Mushrooms
0
1195
Article rating
The euphorbia mushroom (milkweed) is difficult to find on the territory of the country's forests, despite its prevalence. Most often, mushroom pickers take it for an inedible look, so they just walk by.

Description of the mushroom spurge
Botanical description
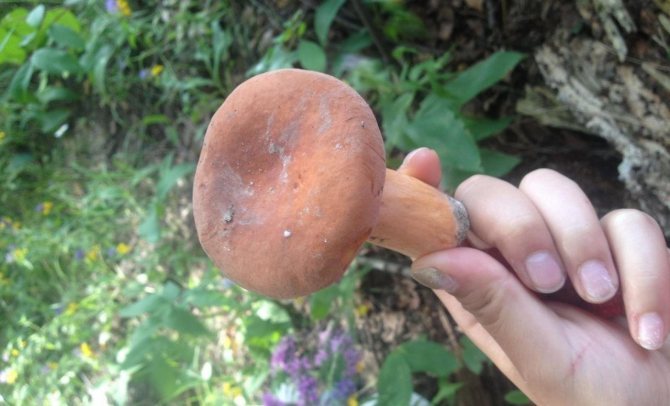
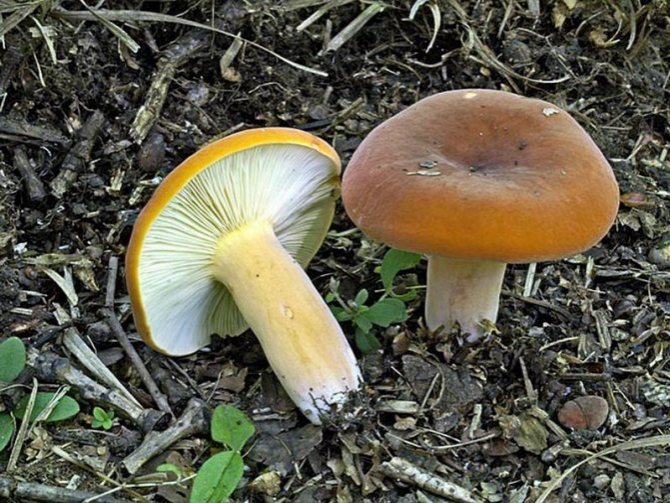
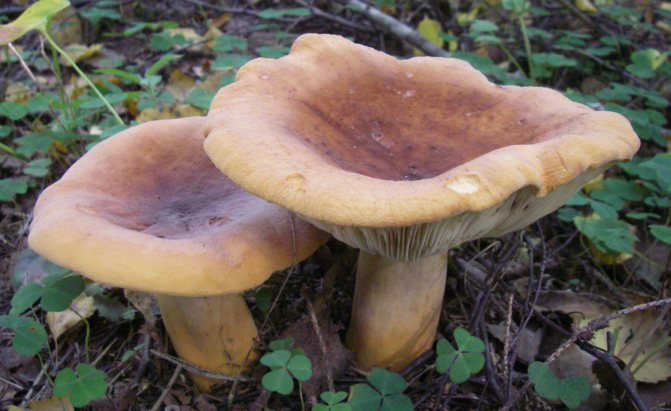
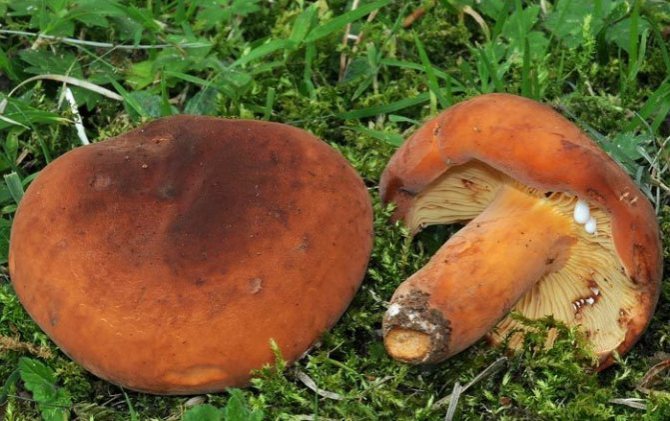
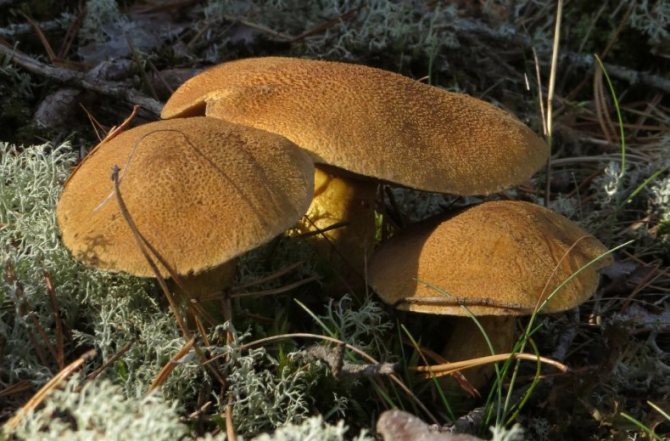
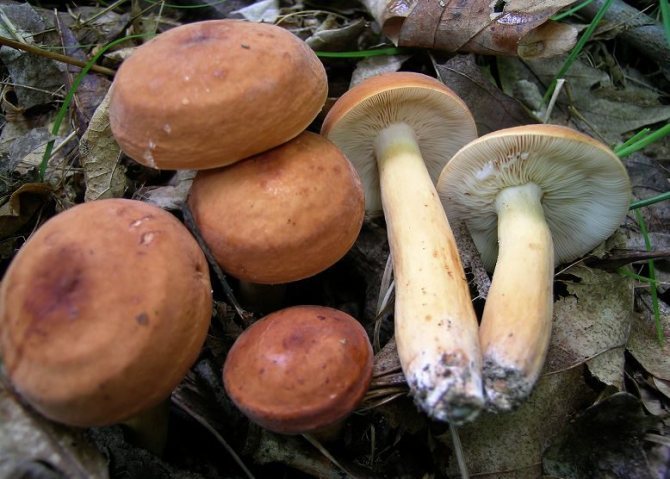
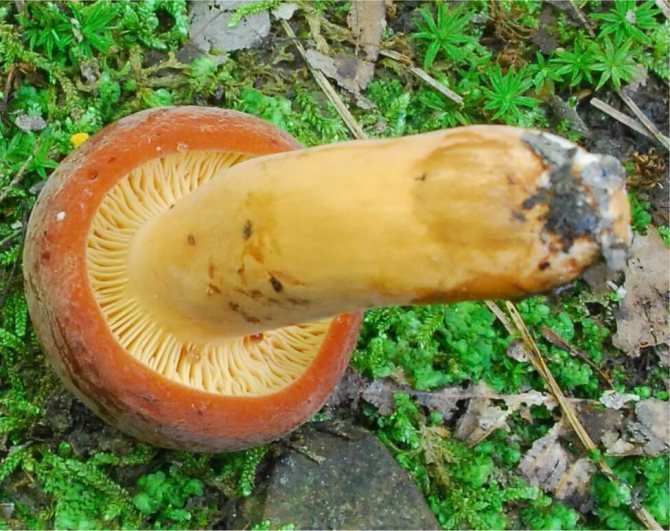
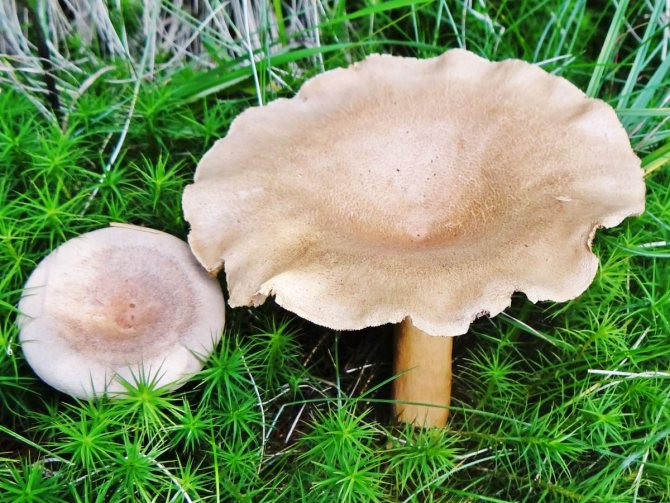
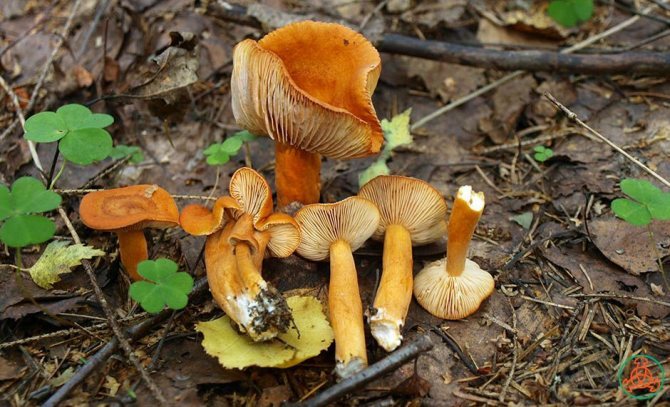
The mushroom cap has a dense, fleshy consistency. It can be up to 10 cm in diameter, and its shape is often flat and convex. It has a funnel in the middle. To the touch, such a leaflet is bare and dry. The colors of the cap can be different - they vary from red-brown to yellow-brown shades. Often the outer surface of the cap can crack.
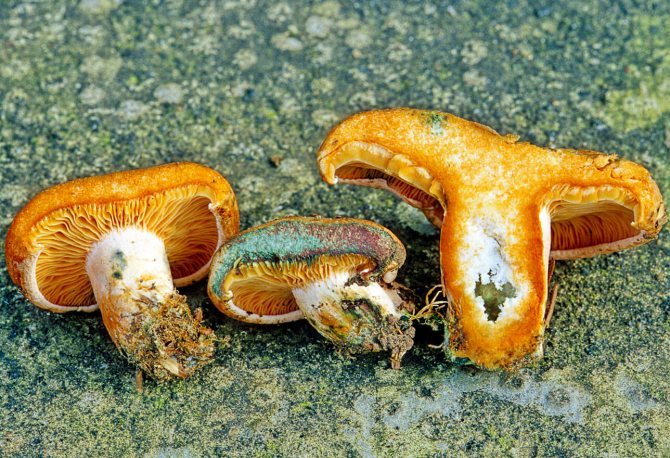
The flesh on the cut of the mushroom is white, but in the open air it becomes brown. There is a milky white juice on the cut. It was due to him that such a mushroom was named with the word milk-lover.
If you compare it with other milky mushrooms, you will notice that the milk jug has milky juice. Outdoors, it darkens and turns black. Also, the pulp of the mushroom is very similar to rubber. It may taste different from other mushrooms. Milkweed juice is pleasant, sweetish. It does not change despite the age of the fungus.
Bearing plates are similar to the outer surface. The inside of the cap can also match in color.
The stem of the mushroom often swells in the middle, and its length can reach 10 cm.
How to distinguish milk from milk
The main trouble for a novice mushroom picker is to collect a full basket of pseudo-weights, brag to neighbors, spend time cooking, and then bashfully throw the crop into the trash. It is much easier to find them: experienced "hunters" pass by, not paying attention to these mushrooms. So you need to know the special signs that a milkmaid can boast of. The mushroom really looks like a lump, but you can still identify it.
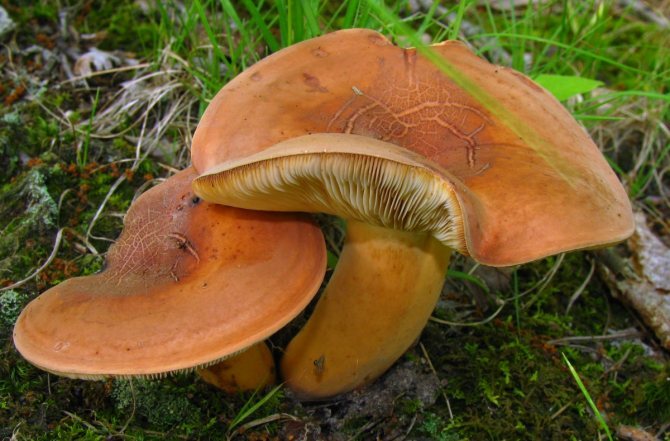
Firstly, the breast is fringed, with concentric zones, and the “fake” is smooth. Secondly, the "milk" secreted by the load quickly turns yellow in the air. The violin juice retains its original color. Thirdly, the flesh of the milkfish is denser and drier. And the caps of the mushrooms, despite the striking similarity, have a slightly different shape: the edges of the mushroom are slightly tucked down, at the squeak they are slightly curled up.


