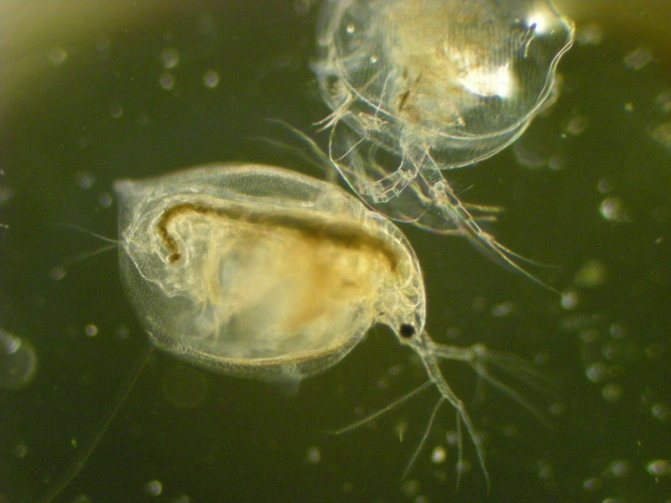
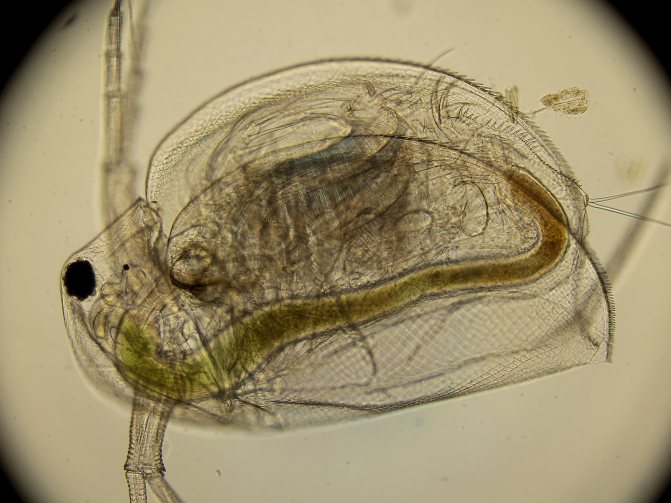
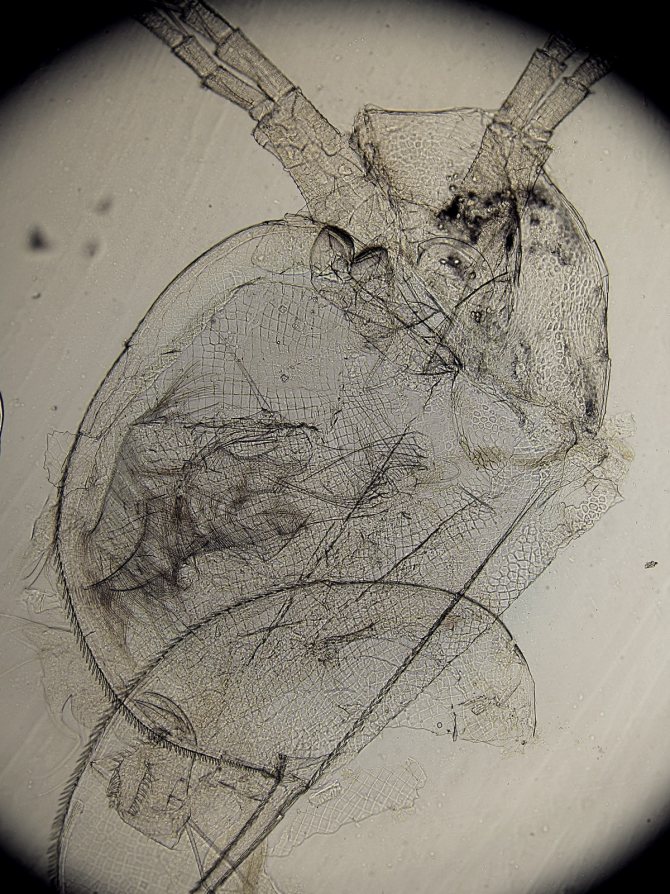
Daphnia is a fairly large genus of cladocerans, in which there are more than 55 species in the fauna. Due to their height (female - up to 5 mm, males - up to 3), these crustaceans received the second name "water flea".
