Moles: description
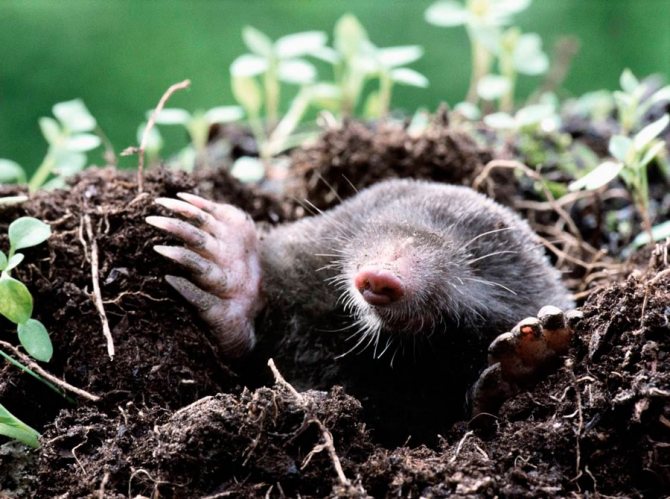

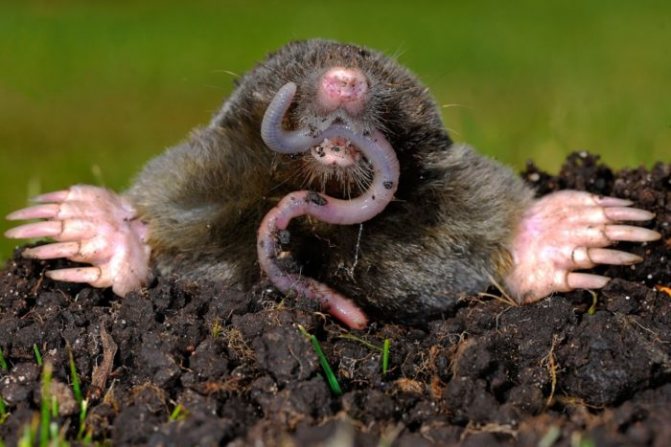
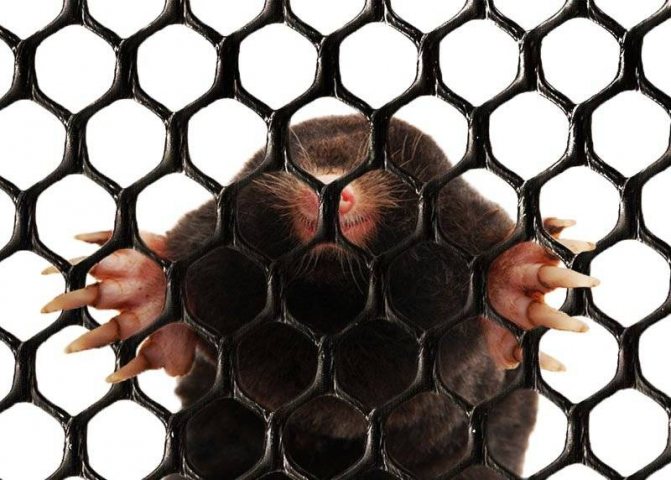
Moles are a family of mammals. If we translate the meaning of the word "Mole", it means "Digger". Moles are found everywhere, both in the forest and in open spaces. Due to the fact that his vital activity takes place in complete darkness, their eyes are underdeveloped, although there are varieties that distinguish light from darkness.
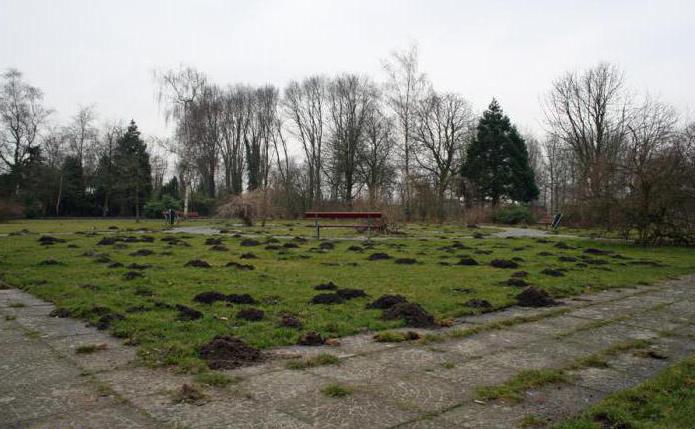
These are soil animals, and they were discovered by small heaps of soil, towering above the surface of the earth. These hills are also called molehills, as they represent traces of the activity of moles. As a result of studying the animal, it was found that moles have very poor eyesight, but hearing, smell and touch are developed at a high level. At the same time, it should be noted that the ears of this animal are located inside.
Appearance
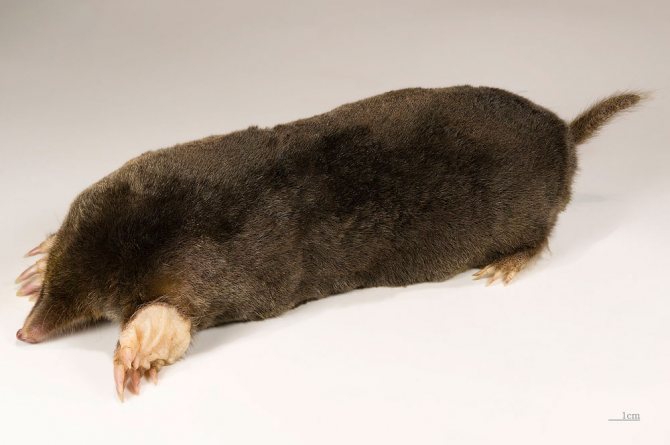


