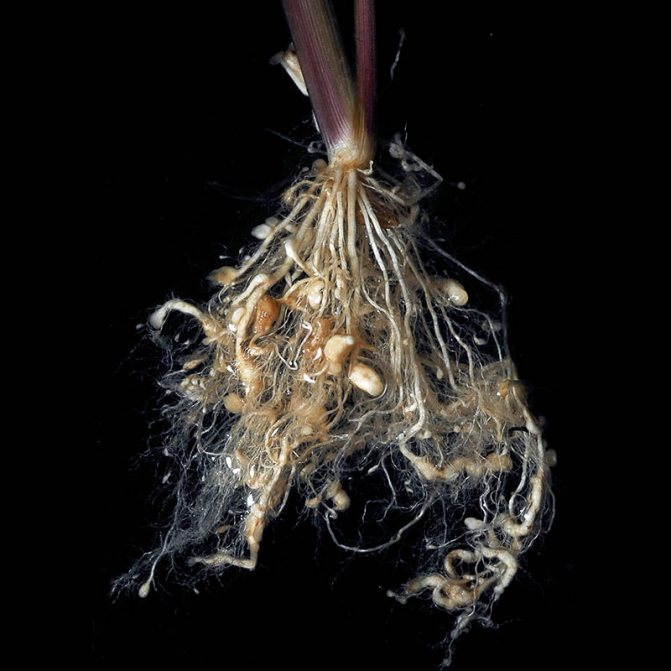
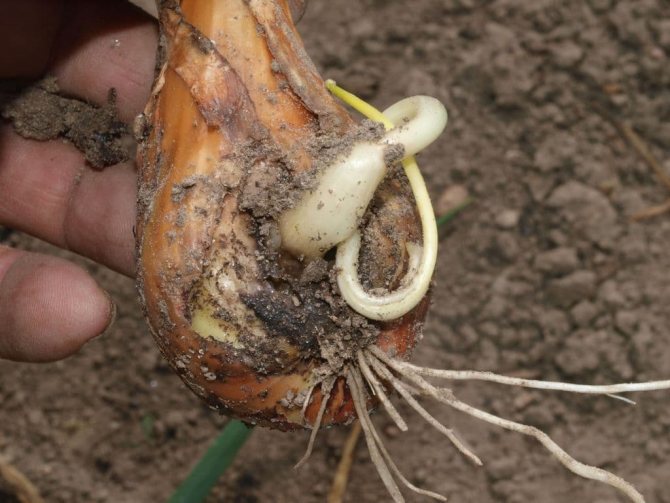
In the middle of summer, I noticed that the carrot in the garden began to grow poorly, its top wilted, despite careful care and watering. I pulled out one carrot and saw that round growths had formed on its roots. All the soil turned out to be infected with root nematode!
The crop from this garden had to be pulled out and burned outside the summer cottage. And I treated the earth with a chemical preparation several times. Only in the next season I landed on this bed. And then another culture, which at the end of the season was successfully harvested. In this article I will tell you how to permanently get rid of a nematode in your summer cottage.
Description of the external signs of nematodes
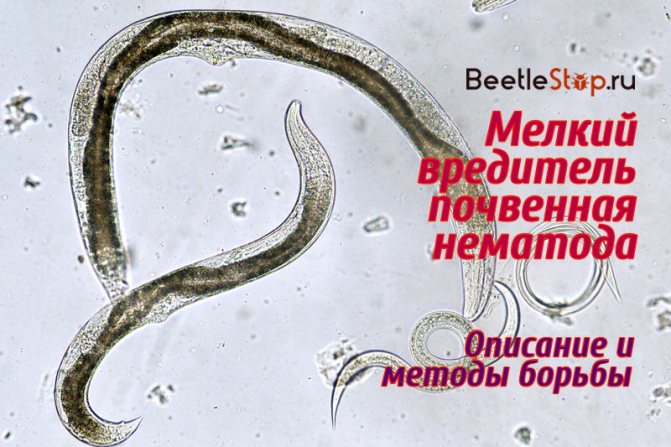
Nematodes are worms that are one to two millimeters long. Female and male individuals differ externally from each other in their sizes. The former are slightly longer. The body shape of worms can be round, oval or oblong, resembling threads.
Nematodes in the soil (the fight against them can be very diverse) are white and beige. The worms have a well-developed muscular system and a protective shell, which is of high density. The head of the worms is very small in size, has movable lips, with the help of which the pests feed.
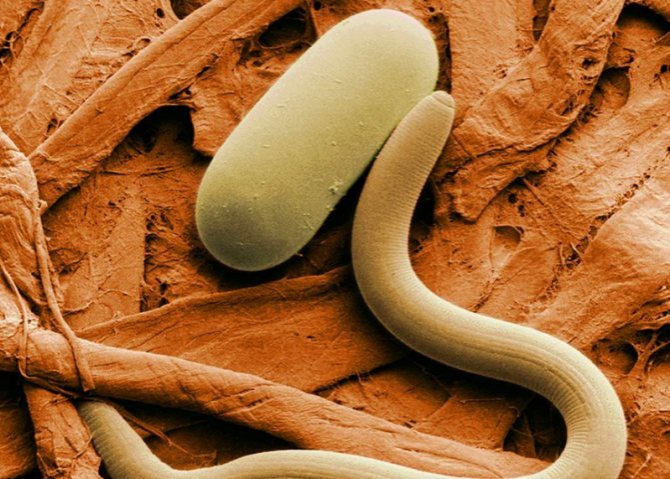
Nematodes reproduce by laying eggs of white color, which can have a round or oval shape. The larvae do not look like adults, they have a white head and a transparent body.