Daphnia is used as live food for fish. And if earlier they went to rivers and lakes for catching, now this species can be bred at home.
What is Daphnia
The common daphnia is a small crustacean. Due to its movement by sudden jerks, it received its second name - the water flea.
Depending on the type, the dimensions can vary from 0.2 mm to 6 mm. Large species reach the size of a small pea and can be viewed without a microscope.
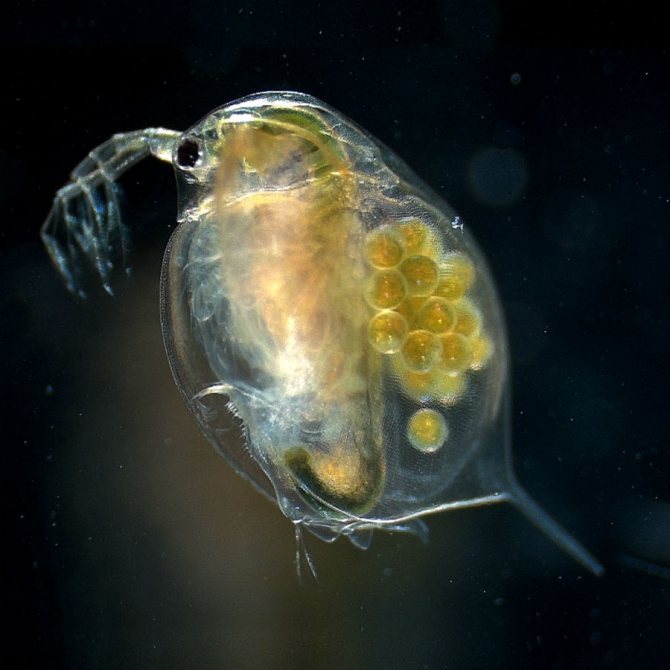
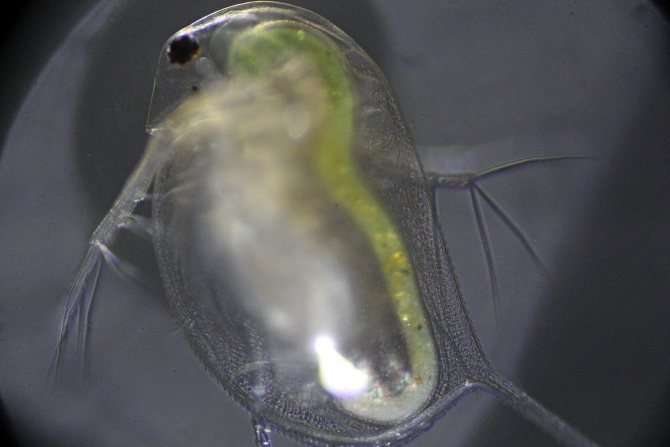
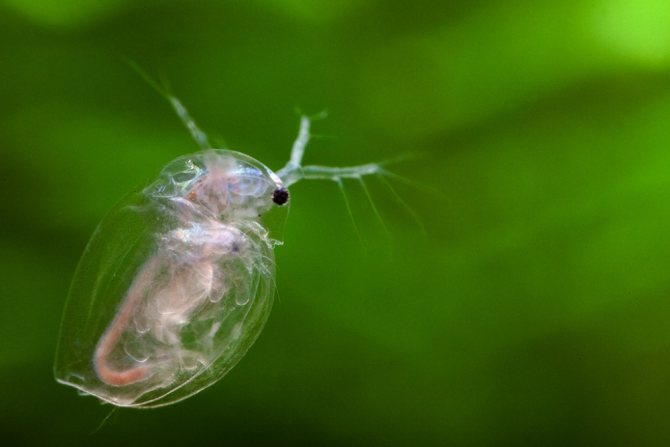
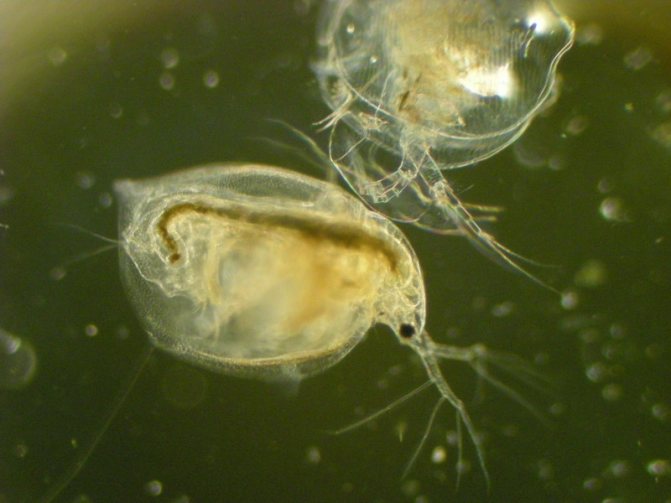
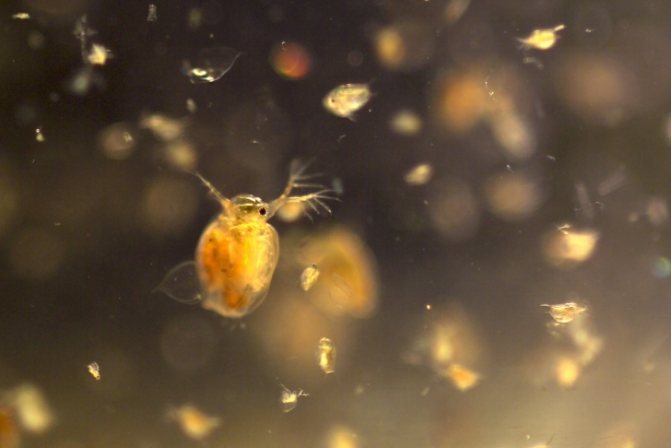
At magnification, the structure of the crustacean is clearly visible. The body of Daphnia is slightly flattened from the sides and has an oval shape. From above, it is dressed in a bivalve leathery shell - carapace, which ends with a tail needle and protects the internal organs.
Head
The head is covered with a hard chitinous cover. On it there is a beak-like outgrowth - the rostrum, under which there are short anterior antennae - antennae that perform the olfactory function due to the short outgrowths with olfactory setae located on them. The posterior antennae, longer, are covered with outgrowths. They help Daphnia move in the water column, making jumps.
Crustaceans have five pairs of complex legs. Daphnia pectorals perform the basic functions of respiration and nutrition. They are located on the head. Within one minute, the crustacean makes up to 500 strokes with them, passing unicellular algae and bacteria suspended in water through itself. The gill sacs are located on the limbs, which are filled with oxygen as they move.
Organ of vision
Daphnia have a paired organ of vision, which is double in sexually mature individuals. The large faceted eye consists of 22 facets. In some species, the number of facets can reach three hundred. The nauplial ocellus is located under the faceted eye.
