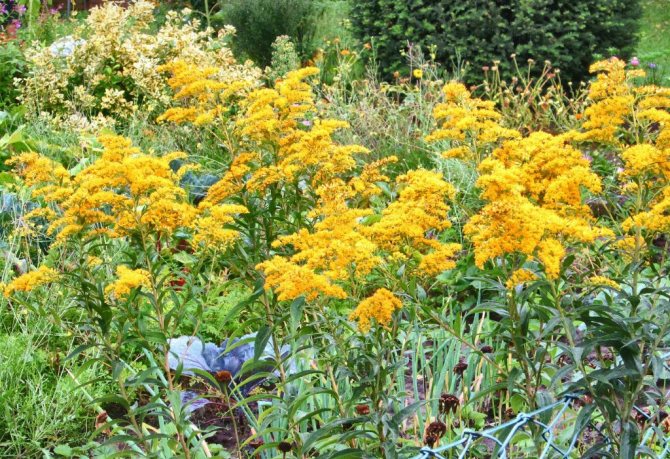
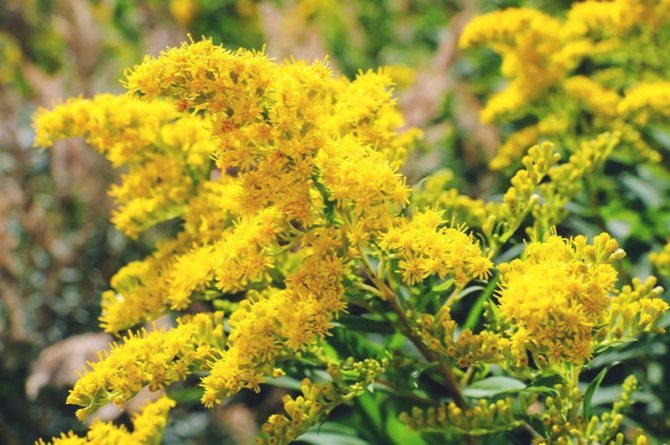
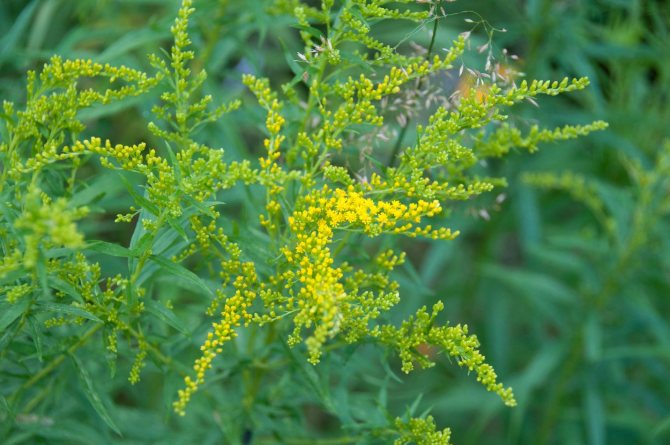
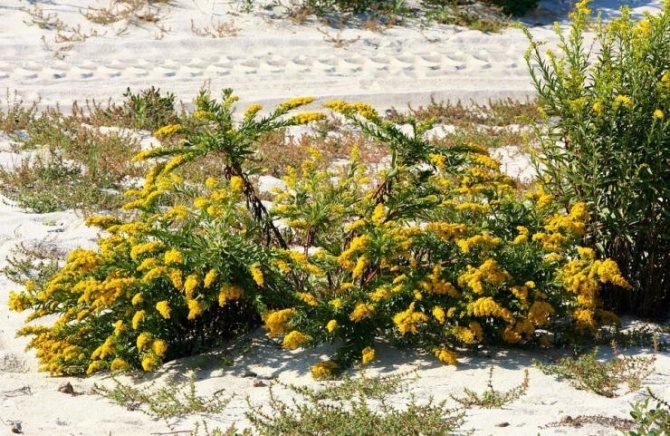
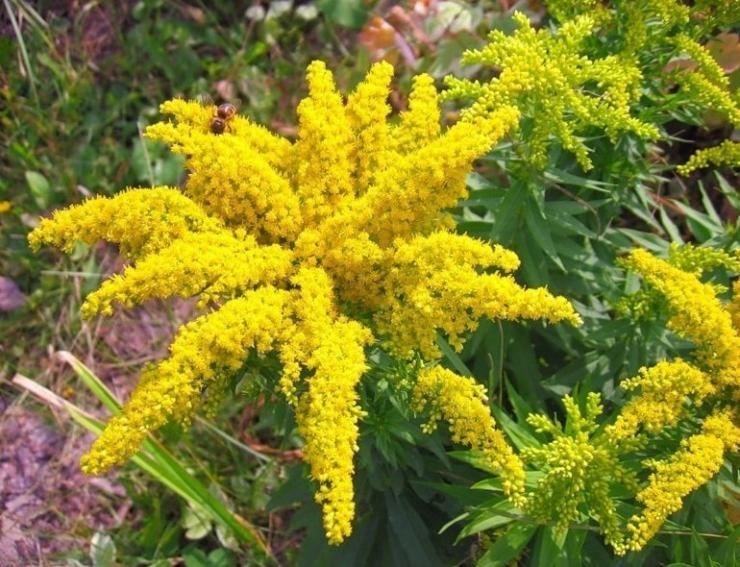
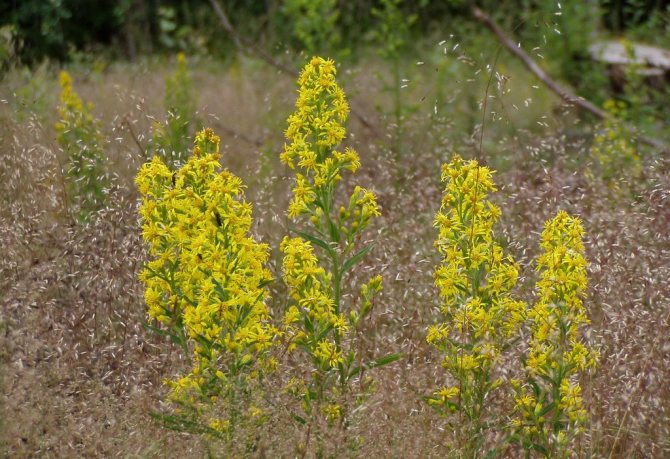
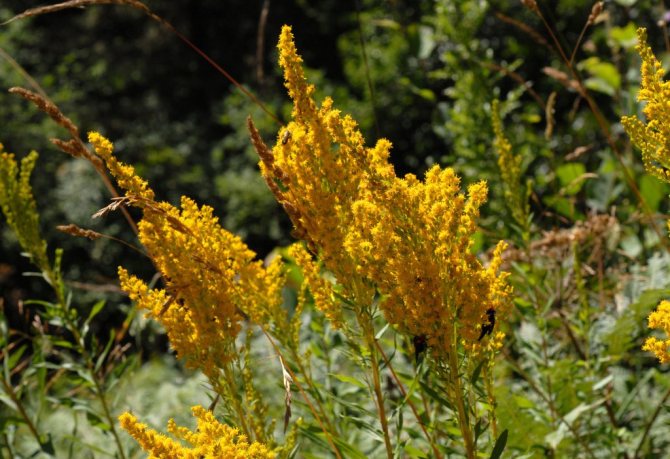
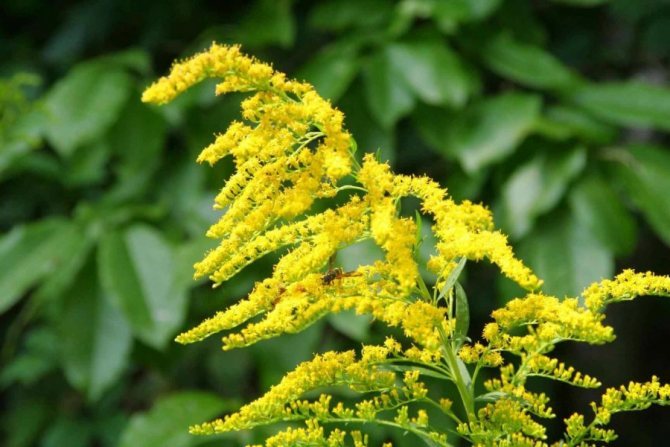
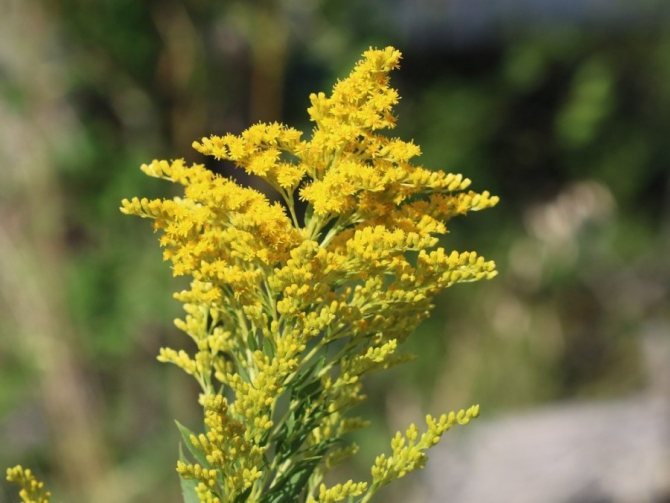
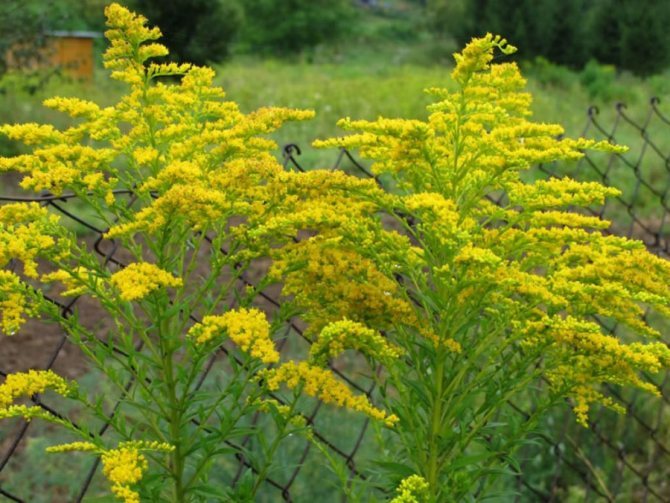
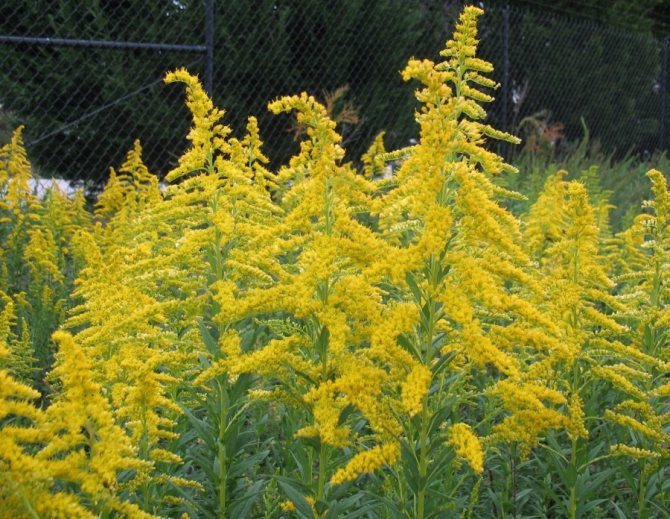
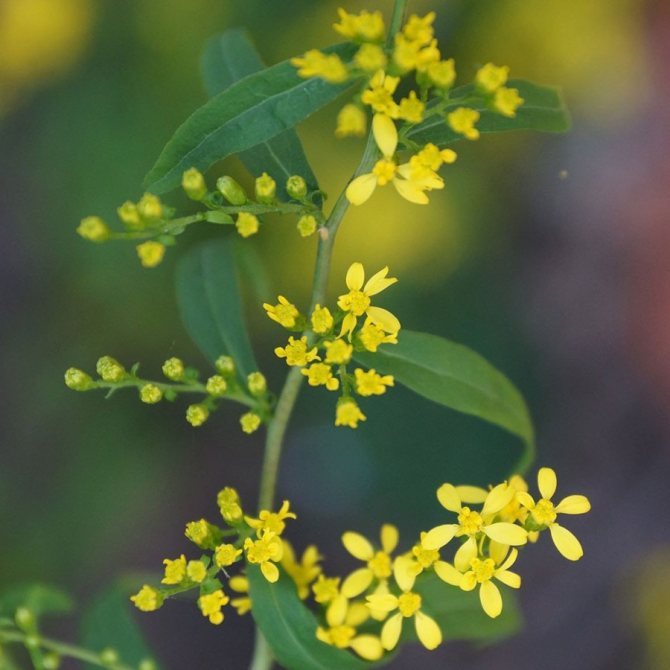
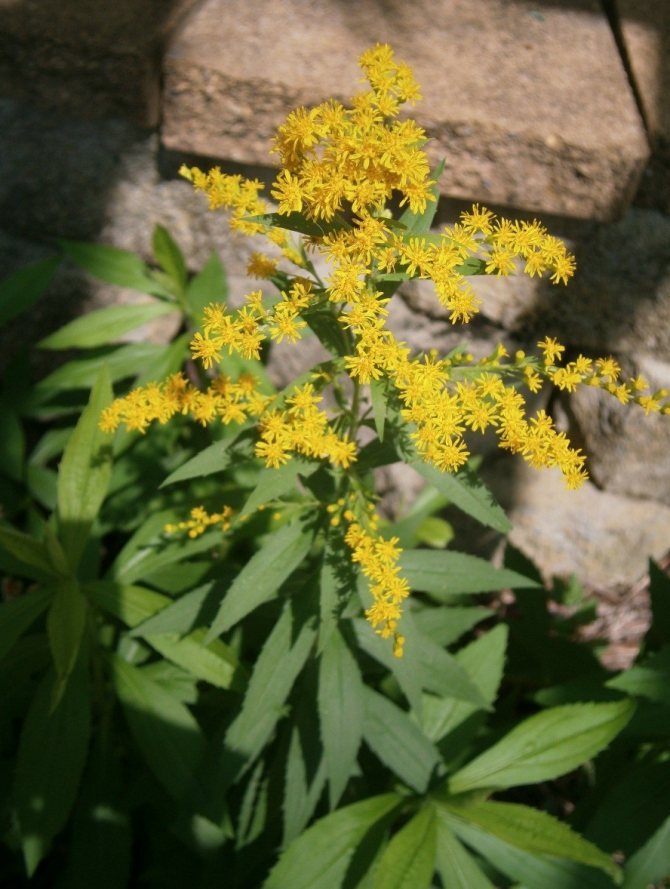
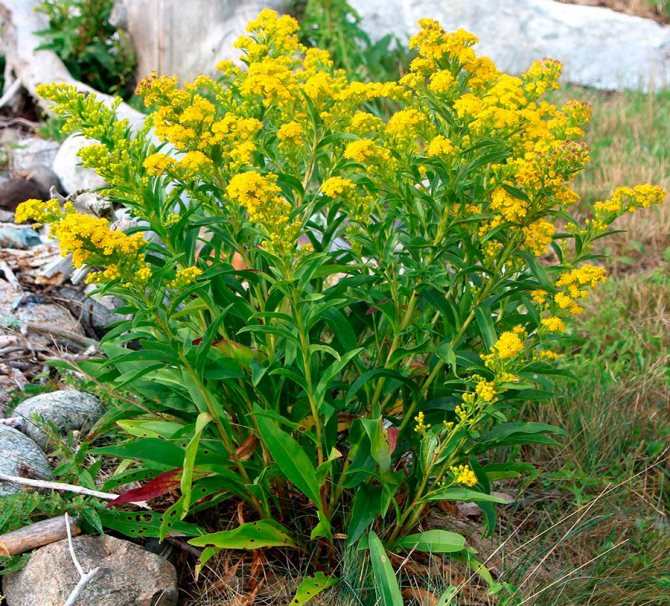
Have you ever seen an unusually beautiful tall plant with lush golden bunches of flowers? If so, most likely it was goldenrod - a spectacular perennial, often found in flower beds. Goldenrod is not without reason popular with gardeners all over the world: it is very unpretentious, winters well, and most importantly, it looks great. Dense inflorescences of a bright honey shade are crowned with dense greenery of shoots and leaves.
Experienced growers know that this culture is not only good-looking, but also very useful. Goldenrod, or, as it is also called, solidago, is widely known in medicine and veterinary medicine. Medicinal properties are confirmed by numerous studies, so the plant is used not only by folk healers. It is part of many herbal preparations and pharmaceutical preparations. Solidago is used for diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system, problems with the bronchi and lungs, various skin ailments, diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
All parts of a perennial have healing properties: both aboveground (leaves, shoots, inflorescences) and underground (roots). Perhaps goldenrod can be called a versatile green healer.
In veterinary medicine, solidago is used in the case of gastrointestinal disorders, as well as externally, for the treatment of purulent wounds.
