Sophia Slavyanskaya Saw a blooming liana
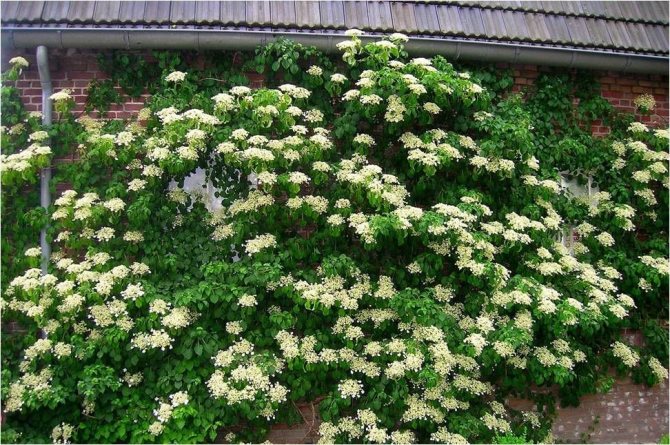
I recently visited relatives in the Moscow region. Their country house was densely entwined with a lush blooming creeping vine, its white large inflorescences emitted a very pleasant honey aroma! It turned out that this is a climbing hydrangea.
I decided to definitely plant such a plant in my country house. Upon returning home, I found information about the best varieties of climbing hydrangea in reference books, magazines and blogs. I'll talk about this in this article.
Stalked hydrangea (creeping) is a liana-shaped garden hydrangea that is widely used in landscape design.
Stalked hydrangea: description of the plant, photos of the best varieties
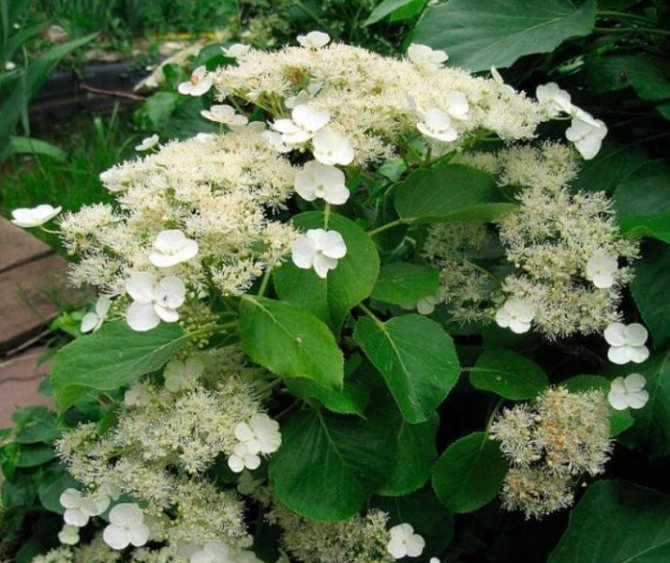
The petioled hydrangea is characterized by the absence of a solid trunk. It is an attractive climbing plant that grows up to 20 meters. It is very popular all over the world.