With an increase in daphnia, the internal organs are clearly visible in the photo. An intestinal canal extends from the mouth opening. A pulsating heart is located on the side of the back. In females, between the body and the dorsal shell, there is a brood chamber in which the eggs are located.

What do water fleas eat?
In their natural environment, crustaceans feed on the simplest organisms: ciliates, bacteria, fungal spores, free-floating algae. In summer, they can be found in flowering water, which is abundant in phytoplankton. In winter, detritus serves as a food source for water fleas.
With the help of the legs, the crustaceans perform rhythmic movements and create a water current. The bristles located on the chest legs filter food. Then it enters the groove, after which it is redirected into the esophagus. Due to their feeding habits, the daphnia culture is often added to an aquarium to purify water from algae.
Interesting!
During the day, one individual is able to filter from 1 to 10 ml of feed in water and consume an amount of food that is 6 times its own weight.
Habitat and conditions
These cladocerans can be found in all ponds and lakes around the world.
Character and lifestyle
Large concentrations of crustaceans are observed in temporary reservoirs - ditches, puddles, small lakes with stagnant stagnant water. Getting into the water, even with a weak current, daphnia filter suspended soil particles and clog the intestines. This makes it difficult for him to move and causes their death.
The crustaceans spend most of their lives in the water column. Some species, filtering the water, feed on microscopic algae, while others live near the bottom and eat dead particles of plants and invertebrates. Some species, halophiles, tolerate drought easily, hibernating.
These creatures are very voracious. The daily intake of food can reach 600% of their own weight. Daphnia's main diet is bacteria, yeast and blue-green algae. The largest concentration of crustaceans is observed in reservoirs with "blooming" water, where they reproduce especially intensively.
