Zonal pelargonium is a beautiful houseplant. But no matter how we get used to seeing it on the windowsill, it turns out that it can also be grown on the street: in garden beds, in flower beds, in parks. It can serve as a good decoration even for city squares. The main task before planting in an open area is to determine the correct plant variety, since not all types of pelargonium are adapted for the outdoors. Of course, caring for her also plays a big role. Despite the fact that the flower is completely unpretentious and hardy, it is necessary to follow the basic rules for the cultivation of this plant so that it pleases the eye with flowering for many years. Therefore, it is necessary to study how to properly care for a flower in winter, and the requirements for care. Then zonal pelargonium at home on the windowsill or in the garden will turn into a beautiful flower bed.

Briefly about what pelargonium is
- This plant is from the Geranium family in the form of a shrub.
- Its natural area is South America. However, at present, it can be found in completely different countries.
- Based on its habitat, pelargonium is very fond of light and warmth. In addition, it is resistant to dry periods.
- The leaves of the flower are characteristic of the Geraniev family - a finger-dissected form.
- A perennial, depending on the variety, will have both a straight and creeping stem.
- Pelargonium zonal flowers are always very colorful, consisting of textured lines. They appear for a rather long period in the summer.
- The average duration of the preservation of the appearance of a plant is 2-2.5 years. After this time, zonal pelargonium must be updated, since the appearance deteriorates.
- Despite the fact that pelargonium and geranium are from the same family, they require different care.


Reproduction
Some varieties can be grown by seed, but the main method is cuttings. Cuttings can be harvested in spring and late summer.
- Pelargonium cuttings root easily, but there are a number of differences depending on the species. To make a stalk, a section of 8-10 cm is cut off from the vertical shoots. You need to cut along the knot or slightly stepping down from the knot.
- The planting material is placed in a mixture of sand and peat and the soil is constantly kept moist. After the roots appear, the seedlings are planted and pinched to stimulate the growth of side branches.
- Pelargonium Large-flowered is more difficult to root than other species. To ensure the success of the procedure, the harvested material can be treated with a root stimulator.
- Pelargonium Zonal rooted well in water. Fragrant varieties do not take root in water, but only rot. Seeds are planted in the spring in light soil.
Before the emergence of seedlings of Pelargonium, it is important to maintain an air temperature of 20 ° -22 ° C. After that, the container with the seedlings is placed in a lighted place and the temperature is maintained at 15 ° C. Pelargoniums planted from seeds will begin to form buds by mid-summer.
Pests and diseases
Geranium is not susceptible to diseases and pests. Rarely, it can be affected by aphids and fungal diseases, characterized by brown spots on the leaves. In this case, the affected leaves are simply removed. To prevent this from happening, you need to avoid stagnant moisture and waterlogging of the soil.
Possible growing difficulties
- Dry areas on foliage - a consequence of too dry indoor air, on the street such problems usually do not arise.
- Wilting leaves - if this happens in the summer, then it is enough just to water the plant and remove it from the sun, but if the leaves begin to wither in winter, then, perhaps, the roots are affected by rot or pests. In this case, young plants are transplanted, and the old ones are divided into cuttings.
