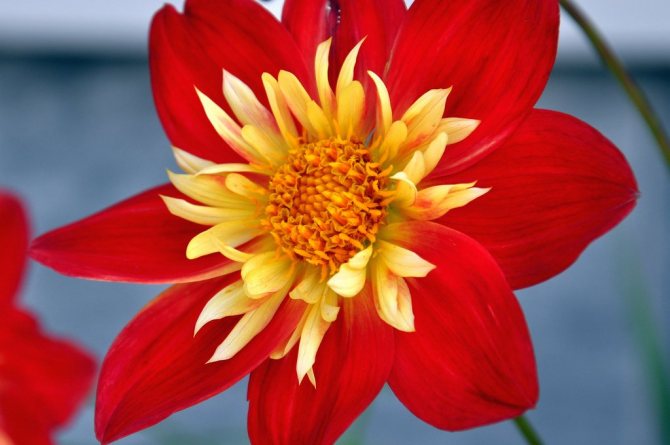
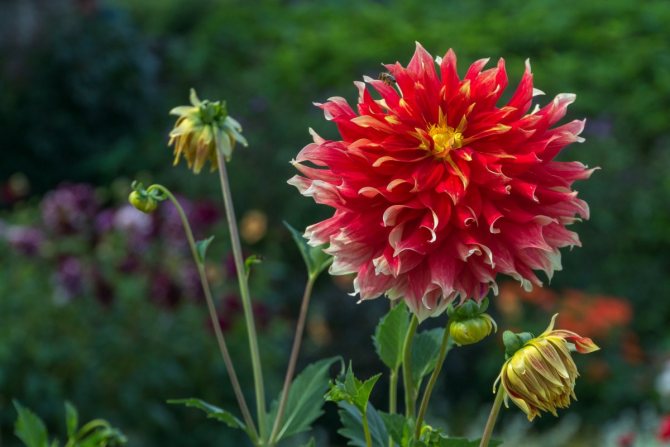
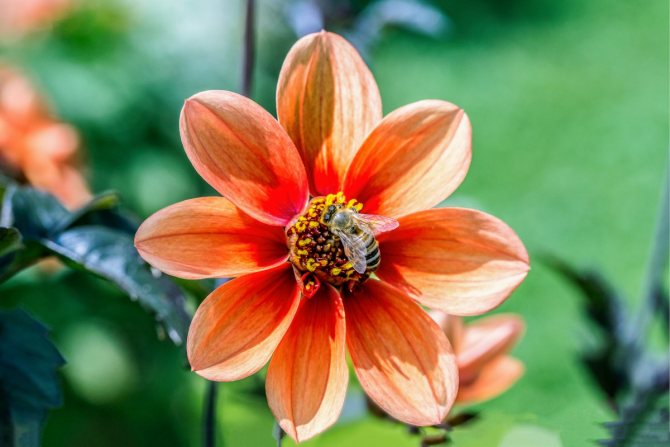
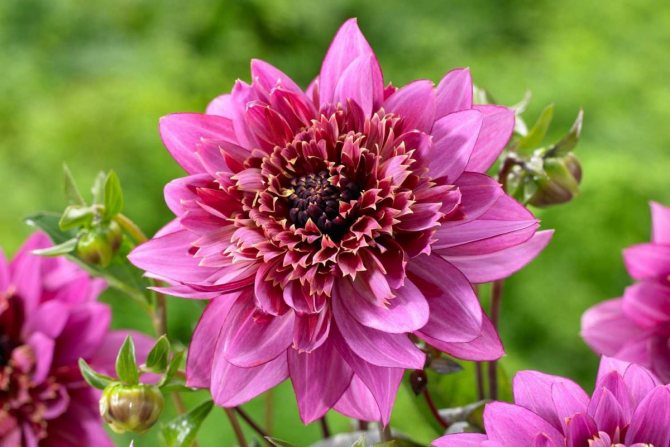
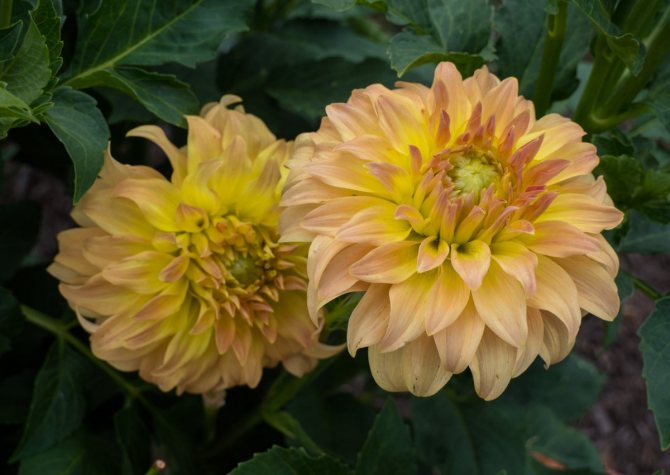
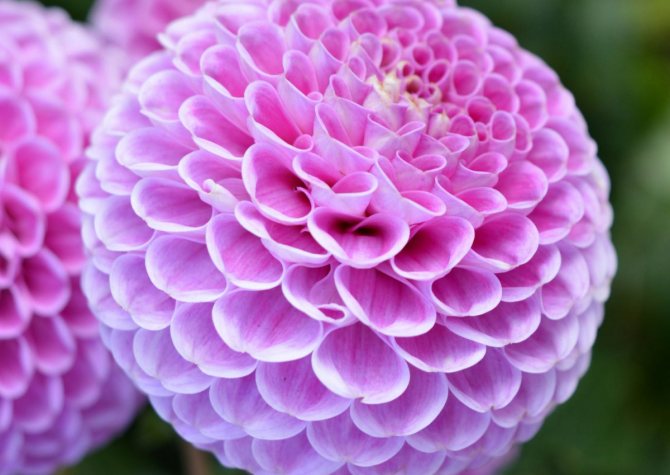
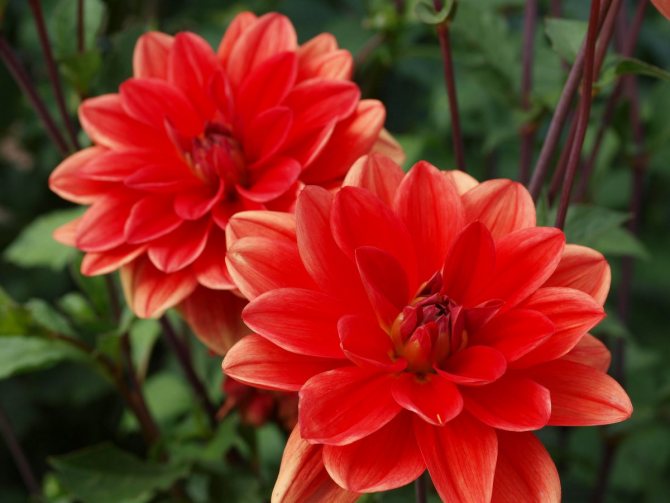
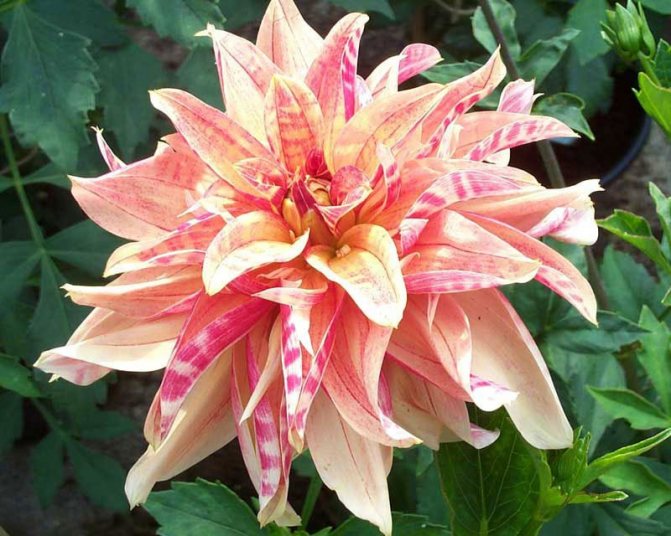
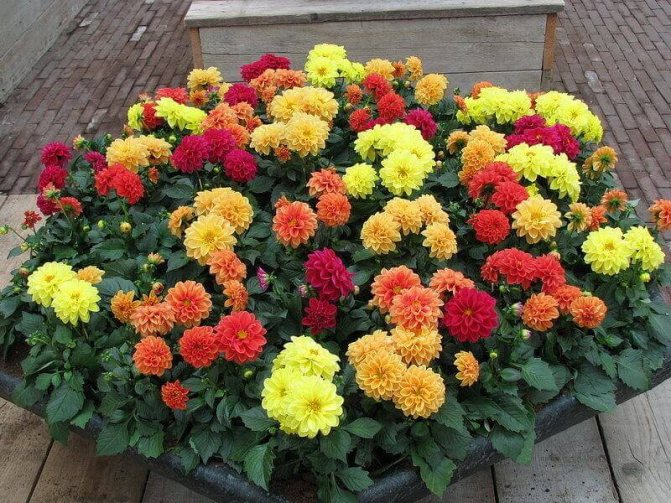
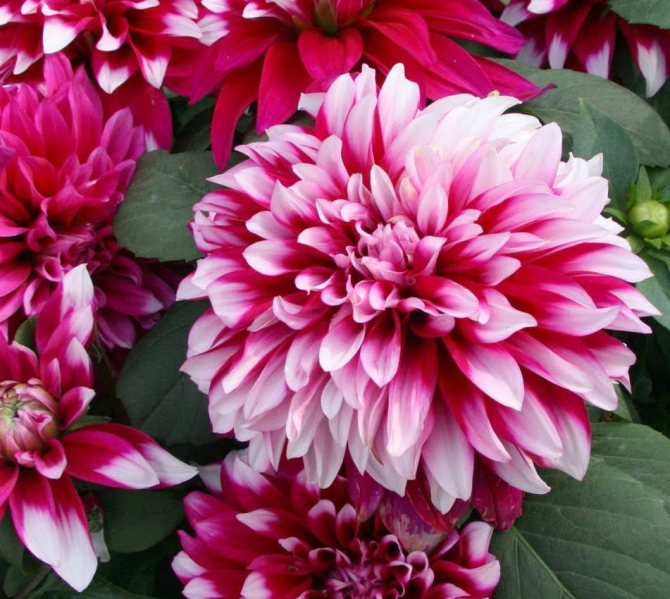
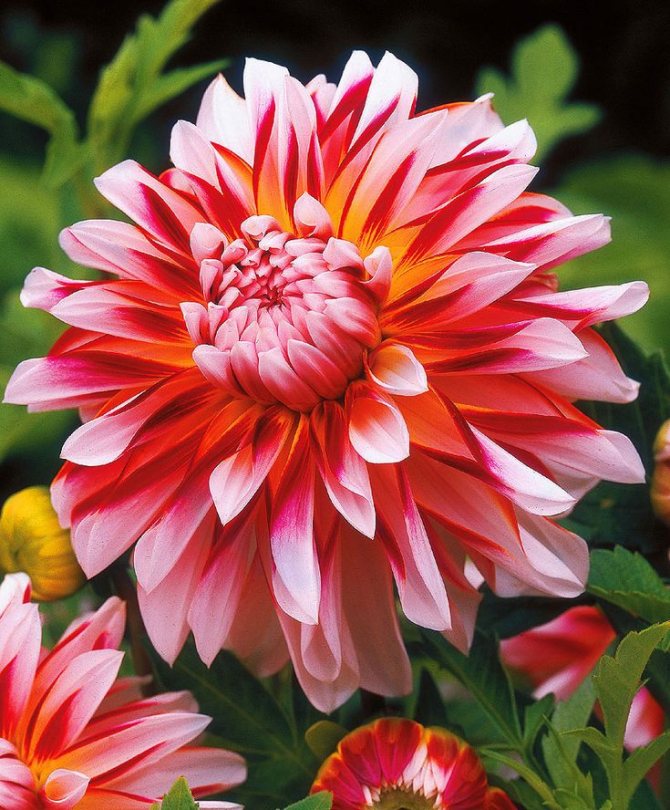
The Garden Dahlia (Dahlia) is one of the most popular flowering plants for outdoor and pot production. This plant from Mexico quickly gained immense popularity around the world. The richness of shapes, varieties and colors makes it ideal for any garden.
Let's find out how to grow annual dahlias, planting and maintenance features in the open field, what conditions need to be provided for the flower to feel good in our gardens.