Daphnia reacts sharply to lighting. In bright light, she tries to stay closer to the bottom of the reservoir.
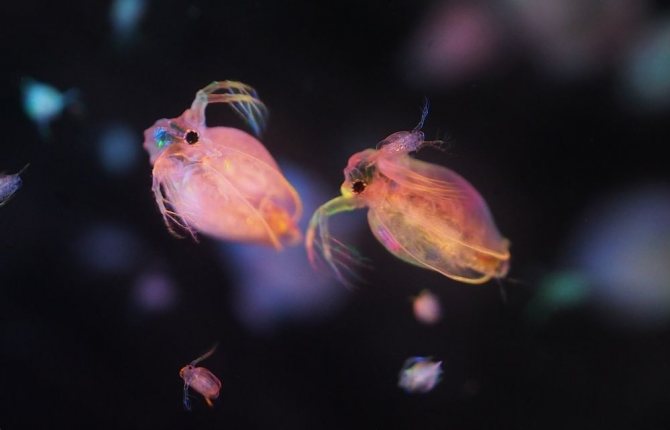


Some dry facts about Daphnia
In fact, there are no guarantees that our hero is exactly Daphnia pulex, it is possible that it is, for example, D. magna, but little depends on the exact classification, the essence of them is the same.
So the generic name is daphnia
(on Wikipedia):
A type: arthropods
Superclass:
crustaceans,
Class:
gill-legged
Superorder:
cladocerans
Detachment:
Daphniiformes
Suborder:
Anomopoda
Family:
Daphniidae
Genus:
Daphnia
So, with the word "daphnia" we call all crustaceans of this genus, not really understanding their species.
Appearance
Sex differences
Under favorable conditions, there are no males in Daphnia. Females give birth to their own kind. When conditions change, some of the females give birth to males.
Individuals of the female and male sex have some differences in the external and internal structure:
- females are larger in size;
- on the head shield and the external integument of females there is a pattern of rhombuses and polygons, which is clearly visible when magnified;
- the first and second pair of legs in males have hook-like outgrowths that allow them to cling to females during mating.
Subspecies
In natural conditions, there are about 150 species of these crustaceans.. Very often, several dozen species of crustaceans live in one reservoir.
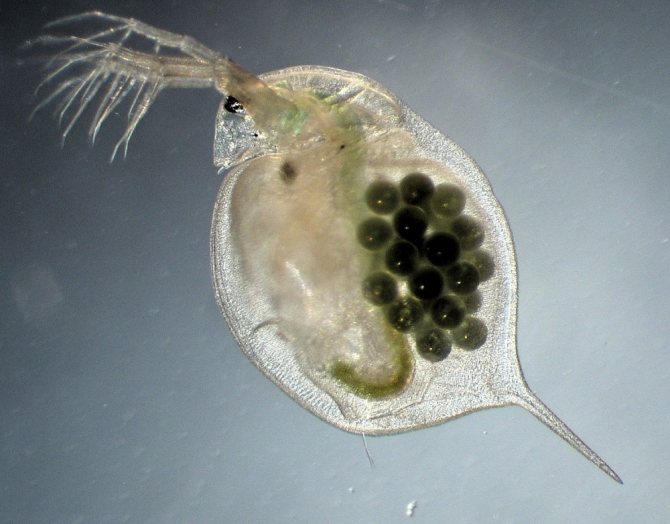
Daphnia magna
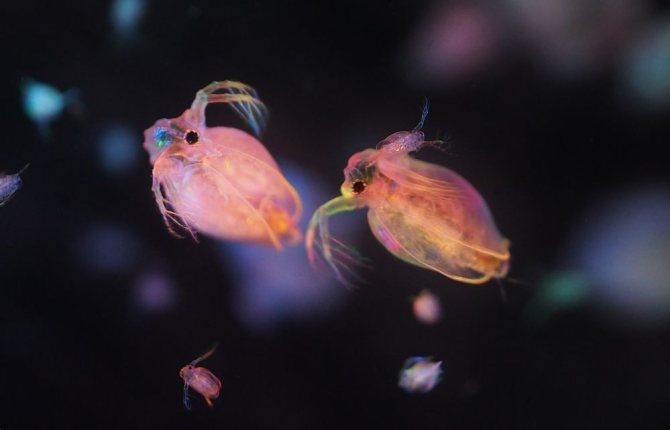
This variety is used as live food for aquarium fish because of its high nutritional value. The body length of the female is 3-5 mm, of the male - no more than 2 mm. Newborns are microscopic in size. The main color of the outer cover is yellow or pinkish-orange. This species easily tolerates a drop in temperature. In nature, it is quite rare, but in places of constant habitat, it is abundant. The lifespan of adult specimens is 3 months.