The liana-like variety is mainly found in Asia. Culture is capable of covering all space and taking the form of various objects. The climbing liana completely fills the territory allotted to it. Therefore, it is often used in landscape design.
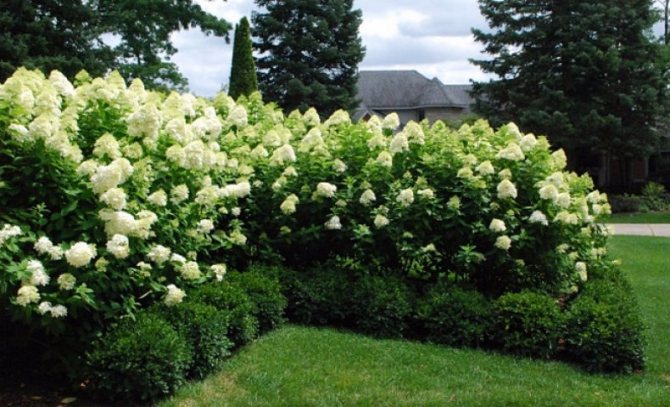
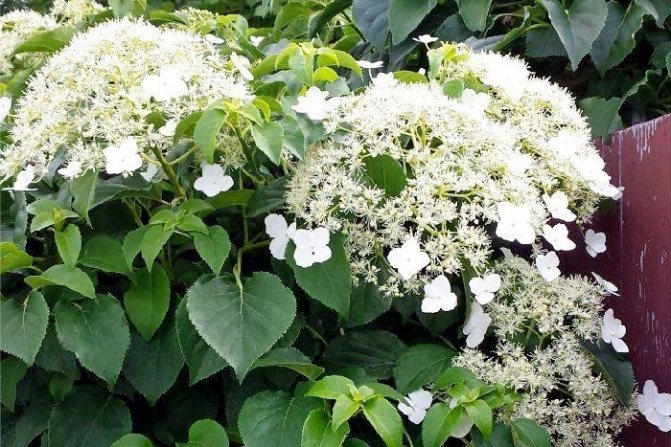
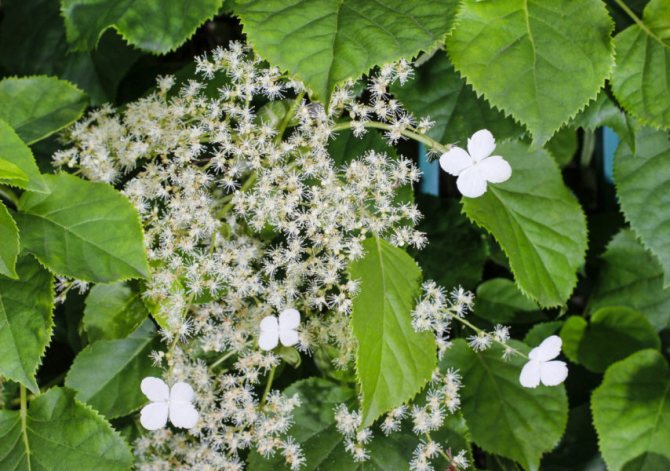
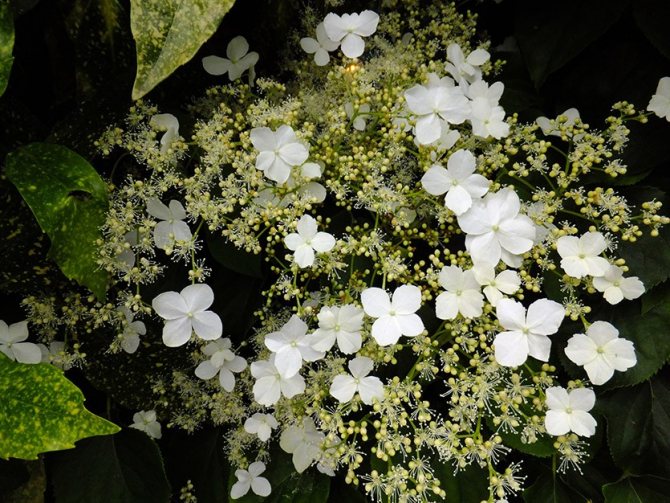
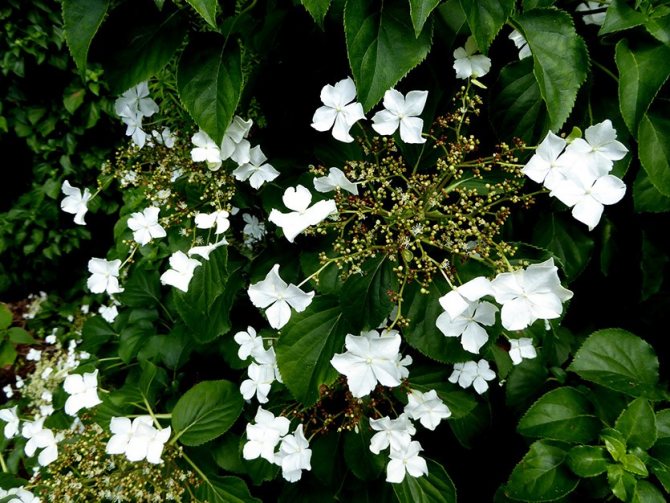
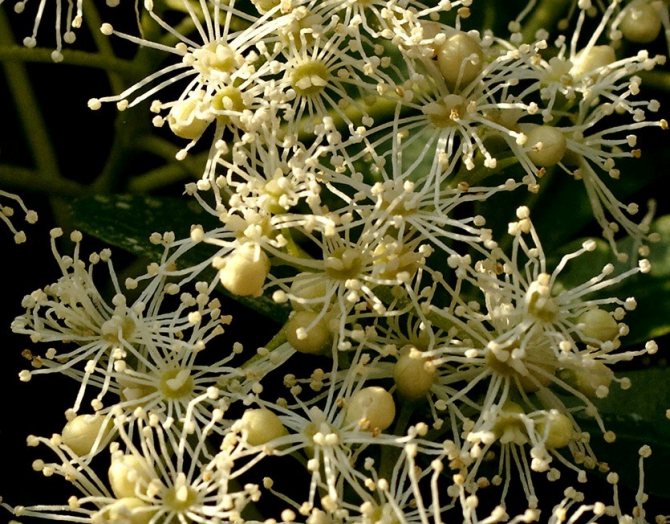
Creeper blooms in June and lasts 2 months. It is characterized by large white flowers. They form loose inflorescences about 25 cm in diameter, which cover the entire bush. As the culture develops, the number of flowers increases.
The flowers have an attractive appearance and delicate scent that attracts insects. Initially, they are white, but then it turns pink.