Dahlias description
Dahlia is a herbaceous perennial. Stems are hollow, depending on the variety, reach a height of 30-180 cm, erect, branching.
In nature, dahlias are common in the mountainous regions of Mexico, Guatemala, Colombia. In natural habitats, the aerial part of the perennial plant annually dies down to the tuberous-thickened, fleshy roots, and the root tubers themselves winter in non-freezing soil. Areas of central Russia are unsuitable for dahlias in winter - these plants freeze in open ground. Therefore, in culture, they have to be dug up for the winter and stored under certain conditions.
Dahlia roots
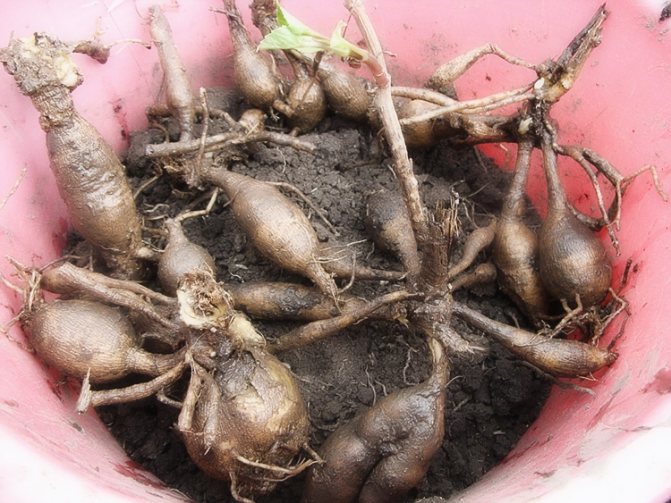
The dahlia root system consists of thickened storage and thin feeding roots. Storage roots, they are also called root tubers or simply tubers, are formed at the base of the shoots of the current year, thicken in the year of formation and live for about 3 years. All feeding roots, as well as slightly thickened storing root tubers of winter storage, do not withstand and die off.
In dahlias, renewal buds are located on the lower part of the last year's shoot and on the root collar of root tubers. There are no buds on the root tuber itself.
Dahlias are most often used in single, group and border plantings.
What are dahlia root tubers
On the roots of the flower, closer to the base of the root, thickenings are formed in which nutrients accumulate. They help the plant through the winter and provide nourishment for young shoots in the spring. If you carefully examine the dug root, you can see that each tuber at the point of attachment to the stem has a kind of growth - the root collar, on which the buds are located. Of these, a new plant begins to develop next year.
The tubers are covered with many small thin roots, with their help the bush receives water and nutrients from the soil. In the center of the root system is the stem. By the time of digging and drying, it dries up and becomes hollow. It easily gets soil and plant residues from the soil. If the roots of the dahlia are removed for winter storage along with the stem, the stem will quickly begin to rot, starting from the base. Putrefactive processes quickly move to nodules, so you can lose all planting material by spring. Therefore, it is in the fall that it is necessary to divide the entire bundle of tubers into separate parts, carefully cutting out all suspicious places.
The disadvantage of this method is that the dormant buds on the tuber neck are better visible in spring.


Dahlias classification
In our country, there is currently no single classification of dahlias. Usually, 10-12 classes are distinguished, differing in the size and shape of the inflorescence, the degree of terry, as well as the shape of the petals.
There are the following classes of dahlias:
- Non-double, or single-row, in which almost the entire basket is occupied by tubular flowers, ligulate flowers (petals) are located in the outer circle in 1 row. Low-growing non-double dahlias with a height of not more than 50 cm are allocated to the subclass (class) Mignon, they reproduce by seeds.