Euphorbia mushroom: photo and description
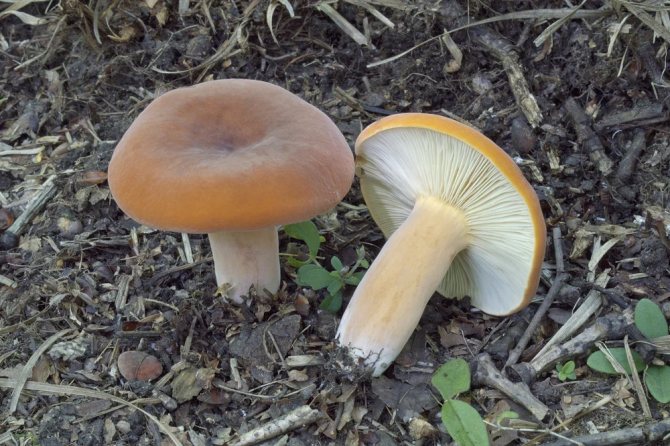
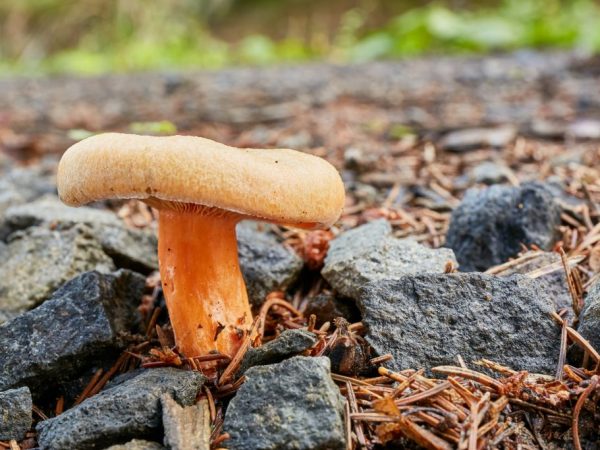
Euphorbia, leaflet, red-brown milk mushroom - these are the names of the same mushroom. It belongs to the genus Mlechnik and the russula family. It is a mushroom with a red-brown cap 4-10 cm in diameter. In young milkweed it is flat-convex, in old milkweed it is funnel-shaped with a bloom.
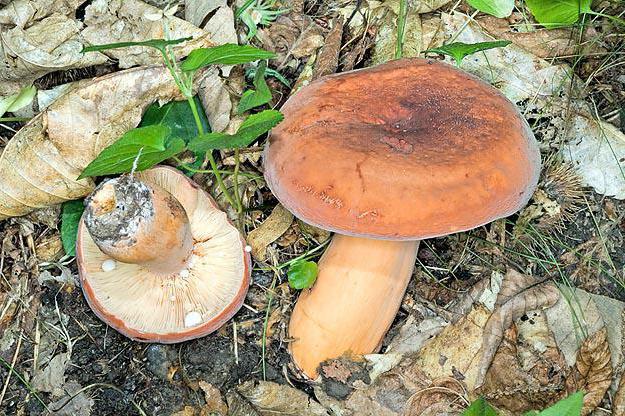


