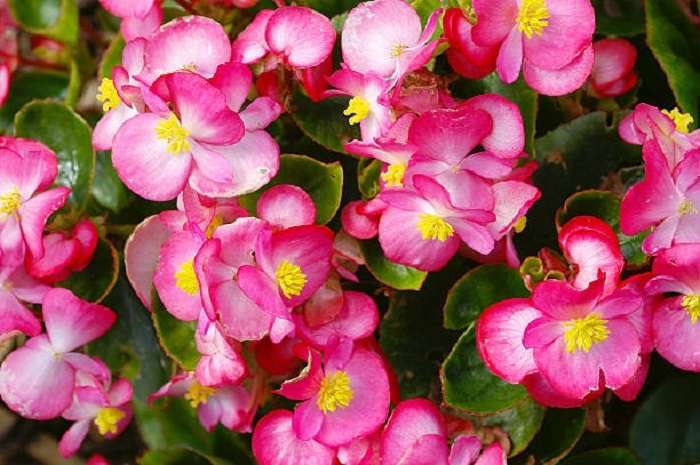
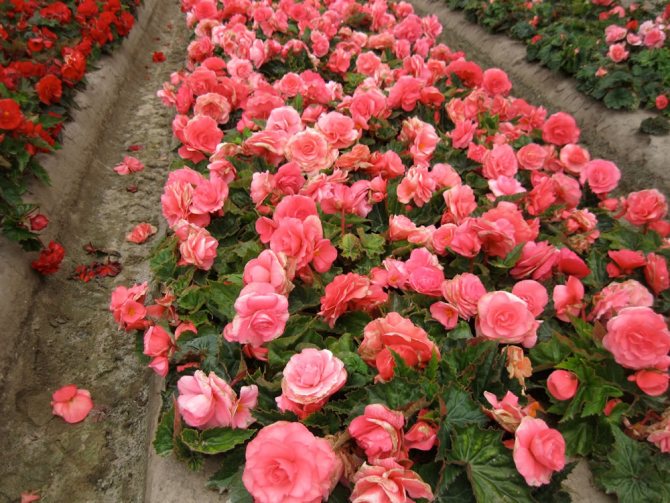
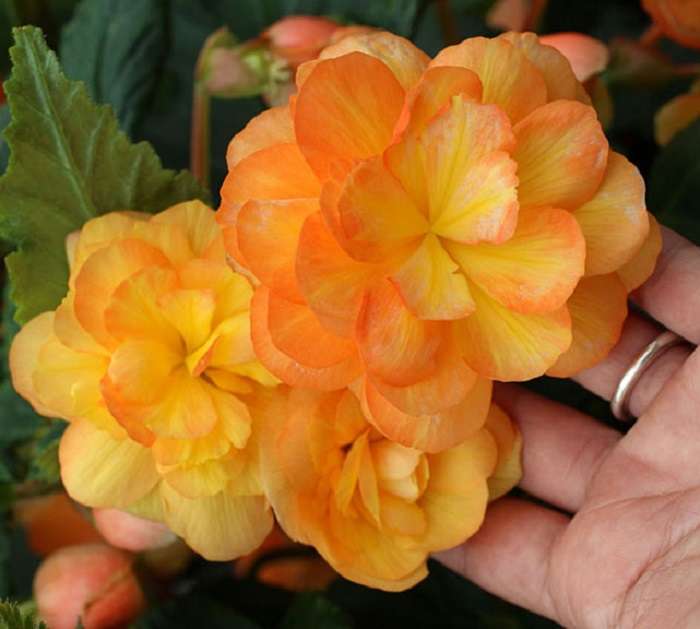
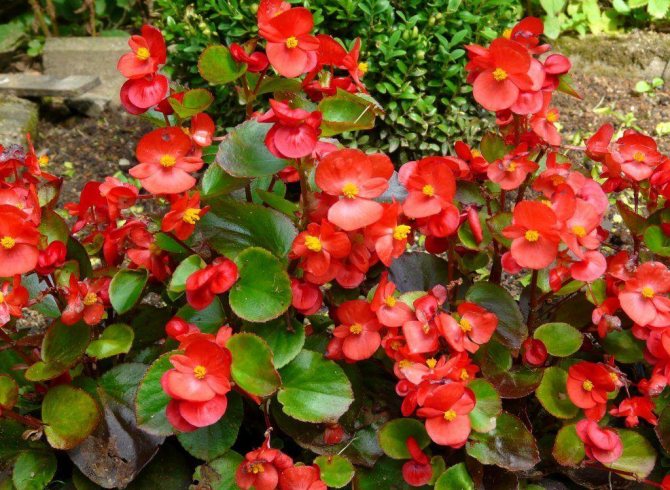
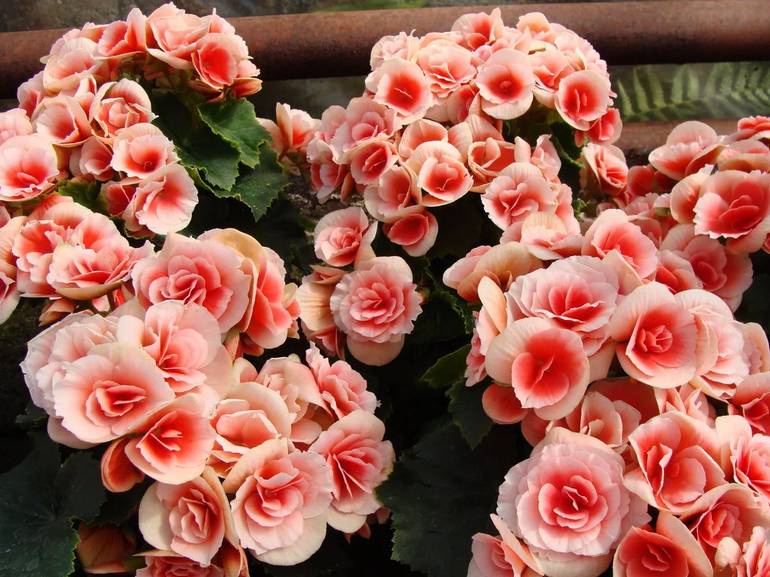
Having got to Europe, Russia, a resident of tropical countries, begonia was first grown in greenhouses. In Russia, the flower was already popular at the time of Bonaparte (for its pointed leaves it was called "Napoleon's ear") and decorated houses and winter gardens. A plant with a beautiful bush shape, delicate inflorescences, a wide color palette, species diversity (there are about 1000 species of begonias) attracted the attention of breeders.