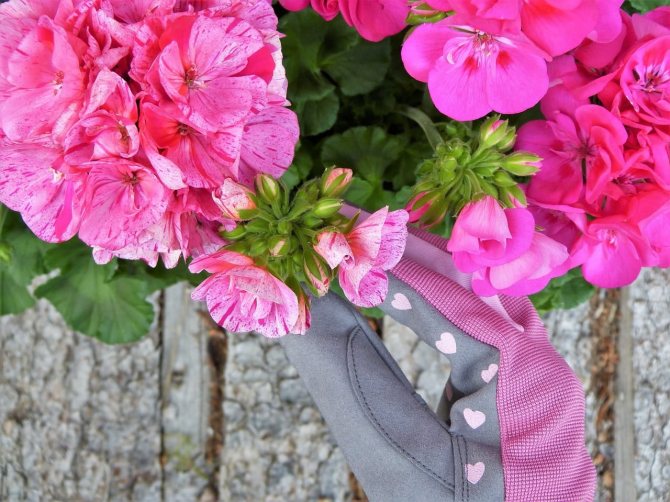


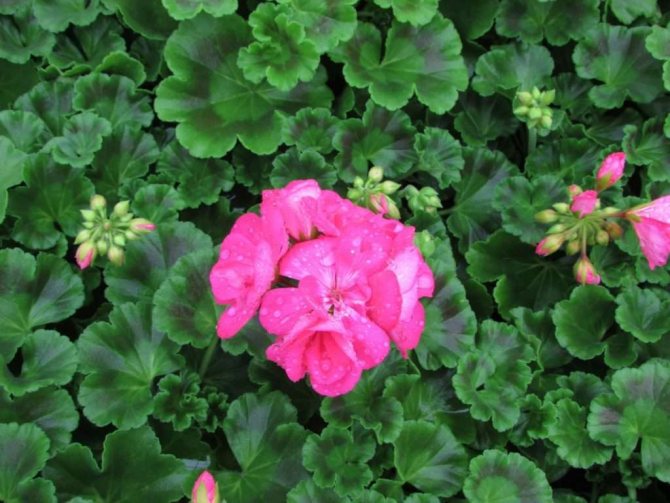
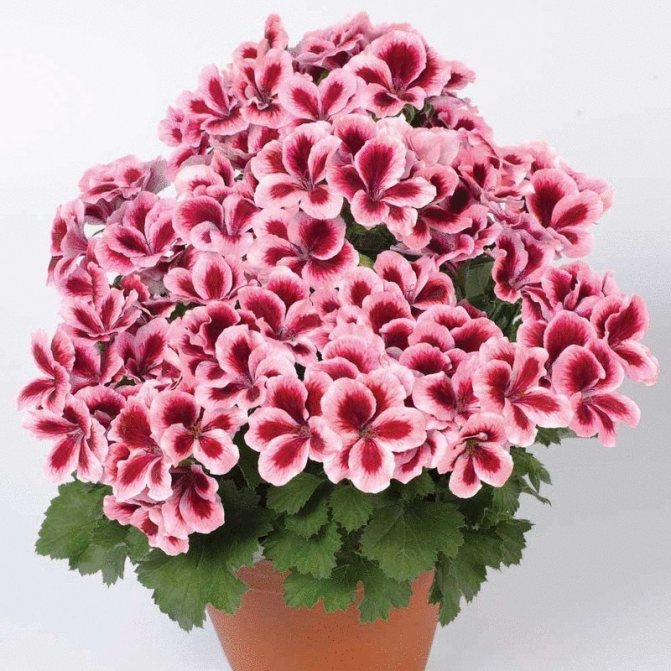
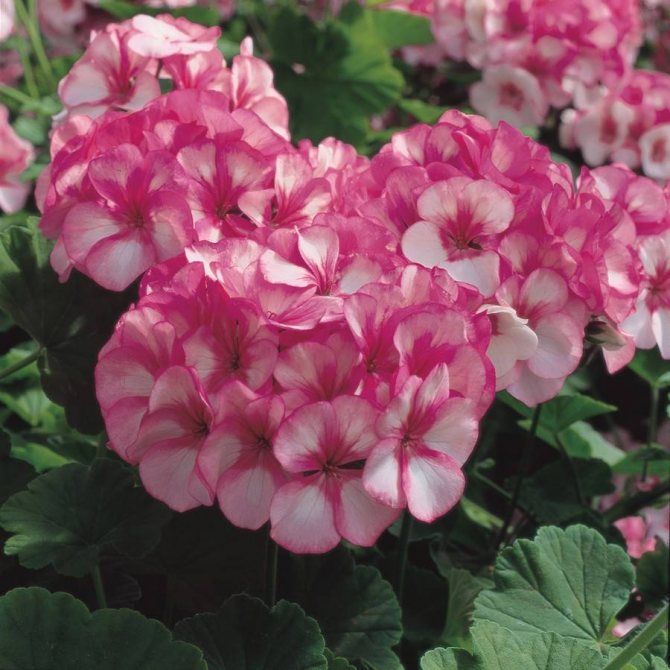
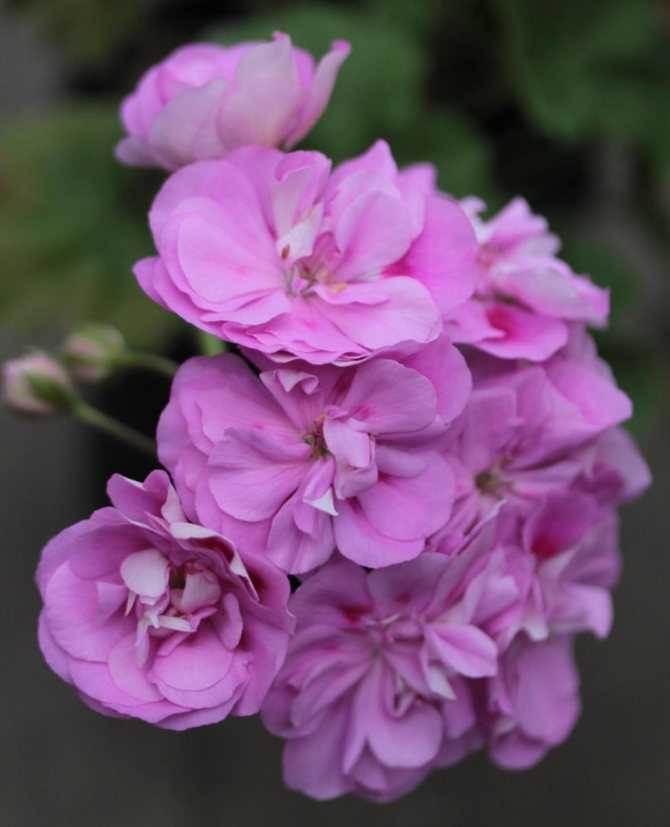
Pelargonium (geranium) with a bright pink inflorescence
Blooming Pelargonium can decorate the windowsill of any apartment or balcony. A huge selection of shapes and colors, long and abundant flowering make this flower very attractive for any grower. And although this flower has long been considered exotic for the majority, it still remains attractive and desirable in any home.
Tags: geranium, perennial plants
- Similar posts
- Petunia seedlings: variety selection, correct sowing in the ground
- Garden chrysanthemum - the secrets of growing at their summer cottage
- How to grow lilies at home
«Previous post
What are the varieties of pelargonium?
Pelargonium has a huge number of different varieties - there are more than 200. But the most popular species, which can often be found on the windowsill or in the garden, stand out.
- Royal. This variety is a wide, small bushes on which large flowers appear. Peduncles are located at the same level with the plant bush. Most often, the variety is used for home breeding. The appearance of a blooming crop can be compared to a fluffy bright ball.
- Tulip-shaped. According to the name, we can conclude that the type of plant is very similar to a tulip. And there is. Flowers have a close resemblance to unopened buds. A variety of shades is presented - from light pink to burgundy. The leaves of this species are very shiny and have a tough texture.