Nematodes, photos in the soil of which look very disgusting, have a well-developed sense of touch, due to the fact that their body is completely covered with tentacles. Pests prefer a dry and warm microclimate, which is ideal for breeding and laying eggs.
There are three types of plant nematodes:
- leafy;
- stem;
- root.
They affect not only garden and garden plants, but also indoor plants. The principle of life is the same for them - they feed on plant juices. However, in terms of body shape, size, habitat, they differ somewhat.
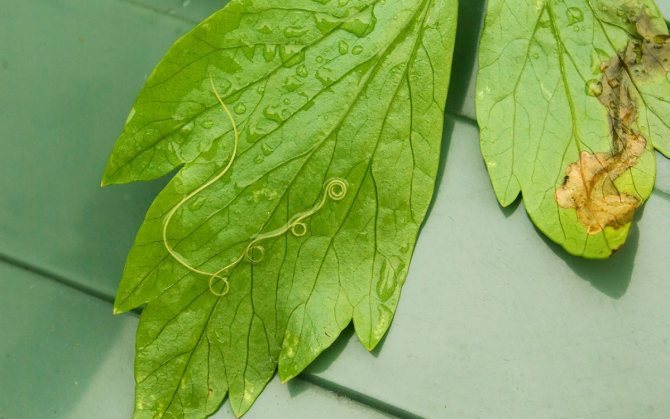
The leaf nematode has a filamentous body. In length, nematode worms reach 1 mm. Have a beige color. They are located on foliage, where they penetrate through damage to the leaf plate or through pores on their lower parts.
- shoots stop growing;
- stems thicken, lose color;
- the buds turn pale, dry up;
- over time, the plant dries up and dies.
Despite the fact that pests love moisture, stem worms can maintain their vital activity, even staying for a long time on dry leaves and scales of plants. They spread with infected whiskers, bulbs, tubers, cuttings, much less often - through seeds or infected soil.
Did you know? The life span of worms can reach up to 2 years.
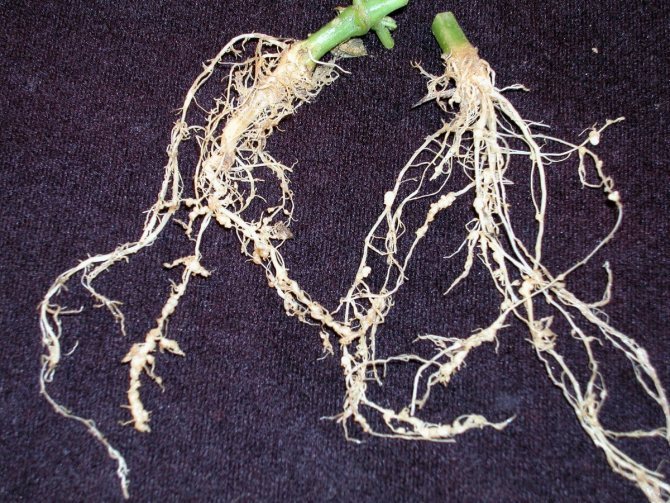
Plants affected by a soil nematode gradually wither, weaken, and stop growing. Foliage curls. The roots below the Gauls stop developing and die off. At the same time, the root beard (thin filamentous roots) begins to grow abundantly. Such roots do not contribute to the growth of the culture, but only take away nutrients from them.
Important! It is important to distinguish between nematode galls and natural thickenings on the roots of some plants that retain moisture.The latter are white in color, while the Gauls are yellow or brown.
Gall nematodes spread through contaminated soil, root debris, seeds, bulbs, equipment, and from nearby plants. Chrysanthemums, ficuses, dracaena, begonias, lilies, aloe are most susceptible to these pests.
These parasites belong to the class of roundworms. There are a huge number of them in the world, some parasitize in plants, and others in a human or animal body. The size of the parasites depends on their species; it is known that there is a nematode with a body length of about eight meters. But soil rarely grows above five millimeters in length. These nematodes that destroy plants, we will consider in this post.
The worms suck out all the nutritious juice from the roots. But the health of the culture depends on the roots. After this attack, greens often suffer from various diseases, since fungi and viruses enter them through damaged parts of the roots.
A sign of infestation with these parasites is not only twisted leaves, but also round growths on the roots. They are usually yellow or brown in color, in parallel with them, the entire lower part of the culture is overgrown with thin roots, which quickly die off. True, there are plants that by nature have the same thickenings on the roots, but they do not contain parasites, but the necessary nutrients and a supply of moisture in case of drought. These healthy roots differ from diseased ones in that they have a uniform color everywhere.