In their natural environment, begonia can be found in tropical rainforests and areas with dry climates in Asia, Africa, South America. The flower is grown almost all over the world.
Tuberous begonia: planting and care in the garden
Despite the species and varietal diversity, all begonias grow better on fertile, slightly acidic, loose soil.

Tuberous begonia
Choosing a place for tuberous begonia
Caring for a flower begins with choosing the right planting site. The flower is photophilous, but at the same time does not like direct sunlight. A place in the garden with light shading will be optimal for him. Shrubs planted nearby can cast a shadow on the begonia, but the flower does not like the neighborhood with trees. Shading can be obtained by placing a canopy of mesh material over the flower garden.
A perennial flower does not deplete the soil, but it is recommended to grow it in one place for no more than 6-8 years. To give the plant a good start, the ground for the future flower bed is prepared in the fall - they dig up the soil of the flower garden, remove the roots of dug crops and debris, bring in humus (a bucket of 1 sq. M).
Watering the flower garden
Flowers don't like dry ground. During the growth of green mass, the flower needs abundant watering, the earth is moistened 1 time in 3 days. The preferred time for watering is morning.
Note! To prevent the delicate flower from getting burned, drops of water should not fall on the inflorescences and leaves when watering.


Flowers don't like dry land
The period from late May to mid-October for begonias is the flowering time. Abundant flowering and large peduncles need nutrients, they are applied by dressing (up to 3 times per season). Watering at this time is reduced by 1.5-2 times compared to the period of vegetative development. An indicator of a lack of moisture is the casting of begonias - when the plant receives less moisture, they wither.
Note! It is necessary to water the plant, irrigating the soil around the bush, but not under the bush, so as not to wash the ground and expose the rhizome.
Top dressing
The flower is fed with mineral fertilizers and organic matter 3 times per season. The first time is to feed the plant immediately after planting in open ground, the rest during the season. During the laying of the buds, fertilizers with a high content of phosphorus and potassium are applied, during the flowering period - with a nutritious composition of complex mineral fertilizers. Since August, the nutrient mixtures are stopped so that the begonia has time to prepare for winter.


The flower is fed with mineral fertilizers and organic matter
Pruning
Proper care promotes the growth of the bush, and its shape is corrected by cutting off the shoots. The first pruning is done when the stems grow up to 8 cm. Extra side shoots are removed, giving the bush the desired shape. With a stem length of about 12 cm, the tops of the shoots are pinched, after which the stems do not stretch in length, but grow, becoming lush.
Note! Begonia shoots are tender, fragile.Garden shears are not suitable for pruning; pruning is done with a sharp knife.
How to protect begonias from diseases and pests
Planting begonia tubers is quite simple if the soil is selected correctly, as well as the temperature and watering conditions are met. In the future, as the plant develops, diseases associated with pests (aphids, spider mites, nematodes) or with improper care (insufficient light, excess or lack of moisture, etc.) may appear.
Begonia diseases: causes and how to eliminate
The most common developmental disorders associated with improper conditions of detention and infectious pathogens include:
| outward sign | cause | decision |
| leaves dry at the edges, begin to curl | dry and hot air | rearrange to a cooler place, periodically humidify the air |
| leaves fall off or turn yellow and wither | too cold | rearrange to a warmer place |
| foliage wilted | polluted air or lack of moisture | take the pot to another room, water abundantly (if the ground is dry) |
| leaves grow small, flowers do not form or flowering is rare | lack of fertilizer | fertilize the soil with organic or mineral fertilizing |
| leaves fade, cobweb found | spider mite activity | use an insecticide or infusion of onions (more details below) |
| powdery coating with greenish and brown tints | gray mold fungus activity | spray with fungicide (benomyl) according to the instructions and put the pot in a dry, cooler place |
| white spots of a powdery consistency | powdery mildew activity | |
| the roots turn black and rot | black root rot fungus activity | stop watering, spray with fungicide, remove to a drier place |
| rot on the surface of leaves and flowers | waterlogging | reduce watering, prevent moisture from spraying on the begonia itself |
| leaves are deformed, yellow spots appear on the surface | activity of the cucumber mosaic virus | destroy the flower, disinfect the pot, replace the soil |
| the leaves have lost their color, on the roots there are influxes | nematode activity |
Pests and how to deal with them
As for the pests of royal begonia, the most dangerous are:
- Spider mite is a rounded insect, bright red in color, less than 1 mm long. They look like numerous bright spots on the surface of the leaf and stems. Leaves cobwebs throughout the plant.