Daphnia pulex
The length of an adult female does not exceed 4 mm, of a male - 1.5 mm. The color of the outer covers ranges from light yellow to red. Outwardly, crustaceans resemble Daphnia magna. The difference lies in the smaller size and life expectancy, which does not exceed one and a half months. The variety is characterized by incredible fertility. Females lay eggs every five days. Each clutch consists of 15 eggs.

Increased productivity
Daphnia production is relatively easy. However, there are measures to increase the productivity of cultivation.
1. Good aeration (good to the extent that the water is oxygenated, but not overly strong aeration) is a major factor in increasing productivity. Some species prefer no aeration, but Daphnia magna grows best in its presence. In addition, it allows to increase the density of the culture, water circulation (which prevents stagnation and oppression of the culture), reduces algal plaque on the walls of the vessel, and also transfers food particles into a suspended state, which is typical for the natural diet of daphnia.
The only drawback is that small air bubbles fill the carapace of crustaceans, which float and cannot feed.The air atomizer should be avoided altogether, or it should be very coarse to create large bubbles. Convenient in terms of aeration is the "bio-foam" filter (the air-lift filter is shown in the photo on the right).
It is commonly used in a fry tank, but is ideal for daphnia. It captures large particles, promotes their decomposition to feed algae. 2. Regular maintenance of cleanliness of the environment and replacement of water 3. Regular selection / collection of crops. This activity maintains constant crop growth and provides daphnia with the opportunity to accumulate oxygen and feed faster. 4.
24 hour daylight hours increase the productivity of daphnia, but this is an optional measure. Also, do not keep daphnia for 24 hours in the dark, because this stimulates crustaceans to form ephippia. 5. The mode and degree of water replacement depends on the nutrient medium used, but, in any case, they are necessary to cleanse metabolites and toxins.
Benefits and harms for the aquarium
They are beneficial creatures that filter the water and regulate the microflora of the aquarium. They serve as live food for many inhabitants of the home reservoir.
The water flea is not able to bite a person or harm aquarium fish, since the crustaceans do not have a piercing-sucking mouth cavity. The bite claims are fiction.
The main harm of copepods is associated with their high allergenicity. An allergic reaction is caused by a dust-like suspension obtained when they are dried for use as dry feed.
If dust particles get into a person, an allergic reaction may begin, accompanied by a dry cough, redness of the eyes, profuse lacrimation, a runny nose, and exacerbation of bronchial asthma. After a while, a rash appears on the skin, itching, burning.
For allergies, seek immediate medical attention or take an antihistamine.
Value as fish feed
The water flea is very often used as food for the inhabitants of the aquarium. Crustaceans contain up to 70% protein. It is given to fish dry, fresh or frozen. Crustaceans are caught in water bodies or bred at home.


How to feed your fish with daphnia
The main rule of feeding is not to overdo it with the amount of food, since daphnia can decompose very quickly, thereby polluting the water and allowing the development of bacteria that can lead to fish diseases. You should also follow these tips:
- always grind the food into powder before use - since large particles do not have time to swell in water, and this is fraught with swelling of the food in the stomach of the fish;
- before use, pour boiling water over the feed and let it brew, then rinse by settling;
- it is recommended to mix with gammarus to improve the nutritional value of the feed.


Dry daphnia can be used both as a main food and as a groundbait.
Thus, daphnia is an ideal live and dry food for fish, which is easy to reproduce, and also does not require special care and maintenance costs. The nutritional benefits of these crustaceans will make your fish healthier and happier.
How to fish yourself from water bodies
Daphnia is caught from late spring to late autumn, until the reservoirs are covered with ice. It is recommended to fish in the morning or in the evening in cloudy calm weather. In such conditions, they rise closer to the surface of the water. For fishing, you can use a regular net made of cloth.