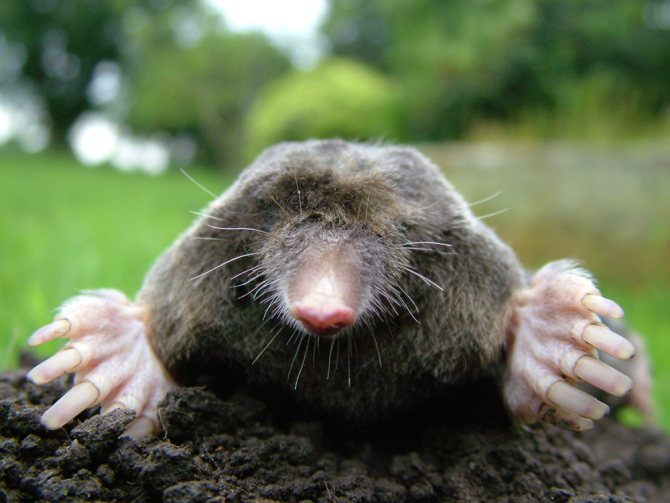
Moles, depending on the variety, can have different sizes and weights. Some of the species are quite small, since they are about 5 cm long, and some of them grow in length up to 2 tens of centimeters, or even more, while the weight can vary between 9-170 grams. The shape of the body is elongated, covered with short but thick fur that grows straight, which allows the animal to move without problems in its burrows in any direction. The main color is black, black-brown or dark gray, which directly depends on the variety, as well as natural habitats.
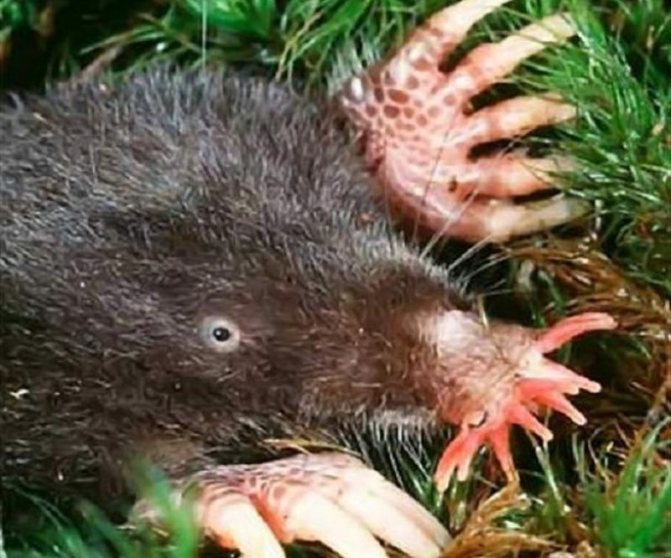
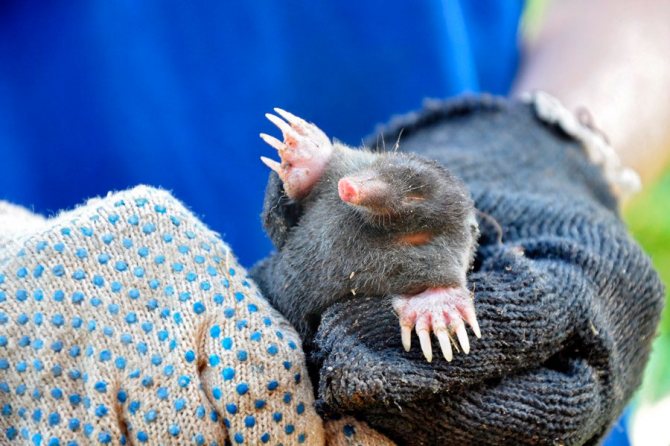
Interesting to know! Molting of moles is carried out from spring and continues until autumn. Short limbs are armed with wide paws, as well as strong and sharp claws, which allows the animal to dig underground tunnels quite quickly. A short tail can be seen at the end of the body.
The head of a mole has the shape of a cone, while there are no auricles on the head. The nose is slightly elongated and resembles a trunk. There is practically no neck and the body immediately passes into the head. The eye sockets are quite small, while it can be said that there are practically no eyes as such, since the lens of the eye and the retina are absent. Despite this, the eyes are closed with movable eyelids. There are varieties of such animals in which the eyes are overgrown with skin. But moles have excellent hearing, smell and touch. The skull is relatively long and conical in shape. In the mouth of the mole, which is closed by rather thin zygomatic arches, there are from 33 to 44 teeth. The shoulder girdle of moles is wide and powerful, but the pelvic girdle is narrow and long.
Character and lifestyle


Moles prefer to live apart, because they do not get along well with their relatives. Despite this, they form pairs in order to reproduce their own kind. Young moles treat each other well, but as they mature, they begin to sort things out among themselves. Moreover, they can be so irreconcilable to each other that they are ready to bite and then eat. Because of these features, young moles are constantly exploring new territories in order to master them later.
In the event of the death of one of the relatives, live moles immediately become the owners of its tunnels. Moles actively mark their possessions due to a special secret that appears on the wool located in the belly of the animal. They do this regularly so that none of their relatives would think that the territory is empty.
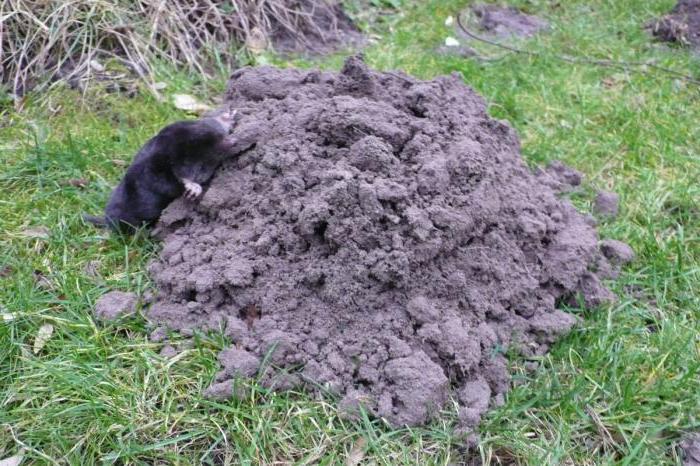
Moles spend almost their entire life underground, digging tunnels in search of food at various depths. If the soil is "light" and loose, then the holes can be at a depth of 5 cm, and if the ground is "heavy" and dense, then the holes can be at a greater depth. Females arrange their nests at a depth of up to 2 meters, while they can be under stumps, under tree roots or under stones. Where there is a mole nest, an upland from the accumulated soil can have a height of up to 80 cm. The nest, as a rule, is covered with dry grass or other natural components.
Moles are constantly on the move in search of food items, since digging holes requires a lot of energy, which must be replenished regularly. With the onset of spring, when there is a lot of moisture, the moles try to move to the hills, but with the arrival of summer, when the excess moisture leaves, the moles easily move to the lowlands. Moles can live their entire lives within their plots. When the weather is hot outside, moles move closer to streams or rivers to quench their thirst.
An interesting moment! Due to the peculiarities of the structure of the wool cover, the mole moves equally quickly along its underground passages, both forward and backward, while it does not have to turn around.
Moles rest several times a day, for a couple of hours. In winter, they do not sleep and continue to dig holes in unfrozen ground. Despite the fact that they are mostly underground, they can be in danger the moment they throw soil to the surface of the earth. Naturally, such cases are quite rare.
How many moles live


Their lifespan depends on various factors. Moles often die from diseases, as well as from predators such as weasels or martens. Parasites can infect these animals with a very dangerous disease such as piroplasmosis.
The average life span of moles is about 4 years., although under favorable conditions, they can live longer.
Molting in moles