- Aphids have different colors (green, gray, brown), the shape of the body is rounded, 2-3 mm long. They look like numerous gray dots.
You need to deal with them immediately after detection. For this, special insecticides are used, which can be purchased at a specialized store:
- thiophos;
- karbofos;
- actellik;
- neoron;
- fitoverm;
- fufanon.
They act clearly according to the instructions. You can also use a home remedy based on regular onions (with brown hulls):
- Chop the onion very finely or pass it through a meat grinder.
- Take a full teaspoon (half a tablespoon) and infuse for 1 week in a liter of water.
- Strain and spray the foliage and stems until the insects are completely destroyed.
PREVENTION TIP
The foliage and especially the stems of the plant that are hidden under the bush must be carefully examined for the presence of these pests and other lesions. The sooner you start dealing with them, the higher your chances of success.
Tuberous seed propagation of begonia
The flower is propagated by dividing the tuber, cuttings, seeds. Growing over a large area (large flower beds in the garden, large areas of landscaping of parks, squares) requires a lot of planting material. The best way to get it is by sowing seeds.
Tuberous begonia: planting and care at home
Note! Begonia seeds are very small.To prevent the plant from planting too densely, they are mixed with sand before planting.
For sowing seeds, prepare a box or container with nutritious moistened soil and expanded clay or other drainage material at the bottom. When sowing seeds, do not sprinkle the sowing on top of the earth.


Reproduction of tuberous begonia from seeds
You need to plant seeds in the middle of winter, before early February, so that the grown seedlings have time to get stronger, and the flower blooms on time, this season. The box is covered with plastic wrap or glass and placed in a well-lit room, the air temperature in which is about +25 ° C. After 2 weeks, shoots appear. When 2-4 leaves appear on the seedlings, they dive. When winter ended and good weather without frost was established (in central Russia it is not earlier than May), it was time to plant seedlings in open ground. It is planted by burying the roots so that the green part of the plant is on the surface. Between neighboring tuberous begonias maintain a distance of 20-25 cm.
The challenges and fun of growing from seed


There are several ways to reproduce tuberous begonias: by seeds, leafy or stem cuttings, by dividing the tuber. Seed cultivation is the most time consuming of them for the following reasons:
- The seeds of begonias are very small, the germination and quality of seeds purchased in the store are sometimes disappointing, especially when there are only 5-10 of them in the purchased package. Good germination is ensured by fresh planting material, especially collected from its own plants.
- Seedlings are not friendly, they are also very small and tender, demanding on conditions.
- Care for seedlings takes a long time, about 4 months, since at first they develop very slowly.
Nevertheless, planting tuberous begonias from seeds and caring for the seedlings is a fun process with the result in mind. Reasons why amateurs go to such labor costs:
- The variety of varieties commercially available as seeds is much greater than as tubers. It is easier to acquire seeds of new varieties of begonias than cuttings or tubers.
- Seeds are much cheaper than tubers and the more preferable the more plants are planned to be obtained.
- With artificial pollination, you can get your own seeds, which give plants with new qualities.
When growing from your own seeds, you can get the right amount of plants of the same variety, which will allow you to implement any design idea.
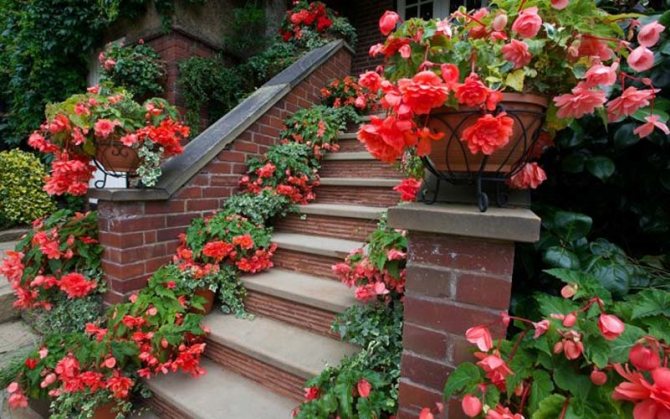


An example of the use of one variety of begonias in design
Reproduction by dividing the tuber
This method is used at home and for the propagation of rare varieties of plants in nurseries.