On the inside, the cap is lamellar, yellow or brown. Milky juice is abundantly released from it, which, when it comes into contact with air, turns brown, like the pulp of a mushroom. Its leg has a thickness of about 2 cm and a length of no more than 10 cm. According to these signs, people easily find a spurge mushroom in the forest. Photos and descriptions of him fully confirm this.
Euphorbia can also be identified by smell. The milky juice secreted from the pulp of the mushroom through the plates does not just turn brown, it also emits a specific fishy odor. Mushroom pickers call it herring. The older the spurge, the more pungent its smell and more unpleasant taste will be. The young mushroom has excellent taste.Unlike other representatives of the genus Milky, the spurge, or euphorbia, has a sweetish milky juice, not bitter. The mushroom tastes like russula.
What is the danger of a mushroom
The rich chemical composition not only helps to fight diseases, but is the reason for the presence of a number of contraindications and warnings in the matter of its use. The euphorbia mushroom should not be consumed by pregnant women, children under 7 years old, mothers who are breastfeeding.


- In case of intolerance to one or more of the components of the fungus, side effects may occur:
- itchy skin;
- atopic dermatitis;
- upset gastrointestinal tract;
- allergic rhinitis or ARVI;
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- headache;
- cough, shortness of breath.
People suffering from kidney disease, cholelithiasis, gastritis and stomach ulcers in an aggravated form should take milkweed-based medications with extreme caution. Hypertensive patients are not recommended to consume more than 1 tsp. infusion per day. The fungus has a stimulating effect on the nervous system, so it should not be eaten in any form later than three hours before bedtime.
The red-brown milk mushroom is a tasty and healthy product, but it is extremely difficult to find it. Often, in search of several mushrooms, you have to walk tens of kilometers through a swampy area, however, believe me, they are worth the effort.
Where does it grow?
If you want to find a milky mushroom, then you can do it like this: it grows in one copy in hard-to-reach places. It can often be found in coniferous or deciduous forests. Good growth is ensured by moss and rotten stumps located close to the growing season.
The pallet is very pleasant to the taste, it belongs to the fourth quality category. They can be eaten salted or boiled. Such mushrooms do not need pre-soaking. But there are also some exceptions. It will be better if you only eat young mushrooms. Adults have a slightly unpleasant odor and taste.
Varieties
The following types of milk lover are distinguished:


• The miller is not caustic.


• The miller is gray-pink.
Such species are considered to be relatively tasty and edible. As for the rest of the lesser known varieties, they are bitter in taste, have a smooth, non-cracked skin and do not have the characteristic milk juice.
Difference from false, inedible mushrooms
This fruit is difficult to confuse with other types of mushrooms. But inexperienced lovers of quiet hunting can easily be identified by confusing the leaflet with a gray-pink milky, which does not emit such an amount of milky juice and has the smell of dry grass.
The gray-pink milky belongs to inedible mushrooms, so you should consider it in the photo very carefully. Euphorbia is quite similar to some of the milky relatives. For example, the hygrophoroid lactic acid is edible, does not change the color of the milky juice, and its plates are located much less frequently than in the smooth.
The conditionally edible non-edible milk jug is much smaller, and the cap is not covered with small cracks.
Growing
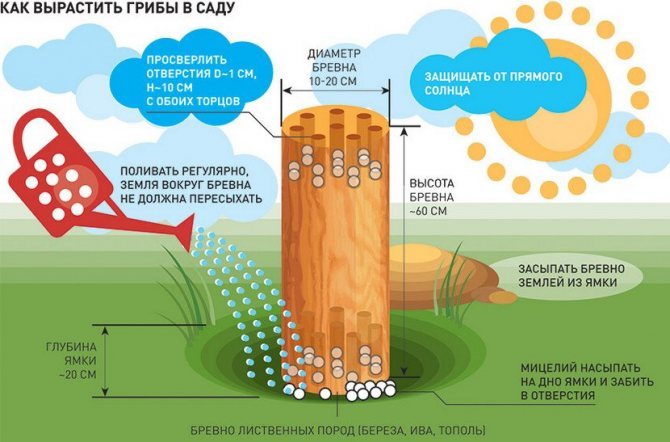
It is possible to grow euphorbia mushroom at home under any tree species, but nut plantings give the maximum germination and yield. In addition, such a neighborhood significantly increases the fruiting of crops due to the formation of mycorrhiza.
Milk lover spores can be purchased at the store and sown according to the instructions:
- Mix 15 g of seeds with 0.5 l of sand or dry soil (per 1 m²).
- Fluff the ground under the tree, reaching the roots, to a depth of 5-15 cm.
- Distribute the mycelium over the area.
- Cover with garden, and preferably forest soil, mixed in equal proportions with humus.
- Pour 10 liters of water for each m² from a watering can with a fine spray.
- Mulch on top with earth and sawdust.
Did you know? Almost two thirds of the mushrooms sold on the world market are
artificially grown in China.You can get the seed yourself... To do this, you need to find old mushrooms, without rinsing, grind in a meat grinder, add water and insist in a dark, warm place for 2 weeks. After a lapse of time, the cake must be removed from above, and the remaining liquid will be a solution of milkweed spores.
Further, everything is done in the same way as with purchased material, only the mycelium will be distributed over the area not in dry form, but by watering. The harvest of the red-brown milk mushroom can be expected in three months, then fruiting, subject to proper watering, will continue until the end of October.

Useful properties of the mushroom
The fruiting bodies of the woods contain a large amount of active substances that have a healing property on the human body. Among them, it is worth highlighting volemolid, which is also known as mushroom ergosterol. Also worth noting here are sterols known in mushroom science. They are also found in sea sponges and corals. It is impossible not to mention the presence of sugar alcohol, volemitol.
In folk medicine, milkweed juice is often used. It must be used externally in oncology in order to cure the tumor. Fresh fruiting bodies contain ethanol extract, which demonstrates anti-cancer activity and suppresses the development of sarcoma.
Milkwort tissue contains cortisone, which is why it is often used as part of antirheumatic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The benefits of the lactarius for the human body
In our country, many milkmen are considered first-class mushrooms, widely used in pickling and pickling. This processing option causes a fairly rapid fermentation of the pulp of the fruit bodies, so the smoothies acquire a very characteristic and pleasant taste. Among other things, meatiness is very highly valued, therefore, after preliminary preparation, the fruit bodies can be used in the preparation of all kinds of mushroom dishes. The use of milkmen has a very beneficial effect on the human body and contributes to:
- strengthening the immune system and blood vessels;
- improving vision in old age;
- strengthening the heart muscle;
- fast tissue regeneration;
- preserving the youthfulness of the skin;
- strengthening hair and nail plates;
- improving metabolic processes;
- restoration of hematopoietic organs;
- improving brain activity;
- balance of water and salt metabolism;
- strengthening of the musculoskeletal system.
Also read: Types of mushrooms growing on a nut: description and characteristics
Medicinal properties and application
A number of special active substances with unique medicinal properties were found in the pulp and milky juice of the mushroom.
The euphorbia mushroom is widely used in folk medicine. Especially appreciated is the milky juice secreted by it, which is used as an antitumor agent. An ethanol-based extract is prepared from fresh milkweed, which is used in folk medicine as a means of fighting cancer. It has been proven that the substances contained in it perform the function of an active antioxidant and inhibit the growth of cancer cells in the body.