[!] Goldenrod contains dangerous alkaloids, so it should be used only under the supervision of a doctor and strictly observe the dosage of drugs.
The plant is famous not only for its medicinal properties, it is truly a storehouse of all kinds of usefulness:
- A valuable essential oil is produced from goldenrod.
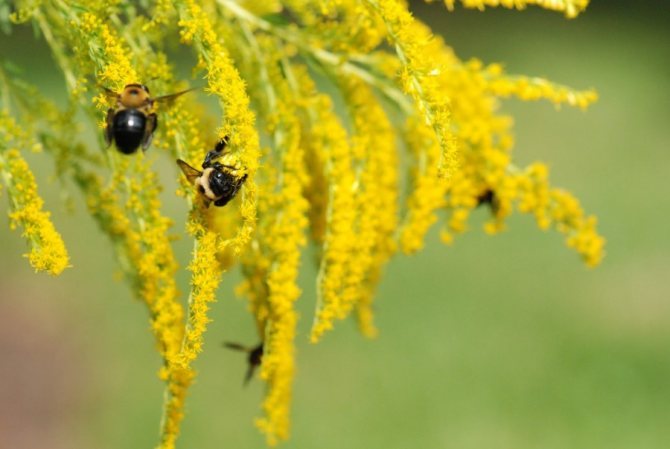
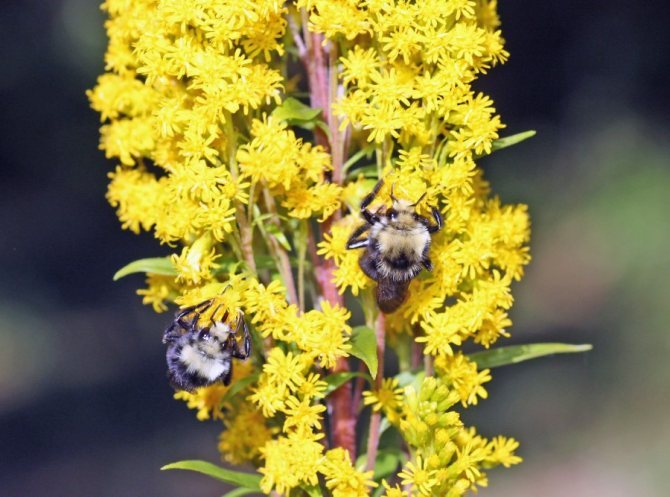
- This flower is an excellent honey plant. Solidago pollen honey has a dark hue and a pleasant spicy aftertaste.
- The young leaves of the plant are edible and eaten by Native Americans.
- Rubber was found in the leaves of solidago, from which they tried to make rubber in the middle of the last century. The experiment failed: it turned out that the resulting rubber has too low strength and elongation. However, this culture has industrial potential and, possibly, research will resume again.
- Goldenrod is a spectacular ornamental plant suitable for landscaping any garden.
The last point should be considered in more detail. The fact is that in Europe goldenrod has long been used in landscape compositions, but North American gardeners have long considered this plant a weedy plant, not giving it enough attention. The situation changed only at the end of the 20th century - now solidago can be found in the man-made gardens of the New World.
Goldenrod is distinguished by its extraordinary vitality, therefore its spread in some countries (China, Germany) led to environmental problems - the plant displaced many natural species, taking their place in their natural habitat. Another significant disadvantage is that solidago provokes severe allergies in some people. However, the above facts do not bother the overwhelming majority of gardeners: they willingly grow a beautiful perennial in their plots.