- Anemonic, they have large petals in 1-2 rows, tubular flowers, long, colored, elongated, rise above the inflorescence with a dense central group.
- Peony have semi-double inflorescences with 2-3 rows of wide petals and a center of yellow tubular flowers. The petals adjacent to the center of the tubular inflorescence are often much smaller, wavy or curled.
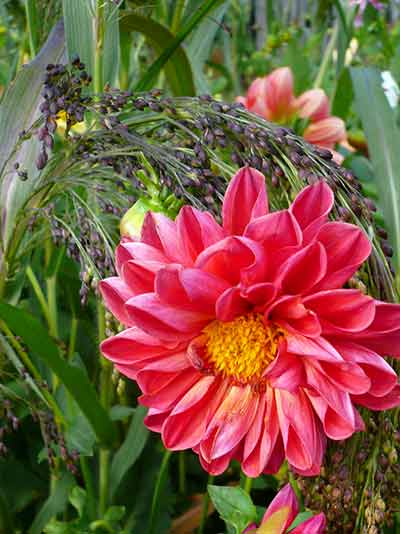


- Collar, this class has 2 circles of petals, while the petals of the inner circle are much smaller than the petals of the outer circle, they cover tubular flowers like a collar. The petals of both circles are colored differently.
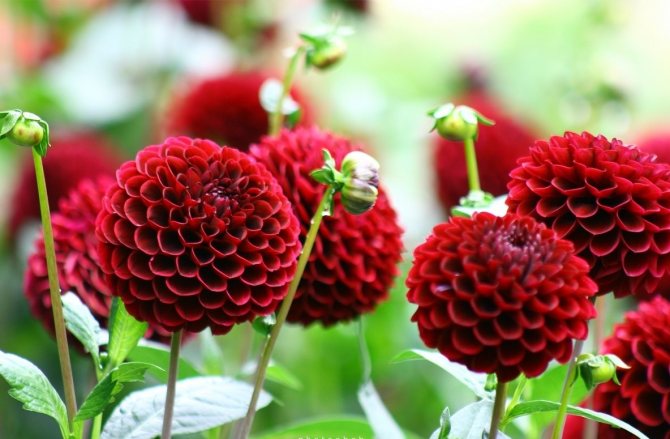
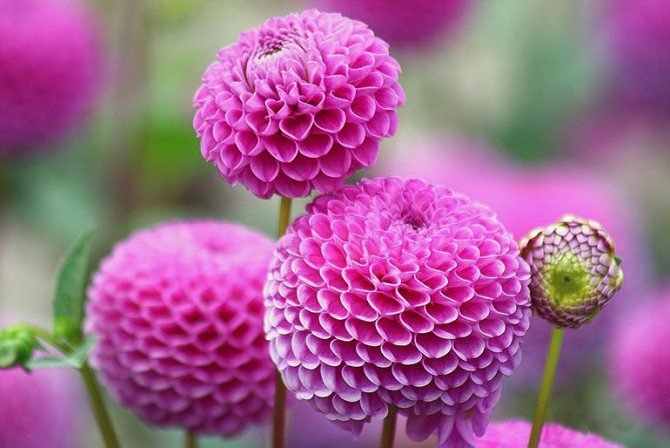
- Spherical have densely double inflorescences with a diameter of 7 to 20 cm, hemispherical or spherical, wide petals with rounded tips, in the lower part (up to half the length), the petals are collected in a tube.
- Pompom dahlias are the same as spherical, but smaller and more rounded, flowers up to 7 cm in diameter. The petal is rolled into a tube along its entire length.
- Ornamental: dahlias of this class have densely double inflorescences with wide, straight, wavy or curved petals in one direction, in the center of the inflorescence the ligulate flowers are rolled and spirally twisted. The size of the inflorescences is from 4 to 40 cm in diameter.


- A subclass (class) of Nymphaeans is distinguished, their inflorescences resemble a white water lily (nymphea).
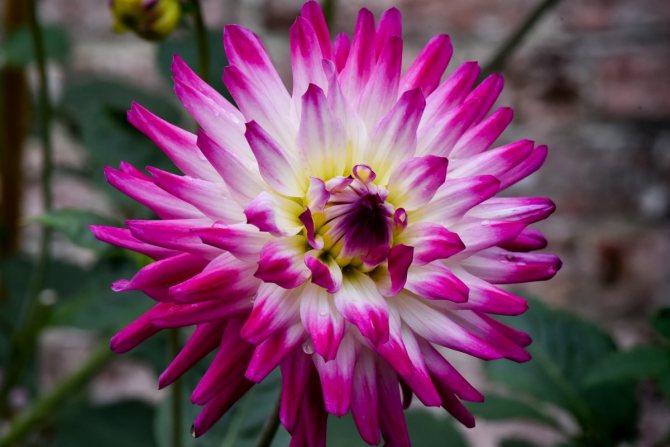
- Semi-cactus have double inflorescences, wide petals, which are folded at the base less than half the length. It is a transitional form between cactus and ornamental.
- Cactus, they have double inflorescences with a closed middle, the petals are rolled into a tube at least half the length. There are varieties with deeply cut petals at the end.
- A subclass (class) is distinguished Chrysanthemum, in which the petals are rolled along the entire length and curved in different directions, resembling large-flowered chrysanthemums.
- Mixed, which includes all new varieties that do not fit the descriptions of these groups.
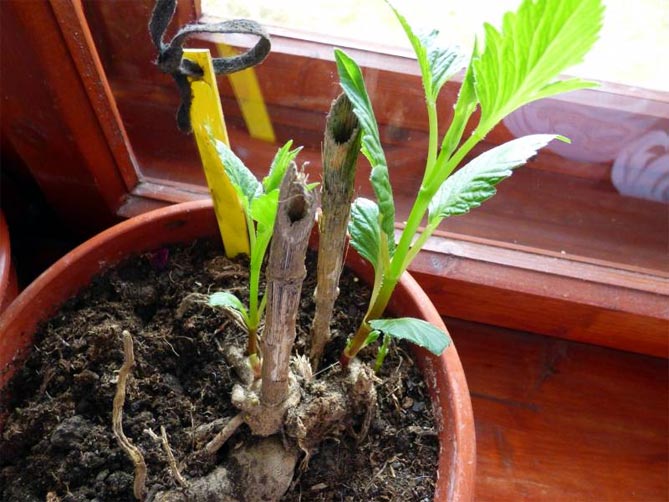
Preparing for spring cuttings
Root tubers are transferred from storage sites at the end of winter. A later distillation is also possible, but in this case, the dahlias will bloom later. Tubers taken from the cellar are examined and darkened with signs of spoilage are separated. The rest are planted in a ready-made substrate or a soil mixture prepared from the fall from garden soil and peat. The soil from the garden is disinfected in any available way:
- freeze for several weeks in bags at temperatures down to -30 ° C;
- steamed in a water bath or heated in the oven;


- treated with specially designed antiseptic agents.
The last 2 methods have a significant drawback - they destroy both soil pathogens and beneficial microflora. Therefore, after warming up, the soil is spilled with biological products containing the necessary microorganisms and left for several days so that they multiply.
Dahlia planting material is planted in the finished substrate, leaving the buds on the surface. Dahlias are germinated in a well-lit place at a temperature of 20-25 ° C and moderate humidity. To maintain the required humidity, the containers are covered with polyethylene or transparent plastic glasses.


Sprouts appear 3 weeks after planting. From this time on, the shelters are removed, the temperature and humidity are reduced. If necessary, the sprouts are illuminated in the morning and evening.
Dahlias growing
Among the basic requirements for a dahlia growing site is good lighting for at least six hours a day.For long flowering and good development, dahlias need sufficient sunlight in the morning and (or) evening hours and some shading from the midday sun. Grown in the shade of large trees, dahlias bloom poorly and do not form viable root tubers.
When choosing a site for growing dahlias, it should be borne in mind that they have fragile stems, so the site must be protected from the wind by trees and buildings. Dahlias do not like drafts, cold winds. Low and waterlogged areas will not work.
Optimal soil for growing dahlias
Dahlias can grow in any soil, but they thrive best in slightly acidic and neutral soils.
Optimal for them is a fatty garden loam rich in humus, or fertilized sandy soil. The soil must be structural, moisture-absorbing and at the same time permeable. They dislike both excess and lack of moisture.
The site intended for growing dahlias must be dug up in the fall, and dug up in the spring. The expediency of double tillage is confirmed by the practice of amateur flower growers. In autumn, when digging, organic fertilizers are applied, and a week before planting, they are dug up a second time.
The soil is cultivated to a depth of 30-40 cm.
Growing and care
Growing a dahlia won't be a hassle. It is important to choose the right planting site for this heat-loving plant. The flower needs to be watered, weeded, high varieties require a garter. It is important not to overdo it with fertilizers, so as not to delay flowering.