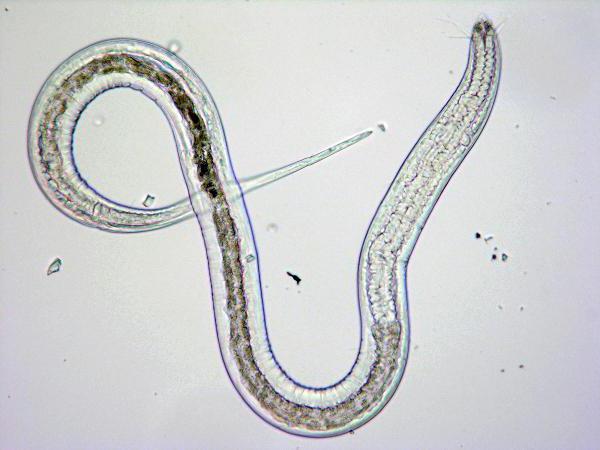
Plant nematodes are of three genera:
- Leafy - They are usually no more than 1 millimeter, move very quickly, spreading destructive viruses, live in leaves. Most often, strawberries and chrysanthemums suffer. The presence of these worms in culture is evidenced by leaves covered with dry spots in a chaotic manner. The parasite usually waits out the winter in fallen leaves, and sometimes in the ground.
- Stem - Their body is filiform, not exceeding 1 millimeter. They develop wrecking activity in stems and buds, emitting toxic substances that clog blood vessels, thereby thickening their tissues. Most often vegetable plants suffer from them: tomatoes, onions, radishes, garlic, cucumbers. They are simply pulled out and burned away from the site.
- Root - These are the most common worms, growing up to 2 millimeters. They damage only the roots of small plants, leaving behind bulges on them. After their attack, the upper part of the culture begins to dry out, despite careful maintenance and watering. Unfortunately, the disease can only be detected by pulling out the greens along with the root system. It is no longer possible to save him. Ornamental plants suffer the most: dracaena, lily, ficus, cyclamen.
Varieties
There are about 20 000 species nematodes. In our country, there are four types of pests that pose a risk to planting:
- Golden nematode;
- Stem nematode;
- Pallid nematode;
- Gall nematode.
What is potato globoderosis?
They differ in color, habitat and lifestyle. For landings, the greatest threat is stem and golden varieties. The most common is the golden nematode.
Golden
It spread in Russia in the 50s of the twentieth century. The golden potato nematode does not pose a danger to humans, but it is a threat to the destruction of a large potato crop. Even during the frost period, the potato golden nematode is incredibly tenacious and remains highly active. With the arrival of the new season, worms infect the garden with renewed vigor.
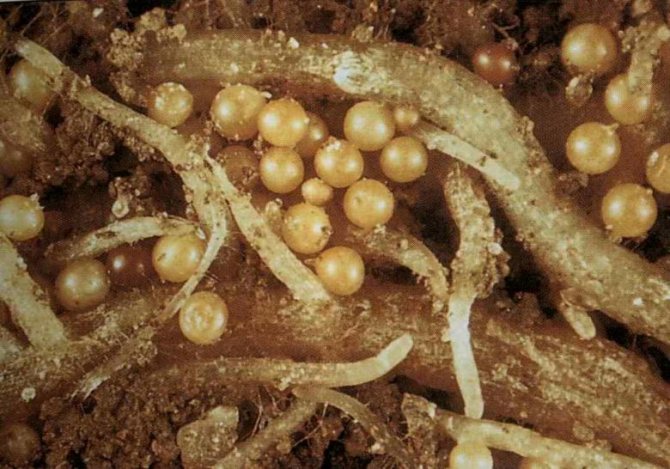

Cysts with golden nematode larvae
The pest blocks the flow of nutrients to the rest of the plant, penetrating the root of the bush and sucking the juices out of it. As a result, the potatoes dry out.
Note! A vegetable infected with a nematode does not grow tubers at all. The roots of such a bush are overly branched.
The life span of males of this nematode species is 10 days. These are small worms that do not consume food at all. The purpose of their existence is the fertilization of the female. The latter have a spherical body, in which eggs appear after mating. Towards autumn, the female's body becomes golden brown, they die, turning into cyst capsules containing a large number of eggs.
Cysts are distinguished by high vitality, and have the ability to stay underground for years. The hatching process of larvae from cysts can take up to 6 years. The capsules are hard-coated. This protection allows you to move in the wind or rain, keeping the eggs intact inside.
Stem
It belongs to the large family of roundworms and most actively attacks plants during the growing season, as well as roots during storage. The length of the potato stem nematode is about 1.5 mm... This type of nematode develops at a high rate, destroying the plantings of many vegetable crops.