- Rosebudnaya. You can also navigate here by name. The flowering culture will transfer the gardener to the park of roses. The flower has a lot of petals, and they are all close enough to each other, which makes them form a shape close to a small rose. Lush buds will serve as a wonderful decoration.
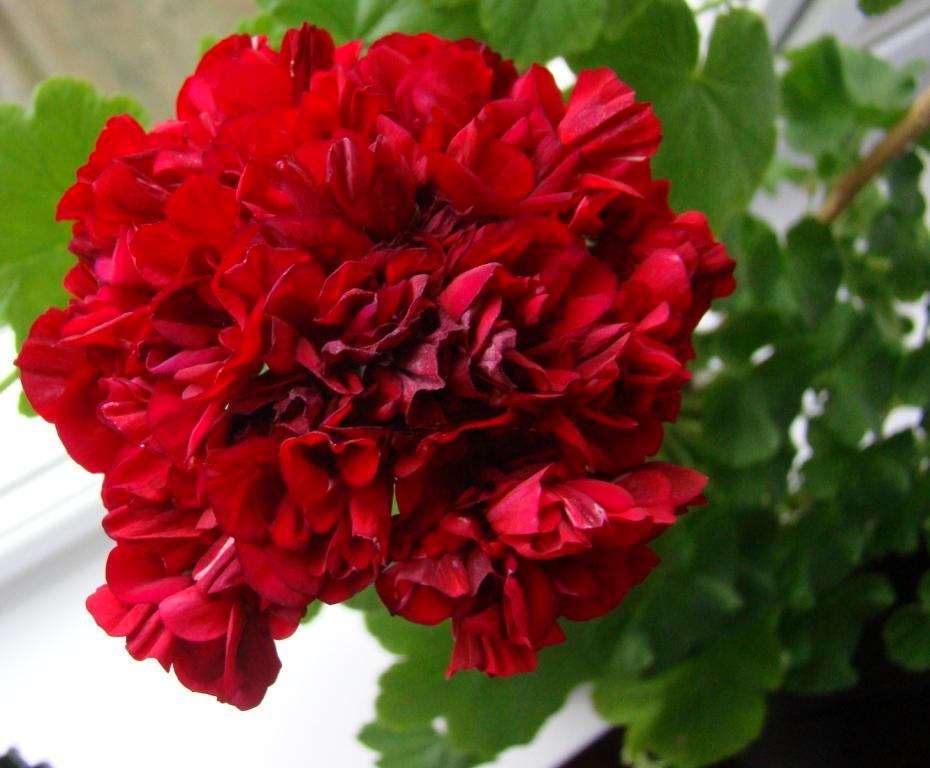
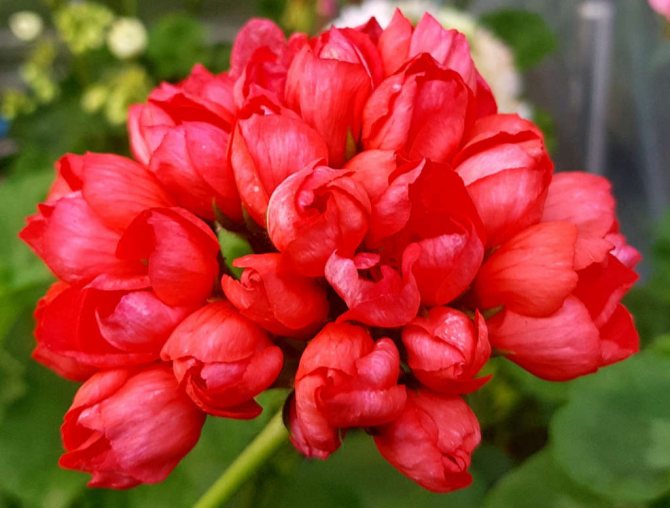
- Terry. Pelargonium inflorescences of this variety are distinguished by terry petals. The color can be found for every taste: raspberry, soft salmon, lilac.
- Angular. The plant will be very tall - up to 100 cm. The shape of the leaves of the species is quite unusual - the leaves are short-peaked, can be compared with oak leaves. Inflorescence in the form of a bright red umbrella.
- Capitate. Compared to the previous variety, this culture will be half as much - about 50 cm. The shrub is constantly pleasing to the eye with its green color. The flowers are also in the shape of an umbrella of pink-purple hue. At the same time, pelargonium emits just a magical aroma.
- Curly. This species is highly branched. The bush will not grow more than 50 cm, but will be evergreen. The leaves are shaped like a heart and grow in two rows. Their edges are ragged, jagged.
- Fluffy. The fluffy pelargonium variety is characterized by thick stems and lobe leaves. The flowers are snow-white in color, while the inner core is bright red. 5-6 such inflorescences are connected together and create an umbrella.
- Fleshy. The perennial of this species has a very small size - only 30 cm. Its leaves are in a lowered state and have a distinct venation. The flowers generally appear either white or pale beige with small red dots.