The wool cover of the animal, due to the peculiarities of life, quickly loses its functions, so the molting process takes place in spring, summer and autumn, but this does not happen in winter, since moles, although they dig, are very few. The places where the new wool has grown are darker, and the wool is almost 3 times longer. At the same time, these places begin to wipe out much faster, since they are in more contact with the surface of the underground passages.
The first molt begins in April and can continue until early summer. First of all, females molt, and then males. New wool grows in place of old, worn out winter wool. Midsummer is characterized by the fact that the second molt begins in these animals, while the first molt occurs in young moles. After the summer molt, the autumn molt immediately begins, after which the best quality coat grows in the moles. Therefore, after this moulting, the coat becomes the thickest, highest, shiny and velvety. The main color is black with a silvery sheen.
Folk remedies for fighting moles at their summer cottage
For many years, gardeners and summer residents have been using methods of fighting moles that have been tested in practice. Sometimes such methods look ridiculous, but when the struggle comes to a standstill, they try to use everything possible.
Homemade sound scarers
It is believed that devices that emit continuous sounds scare the animals away.
For this, summer residents make simple sound scarers from scrap materials:
- Inverted cans or empty beer cans are put on metal pins driven into the ground.
- In the presence of wind, the banks jingle, and the moles do not like this.
- In calm areas, this method is ineffective.
According to this principle, wind turbines (turntables) are installed:
- the lower end of the pole is buried in the ground to a depth of 1 meter;
- when the weather vane rotates, vibration is transmitted to the soil and scares away moles.
In addition, they try to insert cut reeds into dug-in pipes or directly into holes, which, in the wind, emits sounds through the upper hollow part of the stem.
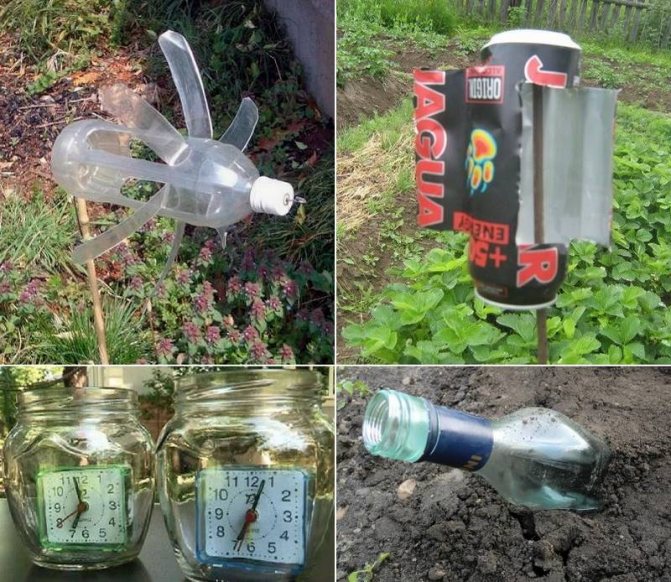
To create a stronger sound, they use an alarm clock installed in a tube dug into the ground. At regular intervals, a sound signal occurs, propagating underground through the pipe.
The ideas to make ratchets and windmills appeared due to the knowledge gained that moles are afraid of soil landslides and react to any vibration. Another theory is that they are afraid of birds of prey, and the sounds produced are reminiscent of the sound of their wings. But it will not work to recreate an exact copy of the rustle of the wings, therefore such methods are ineffective.
Often a mole appears next to a dug ratchet, which means that the mole is not afraid of these sounds. The advantages of such methods are cheap, but the result is zero. After all, animals are accustomed to living in conditions of constant noise from cars, construction equipment, lawn mowers and are not afraid of them.
It is not difficult to make your own scarers. They work according to the same principle, and you can come up with a variety of modifications.
An example of a homemade repeller:
- The structure will consist of a 1.5-meter pin, dug in or driven into the ground (to a depth of at least 30 cm), and an upper part that simulates a propeller.
- It is made from a plastic bottle by making cuts and bending the blades outward.
- Having put the bottle on the pin, it will rotate from the wind, and create vibration that is transmitted along the pin to the ground.
- You can also use several bottles, aluminum cans for the propeller.
- The method is cheap, but ineffective. In the absence of wind, the repeller does not work.
Video: How to make a do-it-yourself sound scarer?
Scare away the smell
Moles have a well-developed sense of smell; they sense prey at a great distance. This property is the basis for the following method of how to breed moles.
Many substances have a pungent, unpleasant, repellent odor:
- Of liquids, kerosene is often used to combat... In a freshly dug mole, you need to push a rag or rag soaked in kerosene deeper, bury the exit. The smell of kerosene will scare away the mole. He will not appear at this place for at least 1-2 weeks. The smell of kerosene quickly spreads along the underground passages, but the animal quickly blocks unnecessary passages and bury them. Over time, new passages will appear, and the old one will bury.
- You can also use vinegar, white spirit, ammonia, creolin... The principle of use is the same as with kerosene, the action is short-term, requiring regular repetition. These smells are unpleasant to the animal and he will leave the place, but will dig new passages in another. So you can scare him away from the beds, flower beds, lawn, but you will need to periodically update the smells in order to block the movement of the mole to the beds.
- Well scares off carbide... Throw a few pieces into the molehill and seal the exit hermetically. When interacting with moisture, gas begins to evolve, which is unpleasant for the mole. It is better to do it in several places at once so that the mole cannot bury one passage and live peacefully on. When the action of gas starts from different directions, the animal will be forced to leave. Carbide helps well with autumn digging, the smell in the ground will be almost everywhere and the mole will not stick to the site.
- Some gardeners try to bury rotten herring in their holes., supposedly this smell is not tolerated by moles and will certainly leave. When all the methods have been tried, but there are no results - from despair and for their own calming, this is also used. But if there is a lot of food on the site, it will not leave, it will walk where there is no smell from the substances.
Homemade traps
Moles are very sensitive and careful. Catching them in a makeshift trap is difficult and time-consuming.
How to make a trap with your own hands:
- Places are determined first, where the animal moves on its own moves constantly.
- If it is a stern passage, he walks over it once to collect worms and larvae. And after dinner, she will not return. It is useless to set a trap there.
- Discovered, the move is destroyed In one place. If the move is restored, then it is permanent and suitable for a trap.
- Carefully open up part of the move, dig a hole below, put a jar or container there (you can fill it halfway with water).
- Top of the stroke be sure to restore using cardboard or plywood, and sprinkle with earth. But the mole is very well oriented, and 1 case in 1000 that it will fall into a trap.
- Most likely, the mole will make a detour around this site and dig a new move.
Plants against moles
Summer residents and gardeners use special plants that moles do not like:
- One of these plants there is a daffodil, where it grows, moles usually do not rage. You can plant these flowers around the perimeter, they are unpretentious, grow quickly. But they do not give a 100% guarantee.
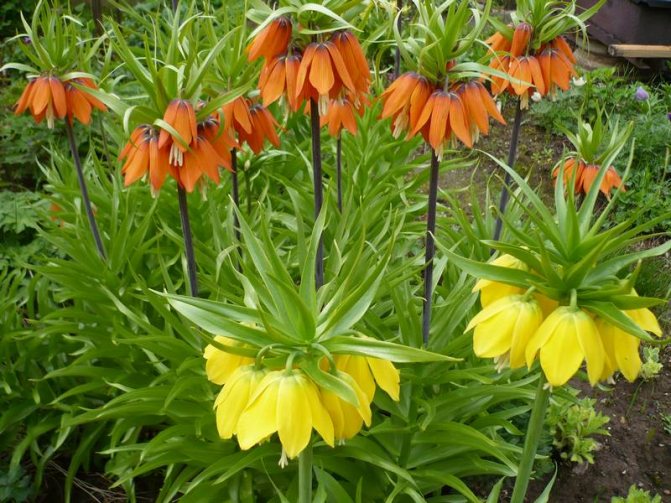
- It is believed to scare away moles imperial hazel grouse, spurge, castor oil plant. It should be borne in mind that the fruits of castor bean and milkweed are poisonous, and if there are small children in the family who can accidentally eat these fruits, then it is better not to plant such plants.
- Marigolds have a specific smell, moles do not dig next to them, but at a distance of 1.5-2 meters, they can calmly make their move.
- Onions and garlic do not scare away moles, they are not vegetarians, they do not eat root crops, so they calmly dig their passages past the garlic and onion heads, bypassing them.
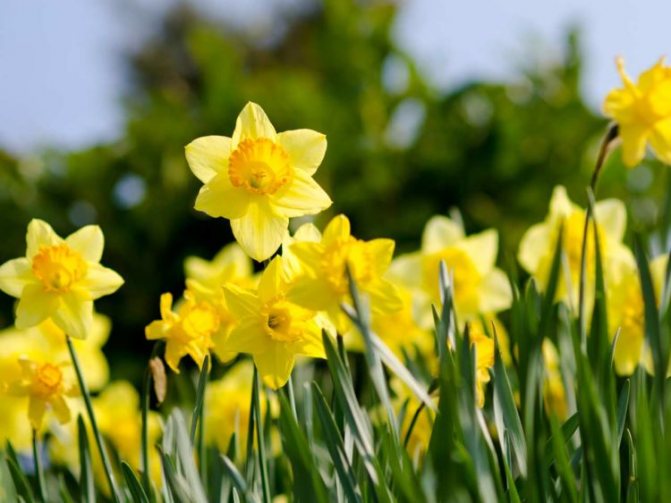