Choosing the right position
When planning a site for planting a garden dahlia, its final dimensions must be taken into account. There are various varieties of this plant, characterized by a varied bush shape, size, shape, color of flowers. It is important to know what size the plant will reach in adulthood.
Low-growing varieties can be planted on beds in the immediate vicinity of low plants; when choosing a place for large specimens, remember that they can drown out other garden flowers over time.
Small deciduous trees represent a good neighborhood for dahlias for 2 reasons:
- trees are the perfect backdrop for gorgeous flowers;
- deciduous trees are ideal protection for flowers from the wind, which can break long stems.
A garden dahlia thrives on a sunny spot. Some gardeners find they bloom longer in slightly shaded areas. However, this is a moot point. Botanists warn that dahlias are more susceptible to disease in the shade.
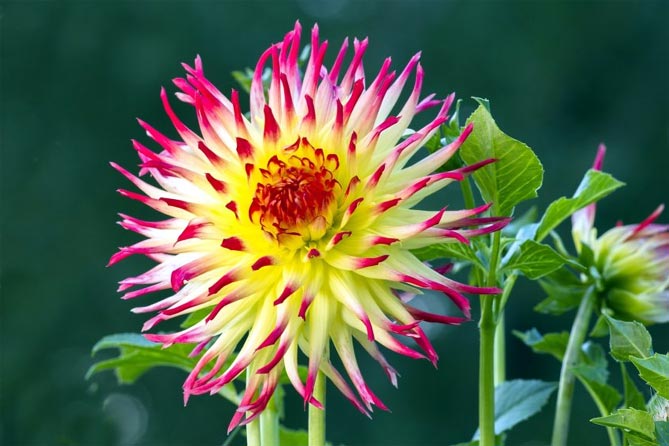


Dahlias like it when it's always a little damp, so the plants should be watered regularly, but not generously. Growing dahlias in dry soil can be challenging. Weakly irrigated dahlia bloom less, leaves wither.
These garden flowers, depending on the variety, can have a height of 25 to 200 cm. Tall specimens resemble small deciduous trees. Dahlias have very fragile stems and break easily, so choose a place protected from the wind and provide them with support. The supports will prevent tall varieties from falling.
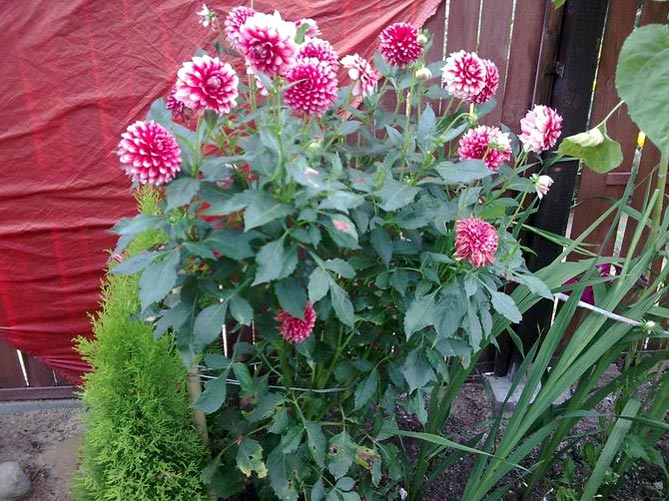


Requirements for soil, watering
The plant needs fertile and well-drained soil for proper development. Too heavy substrates are supplemented with sand, do not forget to enrich the soil with well-rotted compost. However, growing and caring for dahlias is not a hassle because they grow in almost any conditions.
It is important that the area is not too wet, otherwise the tubers will start to rot. A good solution is to use a drainage layer of gravel or small stones during the dahlia planting stage. If we notice wilted leaves in the summer, this means that the plant has too little water.It is very important to keep the soil free of weeds by systematically weeding and loosening the soil.
Pots in which low varieties are planted should have fairly large drainage holes because the tubers rot easily.
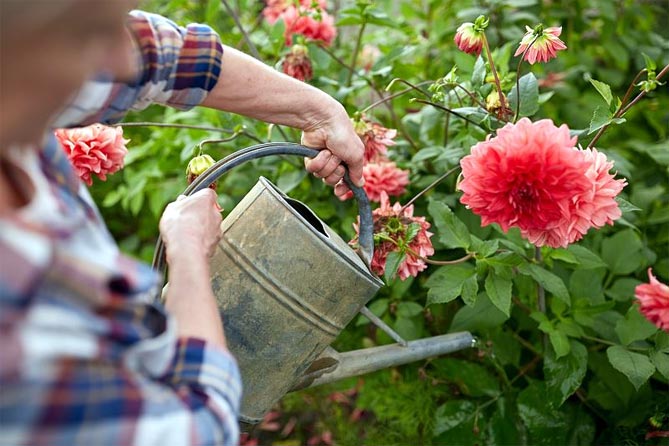


Fertilizer
It is important to remember to properly fertilize the plant. These garden flowers are in high demand for phosphorus and potassium, especially when the buds are in bloom. This is why it is worth feeding them organic fertilizers from spring to July for satisfying dahlia cultivation.
Attention! Be careful with nitrogen fertilizers, otherwise you can get a lot of green mass instead of abundant flowering.
It is recommended to use mineral fertilizers with a slow action in a dose recommended by the manufacturer.
In the fall or spring, it is worth enriching the soil with well-distributed compost, which will not only provide a safe amount of nutrients, but also improve the structure of the soil.
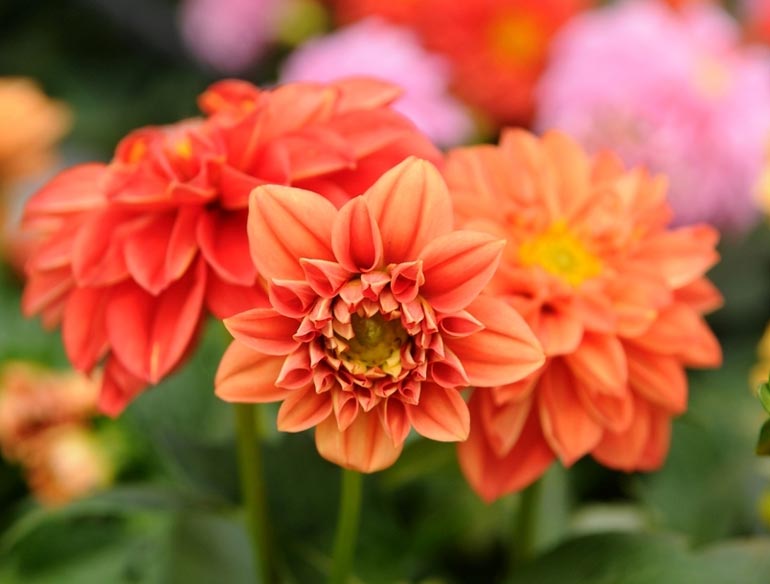


Pruning
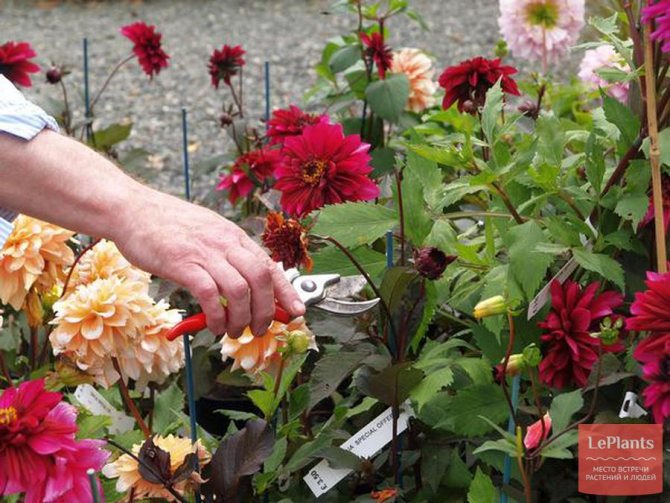
If you want the plant to remain compact, you need to prune it. Then the dahlias quickly branch out, releasing more flower buds. To encourage the plant to grow longer and bloom more, it is necessary to remove the faded inflorescences.
Dahlias planting


