- Wild animals
- >>
- Insects
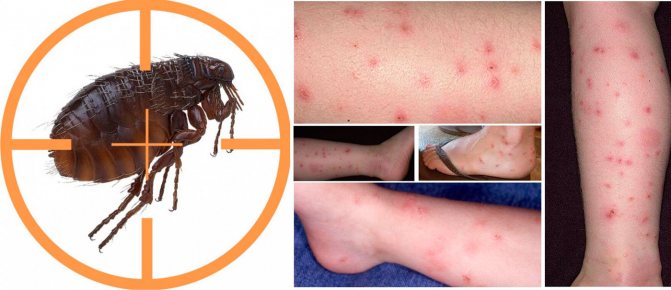
Flea Is a blood-sucking insect that is an important disease vector and can be a serious pest. Fleas are parasites that live on the outside of the host (i.e., they are ectoparasites). As the main agent transmitting the black death (bubonic plague) in the Middle Ages, they were an important link in the chain of events that led to the death of a quarter of the population of Europe.
Varieties of fleas, their distinctive features
At the moment, scientists have described 2086 species of representatives of this family, 4 of which are fossils. These arthropods are classified depending on the main host on which they parasitize (human, feline, canine), and in appearance they have certain characteristics. General information about the most important types of fleas in the economic and medical plans, which are found everywhere on the territory of Russia, is presented in the table:

| Flea species | Main host | Body length, mm | Body shape | Color |
| Doggy | Dogs | 0,75–5 | Laterally flattened | Brown |
| Feline | Cats | Dark, more often black | ||
| Chicken | Chickens | 1,5–2 | Dark yellow to brownish brown | |
| Rat | Rodents | 2–3 | Light to dark brown | |
| Human | Human | 1,6–3,2 | Light brown to black-brown |
Some common names for these parasites are arbitrary and have nothing to do with scientific classification. Such, for example, a species like genital fleas does not exist. This is the popular name for blood-sucking insects that live at home, which combines many other types.
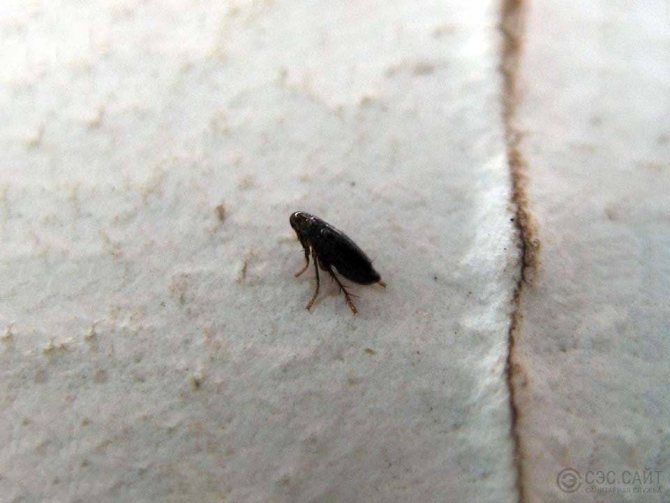
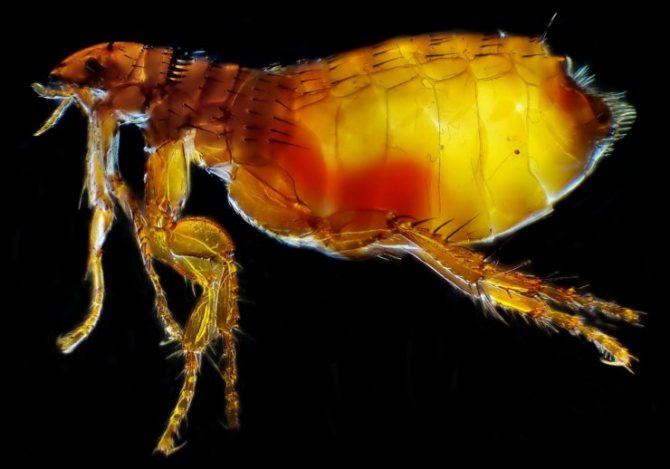
Description and photo of a flea: what does the parasite look like and what is its structure?