Narcissus yellow
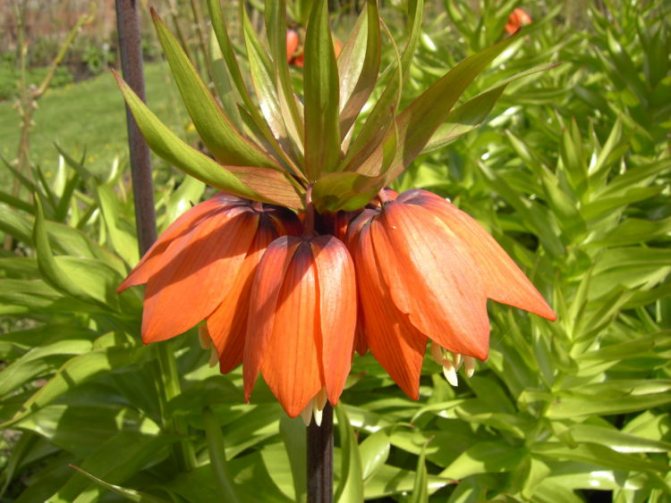


Grouse imperial
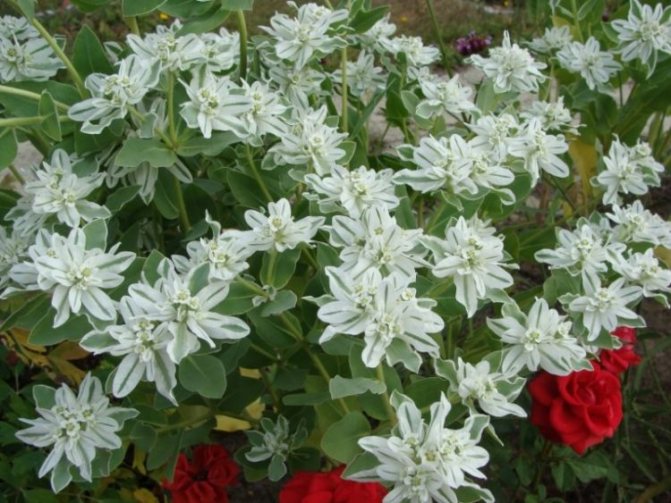


Spurge
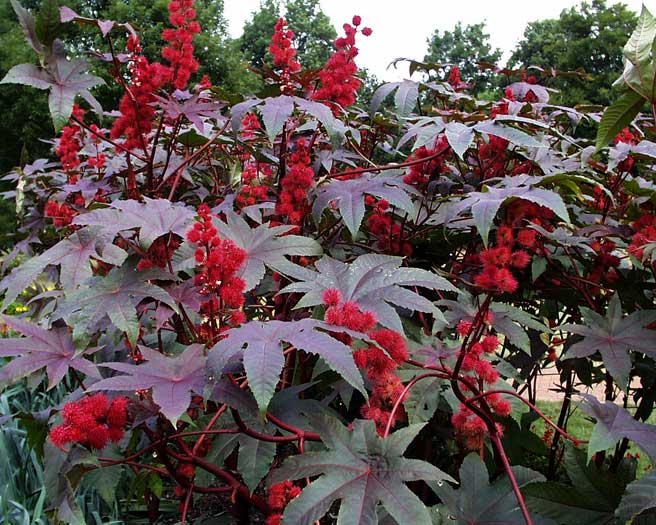


Castor oil plant
Types of moles with photos and names
To date, it is known about the existence of about 40 species of these animals. The most famous species are:
Common mole (Talpa)
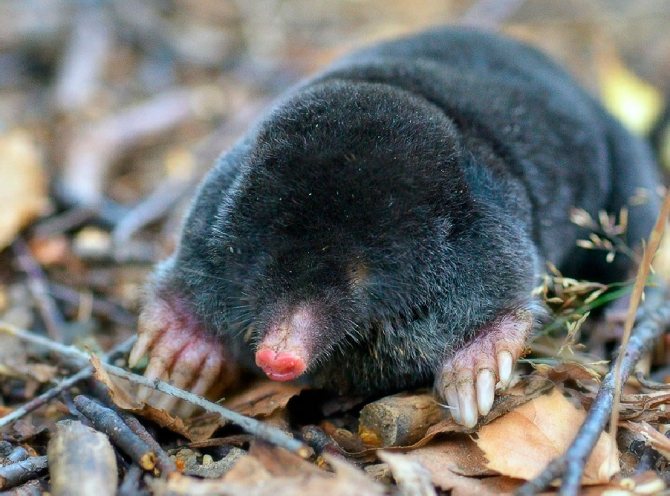


Adults grow in length from 12 to 16 centimeters, while gaining weight from 50 to 90 grams. Tail length from 2 to 4 centimeters. In place of the eyes there are narrow slits, while the eyelids are motionless. The main color is black, but at the same time in the belly area it has a lighter color. Young individuals are characterized by a lighter coat than older moles. They breed once a year. Moles of this variety are found almost throughout the Euro-Asian continent.
Blind Mole (Talpa caeca)
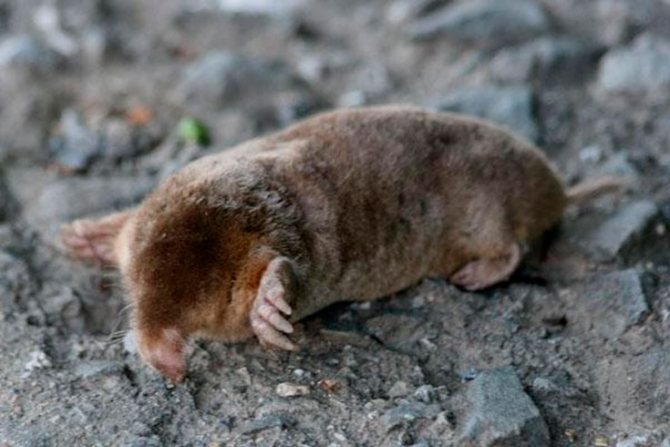