The caught specimens should be put in a tin container and shaken periodically. It should be remembered that at high densities during transportation, they may die. At home, the crustaceans are washed and passed through a sieve to sort by size.


Breeding at home
Breeding crustaceans is straightforward. To do this, it is enough to create suitable conditions.
Container for growing
For growing crustaceans at home, you can use containers with a volume of up to 20 liters, made of glass, propylene or stainless steel. If they are grown in a conventional aquarium, the surface area must be large for gas exchange.
Environment parameters
Daphnia can be grown in almost any environment.
Crustaceans feel most comfortable in water with the following parameters:
- Temperature. The water flea thrives in a body of water with a wide temperature range. The optimum water temperature is 18-24 degrees.
- Salinity. Daphnia belongs to freshwater crustaceans, so the water in the container must be fresh.
- Oxygen. Under natural conditions, daphnia can live in reservoirs with dirty water, so the oxygen level can range from zero to very saturated. Such endurance of organisms is associated with their ability to produce hemoglobin. Crustaceans do not tolerate intense aeration with a large number of small bubbles. With a slow saturation of the oxygen capacity, a layer of foam forms on the surface, which can be destructive.
- Ammonia. Even an insignificant content of ammonia has a negative effect on the organism of daphnia and may affect the intensity of their reproduction.
- Minerals. Crustaceans react sharply to changes in the chemical composition of water. A slight increase in the amount of zinc, magnesium or potassium in the aquatic environment can be detrimental to them. Thus, a slight increase in the amount of copper reduces the activity of daphnia, and phosphorus can cause the death of young individuals.
Aeration
Additional enrichment of water with oxygen is desirable when growing certain species. Aeration promotes the development of phytoplankton and prevents the formation of a film on the water surface. The air flow should be of medium intensity so as not to cause inconvenience.


What to feed
Under natural conditions, daphnia feeds on microplankton, bacteria and yeast.
To obtain bacteria, banana peels should be soaked in warm water and infused for 6-7 days. When the water becomes cloudy, the culture medium can be added to the aquarium at the rate of 0.5 liters per 20 liters of water.
For feeding, you can use dry or wet baker's yeast, which is rich in nutrients. The feed is applied at the rate of 28 grams per 20 liters of water daily.
Chlorella is used as microscopic algae, which inhabits almost all water bodies. To breed such algae, it is enough to place a small amount of water from the aquarium in a warm, well-lit place. In such conditions, algae begin to multiply actively.
To diversify the diet of crustaceans, it is recommended to add a small amount of juice of beets, cabbage or carrots to the water, which will serve as an additional source of vitamins.
How to increase the productivity of growing
Growing daphnia at home is not difficult even for beginners.
To increase productivity, you should use the following recommendations:
- for aeration of the container when breeding crustaceans, an air-lift filter should be used, which is used in cages with fry;
- water change is carried out taking into account the feed used and the volume of the container; if the aquarium is large, then up to 30% of the water is replaced once every 7-10 days;
- collect daphnia regularly; this will help maintain constant breeding and growth of crustaceans;
- daylight hours must be at least 18 hours; providing light around the clock is ideal.
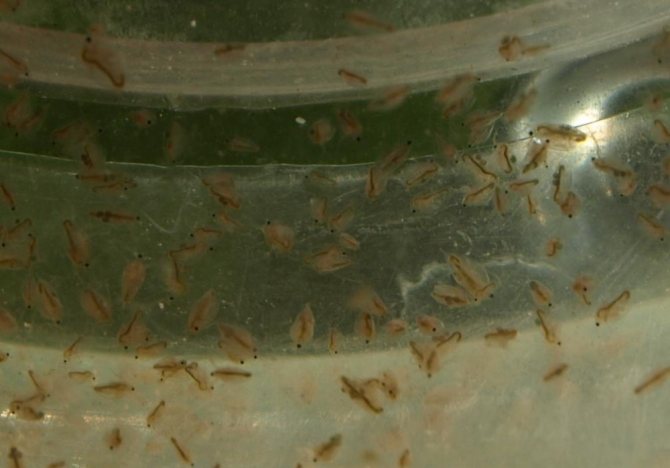


What and how to feed daphnia
For daphnia, there is no specialized feed and no prohibitions on any ingredient. However, you should not use foods for feeding that can cause decay or decomposition in water. These products include:
- banana peel;
- pieces of bacon or trout;
- pieces of meat.