In the fruiting bodies of milkweed, the hormone cortisone and other steroids are found. This determines the scope of use of the mushroom - the manufacture of drugs to combat inflammatory processes in the body and rheumatism.
Application in medicine
The euphorbia mushroom has a large number of beneficial properties, thanks to which it is widely used in folk medicine. The most valuable is milky juice, which has a powerful antitumor effect.


Fresh mushrooms contain ethanol extract, which is often used in the fight against various malignant tumors, including cancer. The presence of cortisone in the composition of tissues allows it to be used in the composition of agents for combating inflammation and rheumatism.
Tincture of milk lover is taken in 1 tsp. 3 times a day for varicose veins, hemorrhoids, gout, otitis media, bronchitis, fever, sore throat, gastrointestinal diseases and inflammatory processes.
With a cold, the nasal mucosa is lubricated with an oil composition. External use of the tincture helps to solve the problems of skin inflammation, cure burns, allergic rashes, and more.
- In addition, the red-brown mushroom also performs a number of other functions:
- blocks the spread and removes bad cholesterol;
- has an antioxidant effect;
- helps in the restoration of the microflora of the digestive tract;
- helps replenish protein and protein stores in a healthy diet.
Milkweed mushroom tincture recipe in oil
To prepare the milkweed tincture in oil, the mushrooms must first be dried. To do this, they are cut into plates 1 cm thick and hung in shaded, well-ventilated places. You can also use an electric dryer.
Important! Before use, the tincture must be shaken thoroughly until smooth.
After the raw materials have completely dried, they are ground into powder with a coffee grinder or blender and poured with linseed or olive oil at the rate of 0.5 liters of oil per 3 tbsp. l. mushroom powder. The container is tightly closed and left to infuse in a warm, dark place for two weeks. You do not need to filter the composition. It can be stored in the refrigerator for several years.
Contraindications
Euphorbia lamellar mushroom contains a large number of medicinal properties. But, before starting treatment, you should learn more about contraindications. Do not use a mushroom-based tincture for children and pregnant women. Also, nursing mothers should refrain from eating these mushrooms. Do not forget that the mushroom contains strong active substances, therefore, if you are not sure that your body is ready for this, you should consult a doctor before eating mushrooms.
How to cook properly
Euphorbia is great for pickling and pickling - it belongs to the fourth or third flavor category, so you should not eat it fried, stewed or boiled.
Before cooking, the mushroom does not need to be soaked, because it is not damaged by insects and does not have high acidity.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
For cooking, it is best to take young mushrooms. However, due to the fact that even at a “young age,” the mushrooms have a specific, albeit weak, aroma that can ruin everything, mushrooms must be boiled for 15-20 minutes beforehand.
It is better not to use old mushrooms due to the strong smell and poor taste.
1 recipe


Mushrooms are delicious when salted
The simplest and most common cooking method is cold salting.
The collected fruit bodies are simply washed with cool water, and then they are laid out in layers in a wooden tub or barrel.
Each layer is sprinkled with coarse salt at the rate of 50 g per 1 kg of milkweed. When all the mushrooms are laid in layers, cover the surface of the last layer with gauze, on it - a wooden circle that matches the size (diameter) of the container and place the load on it. Leave in the cold for a month.
2 recipe
Some chefs prepare mushroom cream soup.
The algorithm of actions is simple: 200 g of butter are melted in a frying pan with half rings of onions until the latter acquires a golden color and a characteristic smell.
Next, 800 g of fruit bodies are fried with onions and oil for 15 minutes. In parallel with this, salt and ground pepper are poured into a saucepan with water.
When the contents boil, pour the food from the pan. After 5 minutes of boiling, 600 ml of milk with a high proportion of fat or heavy cream is poured into the container. On a note. The cream in the cream soup works better - it makes the taste "silky". After that, gradually, with stirring (to prevent the occurrence of lumps), 3 tbsp is poured out. flour.
Once the mixture is cooked, you can give it a little “rest” and puree in a blender.This mushroom cream soup can be served with black bread, croutons or a finely chopped mix of fresh herbs.
Cooking applications
For culinary purposes, it is better to use young mushrooms, since the older the mushroom, the more expressive the specific smell, which is also intensified during the cooking process.
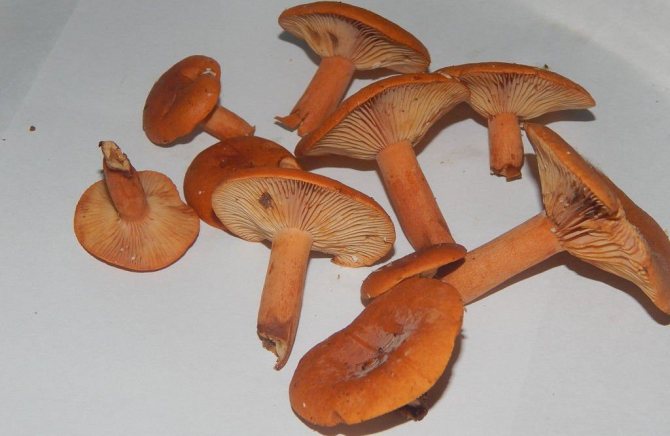


Euphorbia belongs to the fourth flavor category, therefore it is not recommended to cook and fry them., although some mushroom pickers speak of the fried bush as a unique delicacy. Cold pickling allows you to preserve the maximum benefits of mushrooms and get a wonderful crispy snack for the whole winter.
Important! The red-brown lump is never attacked by worms and insects. It doesn't need to be soaked before cooking.
The recipe is extremely simple:
- Rinse the mushrooms under running water.
- Separate the legs from the hats - this way they will fit compactly and correctly.
- Lay the milk mushrooms in layers in a wooden, ceramic or enamel container, sprinkle with coarse salt at the rate of 50 g of salt per 1 kg of mushrooms.
- Cover with 3-4 layers of cheesecloth, on top place a wooden circle that fits the inner diameter of the container (you can use a plate or an enamel lid).
- Place the pot or keg in a cold, salting area for 1 month. During this time, the circle and gauze will need to be washed daily.
- A month has passed - get the mushrooms and enjoy the unique taste.
Preparation
With the right approach to the preparation of the milk jug, such a mushroom will amaze you with its original taste. A specific feature of milkweed is the presence of a fishy odor, which becomes more noticeable with the age of the fungus. During the cooking process, the smell becomes even more pronounced. As for the group of young mushrooms, they have a more pleasant and rich taste.
The mushroom can be pickled, stewed, fried, dried and even salted. Before making salting, it is worth soaking the spurge well. This will get rid of bacteria and give the mushrooms a special flavor. It is worth noting that the milk jug is never damaged by the larvae, so more and more mushroom pickers like to use it raw with salt.
If you want to process the mushrooms, cold salting is the best solution. Rinse the red milk milk jug under water and place in a deep container in layers. Each of them must be sprinkled with salt. For 3 kg of mushrooms, 150 grams of salt is needed. After that, put the container in the refrigerator for a month. After this period, you can taste the mushrooms. If they are too salty, they can be diluted with boiled water. They are great for salads and pizzas.
Milk mushrooms: how to cook. Preparatory stage
The whole problem is in the bitter juice. In addition, the felt milk mushroom has a rather tough pulp, and this must be somehow dealt with. Therefore, in the Union squeaks belonged to the fourth category of edibility, and "over the hill" they are generally considered inedible. Nevertheless, there can be some sense from them. And the preparation of molokan mushrooms begins with their diligent soaking. For him, the prey is sorted out and sorted. All areas sampled by the worms are removed. Holes from punctured branches and needles, if any, are also cut off with a part of the cap. The mushrooms are washed and soaked several times - water is poured into the basin, which will cover the molokans completely, and not very heavy oppression is placed on top so that the mushrooms do not float up.
Change the water as often as possible. After the first night in the water, foam is sure to form. Before filling with new water, the mushrooms are washed several times again. The soak will take about five days. In this case, the mushrooms will decrease in volume - with water, bitterness is removed from them, which takes up to a fifth of the weight. It is not worth "loading" the basin with new milkcaps, it is better to soak them in another vessel, otherwise the bile will not be completely eliminated from them.
Ideally, it would be nice to have a stream under the house with running (and clean!) Water.Then the initial stage would not require excessive efforts - loaded into the grid and tied to the nearest birch tree. Unfortunately, this is an unattainable dream in the city. But if you are engaged in salting in the country, take an interest in nearby reservoirs or unused wells.