It is considered one of the smallest representatives of this species of mammals, since its body length is from 8 to 12 centimeters, and its tail is no more than 3 centimeters long, and weighs no more than 30 grams. The mole has no eyes at all, since they are covered by the skin. The diet of this species includes various insects and their larvae, although it can also feed on earthworms. The breeding process begins with the onset of spring, when the snow is just beginning to melt. Natural habitats are associated with the mountainous regions of Turkey, the Caucasus, as well as Northern Iran.
Long-tailed mole (Scaptonyx fusicaudus)
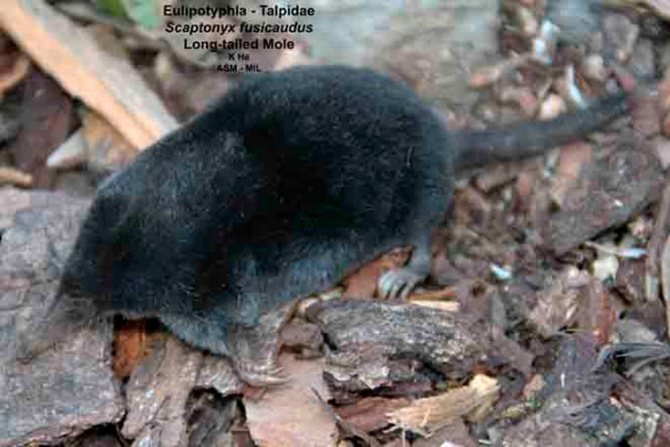


It is even smaller in size, since it grows in length up to 9 cm and no more, while its tail is relatively large and reaches a size of 4.5 cm. The body is covered with rather tough fur. It prefers to live in the highlands of North Vietnam, South China and North Iran with the presence of coniferous plantations. They dig underground passages at a shallow depth.
Caucasian mole (Talpa caucasica)
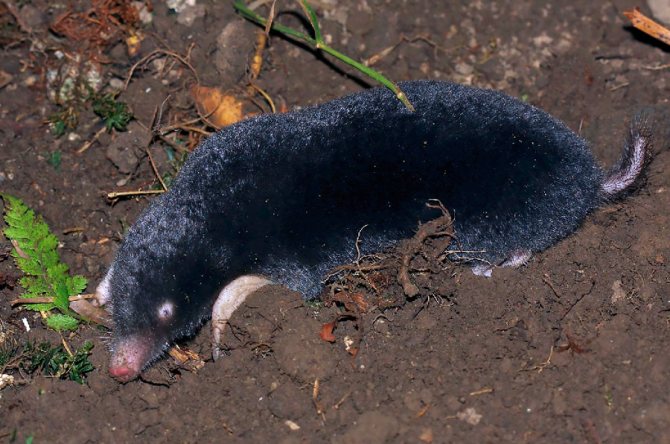


It differs in average sizes, reaching values from 10 to 14 centimeters, with a weight of 40 to 85 grams and a tail length of no more than 3 centimeters. It takes on a brown tint after the molting process. The animal is practically blind, since the eyes are located under the skin. It digs underground labyrinths at a depth of no more than 20 centimeters. The diet is based on earthworms, although it can feed on various insects. Breeds once a year.Lives in the Ciscaucasia, Transcaucasia, as well as in the greater Caucasus.
Siberian mole (Talpa altaica)
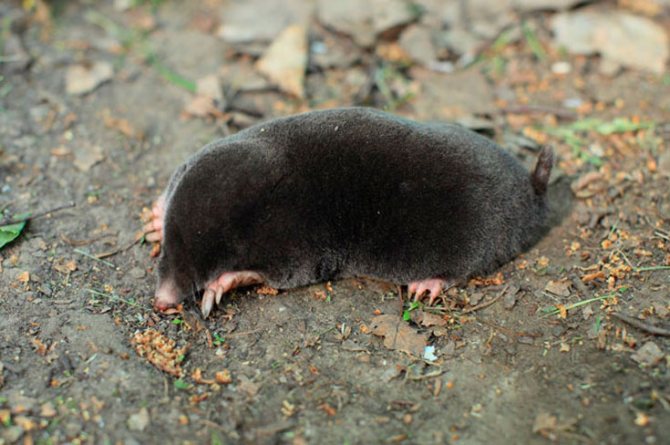


It has a slight resemblance to the European mole, but at the same time it has a slightly larger size. Adult males can be 13 to 19 centimeters long, weighing 70 to 230 grams, while females are somewhat smaller. The tail of these animals is also relatively short, no more than 6 centimeters long. The eyes have a movable eyelid. The main color of the animal is almost black or dark brown, with albinos, as well as red, yellow or spotted individuals. The diet consists of various insects as well as earthworms. The peculiarity of the Siberian mole is that the female bears her future offspring for 9 months. This is due to the peculiarities of the development of the embryo. Despite the fact that individuals mate in the summer, embryos begin to develop only with the arrival of spring. Future offspring are born no later than the end of May.
Japanese shrew mole
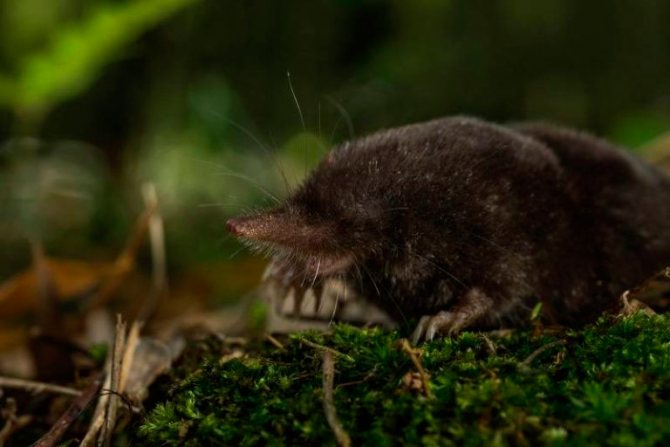


It grows in length up to a maximum of 10 cm, while the length of the tail is only 3 cm. The tail is covered with wool, and a tassel is located at its end. The coat does not differ in the presence of a characteristic shine, while it is thick and soft, either black or black-brown. Can hibernate in bird nests. Inhabits the mountain slopes of the southern islands of Japan. Breeds once a year.
Japanese Mogera (Mogera wogura)
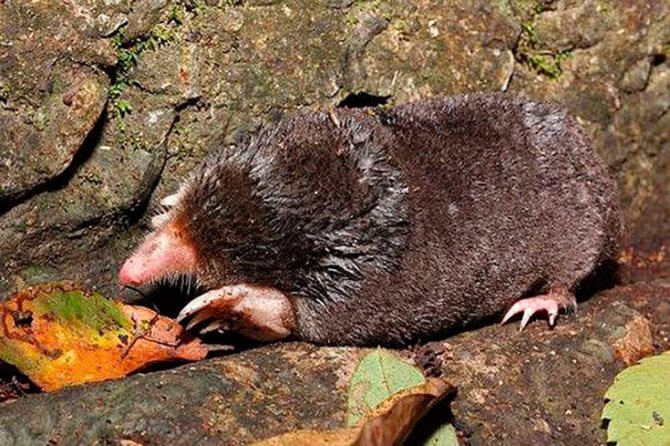