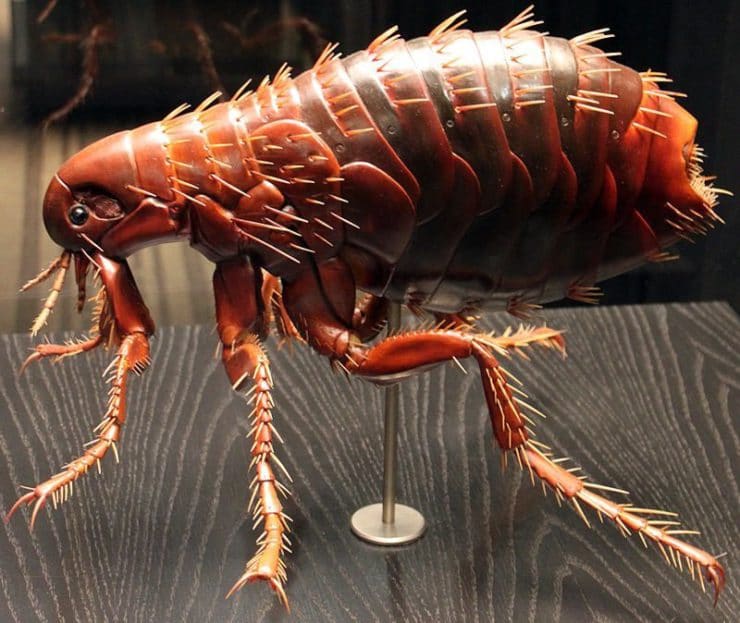
What an insect looks like can be seen in all details in an enlarged photo, and the features of its structure - in the diagram. Description of the appearance and internal structure of the flea:
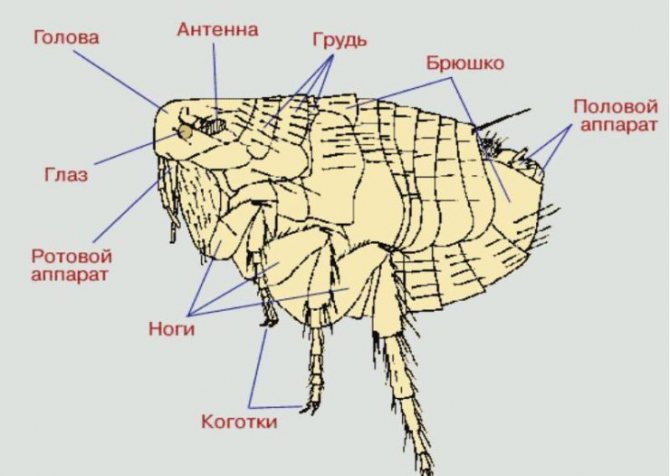

- A narrow, smooth, laterally compressed body, the size of which is too small to be able to see its owner in detail with the naked eye. The size of an adult flea barely reaches 5 mm. Females are usually larger than females. Females of some sedentary bloodsuckers can be very large, after feeding, increasing to 1 cm.The size of these parasites depends on their species. The insect weighs no more than 0.03 g.
- The body, which ranges from reddish brown to black in color, has bristles and spines that help the parasite to move quickly and securely attach to the coat and feathers of its hosts.
- On the head of a wedge-shaped flea, there is a backward-facing piercing-sucking oral apparatus without mandibles and with epipharynx and internal chewing lobes transformed into stylets.
- Simple eyes, behind which there are shortened bristly antennae, are often reduced. In addition to their direct purpose, the antennas serve the male fleas to reliably retain their partners during the mating process.
- The chest is formed by three well-divided and often movable segments.