Tuber preparation
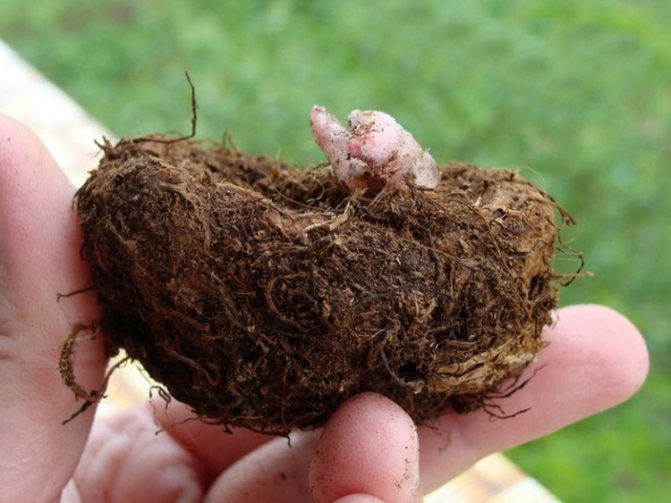
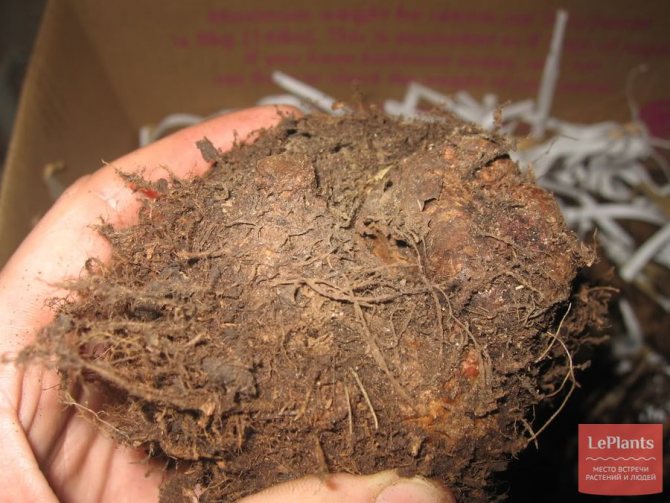
Reproduction assumes the presence of large, more than 6 cm in size, bulbs without cracks, mold, overgrowth. You can determine a healthy tuber by weight - it is dense and heavy, unlike light dried bulbs.
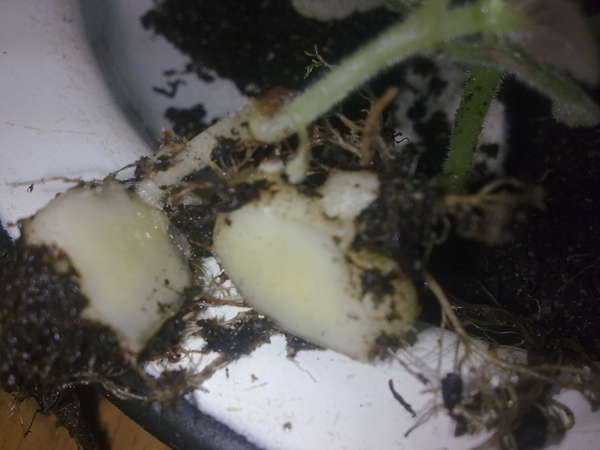


Reproduction by dividing the tuber
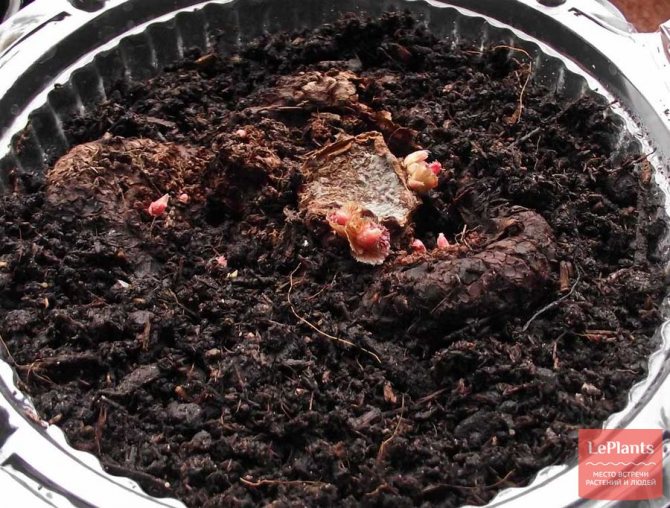
It is optimal to start breeding begonias with tubers in January, when they are in a state of physiological dormancy. The onion is cleaned of rotten sprouts and placed for 40-45 minutes in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate or for half an hour in a solution prepared using a fungicide. The dried onion is cut into several parts, making sure that there are live buds in each segment. The slices are sprinkled with charcoal.
Box and earth
To grow a flower for planting in open ground, prepare a box with soil (it can be prepared by mixing 2 parts of leafy earth with humus, peat, sand, taken in 1 part). The presence of a pallet is required - begonias will need to be watered abundantly. The container is filled with earth, leaving 3-4 cm from the edge.