Individuals of this species grow in length up to 15 centimeters maximum, while the length of the tail is only 2, with a small, centimeters. Adults weigh on average about 150 grams, although there are also more massive individuals. The main color is black, brown and gray, while the abdominal area is painted in lighter colors. The animal feeds mainly on insect larvae, but on occasion it can also dine on earthworms. Underground labyrinths are distinguished by a 2-level scheme. The first level is at a depth of about 70 cm, and the second - at a depth of up to one and a half meters.
Star-nosed (Condylura cristata)
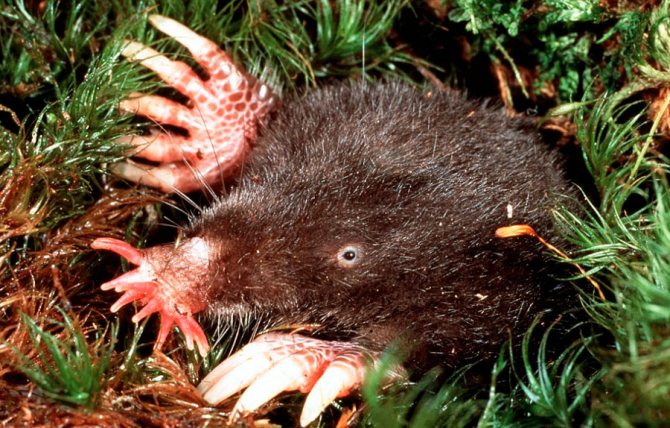


It has a body up to 20 centimeters long or slightly more, while the tail is relatively long, almost 8 cm in length. The tail is scaly type, covered with sparse hairs. For the winter, the tail becomes thicker. The animal has no ears, but you can see very small eyes. The coat is thick, black or dark brown. The uniqueness of the species lies in the presence of a special stigma, somewhat similar to a star, formed by two dozen fleshy processes. This stigma helps the animal in search of food. The two upper processes, which are directed upward, are motionless, and the rest are mobile and quite sensitive. This animal is an excellent swimmer and feels great even under ice. Therefore, his diet consists of fish, as well as earthworms and shellfish. Easily moves, both on the ground and in the snow. The most favorite habitats are associated with the moist soils of the southeastern states of the United States, as well as Canada.
Difference between mole rat and shrew
Unlike a mole rat (he is a gadfly or a blind man), the mole is a predatory animal.
10 best remedies for moles and shrews in their summer cottage
The mole rat is a rodent that consumes only real plant food. Its menu includes:
- wheatgrass-wheatgrass;
- oak and maple seedlings;
- juzgun;
- sagebrush;
- acorns;
- swing.
They also have external differences. A mole rat is much larger and larger than a mole. Above and below it protrude four powerful incisors protruding from the oral cavity. They are the main means of digging soil. Paws are poorly developed, like all rodents. At the same time, the front legs of the mole are powerful and strong, because it is with them that he makes his own moves.
The blind rat, unlike moles, digs bunk holes for itself.The first floor is the nest itself, where the animal lives, stores food, etc. The upper tier is located at a depth of 25 cm, where plant roots are located.


A shrew is distinguished from a mole by the gray color of the coat. Also, unlike him, she belongs to rodents. Another remarkable feature of the shrew is its increased metabolism, which makes it almost constantly in search of food. She eats more worms, larvae and insects per day than she weighs. A mole, by comparison, needs less food, although it is also gluttonous.
Natural habitats
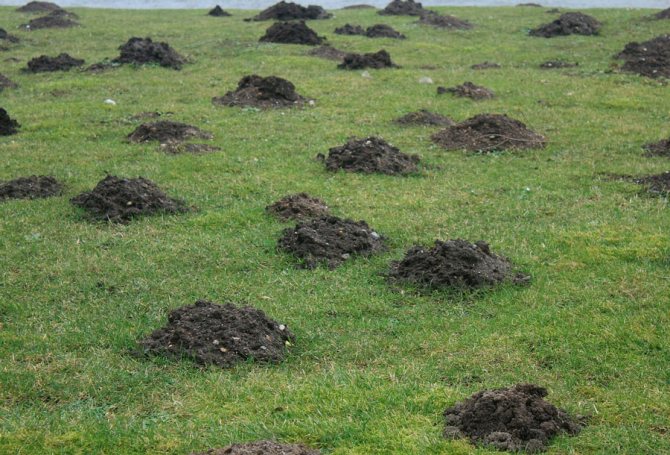


Moles are found almost throughout the Euro-Asian continent, in the USA, in Canada, in Mexico, etc. The only place where there are no moles is in the Arctic regions, and this is not surprising, since in these areas the soil is constantly frozen. It is very important for these animals that the nature of the soil allows them to dig underground tunnels. Almost all species bypass swampy areas.
Moles can be found everywhere: in forest glades, meadows, forest edges, deciduous forests, agricultural land, plains, hills and even mountains. At the same time, moles cannot be found in semi-deserts and deserts, which are characterized by a too hot climate. Moles dig holes for themselves, and their purpose is twofold: firstly, they need them as their home, and secondly, if they do not break holes, they will not be able to get food for themselves.
Construction method
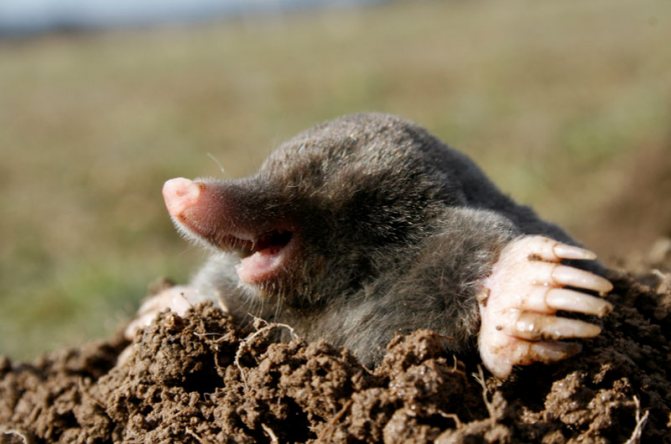
Outwardly, the mole's burrow looks like small loosened hillocks of soil. The animal digs the ground with its front paws, which are in the shape of a shovel, equipped with long, sharp claws. With this equipment, the most dense soil is easily loosened.
The absence of large ears, a sharp muzzle make it easy to move underground, calmly get worms, and catch insects. With its hind legs, the animal throws the soil back, and then transports it out. The places where the deep burrow is located are marked outside by embankments.
Interesting!
In numerous labyrinths, other inhabitants of the underworld can settle, very often they become mice, earthen rats. However, the mole does not surrender without a fight, it calmly drives the invaders out of their possessions.