How to hot pickle spurge
All mushroom pickers who do not want to wait a whole month until the mushrooms are salted will love the hot way of cooking them. In order to salt spurge according to this recipe, it must be boiled for 12 minutes. Then the mushrooms should be thrown onto a sieve and wait until the water is completely drained. Boiled spurge is laid in layers at the rate of 80 g of salt per 2 kg of mushrooms. After that, the container must be placed in a cold place where the required temperature regime is maintained from 0 to 10 degrees.


The euphorbia mushroom prepared according to this recipe can be tasted after 6 days. Mushroom pickers recommend adding it to salads with pickled onions and other vegetables.
General characteristics of lactic mushrooms
The fruiting bodies of any lactarius are represented by a cap and, as a rule, a centrally located leg, in the absence of a cover. Some varieties are characterized by stocky fruiting bodies and rather thick legs. Other species form fruiting bodies, represented by a leg and a medium-sized cap. A significant part of the lactarius has a hymnocarp type of formation of fruit bodies.
Young specimens have a cap with edges tightly attached to the stem, which eventually straighten out and the upper part acquires a flat, flat-concave or funnel-shaped shape. The coloring of the cap surface is quite varied:
- white;
- yellowish;
- orange;
- brown or brown;
- grayish;
- purple or pinkish;
- bluish;
- olive black.
It should be noted that some species of milkmen are characterized by a change in coloration with age. The surface is smooth, velvety, with roughness or scales, and also covered with hairs. The plates are weakly descending or attached to a cylindrical or narrowed, widened at the base or clavate stem, which, as a rule, has the same coloration as the cap. Spore powder is most often light yellow, whitish blue or any other pale, beige color.
Where and when do milkmen grow
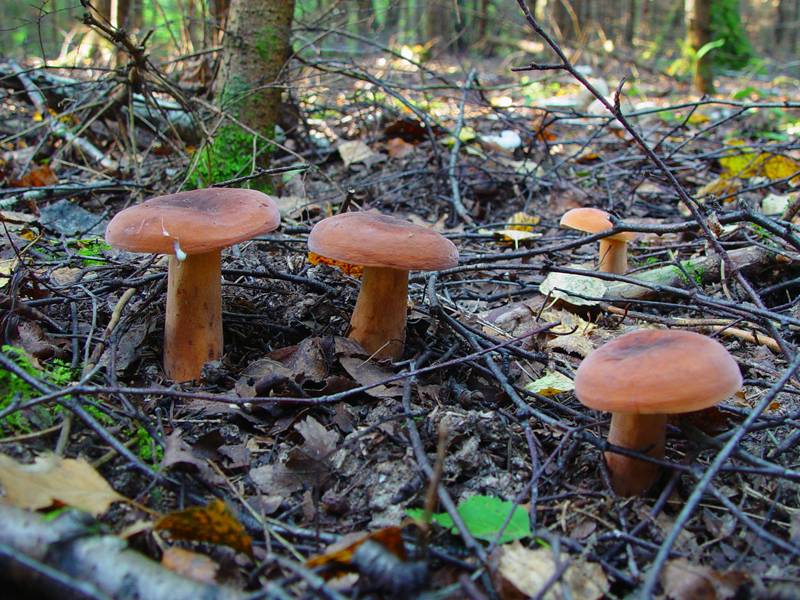
Smoothies are most often found in mixed forest zones and birch groves, as well as in rather rare and young forest plantations, with a large number of conifers or birches. Millers are usually mycorrhizal formations with pines and birches, but sometimes fruiting bodies form under other deciduous trees. Smoothies give preference to areas with high humidity or overgrown with mosses. Such mushrooms grow in whole colonies of different ages., massively forming fruiting bodies from mid-July.
Also read: Habitual and useful: we grow oyster mushrooms in our country house
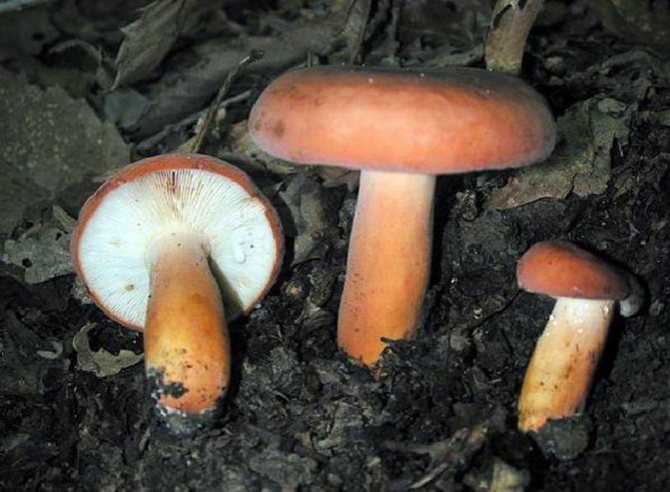
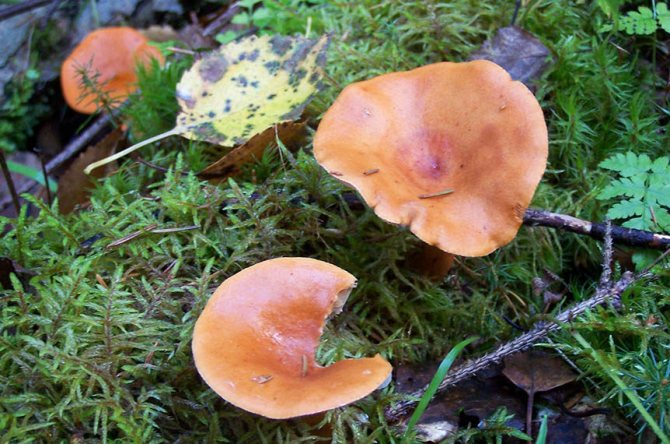
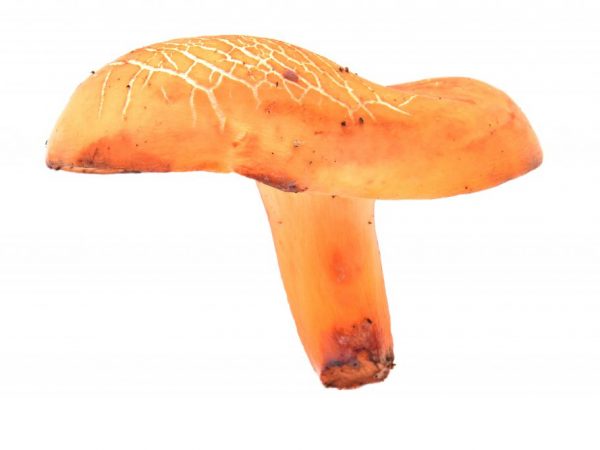
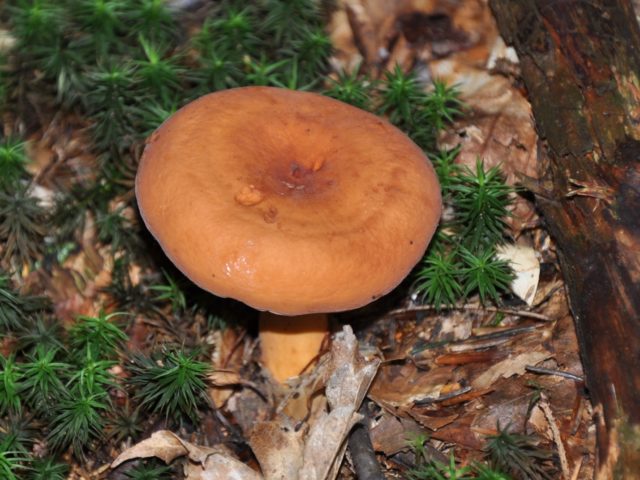
Red-brown Milk (Lactarius volemus)
Milk lover
Spurge