- The head and chest are often equipped with serrated ridges, or ctenidia. No wing buds.
- The abdomen is formed by 10 segments, the sclerites of which are connected by folded membranes.When food enters, these folds are straightened, which allows the abdomen to enlarge. In its posterior part, on the eighth dorsal segment, there is a specific sensory organ - the abdominal sensillium, or pygidium, which is equipped with tactile hairs, which allows it to pick up air vibrations.
- Jumping limbs are well developed, especially the third pair, which provides the jump. The 5-segmented tarsus are equipped with two large claws. These bloodsuckers have 6 legs. On the first pair of legs there are thyroid cokes that cover the mouth apparatus. On the second and third pair of legs, there are large trapezoidal flat cokes.
- The wings are secondarily reduced.
- The male reproductive apparatus has complex characteristics. It is formed by a copulative organ and is equipped with a developed 2-segmented genital claw.
What and how do fleas eat?
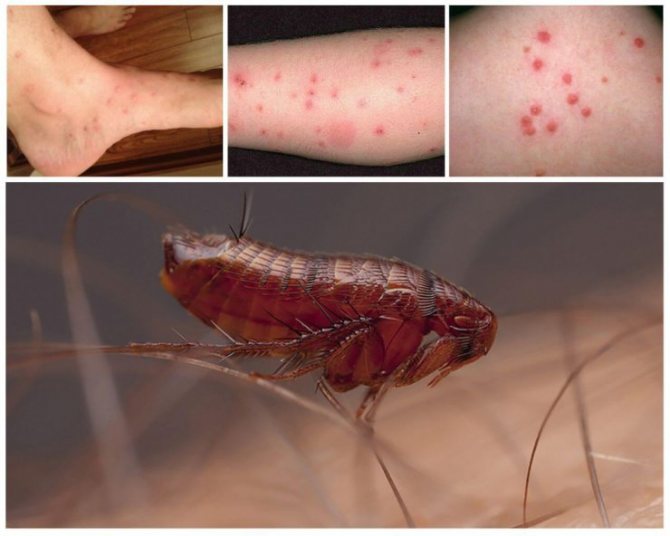

All members of this family, without exception, are obligate hematophages. Moreover, most of the species of these insects are phase, that is, temporary ectoparasites. Usually, bloodsuckers parasitize on mammals, much less often on birds. Under certain circumstances, they are able to drink blood from reptiles. The flea's affection for the owner is more pronounced than that of many of their other “colleagues” (bedbugs, mosquitoes). The degree of connection between the parasite and the "breadwinner" is not the same. By the nature of the relationship between the parasite and the host, there are:
- Nest-burrowing fleas. Most parasites belong to this type. Usually, such bloodsuckers remain on the owner, in whose choice they are not particularly picky, exclusively for the duration of feeding. So, the gopher ectoparasite can use other rodents, domestic animals and humans as an object of food, and the feline eats not only the blood of cats, but also dogs and other warm-blooded animals. Strict specificity in relation to the host is observed only in insects parasitizing bats. The rest of their brothers, in addition to the main breadwinner, can also parasitize on other species of animals.
- Flea wool, spending most of their lives on the host and leaving it in exceptional cases. However, they have not lost the ability to move freely and change the breadwinner. To a greater extent, they are species-specific. Thus, the fleas of the coastal swallow do not feed on other hosts.
- Stationary (sedentary) or semi-stationary skin fleas, which are introduced into the epidermis of the breadwinner or are attached to it with the help of the proboscis. Usually, animals that do not have permanent shelter act as the host for this group of ectoparasites, which greatly complicates the search for another host for bloodsuckers, and they are forced to remain on the body of one as long as possible. There are not so many individuals in the category of sedentary blood-sucking insects. Mostly they parasitize on artiodactyls and marsupials.
In fleas, bloodsuckers are females and males. How long bloodsucking lasts depends on the species. This process takes from 1 minute to several hours. Some genera, such as Echidnophaga and Ctenocephalides, are over-fed. Their food does not always have time to digest.