The optimal food for crustaceans is shown in the table.
| Feed name | Where to get? |
| Powdered algae | Specialty Stores |
| Dry food for shrimp larvae | Specialty Stores |
| Dry yeast with the addition of flour from the layout 1: 1 | Any grocery store |
| Boiled egg yolk | Home cooking |
| Pieces of apples or cucumber (use as top dressing, remove leftovers) | Home cooking |
Do not forget that you cannot overfeed Daphnia. The food must be poured into the aquarium and mixed in the water. Keep track of how long the water is completely cleaned up. If the water becomes clear within a few hours, this means that there was little feed. But if the water remains cloudy the next day, there is too much food.
It is recommended to feed crustaceans 1-2 times a day.
Reproduction
Water fleas are fertile. Sexually mature females are capable of laying 15 to 30 eggs up to once a week. The population is being renewed at a rapid pace. The way of life of the larvae does not differ from that of the adults. After birth, they stick together. In winter, the process of laying eggs slows down. Females lay two eggs once a week.
Features of the
Daphnia are characterized by cyclic parthenogenesis, that is, the ability to reproduce offspring without fertilization. Under favorable conditions, the female gives birth to a population of females.
Embryos develop under the outer cover in the brood chamber and are accompanied by several molts. Young individuals become capable of breeding 4 days after birth. During her life, one female produces offspring up to 25 times.
When external conditions worsen, crustaceans give birth to males, and the next generation lays eggs that will need to be fertilized. From such eggs, embryos are formed, covered with a protective shell. They hibernate and in this state survive drought or a drop in temperature. After the normalization of external conditions, they continue to grow and develop into adults. The next generation again gives birth to females capable of parthenogenesis.
A feature of the reproduction of daphnia is cyclomorphosis, in which specimens with different body shapes are born in different periods of time in the same population. Crustaceans born in the warm season have a long tail needle and an outgrowth on the head helmet.
Individuals born in spring or autumn have a short tail needle, and a helmet may be absent altogether. This is due to the fact that the expenditure of energy for growing outgrowths reduces fertility.
The necessary conditions
Daphnia live and reproduce only in their familiar aquatic environment. Attempts to breed crustaceans in tap water will fail.
A favorable place is an aquarium with a water temperature of up to 25 degrees, good lighting and the presence of food in the form of dry yeast or unicellular algae.
Daphnia do not tolerate large colonies well and can die from lack of oxygen. With the growth of the population of crustaceans, they should be deposited in another container.
Life span
The lifespan depends on the species and ranges from 22 days to 6 months. Large species live somewhat longer than small ones.
Life expectancy is influenced by the temperature of the water. In warm water bodies, metabolic processes proceed faster, which leads to the rapid development of the body and rapid death.
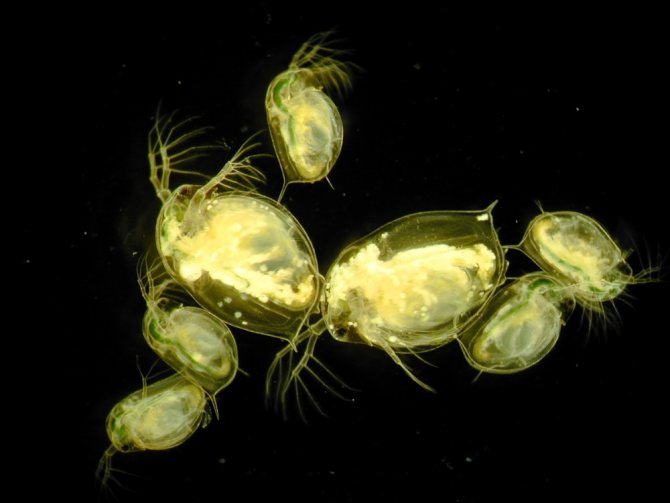