Mole burrow
What does a mole eat
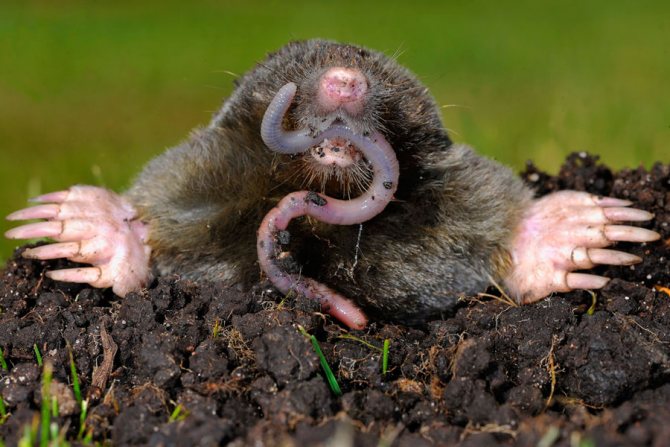


Earthworms form the basis of the diet of many species of moles, although they eat any objects of animal origin that come their way. Therefore, moles destroy many pests of agricultural land, as well as household plots, including wireworms, weevils, May beetle larvae and even flies. Some species of moles eat slugs with success. Mogers eat a variety of butterflies and their caterpillars.
An interesting moment! Moles are rather thrifty animals, as they make supplies for the winter. Often in their pantries, you can find up to several hundred pieces of earthworms. Despite this, in winter, moles continue to dig tunnels and continue to hunt worms, but not as actively as during other periods.
To be constantly in active physical shape, moles eat 6 times a day, while eating up to 60 grams of food, mainly earthworms. In this case, the animal can eat it whole or tear it apart. They eat much less during winter than during warmer periods. They cannot starve for a long time, having endured a hunger strike for no more than 17 hours.
The benefits and harms of moles on the site
Before you start fighting moles, you need to weigh the pros and cons, assess the harm and benefits of its habitat. They bring irreparable harm. Lawns, lawns, planting of young seedlings, greenery irrevocably die after the passage of this animal for feeding.
In this case, a whole furrow of earth rises, several meters long, and when irrigation is carried out, it all falls into these dug trenches. It is painful for the owners to watch the dying harvest.
The mole does not eat plants, does not gnaw root crops, but breaking through the passages, destroys the root system.
Adult plants, shrubs, trees are not very susceptible, but all young seedlings die.
Along with harm, moles are beneficial:
- Eating insects and larvae, he relieves the garden of a number of such pests as: May beetles, bears, wireworms, slugs, snails.
- Loosening the earth, saturates it with oxygen.
- In the area where these animals are disposed of, pests appear that destroy the garden.
Reproduction and offspring
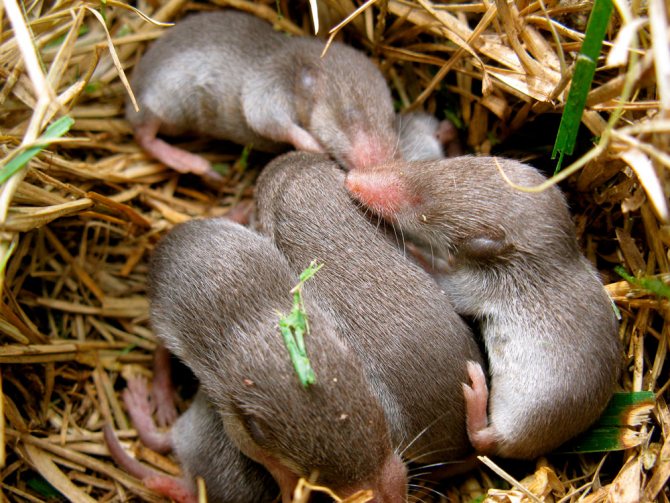


The breeding process of moles is directly dependent on the habitat, although their rut begins at the end of the month of March. Older females mate in earlier terms than younger ones. Interestingly, the mating process is carried out not in burrows, but on the surface of the earth.
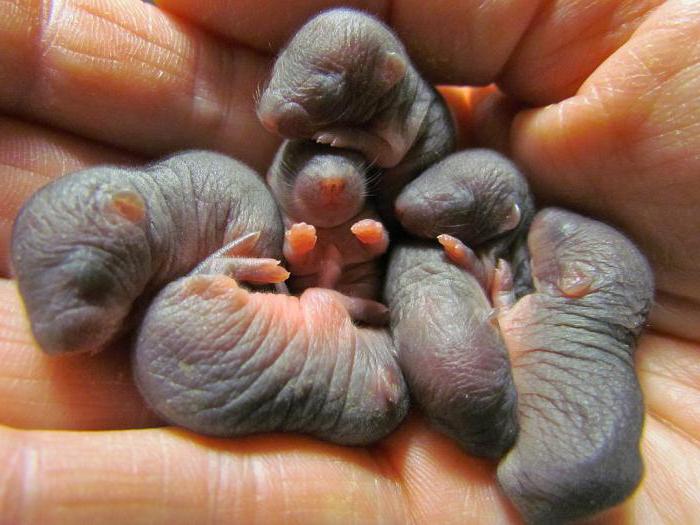
The female bears her future offspring from a month to 2 months, depending on the species, while in Siberian moles this period is delayed by 9 months. At the end of April, the moles begin to give birth to offspring that does not have a wool cover, moreover, they are blind, although it is possible not to talk about the vision of moles. Although these animals breed only once a year, up to 10 cubs are born. It should be noted that the greater Moger reproduces 2 times a year. The offspring born into the world grows by leaps and bounds and within a month reaches the size of adults. Basically, individuals become sexually mature after 1 year of life, although in some species this period begins much earlier.
More about mole mazes
When studying a new plot, moles have to crawl out into the fresh air. Even one animal occupies a large area with moves. They are of two types. The former are called residential. They lie at a depth of 6 to 90 cm and have a radius of 2.5 cm. The animal moves along these manholes to a feeding place or a watering hole. Other moves are needed specifically for the extraction of food. The animals usually lay them in the upper soil layers, where the soil is not too dense. In addition, it is there that worms and larvae live - the main food of moles.
Sometimes traces of these passages can be seen even on the surface of the earth. They appear as long soil rolls formed by swollen arches of passages. This happens if an animal makes a tunnel for itself next to the soil surface, and its vaults cannot withstand the pressure of the animal.
During the laying of new moves, the mole focuses on the hind limbs, and digs the ground with the front ones. They alternately penetrate the ground and move to the sides and back. After that, the animal with its strong head ramps into the soil, pressing it against the running walls.
If the burrow is dug at a depth of 10 cm or more, then the animal does not raise the arch with its head. He has to throw the excavated earth out. As a result, molehills appear - earthen heaps. They are usually small, no more than 15–25 cm in height. Their diameter is also small, but in some cases it reaches a size of one meter.


