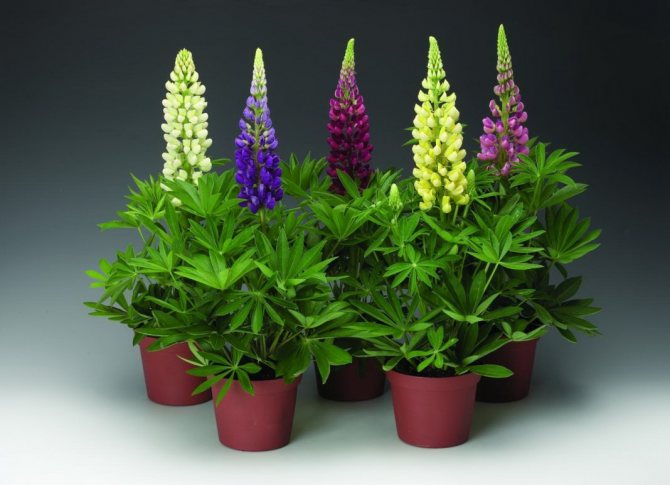
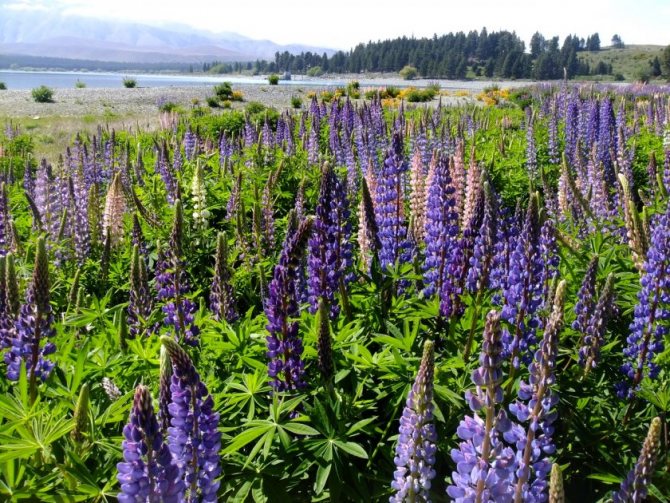
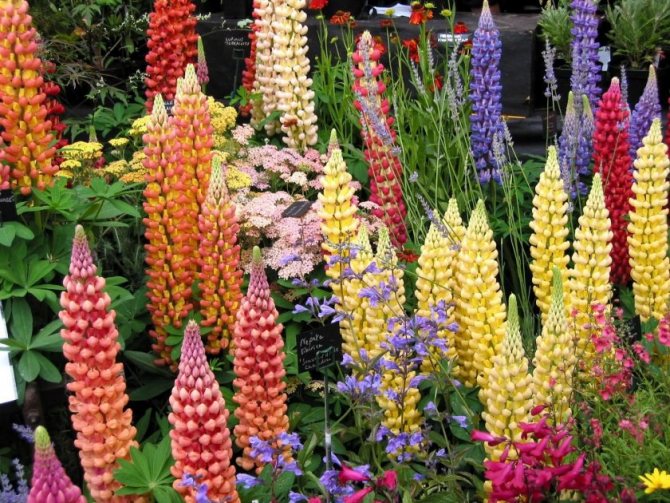
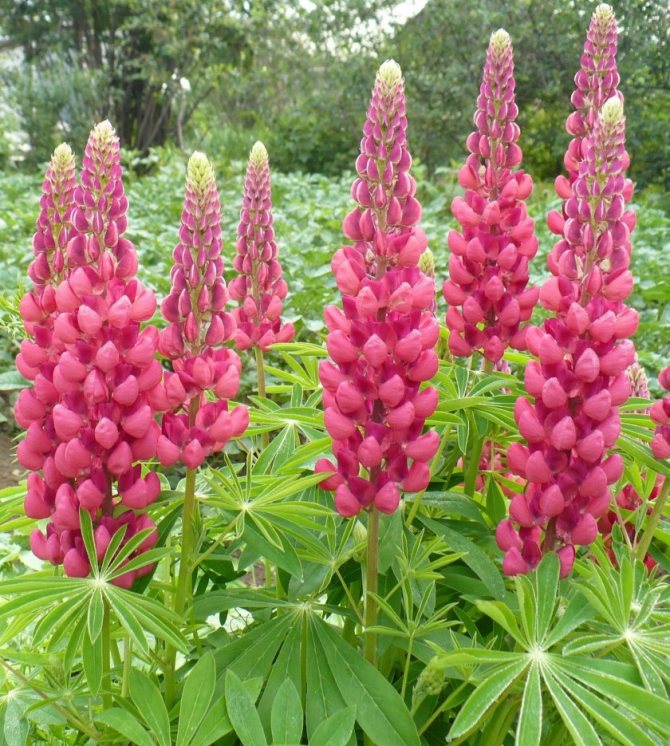
Lupine is a plant of the legume family well known to many of us. This beautiful, bright flower is surprisingly hardy and unpretentious to the surrounding conditions, so you can find it anywhere. Lupine fell in love with gardeners not only for its decorative characteristics, but also for its ability to enrich the soil with useful substances and suppress the growth of weeds. It is quite easy to grow it on your own site - for this you need to know a few simple rules.
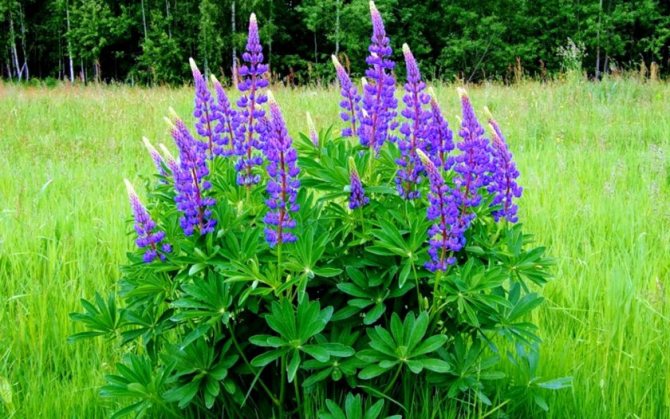
Perennial lupine flower
Description of lupine
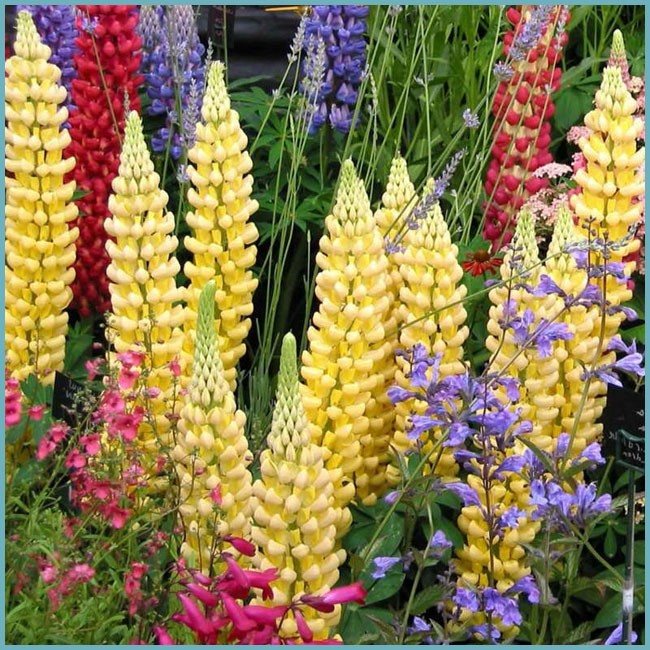
The genus Lupinus is an amazingly diverse plant. The wild, natural species of these plants seem pretty and landscape, but nothing more. And the best hybrids and varieties flaunt such beautiful flowering that they can outshine any much more popular perennial.
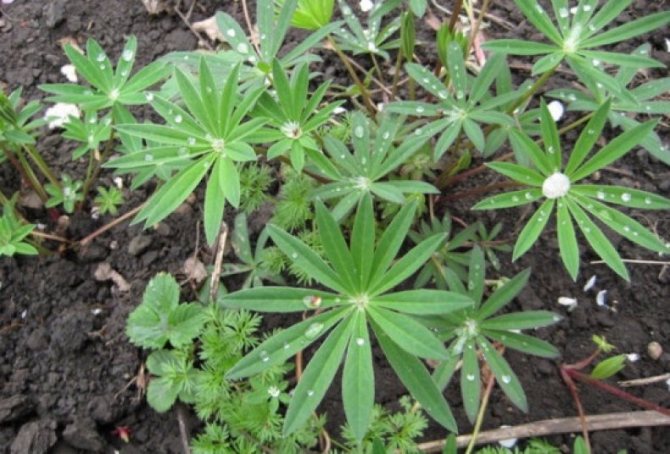
Lupins are truly unique plants. Powerful rhizome herbaceous perennials with surprisingly beautiful leaves - finger-like, on long petioles, exemplary graceful, they form elegant and interesting in texture bushes, from which they breathe cool and splendor, thanks to the dense arrangement of greenery and bluish-cold tint of color.
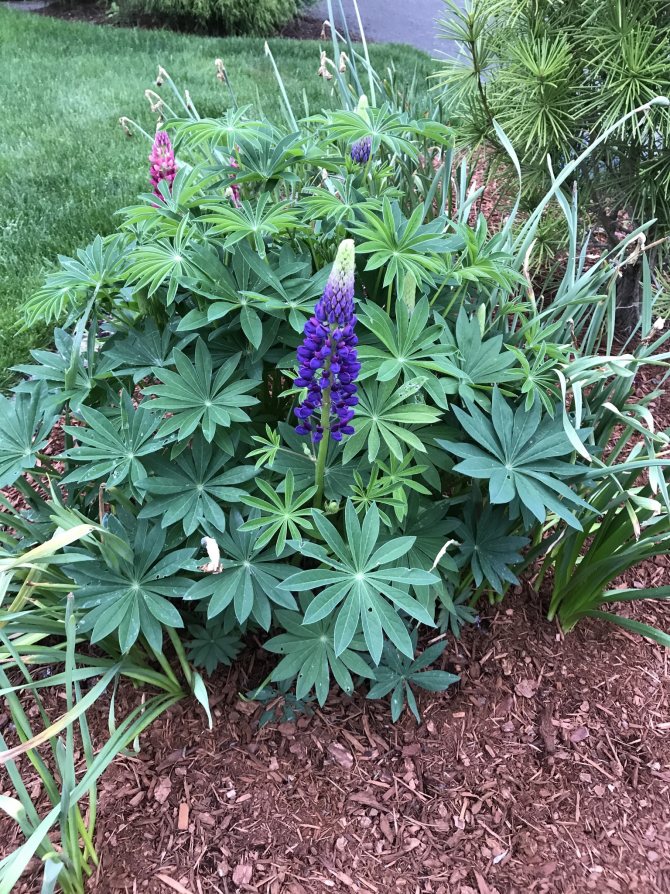
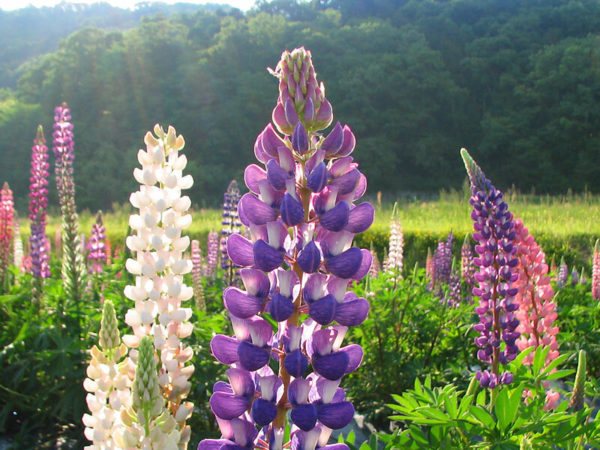
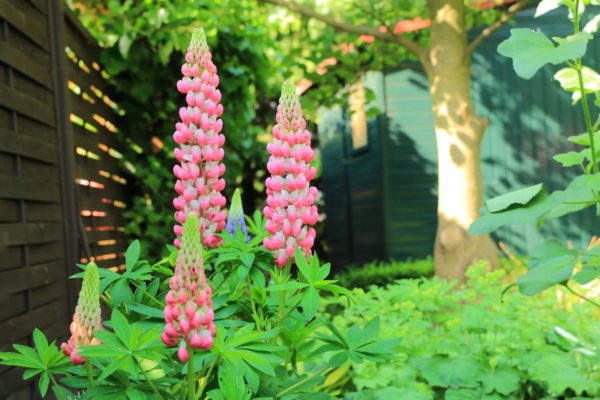
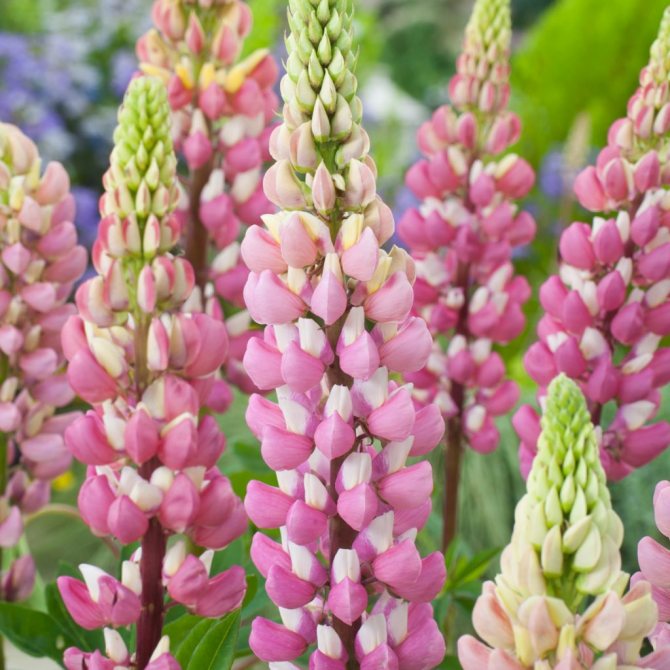
But lupine always surprises not with foliage, but with flowering. Exemplary watercolors - you cannot characterize it otherwise. Tassel-shaped tall candles with delicate watercolor and pastel tones of pink, blue, lilac, lilac, cream, red, purple, blue wonderfully harmonize with each other and create in the plantings the feeling of a blurred color that turns into one another, like the works of watercolorists.
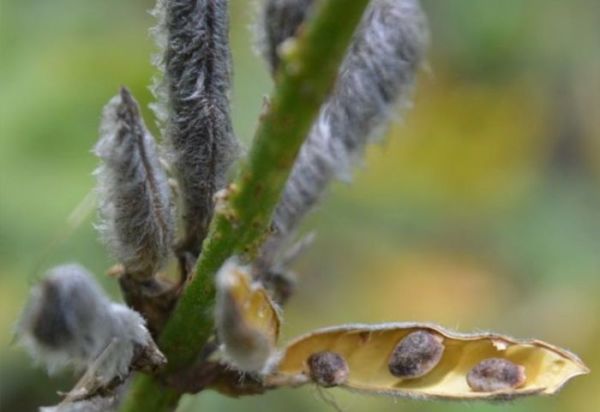
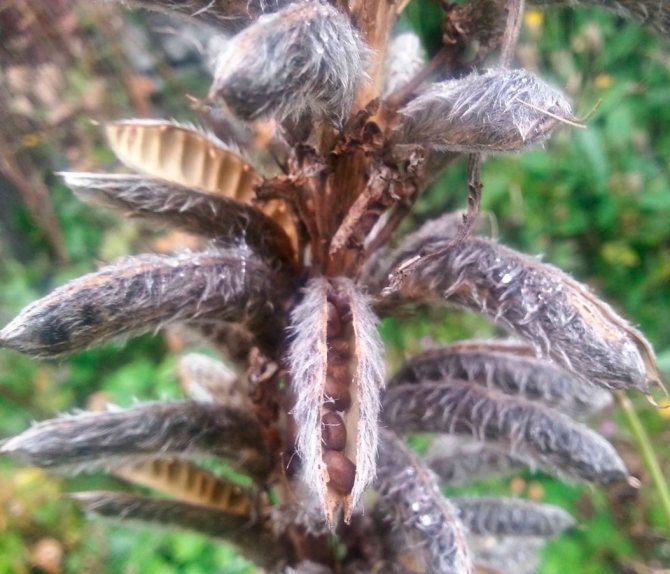
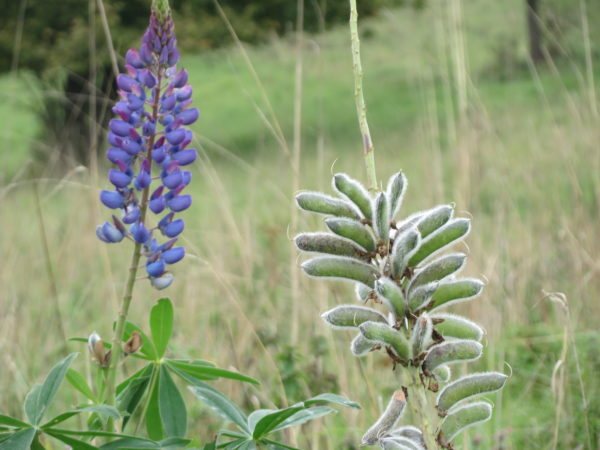
After flowering, lupins are tied with original beans. In some types of lupins, the seeds are larger (in 1 g - only a few dozen seeds), in others - small (up to 200 in 1 g). They ripen well even in regions with harsh winters, but wake up very easily.
The seed method of reproduction is the main one for all annual and non-hardy North American lupines and the second most important breeding method for perennial winter-hardy species and varieties. Their status can be easily explained: when grown from seeds, lupins are far from guaranteed to retain their color features and improved flowering characteristics (which, while maintaining especially valuable varieties, can lead to their loss).
But such a feature in other cases can serve as an advantage: lupins always add the effect of improvisation, naturalness and even wildness to plantings. Subtle changes in shades or completely unexpected colors always give a feeling of novelty and magic, relieve boredom and predictability, give new sensations.
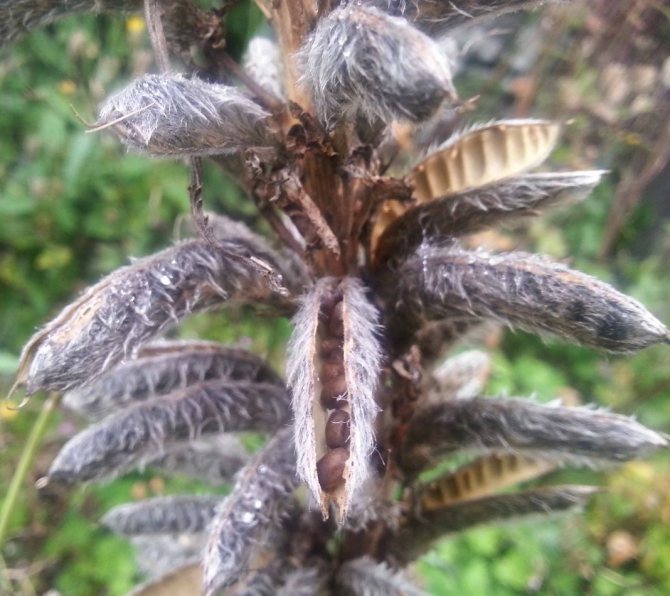