Other fleas (canine, feline) require frequent meals. Having been fed with blood, they do not leave the host's body and move freely in the wool. Certain bloodsuckers, for example Ctenophthalmus, do not need frequent meals, spending most of their lives in the substrate of the breadwinner's nest.
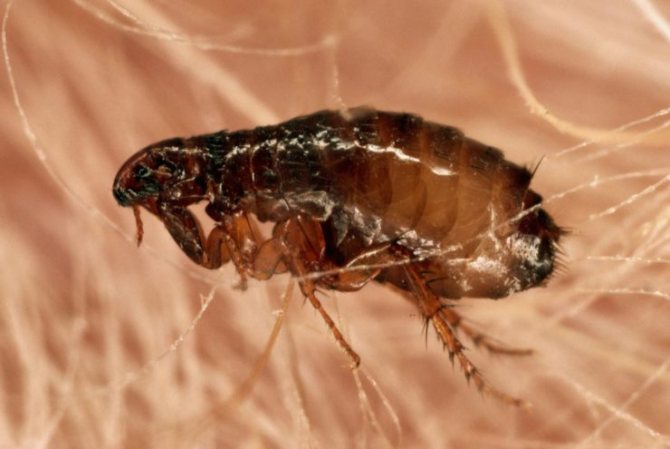
Prevention of the appearance


When insects appear in a house or apartment, the fight against them takes a lot of time and money, especially if the case is neglected and the presence of parasites was later noticed. To prevent this from happening, you must be guided by some recommendations. For example:
- Perform general cleaning of the home on a regular basis.
- Carry out wet cleaning in the apartment exclusively with the use of aromatic substances, such as essential oils of tansy, tea tree.
- Do not forget about caring for your pets, paying attention to their behavior, especially in the summer-autumn period.
Earthen fleas, like other parasites, create uncomfortable living conditions for humans. Despite this, if you wish, by spending a little time, you can prevent the appearance of parasites in your home. If this is not done, then later you will have to spend much more time getting rid of such discomfort.
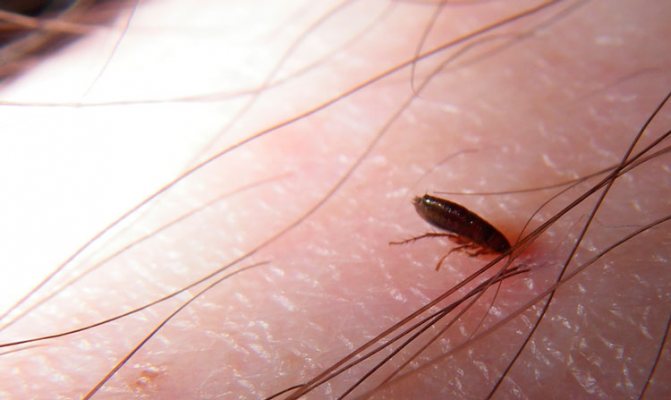
Do fleas live on people, how are they dangerous to humans?


These ectoparasites, regardless of who their main host is, a cat or a dog, do not consider a person as a priority host and do not live on his body. They feel most comfortable on the body of warm-blooded animals covered with wool, or birds with plumage. For this reason, getting into a dwelling, bloodsuckers first of all attack its four-legged inhabitants.