Before planting the dahlia tuber, you must first grow a little at home or in a greenhouse.
It is best to plant dahlias in open ground in the first decade of June, because at this time the danger of late frosts has already passed. First you need to plant tuberous dahlias, later (not earlier than June 5) - cuttings.
If it is possible to cover the plants, an earlier planting is also allowed.
The landing site is prepared in advance. Planting holes are dug in the beds, the distance between the holes depends on the height of the plant. Stakes for garters of dahlias are placed next to them. Their height should be slightly less than the estimated height of the plants. One shovel of humus or rotted manure is usually placed in each hole, and 1.5-2 tablespoons of complete mineral fertilizer or 25 g of superphosphate. All this is mixed well.
For 5-7 days before planting, dahlias are recommended to be placed in places protected from the wind in the garden, preferably in partial shade, so that they get used to the conditions of open ground.
Planting is best done in cloudy weather or in the evening.
5-6 hours before planting, dahlias in pots must be watered until the earthen coma is completely moistened.
Before planting, the plants are watered abundantly, and then carefully planted with a clod of earth in a prepared hole close to the stake.
If the plants were grown not in pots, but in greenhouses or boxes, they lose a lot of roots when they are dug up. For successful survival, plants should be planted in previously abundantly shed soil (in "mud"), sprinkled with dry earth on top.
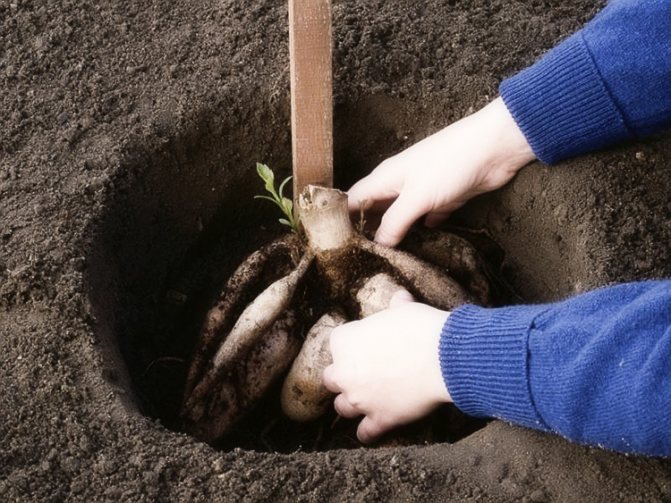
In the soil, planting material is placed a little deeper than it was in a pot or box, the neck of the tuber should be 3-5 cm below the soil level. Seedlings and cuttings should be planted deeper - up to the first pair of true leaves. Planted plants should be watered and mulched immediately with dry soil. Around them, you can make ring-shaped holes that will retain moisture when watering. Tall dahlias should be tied immediately to stakes.
Planting and breeding
There are several ways to breed dahlias:
- seeds;
- cuttings;
- by dividing the root.
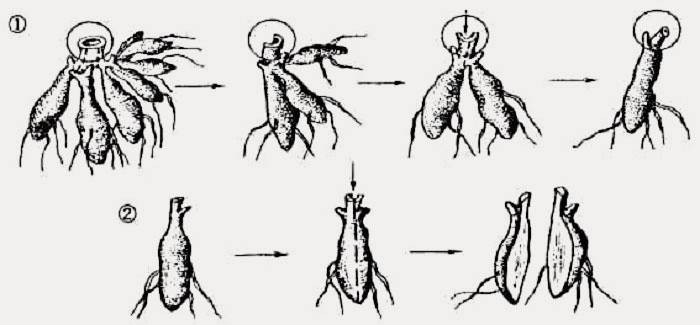
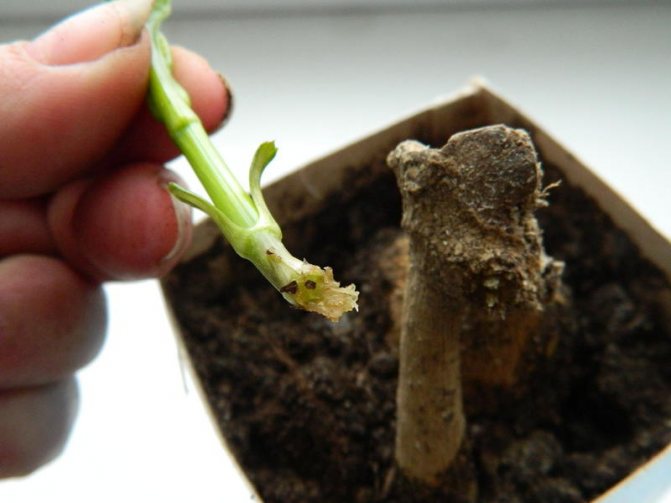
Propagation by cuttings
Dahlias are propagated by cuttings. Cuttings 10 cm long are taken from the mother plant, planted in February-March (best of all with the so-called heel - the lower cut is made under the knot). The ends are dipped into the rooting tool. Then the cuttings are planted in containers filled with a permeable substrate. The containers are covered with plastic wrap. It is necessary to maintain constant humidity and ventilate the plants. Roots should appear in 2-3 weeks.


Reproduction by dividing the root
The most common way to breed dahlias is to split the dahlia rhizomes. The tubers are separated from the mother's rhizome to produce new plants. 2-3 plants can be obtained from one developed rhizome. More dividing will cause these garden flowers to bloom less and form a less showy bush.
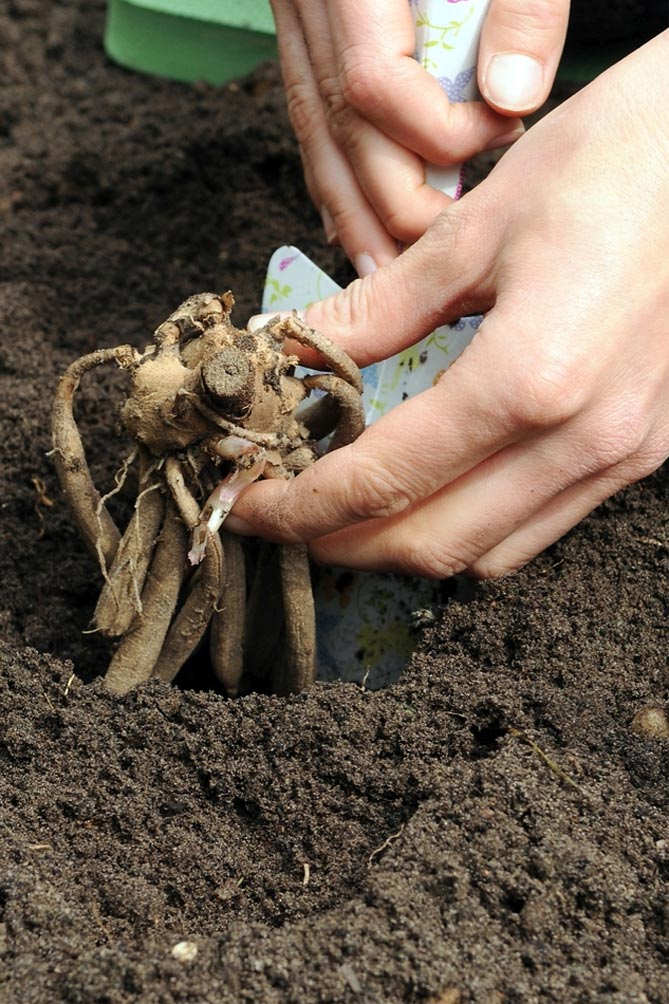