Lupine seeds in pods
Types and varieties of plants
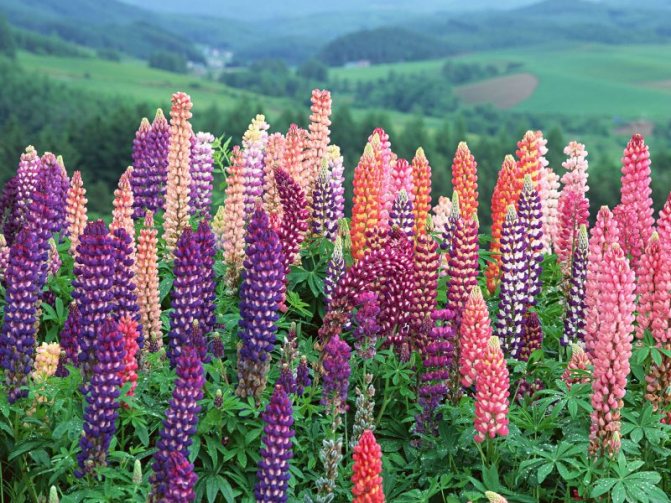


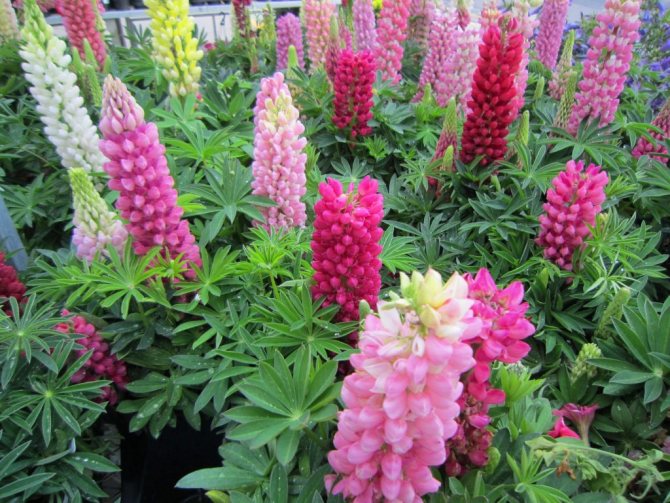
Lupine, often used in landscape design, is also used in the food industry, agriculture and for the manufacture of medical supplies due to its protein (50%), iron, fatty acids and bitter alkaloids (up to 2%) content. Annual varieties of lupine, such as yellow, white, are usually used for industrial purposes. And for the design of flower beds, front gardens from one-year-olds, a hybrid, dwarf, changeable type of flower is used. But the most decorative lupine is perennial.
Lupine multifoliate
The winter-hardy native of the North American region is a perennial herb, reaching a meter in height. Candle-shaped inflorescences 35 cm high consist of small flowers that bloom in early summer and remain in this state for a month. Timely pruning of faded inflorescences allows the perennial to bloom again at the end of the summer period.