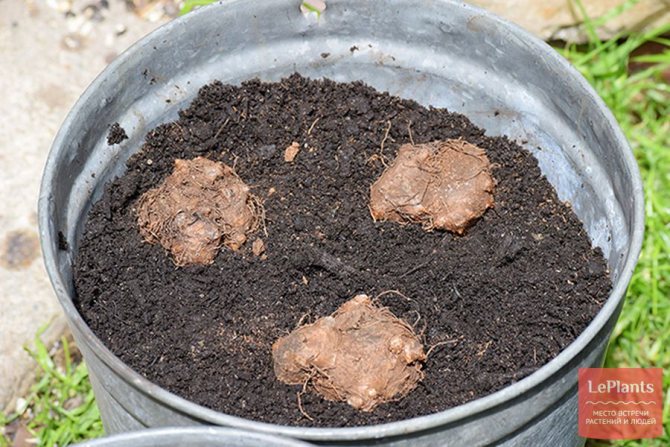
Planting tuber segments
For the segment of the bulb, which is planted in a separate container, a small depression is made in the center in the ground.In a box for several plants, the soil is deepened at a distance of 10 cm and 5 cm away from the walls of the box. To germinate the root, part of the tuber is placed with the convex side deep into the soil. The concave part remains on the surface for the plant to grow upward. When sprouts appear on the planted bulb, they are lightly sprinkled with earth.


Planting tuber segments
Environmental conditions
The bulb will adapt more quickly to growing conditions in the open field if it is not provided with greenhouse conditions. For germination, it is recommended to choose a room:
- bright, but without direct sunlight;
- ventilated, but without drafts;
- with temperatures from +15 to +17 ° С.
Tuberous begonia: reproduction and care
Note! As for the temperature, the recommendations differ - there are tips to germinate the bulbs in a room with an air temperature of 20-22 ° C.
Sprout care
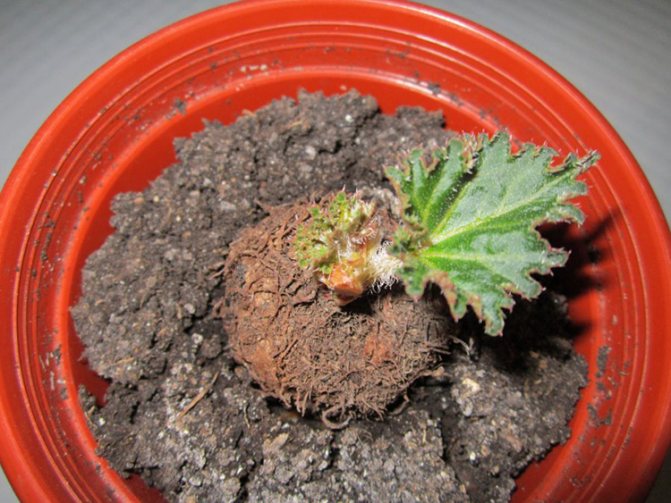
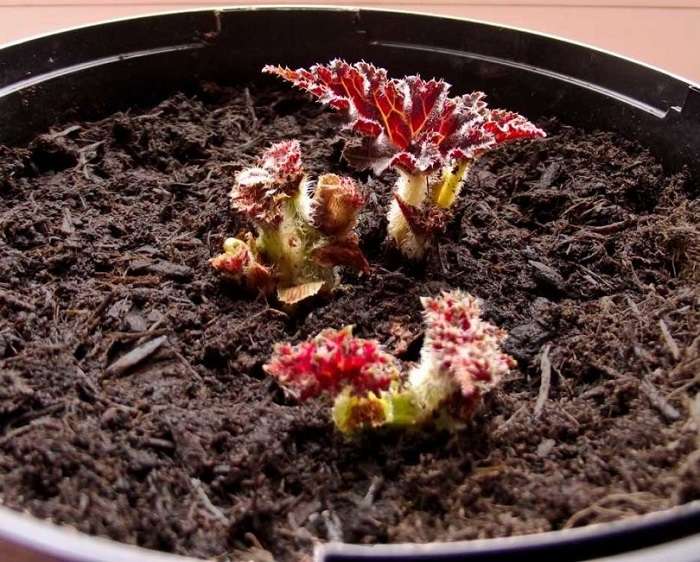
The soil needs to be watered so that it is always moderately moist, but not excessively wet. If there is too much sun in the room, create partial shade by curtains of windows or placing a box of tubers in the shade of plants. With proper care, after 5-7 days sprouts hatch, after the next 15-20 days 2-3 leaves appear. In a month, there may be the first flowering.


The ground needs to be watered so that it is always moderately moist.
In order for young plants to be adapted to environmental conditions, they are taken out for a short time in the garden or on an open balcony. Planting them in a flower garden - in the spring, when there is no longer a threat of frost. The plant is planted at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other, the roots are sprinkled with a layer of earth of 2 cm.
Conditions for disembarkation


Tuberous begonia can be planted in January... The deadline for planting is late spring - the month of May. When landing, it is important to consider some features, namely:
- The tubers that will be planted should not have spots, dents or signs of fungus, but should be dense to the touch. If you plan to buy tubers, then you should do it in March. At this time, the kidneys should already appear.
- First, begonia is planted in light soil. Alternatively, you can use pure peat. And only then the plant is transplanted to a permanent place (in a pot or open ground).
- Care should be taken to plant the tuber on the "right" side. The tubers are planted with the convex side down - roots will sprout from there. The flatter side of the tuber should be at the top, shoots will hatch from it.