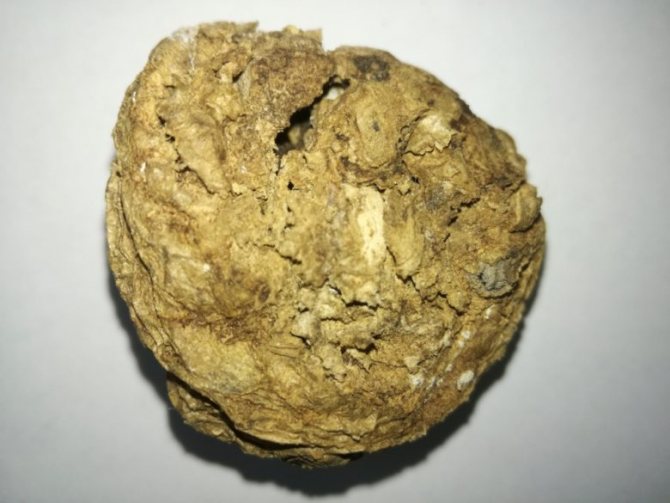


Potato stem nematode
Pests penetrate into the tubers of vegetables, as a result, the trunk of the plant is deformed. The presence of potato stem nematode in plantings can be noticed when small vegetables start to stagnate. The root crop becomes loose and soft, with noticeable worm passages inside. Elevated temperatures destroy the surface layer of this type of cysts.
Pale
It is found all over the world. For the first time, this species of nematodes came to Europe with imported potatoes into Germany in 1913, where it was discovered. Pale potato nematode damages the root growth of many vegetables, but most often affects potato plantings. This species lives in the surface layer of the earth and damages potato fields.
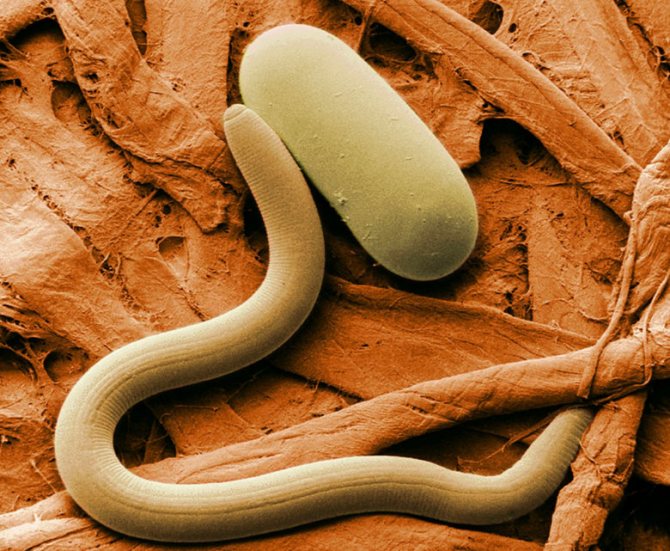

Pale potato nematode
The pallid nematode can be seen in the potato golden nematode habitat. Outwardly, they are similar, except for the color. In the pale, it is stormy brown, and in the golden one, it is yellow. The biological cycle in all nematodes occurs without metamorphosis. In the fall, the fertilized female dies, turning into a dense cyst.
On a note! Crop losses when a harmful worm of this variety is found in a potato field can be from 50% to 90%, and in some cases - up to 100%.
Gallic
The Colombian variety of nematodes, common in Europe, America, Africa, in most cases damages tomatoes and potatoes. The color of the root knot nematode is white, which subsequently becomes transparent.


Gall potato nematode
It got its name from the formation of thickenings (galls) on the rods of vegetables when they are infected. Gauls are located locally on the bases of plants. Infection occurs when infected specimens are used in planting operations.
Control measures
Biological agents are an alternative to chemicals. They are absolutely safe for plants and people, since they do not contain any toxins. One of the most potent drugs in this group is Nematofagin. When using it, you should strictly adhere to the dosage indicated by the manufacturer.
Heat treatment can also be used to control rhizome-eating worms. To do this, the plant is dug out, the damaged areas of its root system are cut off, after which the rhizome is immersed for 5 minutes in water heated to 50 degrees. However, it is important to understand that if the worms managed to infect most of the root system, then this method may be useless, since when most of the rhizome is removed, the plant may not survive.
After the completion of heat treatment, the plant is planted in a new place.In order for it to take root normally and be able to recover, it is recommended to add a small amount of an anti-nematode drug to the bottom of the hole. After planting, the soil should be loosened. This is necessary in order to provide the root system with an adequate supply of oxygen.
Other preventive measures and means of controlling the nematode without the use of chemicals are also conditionally effective. It:
- Compliance with crop rotation.
- Selection of varieties and hybrids that are relatively resistant to nematode damage (for example, for tomatoes - Nagano F1, Eupator F1, Malika F1; for garden strawberries - Festivalnaya, Pearl, Dessert, Saxon, Raketa; for potatoes - Scarlet, Freska, Picasso, Diamant) ...
- Careful selection of healthy seed.
- Warming the bulbs of tubers and corms before planting for 15 minutes at a temperature of about 45-50 ° C or 3-5 minutes at a temperature of 55-60 ° C.
- Before planting soil disinfection with hot water, removal of the top layer, digging and mandatory mulching.