Among the most popular varieties are:
- pink Schlossfrau;
- carmine "Edelknabe";
- white "Burg Fraulen";
- orange "Apricot";
- red "Carmineus";
- white with a pinkish tinge variety "Princess Julianna";
- pink Roseus;
- snow-white "Albus";
- undersized variegated variety "Minaret";
- blue with white sail "Castellan";
- violet-ruby "Rubinkönig".
Lupine angustifolia
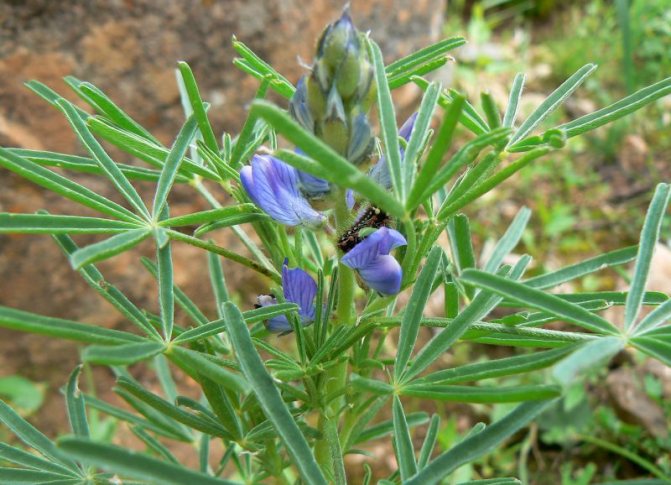


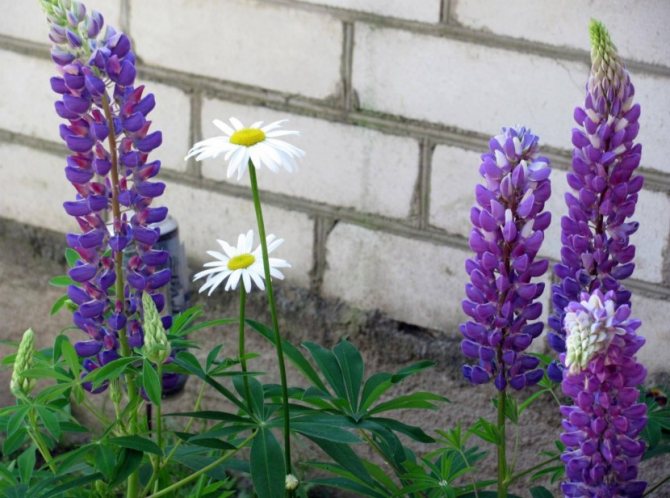
He is also blue lupine - a perennial representative of legumes with a height of up to one and a half meters. The name does not characterize the color of the flowers, which can be not only blue or purple, but also white and pink.
Lupine white
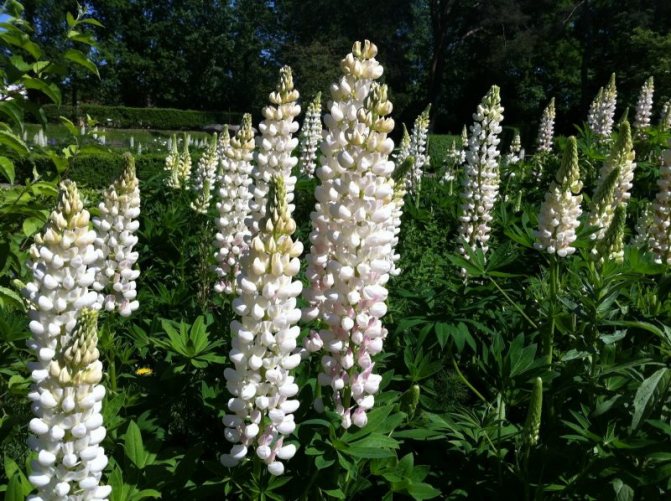


An annual plant, the height of which also does not exceed one and a half meters, has an erect stem, branching in the upper part, covered with palmate drooping leaf plates. Flowers of white, pink or blue hue form an inflorescence in the form of a brush, arranged in a spiral.
Lupine yellow
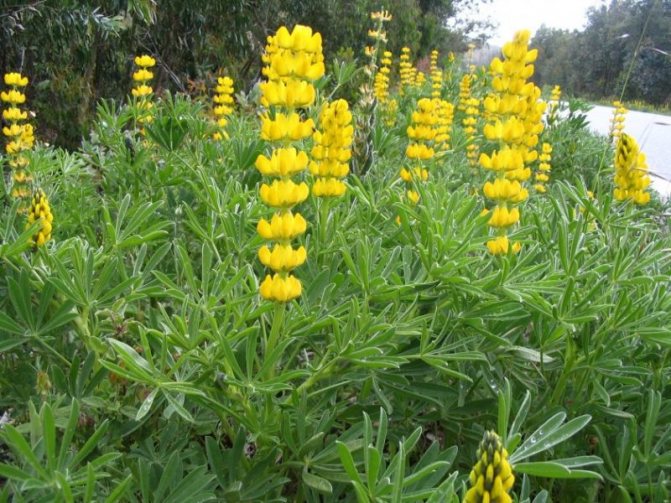


An annual herb with a slightly leafy central shoot, crowned with a racemose inflorescence, which consists of yellow flowers with a scent similar to that of mignonette.
Self-collection of lupine seeds and their selection for sowing
Lupine seeds remain viable for up to 5-6 years. Freshly harvested seeds are preferable to use, but after several years of storage they will germinate perfectly. Moreover, this perennial prefers pre-treatment of seeds before sowing, which significantly increases the percentage of germination.
If you want to collect lupine seeds yourself, then you should carefully monitor the ripening of the fruit. In lupine, the beans crack quickly. Therefore, it is better not to miss the moment when they evenly turn yellow and dry slightly. You can also apply the tying method. In lupins, the fruits are usually cut in several stages.
When buying seeds, carefully check the information about the variety and its characteristics - plant height, planting density, preferred method of propagation and care. Lupins are easy-to-grow plants for which it is not at all necessary to choose only elite types of seeds. Decorativeness and aesthetics are the main guidelines. And in order to become the owner of quality seeds, it is enough to give preference to proven firms and shops.
Three strategies for sowing lupine seeds:
- Sowing in open soil before winter.
- Sowing in open soil in spring.
- Sowing seedlings
These three methods differ in complexity, flowering time, and growth rates. The simplest method is undoubtedly sub-winter sowing, the most labor-intensive is the seedling method.
When to collect and how to store lupine seeds?
After ripening, the fruits of the lupine crack, and the seeds scatter. To avoid this, the seeds must be collected when the beans turn yellow, which are just beginning to dry out. The harvesting process is carried out in several approaches in sunny weather: while on the central shoots the beans begin to turn brown, on the lateral ones - the fruits remain green.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- Seeds are extracted from the pods, distributed over a paper sheet, on which they are dried in a warm and dry room without access to direct sunlight.
- The seed is placed in a glass, paper or tissue container, where it will be stored until sowing.
Winter sowing of lupine
The easiest way to grow lupines and by far the most efficient.It is enough at the end of October or in November, before the first frost, to sow lupine seeds in a garden bed with high-quality, dug up and improved soil. Seeds are sown shallowly, by 2-2.5 cm. For a successful wintering, it is enough to mulch a bed with crops with a thin layer of peat.
Shoots appear immediately after the snow melts, and they develop very actively. And most importantly, the plants will be able to bloom this year (albeit at the end of the season). Caring for young plants is simple: they only need weeding with loosening (or mulching) and thinning with dense shoots.
Lupine's features
Tall and multi-colored candles that enliven the entire garden landscape attire become a real decoration of any garden. They are completely unpretentious, so additional plant care is required.
Lupine is basically a perennial plant, so you won't have to replant or plant again for a long time, and they also have a simple planting and maintenance. The photo shows how to grow lupine from seeds.


Flower inflorescences are candles with a huge number of small inflorescences, they occupy most of the stem. In some cases, the plant reaches a height of up to 1 meter.


Sowing lupine in the soil in early spring
Limitations on the possibility of sowing lupine seeds in the soil directly in the spring imposes the need for their preliminary preparation. So this perennial can be grown only if the sowing site has been prepared in the fall, with two deep digging and correction of the reaction for acidic or alkaline soil types.
Seeds are sown on ridges or in a permanent place immediately after the snow melts (traditionally in April). Seedlings are thinned out when they release 3-6 leaves. Growing requires weeding and loosening the soil, but not constant labor-intensive maintenance.
Lupins sown using this method will be able to bloom only next year.
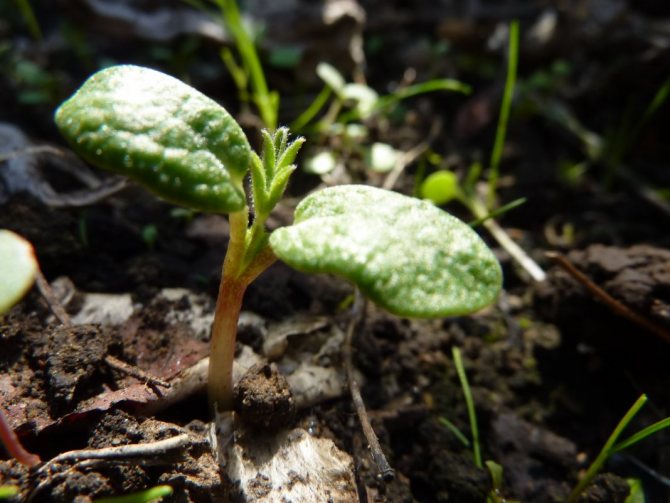


Lupine seedling
How to properly plant lupine in open ground
Planting timing
With seed reproduction of lupine, sowing is carried out at an early stage of spring. You can do seedlings as early as March. If the seeds are planted directly into the ground, then it is necessary to plant after the snow melts and it becomes warm, that is, April is more suitable for this. The site is being prepared in advance in the fall.
Those who prefer to plant plants for the winter will come to the end of October. In late autumn sowing, there are great advantages, there are no particular contraindications.
The seeds will germinate before the onset of the winter period at a comfortable temperature for them. They are immersed in the ground two centimeters deep, after which the site is mulched with peat.
In spring, lupins will sprout, bloom closer to autumn. The seedling method is best used when the second and third leaves appear. To avoid problems with transplanting, they are planted on open ground on time.
Planting by seeds
- Seed propagation in the fall. Seeds are sown in April or October, before winter. Note that they can be stored in good conditions for up to five years. After planting in open ground in the fall, they must be sprinkled with a small layer of peat. In the spring, the first shoots will appear, and by the fall you will have abundant flowering. When planting in a permanent place, a distance of 30 to 50 centimeters is left between the plants.
- Seed propagation in the spring. Seedlings are prepared with the onset of warm spring weather. Seeds are sown immediately to a permanent place - in open ground. The earth is premixed with sand and peat. Loose soil works best. If there are old tubers in this place, they are mixed so that the young plant receives more nutrients and favorable bacteria. Moderate watering is important for the young.
Cuttings
The vegetative method can be used when buds have formed at the base of the stem. Part of the root collar is captured during the cut with a knife and planted in sandy soil.Within a month, young plants will develop a root system, after which they can be planted in a permanent place.
Cuttings are planted in spring using a root rosette that has formed at the base of the stem. In summer, lateral shoots formed in the leaf axils are taken.
The color of lupins with the vegetative method is preserved, which is why it is good.
Site selection and soil preparation
Weakly acidic and slightly alkaline loamy or sandy loam soils are most suitable for lupine. To prepare the soil for planting seedlings in the spring, in the fall, you need to lime the acidic soil.
This is made with flour from dolomite or limestone, per 1 square meter, 5 kilograms are taken. This will be enough for up to 4 years.
Alkaline soil is dug up with peat with a similar calculation: for one square meter, five kilograms of peat are taken.
Strong sprouts of culture are planted in the soil prepared in the fall in the spring, maintaining a distance of 30 to 50 centimeters from each other.
Lupins are very fond of sunlight, so you need to choose a rather spacious place for them. Open places away from buildings, hillocks are well suited.
Soil processing and preparation
For planting lupine, the soil is prepared in advance. The top layer is loosened with a flat cutter or cultivator, which is enough for processing. The land becomes more fertile, making it easier to care for plants.
Then the soil is fertilized with a good organic fertilizer, for example, "Biovit" or another EM-preparation.
Since lupins are sown in late spring or at the end of the year in a narrow-row method with a distance between rows from 15 to 30 cm, and between plants from 5 to 15 cm, up to two kilograms per one hundred square meters are taken for the sowing rate, for example, of a narrow-leaved yellow lupine.
With manual seeding - up to three kilograms per one hundred square meters.
Scarified seeds and EM preparations containing tuberous bacteria significantly increase the quality and quantity of seed germination, and the development of the plant as a whole.
During the decomposition of the remaining parts of the plant, humification is carried out only with a sufficiently moist soil. For dry areas, green manure with irrigation is more effective. In case of periodic droughts, watering is carried out.
One family of lupins and other legumes should not be alternated when planting in the same places, so that the soil does not lose its fertility, and the harvest is good.
Open ground planting process
Do not be surprised if after seed reproduction the flowers will have a different color. This is due to hereditary information that is transmitted by adults through seeds.
- Lupine seeds must be sown for seedlings in loosened potting soil. One part of peat, one part of sod land and half of a part of sand are taken.
- Before sowing, the seeds are mixed together with the old tubers ground into a powdery substance. Nitrogen-scavenging bacteria will proliferate easily.
- The first shoots will be visible after one to two weeks. For simultaneous appearance, the crops are covered with a moistened gauze cloth and kept in a warm place.
- When the third leaf appears, the seedlings are planted in their permanent place. It is not worth delaying the transplant, as problems with the root system may arise.
Soil and containers for sowing lupine
Lupines can be sown in any large containers and bowls - boxes, plastic containers, etc. The height of the containers does not matter much, but keep in mind that lupins are not very fond of transplanting, and in deeper boxes it is easier to avoid trauma to the roots.
For sowing lupine seeds, any universal soil mixture is suitable - a special purchased substrate for seedlings or self-prepared soil, consisting of turf soil and peat with the addition of half the amount of sand. The main thing is that the soil is loose, air and water permeable.
A very important additive that will allow the seedlings to develop much faster due to the activation of the growth and spread of nitrogen-fixing bacteria so necessary for lupine is crushed tubers collected from the roots of adult lupins. It is better to collect them from the roots of the oldest specimens and literally grind them into powder. True, you should not rush to add such an increase directly to the substrate: it is best to mix the seeds themselves with the resulting powder.
History and interesting facts
The name of the flower comes from the Latin word lupus, which means "wolf" - for this reason it is often called wolf beans.
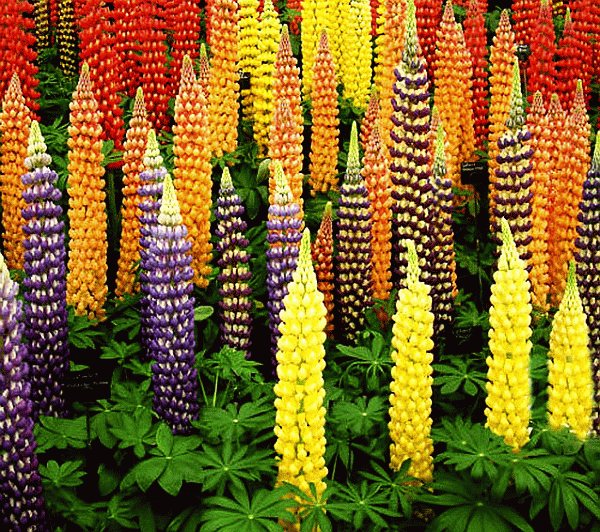


