Creating a unique landscape design at your summer cottage is a very exciting activity, because with the help of certain plants you can create not only beautiful flower arrangements, but also hide minor flaws in buildings. The curly honeysuckle Caprifoil is ideal for this, which, with proper care, will constantly delight you with its fragrant flowers.
This article is a detailed instruction for planting and caring for this crop. We will consider the main features of this plant, the rules for planting a shrub, as well as the rules of care that must be followed for the full development of the culture.
Photo and description of honeysuckle Caprifol
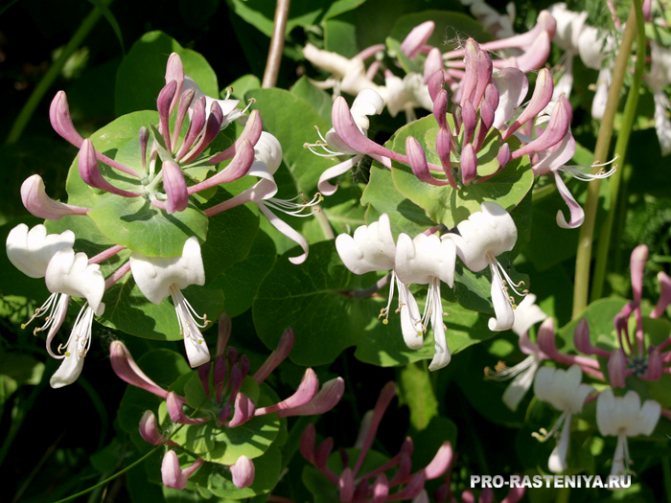
Honeysuckle is a decorative subspecies of honeysuckle with vertical flexible branches that braid well any support that is nearby. With proper care, the crown diameter of a shrub can be quite large. Due to this, the culture is often used to create vertical flower arrangements or decorate buildings and fences (Figure 1).
Honeysuckle Honeysuckle is also called fragrant, as its buds smell very nice during flowering.
Note: The name of the shrub in Latin is slightly different from the traditional name. It sounds like this: Lonicera caprifolium, which is the basis for the third name of the variety - goat honeysuckle.
In nature, this shrub is found in southern Europe and the Caucasus, although it has been successfully cultivated in gardens around the world for many years. Moreover, modern breeders have created a huge variety of varieties of hybrid honeysuckle Caprifol, which is characterized by increased resistance to diseases and adverse environmental factors, such as drought or sudden temperature changes.