The division is carried out immediately before planting the plant or in March-February - before placing the tubers in containers.
Attention! Gardeners recommend pruning the first shoots of the tuber because they are too weak.
The resulting tuber wounds are treated with, for example, charcoal and slightly dried before being placed in the ground.
If the separation is carried out in February, the separated tubers are planted in a light peat substrate, mixed with the rooting agent and kept for a month at a temperature of about 15 ° C. Then, seedlings with several centimeter shoots and always with a lower part, the so-called heel, are transplanted into pots filled sand, and move to a warmer place.
Landing dates
Now the question arises, when to plant dahlias so that the spring frosts do not harm them? The best time to plant dahlias is the first half of May. It takes them about 2 weeks to produce leaves, after which the risk of freezing will pass. Plants planted in late May will bloom in the second half of summer.
To get young seedlings earlier, you can speed up the process by transferring the tubers to a warmer room in early spring and watering regularly. Then they will sprout earlier.
Dahlia planting step by step
- Strongly dried tubers are soaked in warm water for about 3 hours before planting to accelerate germination.
- Before planting, the tubers should be soaked for an additional 15 minutes in Topsin fungicide solution.
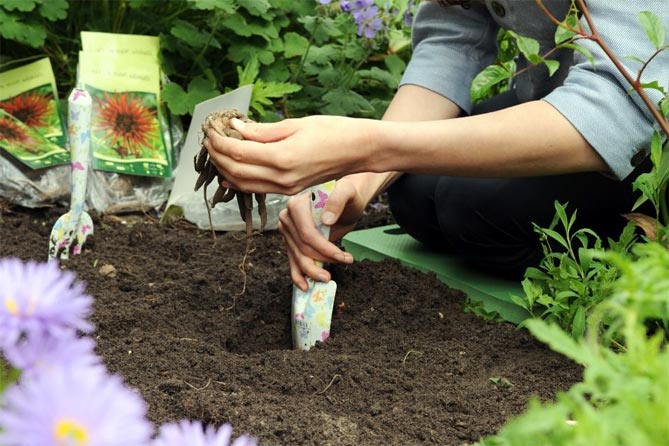
- When planting, we dig a hole much larger than the tuber so that it can develop freely. The depth of the pit is at least 40 cm.
- Then we pour a mixture of the substrate with manure or compost on the bottom. This will provide the seedling with the required amount of nutrients. The reaction of the soil should be slightly alkaline or neutral. If the soil in the garden is poor, you can use an all-purpose gardening medium (pH 7) or mix it with soil or compost.
- When planting dahlias in the ground, the appropriate distances between the plants should be observed. Dahlia tubers are planted in early May at a distance of 70 × 100 cm, the distances vary depending on the height of the future plants:
- for very tall varieties, this distance should be 1 meter;
- for tall people - 70 cm;
- for medium height - 40 cm;
- for dwarf ones - 20 cm.
- If there is a possibility of frost, the seedlings are covered with non-woven material. The root collars must be sunk into the ground. The plants are planted to such a depth that the tuber is covered with about 5 cm of soil.
Attention! Do not plant seedlings with visible symptoms of mold or mildew. When buying seedlings, you need to pay attention that the seedlings are vigorous, elastic, with pubescent leaves or buds. If rot or mold appears on the tubers after storage, you need to cut off the affected fragment and protect the wound with a fungicide, or discard it if the disease has affected most of the tuber.


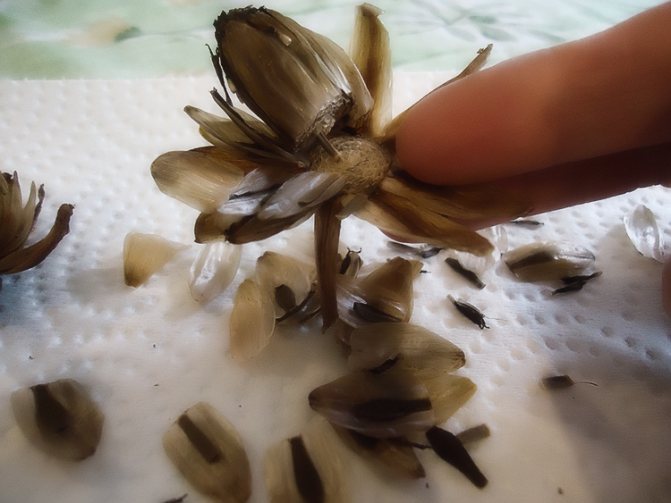
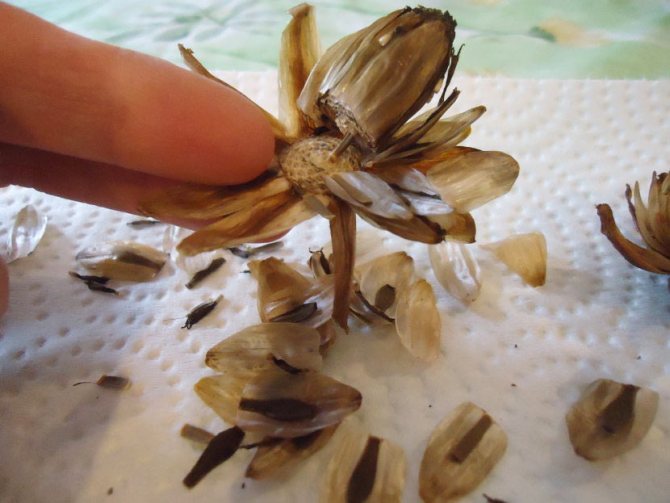
Dahlias from seeds
Another way to get dahlias is by sowing seeds. Some varieties of dahlias reproduce easily with seeds and the resulting seedlings can have extremely bright flowers. However, this method of propagation does not give confidence in obtaining new plants that will repeat the characteristics of the mother.
Seeds are easy to harvest because these garden flowers produce a lot of them in the fall. The seeds can be purchased at garden stores. The package contains an accurate description of the variety and instructions for sowing. By purchasing a mixture of seeds, we get varieties of different colors.
At the turn of February and March, seeds are sown in pots and covered with a thin layer of earth. Dahlia seeds germinate quickly.After about 2 weeks, the young seedlings should be distributed in separate pots.


Planting seedlings of dahlias from seeds can begin in the second half of May, after hardening of young plants. For hardening, in April, when the weather permits, you need to take the containers out into fresh air for several hours, gradually increasing the hardening time.
Dahlias care
After planting, the plants are watered regularly and abundantly. Lack of moisture leads to a deterioration in flowering, growth retardation and lignification of the stem. Watering dahlias in the evening. After each watering, the soil is loosened. Dahlias respond well to mulching: it reduces water consumption during irrigation and reduces the number of weeds. It is better to use rotted manure or peat as mulch.
After 5 - 7 days after planting, when the dahlias take root, top dressing is carried out, the interval between which should be 10 days. The plants are pre-watered. It is best to make a hole 10 cm deep around the plant, and fill it with top dressing. After that, the hole is leveled. For feeding, an infusion of mullein is usually used in a ratio of 1:10, adding superphosphate (10 g per 5 l of water) and nitrogen fertilizers to it. It is very good for dahlias to make several top dressing with superphosphate (25 g per 5 l of water) with the addition of wood ash (3 - 4 handfuls). Top dressing is carried out in June and in the first half of July.
In August, it is worth feeding only once with potassium sulfate (30 g per "bush") so that the tubers ripen better. It is not worth getting too carried away with nitrogen fertilizers, since the "bush", to the detriment of flowering, will gain a large vegetative mass, in addition, tubers are formed from a plant overfed with nitrogen, which are very poorly stored. Watering and feeding is stopped since September.
To obtain a beautiful strong plant with good inflorescences, dahlia bushes must be formed.
Methods for forming a dahlia bush:
During the growth period, the shoots growing from the root collar are periodically removed. It is necessary to take into account when growing dahlias that no more than three stems should be left in the bush. If more shoots are left on the plant, then the dahlia inflorescences will be much smaller and less decorative. Usually tall
dahlias form into one stem, and medium-sized ones - into two.
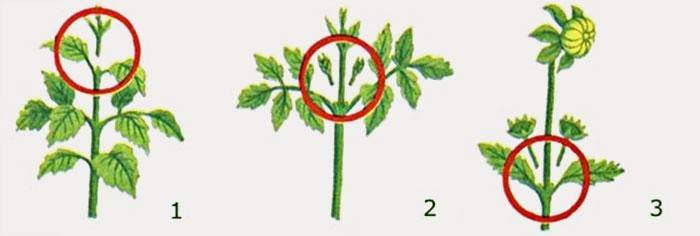
It is necessary to regularly break out the appearing stepchildren - lateral shoots growing in the leaf axils. The stepsons are removed as early as possible in order to less injure the plant. Remaining on the bush, they strongly thicken it, delay flowering and reduce the quality of the inflorescences. The work is carried out until lateral shoots with buds appear at the top of the stem.
To obtain a larger number of inflorescences, the main shoot is pinched over the 4th or 5th pair of leaves. Otherwise, all the forces of the plant will be directed to the formation of a single bud - the first, strongest flower. This natural goal is based on the plant's desire to set full-fledged seeds, because all living things yearn to continue their kind. On such an unpicked bush, you may no longer see more flowers.
Remove the central bud or central and one of the lateral ones. Such an operation leads to lengthening and strengthening of the peduncle, and an increase in the size of the inflorescence. This is done to obtain very large cut or show specimens.
If the inflorescences were not cut, then they are removed as soon as they begin to fade, since otherwise the development of buds is delayed and the appearance of the plantings deteriorates.
In the second half of summer, the lower leaves are removed on the stem at a height of up to 30 cm. This prevents its excessive thickening in the lower part, which, in turn, contributes to a better overwintering of the tuber nest. At the end of August, the plants are spud up to a height of 10-15 cm. This method eliminates the possibility of freezing of tubers and replacement buds on the root collar and the lower part of the stem, and ensures greater safety of the nest during winter storage.If possible, the plants are spud up in July as well. Early hilling has a different purpose - to improve the conditions for tuberization and increase the resistance of the shoot to breaking out. Loosening and weeding are carried out as usual.
Growing dahlias: how to form bushes