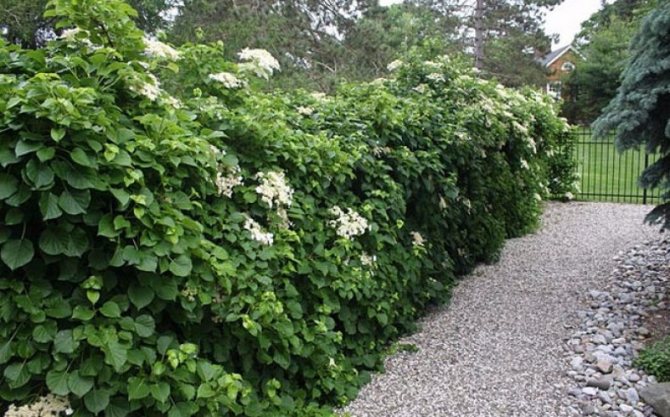
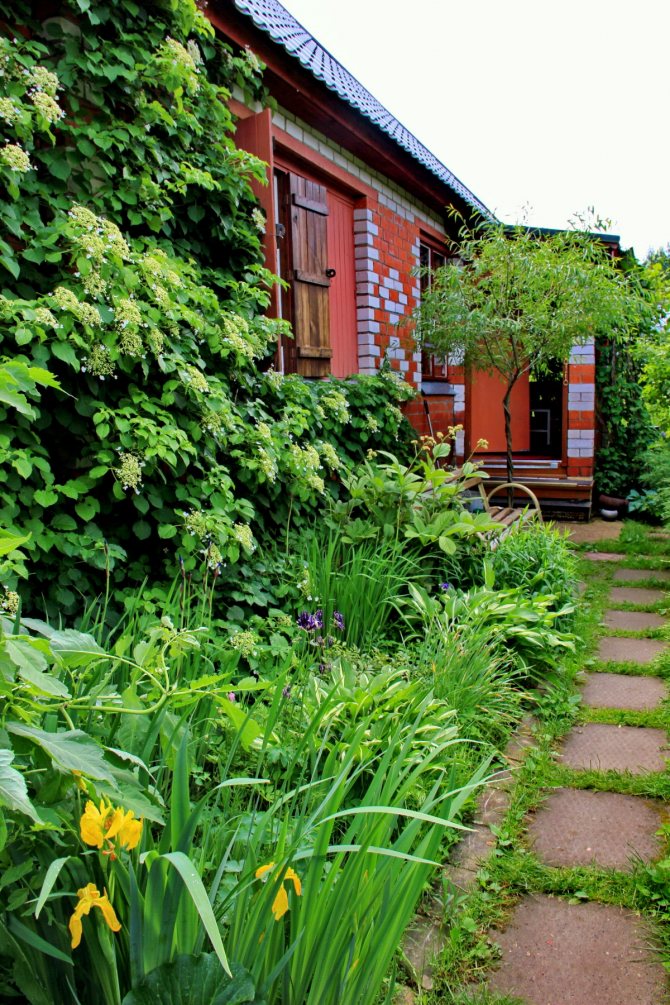
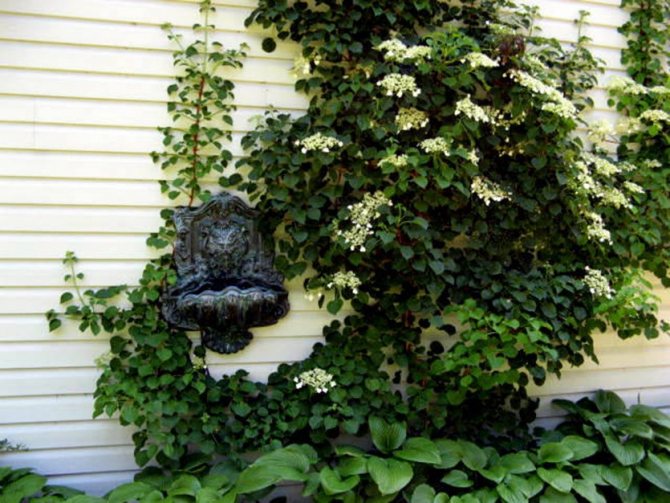
Photo selection of various options for using petiolate climbing hydrangea in landscape design:
Advantages and disadvantages of growing a plant
The petiolate hydrangea has many advantages:
- excellent decorative properties;
- unpretentious care;
- frost resistance.
The disadvantages of a plant include the following:
- the need to land on a lighted area;
- the risk of developing fungal and viral diseases;
- the likelihood of being hit by harmful insects.
Popular varieties
Popular varieties of climbing hydrangea:
- Cordifolia (Cordifolia). It is a dwarf culture with dark glossy leaves. They are distinguished by their rounded shape. The plant has characteristic features. These include a honey aroma and an unusual shade of the lower part of the leaves.