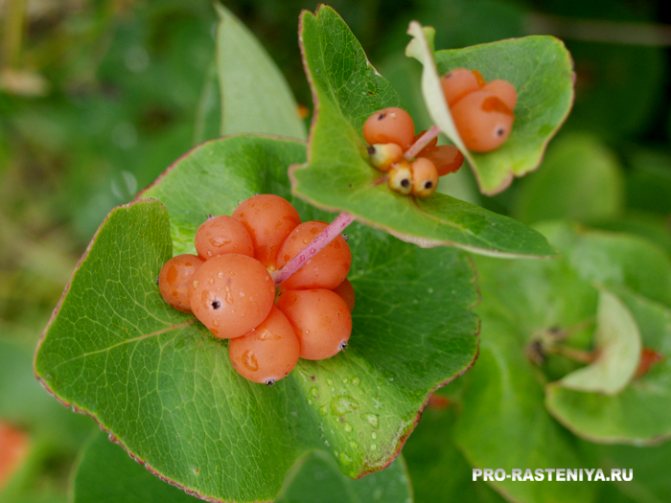
Figure 1. Inflorescences and fruits of the bush
Among other features of the shrub, it is worth highlighting:
- The length of the shoots of honeysuckle can reach 6 meters. They curl, so Caprifol is great for landscaping.
- You can determine the age of the branches by their color: the young are covered with light green bark, while the old ones have a brown tint.
- Honeysuckle leaves are elongated and elliptical and can grow up to 10 cm in length. A characteristic feature is that the top of the leaf plate is light green, and the bottom is gray.
- The inflorescences have a very unusual shape and a rich pleasant aroma, which intensifies in the evening. Flowering begins in May and ends at the end of June.
When the flowering period ends, bright red berries form in place of wilted buds. It should be remembered that these fruits are not edible, and therefore cannot be eaten. Moreover, they can cause severe poisoning, although their bitter taste is clearly not conducive to eating.
How to plant honeysuckle in the fall, varieties for the Moscow region
All regions of Russia except the southern ones are suitable for honeysuckle. The plant easily tolerates frost even during the flowering period. In the conditions of the Moscow region, low bushes feel better. For this area, breeders have developed several special varieties:
- Gzhelka. Ornamental shrub, used as a hedge. The berries are sweet. Up to 2 kg of berries can be harvested from one bush.
- Titmouse.Dense crown, berry taste is devoid of bitterness, refreshing aroma.
- Moskovskaya 23. The variety has a high yield. You can pick up to 3 kg of berries from a bush.
In total, more than 20 varieties have been bred for the Moscow region: Eternal Call, Ramenskaya, Viliga, Kingfisher, Soska, Princess, Lakomka, Shiny.
In the conditions of the Moscow region, they also feel good: Morena, Cinderella, Berel, Blue Bird and Amphora.
Landing rules
Since the honeysuckle Caprifoli is an exclusively ornamental crop, its cultivation in the garden should be aimed at ensuring that the culture has enough space for normal development (Figure 2).
Note: It is necessary to plant a shrub immediately to a permanent place, since Caprifol is very difficult to transfer a transplant. Therefore, the choice of location must be taken very responsibly.
To plant honeysuckle correctly, you should take into account the peculiarities of the shrub. First, you should choose a well-lit place. Of course, placement of the culture in the shade is also allowed, but in this case you should not count on abundant flowering. Secondly, try to choose a site in such a way that the grown shrub is protected from drafts. They also have a very negative effect on the development and flowering of the plant. Growing decorative climbing honeysuckle in the open field, take care in advance of the support on which the flexible branches of the plant can be fixed.
The choice of planting material plays an equally important role. It is advisable to buy two-year-old seedlings. Their height already reaches 30 cm, and the stem has several branches. Such a culture will take root well in a new place, and you can count on abundant flowering.
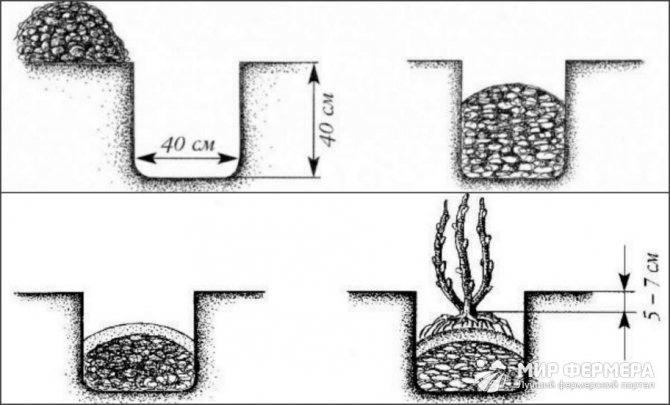

Figure 2. Scheme of planting shrubs
If you are interested in how to grow honeysuckle correctly, first of all you will have to take care of planting a plant:
- A hole 40 cm deep is dug in the selected area. It is desirable that its width is also 40 cm, then the plant will be comfortable.
- A drainage layer is poured at the bottom of the hole: expanded clay, sand or crushed stone.
- Fertilizers must be applied to the pit. Since the culture does not tolerate transplanting, but in one place one will grow for several years, therefore the soil should be as fertile as possible. You can use manure, compost or humus as top dressing.
- If the soil on the site is sandy, you can add a little clay to it, and lime to the acidic soil.
- A small mound is made at the bottom of the hole, a seedling is installed in its center and the root system is straightened.
- Next, the plant is covered with soil so that the root collar is deepened by 5-7 cm.
At the final stage, the soil around the seedling is compacted and watered. It is important that one young plant requires about a bucket of warm water. It is advisable to lay out a layer of mulch on top, which will prevent moisture evaporation. If you need to plant several seedlings at once, it is advisable to place them at a distance of one and a half meters from each other.
Some people choose to grow honeysuckle from seeds. However, this method is not considered effective at home, as it takes too long to get a healthy adult plant.
How to propagate Caprifol
For hybrids bred by breeders, only vegetative methods are suitable to ensure the preservation of varietal traits. Natural honeysuckle can be propagated by seeds, but the process is long and laborious.
Seed Honeysuckle
The method is not popular, since Caprifoli seeds do not differ in germination. They are collected from ripe berries, washed and dried. Stratification is mandatory - the seeds are mixed with wet sand or peat, poured into a small container and put into the refrigerator until February-March next year, periodically spraying the soil.Another option is stratification in the ground: seeds are planted in August in grooves 2-3 cm deep, sprinkled on top with a mixture of peat and humus (layer 10-12 cm).
Seeds from the refrigerator are planted in shallow containers in a mixture of peat, humus and sand (2: 1: 1). The substrate should be slightly moistened, they are also sprinkled with soil on top and sprayed. Then you need to create a "greenhouse" using plastic wrap or glass and do not remove it until shoots appear, only airing the planting for 5-10 minutes daily.
You can plant seeds directly into the ground, but in this case, the already low (less than 50%) germination rate still falls. In the summer, they will need regular watering as the soil dries out and protection from direct sunlight.
Honeysuckle seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place next spring, when they grow to 25–30 cm. In the first two years, they need careful shelter for the winter.