Lactarius volemus (Fr.) Fr., Epicr. syst. mycol. (Upsaliae): 344 (1838)
Description
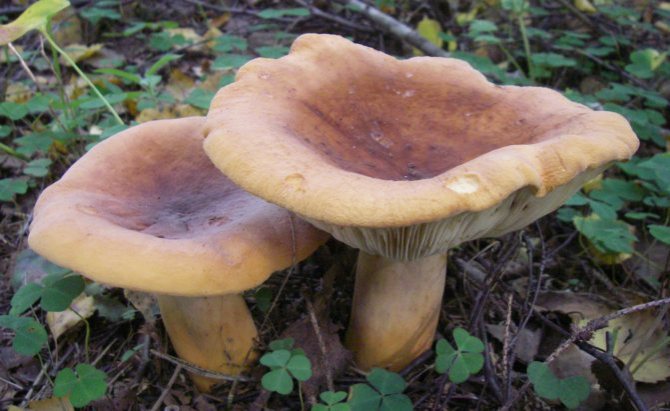
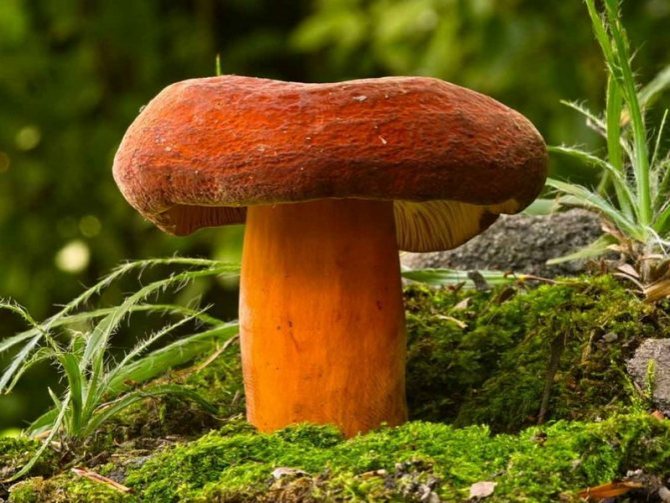
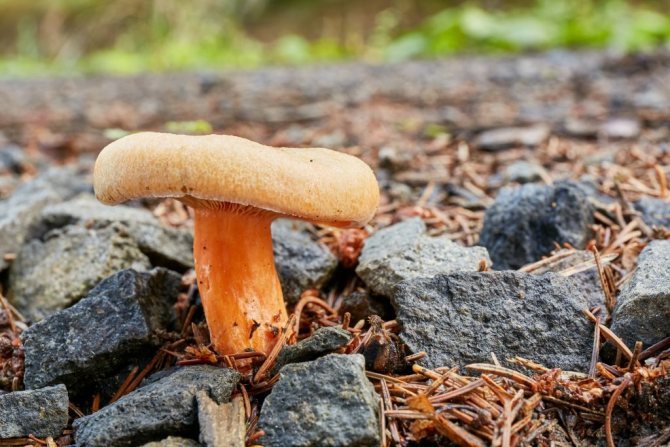
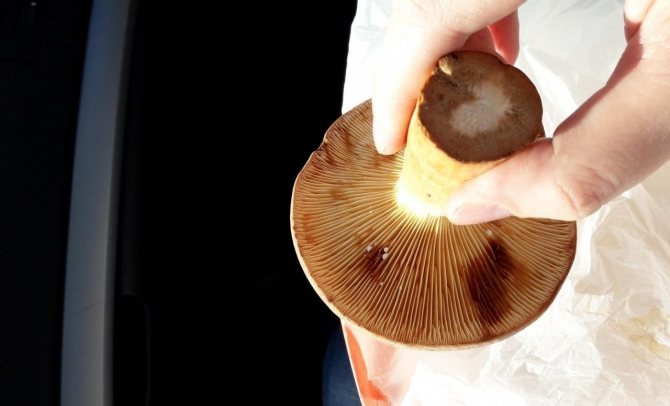
Hat with a diameter of 5-17 (up to 16) cm, convex in youth, then prostrate, possibly pressed in the center, and even up to concave. The edge of the cap is straight, thin, sharp, first tucked up, then straightened and even raised. The color is reddish-brown, brownish-brown, in rare cases, rusty or light buffy. The surface is velvety at first, then smooth and dry. Often cracked, especially in dry conditions. There is no zonal coloration.
Pulp: White, yellowish, very fleshy and dense. The smell is described in various ways, mainly as a herring (trimethylamine) smell, which increases with age, but there are also more interesting associations, for example with pear flowers [2], or not indicated at all [1]. The taste is soft, pleasant, sweetish.
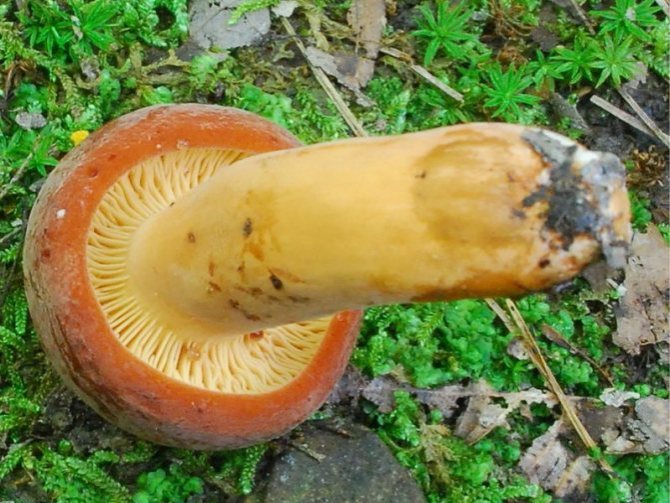
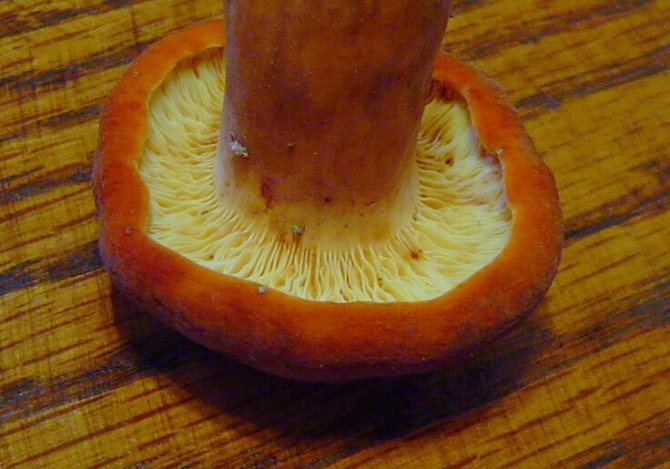
LPs frequent, from adherent to weakly descending, creamy or warm skin shades, often forked at the leg. There are shortened plates (plates).
Milky juice copious, white, turning brown and thickening in the air. For this reason, this type of lactarius turns brown and everything else if damaged - pulp, plates.
Leg 5-8 (up to 10) cm in height, (1) 1.5-3 cm in diameter, hard, often made, the color of the cap, but slightly paler, smooth, may be covered with fine pubescence, which looks like frostiness, but is not felt to the touch ... Often tapered to the bottom.
Spore powder white. Controversy close to spherical, according to [2] 8.5-9 x 8 µm, according to [1] 9-11 x 8.5-10.5 µm. The ornamentation is ridged, up to 0.5 µm in height, forming an almost complete network.
Habitat
Occurs from July to October. One of the earliest milkmen. Grows in deciduous, mixed and spruce forests (according to [1] - in general in all forests). According to [2], it forms mycorrhiza with oak (Quercus L.), common hazel (Corylus avellana L.) and spruce (Picea A. Dietr.).
Similar species
Given the "power" of this mushroom and the abundant brownish sweetish milky juice, perhaps, it has no similar species. The most similar lactic to him, perhaps, is the hygrophoroid lactarius - Lactarius hygrophoroides, but it is easily distinguished by non-brown milky juice and rare plates. Quite conditionally, rubella (Lactarius subdulcis) can be attributed to similar species, but it is thin-fleshed and slender. The same applies to the orange lactarius (Lactarius aurantiacus = L. mitissimus), it is not only small and thin, but also late, does not overlap in terms, although it grows in exactly the same biotopes with spruce.
Read also: Delicious pickled mushrooms from grandma
Edibility
An edible mushroom that can be eaten raw. It is good in raw salted or pickled form, without any heat treatment. I don't like it in another form because of the "wooden" pulp, although, they say, mushroom caviar is good from it. I hunt him specifically and purposefully, for the sake of a raw ambassador.
References 1) Verbeken, A. & Vesterholt, J. 2008. Lactarius. - In: Knudsen, H. & Vesterholt, J. (eds.): Funga Nordica, 82-107. 2) Flora of Belarus. Mushrooms. In 7 volumes. Volume 1. O.S. Gapienko, Ya.A. Shaporova, 2012, Boletales. Amanitales. Russulales.
Video about the miller mushroom:
| Name: | Milk lover |
| Latin name: | Lactarius volemus |
| A type: | Edible |
| Synonyms: | Euphorbia, Galorrheus volemus, Lactifluus volemus, Amanita lactiflua, Lactarius lactifluus, Lactifluus oedematopus, Lactarius oedematopus, Lactarius ichoratus, Galorrheus ichoratus, Lactifluus ichoratus testus) |
| Characteristics: |
|
| Systematics: |
|
The miller mushroom is one of the popular lamellar species belonging to the Syroezhkovy family. Belongs to the conditionally edible group. It is in high demand among mushroom pickers, it is recommended for pickling or pickling.