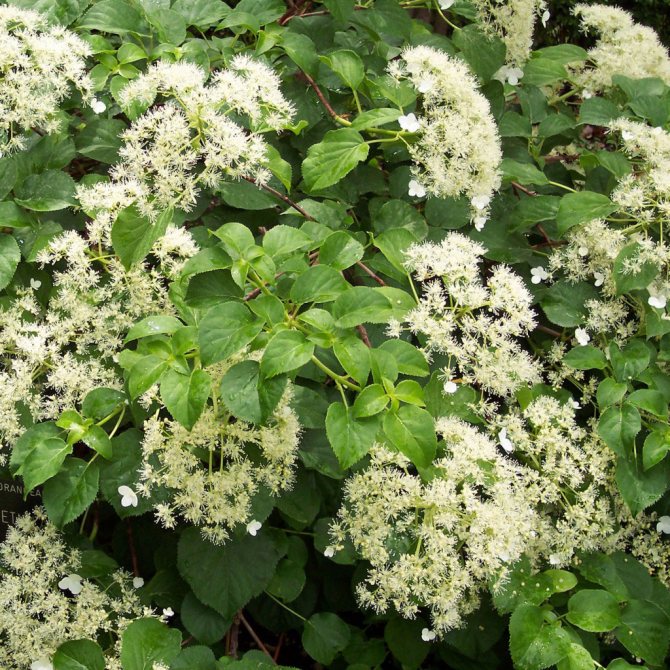

- Miranda (Miranda). It is a beautiful plant, characterized by a green-yellow stripe at the edges of the leaves and white flowers. Petiolate hydrangea Miranda is fixed on a support due to aerial roots and grows up to 10 m. Flowering begins in the first half of summer.


- Petiolaris (Petiolaris). This culture is considered the highest. It can grow up to 25 m. Petiolaris petiolar hydrangea is often used for decorative purposes.
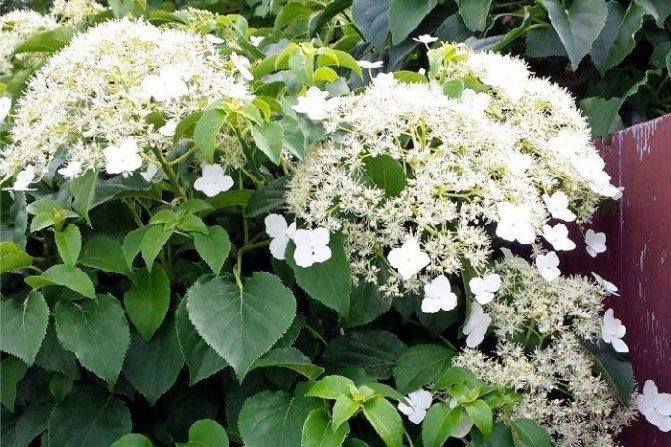


Application in landscape design
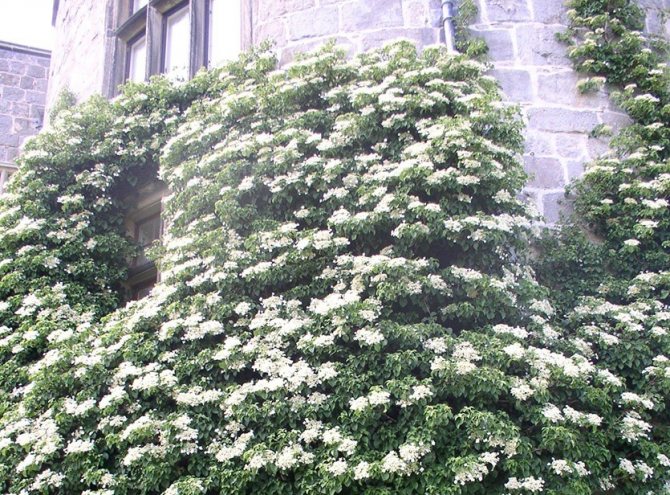
In professional landscape design and amateur gardening climbing hydrangea Petiolaris is used to improve gazebos, garden arches or lattice fences. Also, the variety is often used to decorate the walls of all kinds of garden buildings, as well as the trunks of tall tree-like plants.For this, all kinds of mesh or other structures are installed around the object, braiding which the hydrangea completely hides the primary background.


Planting method
To plant a crop successfully, it is important to choose the right seedling. Buying a petioled hydrangea is quite simple. It is sold at nurseries and gardening stores.
To plant a petioled hydrangea in the soil, it is worth making a depression 40x40 cm in size.Its depth should be about 50 cm.If heavy soil is observed on the site, the size of the hole is increased.
Drainage from crushed bricks or gravel must be placed at the bottom. The thickness of this layer is 10 cm. It is recommended to pour a fertile soil on top with a layer of 10-15 cm.
Place a seedling in the hole, spread its roots and sprinkle with fertile soil. It is important to control that the root collar is at ground level. After planting, the bush is recommended to be watered well.
On top, apply mulch from sawdust, pine needles or peat. With the help of mulch, it is possible to retain moisture in the soil, stop the development of weeds and protect the roots of the plant.