Perennial lupine: a striking flower
The homeland of lupine is North America, but its area of growth is much wider, because it takes root not only at sea level, but also at an altitude of up to 5 thousand meters, and alpine species often reach four meters in height. People have known this plant since the time of Ancient Greece - there, the tombs of the pharaohs were decorated with its inflorescences. Initially, the flower was considered a common weed, but after the appearance of hybrid species, it began to be grown for decorative purposes. A special contribution to the cultivation of lupine was made by the world famous breeder Russell, who bred the most beautiful and beloved varieties of gardeners: "Main Schloss", "Splendid", "Burg Fraulin", etc.
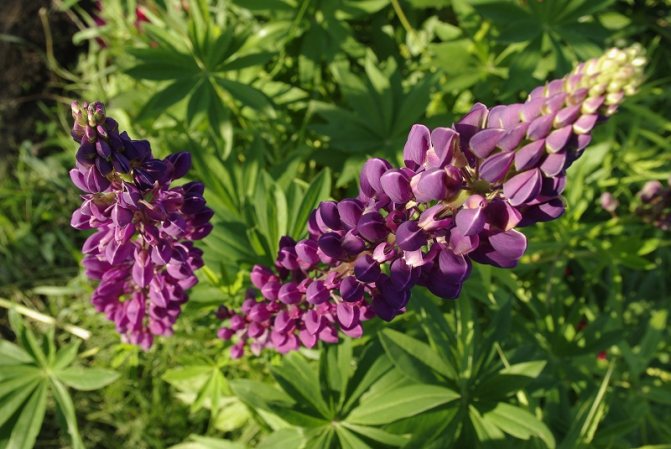


Lupine Perennial (Lupinus polyphyllus)
Some plant species contain a substance called lupinine, which is a powerful natural poison. But "safe" flowers are often used as animal feed, as they contain a large amount of protein and proteins. Also from lupine, oil is obtained for the cosmetic industry, which in its characteristics is close to olive, but does not contain substances that slow down the gastrointestinal tract.


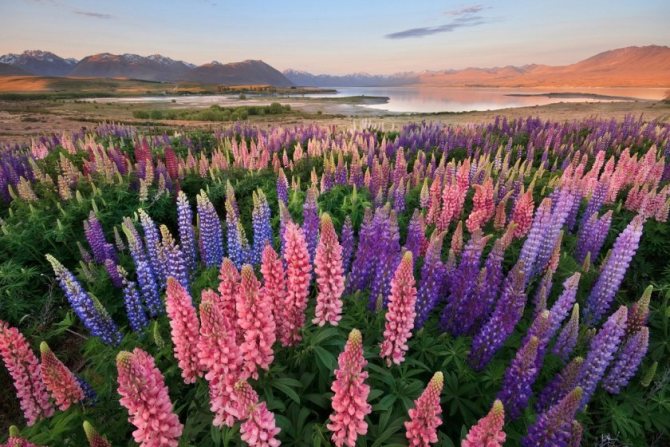
Lupine by the lake
But the greatest use of lupines is found in gardening, since its cultivation has a beneficial effect on the quality of the soil. The roots of the plant are pivotal, and can reach a meter or even two in depth, making the soil looser. In addition, there are small bumps on the root system of the flower, which are capable of absorbing nitrogen and enriching the soil with it. Finally, the decaying processes of lupine can serve as an organic fertilizer - to reduce acidity, they are buried in the ground to a depth of 20 cm.


Perennial lupine
Lupine seed pretreatment
To improve germination and obtain more uniform seedlings, ready for cutting at the same time, it is advisable to pre-soak lupine seeds. Without soaking, they do not germinate as amicably and not at the same time. To soak, it is enough to moisten gauze or a cloth in warm water, sprinkle the seeds on half of it and cover them on top with the second free part. On a platter in a warm place, the seeds will quickly pick up, and as soon as the first signs of activation appear, you can start sowing.
Immediately before sowing, it is advisable to mix the seeds with the powder from the lupine tubers, due to which the bacteria they need will rapidly develop on young seedlings.
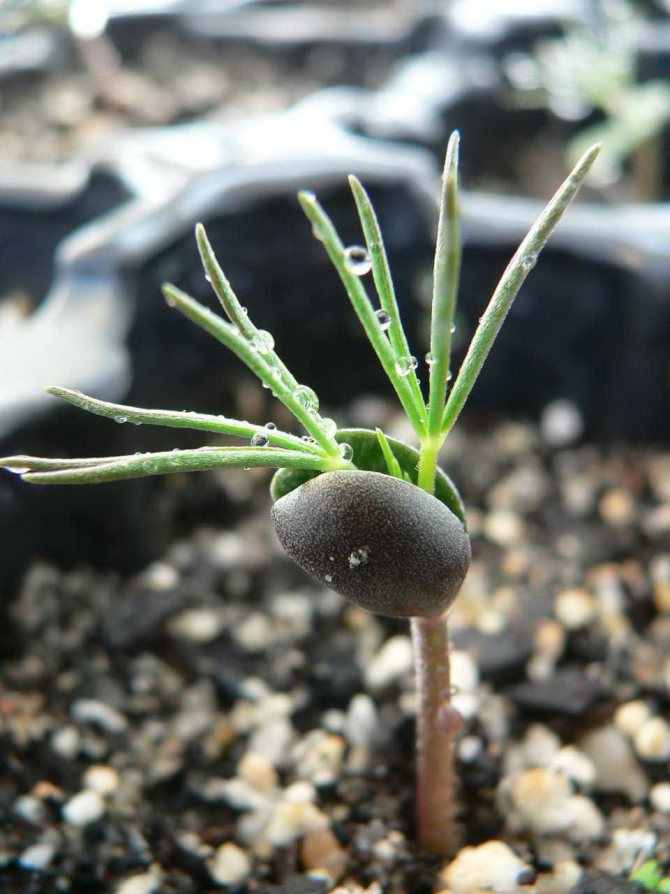


Lupine seedling
Seed collection
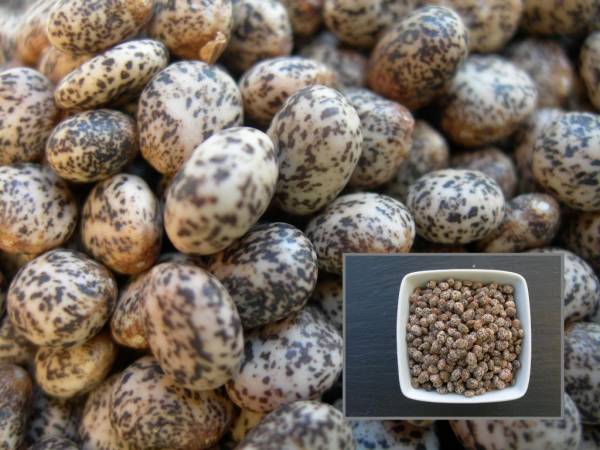
After flowering, seeds are formed in place of the buds. When ripe, the formed capsules open and small seeds are scattered.
If you miss the moment, the ripened beans will crack and the seeds will crumble, so to do this, it is necessary to tie the trunk with gauze when the beans ripen and then the seeds will be collected.


You may be interested in: Cyclamen: description, types, cultivation and care at homeMalva perennial - planting and care in the open fieldOleander - care and cultivation at home
Sowing lupine seeds
For growing lupine seeds, it is considered optimal to sow them in early spring - in March or April, so that after 30-50 days cold-resistant lupins can be planted in the soil.With favorable weather and pre-planting treatment, it takes only 30-35 days for lupins to germinate and develop up to 5-6 leaves.
The substrate is slightly moistened, avoiding overflow, just before sowing.
The seeds are sparsely scattered over the moistened substrate, trying to evenly distribute them over the soil so that they do not need a pick at all (at the stage of 5-6 leaves, the plants should not interfere with each other).
The sowing depth is standard (on top of the seeds cover 3-5 mm of sifted soil).
Lupine species
There are plenty of varieties of lupins. Breeders know more than 200 plant varieties, but only no more than 10 species are actively cultivated. Most lupins are wild plants.
Shrub lupins are found in nature, they are by far the most interesting to breeders. This variety perfectly crosses, perfectly adapt to any weather conditions.
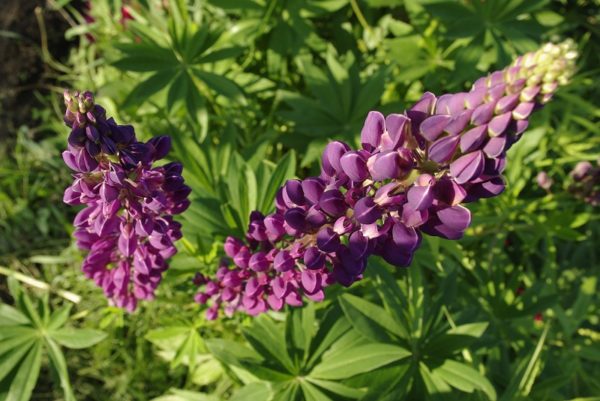


Diving seedlings and caring for young lupins
Diving for this plant is not carried out, trying to transfer the seedlings directly into the soil. The cold resistance of lupine, provided that it is rarely sown, quite allows the procedure to be carried out without additional transplants. But if the seedlings are too dense, then it is better to carefully dissect when 2 - 3 true leaves appear.
Young lupins do not need additional feeding, the latter can disrupt the process of formation of the root system and complicate transplantation due to the too rapid growth of young seedlings. For seedlings, moderate, careful watering is continued, maintaining light soil moisture.
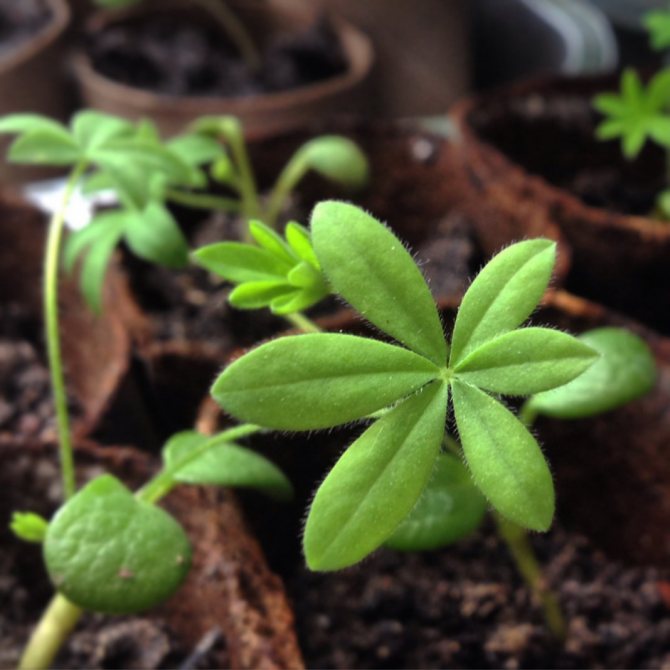


Lupine seedlings with real leaves
Cuttings and other methods of propagation
Vegetative propagation of lupine allows you to preserve the color of the plant, but is suitable only for young bushes, as they are less hardy and take root too deeply. To obtain a cutting, you need to cut out a lateral shoot with a sharp knife (one of those that form in the leaf axils) - such cuttings should be planted in the summer. If the planting will be carried out in the spring, you should use the root rosettes, which are formed on the stems from below.