- Thick-stemmed. Here the name speaks for itself - the stem of the culture is very thick, and the plant itself reaches about 20 cm in size. Compared to other types of pelargonium, this is quite small. The wide leaf has silvery pubescence. The flowers appear in the form of standard umbrellas, but the colors range from yellow to purple.
- Fragrant. This shrub is distinguished by its branches and, of course, a strong aroma that does not come from flowers, but from the leaves of the plant.The standard inflorescences take the shape of an umbrella.
- Large-flowered. For outdoor cultivation, the large-flowered variety is not quite suitable. He is very moody and requires special care. The plant will not be able to without constant heat. Its height is from 30 to 60 cm, which is an average indicator. The inflorescences are corrugated and large in size.
- Klobuchkovaya. This species is notable for its dense terry, bright green foliage, which is lowered down. The flowers are purple-red.
- Dirty. Another variety that grows almost the highest. Its size can reach about one and a half meters. The leaves are rounded dark green, planted on a rather fleshy stem. And the bush is decorated with bright scarlet flowers that can be compared to lights.
- Ivy. As for this variety of pelargonium, it is not at all suitable for planting in open areas. Cold snaps are destructive for him. The foliage of this culture can be compared to ivy. The inflorescences are very variegated.
- Pink. Based on the name, it can be understood that the inflorescences have a pink tint. They are located on a branching bush.