Honeysuckle seeds Honeysuckle are not distinguished by good germination and require pre-planting preparation, therefore, amateur gardeners rarely resort to this method of reproduction.
Cuttings
Planting material is harvested in mid-July. Choose older shoots that break easily. They are cut into cuttings about 10 cm long with 2-3 growth buds. Only the top two leaves are left, cutting them in half.
The lower cut is made obliquely, cuttings are soaked for 3-4 hours in any root formation stimulator. They are planted in a greenhouse at an angle of about 45 ° with an interval of 15-25 cm, deepening by about a third. For the winter, the plantings are carefully insulated, in the spring the surviving specimens are transferred to a permanent place.

The grafting procedure for honeysuckle Caprifoli follows the same algorithm as for any other plant that can reproduce in this way
Video: propagation of honeysuckle by cuttings
Rooting layers
The method is very popular due to its simplicity. It is enough in April to bend the shoot to the ground, lay it in a trench 5–7 cm deep, cut the bark from below by 1.5–2 mm, fix it in this position and sprinkle it with humus. The area is watered abundantly during the summer. By the end of summer, shoots should appear. The seedling is separated from the mother plant and transplanted to a permanent place the following spring, providing a secure shelter for the winter.
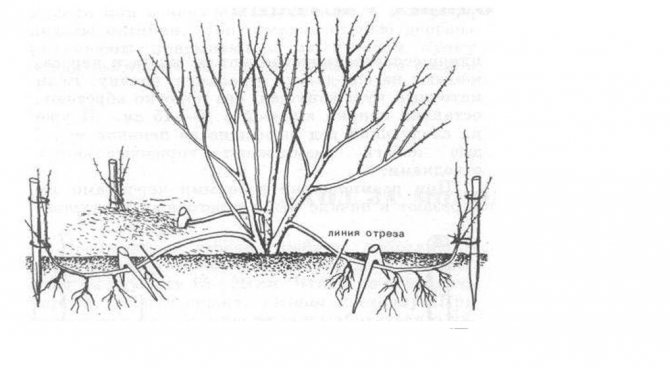

Rooting of layers for honeysuckle Caprifol is almost guaranteed to give a result, the gardener spends a minimum of time and effort on such reproduction
Watering and feeding
The advantage of Honeysuckle Caprifoli is that its cultivation is not particularly difficult. The culture is quite unpretentious in terms of watering: usually no more than 5 abundant waterings are required for the whole summer. However, if the weather is rainy, there is no need to add additional moisture (Figure 3).
Note: After rainfall or watering, be sure to loosen the soil around the decorative honeysuckle. This will help moisture to flow to the roots faster, and the water will not stagnate at the roots. In the process of loosening, care must be taken, since the root system of the plant is close to the surface.
If we talk about top dressing, then, unlike watering, it should be fairly regular. However, it is worth applying additional fertilizers only from the third year of the shrub's life. Until that moment, care and cultivation is limited to watering and loosening the soil, since the shrub received all the necessary nutrients directly during planting.


Figure 3. The plant needs sufficient watering
Taking care of Honeysuckle Honeysuckle in terms of feeding is easy:
- In the spring, nitrogen preparations can be added to the soil, which will help the culture to more actively build up green mass. To do this, you can use both organic (humus, manure, compost or liquid infusion of bird droppings) and minerals.
- In summer, it is advisable to feed the ornamental shrub with nitrophos by dissolving 20 grams of the substance in a bucket of water and carrying out root watering.
- In autumn, double superphosphate and potassium salt are used for feeding. Under each bush, you will have to add 15 grams of each substance dissolved in a bucket of water.
This amount of fertilizer will be enough for the full growth and development of the shrub. However, you should remember to observe the dosages, since an excess of fertilizers can have the same negative consequences as their lack.
Pruning honeysuckle
Like all cultivated plants, the shrub must be thinned from time to time. This is necessary for the ripening of more juicy and large fruits. And it is also important that the plant fits harmoniously into the existing landscape. Therefore, seasonal sanitary and molding pruning is carried out.
Sanitary pruning