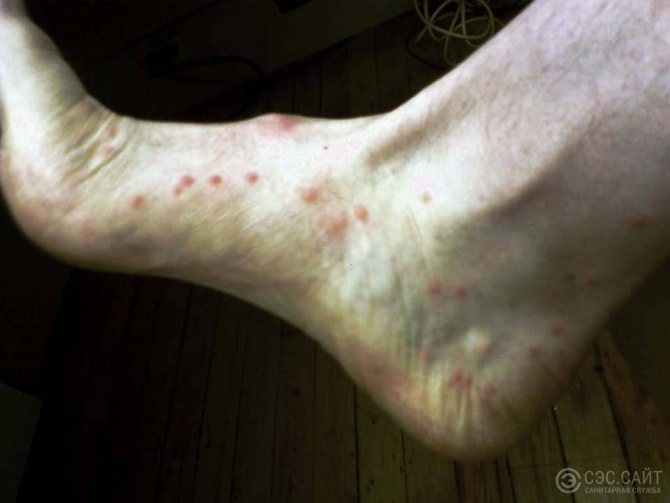
At the same time, it does not matter for them what kind of blood will serve them as food. They bite people, but this happens less often than attacks on animals. Parasites transfer to human blood due to the lack of a nearby main host or lack of food due to an excessive number of fellows parasitizing on the body of the priority victim.
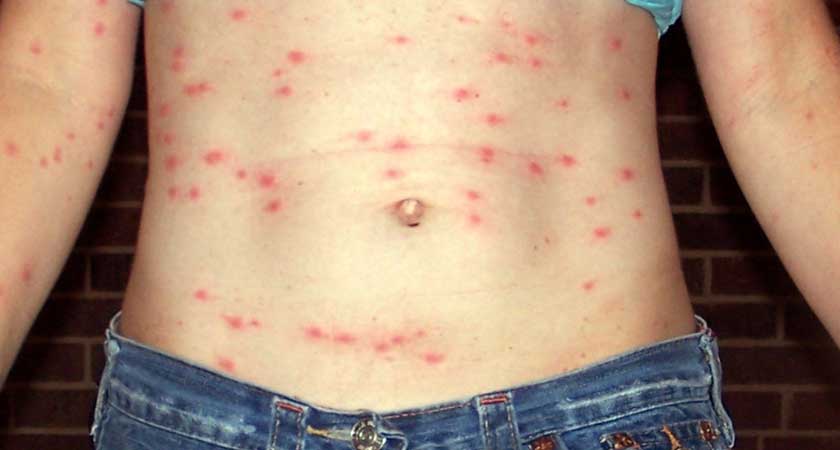
Fleas are dangerous because their bite can provoke an allergic reaction. The risk group includes small children, allergy sufferers and the elderly. In addition, they carry various diseases, including fatal ones.
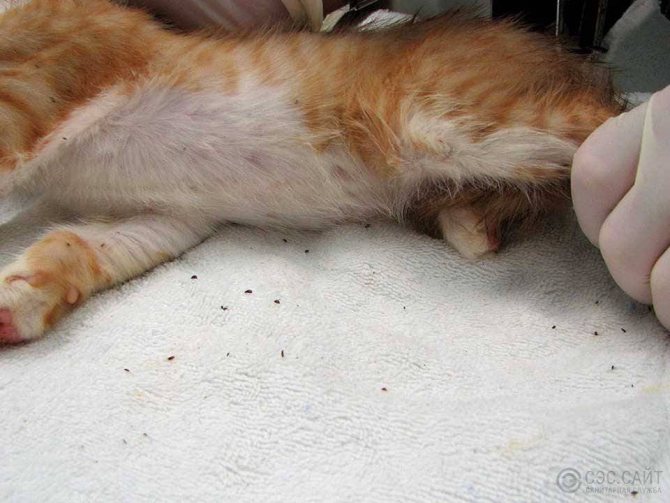
Parasites in pets
When the owners see that black fleas are on the body of a pet (cat, husky, poodle or parrot), they often panic. But you should not do this, it is not difficult to get rid of bloodsuckers. Now on the market there are many effective and safe tools to help quickly solve the problem. They come in the form of drops, shampoos, collars. Here is some of them:
- drops of "Simparica";
- drops "Stronghold";
- ampoules with drops "Bayer Advantix";
- medicine in tablets "Nexgard Spectra";
- collar "Foresto";
- tablets "Bravecto";
- drops "Frontlay";
- collar "Bayer Kiltix";
- spray "Bolfo";
- Front Line aerosol;
- phytoelita shampoo;
- shampoo "Celandine".