Propagation by cuttings
Hardening and planting lupine seedlings
It is advisable to transfer lupine to a permanent place 20-30 days after germination. Under the condition of favorable weather and normal development of young plants, 5-6 true leaves are formed in lupins by this time. If growth is slowed down, then you still need to wait for the appearance of 5-6 leaves and forget about the timing, if the plants are strong, you can transplant them at the stage of 3 - 4 leaves. For lupines, the timing of planting (or rather, the stage of plant development) is extremely important.
If you are late with planting, let the lupins grow more in seedlings, then they will tolerate the transplant much worse. In fact, after the appearance of the 7th leaf, the adaptability of the plant deteriorates two or more times. Therefore, the younger the plants that are transferred to the ground, the better. If the plants are strong and the weather is favorable, the lupine can even be tolerated with three leaves.
For lupine with its cold resistance, planting can be carried out in early May and even late April, if serious spring frosts have ended or if you have the opportunity to cover the seedlings with non-woven materials.
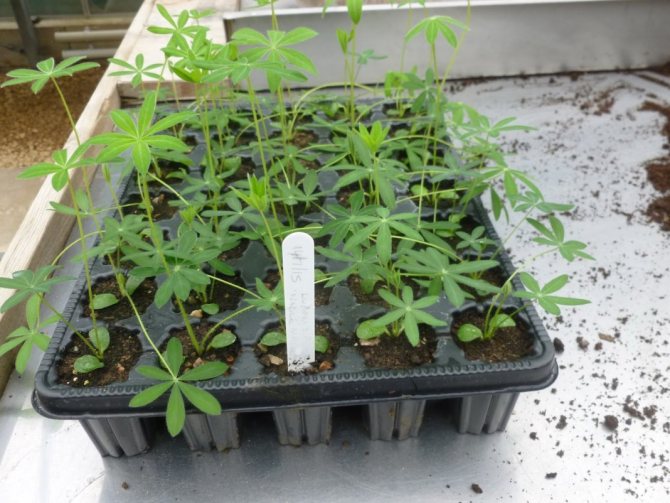


Seedling lupine
Lupine: diseases and pests
Lupine, along with other legumes, is affected by insects and diseases. Sowing material and seedlings are often damaged by wireworms, beetle larvae and gnawing moth caterpillars. The greatest harmfulness is noted in the spring period, which accounts for the slow growth of the plant and active nutrition of the pests. Weevils can also harm plantings. To combat soil-dwelling pests, which include the wireworm, pre-sowing seed dressing is used. A similar event will also protect the culture at the germination stage.


Adult plants, as a rule, are damaged by sucking pests (thrips, bedbugs) and leaf-eating scoops, for protection from which timely insecticidal treatments are carried out according to the manufacturer's instructions. Excessive watering and a violation of crop rotation can lead to the development of fungal diseases, from which rust, root rot, mosaic, and fusarium are released.
So, unpretentious lupine looks great in combination with other crops, being placed in the center of flower arrangements. The lower plants surrounding it are an excellent protection of the flower from strong winds.
Planting lupins
Young lupins do not tolerate transplanting well, and for this culture it is desirable to carry out a complete transshipment while preserving an earthen coma around the rhizome. It is better to prepare sites for planting lupine seedlings in advance. They need sunny places, but lupins are undemanding to the soil (although they bloom most effectively on loams with a neutral or weak reaction).
The optimal distance for planting lupins is from 30 to 50 cm, depending on the height of the variety.
The only care that lupins grown through seedlings will need is neat protection in the first year of growing. Removing weeds before building up sufficient green mass, loosening the soil after precipitation and feeding the next year after planting with a half dose of full mineral fertilizers or potassium-phosphorus fertilizers (the plant provides itself with nitrogen) - that's all the measures. In the future, it is worth monitoring the pouring of soil to the bare root collar and regular rejuvenation with a frequency of once every 4-5 years.
Brief description of the plant


The plant has a powerful root system that penetrates up to 2 m deep. On the roots are the tubers of nitrogen-containing bacteria, which are able to absorb nitrogen from the air and include it in their biomass. The alternate, palmate-compound leaves on long petioles are located on herbaceous or woody stems, reaching from 0.5 to 1.5 m in height. Branches can be either erect or creeping.
Flowers with white, blue, yellow, red and other colors form racemose inflorescences at the top of the stems. The beans are straight and slightly curved, with a leathery, uneven surface. Depending on the species, the seeds differ in shape, size and color. Their surface is usually smooth or covered with fine cells. In Russia, this plant is mainly used for the design of garden plots.
Threatening factors
Aphids, tuberous weevils and sprout fly larvae are the most common pests. Harm the green manure during flowering. Special solutions of insecticides will help to get rid of parasites.


Among the diseases of green manure, the most famous are gray and root rot, fusarium, spots and mosaics of various types, rust and phomopsis.


But do not be too afraid of them if you do everything right in both planting and content. The flower should be planted again in the same place after 3 years.


An unusual way to grow lupine
In the fall, you can scatter lupine seeds under trees. This flower takes root well near apple, cherry, plum and other fruit trees.
After winter, in spring, you will see a whole garden of lupines. Seeds of different colors are best suited for this. Then you will receive colorful and bright flowers already in April.


Care
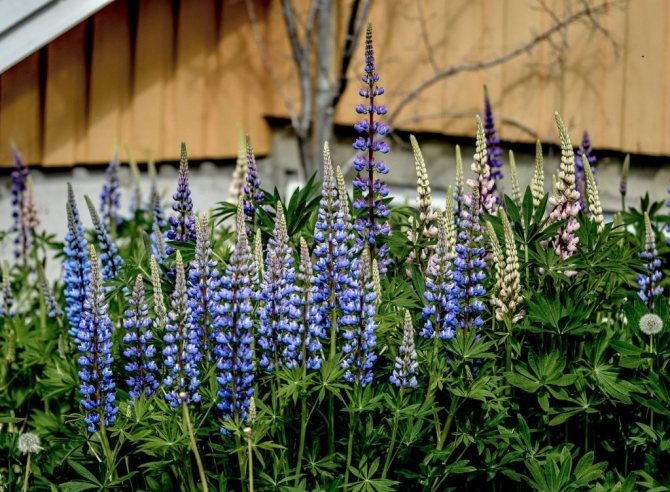


An unusual plant will decorate your garden
After planting, during the period of flowering and growth, it is not particularly necessary to care for lupine. FROMAmo plant is capable of producing nutrients, repelling many pests. But in order for the garden flower to grow normally and please the eye, you need to help it.
The basic rules for caring for lupines in the garden are as follows:
Watering It is carried out immediately after disembarking the seedlings.Further, the stems can not be watered, but in case of drought during the budding period, you can please the bushes with moisture. The rest of the time, natural moisture will be enough for lupine.
Weeding Lupine loves to grow without weeds and on loose soil, which is why it is necessary to regularly weed the area with lupins. Loosening will stimulate the plant to splendor, flowering will be more violent and long lasting.
Regular pruning In order for the bush to please the eye until the very frosts, it is necessary to regularly cut off the brushes that have faded. This will not only transform the plant, but also stimulate the re-flowering of the stem.
Top dressing The plant does not need feeding, it itself is a siderat. For perennials, it is advisable to add superphosphate or potassium chloride before flowering, so the inflorescences will delight the eye longer. In addition, experienced florists recommend pouring a tablespoon of ash next to each bush after the opening of the first flowers.
Wintering Most types of garden lupins tolerate the winter cold well. But still it is worth playing it safe and covering the boles before frost. To avoid freezing, you should carefully choose varieties and species, give preference to frost-resistant ones, which are recommended for your region.
An important point in caring for lupins in the summer during the flowering period is the garter.... Tall brushes are tied to pegs so that strong winds or summer downpours do not break the inflorescence.
back to menu ↑
Read also: TOP-55 Blue flowers and plants for your home and garden. Indoor and outdoor, perennial and annual (85+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Growing from seeds
Seed germination lasts up to five years. Perhaps that is why the seed propagation method is considered so popular among flower growers.
Seed selection
It is recommended to purchase seed from specialized stores, botanical gardens or greenhouses. They are treated against infections, have an excellent germination rate and ensure that the flowers are varietal.
Seeds collected with their own hands, even after healthy, lush-flowering lupins, usually do not retain varietal qualities during subsequent sowing. The lupine will grow, but will most likely have its original wild hue - blue or purple. It may be possible to preserve the pink or yellow color, but the white is lost unambiguously.
Sowing
The most favorable time for planting seeds is the beginning of spring.
Prepare containers with a mixture of peat and sand, the substrate should be sufficiently loose, "breathable". Buy a special substrate from a flower shop, it will be much easier than making it yourself.
Soak the seeds overnight in standing water at room temperature, and then slightly deepen them into the soil and cover with foil to create a microclimate. There is no need to water - the store substrate has a slightly damp texture.
Seedling care
Place the containers on the windowsill close to the warm radiator. Check the soil periodically, if it is dry, then moisten it with a spray bottle. The first sprouts with two leaves will appear very soon.
In another two weeks, they will hatch third leaves. If weather conditions do not allow them to be transplanted into open ground, then it's time to divide the seedlings into separate pots (dive), otherwise the roots will intertwine so that it will be difficult to separate the sprouts (this will definitely not work for them).


Photo: https://enn.imadeself.com/photos/lupine-lupinus-leaf-plant-nature-3325111/ After three to five leaves grow, the seedlings can be transplanted into open ground, but it is desirable that the soil is warm enough and there was no threat of recurrent frosts.
A little about fertilizer for lupine
It is worth starting to feed this plant in the spring of the second year after its planting in the soil. For this, fertilizers are used rich in minerals without the presence of nitrogen.


For one square meter, you will need about 20 grams of superphosphate, as well as 5 grams of calcium chloride. After this, feeding will be required for all subsequent periods of spring until the death of the plant.


Planting in the fall in the ground
Prepare the place in advance by removing weeds, adding fertilizers and good soil.


Seeds are scattered over the surface and sprinkled with a layer of peat.
During the winter, they will undergo the necessary processing and will delight you with flowering in the first season.


You may be interested in:
Perennial flowers for a summer residence How beautiful, bright and rich flowering can be in a summer-spring-autumn garden, if you choose the right flowers for ... Read more ...
Pests and diseases
Lupine is a fairly resistant plant, but sometimes it is attacked by diseases and pests. During the formation of buds, there is a risk of damage to aphids, and the larvae of a sprout fly can also choose a place on the plant.
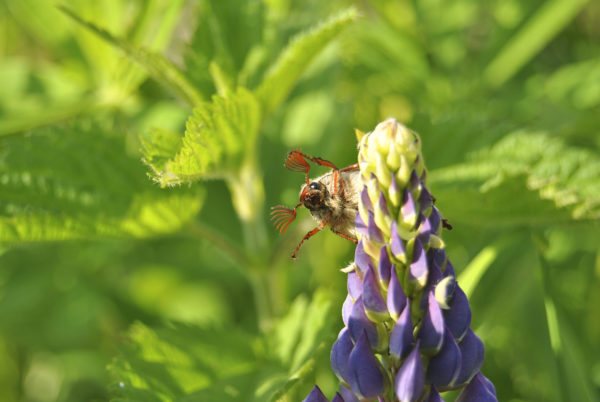


May beetle is able to eat a flower. Beetles, if any, will have to be collected manually, and from all other pests, treat the plant and soil with insecticides.
From diseases, the flower is threatened by gray or root rot.
If you provide proper care for perennial lupines, then all diseases and pests can be avoided by organizing proper planting and care.


