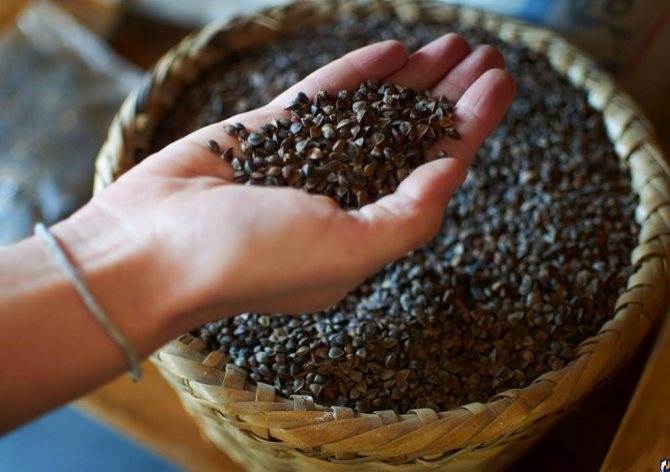
Sowing buckwheat - description
The people call such cereals Greek or black wheat, buckwheat. This is the type of cereal of the Buckwheat family, which is processed into buckwheat, beloved by everyone in our country - the basic product in the diet of most Russians.
In addition to unground, in Russian cuisine they use buckwheat prodel, as well as buckwheat flour. The mass cultivation of buckwheat began in the seventh century, when it was brought from Byzantium. Then it was called Greek wheat. Monks who came from Greece to our monasteries also brought buckwheat seeds with them.
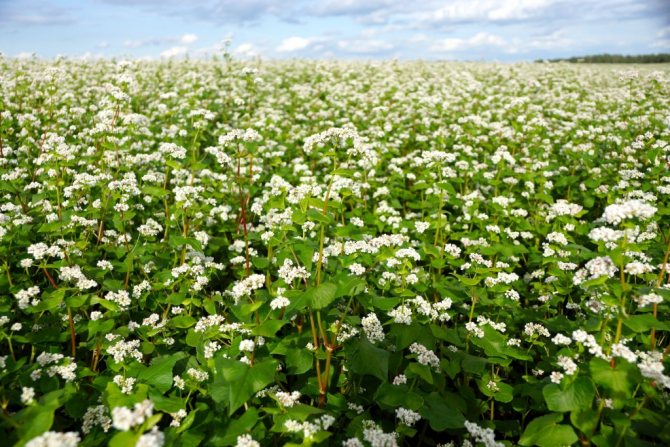

In June-September, the plant enters the period of budding and flowering.
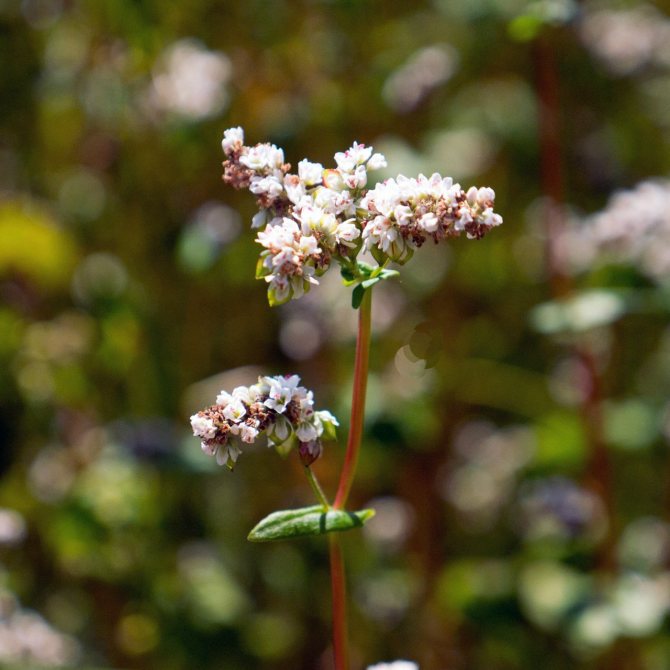
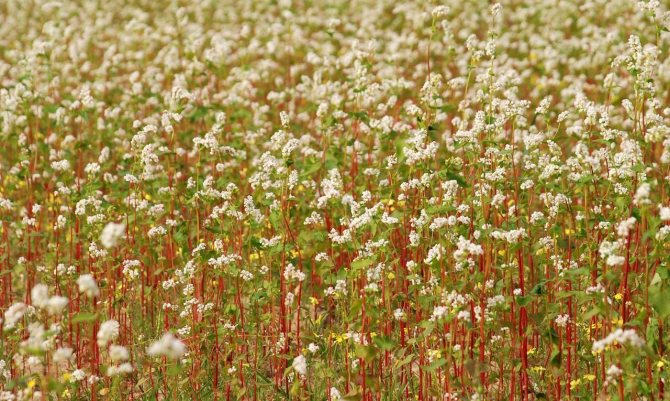
Common buckwheat can be identified by its erect, ribbed, reddish (darkens with growth) stem up to 70 cm tall, with two types of leaves. The lower leaves, in the shape of a heart, have a small petiole, the upper ones are in the form of an arrow hugging the stem.
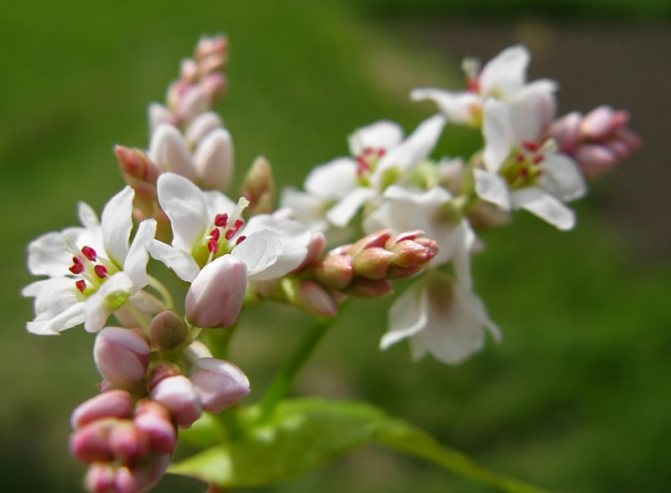
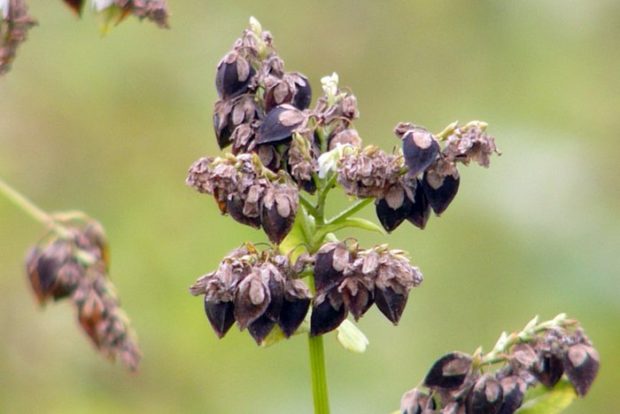
The flowering period for buckwheat is June-September. At this time, brushes with pink, white or red fragrant flowers on 5 petals appear. Buckwheat is an excellent honey plant: bee hives are always located in the vicinity of fields sown with this crop. The fruits of the cereal are triangular, brown or gray in color in the form of a nut with sharp edges, covered with a film sheath.
The cereal is harvested in September-October. The plant is moisture-loving, loves warmth, therefore it is cultivated in regions with a mild climate.
Buckwheat gives itself to a person completely: first of all, it is dietary cereal, as well as wonderful honey with special medicinal properties. The aerial part of the plant is processed to obtain components of various drugs - phagoprin, rutin, rutamine, urutin.
Buckwheat honey is of particular value. It differs from the usual floral counterpart with an amber color in darker shades (over time, the tone may change to a lighter one) and a special aroma. As a medicine, it is prescribed for anemia, iron deficiency, chronic bronchitis.