Milk lover
| Group: | Lamellar |
| Plates: | Brown |
| Color: | Brown or dark ocher |
| Info: | The plates darken when pressed, secrete juice |
| The Department: | Basidiomycota (Basidiomycetes) |
| Subdivision: | Agaricomycotina (Agaricomycetes) |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes (Agaricomycetes) |
| Subclass: | Incertae sedis (indefinite position) |
| Order: | Russulales |
| Family: | Russulaceae (russula) |
| Genus: | Lactarius (Miller) |
| View: | Lactarius volemus (Warbler) |
It belongs to edible mushrooms of the 3rd or 4th category of nutritional value (according to various sources). It is believed that the milk lover can be eaten raw, but many mushroom pickers are frightened off by the herring smell, which is characteristic of mature specimens. In the west, it is considered a delicacy.
Description
The milk lover is distinguished by abundantly secreted juice, which quickly thickens and forms white drops on the surface of the mushroom.
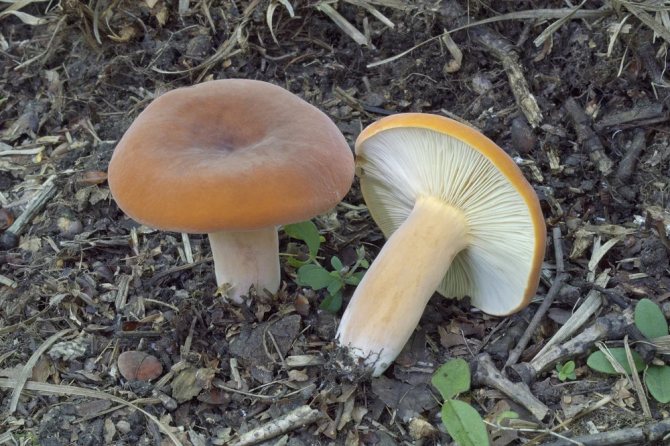
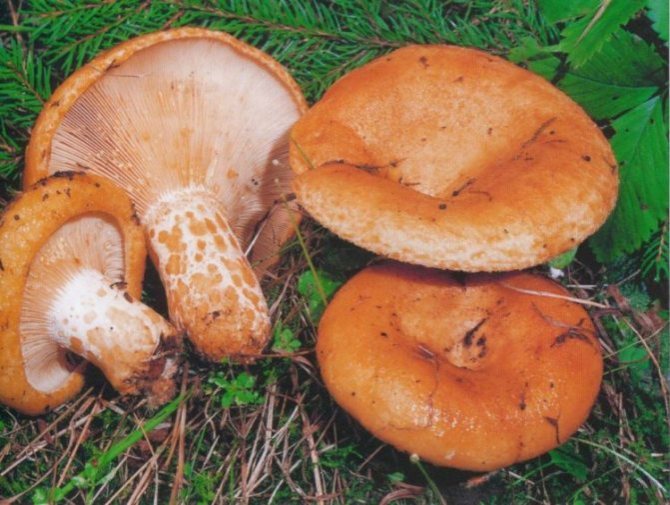
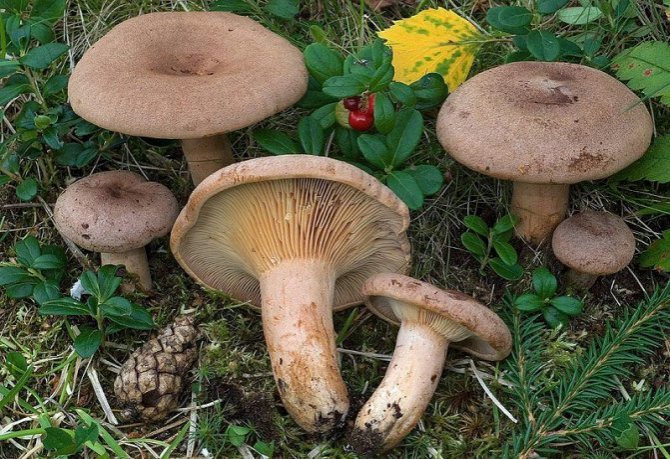
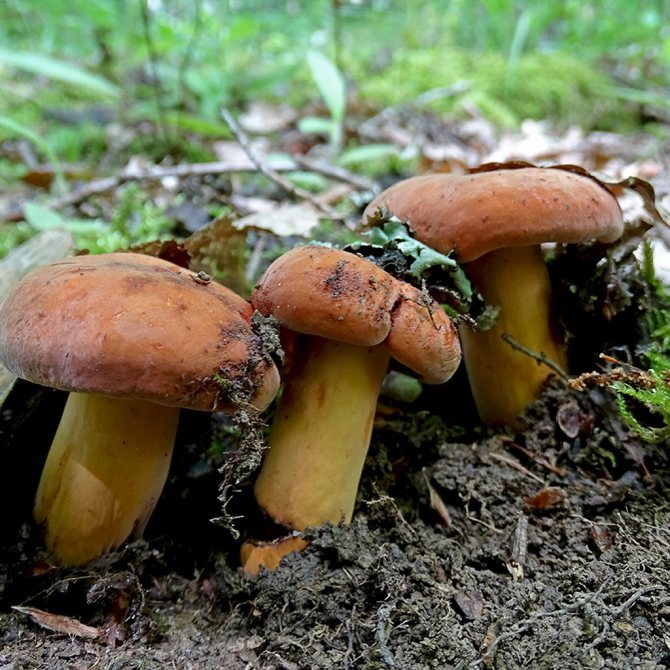
Hat
The cap of the milk lover is very thick, often irregular in shape, in mature mushrooms with cracks. It reaches 15 cm in diameter. The surface is dry, evenly colored brown or dark ocher.In small milkweed, the cap is convex, and in the process of growth it unfolds upward and resembles a funnel. The edges of the cap in both young and adult specimens are bent downward.
Leg
The leg of the thresher is relatively thin (no thicker than 2 cm in diameter), about 10 cm long. It has the shape of a cylinder. The color is about the same as the hat or a little lighter. Often has a bulge in the middle.
Spore-bearing layer
The hymenophore or spore layer of the milk lover consists of plates. The plates are slightly lighter in color than the mushroom itself. If you press on them, the plates take on a darker color.
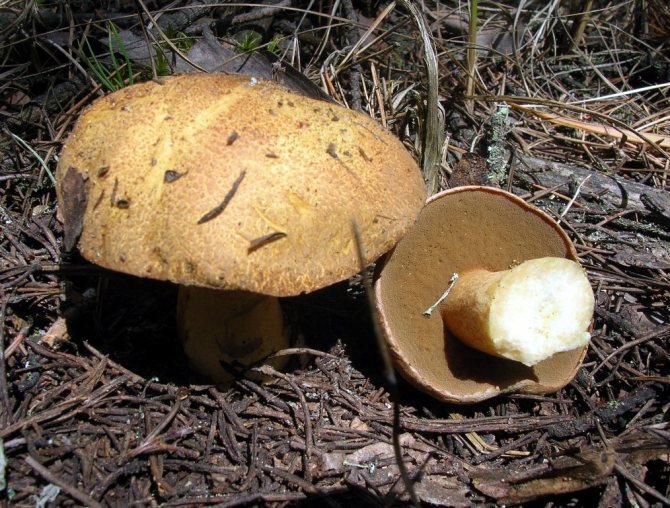
Pulp
The flesh of a reddish-brown milk mushroom or milk lover is yellowish, hard and brittle. It exudes a sap that is white at first, but quickly darkens in air to brown. In addition to changing the color of the juice, its thickening is also observed, it becomes viscous. Overripe specimens have the smell and taste of stale herring.
Spore powder
Milkweed has white spore powder in the plates. The spores are round, small. They are colorless individually, but appear white in large numbers.
Spread
Milkworms can be found in both deciduous and coniferous forests. They grow both individually and in groups. Most often they can be seen near roads, in mountainous areas, along paths. Especially the thresher loves humid places and the proximity of rotten stumps and moss. Euphorbia is more common in southern Russia.