Natural enemies of moles
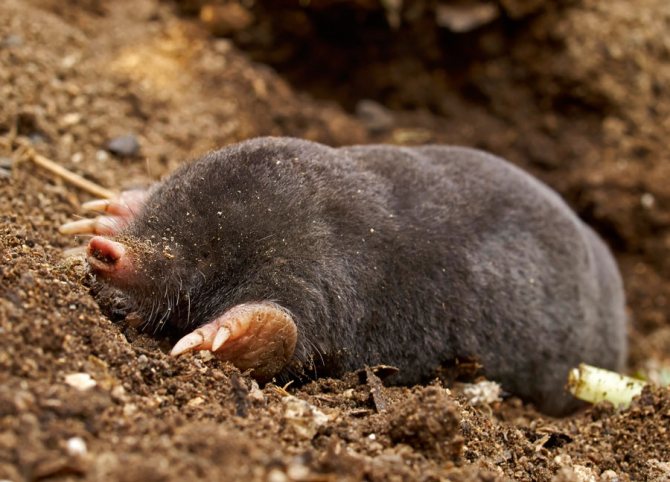


Moles do not have so many natural enemies, since they have been underground for almost their entire life. In addition, moles are capable of emitting a specific odor that frightens off many predators. As a rule, they are in danger when they find themselves on the surface of the earth, although such a predator as a weasel easily makes its way into the underground tunnels of moles and hunts them in their own burrows. Many moles die as a result of spring floods and drought. A person also participates in the process of killing moles, since they can cause significant damage to horticultural crops. Out of ignorance, some gardeners and gardeners believe that moles feed on plant roots, although in fact this is a delusion. They can only do damage by undermining the root system. As a result, the plant may die.Therefore, people try to get rid of such a neighborhood and fight moles in every possible way, sometimes adopting completely inhumane methods of struggle.
How can moles be prevented?
Fighting is harder than taking preventive measures. So that moles do not migrate from neighboring or abandoned sites to a fertilized and ennobled garden, deterrent measures can be taken.
If the animal has tried the abundance of food in the beds, it is difficult to expel it from such a place. But you can scare off by carrying out treatment along the perimeter of the fence with substances, the smell of which does not like the mole.
Tips on how to protect the area from moles:
- Make a foundation when installing the fence. Moles dig tunnels at a depth of 50 cm; they will have to deepen it by the same amount.
- Slate is dug in along the fence or a grid to a depth of half a meter, and above the surface of the ground, leave an edge at a height of 20 cm. This work is difficult, costly, especially if the site is large.
- In autumn, you can scatter carbide for digging., from the action of autumn rains, it will begin to emit gas, which moles cannot tolerate. The smell will scare off their appearance, but when it disappears, the animals will try to return.
Population and status of the species
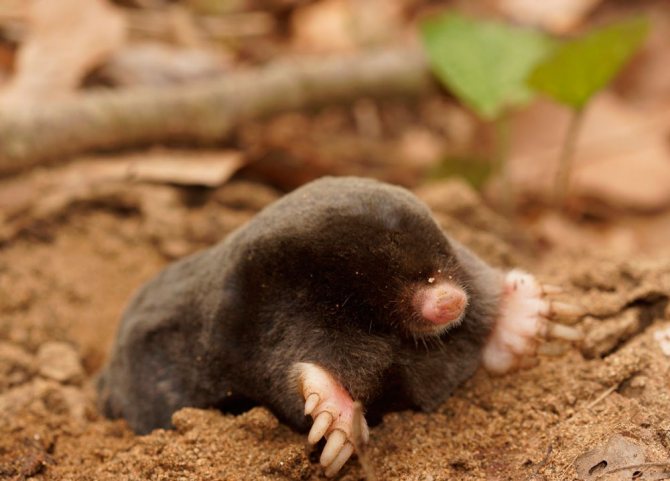


As a rule, moles live separately, regardless of gender and protect their possessions, both males and females. Pairs are formed only for the mating period, after which the males leave the females and do not take any part in raising their offspring.
An important point! With the arrival of spring, males are engaged in increasing their controlled territories. There are 5-30 individuals per hectare of land, which depends on both the variety and the living conditions.
The common mole was recently considered as an object for the fur trade, although this animal plays a very important role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem of our Planet. To date, no one is engaged in this fishery, therefore the total number of moles depends on many natural factors that affect the reproduction process of these animals.
Danger to humans
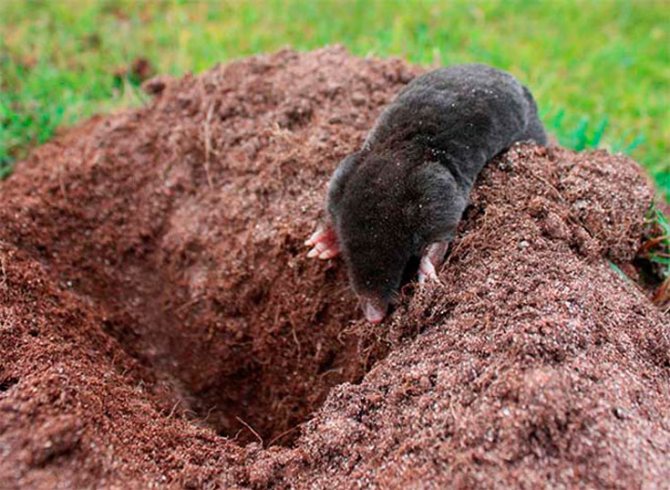


A mole will never attack a person, especially since the mole spends most of its time underground. When a mole appears on the surface of the earth, it sees practically nothing. When you try to pick it up, of course, the animal will begin to defend itself and can bite, especially since it has teeth. At the same time, even the captured moles, if treated carefully and not aggressively, do not try to bite a person, but at the same time they make sounds similar to the squeak of a rat. Most likely, the animal begins to panic and tries to scare a person or a foreign living object.
What wormholes and tunnels look like
The presence of moles on a particular site can be judged by the appearance of the earth's surface. At the same time, you can see a large number of cone-shaped hills of freshly dug earth. In the process of digging underground passages, the mole pushes the soil upward. The depth at which the animals dig holes is generally from 2 to 5 meters.
Most of the time the mole spends on digging holes and moving around them. This lifestyle requires a lot of energy and requires an intense diet. If the mole does not receive food within 17 hours, this will lead to its death.
One of the reasons why moles come to orchards and vegetable gardens is that there is cultivated and well-moistened land in which it is relatively easy to dig underground passages. In addition, moles have their own natural enemies. Living in close proximity to human habitation, they have the ability to avoid them.
Living in the garden, moles leave much less footprints, because the soil there is loose and there is no need to push it to the surface.
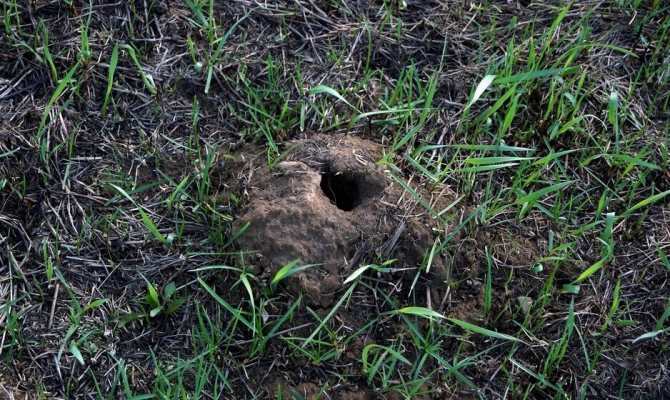


Wormhole