Sanitary pruning of plants is carried out in late autumn or early spring. There is a general methodology that is recommended to be followed.
All branches of the bush are examined first. Fortunately, this is easy to do, because the plant is not covered with foliage. Determine the skeletal branches that will be worked with a pruner, garden shears, or a hand or electric hedge trimmer. The skeletal branch is easy to spot. As a rule, it is longer and larger than the rest. Then they start pruning in accordance with some principles:
- we shorten the skeletal branches to the required height;
- we cut off all dry and broken fragments;
- we remove the processes growing deeper into the bush, which thicken the honeysuckle;
- if the goal is to rejuvenate the bush, then all branches are cut from the ground under a small stump.
Form trimming


Formative plant pruning, in contrast to sanitary pruning, is carried out when the shrubs are covered with foliage. The task of trimming is to give the most suitable aesthetic shape. In this case, the object is a green crown, which is worked with the help of improvised tools. To save time and effort, it is recommended to use an electric garden brush cutter.
Disease and pest control
Like all crops in the garden and in the garden, Honeysuckle can infect diseases and pests. To keep the honeysuckle bush healthy, it is important to notice the symptoms of pathology in time and take timely measures to eliminate them.
Next, we will look at the main pests that are most common on honeysuckle, as well as diseases that can affect the crop.
Insects and pests
There are not so many insects that can harm ornamental shrubs and reduce the intensity of its flowering. However, if you do not notice the pest colonies on the plant in time and do not take action, the culture may weaken, and the flowering time will shift (Figure 5).
The main pests of culture include:
- Fingerwing caterpillar and leafworm: each of these pests is dangerous. For example, the first type of caterpillar prefers to feast on honeysuckle berries. For humans, they are not edible, but after being hit by such a caterpillar, the fruits begin to fall off, and the bush takes on an untidy appearance. The leafworm is a more dangerous enemy, as it feeds on the leaves of the bush and sucks the juices out of it. With a massive defeat by such a pest, the shrub may even die.
- Shield is also considered a very dangerous enemy. This insect causes serious harm to the bark and drinks the juices of the plant. If measures to combat the scabbard were not taken in time, the honeysuckle will first begin to wither, and then completely die.
- Aphid also likes to settle on leaves and young shoots of honeysuckle. They feed on plant juices and can seriously weaken it.


Figure 5. The main pests of honeysuckle
As a rule, insecticides are used to combat insect pests, but in case of minor damage they can be eliminated with folk remedies.
Diseases
Honeysuckle bushes Honeysuckle are surprisingly resistant to disease, but under certain conditions they can still suffer from some pathologies. As a rule, most diseases are provoked by fungi, and the reason for their spread is improper crop care (Figure 6).


Figure 6. Manifestations of bush diseases
Regardless of the type of disease affecting honeysuckle, this will affect the appearance of the bush. It lags behind in growth, blooms poorly and loses its decorative effect. In most cases, to combat fungal diseases, special fungicide preparations are used, which are sprayed on the affected bush.
Pruning in the fall
Pruning of decorative honeysuckle honeysuckle is usually carried out in early autumn, when the buds have not yet awakened after wintering and the plant will not experience stress from this procedure (Figure 7).
The main purpose of this manipulation is to form the crown of the desired shape and direct the shoots in the right direction. It is usually customary to cut, or rather shorten, the three strongest stems. They are cut by one third, and any weak or damaged branches are completely removed.
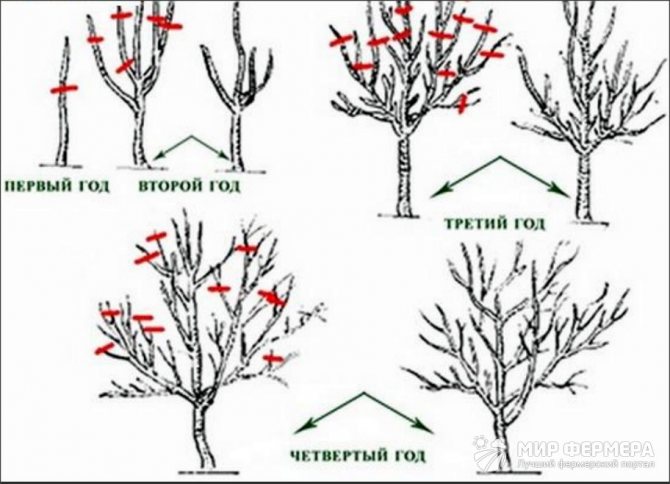