- Regular planting maintenance - weeding and thinning.
- Careful watering - drops of water should not remain on the stems and leaves for a long time, because this promotes the development of nematodes.
- Planting phytoncidal plants in the aisles that help repel pests, for example, marigolds or calendula.
- If an infection is detected during the growing season, timely cleaning of the affected and weakened plants.
- After harvesting, harvesting all plant residues from the site, removing (burning) all remaining contaminated plant material along with the surrounding soil.
- To increase fertility and partial destruction of the nematode, it is good to sow the site vacated after harvesting in August - early September with grain (preferably winter) crops. First, the site is cleared of weeds and plant residues, the soil is loosened and only then it is sown with grain "randomly" to a depth of 2-3 cm. When stable frosts occur, the soil is dug up together with winter crops, making a full rotation of the seam. So it is enriched with organic matter and frees itself from the most dangerous pest - the nematode, which, in such unfavorable conditions for it, simply freezes out.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: What does thrips look like on plants
Alas, a truly effective fight against this pest in the garden and vegetable garden today is possible only with the help of nematicides - a group of chemicals that destroy herbivorous nematodes.
Some of them can be used as fumigants - poisonous gases that poison pests when entering their respiratory system (carbation, chloropicrin, nemagon, methyl bromide).
Others (organophosphate compounds, derivatives of carbamoyloximes and carbamates) - as a contact poison that poisons worms by absorbing directly through their integuments (methyl mercaptophos, malofos, phosphamide, lindane) or systemic action that make the plant poisonous to nematodes (for example, dimethoate).
Fumigant nematocides are used by introducing them into the soil, as well as for pre-sowing treatment of seeds, bulbs, tubers or seedling roots in the fight against worms parasitizing on plant roots. Organophosphate nematocides - a method of spraying plants to destroy leaf and stem nematodes.
Some nematicides (for example, chloropicrin) have a complex effect, being at the same time fungicidal, insecticidal and herbicidal agents. They lead to complete sterilization of the soil (sowing on it is possible only 20-50 days after treatment, and for especially toxic ones - and at all only in the next sowing season).
In general, all of the above chemicals must be used strictly according to the instructions and in compliance with all TB rules - the methods, norms and timing of their use vary greatly and depend on the types of nematodes and the protected plant, on the form and properties of the drug, on the type of soil and environmental conditions at the site.
As a rule, organophosphorus compounds are less toxic than nematicide fumigants, and they also have a much lower consumption rate.
It is very difficult to get rid of this pest, and a culture heavily infected with it is almost always thrown away or burned outside the suburban area. If the plant is slightly infected, then it can still be saved. And at the same time, the contaminated soil is carefully cultivated. If the number of pests is small, then they start with folk recipes, in more severe cases they switch to chemical preparations.

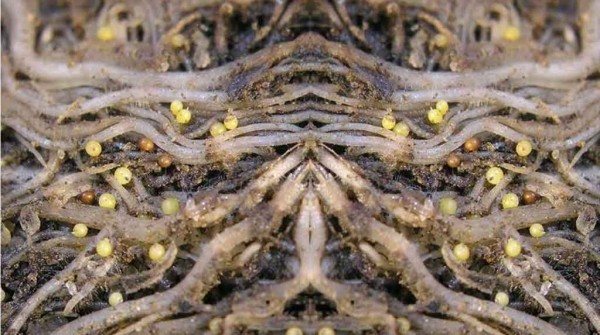
Mass reproduction of the pest begins when the air temperature is kept at 20 ° C with a humidity of at least 50%. If all summer there are such conditions of air temperature and humidity, then about 3 generations of nematodes will grow.
Even if nothing grows on this land, it will still be able to live in it for several more years. Many gardeners, in order to avoid the massive spread of this pest, use crop rotation every three to four years. For example, a pest that feeds on carrots last season will not be able to feed on onions in the same garden as it is used to that food. Then he dies.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes are usually resorted to only in mild cases of infection.
- Trimming roots - If there are very few growths, then they can be trimmed, but you should not get too carried away with this, since the plant does not always have time to grow new roots. The edges are treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- Hot water - The water should be no higher than 50 ° C, otherwise the culture may boil. The infected greens are pulled out together with the root system, washed from the adhering soil, and then briefly placed in a bucket of hot water. 20 minutes is enough for all adult parasites to die. But only hotter water can destroy eggs. In this case, you can take a risk and raise the water temperature to 60 ° C.
- Urea - Add 500 grams of urea and a kilogram of chopped potato sprouts to a ten-liter bucket of water. After that, the infected beds are watered with this agent.
- Marigolds - They make a tincture of them that successfully gets rid of pests. About a kilogram of dried raw materials are soaked in a ten-liter bucket of liquid for about two days, then they are passed through a sieve and the soil is watered.
- Poisonous hogweed - They also make a tincture from it, but the whole procedure is done in rubber protective gloves, since the juice of this plant is poisonous. About a kilogram of this herb is soaked in a bucket of liquid for exactly one day, after which it is filtered and watered.