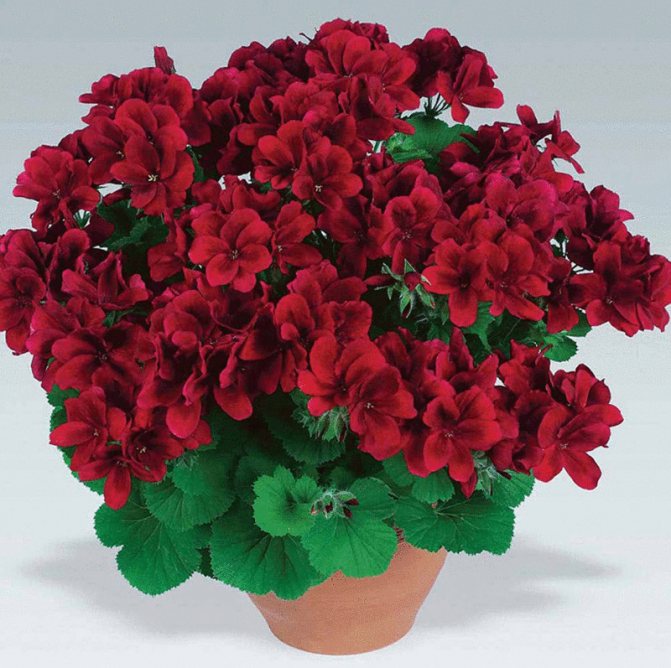
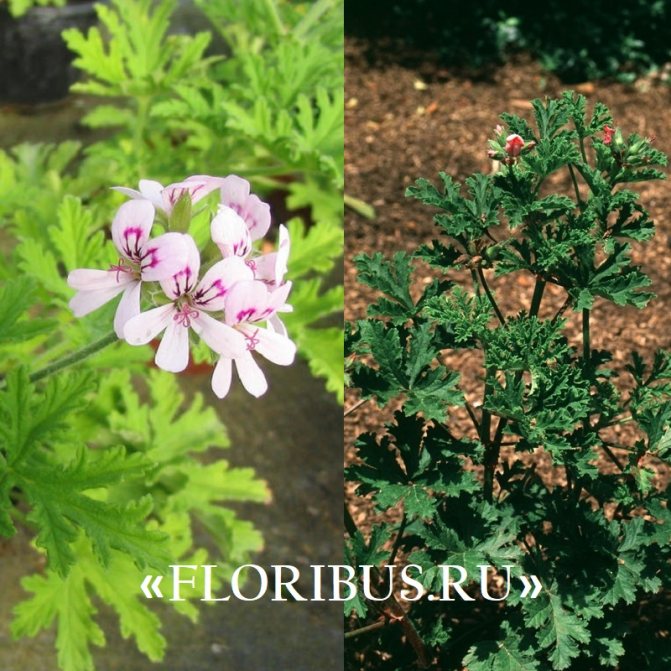
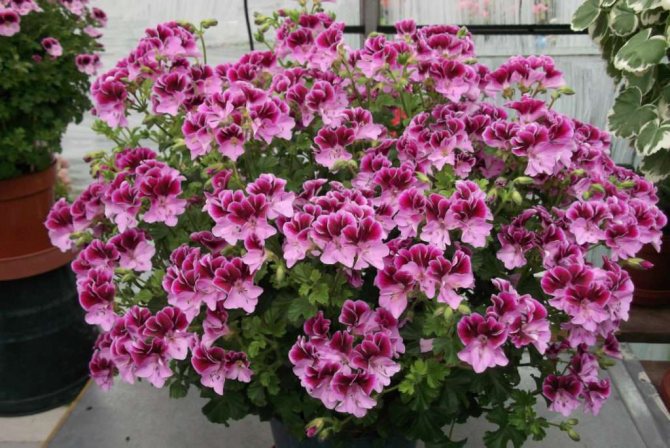
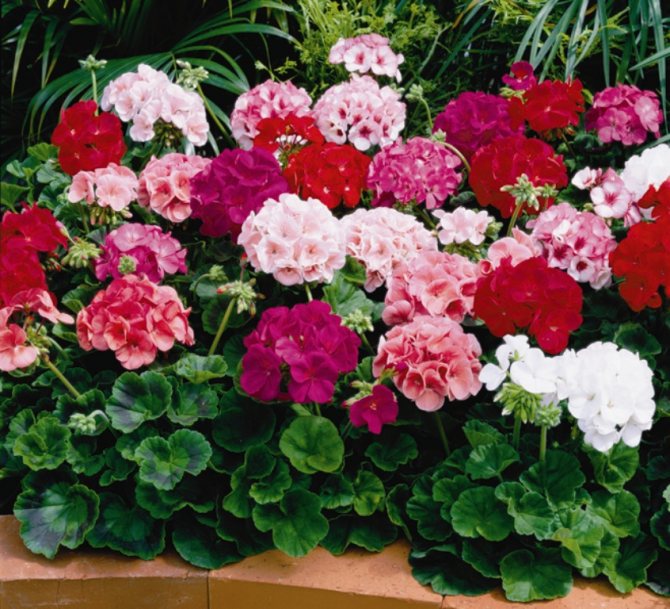
- Pelargonium is zonal (varieties, we will consider a photo later). This is the most common and unpretentious type. It is perfect for breeding both on the windowsill and in parks and gardens. The zonal pelargonium leaf has a clear pattern. The shrub is very resistant to drought and other critical conditions. Even frost up to 5-6 0С is not terrible for him. Therefore, it is so popular among flower growers.