If you propagated dahlias with tubers, then you need to know that the bushes should be formed from such seedlings. It is best to leave no more than 2 powerful and strong shoots, and remove all the rest mercilessly. If you were engaged in cuttings, then it is best to leave one stem, but the top should be pinched so that the bushes have voluminous foliage and green mass.
If you grow large-flowered varieties of dahlias, then do not forget to regularly remove all stepchildren, namely the side shoots. Moreover, this must be done in a timely manner. Try to cut the stepchildren as close to the main stem as possible. If you do not do this, then your flowers will grow slowly and bloom less luxuriantly.
In addition, in large-flowered dahlias, the growth of the main stem may disappear, stepchildren will interfere with the development of the plant. If you break them too close to the surface of the ground, fungal infections can enter the wound. Therefore, shoots that are too low should not be removed, otherwise the plant may die in the future.
Remember to break off the side shoots to the point where the bud is formed. It is better not to engage in formation during flowering.... Remember, too, that many varieties of dahlias simply do not stepchild, so before removing shoots, carefully study the features of a particular type of plant.
However, in many varieties of dahlias, not only shoots, but also buds should be removed. This is done mainly in order to further cut flowers, sell plants. Usually the buds are formed by three things per inflorescence. Or rather, not in an inflorescence, but in a group.
The middle bud blooms more intensely. However, his peduncle is the shortest, so cutting it off is very inconvenient. If you want the remaining two buds to bloom more intensely, the middle bud should be removed. Just the remaining flowers have longer flower stalks, so you can easily put these dahlias in a vase.
In order for the bushes not to lose their decorative effect, you should also remove faded buds. They spoil the decorativeness and appearance of the plant. Basically, all varieties of this culture are quite high. However, you can easily grow a short bush. Only for this you should adhere to separate rules.
At the end of winter, some tubers should be planted in a nutritious soil and placed on a windowsill. In this case, the air temperature should be high enough, not lower than + 15 degrees. When the first shoots appear, you will need to leave the strongest shoots. The cut branches can be used as cuttings.
When the fourth pair of leaves forms on the bush, the top should be shortened. Thus, 2 will develop from one stem, when a pair of leaves appear on them, they should be re-pruned. Usually, such bushes grow no more than 1 meter in height, so you can grow miniature, low-growing dahlias.
Dahlia diseases and pests
Dahlias are susceptible to diseases such as viral mosaic, powdery mildew, bacterial cancer. If the plant is infected with a viral mosaic, then light green spots of various sizes and shapes or yellowing can be found on the leaf plates, which stretch along the veins of the leaves. Lesions are also evidenced by a short peduncle, a shortened internode, a dwarf plant, and an atypical color of the petals. The most effective means of control in such cases is considered to be careful culling of diseased plants, as well as their burning.
Bacterial cancer is found, as a rule, on the tubers when they are dug up or in the fall.First, ugly buds appear on the root collar of the affected plants, and then growths. In autumn, all affected tubers should be discarded and then burned.
On pest dahlias, slobbering pennits, flower beetles, slugs and aphids are often found.
Spraying with urea (1 g per 250 ml of water) or mullein infusion (1:10) helps with slobbering pennies, powdery mildew, aphids, as well as flower beetles. Spraying is carried out in cloudy weather or in the evening.
Aphids are fought with the help of onion peel infusion, garlic infusion, chlorophos (5 g per 5 liters of water) and ash.
To get rid of slugs, you can treat the leaves with a 10% decoction of capsicum.
When dahlias bloom, their buds are often spoiled by pests - two-tails (earwigs). These insects gnaw the delicate tissues of the bud, so that the inflorescence blooms ugly. These pests do their dirty work at night. To save the plants from damage by these pests, at the first appearance of signs of an attack by two-tails on dahlias, you need to periodically (about once a week) treat the dahlia bushes in the evening with a decoction of protective plants - celandine, wormwood and other useful herbs. This will keep the beautiful dahlia blossoms intact.
How to store dahlias in winter
After the dividing procedure, you need to check each part of the tuber for brown or red spots. If you find any, you need to immediately get rid of the sick specimen.
The remaining tubers are washed and treated with a fungicide for disinfection. Tubers are dried on a sheet of paper. At this time, you need to mark the varieties with the help of tags.
The tubers are stored at a temperature not lower than +1, but not higher than +5. The basement is ideal for such purposes. Tubers are pre-placed in bags with sawdust. If the indoor humidity is low, then sand can be used.
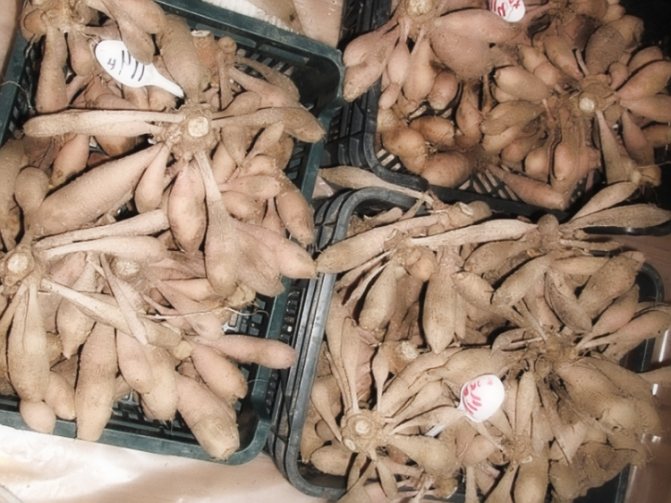