Care features
In order for the bush to bloom profusely and develop fully, it needs to be provided with high-quality care. For this, it is recommended to follow certain rules.
Watering mode
Hydrangeas need a lot of moisture. This flower requires systematic watering. Pour 30-50 liters of water under 1 bush. It should be warm and well-kept.
In dry weather, it is recommended to water the flower twice a week. On rainy days, it is worth moistening the soil once a week. Mulching the beds slows down the evaporation of the liquid. In such a situation, 1 watering per week is sufficient.
Top dressing
For abundant flowering, hydrangea should be properly fed. Fertilizers are applied several times. The first time it is done in the phase of active growth. To do this, it is necessary to combine 30 g of sulfuric potassium and superphosphate, and also add 20 g of urea. These substances are mixed with water.
The next time, fertilizer is applied during the formation of buds. To do this, it is recommended to mix 60 g of superphosphate and 40 g of potassium sulfate. Substances should be dissolved in water.
Hydrangea requires feeding at the end of summer. At this point, 15-20 g of compost or rotted manure should be added under each plant.
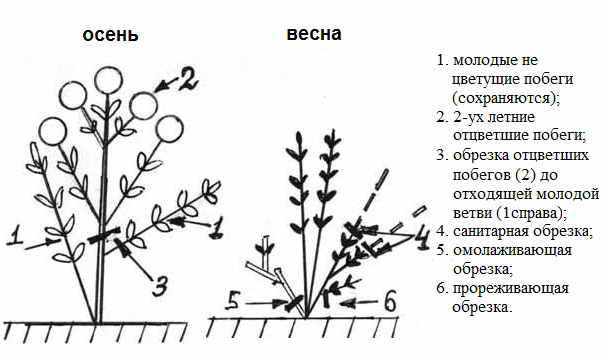
Pruning
Hydrangea inflorescences are mainly formed on the shoots of the current year. If you do not prune the plant, it becomes denser and looks unkempt. Such a culture does not bloom well. To cope with the problem, pruning is carried out. To do this, you must observe the following rules:
- It is recommended to prune the bushes 3-4 years old.
- The procedure is carried out in early spring.
- After pruning, 6-10 powerful shoots should remain.
- It is recommended to shorten annual shoots. 3-5 pairs of kidneys should remain on them.

Preparing for winter
Stalked hydrangea has excellent frost resistance, it can be grown in the Moscow region or even in Siberia. At the same time, it is recommended to cover young plants for the winter, since the sprouts may freeze slightly. For this, the shoots should be placed on boards and covered with spruce branches or leaves. This is very important for the northern regions.
Care problems
When growing a crop, you can face the following problems:
- Leaves and shoots wither and die... This is often the result of parasite attacks. Insecticides allow you to cope with them.
- The leaves become lighter... Most often this is due to the appearance of chlorosis. It is associated with poor-quality drainage, excess humus, lack of magnesium and iron in the soil.
- The bush is covered with black spots... This is due to the development of gray rot. Bordeaux liquid helps to cope with the problem.
Top dressing
If you want the hydrangea to bloom in full force, you need to carry out a comprehensive feeding at least twice a year - before and after the hydrangea bloom. At the beginning of spring, the hydrangea is fed with a solution of 20 g of urea per bucket of water on the basis that three buckets of such a solution will be needed to feed an adult plant. After flowering, the hydrangea is fed with complex mineral fertilizers. Throughout the summer, you can fertilize the hydrangea from time to time with slurry, but observe the measure so as not to overfeed the plant, otherwise large inflorescences with their weight can break fragile branches. Just in case, tie up the shoots to prevent this from happening.
Reproduction
Hydrangea cuttings
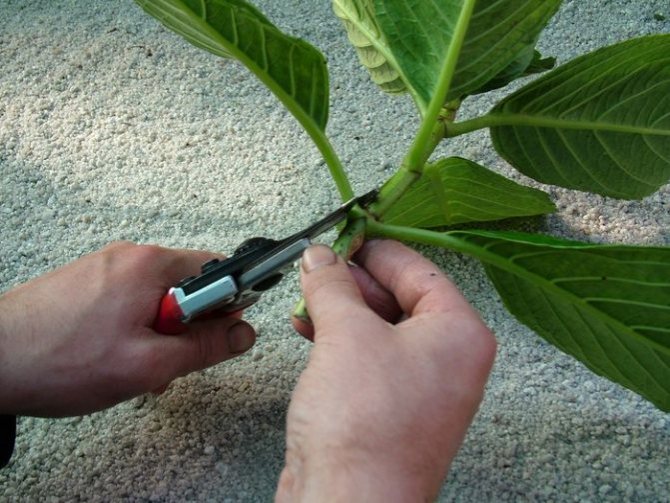
You can propagate climbing petiolate hydrangea by dividing, cutting or layering. If a plant develops abundant growth, fresh shoots are separated from it. They are shortened, and the root is pruned. Shoots can be planted in a hole and watered thoroughly throughout the month. It is best to carry out the procedure in the spring.