Due to its unique composition and nutritional value, buckwheat honey is a universal remedy for curing a wide range of problems related to human health.
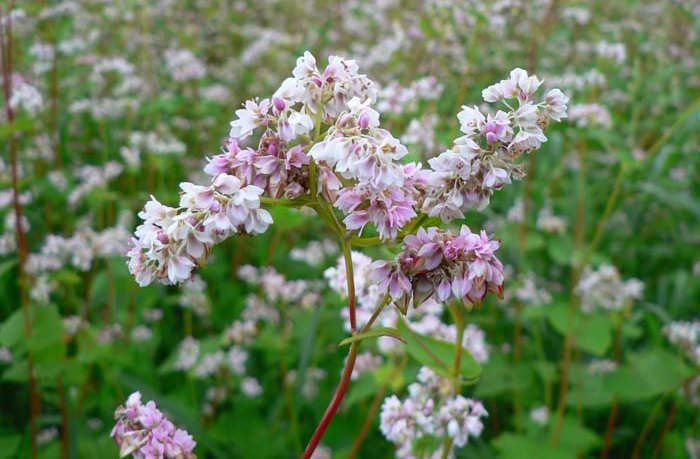
Buckwheat during flowering
Cultivated buckwheat is a well-branched and tall plant with a developed and powerful root system. The average height of the stem varies depending on the type and variety, but usually ranges from 70 to 110 cm. The root of the plant has an increased physiological activity, which explains the property of buckwheat to displace weeds from the fields. The three-tiered root system can lie at a depth of 1 m or more, providing the culture with all the necessary nutrients, even in poor soil.


The stem of buckwheat is hollow and slightly ribbed, branched, 2.5 to 8.5 mm thick. The branching zone is located just above the lower cotyledon node. The leaves are pointed, triangular or oval. From the axils of the fourth-order leaves and branches, thin and hairless peduncles are formed, on which an inflorescence of 2-5 flowers is formed over time. With good care on one plant, up to 3000 milky white, pinkish, red or white-pink flowers are revealed during the flowering period.
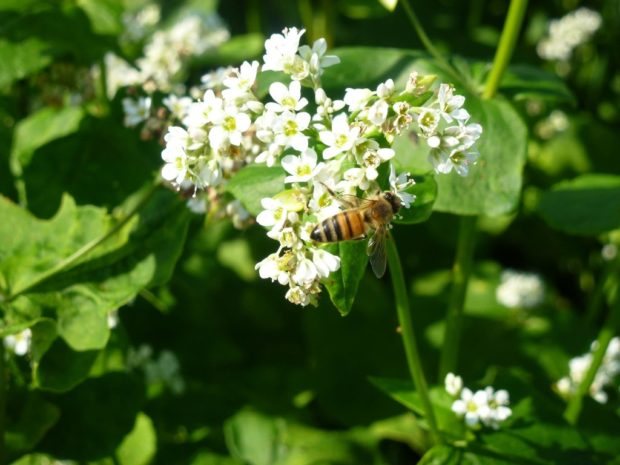


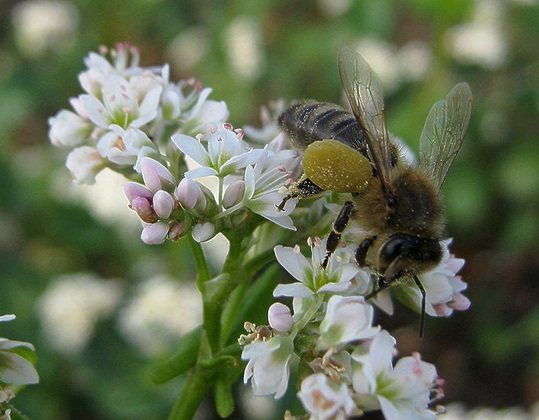
Varietal buckwheat blooms since the end of the formation of the root system, and this period is the most energy-consuming in the life of a plant. The mass of the aboveground part of buckwheat increases 2-4 times during flowering. Despite the fact that breeding buckwheat varieties are cross-pollinated, bees are needed for a good harvest. Flowers have open and easily accessible nectaries for insects, which facilitates pollination work.
How is the harvest going
Like the flowering period, buckwheat has a long ripening period. Buckwheat groats grown in Russia are usually harvested from the fields in a separate way. Due to the extended ripening period, it is difficult to determine the start date for harvesting fields. During early harvesting, yields are reduced due to the large number of unfulfilled grains, and late harvesting suffers losses due to abundant shedding of grain. Also, the determination of the start date of harvesting is hampered by the tendency of buckwheat to secondary fruit formation. It occurs if at the beginning of fruit formation there was a drought, followed by heavy rains.


Usually, farmers start by harvesting those buckwheat fields where about 75% of the grain is ripe. Mowing and swathing takes up to 5 days, and by the time the work is finished, the grain is ripe for 95-98% of the field. To determine the percentage, a seed sample is taken from 10 plants in 5-7 different sowing places, and the number of mature seeds is calculated from the total number. If during harvesting the weather is dry and hot, then it is advisable to mow in the morning and in the evening: at this time the stalks do not break, and the grain falls off less.
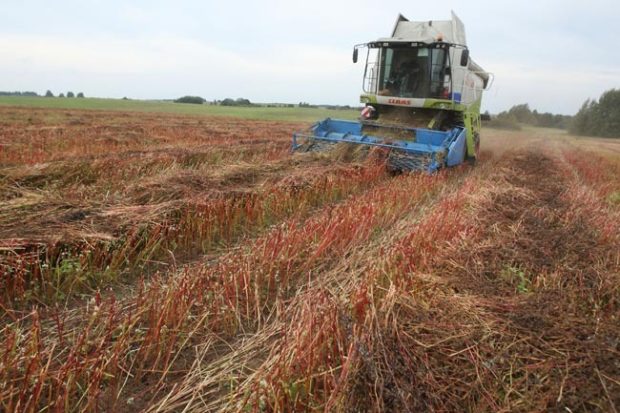


Mowing is carried out using combine harvesters with mounted headers (ZhVN-6A, etc.), and for mowing clogged or lodged buckwheat, headers of the ZhKS-4A class are used. The rolls are threshed usually 3-6 days after mowing at a grain moisture of 14 to 17%. After threshing, the grain heap must be passed through cleaning machines to screen out chaff seeds and weeds, and then dried to standard moisture content or sowing condition if the grain is to be used in the next agricultural year.
Growing buckwheat
For seeds to germinate (they are sometimes used in dietary nutrition), 7-8 ° C is enough. If the ground warms up to 15 ° C, seedlings will appear on the 7-8th day. Buckwheat is sown late, when the threat of frost completely disappears. Soil temperature should be 12-15 ° C.
A lot of time passes from the appearance of the first shoots to budding, further growth and maturation are accelerated. Before the seeds appear, the plant must accumulate 70% of the total dry matter. A comfortable temperature for the culture is about 20 ° C.