Dahlia tubers cleaning
The dahlia tubers begin to harvest when most of the leaves have hit the first severe frosts, but the big frosts have not yet come. They are usually dug out in late September - early October at freezing temperatures in good weather. So that the dahlia tubers can be well ventilated, at a height of 10-15cm. the stems are cut from the soil surface and the tubers are carefully dug out, being careful not to damage them. First, the neck is freed from the ground, then the tuber is dug in from all sides at a distance of 25-30 cm from the neck and carefully removed. The dug dahlia tubers are washed from the ground, dipped in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate and placed under a canopy to dry. You can put them upside down with the rhizome, thus allowing all the moisture to drain, leaving the water from the rhizomes and from the hollow part of the stems. First, they are dried at a temperature of 15-18 degrees in the air, then I am indoors. Having dried the rhizomes of dahlias, they are laid for storage.
Dahlia breeding
I would like to start new varieties, such as from a neighbor, share my own with her. And how to do it, there is not always enough knowledge. Not everyone knows that dahlias can be propagated not only by tubers, but also by cuttings. Exists There are 3 main ways.
Dividing tubers
The method of dividing root tubers is more popular. In the spring, before planting, you need to select healthy planting material, disinfect in a manganese solution. Divide the tubers into parts so that on each fragment obtained there are 1-2 eyes and a piece of the root collar. Places of cuts are powdered with charcoal.
Seed propagation
This method is used by breeders to develop new varieties. In addition, it is used for one-time cultivation of annual varieties of dahlias.
Propagation by cuttings
In March-early April (they start earlier, but then the plants need illumination), they prepare the soil, add sand, humus. Tubers are planted there. When the sprouts that appear grow up to 10-15 cm, they are carefully cut and placed in a solution of root, other growth stimulants or a rooting substrate. The sprout must have several internodes.A container with cuttings placed in a moist substrate is wrapped in cellophane. After 15-20 days, the cuttings take root, they are transplanted into small pots with sandy soil, where they are kept until they are planted in the ground.
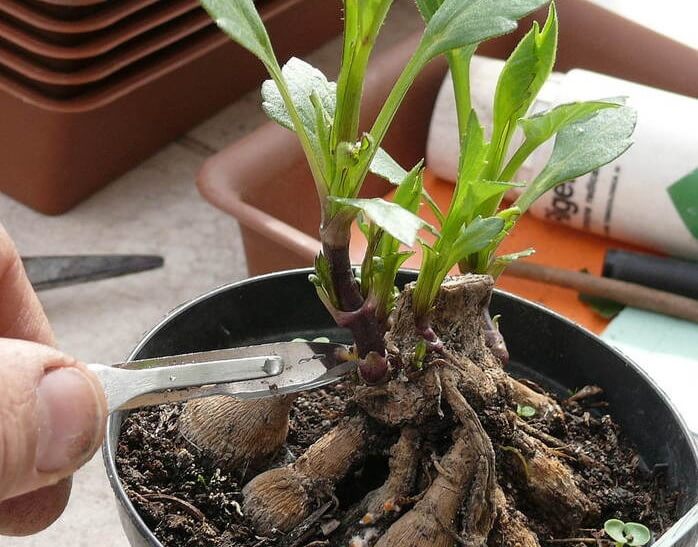


The optimum temperature for growing is at least 22 ° C, humidity is at least 70%.
New eyes wake up on the rhizome, from which processes sprout.
Plants grown in this way bloom better. All the characteristics inherent in the variety are preserved.
Dahlias storage
Dahlias are best stored in a cool, dark, ventilated, dry place with a temperature of about + 5 degrees.
It can be a subfloor or a non-freezing basement. We put the dahlias in one layer in boxes and cover them with peat, sand, ash, moss or sawdust. For pouring dahlia tubers
you can use perlite and other suitable materials. But the best option may be coniferous sawdust or moss: at the same time, the rhizome does not dry out and breathes, and the sawdust and moss give the tubers stored in them an optimal proportion of moisture and at the same time disinfect. Storage with ash gives very good results, as it is an excellent disinfectant material.
For urban gardeners in the absence of a basement and a shortage of storage space, the second method of storing dahlia tubers is more suitable. Choose a suitable box for the tubers, make several holes with a diameter of 8-10 mm in the side walls for ventilation and normal gas exchange of the rhizomes.
Lay a layer of dahlia tubers at the bottom of the box and fill it with (sawdust, perlite, etc.). Place another layer of tubers on top, and again cover with the materials used. Fill the box to the top and place it in the coolest place in the apartment.
In autumn, until frost sets in, dahlias can be stored on the balcony, and when it gets cold, the box with tubers can be brought into the apartment and placed at the balcony door.
If there is a possibility of intensive drying of tubers, they are placed in plastic bags. When storing tubers in bags, care must be taken to ensure that there is a layer of insulating material between the film and the tubers. Moisture vapors formed during the respiration of tubers condense on the walls of the bag and cause rotting of the tubers in contact with them. Several times during the storage period, it is necessary to selectively open the packages and check the condition of the tubers. If there is a danger of the stored material drying out, the substrate is slightly moistened; when the substrate moisture appears, the bags are opened for ventilation. When rotting is detected, the affected area of the tuber is cut out to healthy tissue, the cut site is treated and dried in air for about a day, and then laid back.
Landing rules
When buying tubers in the store, be sure to inspect them so that there are no rot spots. Look for a bud or sprout that has hatched. Landing time is the second half of May.
Dig a small hole (35 * 35 * 25 cm), pour abundantly, add rotted manure to the bottom, sprinkle it with earth to protect the roots from burns. Wood ash can be added. Dip the tuber into the prepared hole, sprinkle with soil. Watch the root collar, do not deeply deepen. Young shoots grow from buds located near the root collar. Be sure to water again. Cover or cover with black plastic.
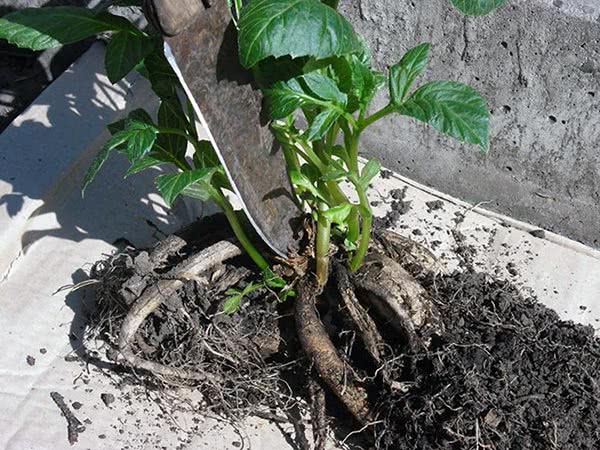


Helpful Hint: Keep the distance between low and dwarf bushes 40-50 cm, medium-sized - 60 cm, and tall - 70-80 cm.
Flowering begins 30-70 days after planting in the soil and lasts until the onset of cold weather. To accelerate the flowering period, experienced florists suggest planting tubers in pots or other containers with nutritious soil earlier. Germinate them in a lighted place on the veranda, loggia. Then pre-harden and plant in the ground. Protect from frost.
It's important to know! If you notice the affected areas, then immediately remove them to healthy tissues, treat the cut sites with brilliant green and dry them.
Dahlias photo
Add a comment
JComments
How and when to pinch dahlias
This procedure is carried out in order for the buds and stems to grow large. The scheme for pinching dahlias is similar to that used for pinching tomatoes: all lateral shoots emerging from the axils of the leaves are broken.
Important! Small-flowered, undersized, pompom varieties are not subjected to pinching.
On large bushes, in addition to the stepsons, the lower leaves are also removed. Thanks to this, the root tubers will ripen better, which means they will be well stored. Faded buds are cut off so that they do not take away the plant's strength for development.
Dahlia partners
Dahlias are great with any plants - both perennial and seasonal - provided they love the same conditions: sunny, warm areas and loose nutritious soil.
Great partners for dahlias are cannes, gladioli and montbrecia - related to them in terms of growth and agricultural technology. The combination of dahlias with gladioli is one of the canonical garden duos.
From annual plants, marigolds, and kosmeya, and lavatera, and scented tobacco, and zinnias, and pelargoniums, as well as calendula, mallow with their tall candles of inflorescences, are suitable partners for dahlias. The autumn charm of dahlias can be emphasized with the help of asters, but you need to be careful: too similar inflorescences can present asters in an unfavorable light; when choosing partners, it is better to focus on the maximum difference in the structure of inflorescences.
Large-leaved horticultural crops perfectly emphasize the beauty of the plant - from the steep and the buzulnik to the ornamental quinoa and castor bean. Among herbaceous perennials, phloxes, daylilies, goldenrod, yarrow, helenium, monarda, veronica, sage, delphinium, sedum, perennial asters, decorative bows, crocosmia, lychnis, coreopsis, rudbeckia, geese, millet, miscanthus are considered the best partners for dahlias.
With the help of dahlias, you can add autumn accents to groups with barberries, maples, tree trees, rose hips. Revitalizing large ensembles and playing the role of "padding" for decorative giants, dahlias seem to highlight the main plants and give a new sound to their beauty in the second half of the summer season.