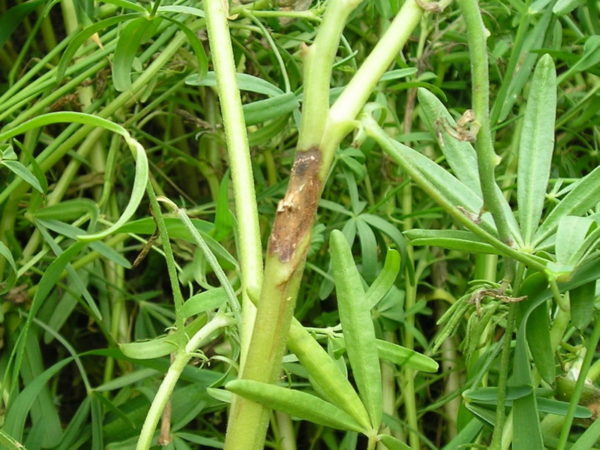
- Bacterial spot appears on seedlings and adult plants. First, you can observe dark brown spots, then the stems begin to rot, the plants die as a result. On older flowers, stems, beans and leaves are affected. A disease is caused by a rod-shaped bacterium: Pseudomonas lupini Beltjukova et Koroljova.
- Brown spot begins to infect from the stems, then moves to leaves, beans and seeds. Closer to the root system, noticeable dark brown dots of 2 mm appear. On young leaves, spots are observed in the form of dots with a light green border.


- The causative agent of the disease is a mushroom: Ceratophorum setosum Kirch.
Appears as black spots. Development occurs in rainy weather or with excessive watering. Therefore, special care should be taken after the plant.
- Root rot begins to affect seedlings, in rare cases it can touch adult plants.
At seedlings, at first, the root system begins to rot, after which it passes into the neck of the root. Seedlings change color and sometimes die before they appear on the surface of the soil. In the affected flower, deep brown ulcerative wounds appear on the surface of the cotyledon.


These lesions can sometimes turn into dark shades. The affected areas have darkening along the edges of the leaves. In an adult Lupine, the leaves begin to turn black, and the roots die off, after the defeat will touch the stems.
Important!
As soon as the first signs of the disease appear on lupine, control measures should be urgently applied, otherwise you may lose not only flowering, but also completely the plant.
- Fungi from the genus Fusarium Link, including the undersized fungus Pythium debaryanum Hesse, are considered the causative agents of rot in the root system.
Mushrooms of the first option appear in wet weather. A white or light pink bloom forms in the affected areas. After emergence, development occurs rather quickly. Mushrooms develop through their spores.

- The mosaic appears on young leaves as small brown spots.
The affected leaves become smaller in size in relation to healthy ones, and they curl around the edges. On the transverse section of the cut, the affected area is observed.
The only plus of this disease is that the affected leaves immediately fall off. As a result, there is only one healthy stem and leaves that have not had time to be exposed to the fungus.


- The causative agent of the disease is considered to be a pea mosaic virus: Pisum virus 2 Smith, carried by aphids. Mosaic can be the only reason for a significant amount of the harvest. Bacteria can survive in seeds, on rotten debris.Therefore, in order for perennial lupine to always look beautiful and healthy, it is necessary to follow the rules of planting and care.
When does lupine bloom?
This ornamental plant blooms in June - first half of July. In warm autumn, if the faded inflorescences are removed in time, the flowers bloom again. The wolf bean is suitable for creating a variety of perennial beds, combining perfectly with other plants. Combinations sown by a group on the lawn give an unusual decorative effect.
Flowers can be cut and placed in vases. It is best to cut the inflorescences when at least half of the flowers in the inflorescence develop.


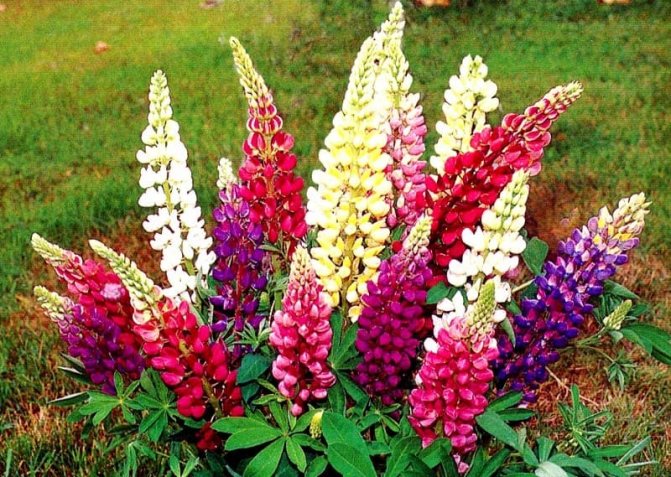
Lupine varieties: photo
The benefits of lupine
In addition to decorative properties, lupine also has a number of useful properties:
- The plant is an excellent green manure. In addition to decorative ones, there are forage varieties. But both are capable of improving the soil, like many legumes. They absorb nitrogen-containing substances from the soil and give back pure nitrogen, which is necessary for plant nutrition. The green mass of young flowers is often cut off and the ground is plowed with them.
- Some peoples use lupine stems in papermaking.
- The seeds and the beans themselves look great in a variety of crafts.


- The pharmaceutical industry cannot do without this plant. Extracts from it are used in medical plasters.
- It is added to cosmetics and soaps for its antioxidant and anti-aging properties.
- On some marine and river farms, lupine is added to fish feed. And breeders also add seeds to rabbits.
- Beans are used in cooking and contain over 300 calories per 100 g.


Fact!
Although lupine is used in folk medicine, some parts of it are poisonous to humans.
Use in the garden and beyond
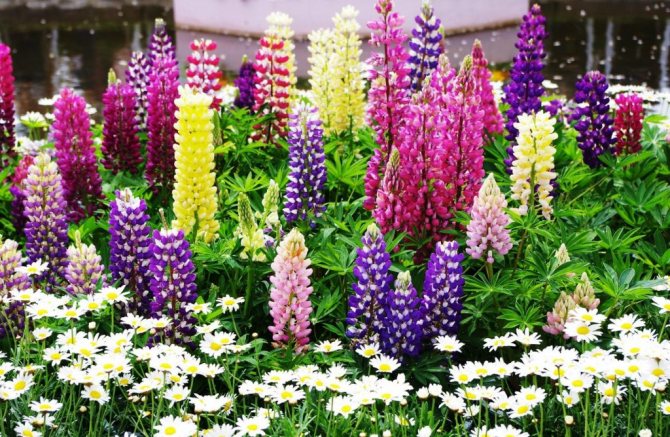
Dense inflorescences, similar to candles, make lupines a wonderful decoration of the site. It is planted in the center or in the middle tier of a flower garden, on rocky slopes, along the curb or walls of buildings. Delphinium, phlox, hosts, irises and lilies can become neighbors in the flowerbed.
Lupine fruits are able to saturate not only animals. For a long time, in various countries, flour was made from them, which was added to baked goods, ice cream, confectionery, and hot dishes. The high protein and fat content increases the nutritional value of these foods.
In traditional medicine, the extract from the plant has become the basis of the drug "Ixim Lupine" - a broad-spectrum antibiotic. A decoction of stems and leaves is used by traditional healers to treat gangrene, ulcers and tumors.
Description
Lupine is native to the Mediterranean, Africa and South America. It can grow not only on the plain, but also at almost five kilometers height, as well as in the desert.
The name lupine is translated from Latin as a wolf, and in Russian it is sometimes called "wolf berry". It belongs to the legume family. It can be herbaceous and shrub.


You may be interested in:
Perennial shrubs that bloom all summer How would you like the garden to always look festive and bright, not only in summer, but also on cloudy autumn days, and even better - and ... Read more ...
It has long roots extending more than 2 m deep.
Like other beans, it can absorb and process nitrogen with the help of shoots on the roots, saturating the soil with them.
The bush is erect, the leaves are palmate green.
The height of the plant depends on the variety.


The inflorescences are large, with many flowers of various colors. Some species are bi-colored or gradually transition from one color to another. Duration of flowering of perennial lupine is about a month.
The seeds are hidden in bean boxes.
Growing seedlings
The unpretentious species takes root well and germinates quickly enough. Even a novice florist can create the necessary conditions.
Soil and capacity
The soil should be nutritious: 1 part of sod land and peat + half as much fine, sifted sand. Before placing the seeds, the substrate is slightly moistened with a spray bottle.Soil for lupine is useful not only nutritious, but also loose so that the beans do not rot.
Germination of seeds is carried out in large containers with compartments or individual pots. High quality peat pots, yogurt containers, disposable dishes with a volume of about 200 ml are suitable.
Important! Before planting, the seeds are combined with a powder made from dried lupine roots. The essence of the method is to activate the reproduction of nitrogen-absorbing bacteria.
Seedling care
Important nuances:
- After planting, the seeds are lightly sprinkled with soil, sprayed, the container is covered with a stack or film.
- For germination of seedlings, a temperature of + 20 ° C to + 22 ° C is needed.
- Periodically, the substrate is moistened, but not poured, otherwise the seeds will rot.
- The container with seedlings should be in a bright room, but not in direct sunlight.
Transplanting
Moving the grown lupine into the ground is allowed only after the appearance of the third, real leaf. Do not wait for the plant to grow too large and elongate: late transplanting can damage the rapidly growing, stubby root system.
Many species do not tolerate cold well, and it is necessary to plant seedlings in a flower bed or summer cottage after the complete cessation of night frosts and warming up of the soil. The timing is slightly different for each region.
Fertilize with ash and cover for the winter
| Watering
|
| Fertilizer
|
| Post-flowering care
|
| Preparing for winter
|
Decorative flower or solid use?
Contrary to popular belief, lupine is not only an ornamental, but also a very useful plant, the raw material of which is used in various fields of human activity, for example:
- lupine seeds are used in food production, the manufacture of medicines and medical plasters, soap making, the production of cosmetics, plastics;
- stems often serve as raw materials for making various decorative products;
- fresh flowers are often used as an element of decoration for special wedding zones, photo zones, etc .;
- straw from this flower is used as an industrial raw material in the paper industry.
The fodder variety of this plant is grown for the sake of feeding livestock; fish farms often feed fish with the seeds of this plant.


Some varieties of lupine are used for animal feed, others are an excellent green manure for other crops, and in addition there are many other uses for this plant.
In addition, any variety of lupine can act as a valuable fertilizer, green manure - a plant that is grown specifically for subsequent digging into the ground in order to:
- improve the soil structure;
- stop the growth of weeds;
- enrich with nitrogen.


One hectare of lupine on the nutritional value of the total green mass when digging into the soil has an effect equivalent to 20 tons of manure
For all its benefits, lupine is the most unpretentious plant, there are no difficulties in caring for it, even when it grows in large quantities. That is why, you can call this plant widespread everywhere, despite the fact that its original habitat was the northern part of America.
Choosing a soil for growing
The correct selection of soil is the key to the success of cultivation.The plant prefers slightly alkaline or slightly acidic loams. Excessively acidic soil is contraindicated for a plant: it will stop blooming, and the foliage will become faded. Liming of soil in areas with lupins is carried out every 3-4 years.
An excess of alkali in the soil will lead to the development of diseases. To plant flowers in alkaline soil, the area must first be watered with a weak acidic solution or peat added to the soil.
The flower is not very picky about the fertility of the soil, it can even grow on sand. For a bright and lush flowering, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are added to the soil.
Important! Nitrogen is not added under the plant, since it itself produces this substance in symbiosis with nodule bacteria on the roots. From fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers, the plant begins to wilt and may die. For the same reason, the flower cannot be planted in soil that has been fertilized with compost.
Lupine: Combination with other plants
Lupine looks good in mixed plantings with other plants, so it is often used in landscape design. It is best to plant it in the middle of a flower garden: plants of medium height, planted in front of the lupine, will effectively complement and emphasize its beauty, as well as protect it from the wind and prevent it from overgrowing. Pair well with lupine
- hosts;
- irises;
- daylilies;
- phlox;
- delphiniums;
- nivyaniki.