Buckwheat is not only a thermophilic culture: it needs high humidity. It is in such conditions that the maximum yield occurs. Fragrant inflorescences appear 18-28 days after germination. The culture ripens within a month, on the 25-35th day from the moment the first flowers appear.
Bees significantly increase the buckwheat yield, so it is advisable to put an apiary on the field at this time. The growing season is 60-120 days.
Buckwheat as siderat (video)
This crop is usually planted quite late, so the main task during soil cultivation is to retain moisture. In addition, it is necessary to follow the rules of crop rotation, planting buckwheat after the "right" crops. The best predecessors of buckwheat are:
- winter crops;
- peas, beans, soy;
- cultivated.
It is better not to plant this cereal after grain crops, since the soil is heavily contaminated with weeds, which significantly reduces the buckwheat yield. Also, the yield of this cereal crop will be low if it is planted after potatoes, diseased with a nematode, or after oats.
But buckwheat itself most often displaces weeds from the field, therefore, where it grows, herbicides are not used.


Preparation of medicinal raw materials
The tops of the flowering aerial parts, as well as cereals (ground powder), are of medicinal value.
It is better to harvest raw materials in June, at the very beginning of flowering, when the green mass has not yet lost its strength. The leafy part of the stem, together with the flowers, is dried in a dark, ventilated place or in special dryers at a temperature of 30–40 ° C. When fresh, this part of the plant is toxic, so you should not use it for the preparation of medicines, but during processing, all the poisons evaporate.
Buckwheat (groats) is harvested in September-October, as it ripens. It is not found in the wild today, but cultivated varieties are cultivated everywhere - in Russia (up to the Urals), and in Belarus, and throughout Ukraine. Straw and other wastes from grain processing serve as valuable animal feed.
Where and how does it grow?
Buckwheat fields in Russia can be seen primarily in the middle lane. Moderate heating is very important for this plant. If the air temperature exceeds 30 degrees, it immediately affects the culture very badly. In this case, the ground must be thoroughly warmed and fully illuminated. Most often, they try to plant buckwheat surrounded by trees (to protect from the piercing wind), bring it closer to water bodies


Buckwheat differs only in minimal capriciousness. But there are still preferred soils for it. The crop gives the highest yields in the forest-steppe zone. Experts, choosing a site for buckwheat fields, are looking primarily for light, loose soil. She is likely to keep warm in all conditions.
Preferred soils are those that contain a certain level of nutrients. In autumn, the depleted soil must be saturated with organic matter and mineral compounds. Both excessive acidity and significant alkalinity are unacceptable. The disadvantage of dense soil is that water can accumulate there. Best of all, if the same fields have grown before:
- beans;
- winter plants;
- row crops;
- peas and soybeans.
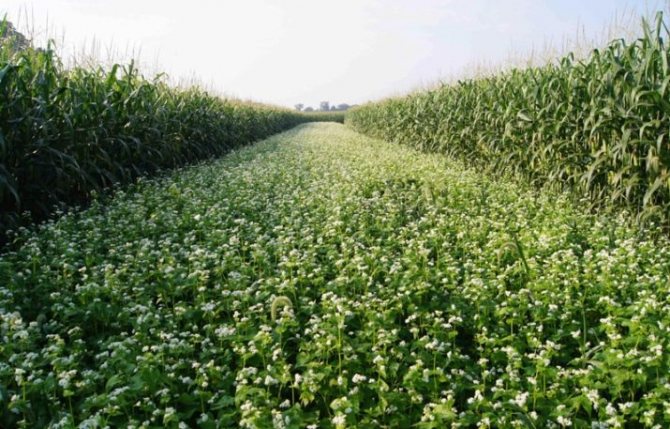


Buckwheat cannot be planted after grain plants. They lead to significant weed contamination. Such herbs significantly reduce the fertility of the crop. With caution, it is worth planting buckwheat where potatoes were previously sick with a nematode or oats grew. However, this crop effectively drives many weeds from plots of land, therefore it is grown without the use of herbicides and is used as a green manure.
In addition to Altai, significant areas are occupied by buckwheat in Bashkiria and in the vicinity of Stavropol, in Primorye and Krasnodar. Her role is noticeable in Orenburg and Volgograd. Buckwheat is also obtained in Saratov, and even noticeably further north (in Tula). It grows in black earth regions - near Kursk, Orel and Lipetsk. Interestingly, in Russia 3 times more buckwheat is grown than in the PRC.
Application in traditional medicine
Physicians and pharmacists are more interested not in cereals, but in the leafy part of the plant. Rutin is obtained from the green mass. This vitamin is indispensable in the prevention of vitamin deficiency, capillary toxicosis, hemorrhagic diathesis, retinal hemorrhage, rheumatism, septic endocarditis, glomerulonephritis and other vascular pathologies.


Rutin is obtained from the green mass of buckwheat
Preparations based on buckwheat are used in the treatment of affected vessels, when the damage is associated with the aggressive effects of anticoagulants, salicylates, arsenic compounds, X-ray therapy and oncological blood pathologies.
In drug therapy of hemorrhages, rutin is prescribed in combination with vitamin C. The presence of levicin causes the use of drugs for hepatic, cardiovascular and renal insufficiency. Improves the taste and medicinal properties of the parallel use of milk.
Buckwheat is included in the diet for weight loss. It is recommended for elderly and sick people after serious illnesses to strengthen the immune system.
Buckwheat is a valuable food crop
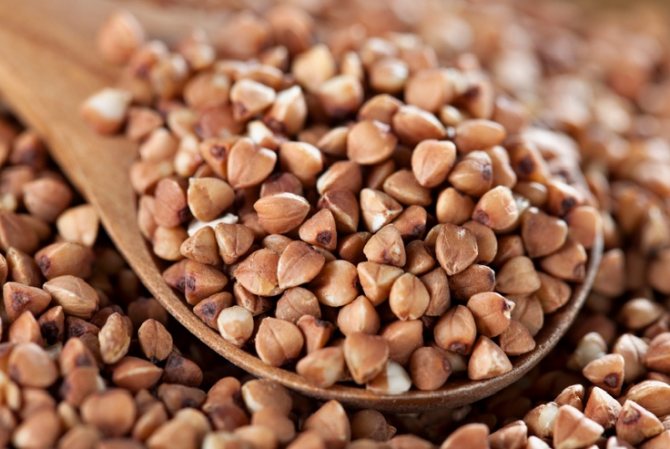
Buckwheat is a valuable food crop. Its grains (unground) are processed into cereals and flour. Buckwheat is distinguished by its high taste and excellent nutritional value.
Buckwheat protein is more complete than cereal protein. From grain processing waste, cattle feed is obtained. Calcium carbonate (potash) is obtained from plant ash, and vitamin P is obtained from leaves and inflorescences. Buckwheat is an excellent honey plant.
This plant is grown on the territory of Russia, Ukraine, Belarus. Well, they are also eaten in other territories. Buckwheat is a common product due to its nutritional value, the healing properties of the plant itself and the ability to prepare various dishes.