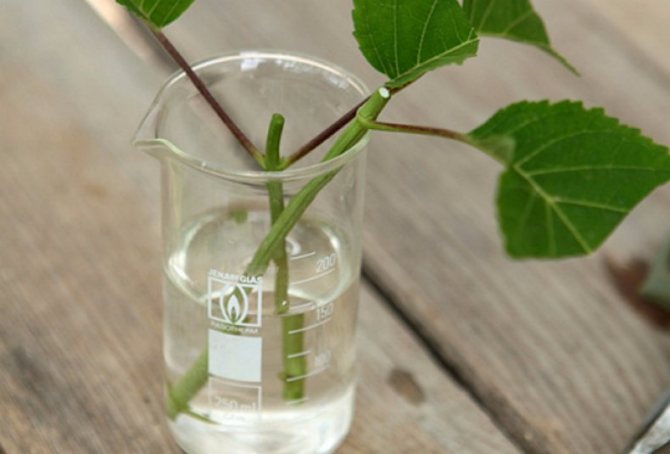
When breeding a culture by cuttings, it is worth using lignified branches. Their length should be no more than 15 cm. The procedure should be carried out at the beginning of summer. From a shoot with 2 nodes, it is worth cutting off the top and removing 2 lower leaves.
After that, treat the plant with a growth stimulant and put it in a box filled with peat and sand. The composition must be wet. Cover the container from above with foil. When the culture is strong, it can be opened.
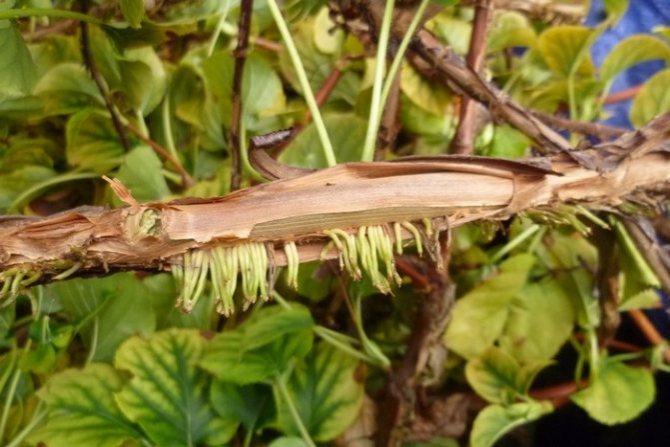
To breed a bush with layering, it is recommended to attach the lower branch to the ground. In this case, the soil should be loose and moist. In the area where the branch touches the ground, it is worth making an incision and sprinkling it with peat. It is worth carrying out the procedure in May or August.
Diseases and pests
Common diseases of petiole hydrangea include the following:
- Chlorosis... Pathology is caused by iron deficiency. In this case, the leaves acquire a yellow tint, and the veins remain light green. The disease leads to the weakening of the plant. Special fertilizers will help improve its condition.
- Powdery mildew... This is a fungal infection that provokes the appearance of yellow spots on the leaves of the culture. After some time, the outer side of the leaves turns brown and acquires clear contours. From the inside, the foliage turns purple. Fungicides will help to cope with the problem.
- White rot... Fungus leads to the appearance of problems, which provokes damage to the root system. This often causes the death of the plant. With the development of the disease, the shoots turn black, a white bloom forms. Fitosporin helps to cope with the problem.
- Gray rot... With its development, the foliage and branches of the culture acquire a watery structure and become covered with black spots. Fundazol or Pure flowers will help to cope with the problem.
- Ring spot... This is a viral infection that causes necrotic spots on the leaves. It is impossible to cope with the disease. In such a situation, the plant must be destroyed.
Of the pests, the petiolate hydrangea is affected by gall nematodes, spider mites, and aphids. To cope with them, insecticides and acaricides are used. When a large number of snails appear on the liana, they should be collected by hand.
The petiole hydrangea is a common ornamental plant that is grown by many gardeners. To achieve abundant flowering, it is important to provide the culture with comprehensive care. It should include timely watering, fertilization, pruning.
Perennial deciduous vines
This is the most numerous group of all types of vines. Their advantage is unpretentiousness, ease of maintenance, as well as a large annual increase. Under favorable conditions for development in 2-3 seasons, some deciduous climbing plants are able to completely braid the fence, gazebo or wall of the house. The disadvantage of most of them is the ability to form shoots, which can be difficult to cope with.To control the growth of the root system, it is recommended to enclose each plant with a curb dug to a depth of 30 cm.