Drops drip onto the withers, the animal is not bathed 3 days before treatment and the same amount after it. The shampoo is effective for significant contamination, use it according to the instructions. It is also worth periodically bathing animals in anti-block shampoos to prevent infection. The treatment, if necessary, is repeated after 2 weeks in order to destroy the larvae hatched from the eggs. Means scare away and act so that fleas and other parasites die.
The collar has little effect in the fight against insects, they do not disappear completely. But he is good at scaring off parasites so that they do not attack pets. It is required to put it on 3 days after using the drops or immediately after applying the shampoo. Pyrethrin is toxic to cats and is only used for treating dogs. The same preparations are suitable for the treatment of domestic parrots, hamsters, guinea pigs, only the doses are 2-3 times less.


There are many effective and safe flea remedies for animals
Which diseases are carried by fleas?
These insects are dangerous because they can be carriers of pathogens of a number of diseases, some of which can cause the death of a sick person. By themselves, they cause 2 diseases in the bitten one: pulicosis and sarcopsillosis, or tungiasis. The infections they carry depend on the species of the parasite. Flea saliva that enters the bloodstream of a person when bitten can become a source of the following diseases:
- plague;
- tularemia;
- typhoid;
- salmonellosis;
- brucellosis;
- listeriosis;
- rickettsiosis;
- hepatitis B and C;
- encephalitis;
- trypanosomiasis, etc.
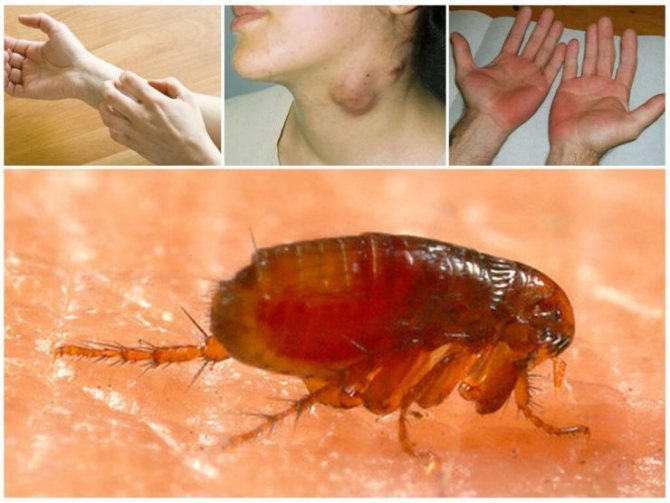

Most bloodsuckers can transmit infections. The total number of diseases transmitted by them is more than 25 names. Also, these ectoparasites can act as intermediate hosts for some parasitic worms, such as common nematodes.
Infection routes
Fleas are carried indoors by pets or rats and mice, which they get on from the dirt and foliage lying on the ground. Once inside, they will settle on carpets, furniture, houseplants, and draperies. A warm and humid habitat is ideal for them. Cold temperatures slow down their life cycle, so summer is the perfect time for them to reproduce and develop.
Also, fleas can migrate from neighboring infected premises, from the basements of the building and entrances.
What role do fleas play in nature, do they benefit?
Insects cannot be viewed solely in terms of whether they are harmful or beneficial to the environment. The role of some of them in nature is reduced only to participation in the food chain. Larger creatures survive by feeding on weaker and smaller relatives. As soon as only one link falls out of the chain, the entire system of the food process collapses, which will entail serious consequences for the environment.
The role of fleas is to serve as food for other representatives of the fauna. We are talking about ants, which are known to make an invaluable contribution to natural processes.
In fairness, it is worth noting that ants are unlikely to die if such a component as fleas disappears from their food supply, because they feed not only on these bloodsuckers.
Loading ...