It is very easy to recognize the buckwheat plant by its reddish stem, flowers collected in a brush, pinkish tint, branching leaves. Plant height can reach one and a half meters. It is an annual plant that blooms in mid-summer (around July) and ripens only in August.
Buckwheat in folk medicine
Here are some recipes from a famous herbalist herbalist:
- Buckwheat flour for anemia. Sort out, rinse and heat the groats. After cooling, grind the grain. Take buckwheat flour in 2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day. You can drink it with warm milk or add warm milk to the powder. The course of treatment is 1 month.
- Flower broth for diabetes and vascular problems. Boil a teaspoon of dried buckwheat flowers in half a liter of water for 5 minutes. Insist 2 hours. After straining, drink 100 ml 3 times a day. The course of treatment is a month.
- Tea for arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis. Put 1 tbsp in a teapot. l. dried flowers and pour boiling water over. Drink 2-3 times a day (like regular tea).
- Infusion for sunburn, radiation, deficiency of routine. Heat 200 ml of water, add 1 tbsp. l. dry raw materials (flowers, leaves), keep on fire for 15 minutes (it is better to steam it). This amount gives the daily rate of routine.
- Tincture to improve blood supply, strengthen blood vessels. For 100 ml, you need to take 5 tbsp. l. dry flowers. Insist 2 weeks, drain. Drink 1 time a day, 1 tsp. before meals. The course is 1 month.
- Compress for purulent wounds. Fresh foliage should be chopped into porridge or simply folded leaf to leaf. Put the blank on a napkin and bandage it to the wound. After an hour, the compress must be removed.
- Buckwheat leaf can be used as a plantain to stop bleeding. The plant is toxic - be careful.
- Buckwheat flour powder. Instead of talcum powder when processing baby skin, you can take buckwheat flour. Any diaper rash can be treated in the same way.
- Warmer for the lower back or bridge of the nose. Buckwheat keeps heat for a long time, besides, when heated, it also releases useful substances. Therefore, it is used for rhinitis, sinusitis, radiculitis. Prepare a cotton pouch (a clean sock is enough for the bridge of the nose). Roast the groats in a frying pan until they crackle slightly. Pour the grain into a bag and apply to the problem area after cooling to a comfortable temperature.
- Buckwheat honey also has healing properties. It is indispensable for protracted bronchitis, anemia, gastrointestinal tract pathologies.
Description and composition of buckwheat
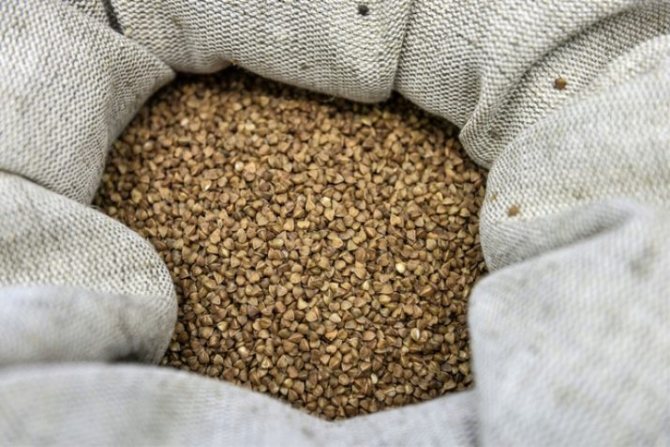
Sometimes buckwheat is thermally processed and raw or green. Unlike fried cereals, green buckwheat can sprout. Buckwheat can be stored for a long time. It is obtained after threshing and dehulling the grains.


The cereal contains:
- 60% carbohydrates (starch and sugar);
- well digestible proteins (a lot of lysine and methionine);
- fixed oils;
- organic acids;
- vitamins (riboflavin, thiamine, folic acid, tocopherol);
- mineral salts (Fe, P, Ca, I, Zn, Co).
Buckwheat is used in cooking for the preparation of various cereals, casseroles, buckwheat flour, salads with sprouted grains.
Contraindications and undesirable consequences
The high concentration of rutin, which is included in all buckwheat-based medicines, makes all drugs dangerous for people with increased blood clotting.
Fresh leafy part of the plant and preparations based on it are not recommended to be taken orally due to the high probability of undesirable consequences, since it is poisonous. Restrictions do not apply to the external use of the plant - in the treatment of wounds, freshly harvested leaves work as an antiseptic and coagulant.
Buckwheat as a honey plant
It is buckwheat honey that is considered one of the best among beekeepers. Buckwheat flowers are excellent honey plants, their flowering time directly depends on weather conditions. In the sunny season, buckwheat inflorescences do not fade for up to 1.5 months. The scent of small flowers attracts bees. These flying insects from one hectare of buckwheat collect up to two hundred kilograms of honey that is very useful for health, which has a rather sharp aroma and taste.
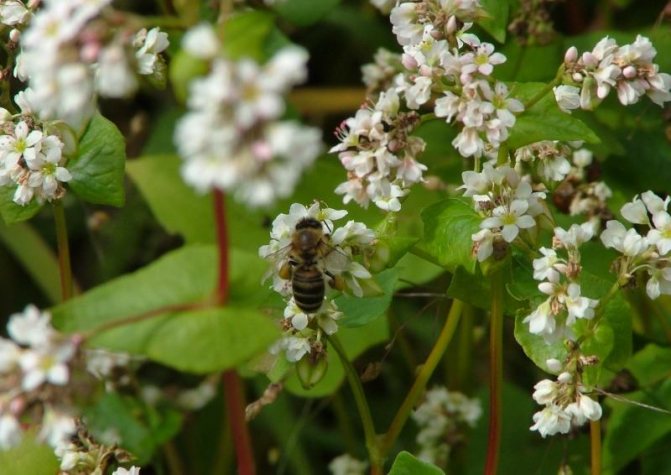


The color of fresh buckwheat honey is brown. It does not crystallize for a long time. And to eat regularly pure buckwheat honey should be people with the following diseases:
- with high blood pressure;
- various diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- improves metabolism in the body;
- increases hemoglobin, contains a large amount of iron, therefore it is recommended for expectant mothers to eat;
- necessary for those recovering from surgery or large blood loss.
Application in nutrition
In cooking, soups, casseroles, cereals, jelly, pancakes and other pastries are prepared from kernels or chaff and flour. Buckwheat flour is also sometimes added to confectionery.
The physiological norm for one person is 7–8 kg of buckwheat per year. Here are a couple of the most popular recipes.
Buckwheat soup
In the broth, boiled in half, put pieces of potatoes, buckwheat calcined on the fire, bay leaf (if the broth is not chicken) and boil for 15 minutes. Season with browned onions and carrots.
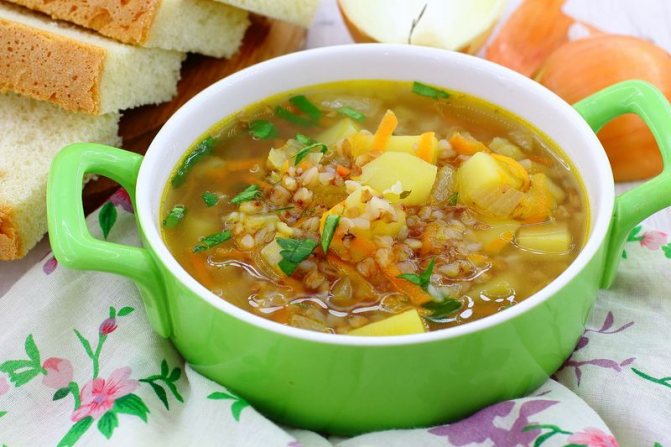