Lupine with other plants
A prerequisite for good growth and the preparation of beautiful and harmonious compositions of lupins with other plants is the observance of several rules:
- Pick up plants with similar requirements for soil, moisture and light as lupine companions.
- Plants with a short flowering period are inappropriate.
- It is necessary to take into account the timing of flowering and the height of the plants.
- Choose plants with a contrasting inflorescence shape lupine.
Growing problems and ways to solve them
The flower is affected by diseases and pests if the rules for caring for it are not followed or the requirements for the selection of a site are violated. The following conditions are harmful to the plant:
- a sharp change in temperatures;
- insufficient illumination;
- waterlogging of the soil.
A common problem is yellowing of the leaves. The reasons for this phenomenon are alkaline soil, lack of moisture, excess nitrogen in the soil. Liming the soil and timely watering helps to prevent this problem.


Sowing of lupine in the early stages contributes to a lesser development of diseases.
In unfavorable conditions, diseases develop:
- Powdery mildew. It affects the plant when cold and high humidity are combined. White bloom appears on the leaves. The plant is sprayed with Topaz, Fundazol or copper sulfate.
- Gray and brown rot. It develops against the background of waterlogged soil and thickened plantings. The plant begins to wither, dry out, a grayish or reddish bloom, brownish spots appear on the leaves. Treatment is carried out by spraying with Fitosporin preparations, Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate.
- Fusarium. Fungal disease that manifests itself during the budding period. Leaves begin to turn yellow, then turn brown, curl. They destroy the fungus by spraying with Fitosporin, Baktofit preparations.
Lupine is practically not attacked by common garden pests. But some insects can settle on a plant and cause serious harm to it:
- Phytophages: wireworm, sprout fly, May beetle larvae. These pests can attack seeds immediately after sowing outdoors. To combat them, the site is treated with an insecticide before planting.
- Aphid. Attacks inflorescences during budding. If black dots are found on the peduncle, the plant is sprayed with the preparations Aktara, Aktellik, Iskra, Alatar.
Post-flowering care


What time to collect seeds
After full ripening, the lupine bean cracks, and seeds fly out of it in different directions. In order to have time to collect them before they spill out, it is recommended to cut off the fruits after they turn yellow and begin to dry.You will have to cut it several times until you get the desired number of beans.
How to care after flowering
After flowering is over, in the first days of October, foliage and peduncles are pruned, and seeds are collected, if necessary. Perennials will need hilling, which will help cover the root collar with earth if it is exposed. Then the surface of the site is covered with a thick layer of sawdust so that the flowers do not freeze in winter.
Varieties
As already mentioned, there are about 200 subspecies of lupine in the world, but only 10 of them are domesticated. Nowadays, many breeders are working on the development of new colors, which will differ significantly from the existing ones.
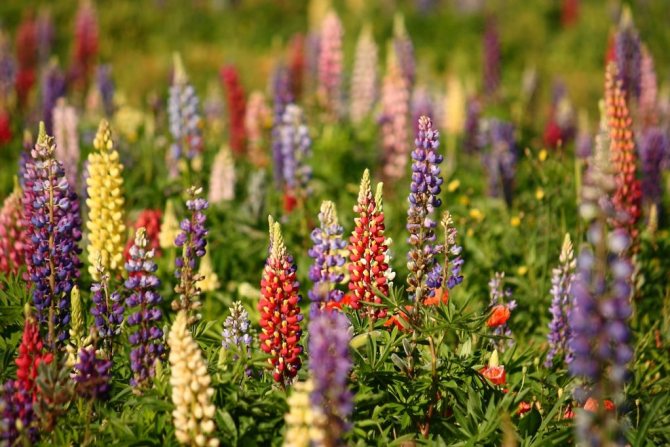


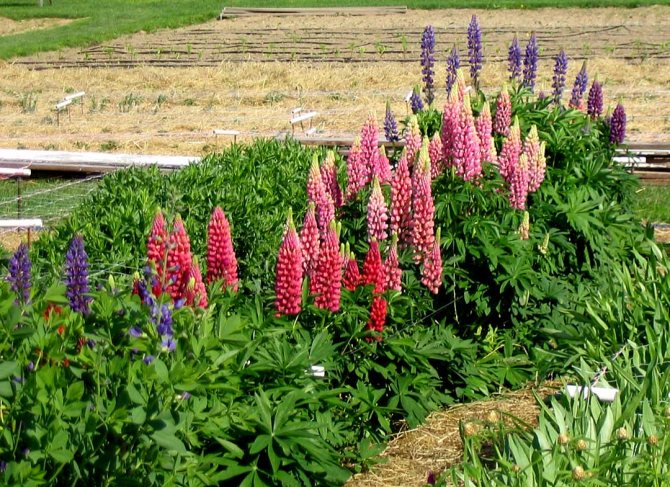
Lupine field
In multi-layer plantings, species of standard sizes are used, they look great on a distant view, they do not get lost among other plants. Most often, boles reach heights of up to 1m, but this largely depends on the soil.
It is best to pick up the plants so that they do not have sharp dividing lines, the rows should smoothly merge into one another. Then your flower bed will look like a flower bedspread.
There are also dwarf varieties, they are planted near curbs or in order to separate one part of a garden or flower bed from another. Border lupine reaches a height of no more than 20 cm and has many different colors. The methods of growing a flower are completely identical with the cultivation of other species.
Neighborhood in a flowerbed is important, it is worth carefully choosing neighbors for a lupine, the surrounding flowers should not be higher than the stem.
Lupine will get along well with:
- irises
- daylily
- hosts
- delphiniums
- phlox
- nivyaniks
These plants will not allow the rhizome to grow, and the nitrogen released by the plant will give enough vitality to its neighbors. Near lupine, all of the listed varieties of flowers will be especially bright.
Next, we will get acquainted with the most popular species that can most often be found in flower beds and in gardens:
back to menu ↑
See also: Alyssum: species and varieties of plants, sowing seeds in open ground and caring for a rainbow carpet on the site (130 Photos) + Reviews
Roussel
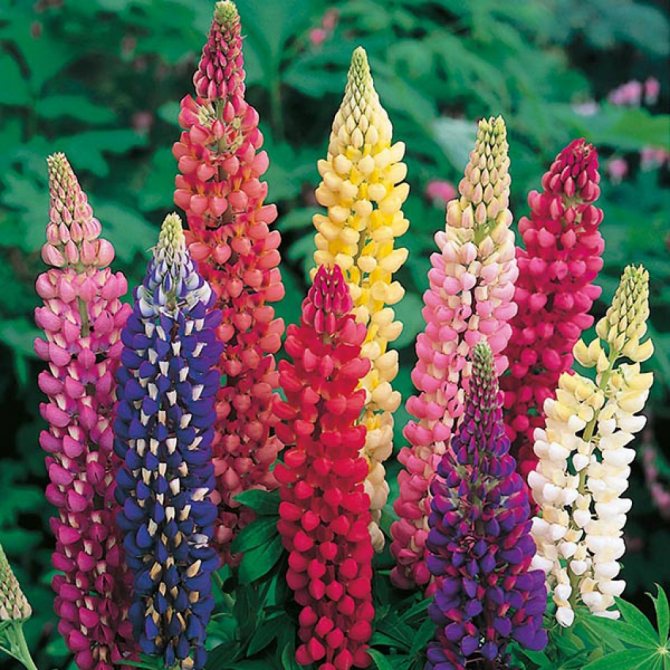


Lupine Roussel This variety is referred to as perennials, usually seeds are sold in special stores with a mixture. The team includes stems with different brush colors, they can be yellow, white, carmine, pink, blue.
The stem is characterized as follows:
- erect plant, with a powerful trunk
- reaches a height of 1-1.3 m
- each brush is about 30-40 cm
- grows best in sunny areas, tolerates partial shade
Propagated by seeds, sown in open ground in early spring or before winter. The variety does not require special care, weeding, loosening the soil and periodic watering in drought will be enough. For the winter, the stem must be pruned, although the variety is considered frost-resistant, it does not hurt to cover or mulch. Lupine Roussel will perfectly tolerate short droughts, but during the flowering period it is better to slightly increase watering, then the brushes will be brighter and will delight the eye a little longer.
A distinctive feature of the variety is that the brushes can be used for cutting, this stimulates the re-flowering of the stem in July-August. The plant looks great in group plantings, single copies are also good. Roussel is one of the most nitrogen-containing varieties of garden lupine.
back to menu ↑
See also: Anemones: 25 species, features of reproduction and care, planting in open ground, forcing in winter, a description of the medicinal properties of the plant (50+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Russell's Red Flame
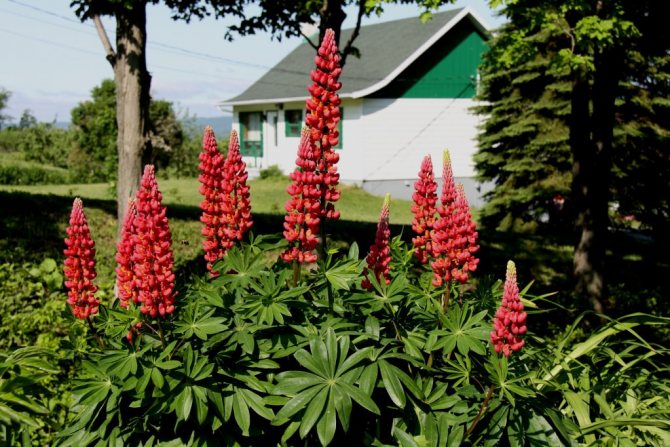


Russell's Red Flame A perennial with its bright, carmine-red tassels looks great against the backdrop of a hedge. Perfect for group plantings, it will be an excellent distant background for the rest of the flowers of a multi-layer bed. This variety will create a spectacular landscape and solo, scarlet brushes look great on any area, and the green foliage will only favorably emphasize the saturation of the color of the flowers.
The plant is sown according to the generally accepted rules for lupins; with the correct work, flowering begins in late May-early June and lasts about a month. Re-flowering is possible if the cut rules are followed.
An adult bole has the following characteristics:
- plant height up to 1 meter
- flowers collected in a brush occupy about 45 cm on the stem
- the brush itself is quite dense, has many colors
- flowers are medium, up to 2 cm each
- leaves are large, finger-shaped
A distinctive feature of the variety is the special aroma of flowers, their aroma is delicate, but persistent, especially spreads in the evenings.
Reproduction is best done by seeds, cuttings may not always give the expected result. Seeds purchased in specialized stores will have a high germination rate and always guarantee an excellent result in accordance with the color of the brush.
back to menu ↑
Read also: Ageratum: description, planting in open ground and caring for it at home (30+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Governer
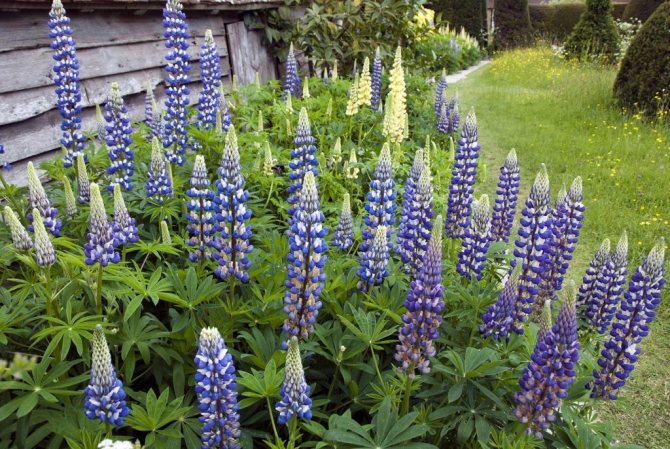