Similar species
Euphorbia has no resemblance to poisonous mushrooms.
Here are some of his "doubles":
- Hygrophoroid milky
It differs from milkweed in a rare arrangement of plates. It is very rare, mainly near oak trees. Edible too.
- Miller neutral
This mushroom is more brownish with dark areas. Its juice, unlike milkweed juice, has a yellow color. Edible.


- Miller pink-gray
Has a colorless sap. It smells like hay. Conditionally edible just because of its specific smell.
Has a more orange color and "pubescent" leg. It turns green on the cut. Edible.


An experienced mushroom picker can easily distinguish the spurge mushroom from the rest. Moreover, it comes across quite rarely.
Summing up
Do not rely on traditional medicine dogmas alone. Before using the support as part of a treatment or simply as part of a meal, it is worth analyzing your condition and discussing this decision with a nutritionist, therapist or gastroenterologist.
In addition, the mushroom itself is quite difficult to get: it is rarely found in accessible points of the forest. But even an old euphorbia found can disappoint with its specific taste.
Podorekhovik belongs to the genus Millechniki, which is a member of the Russula family. A peculiarity of the mushroom is the absence of strong bitterness, which is characteristic of milkmen. In addition to good taste, the fruit has healing properties, because it contains biologically active substances.
It is difficult to find this mushroom in the forests of our country - it is considered a rather rare species. In order not to miss the opportunity to put the nut mushroom in your basket on occasion, you should carefully read its photo and detailed description, remember the characteristic features.
Harm and contraindications to the use of milk lover


It is recommended to use this product no later than 2-3 before bedtime. This is due to the fact that it is a rich source of fiber and takes a long time to digest. As a result, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and insomnia may occur. If you eat too much of it, you may experience severe heartburn, nausea, diarrhea or constipation, and abdominal pain. After this, increased thirst often occurs and is tormented by a lack of appetite. With such problems, you should arrange a fasting day, using only liquid (water, kefir, weak tea).
Relative contraindications to the use of milk lover in cooking are:
- Pregnancy
... In an "interesting position", especially in the first trimester, toxicosis may worsen. It is also dangerous that eating this mushroom increases the risk of developing allergies. This is especially true when it comes to fried or pickled food. - Ulcer and colitis in the acute stage
... You should not eat euphorbia if you are worried about acute abdominal pain, constipation and heartburn. Fiber, which is contained in the caps of the mushroom, further aggravates the situation, as it actively affects the walls of the digestive system. - Kidney problems
... Due to the presence of nitrates in the composition and a high percentage of water, the load on them increases, which entails a disruption in the work of this organ. This often occurs with pyelonephritis. - High blood pressure
... We are talking about those situations when it regularly rolls over 150. This condition is called hypertension, which is considered a serious illness. With it, you should reduce the use of water, in large quantities contained in the milk jug.
Important! Even if you have not found any contraindications for milk lover, you should not get carried away with fried and pickled mushrooms, they are harmful to the liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines and pancreas.
Salting directly
So, you have fully prepared milkcap mushrooms. How to salt is a separate song, although not too difficult to perform. In the absence of a tub, it is recommended to use an enameled bucket without chips on the inner surface.
Large caps can be cut - purely for ease of use. Mushrooms are layered with halved garlic (about the head will go away), thin circles of horseradish root, lemongrass and black currant leaves, dill seeds (or its umbrellas). Black peppercorns are also acceptable, but not too much. Each layer is sprinkled with a coffee spoon of salt. The top of the bucket is closed with clean gauze, a wide plate and a load are placed on it - a three-liter bottle of water will be enough. Monitor the condition vigilantly: if mold forms on the gauze, it must be washed. Better to replace it with a new one, it is not so expensive.
The milkmaids will be salted from a couple of weeks to a month, depending on the temperature. The warmer - the faster, the colder - the tastier. It is better to keep them cool, and use them like any other salted mushrooms.
Nutritional value and taste of edible milkers
The calorie content and nutritional characteristics of smoothies vary greatly depending on the species characteristics, as well as the growing conditions. Lamellar mushrooms belonging to this genus are rich in:
- tyrosine;
- glutamine;
- leucine;
- arginine;
- lecithin;
- palmitic acid;
- stearic acid;
- butyric acid;
- acetic acid;
- phosphatides;
- essential oils;
- lipoids;
- glycogen;
- sugar alcohols;
- fiber.
The mineral composition of the lactarius is extremely rich in such components as potassium, phosphorus and calcium. Also, the mushroom pulp contains trace elements represented by iodine, zinc, copper and arsenic, and substances useful for human life in the form of mycoinulin and parodextrin, tregazolite and lycosot, which provide the taste characteristics and nutritional value of mushroom pulp of all edible varieties of smoothies.
Second stage: boiling
The next step is much less time consuming. The soaked milkcaps are loaded into a larger pot, filled with fresh water and brought to a steady, but not excessive boil. You need to cook for a short time, about five minutes, during which your task is only to remove the rising foam with the remains of debris with a slotted spoon. It is not enough to drain the water; it must be well drained. Usually mushrooms are laid out in portions in a colander. When, after shaking it, the drops do not fall, you can lay the next portion.




















