The Latin name of the plant - solidago (from the word solidus, translated as "strong" or "healthy") refers to the medicinal properties of the culture.In the Russian language, the name goldenrod took root better - according to the shade of golden inflorescences, although earlier this flower was called differently in each province. According to the botanical dictionary of N.I. Annenkov, perennials were called flea, yellow flowers, goldfishes, scrofula, fly, honey cake, scabbard, black grass, wild chicory, etc. In English speaking countries, the plant is known as goldenrod - a golden stem.
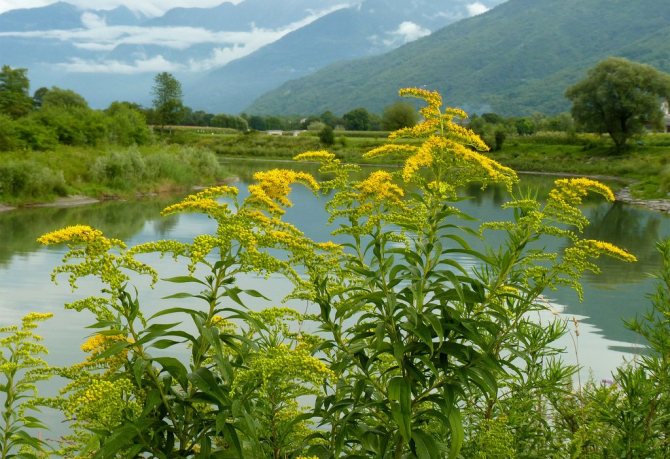
It is difficult to name the homeland of goldenrod now - the culture has spread widely across the globe, but most species are usually found in North America and the temperate zone of Eurasia. Most often, the plant settles in open spaces: glades, meadows, forest edges, and in America it prefers sunny prairies and savannas.
Botanists classify solidago (lat. Solidago) as a tribe aster (lat. Astereae), aster family (lat. Asteroideae) of a numerous family of asteraceae (lat. Asteraceae). The closest relatives of goldenrod in the plant world are aster, daisy, callistephus, grindelia.
The genus unites large herbaceous perennials, the height of which, depending on the species, varies from 10 to 120 cm. These are rhizomatous plants with an erect or creeping stem. Shoots, as a rule, are unbranched or sparsely branched with a smooth or fleecy surface. The leaves are arranged alternately on the stem, their shape can be elongated-lanceolate, elliptical, ovoid, and the edges are smooth or jagged.
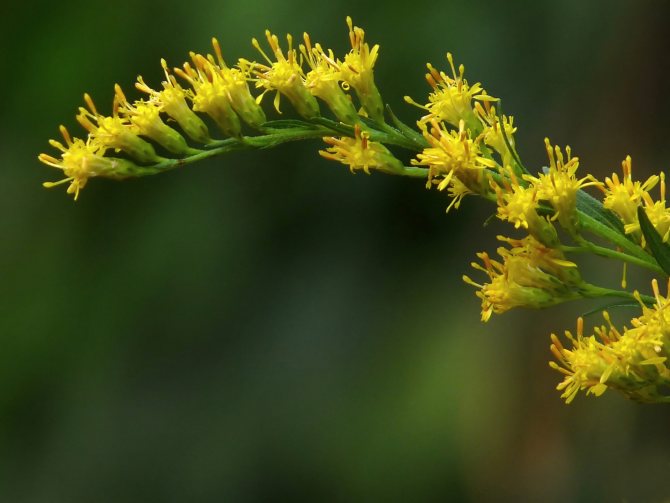
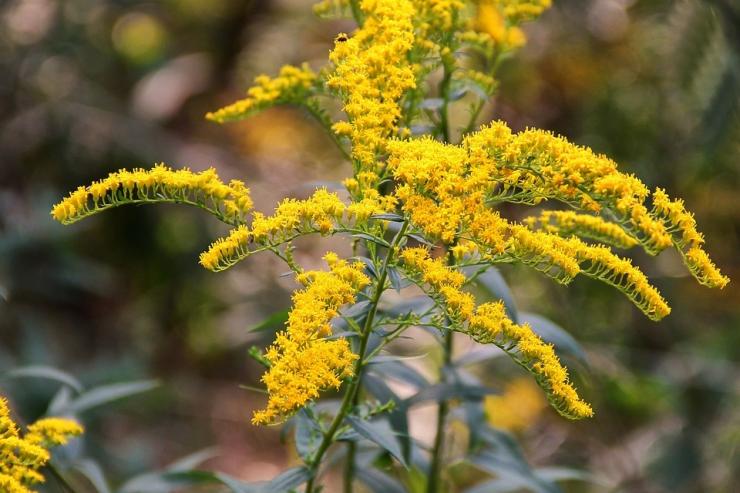
In summer or early autumn, lush golden-yellow inflorescences appear, consisting of a large number of small single ligulate and tubular flowers. Flowers are collected in dense baskets, and those, in turn, in a panicle, scutellum or brush. After flowering, the fruit appears in the form of a narrow achene.
Features of goldenrod