- Calendula officinalis - This remedy is good because it can be used both for prevention and for treatment. This tincture can be watered on the soil every week. To do this, stir ten tablespoons of dried grass in a ten-liter bucket of liquid. Insist exactly one day, then watered. You don't need to filter.
- Onions - To make a tincture, a pound of chopped onions is poured with a bucket of liquid. The next day, pass through a sieve and water the beds every week. Three procedures are enough.
Chemicals
If folk remedies did not help get rid of the misfortune, then chemical preparations can be used. The most effective and popular are:
- Vidat.
- Methyl bromide.
- Dimethoate.
- Karbofos.
- Carbation.
- Lindane.
- Methylmercaptophos.
- Nemagon.
- Nemaphos.
- Rogor.
- Phosphamide.
- Chloropicrin.
They are used strictly according to the instructions, some of them can be reused after a few days. Some preparations can be used as a spray. This procedure is performed only in the evening and in calm weather. Unfortunately, most of these preparations cannot kill eggs due to their very dense shell. Therefore, it is recommended to repeat the treatment after a while, when the larvae hatch from the eggs.
Siderata
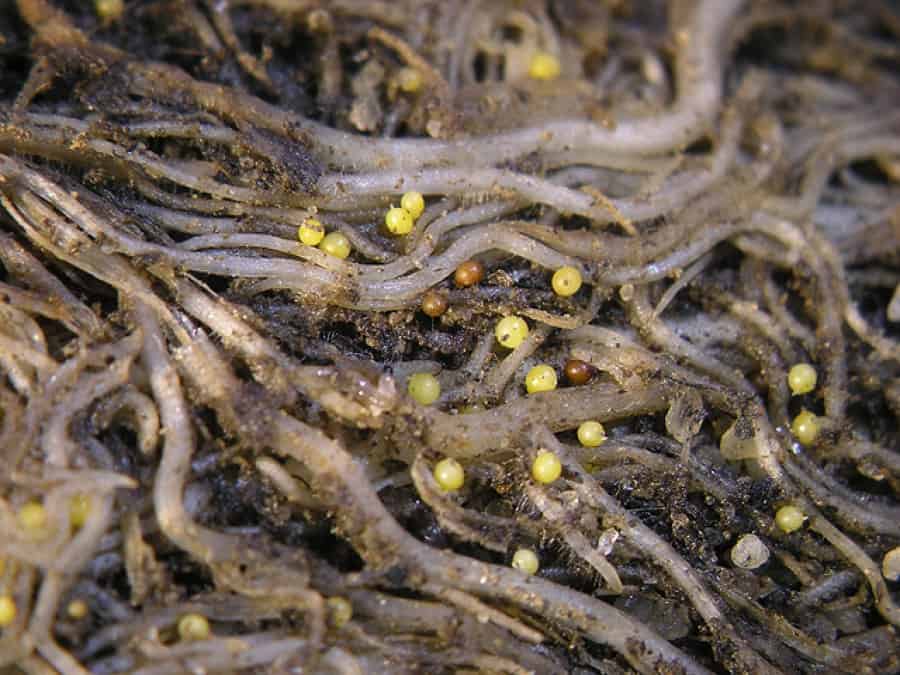


If you plant all the soil with green manure, for example: beans, peas, beans, marigolds, clover, they will be able to destroy about 85% of pests in a season. They need to be planted so that the distance between them is at least 4 centimeters.
In the next season, only a culture resistant to nematodes is grown in this place, since a certain percentage of parasites still remain in the soil. It is not recommended to grow cucumbers in such land for about five years, since they are very easily captured by pests.
Vegetables grown in contaminated soil are not recommended to be propagated. And also they are not kept next to healthy ones. If possible, they are simply burned. For planting in specialized gardening stores, new planting material is purchased, which is guaranteed to be free from contamination.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself: Can a two-tail crawl into the ear
Leaf nematode
The appearance of a nematode in the soil on a personal plot (the fight against them gives a lot of trouble to many gardeners) is accompanied by the following signs:
- foliage loses its normal color and becomes covered with brown spots;
- leaves begin to curl;
- petioles increase in size;
- the plant begins to grow and bear fruit poorly;
- the buds are covered with brown spots during the flowering period;
- glossy spots appear on the lower part of the leaves, which then turn brown.
If you do not start pest control in time, the plant will gradually dry out and eventually completely rot. At the same time, the solution of this problem should be approached in a comprehensive manner, since nematodes in the soil (the fight against them is very difficult) are able to withstand any frosts and will begin to devour other plants next year.
- Strawberry;
- chrysanthemum;
- indoor fern;
- orchid;
- Money Tree;
- aster;
- dahlia;
- carnation.
Therefore, if you are growing these plants, it is very important to take certain preventive measures in advance to protect them from nematodes. We will talk about them a little later.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of this dangerous pest, you need to follow these simple rules.
- It is undesirable to use garden soil for growing seedlings or home plants; it is better to purchase it in a specialized store. But if this is not possible, then the garden soil is thoroughly disinfected.
- After harvesting each harvest, all the soil is cleaned of leaves, weeds and residues of greenery, since worms hibernate in them.