Buckwheat dumplings
Prepare buckwheat flour using a coffee grinder. Add a little salt and soda, quenched with vinegar, egg, cream and butter (vegetable). Part of the buckwheat flour can be replaced with wheat flour. The dough should be firm, smooth and loose. It is convenient to shape the dumplings with a spoon.
Collect half and dip the dough in boiling milk or water. Cook over low heat until tender.
Almost unknown in Western Europe, buckwheat has firmly and for a long time settled in the countries of Eastern Europe, in Russia - it is one of the most important cereal crops. It was not for nothing that the commander Suvorov considered buckwheat porridge the food of heroes. Buckwheat flour was poured around the house to protect it from harm.
To save the family from poverty, buckwheat was always kept in the kitchen. And today it makes up a significant part of the diet of many Russians, fully justifying the popular wisdom: "Rye bread is our own father, buckwheat porridge is our mother."
Where buckwheat is grown
In world grain production, buckwheat is not as important as wheat or oats, but many countries grow high-quality buckwheat for feed and food purposes. In some regions (Altai in Russia, central regions in China, etc.), field buckwheat is actively growing as a weed plant: it differs from varietal in lower yield and unsuitability for flour production.
Rating of Russian regions by acreage
In 2016-2017, the Altai Territory became the leader in terms of growth in the area of cultivation of crops. The sown area has grown by almost 95 thousand ha. In the Penza region, the increase in fields exceeded 17 thousand hectares, and in Bashkiria - 12 thousand hectares. A significant increase in cultural fields was observed in 2020 in the Saratov, Novgorod regions, Tatarstan, Voronezh and Kemerovo regions, in the Republic of Khakassia.


Buckwheat seeds Arno Canada
Areas of cultural cultivation of buckwheat according to sown areas in Russia look like this:
- Altai Territory - 561 thousand hectares with an average yield per hectare of 11.5 centners;
- Bashkortostan - 99.5 thousand hectares with a yield of 10 c / ha;
- Orenburg region - 86 thousand hectares with a yield of 10.6 c / ha;
- Oryol region - 75 thousand hectares and 11.3 centners / ha;
- Kursk region - 32 thousand hectares and 12.4 c / ha;
- Voronezh region - 31.5 thousand hectares and 11.4 centners / ha.
The regions with the record for the number of sown fields also include the Chelyabinsk and Tula regions, Tatarstan, the Penza region and the Krasnodar Territory.
Factors influencing the growth of cultivated land
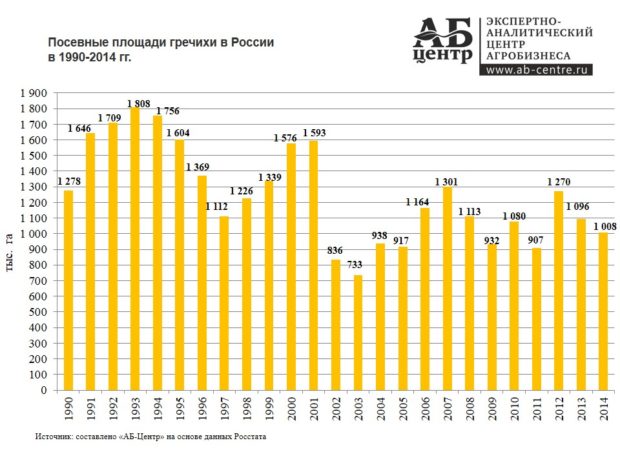
The main factor that influenced the increase in the area of cultivation is an increase in demand for cereals and a high price level. Gross harvests increased more than the sown area and reached record levels: 1,187 thousand tons against 860 thousand tons in 2014-2015.Along with the record production rates in recent years, export and import shipments have decreased, which made it possible to support the domestic market and manufacturers. High prices for cereals made it possible to grow buckwheat with minimal risks to the farm, which increased the interest of farmers in the crop.

An additional factor that made it possible to increase the sown fields is climatic and soil conditions. In the regions where food buckwheat is grown in Russia, the condition of the soil has improved due to the application of fertilizers, and milder winters are also observed.
Other countries where the culture is grown
In 2020, Russia was the leader in buckwheat production. In the second place in the production and consumption of buckwheat porridge in the world is China with a yield of 405 thousand tons. In the top ten countries:
- Ukraine - 180 thousand tons;
- France - 122 thousand tons;
- Poland - 120 thousand tons;
- Kazakhstan - 90 thousand tons;
- USA - 75 thousand tons;
- Brazil - 63 thousand tons;
- Lithuania —50 thousand tons;
- Japan - 30 thousand tons


Also, good harvests are taken in Tanzania, Latvia, Australia and Belarus. The main importing countries of cereals are Japan, France, Italy and Spain, and the leading exporting countries with a market share of up to 70% are the USA, Poland, Russia and China.
When is the harvest?
As already mentioned, buckwheat blooms systematically over a long period of time. There is no way to wait until the brushes are fully ripe. Therefore, they begin to harvest when the lower grains ripen, when they acquire a brown color. In a healthy plant, then almost ¾ of the formed seeds reach the technical maturity. A careful selection of the time of its mowing helps to exclude shedding of buckwheat.
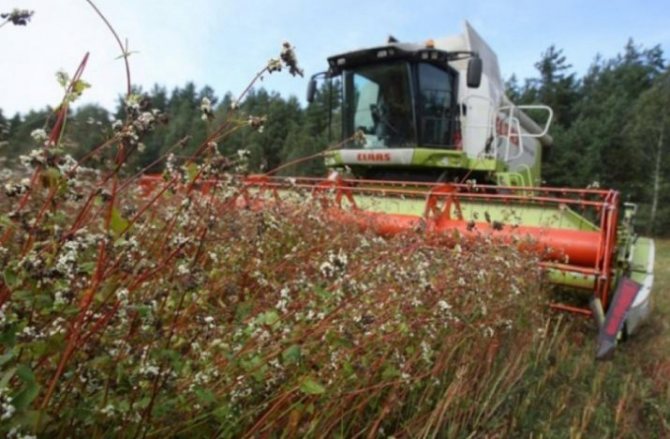


This work is done in the early morning hours or after sunset. At such a time, the high humidity of the air helps to exclude negative phenomena or radically reduce them. Modern harvesters for harvesting buckwheat are capable of processing grain kernels during the harvesting process. In most cases, fruits are harvested from September 20 to 30. An exception is made only when the weather is atypical, which impedes the development of plants or is favorable to it.
The harvested crop is threshed immediately. The resulting grain must be sorted out and sent to the winter warehouse. Sorting is carried out immediately - what to use for sowing and what to ship to consumers.