Aconitol vineyard
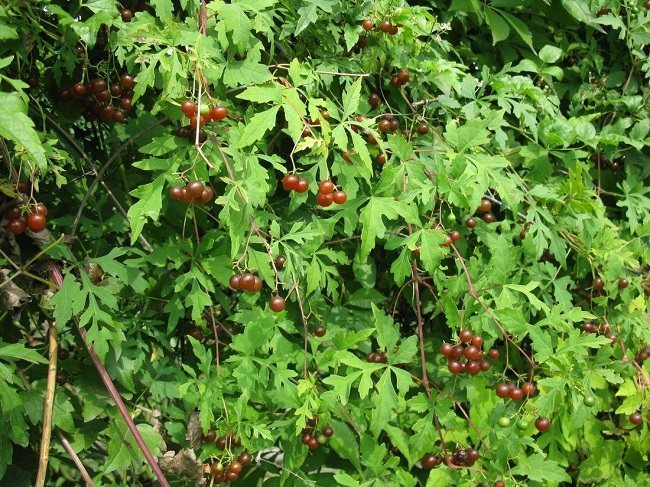


Ampelopsis (grapevine) is aconitolous, it is a liana reaching a length of 8 m. During one vegetative period it adds up to 3 m. The advantage is beautiful deeply dissected leaves. The vineyard is especially magnificent in autumn, when the foliage acquires a rich golden color.
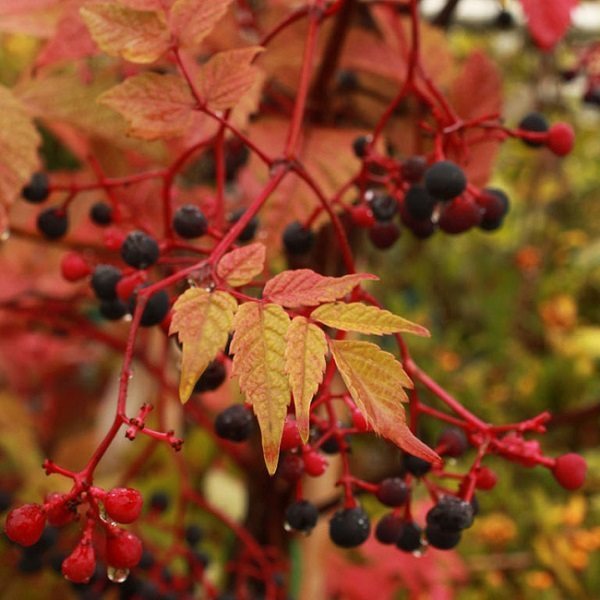


Small berries hanging in beautiful bunches that resemble multi-colored beads during ripening are also decorative. Liana is resistant to diseases and pests, perfectly tolerates pruning. For landscaping, it is enough to use 1 plant for every 4 m of the fence.
Maiden grapes
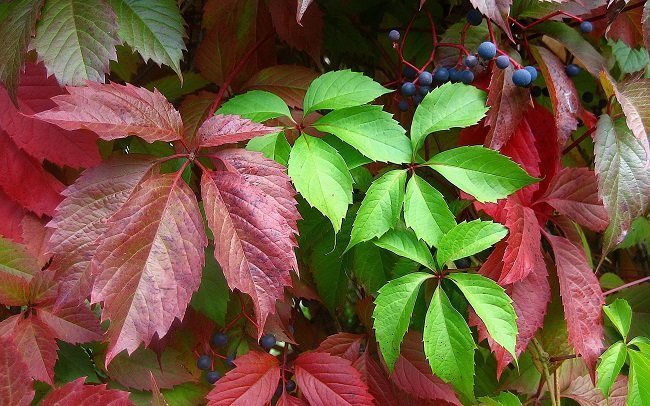


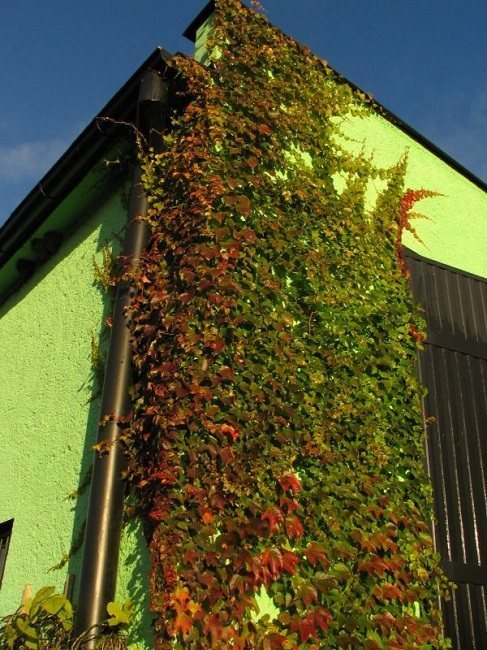
The most common in temperate latitudes is the five-leafed and attached maiden grape. It grows rapidly, does not react to dustiness in the air, and is almost not damaged by pests and diseases. If you need an unpretentious plant, it is better to opt for a five-leafed subspecies. It grows on almost all types of soil and is resistant to freezing of the soil. A prominent representative of the five-leaf grape is grade "Murorum"... It is distinguished by a strong leafiness of the vine and a more uniform (in comparison with the specific maiden grape) surface coverage. In autumn, the foliage takes on a deep red color and glossy shine.