Planting tuberous begonias in a pot
When growing begonias as a houseplant, questions arise - what kind of pot does a flower need, what care does home begonias require, how to properly grow begonia from a tuber in a pot?
Healthy bulbs are chosen for planting. Any flower pot is suitable - plastic, ceramic, clay. It is important that it is not large (in a flower planted in a large container, the root system develops to the detriment of the growth of the ground part). The optimal size will be a pot with a height and diameter of 8-10 cm. At the bottom of the vessel there should be holes to drain excess water, a layer of expanded clay, pebbles, and other drainage is also required.
The soil for indoor tuberous begonias can be bought ready-made or prepared by mixing peat, leafy soil, sand in a ratio of 2: 2: 1, or 3 shares of leafy soil and 1 part each of sand, peat, humus. You can add charcoal to the composition.
The bulb is kept in a fungicide solution for half an hour before planting in a pot. The dried tuber is placed in a small hole made in the center of the pot, with a notch up. It is not necessary to deepen and sprinkle the tuber with earth - only 2/3 of it should be in the soil. After planting, the ground is watered.
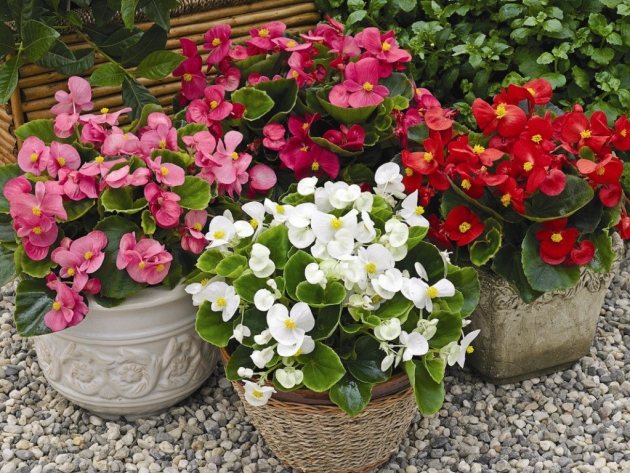


A flower pot will fit any
Fern in the garden: planting and care
Note! It is necessary to moisten the ground so that drops of water do not fall on the bulb.
When sprouts appear in a week, the tuber is sprinkled with earth.
When do you need to transplant?
As the tuberous begonia grows and develops, it needs a transplant. Root system tightness is destructive... In this case, the plant will gradually wither away, and the flowering will become scarce and gradually stop altogether. A timely transplant into a more spacious pot will help here.
When is the best time to do this?
As a rule, the optimal time for transplanting begonias, as for all plants, is spring. It is recommended to do this even before the sprouts develop, so the best period is the beginning of March.
Recommendations
To successfully transplant begonia, you should adhere to the following instructions:
- Carefully remove the begonia tuber from the old pot, after watering the soil well.
- Clean it from dry and rotten roots. If there are rotten areas on the tuber, it is necessary to cut them off with a knife. Sprinkle the cuts with chopped charcoal.
- Place the tuber in the manganese solution for 30 minutes. This procedure is carried out for the purpose of disinfection.
- Place the plant in a pot with pre-prepared soil. Since begonias have a shallow root arrangement, the pot should be chosen not deep, but wide enough. When using a deep pot, fill the third part with gravel.
IMPORTANT! For faster germination of shoots, do not completely cover the tuber with soil. It is best to add soil as the plant grows.
Fertilizing for abundant flowering and basic rules for caring for begonia in the ground
Tuberous begonia requires regular and abundant watering, top dressing. The flower is fed with mineral and organic fertilizers. The main mistakes in caring for him were:
- insufficient watering and excessive soil moisture;
- oversaturation of the plant with mineral fertilizers or organic matter;
- feeding the flower immediately after planting or transplanting (the transplanted begonia, so as not to slow down the development of the root system, is fed only a month after planting);
- making the ailing flower dressings in large doses (you need to take care of the ailing begonia by gradually increasing the dose of nutrient mixtures);
- are destructive to the flower feeding at rest.