See how buckwheat grows in the next video.
Soil preparation


For buckwheat, autumn plowing or digging of a small plot of the dacha is necessary. Usually they dig or plow to a depth of twenty centimeters. In the spring, to preserve moisture from melting snow, snow retention should be done, or moisture should be covered from losses.
Be sure to cultivate the soil in the spring with appropriate devices. A suburban walk-behind tractor is ideal for these purposes. Having loosened the top layer of the soil, it is harrowed, in order to determine the places-depressions for the seeds. It is not advisable to plow or dig up the plowing in the country in the spring in order to prevent the loss of spring moisture in the soil.
Digging a summer cottage for buckwheat in the spring is necessary in case of excessive moisture or strong compaction on the ground.
When various weeds or their organs are found on the soil, which can lead to reproduction, they should be selected so that there is no clogging of the area with weeds.
Content
Different sources say different data about the homeland of buckwheat, most often Ukraine is mentioned, as well as North India and Nepal, where it is called "black rice". [ source not specified 898 days
] Wild plant forms are concentrated on the western spurs of the Himalayas. Buckwheat was introduced into culture more than 5 thousand years ago.
In the 15th century BC. e. it penetrated into China, Korea and Japan, then into the countries of Central Asia, the Middle East, the Caucasus, and only then into Europe (apparently, during the Tatar-Mongol invasion, therefore it is also called the Tatar plant, the Tatar). In France, Belgium, Spain and Portugal, it was once called “Arabian grain”, in Italy and Greece itself - Turkish, and in Germany - simply pagan grain. The Slavs began to call it buckwheat because it was brought to them from Byzantium in the 7th century [4]. According to another version, it was cultivated mainly by Greek monks at monasteries [5].
In many European countries it is called "beech wheat" (German Buchweizen) because of the similarity of seeds to beech nuts. Hence the Latin name of the genus Fagopyrum - "beech-like nutlet".
In the folk calendar of the Eastern Slavs there is a day called Akulina-buckwheat, which falls on June 13 (June 26). The name is associated with Saint Akilina. She was considered the patroness and accomplice of the buckwheat harvest [6], and Akulina's day on June 13/26 was the last sowing date for this crop.
Flowers, collected in loose inflorescences, are white or pink in color. They appear in July and attract bees.
Read also Borscht with cauliflower recipe with photo
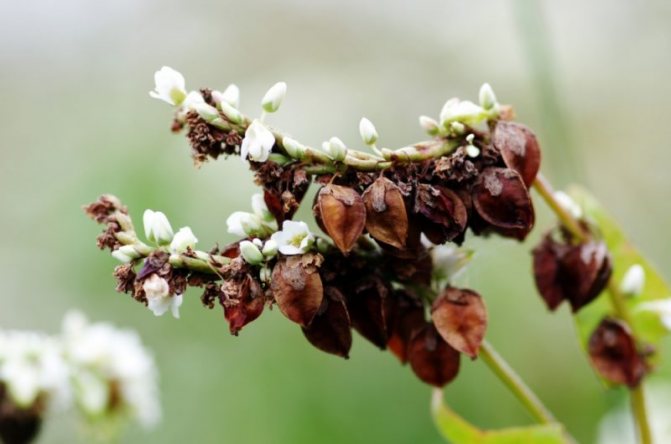
After the plants have faded, small triangular seeds are tied on them, ripening in September - October. They have a three-sided shape, light green color and sizes from 5 to 7 mm in length and 3 to 6 mm in thickness. The buckwheat fruit is a triangular nut. The fruits ripen very unevenly: the lower, ripe, easily break off and crumble, while the top is still covered with flowers.
Buckwheat is a late culture. In Russia, harvesting begins in late August - early September.
Of the nematodes, the microscopic rye eel (Tylenchus devastator Kühn), penetrating into the stem, retards the development of the entire plant, especially the inflorescences, and causes disease.
Buckwheat contains a lot of iron, as well as calcium, potassium, phosphorus, iodine, zinc, fluorine, molybdenum, cobalt, as well as vitamins B1, B2, B9 (folic acid), PP, vitamin E. The flowering aboveground part of buckwheat contains rutin, phagopyrin, protequic, gallic, chlorogenic and caffeic acids; seeds - starch, protein, sugar, fatty oil, organic acids (maleic, menolenic, oxalic, malic and citric), riboflavin, thiamine, phosphorus, iron. By the content of lysine and methionine, buckwheat proteins surpass all cereal crops; it is characterized by high digestibility - up to 78%.
Carbohydrates in buckwheat, as well as in other cereals (pearl barley, millet), are about 60% [8]; the available carbohydrates are absorbed by the body for a long time, due to which, after eating buckwheat, you can feel full for a long time. When stored for a long time, buckwheat does not turn rancid, like other cereals, and does not grow moldy at high humidity.
Getting honey
Buckwheat is the main honey plant for many regions of Russia with light sandy loam soil. The fodder base of beekeeping and the production of honey there largely depends on the state of buckwheat sowing. In favorable years, up to 80 kg of honey is obtained from 1 hectare of crops in areas with normal moisture (in arid regions, honey collection from buckwheat is extremely unstable).As a cross-pollinated, mainly entomophilous plant (pollinated by insects), buckwheat requires at least 2–2.5 colonies per hectare [9], which also provide up to 70% of seed production.
Buckwheat flowers give a lot of nectar and greenish-yellow pollen. Abundant nectar release is observed in warm and humid weather in the first half of the day (in hot and dry weather, bees stop taking nectar). Buckwheat honey is dark, brown with a reddish tint, fragrant, spicy [9].
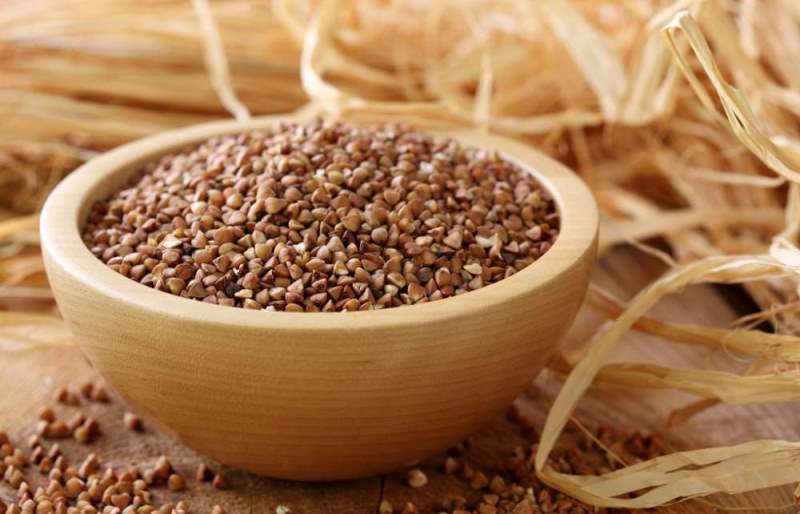
Eating edit
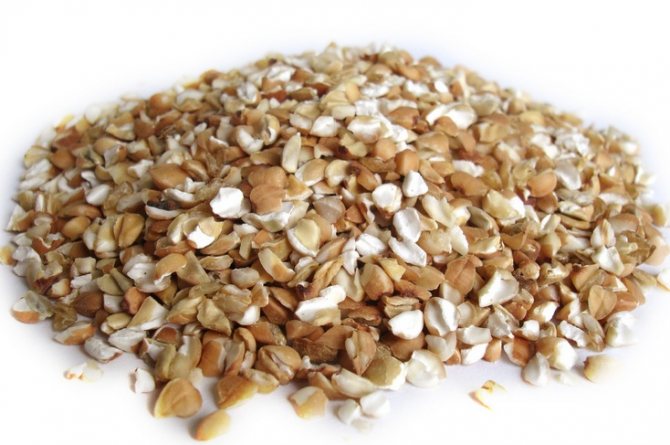
Buckwheat fruit is a common food product. Several varieties of cereals are known: unground
- whole grains, large and small
done
- crushed grains,
smolensk groats
- crushed kernel. Groats on sale, hydro- and heat-treated (from black to light brown), are used to make buckwheat porridges, casseroles, puddings, cutlets, soups, and buckwheat tea is also popular in the East. Buckwheat grain is ground into flour, but due to the lack of gluten, it is unsuitable for baking bread without adding ordinary flour. It is used for pancakes, pancakes, tortillas, dumplings.
From a mixture of buckwheat and wheat (or other) flour, noodles and pasta are obtained, which are traditional for Japanese (soba) and Alpine Italian (pizzokeri) cuisines. In France, traditional Breton pancakes (fr. Galette bretonne) are made from buckwheat flour. The traditional dish of Eastern European Jews is “varnishkes porridge” - buckwheat porridge mixed with noodles. It is widely used as a side dish in the countries of the former USSR (in the form of porridge) and very little in Western European countries, with the exception of the aforementioned examples. In recent years, a slight increase in the consumption of buckwheat products in the West is associated with its use for dietary purposes.
Uncooked cereals (grassy green) known as "Green buckwheat"
, is considered a dietary and "healthy" product, and it costs two or more times more expensive than ordinary processed buckwheat. Porridge and other dishes are also made from it. In China, unroasted buckwheat grains are used to make tea, which is believed to lower blood pressure [10].
Buckwheat and flour are stored for a long time and are very suitable for storage in army warehouses, since the fats they contain are resistant to oxidation.
Biological Pest Control Edit
Buckwheat is now being studied and used as a source of pollen and nectar to increase the number of predatory insects for biological pest control in New Zealand [11].
Medical applications
The tops of flowering plants serve as raw materials for obtaining rutin, which is used in medical practice for the treatment of diseases accompanied by increased permeability and fragility of blood capillaries. Rutin and phagopyrin are abundant in flowers and upper young leaves of buckwheat, a decoction or infusion of which is indicated for hemorrhagic diathesis, hypertension, measles, scarlet fever, atherosclerosis, radiation sickness and other serious health disorders. Buckwheat is used for varicose veins, hemorrhoids, rheumatic diseases, arthritis and as a prevention of sclerosis. The high content of lecithin determines its use in diseases of the liver, vascular and nervous systems. Able to raise the level of dopamine (a neurohormone that affects physical activity and motivation).
In folk medicine, a decoction of the plant is recommended for colds, and also as an expectorant for dry coughs. For medicinal purposes, flowers and leaves are used, harvested in June - July, as well as buckwheat seeds - as they ripen. In the old manuals, buckwheat porridge was recommended for large blood loss, colds.Buckwheat is rich in folic acid, which stimulates hematopoiesis, increases the body's resistance to the effects of ionizing radiation and other adverse environmental factors. The significant amounts of potassium and iron contained in it prevent the assimilation of their radioactive isotopes. For diabetics, this cereal replaces the consumption of potatoes and bread.
Poultices and ointments made from buckwheat flour are used for skin diseases (boils, eczema). Fresh leaves are applied to wounds and abscesses. Flour and powdered leaves are used as powders for children.
Buckwheat honey is used for anemia, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and skin diseases.
The largest buckwheat producer in the world is Russia, in 2016 it produced almost half of the world's crop production (1.186 million tons out of 2.396 million tons).
Read also Varieties of onion sevka for the Moscow region
The buckwheat yield in Russia is about 8-10 centners per hectare, which is almost two times lower than, for example, wheat. The maximum yield is 30 c / ha (3 t / ha or 300 t / km²). Thus, the FAO database [12] provides statistics for Russia:
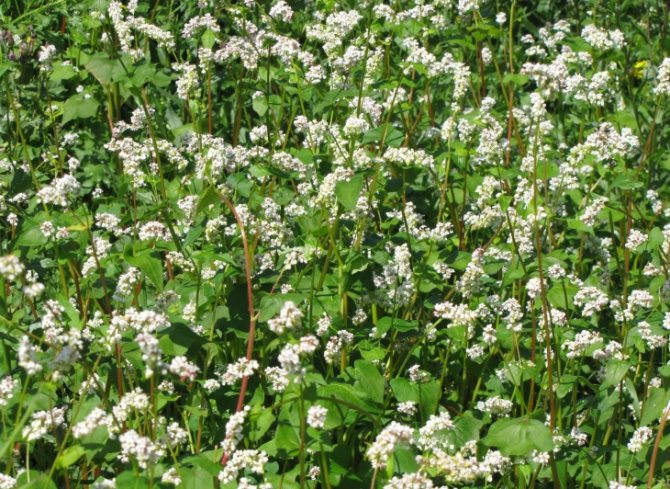
Buckwheat is a very useful product that has medicinal properties. In the photo, buckwheat seems to be an ordinary plant, but this is not entirely true. How much benefit this crop brings. Buckwheat is widely and versatile used in many industries. Have you seen how buckwheat blooms? The photos below will allow you to enjoy the beauty of buckwheat fields.
The importance of cereals in the household
7 reasons to plant buckwheat in your garden:
First of all, it is a valuable cereal known for its dietary and nutritional properties for the human body. Its chemical composition contains a lot of potassium, calcium, iodine, zinc and iron. The fruits of the plant contain a large amount of vitamins.
Buckwheat is an insurance crop; in the event of the death of early plantings, it is planted in the vacant place as a green manure.
Growing buckwheat
The plant displaces weeds, suppresses and kills them at the root, leaving behind a perfectly clean area.
Waste left over from grain collapsing, straw and chaff is excellent livestock feed. Crushed husk or ash from it is a useful fertilizer for the garden. It is characterized by specific root secretions that reduce the attack of other crops-followers by rot.
The plant is an excellent honey plant and is one of the most important crops for beekeeping. Planting on a buckwheat site is a great way to attract beneficial insects to it.
The leaves of the plant have medicinal properties - antiseptic and sedative.
Not only for porridge
At a temperature of + 15 ° C, the first shoots appear, from which plants with an erect stem quickly grow, changing color from gentle green to bright red as they mature. At the same time, the triangular leaves always remain green, which, in combination with pink flowers, gives the buckwheat field a very effective look.