- Throughout the season, weed and loosen the beds regularly.
- Diseased or damaged parts of the greenery are removed in time.
- Dig up all the soil every autumn.
- In the summer, it is undesirable to transfuse the culture, since the worms love moisture.
- Observe the crop rotation.
- Choose the varieties carefully for planting. Seeds and seedlings must be healthy.
- Before planting, the tubers and roots of the bushes are kept in very warm water for about 15 minutes.
- Water the entire soil with boiling water before planting.
Stem nematode
Stem nematodes in the soil of indoor plants are a very common occurrence encountered by many growers. This type of worm grows up to one millimeter in length. It affects the stems, leaves and flowers of the plant, getting on them through the rhizome.
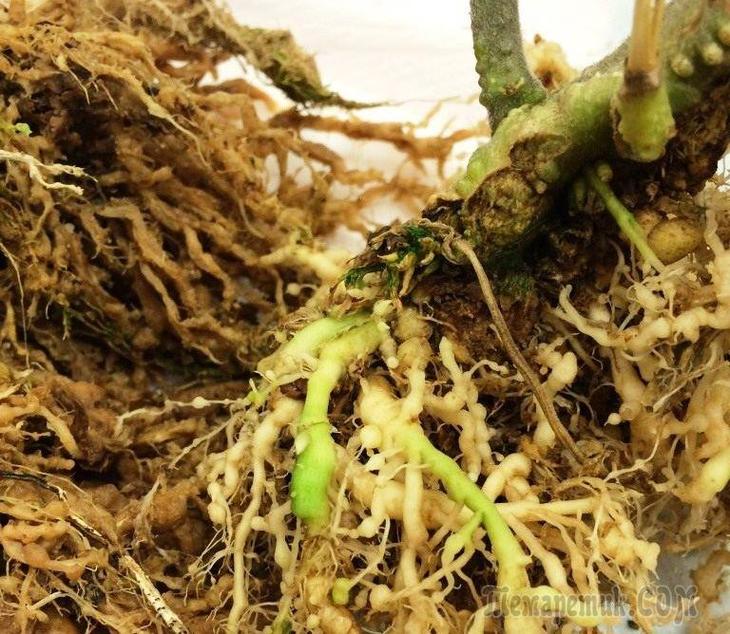


The presence of these pests can be recognized by the following manifestations:
- plant growth slows down;
- the thickness of the stem increases, the color of which fades;
- blossoming buds dry up very quickly and fall off;
- in the absence of any pest control measures, the flower dies.
Roundworm biology
They reproduce in two ways:
- The female is on the surface of the root and lays eggs in a sac, from which the larvae first enter the soil, and then make their way into the root system of the host plant, after which it becomes infected.The female is completely in the root tissues and lays eggs inside it. The hatched larvae move along the root tissues and settle in it for nutrition and development. They are no longer affected by biological methods of protection.

It should be noted that the larvae from the roots, under favorable conditions, are able to move through all organs of the plant.
Root nematode
Some gardeners claim that nematodes on strawberries are afraid of marigolds and calendula. With prolonged spraying of the culture with a tincture prepared from these plants, dissolved in water, you can get rid of the worms. Processing should be carried out 2 times a day for 3 weeks.
For example, marigolds are deadly for nematodes, only varieties of small marigolds with a strong odor must be used. And the excretion of calendula roots expels nematodes, stimulating the vital activity of beneficial soil inhabitants. The roots of Gaillardia, Rudbeckia, Coreopsis secrete substances that the nematodes cannot tolerate.
The eggs and larvae of root nematodes, despite their adaptability, need certain conditions for a successful existence and reproduction, they must be: moist, warm ground (low temperatures prevent reproduction), slightly acidic soil (regular liming suppresses the spread of nematodes), sandy soil (sandy structure facilitates the movement of nematodes, provides them with oxygen).
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Destruction of bedbugs in Moscow. Treatment of an apartment from bedbugs at a price of 1600 rubles.
Root nematodes live in the soil most often near the roots of plants. First of all, vegetable crops suffer from them. This type of nematode can be divided into the following three groups - root root gall nematodes, free living and nematodes with free cyst formation.
How to deal with a nematode
In autumn, with the onset of stable frosts, the soil is dug up together with the winter crops, making a full rotation of the layer. With this method, the soil is enriched with organic matter and, in addition, is freed from the nematode - the most dangerous pest that has risen to the roots of cereals. After such measures, the damage to vegetable crops by the nematode will be much reduced ...
The root nematode has the largest body size, which is yellow or brown in color and can reach a length of 2 millimeters, so it is very easy to distinguish it from other species. This pest poses the greatest danger to plants, since it affects its root system. In this case, the plant completely stops growing, and also gradually withers, until eventually it dies at all.