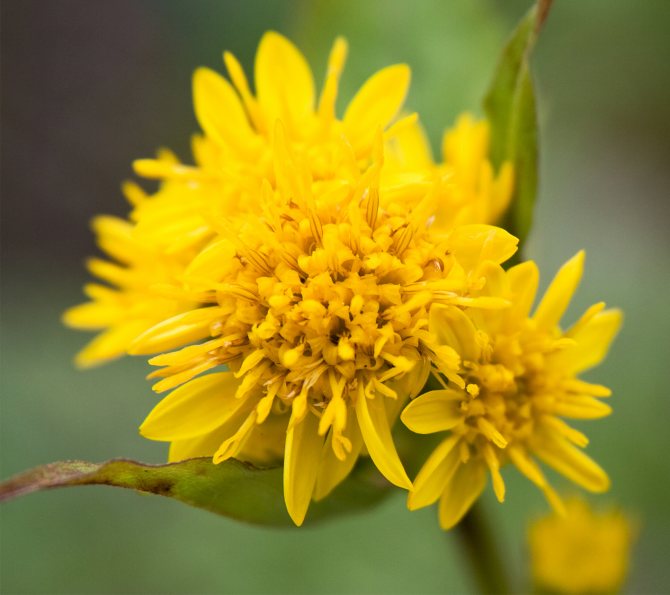
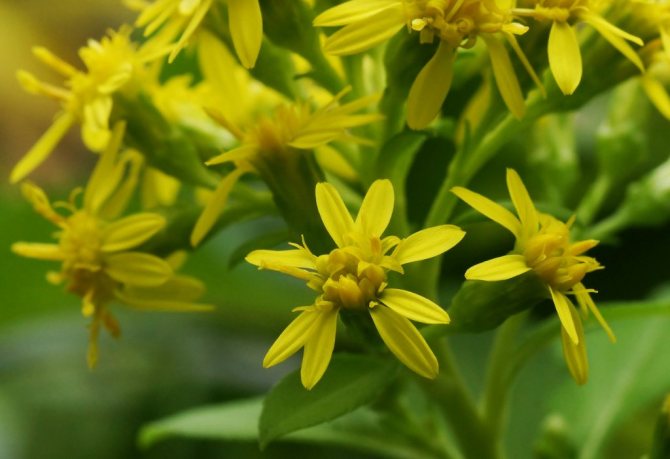
Goldenrod is a hairy or bare herbaceous plant. On erect shoots, there are alternately arranged leaf plates with a serrated or solid edge. The shape of the inflorescences can be racemose, paniculate or corymbose; it includes many baskets. In these baskets, the pistillate marginal flowers can be colored in various shades of yellow, in some cases they are very small, which is why they simply cannot be seen from under the ciliated edge of the wrapper. The disc contains bisexual tubular flowers with a yellow corolla. Flowering occurs in late summer or early autumn.
Chemical composition
The herb of canadian goldenrod contains:
- flavonoids;
- triterpene saponins;
- diterpenes;
- substances with a tanning effect;
- nicotinic acid;
- chlorophyll;
- resin;
- essential oil;
- Sahara;
- carotene;
- vitamin C;
- organic acids;
This composition gives the plant antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, choleretic, diuretic and astringent effects. In addition, the yellow flower helps to strengthen small blood vessels and stabilizes metabolic processes in the body.
Planting goldenrod in the ground