Having studied all the varieties of pelargonium, we can conclude that it is best to give preference to the zonal species.


Plant care at home
Caring for zonal pelargonium will not cause much trouble. This plant is perfectly adapted for indoor conditions in winter and outdoors in summer. One has only to observe the simple conditions of detention - in time to inspect the plant for parasites, thin out the leaves and remove faded flowers.
Lighting
The homeland of the flower is a region with a lot of sun. Pelargonium is a light-loving plant, but it can also withstand partial shade. In the shade, the flower stretches, the foliage acquires a pale color, the flowering period is reduced or cannot bloom at all.
Even in winter, during the dormant period, it is necessary to provide good lighting, otherwise the plant will stretch out strongly, the leaves will turn pale, in the lower part of the trunk they will disappear, become sparse, the stems are bare.
Temperature
Compliance with the temperature regime and ensuring a dormant period will help to get an early and long flowering. With the onset of cold weather (zonal pelargonium is able to withstand up to 5-6 degrees), the flower is taken into the room. For wintering, a cool, well-lit room is suitable, where the temperature will not drop below 10-14 degrees. This will allow flower buds to form and obtain lush, timely flowering, as well as slow down the growth and development of the plant, not allowing it to stretch too much.
Watering
Pelargoniums in the wild live in regions with an arid climate, they are able to tolerate short-term drought, accumulating moisture in the fleshy leaves. But waterlogging can lead to the death of the plant. To ensure optimal conditions during transplanting, a good drainage layer must be placed on the bottom of the pot. It is not worth watering a lot, but regularly so that the soil has time to dry out completely.


Air humidity
Since the natural habitat of the flower is a region with a dry climate, pelargonium easily adapted to indoor conditions. In winter, when district heating is in operation, the air can become too dry. This will manifest itself in yellowing and drying of the tips of the leaves. In this case, it is undesirable to spray, drops of water on the leaves and stem of the plant can lead to rotting. Better to put the pot on a tray with water and pebbles. You can place a container of water next to the pot.
Fertilizing
At different times of the year, a different complex of fertilizers is required. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers will help to wake up after hibernation, wake up the kidneys and gain fast and lush growth of green mass. In April, the plant must be prepared for flowering. To do this, from the beginning of the month, it is better to use phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.
Pruning
Zonal pelargonium tolerates pruning well - to get a lush and abundantly flowering bush, pruning must be carried out twice a year. The most important pruning is autumn, it is carried out after an active growing season in the second half of September or in October.
The plant is pruned to 1/3 or 2/3 of the total height.
Pruning in spring is cosmetic, it is done if the plant is very stretched during the winter. It should be done very carefully. Pruning too much in spring can rob the plant of its flowering or delay it. You can just pinch the top of the shoot. But at least three buds should remain on each stem.
Trimming is carried out with a sterile tool (blade or clerical knife) at an angle. The cut site must be treated with charcoal or cinnamon powder.
Soil: composition, characteristics
The soil for the flower should be loose and not oversaturated with nutrients. It should not contain moisture-retaining substances such as sphagnum.
A composition of:
- 2 parts of sod land;
- 2 parts of humus;
- 2 pieces of leafy land;
- one part of peat and sand.
It is imperative to have a drainage of at least 2 centimeters - from expanded clay, broken brick or fragments of clay pots.