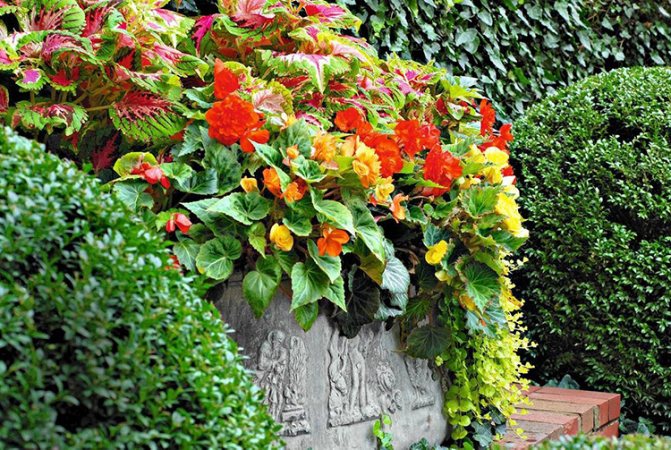
Benefits of using in landscaping
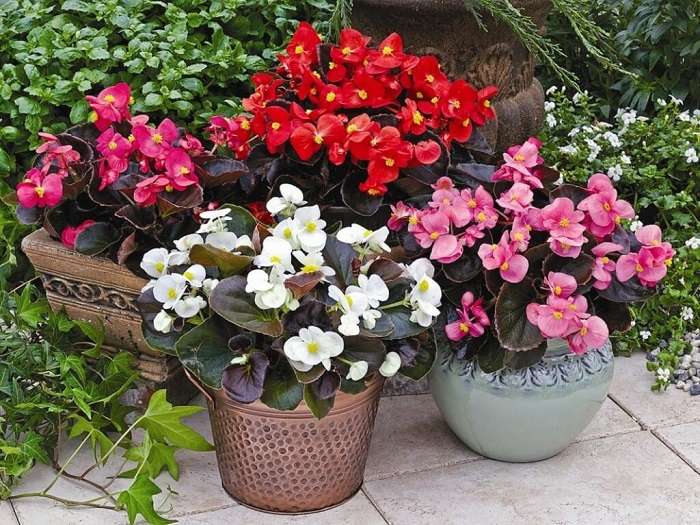
A wide range of colors of plants allows you to create compositions and is often used in landscape design.
Benefits of begonia:
- the plant is unpretentious in care;
- saturated colors;
- used for planting in a pot;
- can be used as a cover for flower beds;
- you can create various curly designs;
- street begonia is used to create slides;
- goes well with various plants.
Disadvantages:
- planting begonias in an area with constant sun exposure can contribute to the absence of inflorescences on the bushes;
- In the fall, begonia must be dug up, which can cause discomfort for large compositions.
The plant has a long flowering period and is an ideal garden decoration.
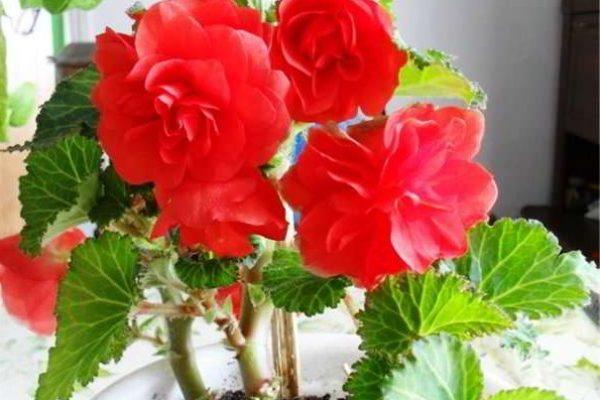


Prevention and treatment of tuberous begonia
If the planting and caring for tuberous begonia is correct, the flower grows healthy and demonstrates its decorative effect as much as possible. But begonias have pests - aphids, scale insects, whiteflies, thrips, nematodes that cause flower disease. For pest control, special formulations for treating begonias are used, they can be found in gardening stores.


The flower grows healthy thanks to proper care
The flower is susceptible to fungal diseases: powdery mildew, gray mold, bacterial and ring spot. The reason for their occurrence is a deviation from agrotechnical standards - excessive watering, inappropriate composition and acidity of the soil, improperly applied top dressing, poor storage of tubers.
Treatment of fungal diseases is carried out by spraying on the leaf with fungicides, Bordeaux liquid, and copper sulfate solution.
Choosing the right tuber
Botanists classify tuberous begonia into four types:
- large-flowered;
- small-flowered;
- mid-flowered;
- ampelous (having hanging stems).
The main difference between these species is in the size of the tubers, the color of flowers and leaves, as well as their shapes (double and non-double in the former and corrugation and serration in the latter).
When growing begonias, priority is given to choosing the right tuber. In this matter, you should not chase after cheap and promotional goods, which can often be found in large supermarkets and from individuals in spontaneous trade stalls. In such cases, there is a high risk of getting poor quality material that will not give good results even if the plant is carefully cared for.
When buying, it is worth excluding tubers that have the following characteristic disadvantages:
- soft and sluggish to the touch;
- looks dehydrated;
- has external damage;
- covered with a whitish bloom or individual molds.
It is desirable for the buyer to inspect each tuber separately, it can be difficult when buying prepackaged tubers in sachets, sometimes also having an opaque polyethylene surface. When probing the material in such packages, you should opt for elastic and dense tubers of large size. Waking up kidneys will be a sure sign of a good purchase.
As a rule, begonias tubers, ready for the planting season, appear on sale by the end of winter. They are delivered from Holland. Having bought planting material in a store on cold winter days, you should take care of reliable transportation to your home. Begonia does not tolerate cold, and taking it out of a warm room into frost can cost it its life. Usually sellers pack tubers in small bags filled with peat or sawdust and insulate them with paper.
How to keep begonia tubers in winter
Begonia cannot survive the winter outdoors, so its tubers are dug up in the fall. Storing begonia bulbs requires following simple guidelines:
Begonia bulbs are dug up with the arrival of the first frost, working carefully so as not to damage. A garden fork or scoop is used. The tubers are sorted out, the stems are cut, leaving 2-3 cm of them on the bulb and, without clearing from the ground, placed for drying in boxes, which are taken out in a warm, dry, ventilated room. After 2 weeks, the tubers are cleaned of soil and the remains of the stems and placed, covered with sawdust or dry peat, in plastic bags or, sprinkled with sand, in a box. The packed bulbs are then placed in the selected storage location.