The air around the blooming buckwheat field is filled with a sweet aroma.
Flowering begins at a temperature of + 25 ° C, 3-4 weeks after germination. Frosts during the entire vegetative period, and especially during flowering, are destructive for buckwheat. Any sudden change in temperature can lead to crop loss.
Buckwheat is usually grown under the protection of a forest. Trees protect the field from drought and sudden cold snap, from drafts that are undesirable for delicate plants. If there is a reservoir nearby, buckwheat will grow even better. This culture is responsive to the introduction of potash, phosphorus and nitrogen fertilizers. But buckwheat does not tolerate pesticides, just as it does not tolerate genetic experiments on itself. That is why buckwheat can rightfully be considered one of the most environmentally friendly products.
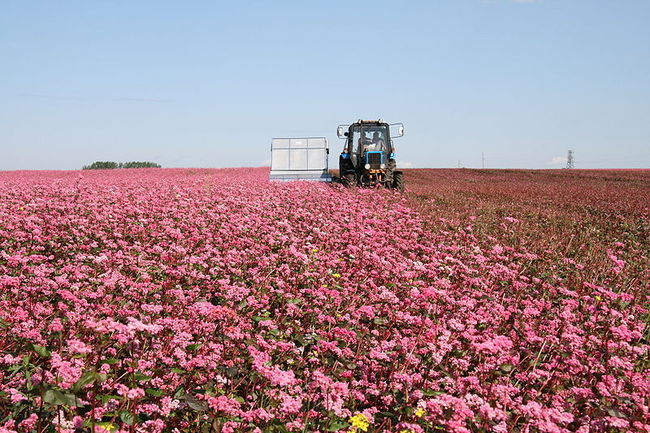