When sowing goldenrod, it should be borne in mind that its seeds become non-germinating relatively quickly. In some species, seeds do not form at all, and in some, they do not have enough time to fully mature. However, there are also species that reproduce well by self-seeding. In this regard, seed propagation of goldenrod is not very popular with gardeners.
But it is still possible to grow such a flower from seeds, and it is recommended to do this through seedlings. The container is filled with soil mixture, and seeds are evenly distributed over its surface. Then the container must be covered with a film or glass on top and removed to a warm (from 18 to 22 degrees) and well-lit place. The first seedlings should appear after 15–20 days.
It will be much easier and safer to buy ready-made seedlings in a garden pavilion, while they can be planted in open soil both in spring and in autumn. It is necessary to choose bushes that are strong and branched, there should be no specks and plaque on their surface, also carefully examine them for the presence of harmful insects.
For growing such a frost-resistant plant, you can choose a sunny or shaded area. Any soil is suitable, but best of all, such grass grows on wet and heavy soil, in this regard, during the preparation of the site for planting, it is not necessary to add baking powder (including sand) to the ground. During planting, a distance of at least 0.4 m is maintained between the bushes. Depending on the type and variety of the plant, from 2 to 5 bushes should be planted on 1 square meter.
The subtleties of growing an ornamental culture
The advantages of culture are that it reacts equally positively to both sunny and shady areas. Gardeners practically do not encounter problems when growing goldenrod.
Location
When choosing a location for growing solidago, take into account that the plant is aggressive and instantly fills the entire area, therefore, self-seeding must be controlled. Solidago does not make any demands on the choice of soil. Suitable for growing and heavy clay soils and light fertile. Whether the site will be in the sun or in the shade all day, this will not affect the growth of the plant in any way.
Preparation of planting material
Most often, seedlings are purchased for planting in a specialized gardening store or cuttings are prepared on their own. No special preparation is required before planting; for better rooting, the cut or roots are treated with a growth stimulator.