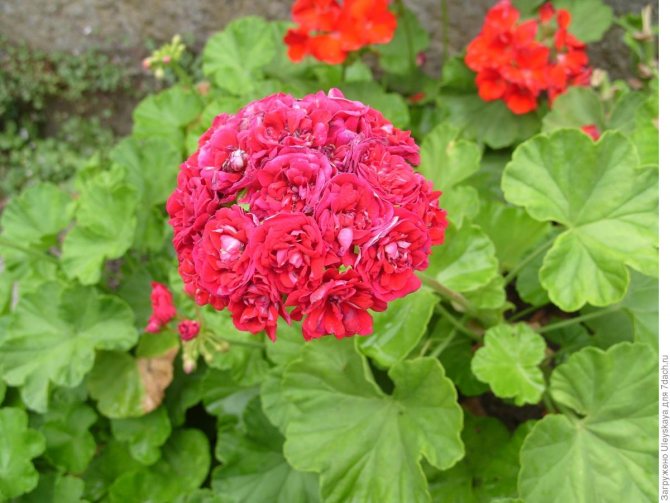


What are the varieties of zonal pelargonium?
In order to easily navigate when buying, you need to know the main varieties of this plant.
By height:
- From 42 cm in height are called tall.
- With a height of no more than 40 cm, they are medium-sized.
- Less than 12.5 cm - undersized.
By petals:
- Up to five petals per flower are simple.
- 5 to 8 petals are semi-double.
- More than 8 petals are terry.
By the form of flowering:
- Bouquet - standard umbrella-shaped inflorescences.
- The stellate ones have pointed teeth on the petals.
- Cactus-flowered with narrow petals, which are similar to dahlias.
- Phloxoflores are distinguished by two shades in one inflorescence - white and crimson at the edges.
- Tulip flowers correspond to the name and resemble a bud in shape.
- Pink-colored. Their flowers are very reminiscent of rosebuds.
- Carnation flowers can be compared in inflorescence with a carnation due to the dissected wavy edges.
Leaf color and shape:
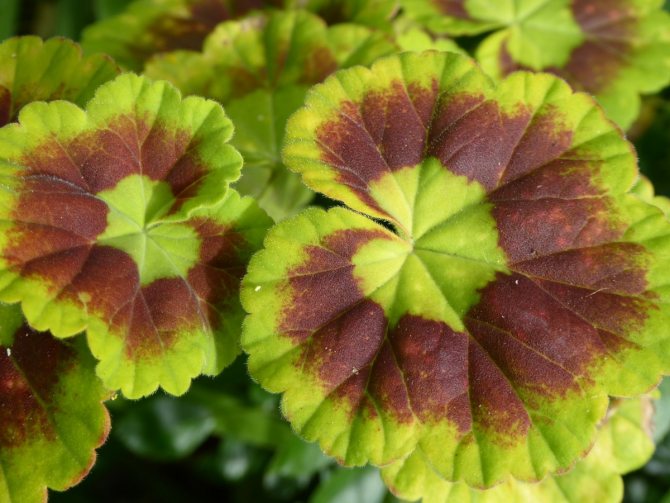
- Green. The leaves are special in that they have circles either a shade darker or a shade lighter than their own in the form of a horseshoe.
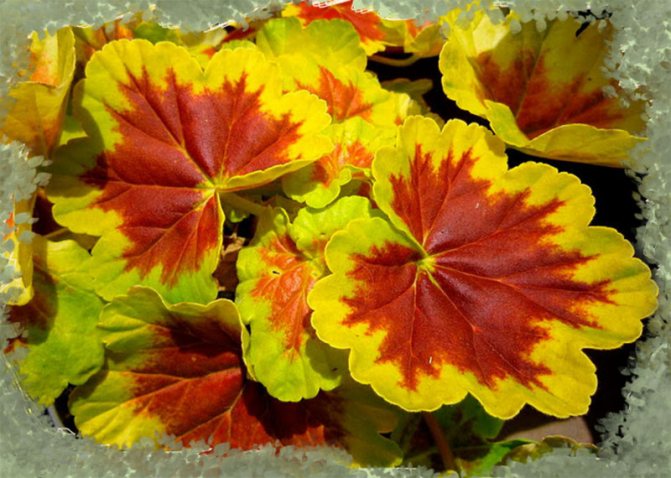