Figure 7. Scheme of crop pruning depending on age
It should be borne in mind that only plants over six years old need formative pruning. Sanitary pruning done in spring or autumn will be sufficient for young honeysuckle bushes.
Culture care
Honeysuckle Honeysuckle grows well if you find the right place for it. Some gardeners hardly care for her at all. And yet, in order for it to please with flowering, you will need to follow certain rules.
- Watering. It is necessary to provide moderate watering so that the soil does not dry out. The puddle should also not be in the root zone, otherwise the root will rot. If it rains from time to time in summer, you can do without watering altogether. But during a drought, it is required to water the bush more often.
- Weeds uprooted if they appear. It also does not hurt to loosen the earth 2 times a week. And so that weeds do not grow, and it is not necessary to loosen the ground often, you can simply put mulch in the root zone.


You can get rid of insects by treating shrubs with insecticides like Confidor, Aktara, Biotlin.
- Pruning carried out regularly, several times a year to form a bush and prevent diseases. Usually diseased branches are cut, those that grow incorrectly and are too long.
- Fertilizers make 3 times a year. In spring, nitrogen is needed (droppings, urea, nitrophoska). In the summer, you can also take nitrogen products, such as nitrophoska, since the plant should be bright and green throughout the warm season. But in the fall, it is better to use superphosphate and potassium sulfate. Compost, humus, wood ash are suitable from organic matter.
Interesting!
If you provide honeysuckle Caprifoil with reliable support and regular pruning, a beautiful, bright bush with excellent decorative qualities will grow.
For the winter, an adult plant does not need to be insulated. But if the honeysuckle Caprifoil is young, you need to insulate the near-trunk zone with peat, bend the pagons to the ground and cover with spruce branches or similar material, and on top with agrofibre. This will save the bush from frost.
Shelter for the winter
Special attention should be paid to the shelter of the honeysuckle Kaprifol for the winter. Despite the fact that this culture normally tolerates both frost and hot weather, it is advisable to shelter it from severe frost in winter.
The winter hardiness of the plant can be called moderate. For example, in central Russia, a bush can winter without shelter, but only if its roots are covered with a layer of snow. In the northern regions, covering the crop with a layer of organic mulch or non-woven covering material is a prerequisite for growing.
Experienced gardening tips
Decorative curly honeysuckle Caprifol is actively used in landscape design, since it can be used to carry out vertical gardening of fences and buildings.
However, in order for the plant to quickly gain green mass, and the smell of opened buds to please its owner, some growing secrets must be taken into account:
- Watering the bush is not at all necessary. The procedure is carried out only in dry summers. The rest of the time, the culture will have enough natural precipitation.
- In order for the plant to develop rapidly and bloom actively, it is advisable to plant it in a sunny, but protected from drafts area.
- Fertilizing is a prerequisite for plant care. Fertilizers are applied not only in early spring, but also in summer, so that crops grow faster and bloom more actively.
In general, due to the culture's resistance to pests and unpretentious care, Caprifol's honeysuckle can be safely called an excellent option for those who want to decorate their summer cottage with a beautiful and unusual plant. Details are in the video.
Description of the plant
There are a large number of types of honeysuckle, there are more than two hundred of them, and everything can be divided into three main types:
For growing in the garden, fragrant honeysuckle is best suited. There are about ten main types of this ornamental plant. The most popular are shrubs and climbing varieties. The most common vine in the gardens of Russia is the honeysuckle Caprifol. This plant can be planted in areas such as:
- Gazebos;
- House walls;
- Terrace;
- Porch.
Gardeners prefer the Caprifol honeysuckle variety due to its exceptional qualities, as well as ease of maintenance and the ability to grow without much effort. This plant, during the flowering period, can exude a very strong aroma and will decorate any backyard.
Honeysuckle belongs to lianas and is a climbing honeysuckle. It grows as a lush bush. She has very beautiful dark green leaves and small light flowers. Honeysuckle Honeysuckle can have different shades of flowers, for example:
This shrub begins to bloom in early summer and a wonderful scent spreads throughout the garden. A feature of honeysuckle flowers is that they have very long stamens protruding forward. They tend to be bunched and nestled in the lush foliage of the bush.
The flowering period of honeysuckle is very short, no more than three weeks. If you cut a few flowers, they can last no more than three days, after which they begin to fade.
In one season, the branches of honeysuckle can grow up to 2 m long. The shrub lives in the garden for about 30 years and is considered a long-lived flower. It can also tolerate even very severe frosts, and if some of the stems freeze, the plant recovers very quickly.
Honeysuckle Kaprifol differs from others for its beautiful leaves, which can be blue-green and do not change color until late autumn.






