Timing and planting process
It is allowed to plant a hybrid goldenrod in open ground both in mid-spring and early autumn. The step-by-step algorithm consists of the following stages:
- The soil in the selected area is dug up, humus is introduced into it.
- A separate hole is made for each seedling. In this matter, they are guided by the size of the root system.
- Any mineral complex is added to each hole.
- Gently spread the roots of goldenrod along the bottom of the hole and sprinkle with soil, lightly crush.
- After planting, the plant is abundantly moistened.
Care for goldenrod in the garden


Watering
Goldenrod is distinguished by its resistance to drought, therefore it does not need to be watered systematically. But during a prolonged drought, when the soil on the site dries up completely, the risk of damage to the plant by powdery mildew increases. Therefore, during this period, flowers will need systematic abundant watering.
Fertilizer
Goldenrod is fed only a couple of times during one season, and this procedure is carried out in spring and autumn. For top dressing, a mineral complex fertilizer (in liquid form) is used, while during the first top dressing the solution should contain from 10 to 20 percent nitrogen, and during the second - no more than 10 percent (you can do without nitrogen altogether). In spring, wood ash can be used for feeding, but it is not recommended to regularly add it to the soil.
Garter and transplant


Vigorous varieties and types of such a plant may need a garter to the support, the fact is that due to strong gusts of wind, the bushes can lie down. After a few years, such a perennial can grow very much, in this regard, experts advise, once every 3 or 4 years, remove the bush from the soil, divide it into several parts, which are planted separately on a new site. An older plant is much more difficult to transplant, since in most species the root system goes very deep into the ground.
Pruning
In late autumn, the bushes are recommended to be shortened to 10-15 centimeters from the ground surface.In the spring, after the goldenrod begins to grow, all weakened stems should be removed, as well as those that grow inside the bush. In this case, the bushes will be powerful, spectacular, and they will bloom in a timely manner and magnificently.
Diseases and pests


Most dangerous for such a plant is a fungal disease called powdery mildew. A whitish bloom forms on the aerial parts of the affected bush. The development of this disease is facilitated by very hot and dry days in the summer, thickening of the planting and an excessive amount of nitrogen in the soil. In this regard, when planting, it is imperative to observe the recommended distance between the bushes, and they should also be planted in a timely manner so that they do not have time to grow much.
Less often bushes get sick with rust. Affected plants must be dug up and destroyed, and the remaining bushes are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate or another agent with a similar effect for prevention.
Such a plant is distinguished by a fairly high resistance to pests, but such an insect as Corythucha marmorata can still settle on it, it has an extremely small size. Argyrotaenia citrana caterpillars can also settle on the foliage, which twist it. If goldenrod is grown for decorative purposes, then insecticides can save it from pests. And the species grown to obtain medicinal raw materials are processed exclusively with herbal infusions.
Scope of distribution


Canadian goldenrod is widespread, but its native continent is North America. The plant also grows almost throughout Europe.
Vast thickets are found in America and Asia. It is often found in illuminated areas with sandy and light soil, at the edges of forests, next to roads. In villages, yellow flowers can often be seen near houses.
Types and varieties of goldenrod with photos and names
Below, those species and varieties of goldenrod that are most popular with gardeners will be described in detail.
Goldenrod Shorti (Solidago shortii)


It is a perennial branchy plant native to North America. The height of the bush is about 1.6 m, it is decorated with smooth oblong-lanceolate leaf plates serrated along the edge. The length of the panicle pyramidal inflorescences is about 0.45 m, they include baskets of a golden yellow hue. The most popular is such a variety of this species as Variegata: there are stains and yellow spots on the surface of green leaf plates.
Goldenrod rugosa (Solidago rugosa)


The homeland of this species is also North America. In nature, he prefers to grow in swamps, bogs, wet meadows and roadsides. In America, such a perennial plant is called the coarse-stemmed goldenrod. Its rough brownish-red shoots are about 200 cm tall, smooth and straight. The bush also has a creeping rhizome. The shape of the leaf plates is oblong or oval, their width is about 20 mm, and their length is up to 90 mm, the edge is serrated. This species has no basal leaf plates. One-sided brushes consist of small yellow baskets. And these brushes are part of the drooping panicle, the length of which is about 0.6 m.
Dahurian goldenrod (Solidago dahurica = Solidago virgaurea var.dahurica)
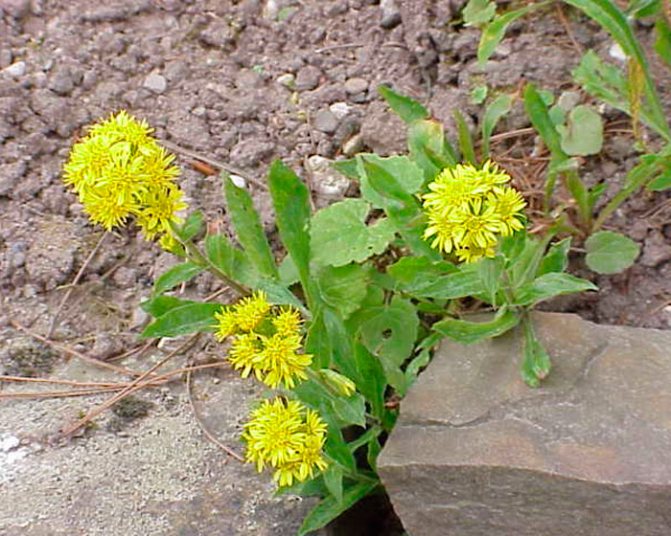


This species is native to Siberia. It is a meter high bush with powerful simple shoots that branch only in the inflorescence. The upper part of the stems is covered with short hairs, while the lower part is naked. The stem leaf plates have short petioles, and the basal ones are long-petiolate. The shape of the serrated leaf plates along the edge can be lanceolate, oblong or ovoid, they sharpen to the apex. There are short hairs on the veins and edges of the plates.A simple racemose or narrow panicle inflorescence consists of a large number of small yellow baskets.
Canadian goldenrod (Solidago canadensis = Solidago canadensis var.canadensis)
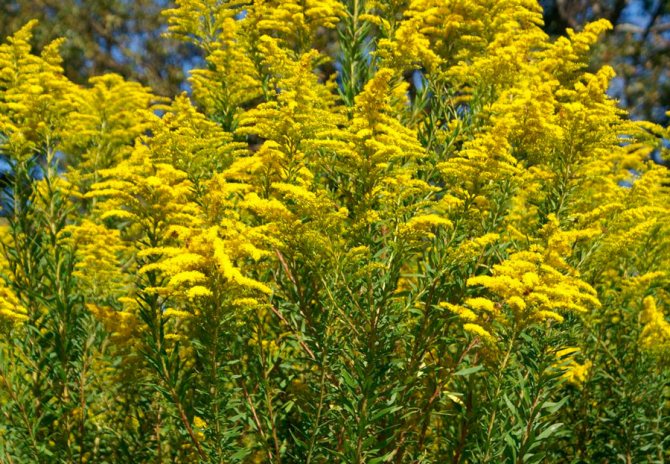