Governer This type of lupine has become the basis for breeding many varieties and hybrids for the garden. The resulting stems are distinguished by large colors, and the brush in which they are collected is denser. The governer is otherwise called multi-leaved, since its stem is covered with many large leaves.
Govrner is classified as a frost-resistant species of lupine; it is used for cultivation in multi-layer flower beds and long-range ridges.
The general characteristics of the trunk are as follows:
- an adult plant reaches a maximum height of 1.4 m;
- refers to perennials;
- inflorescence brush can reach 45 cm;
- the flowers are large, tightly pressed against each other;
- the color of the flowers is blue-white, bright;
- the stem blooms for 3-4 weeks, depending on the soil and watering;
- when trimming the brushes, re-flowering is possible in August;
- develops better on light soils;
- perfectly tolerates sunny areas, but not against partial shade;
- leaves are large, with slight pubescence on the underside, have a bright green color.
Brushes look great in prefabricated bouquets, but won't last long. Governer loves to solo, but it is better to admire him in a flower bed. The species is usually propagated by seeds, but cuttings also give good results.
back to menu ↑
See also: What to plant under the trees: flowers, plants or vegetables? In the garden or garden in the shade (40+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Chatelain


Lupine chatelain A perennial with the most interesting color is the Chetelain species; the stem will also differ from its relatives in the height of an adult plant. Most often it is used in the middle line of multi-layer ridges. To soils, like all lupins, it is not picky, but it will develop better on light, loose soils, without stagnant water.
Sowing in open ground is carried out in accordance with all the rules and recommendations for this variety, seedlings appear under proper conditions in a month, flowering will not be earlier than the second year of life.
Chatelain has the following characteristics:
- the height of an adult plant reaches a maximum of 90 cm
- fingerlike leaves on high legs are alternately located along the stem
- brush can reach 35 cm
- flowers have a pleasant pink-white color
- each flower is medium size
- weak aroma during flowering noted
Abundant flowering takes place in June-July, when the brush is cut, the re-emergence of peduncles is possible. Some growers grow this species as a low hedge that divides the garden into plots.
The secret in growing is keeping the distance between the bushes, it should be at least 20 cm.
back to menu ↑
See also: Forsythia: description, planting in the open field, leaving the Moscow region to Siberia - mini-encyclopedia (80+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Russell mix


Russell mix Perennial Russell has many variegated brush colors, most often sold in prefabricated mixes of various colors.The cultivation is standard, the species is distinguished, among others, by high rates of survival even in the most severe natural conditions. Lupine of this species will easily endure drought, with proper shelter it will overwinter perfectly and in May will delight you with lush flowering.
The best places to grow will be sunny areas of the garden, but partial shade will not affect the trunk. Weakly alkaline and slightly acidic loams will allow the plant to fully show its beauty.
Russell's metrics are:
- height of an adult trunk is about 50-70 cm
- the brush is large enough, can reach 35 cm
- flowers have a variety of colors, the most common are pink, purple, blue colors
- the flower is of medium size, fragrant
The view is not suitable for a cut; it is best to admire it in its natural environment. In flowerbeds, it is better to place them in the middle rows, the low height facilitates the use in flower beds.
A feature of the species is the splendor of each brush, so there should be enough space between the plants when planting.
back to menu ↑
See also: Quince: rules for planting in open ground, caring for a fruit tree with fragrant fruits from the Moscow region to Siberia. Reproduction methods (35 Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Passion


Passion One of the most spectacular types of lupine is called Excitement, its flowers are simply gorgeous. There are no particular difficulties in sowing and further care, everything is according to the standard scenario. A peculiarity of the species is its variegation and splendor of the brush with flowers. Excitement is characterized by:
- the plant can reach 1 m in height
- a brush with flowers takes about 45 cm
- each flower is medium in size, in rare cases it can reach 4 cm
- the main use of the trunk on multi-layer flower beds and ridges in the background
- brushes are not suitable for a cut, they will not be able to please with freshness for a long time, they will quickly begin to fade
It is often used near a hedge or to create a colorful carpet in one part of the garden.
back to menu ↑
Read also: Aquilegia: 25 most common species, planting, care and reproduction rules (70+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Minaret undersized


Minaret undersized A low-growing perennial of the species looks great as a curb plant, it is often used precisely to separate sections of a garden or flower beds. The minaret will give preference to fertile soil in an area well-lit by the sun. Reproduction by seeds is preferable, but the separation of the kidney along with the root collar has proven itself well.
The variety looks great when cut; it stands in vases for a long time. Cultivation is carried out through seedlings or direct sowing into heated soil. Sowing seeds can be carried out in early April or before winter. Cutting the inflorescences will stimulate the plant to bloom again.
It is not difficult to recognize the stunted Minaret:
- the height of an adult plant does not exceed half a meter
- flower brush can reach 25cm
- flowering lasts more than a month
- leaves are green, finger-shaped on a petiole, large
- it is bad to tolerate sudden changes in temperature, therefore, when growing, it is worth considering the weather conditions
In order for the bole to grow and develop successfully, you should regularly loosen the soil and remove weeds, superphosphate is preferred among fertilizers.
back to menu ↑
See also: Perennial asters: description of 13 species, care and planting at home, methods of reproduction and growing from seeds + Reviews
Rhapsody


Rhapsody The variety is classified as a perennial of medium height, excellent for growing on "bad" soils of the site. It will withstand the winter cold in the shelter, summer drought is also not terrible. But stagnant water or flooding in the spring can destroy the trunk. Flowering is observed in the second year of life, flowers have a varied variegated color.
The general characteristics are as follows:
- perennial grows up to a maximum of one meter
- pyramid-shaped brush is up to 50 cm long
- flowers are large, each up to 3 cm
- dense inflorescence, flowers are close to each other
- great for cutting, it continues to live and smell in water
- leaves are large, emerald
The variety is used in the first year for landscaping, volumetric balls will delight the eye with luscious greenery. In the second year of life, the plant will throw itself into the eyes with variegated brushes of flowers of various colors.
back to menu ↑
See also: Badan: description, types and varieties, planting and care in the open field, medicinal properties and contraindications (60+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Tree-like
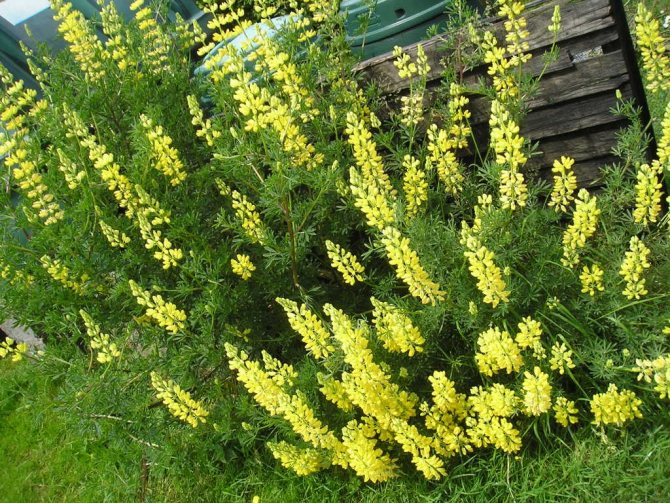


Tree lupine Perennial, which differs from other varieties and species with a powerful trunk with a kind of bark. The bole can reach a height of 1.5 meters; under proper conditions, two-meter plants are also found. The flowering period begins in the second year after sowing the seeds, and lasts a little more than a month. Usually takes place in July-August, brushes are large, fragrant, flowers can reach 5 cm.
In the middle lane, this species does not grow, even with shelter and mulching it often freezes completely... The southern regions are great for tree lupine cultivation.
Some gardeners plant several tree-like lupins with different colors on their site at once, they look very impressive during the flowering period, but the leaves are no less decorative. Luscious greenery will transform any garden.
Pests
- Seeds and young parts of the plant are especially easily exposed to pests such as: wireworms, larvae, beetles, sprout flies, centipedes, caterpillars.


At the beginning of the spring season, the conditions do not allow the plant to develop fully, the pests of young shoots are lupine, striped, bristly weevils, the mowers immediately begin to act. During the growing season, significant harm can be caused by sucking dangerous insects: aphids, bugs, thrips.
Interesting!
Of the vast number of 53 harmful species that have been noted around the world, an incredibly large number of coleopteran insects are observed in our country. The indicator of these pests is equal to 37.7%. Lepidoptera come after the list, their number is 26.4%. There are many more different types of harmful insects, whose origins are hidden from view, but scientists hope that they are not as striking as the ones listed above.


- Among all the listed insects, the alfalfa aphid stands out. Insect pests initially damage the leaves and flowers. Often, the plant is exposed to the same action when leaf-eating scoops appear, usually cabbage, alfalfa, gamma scoops. Leaf rollers also do a lot of harm. On rare occasions, lupine exposes bean moths, caterpillars that prefer to eat grains inside mature beans.
- In addition, in the stalks of lupine, the development of caterpillars of the stalked moth is quite often observed, after its appearance, the stalk of the plant breaks.
To maintain the health of the flower, it is recommended to often look after the condition of the plant. After all, it is thanks to this that gardeners can save the life of their garden, and not just one culture.
Benefits on the farm
Periodically, plants should be planted in the garden that improve the quality of the soil (green manure). One of them is lupine. The developed root system develops quickly and effectively loosens the soil. It makes it lighter, more permeable. At the same time, the roots hold together too light sandy soils, forming a fertile layer and protecting against erosion.
It is best to grow an annual lupine as a green manure. Already in 2 months, it builds up a large green mass, which allows the plant to be used after harvest. In the process of growth, nitrogen-fixing bacteria saturate the soil with nutrients, which, when decomposed, process worms and microorganisms. One sowing is similar to the application of 200 kg / ha nitrogen. Also, the resulting humus contributes to the uniformity of the earth. To enrich the soil, lupine is cut off and the site is dug up at the budding stage.The decomposition process takes place quickly with sufficient humidity.


Also, the plant is an excellent forage crop. Its fruits contain a lot of fat. Lupine shows the highest productivity on acidic soil. For the preparation of animal feed, it is customary to use white and yellow species. Blue-flowered varieties contain too many alkaloids. They not only impair the taste, but are also poisonous. But it is these alkaloids that scare away harmful insects. The parasites eat the leaves and die, so the blue lupine should be planted near the beds.
Lupine in landscape design
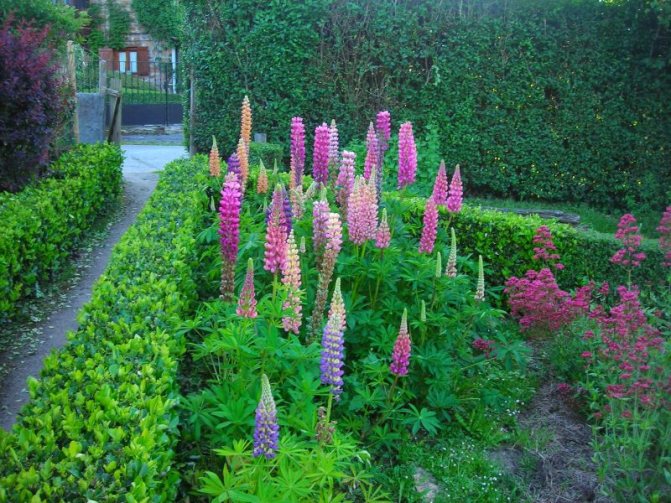
Do not underestimate the role of lupine in landscape design; with proper use of its merits, it will become the king of any suburban area. Lupine fits perfectly into any style direction: from classics to modern concepts, or simply creates a “wilderness area”. Combines with many plants.


Lupine in landscape design
Most often, lupines are located in separate groups with other perennials in a mixborder, or on an open lawn. Lupine looks good at the entrance area, in the front garden near the house or along the buildings. In group plantings, lupines are placed in the background. Low-growing varieties are used for planting along curbs. You can combine lupines of different varieties and colors or create monochromatic compositions, it all depends on your imagination and the impression you want to create.


