The main condition for the environment is coolness (temperature 5-9 ° C) and dryness (room humidity 80-85%). You can save the planting material in a ventilated cellar or basement, on a refrigerator shelf.
If you take care of begonia correctly, it will become the queen of flower beds, giving the garden originality. And the main thing in care is timely watering and top dressing.
Features of the
Tuberous begonia (Begonia Tuberhybrida) is a perennial herb that appeared as a result of crossing several types of begonias. Has juicy branching stems. The leaves are large, heart-shaped. Plant height, depending on the variety, ranges from 17 - 77 cm... The rhizome of the plant is thickened, tuberous, up to 6 cm in diameter.
Tuberous begonia is divided into the following types:
- small-flowered (3 cm in diameter);
- mid-flowered (up to 7cm in diameter);
- large-flowered (7 - 20 cm in diameter);
- ampelous.
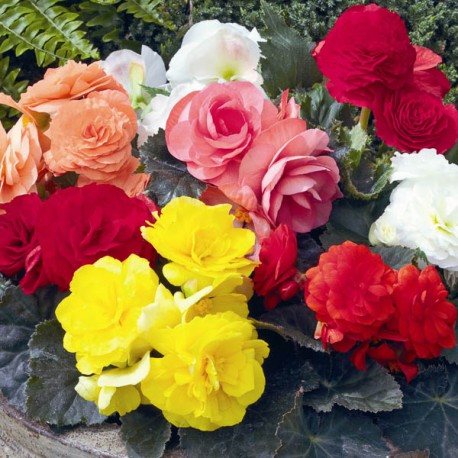
Tuberous begonia has a variety of colors: red, pink, yellow, white and many other shades.
REFERENCE! Long flowering is an important feature of tuberous begonia. Indoors, it blooms from May to October, and outdoors from June to September.
Views
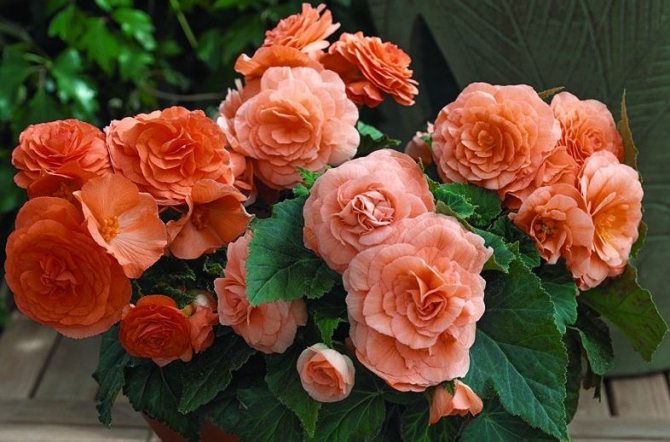


Begonia in the garden is planted for design. For this, three types of plants are usually used.
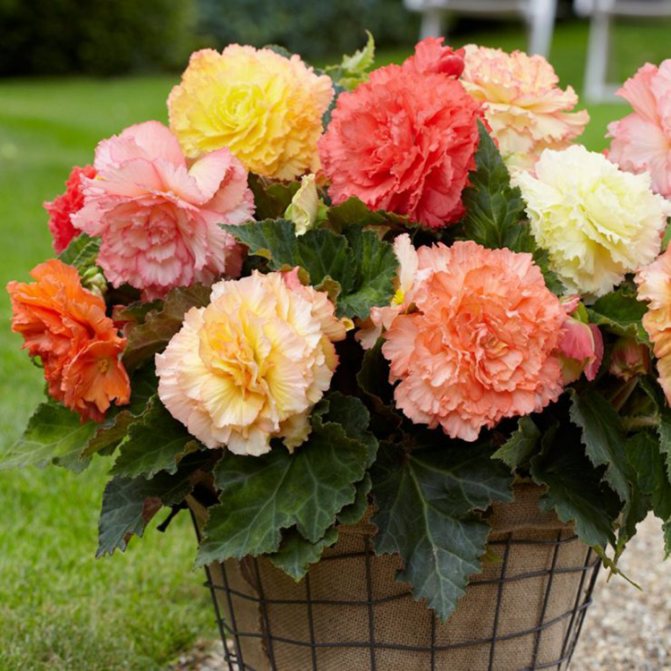
- Tuberous grows no higher than 30 cm.The variety is distinguished by large flowers that amaze with the abundance and brightness of colors. The flowers of these varieties of begonias are heterosexual: both male and female flowers bloom on the same bush. The flowering time is very long. Flowers have different shapes: lotus, roses, carnations.
- Hybrid begonia is a separate type of ampelous type. Long hanging twigs are decorated with whole caps of flowers.
- The ever-flowering begonia has a large number of varieties. The bushes of this plant are usually up to 15 cm high. The leaves of the ever-flowering plant are small, oval, smooth. There are different colors: green, brownish, dark red and others. Growing this variety is not difficult for experienced gardeners and beginners.