This species is found naturally in North America. The height of a perennial plant is about 200 cm. The rich green leaf plates have an oblong-lanceolate shape. The length of the pyramidal panicle inflorescence is about 0.4 m, it consists of a large number of small baskets of a golden yellow hue. This species has been cultivated since 1648. Among gardeners, the ornamental variety - Patio is popular: the height of a compact bush is about 0.6 m, it does not need a garter, it is decorated with golden baskets collected in bunches.
Common goldenrod (Solidago virgaurea)
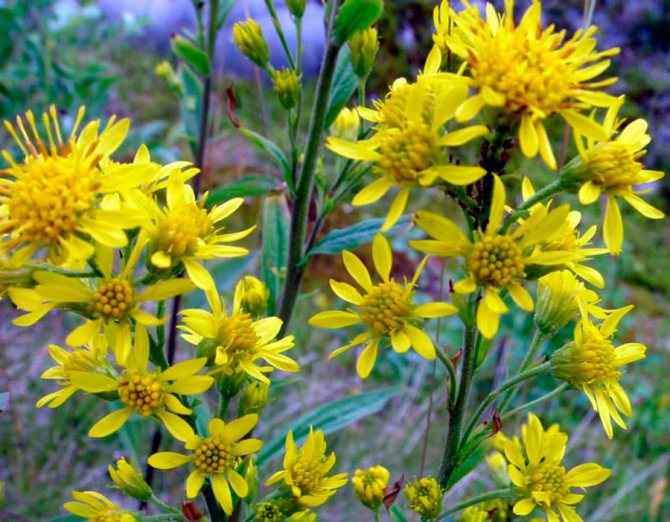


In nature, this plant is found in Western Europe, Western Siberia, the Caucasus, in the European part of Russia, and also in the western regions of Eastern Siberia. Simple straight or branched shoots reach 0.6–2 m in length. Alternate whole leaf plates have a lanceolate or linear-lanceolate shape. Complex inflorescences can be racemose, paniculate or spike-shaped; they include a large number of yellow baskets.
Goldenrod highest (Solidago altissima = Solidago canadensis var. Scabra)

Such a North American plant in nature prefers to grow on the prairies, in wet meadows, in deserts, open forests and on roadside. In America, this species is called tall goldenrod. On the surface of straight shoots there is pubescence, their height is about 1.8 m. The surface of simple lanceolate leaf plates is streaked with parallel veins, the edge is jagged. The upper foliage is entire. One-sided brushes consist of lemon-yellow baskets. These brushes are collected in one-sided panicle inflorescences, the length of which is about 0.35 m. Such a plant is considered an excellent honey plant.
Goldenrod hybrid (Solidago x hybrida)
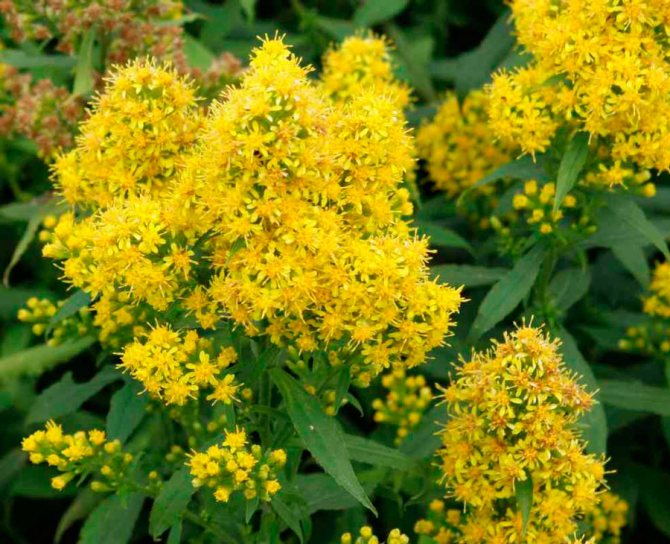


This species unites all hybrids created by breeders. For their removal, a species is used - Canadian goldenrod. Popular hybrids:
- Goldstral... A meter-high bush is decorated with panicle-shaped inflorescences about 0.2 m long, which include golden-yellow baskets.
- Kronenstahl... The height of the plant is about 1.3 m.The inflorescences consist of golden baskets, while their length is about 0.25 m.
- Spetgold... On a bush of a meter in height, inflorescences of a lemon-yellow hue grow, having a length of about 0.2 m.
- Frugold... The height of the plant is up to 1.2 m, and the length of the yellow inflorescences is about 0.25 m.
- Schufelgeiser... The plant is decorated with panicle yellowish inflorescences. The bush itself reaches a height of 1.4 m.
- Goldking... The bushes reach a height of about 1.5 m.The length of rich yellow panicles is up to 0.35 m.
External description
Canadian goldenrod belongs to perennial herbaceous plants. It is also called yellow flowers, scrofula, golden rod and life-giving herb. It can grow up to two meters in height.
Goldenrod has a strong root system. Growing up, it captures more and more territory and does not allow all other plants to grow.
Numerous leaves are located along the entire length of erect stems, and the stems are lignified at the base. The shape of the leaves is lanceolate - linear, each of them has three veins. At the tops, the leaves are pointed.
Goldenrod begins to bloom in the second year of life. This happens in the middle of summer and the flowering time lasts for one and a half months.
The diameter of flower baskets reaches no more than five millimeters. The inflorescences themselves are yellow and form spreading panicles. The yellow flower has a weak aroma and a bitter - spicy taste.
Goldenrod properties: harm and benefit
The healing properties of goldenrod
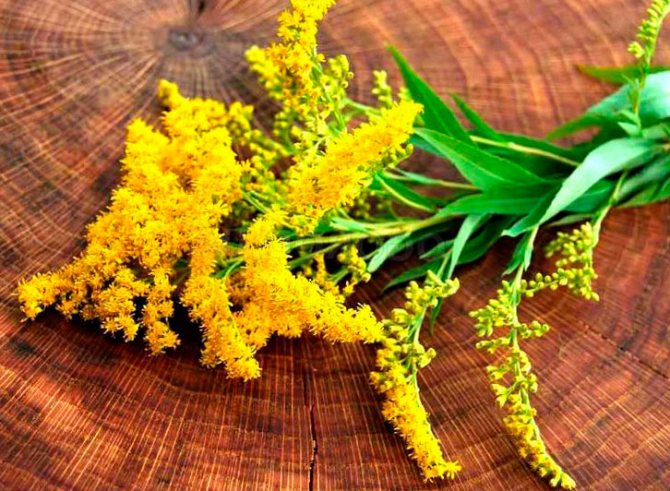