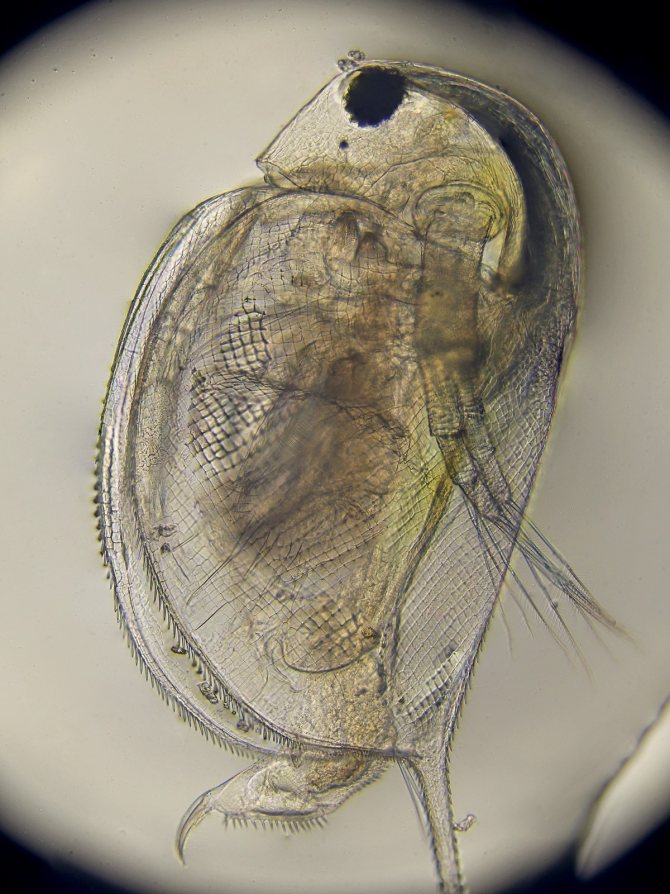
Structure
Photo can be enlarged
A little more about the structure of Daphnia. This is the name aquarists use for a variety of cladocerans. You can get an idea of their appearance in the photo. In all representatives of Daphnia, the body is strongly compressed from the sides and covered with a chitinous bivalve shell fastened on the back. There are two eyes on the head, which in sexually mature individuals can merge into one compound eye, and in some species there may be another additional peephole next to it.
Also on the head are two pairs of so-called antennae, the rear of which are large and additionally equipped with bristles that increase their area. It is due to the wave of these antennas that daphnia move in the water. When stroking with antennas, the body of the crustacean receives an abrupt forward motion, for which the daphnia received the second, popular, name "water flea".
Daphnia reproduce quite unusually from a human point of view. Females have a cavity called a "brood chamber" located on the back and protected by the upper edge of the shell. In the summer, if conditions are favorable, 50-100 unfertilized eggs are laid in this cavity. They also develop there. Of these, only females are hatched, which leave the chamber, and the adult female then molts.
After a few days, the process is repeated. During this time, young females also grow up and join the breeding process. With a successful combination of circumstances, reproduction proceeds like an avalanche. This is where in the summer, in small reservoirs, Daphnia are often simply teeming, and the water seems to be colored reddish.
With a decrease in air temperature, at the end of summer and at the beginning of autumn, males begin to appear from some of the eggs, they fertilize the females and they have eggs enclosed in a dense shell. They are called the Ephippians. They are able to withstand drying and winter frosts, and can be carried by dust. Next spring, warmth and moisture will awaken them to life. Females will hatch from them and the cycle will repeat.
Daphnia price in the form of feed
Daphnia contains a large amount of protein, therefore, in any form it serves as a good food for aquarium fish.
Moreover, it is affordable. A package of dried daphnia weighing 100 grams costs 30-50 rubles, frozen - up to 100 rubles. Live food can often be found in pet stores. They are distinguished by a short shelf life and are not inferior in nutritional value to frozen ones.


Buy daphnia moin eggs
Terms of order: Sending a distribution of daphnia in the form of sand containing ephippia (daphnia eggs) and weighing 30 g (1 tbsp. Spoon) is possible in a registered letter envelope in 3 sachets. The breeding is concentrated and one sachet is enough for breeding daphnia. Shelf life in a cool dry place is unlimited.
I will inform you of the postal identifier number immediately after sending the letter. You need to inform me to my email address: your name, full address and pay for the order by listing 450 rub. to the Sberbank card (amount including postage throughout Russia).
(Attention! The amount of the order in the near abroad: Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Belarus, etc. in view of the additional payment for registration of a registered letter will be 750 rubles).