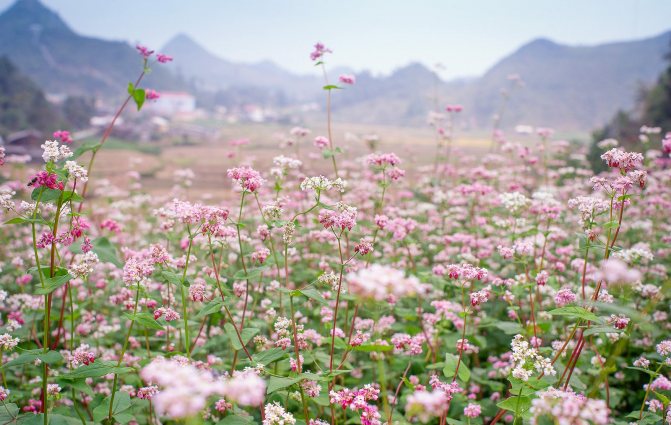
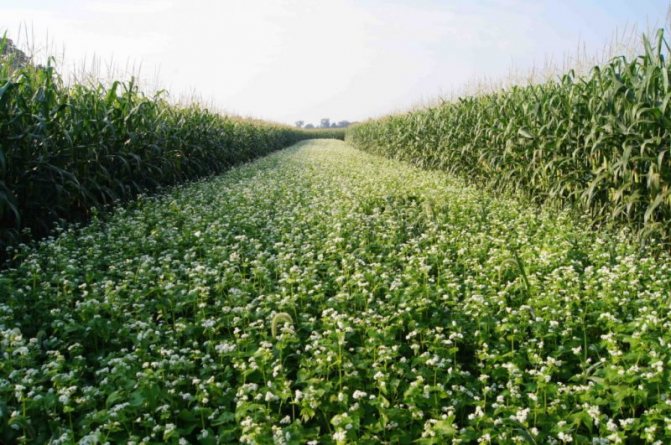
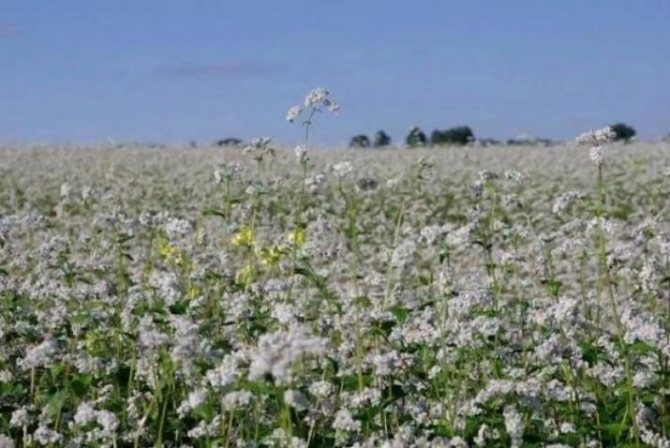
The blooming buckwheat field is colored in all shades of pink.
Buckwheat flowers are amazing.One by one, starting from the bottom, small pink flowers with five petals bloom, forming lush, rich clusters. Each of the 600 or even 2000 flowers in the inflorescence blooms for just a day, and the entire brush blooms continuously for two months. Therefore, buckwheat ripens gradually, from the bottom up. It is simply unrealistic to wait until the brushes are fully ripe, so harvesting begins when the lower, largest and fullest grains are poured and brown. By this time, about 70% of all formed grains reach technical ripeness.


The brush collects from 600 to 2000 small flowers.
During the flowering period, experienced farmers put hives along the buckwheat field. Pollination by bees increases the yield of buckwheat by 50-60%, which cannot be achieved by any other, even very expensive, methods. Healthy and tasty buckwheat honey, famous for its quality, further enhances the attractiveness of such "cooperation" between farmers and beekeepers.


Bees pollinating buckwheat significantly increase its yield.
So that the buckwheat does not crumble, they mow it early in the morning or late in the evening, when the air humidity is higher. Special harvesters produce not only the collection, but also the initial processing of buckwheat kernels. However, how buckwheat is obtained is a topic for a separate conversation.


The first to ripen are the lower, most full grains.
If you do not live where this valuable crop is grown, and have not seen how buckwheat grows, photos of its flowering fields will be of interest to you. Of course, even the most successful pictures will give only a small idea of their attractive beauty. Not to convey to them the enchanting aroma that fills the summer air. It is possible to fully experience this only by visiting the places where buckwheat grows.
Buckwheat is a culture that first made itself felt four centuries ago. A lot of time has passed since then, but this culture is widely used by people today and all because it contains a large amount of useful substances. These are various acids, and a large amount of starch, and vitamins, and calcium, and phosphorus, and so on. As for the flowers of this plant, it is in them that the accumulation of such a component as the glycoside rutin is noted, which by its properties resembles the action of a vitamin R
... In the herb of this plant, not only tannins were found, but also rutin, as well as flavonoids and phagopyrin.
The broth, which is prepared directly from buckwheat flowers, is especially popular among the people. This broth should be taken instead of tea.
The healing and beneficial properties of buckwheat
It is prepared quite simply: you need to take two teaspoons of raw materials and steam it in one glass of boiled water. The resulting broth can be used to treat not only hypertension, but also radiation sickness, bronchitis, atherosclerosis, scarlet fever and some other ailments. We note right away that such a decoction should be taken in the amount of two to three cups a day. The duration of treatment is two to three weeks. If you need to get rid of a dry cough, then it is best to prepare a steam from the flowers of this culture.
Blooming buckwheat grass is popularly used to treat anemia, diseases of the nervous system, kidney disease, gastrointestinal pathologies, and leukemia. Since these flowers contain rutin, this fact makes it possible to use them for the treatment of all those ailments in which there is a violation of vascular permeability.Before use, you must consult with a specialist.
Content project coordinator.
Channel:BuckwheatGive feedback
Back to top of page
The information posted on our website is for reference or popular and is provided to a wide range of readers for discussion.Prescription of medicines should be carried out only by a qualified specialist, based on medical history and diagnostic results.
October 12, 2010
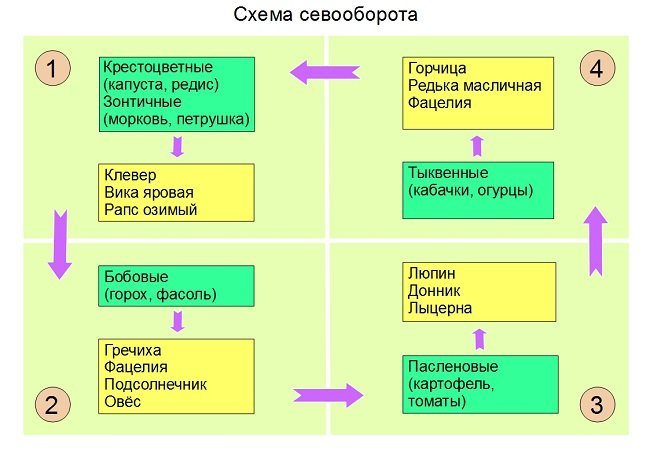
Good and bad predecessors
As with planting any agricultural crop, when sowing buckwheat, the rules of crop rotation should be observed, that is, it should be placed only in the area where plants belonging to the same family that have common diseases and pests have not previously grown.
According to them, buckwheat should be planted after crops that have the property of improving the condition of the soil. These are legumes and winter crops. Good predecessors for the described plant are potatoes, corn, beets, winter wheat, flax, and lupine. Unsuccessful choice of a place to sow buckwheat where spring cereals, sunflowers, and sorghum used to grow.