The healing properties of goldenrod are used in both traditional and informal medicine. The composition of such a flower includes organic acids, coumarins, essential oil, phenol carboxylic acids and their derivatives, flavonoids rutin and quercetin, saponins, glycosides, alkaloids and terpenoids. Thanks to this composition, the plant has a powerful anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxidant, diuretic, antispasmodic and wound healing effect.
In alternative medicine, this plant is used for improper exchange of uric acid in the body, scrofula, jaundice, cutaneous tuberculosis, indigestion and gallstone disease. It is also used in the treatment of stomatitis, bleeding gums, tonsillitis, gingivitis and to eliminate unpleasant odor from the oral cavity. This flower disinfects wounds and accelerates their healing, therefore it is used for edema, suppurating inflammation of the skin and fractures.
Funds made on the basis of goldenrod are used in the treatment of oxalate and urate stones, prostatitis, urethritis and even impotence. Gynecologists recommend taking them to women suffering from cystitis or candidiasis.
The rhizome of such a plant is also used as a healing raw material. It can help in the treatment of skin diseases and burns, as well as to eliminate the effects of stomach ulcers and hepatitis. It is also used to increase sexual activity, to treat urological diseases, to eliminate intoxication of the body caused by food poisoning. Goldenrod root also helps treat diarrhea in pets.
Goldenrod honey also has medicinal properties. It has an antimicrobial effect, it is used to increase the body's immune forces, and also to normalize metabolic processes. Compresses are made from such honey, which can help with skin inflammations, and they also eliminate swelling well. It also helps great during the treatment of sinusitis, tonsillitis and rhinitis, as well as meningitis.
In pharmacy kiosks, an extract of goldenrod from fresh inflorescences is sold; it is recommended to take it to normalize the work and restore the urinary system.
Contraindications
It is important to remember that in addition to useful properties, there are contraindications. Goldenrod contains a small amount of toxins that, if overdose, adversely affect the body. Medicines based on solidago are contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, as well as for children under 14 years of age. The plant should not be used for diseases of the kidneys and circulatory system, as well as in the presence of allergies. If you feel unwell, you should immediately stop taking drugs and consult a doctor.
Post Views: 1
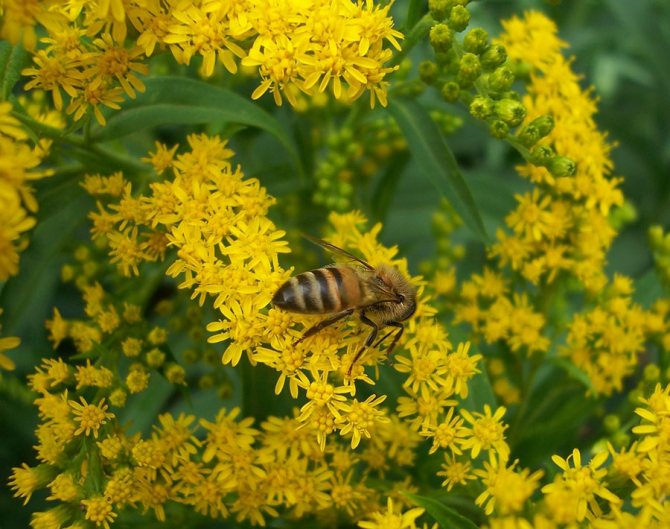
Honey plant
How else can canadian goldenrod be applied? The plant is distinguished by a high content of nectar in its flowers, which is produced throughout the day. For the entire period of its flowering, which is about two months, bees are able to collect up to 100-150 kg of honey from one hectare. This product has a tart taste and a bitter taste. Its color is dark brown. Honey in its liquid consistency is stored for no more than 1-2 months. After that, it crystallizes.
Goldenrod honey is also used in traditional medicine. After all, this beekeeping product has many medicinal qualities, which are due to the presence of nutrients in the plant itself. In addition, the nectar processed by the bees becomes even more valuable. Goldenrod honey has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Its use helps to fight kidney diseases and diseases of the urinary tract. In addition, this valuable beekeeping product helps with dermatitis and eczema.Its use allows you to strengthen the immune system, as well as have a positive effect on metabolic processes.
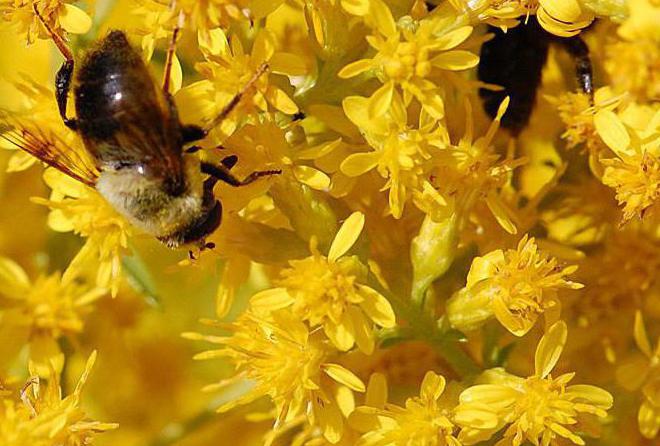


Traditional healers recommend such honey not only orally. It can also be used in ointments and compresses. Such its use can heal eczema, edema, dermatoses, long-term healing wounds, as well as skin irritations.
Honey also has a beneficial effect on the digestive, cardiac and nervous systems. This product is also considered an excellent remedy for the treatment of sore throats, meningitis, rhinitis and sinusitis.
Other Possible Health Benefits
Several studies have tested goldenrod for other purposes, but much more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness in these areas.
Preliminary studies have looked at goldenrod for:
- Weight control. Test-tube and mouse studies show that goldenrod may fight obesity by regulating genes that control fat synthesis and fat cell size. For this reason, the herb is used in some slimming teas (,).
- Cancer prevention. According to in vitro research, goldenrod extract may kill cancer cells. In addition, a study in rats showed that injections of goldenrod extract suppressed the growth of prostate cancer tumors ().
- Heart health. Rats receiving goldenrod extract orally every day for 5 weeks prior to induction of heart injury had 34% lower levels of the blood marker for injury after heart injury compared to controls ().
- Anti aging. A test-tube study showed that goldenrod extract delayed the accumulation of old, poorly functioning skin cells. It can inhibit premature aging of the skin ().
Due to the lack of human research in these areas, it is unknown if goldenrod will have the same effects on humans.
Preliminary test-tube and animal studies show that goldenrod may help with weight control, have cancer-fighting properties, support heart health, and slow skin aging. However, these potential benefits have not been tested in humans.