How to prevent serious infection
As you know, it is almost impossible to completely destroy the rootworm nematode. For this reason, greenhouse farms are usually faced with the question of how to reduce the number of parasites to a safe limit and prevent large crop losses. Proper prevention will help here, which is based on:
- timely destruction of weeds;
- increased spillage of the substrate in the greenhouse, which should alternate with drying;
- laying manure in the soil;
- spilling the substrate twice with infusion from the plant that is currently being processed, and alternating it with drying the soil;
- growing peas and beans, which are trapping plants for root root nematode, as well as watercress, which can dramatically reduce the number of harmful individuals.
What is the danger of nematodes to plants?


Before discussing how to get rid of nematodes in the soil, it is necessary to talk about the danger these pests pose to the flora. Devouring plants, the worms, together with the juice, draw out all the nutrients from them.In addition, the waste products of these pests are very strong toxins that poison plants, which lose their normal shape and color, stop growing and developing, and also bring significantly less harvest.
The whole difficulty of dealing with nematodes lies in the fact that their presence is very difficult to detect in a timely manner. It is impossible to do this with the naked eye due to its too small size. Leaf and stem worms can only be seen through a magnifying glass, and root worms live in the ground, so you will have to dig up the plant altogether. In this case, the root system will be covered with brown seals.
It is worth noting that because of the toxic substances emitted by nematodes, burns and irritations may appear on the skin, therefore, when fighting worms, be sure to use long-sleeved clothing and gloves.
The most effective remedies
Novice gardeners have never heard of fulmigation, which is the most effective pest control method. What is soil fumigation against nematodes? This is the treatment of plants and soil with special poisonous substances and their vapors. You can buy chemicals at any gardening store. Experienced farmers recommend using "Nefamos", "Dimetoat" or "Vidat", which are sprayed with plants.
To make them more effective, chemical treatment of crops is best done on a clear, calm day. If the plant has been infested with root nematodes, the chemicals are diluted with water and added to the root system. It is worth noting that these agents only kill adult worms, so spraying is recommended several times so that the larvae also die.
The main and, perhaps, the only effective folk remedy for fighting the nematode “cheap and cheerful” is spilling the soil with boiling water on the eve of planting. High temperatures are detrimental to tiny nematodes and after such a procedure their number on the site really decreases noticeably. You just need to remember that for a real effect, the earth must be saturated with hot water with a temperature of at least 50-55 ° C to a depth of at least 15-20 cm.After that, it can also be covered with polyethylene to cool down more slowly.
Alas, the measure is not fully effective. Although a significant number of nematodes live in the surface layers of the substrate and, as a rule, die during such thermal disinfection, some pests can migrate into deeper layers of the soil and escape.
In addition to the soil, the affected plants themselves can be treated with hot water - this mainly concerns the bulbs and roots affected by the root nematode. They are washed from the ground and then soaked in hot (45-50 ° C) water for 10-30 minutes. As a useful additive, formalin at a concentration of 0.06% can be added to this water.
So, the most effective remedies for nematodes in the soil are chemicals, but they are very toxic, so their use can be both beneficial and harmful. Therefore, rather than dealing with pests, it is better to try to prevent their appearance.
To do this, take the following preventive measures:
- fight weeds regularly;
- remove fallen leaves in a timely manner;
- remove yellowed foliage from plants;
- transplant plants periodically;
- fluff the ground regularly;
- choose planting material carefully;
- do not water the plants with too much water;
- Dig up your backyard every fall.
Traditional methods of treating the earth from a nematode
Coping with the pest is not an easy task, especially during the period when the nematodes are in the ground. Yes, and there are no ways to guarantee the complete destruction of the pest; preventive measures will rather help here.
- First of all, when an infected plant is found, it must be dug up and burned, in no case should such a plant be put into compost.
- You always need to monitor the condition of the soil, nematodes often settle in acidic soil.
- If, after a long wait, the legumes have not sprung up, you need to dig out the seeds, they may already be chosen by the nematode, the worms completely encircle the seed. You can apply film mulching, from the sun exposure the soil under the film will warm up strongly, and nematodes die under the influence of high temperatures.
- Plants capable of destroying the pest are ammobium, cumin, helihrizum and acroclinum.
Root nematodes
And those who have soils available for sale generally benefit - feel free to use the Zashchita soil. It contains predatory nematodes that supplant even the potato nematode, even the strawberry nematode. When planting, add a tablespoon of this mixture under each tuber / bush, and this will be the best bio-protection against herbivorous nematodes for many years - cute predators will perfectly take root in the garden bed and winter calmly. The only condition - do not overdry the open mixture, otherwise you will ruin the biological product.
Since nematodes cause significant damage to the harvest of many crops, the question of their destruction is quite acute. At the same time, you need to understand the types of these pests, since they all differ in their characteristics, which requires a special approach to their extermination. This article aims to inform gardeners and gardeners on how to properly combat this insidious enemy of horticultural crops.
Plant nematodes are divided into stem, leaf and root nematodes, depending on which part of the plant the worms live in. The length of the pests depends on their type and can reach a length of 8.5 meters. In fact, plant worms are quite small, although males are always larger than females. Depending on the species, the shape of the worms can be thread-like, lemons, or barrel-shaped.
Eggs of nematodes are white and round in shape. In this state, eggs do not have a negative effect on plants.