and microbes. The bush consists of alkaloids, essential oils, glycosides, tannins, organic acids.
Gorse is used for the preparation of medicines that help with hepatitis, rheumatism, allergic dermatitis, malaria, stomatitis, sore throat, bronchial asthma. Fresh plant juice is often used to remove warts and papillomas.
Application
The plant is actively used in homeopathy and traditional medicine.
In medicine
The medicinal properties of gorse:
- hemostatic;
- choleretic;
- fortifying;
- vasodilator;
- antibacterial.
It is actively used for:
- hypothyroidism;
- nervous breakdowns;
- jade;
- liver problems;
- gout;
- uric acid diathesis;
- tumors in the gastrointestinal tract;
- thyroid problems;
- respiratory tract diseases;
- uterine bleeding;
- migraines;
- rickets;
- jaundice;
- malaria;
- constipation;
- hemorrhoids;
- cystitis;
- fractures.
Such a wide spectrum of the plant's action is provided by its constituent alkaloids, essential oils, glycosides, tannins, flavonoids, and organic acids. It is they who endow the gorse with the listed medicinal properties.
In dermatology
For the treatment of skin problems, alcohol tinctures and decoctions from dyeing gorse are widely used. They have an antibacterial effect, which allows you to quickly overcome fungus, furunculosis, lichen, scrofula. They are also actively used for the manifestation of dermatitis, pyoderma, dermatomycosis. For some diseases (lichen, scrofula), in addition to rubbing, it is necessary to take baths from gorse.
From the inflorescence, you can prepare lotions for hardened calluses and warts:
- Lotion recipe for corns and warts. 50 grams of dry inflorescence and the same amount of fresh beans are poured into 500 ml of vodka and infused in a well-closed container for seven days. It is necessary to shake the tincture periodically. After a week, we decant the liquid and make lotions on problem areas several times a day. The duration of treatment is 10 days.
- Recipe for eliminating lichen and scrofula: You will need 4 tbsp. l. crushed flowers and gorse foliage. We fill them with a liter of boiling water and stand for an hour. Strain and pour into a bath with a water temperature of 35-37 degrees. Lie in the bathroom for twenty minutes. The frequency of the procedure is two times within seven days. This procedure should be combined with other disease control methods.
In other areas
All parts of the plant contain a yellow dye - scoparin, therefore leaves, flowers and young shoots are actively used to produce bright yellow and green paint. She dyes wool, silk. Yellow varnish is also produced from the inflorescences.
It is a good honey plant: bees are very fond of collecting nectar and pollen on it.Goats and sheep are very fond of eating gorse. If the cows do not have any other good food, then they will also gladly eat the plant, but then their milk and products from it (cheese, butter) will have a bitter taste.
Dyeing gorse has a decorative shape, which is good for landscaping and decorating areas with limestone soil. The decorative form has a longer flowering period. You can also use it to strengthen the hillsides.
The plant is able to retain nitrogen in the soil, therefore it is actively used to saturate soils with this element. In enriched fields, the yield is improved. The people living in the eastern Transcaucasia eat young shoots and buds. They are treated with boiling water or steam, and then pickled.
2. Varieties:
2.1. Dyeing or bloodthirsty gorse - Genista tinctoria
Low-growing deciduous shrub with green, profusely branching stems up to 60 - 90 cm high. Leaves are green, compound, consist of 3 oblong - oval or oblong - lanceolate segments up to 2.5 cm long with slightly pubescent edges. The flowers are golden yellow, typical for leguminous plants, collected in inflorescences - apical panicles, open sequentially - from the base to the tops of the shoots. The flowering period is long, beginning in July - August. A yellow dye is obtained from flowers and young shoots of plants of this variety.
2.2 Spanish gorse - Genista hispanica
A small deciduous, multi-stemmed shrub with a rounded crown up to 75 - 80 cm high. The green stems of the plant bear small sharp thorns. Leaves are small, green, compound - consisting of 3 oblong segments. During the flowering period, which occurs in late spring - early summer, the plant adorns itself with numerous golden flowers, located mainly on the tops of the stems.
2.3. Thorny gorse or Ulex - Ulex
Thorny evergreens with multi-branched thorny shoots of green color. Each shoot is abundantly covered with long and sharp spines. Leaves are green, simple, arranged alternately or collected in whorls. The flowers are golden yellow, abundantly cover the upper part of the shoots.
2.4. Genista lydia - Genista lydia
Low deciduous shrubs up to 60 cm high, with abundantly branching, thin, lodging shoots. Often grown as ground cover plants or as ampelniks - when long, thin stems hang in a beautiful cascade over the edges of the pots. The leaves are small, green, simple, arranged alternately. The flowers are golden yellow, cover the plant so abundantly that they often completely hide the shoots and leaves.
2.5. German gorse - Genista germanica
Shrub up to 60 cm high with erect or lodging stems covered with small thorns. Young shoots are green, covered with slight pubescence. Leaves are simple, oblong-lanceolate, also covered with a small downy. Flowers lemon-yellow or golden, abundantly cover the tops of the shoots in May-June.
You may also be interested in:
Gorse is a genus of flowering, perennial woody plants that includes about 100 species of non-thorny or thorny shrubs, dwarf shrubs and even lianas of the legume family.
Most species are native to the regions of Western Europe, the Mediterranean and Northwest Africa.
In gorse care, it is absolutely unpretentious and, in favorable conditions, is able to revive the garden with its bright flowers for many years.
Gorse: Signs and superstitions
Gorse has long been endowed with magical properties, and far from good ones. It is believed that if you bring this plant into your home, it will lead to illness and death of family members or to misfortune.
Also, the branches of flowering gorse are considered a powerful talisman against evil spirits. To drive her out of the house and prevent her from appearing in it, a bunch of branches tied with a willow twig should be hung above the front door from the outside.
Those who believe in its negative, it is better to admire this beautiful plant in their garden, creating unusual compositions of gorse with other plants, decorating them with rock gardens and slopes in the local area. In this case, it will only bring positive emotions and will not harm the inhabitants of the site.