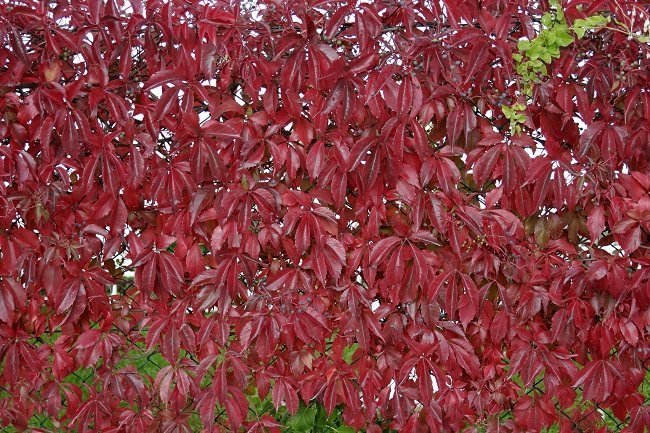


The dignity of the attached maiden grape is its unique ability to climb on a flat vertical plane without using a support.


Gardeners' opinion
Numerous reviews of gardeners about the cultivation of climbing petioled hydrangea confirm the popularity of this culture.
I really like the petioled hydrangea. In appearance, it resembles a liana. I planted a plant around the gazebo. Thanks to this, it was possible to get a shadow and decorate the site.
Irina
This plant needs bright lighting. Only in such conditions will it be able to bloom normally. In addition, it is important to apply fertilizers on time.
Veronica
Perennial evergreen vines
Late autumn comes, and all the charm of deciduous plants disappears - only bare branches remain. Not so with evergreen vines, they retain their flavor all 24 months of the year. Of course, there are not so many of them in comparison with deciduous ones, but they are able to revive the garden at any time.
Ivy
The most common representative of evergreen vines is common ivy.
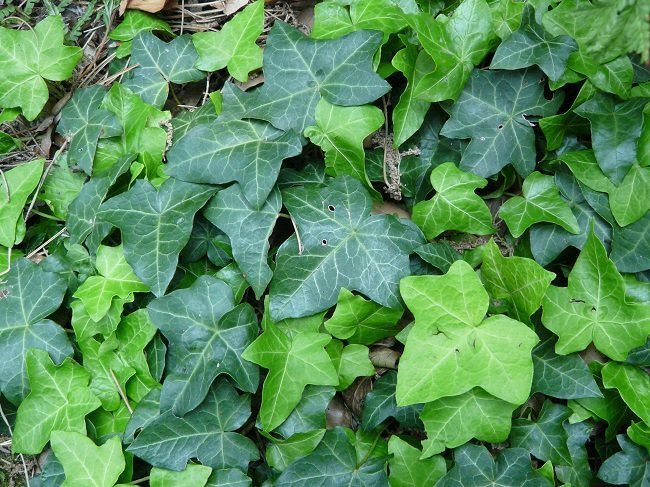


A plant dug out in natural conditions easily takes root in the garden. Unlike deciduous vines, it grows somewhat slower, but it is distinguished by good frost resistance and high decorative effect of the leaves. The plant is able to climb to great heights using aerial roots. They grow into wood, plaster, masonry joints, and firmly hold the plant against sheer walls. Under natural conditions, ivy grows in shady forests, therefore, it is advisable to provide the plant with at least a diffused shade in the garden area.
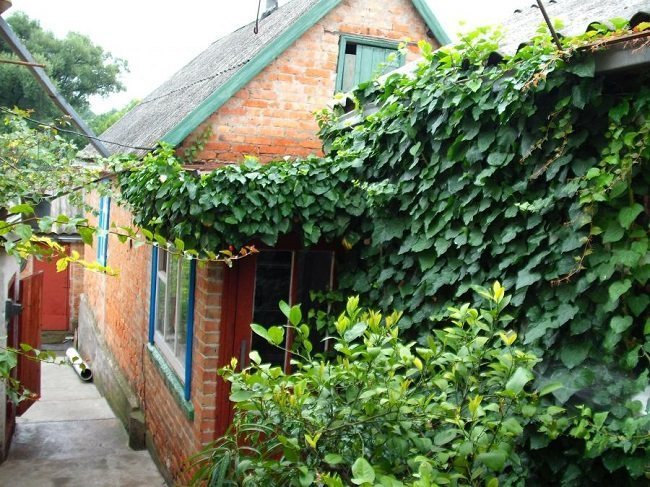


There are several varieties of ivy, differing in the shape and color of the leaf. Colchis ivy, which has variegated foliage, is especially decorative. But it is less hardy and grows more slowly than the species plant. In addition, young shoots need a garter.





