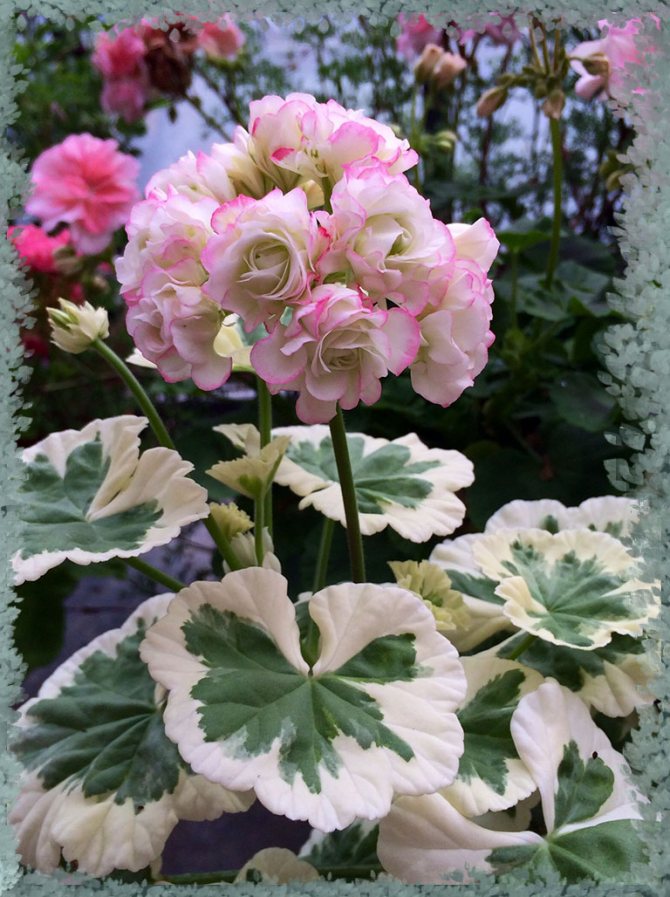
- Variegated. This variety breaks down stereotypes about flowers, as it is grown not because of beautiful inflorescences, but because of the beauty of the leaves. They have a very bizarre color and shape. The color of the leaf excites imagination - it can be pink, bronze, yellow, etc.


Popular types and varieties of royal geraniums with photos
Varieties are conventionally divided into some groups:
- Candy Flowers;
- Angels.
The first group includes large-flowered varieties:
- Cambi - this variety has delicate flowers. They consist of two flowers that have light streaks and a speck on the petals.
- Camred - a variety characterized by cherry blossoms. There is a black spot on the petals.
- Camdared - a variety characterized by dark red flowers. The reverse side of the petals is light.
The second group of Angels includes undersized varieties. They are characterized by flowers that resemble pansies. These include the following varieties:
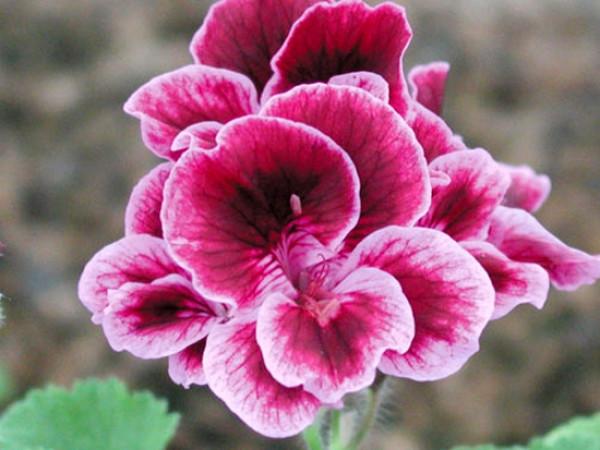
- Spanish angel - a variety with bushes up to 35 cm. Flowers are medium, two-colored. The flowers are dominated by dark red petals with the lower ones - lilac.
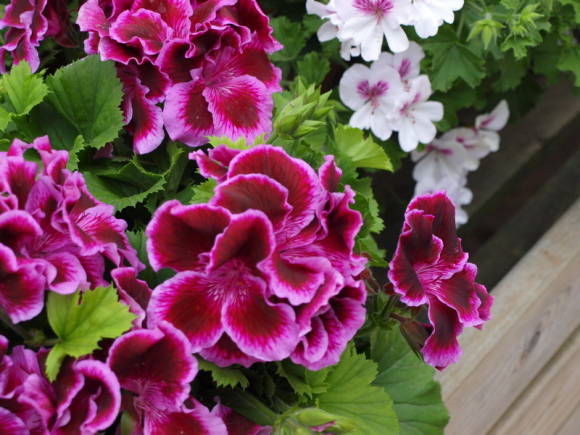
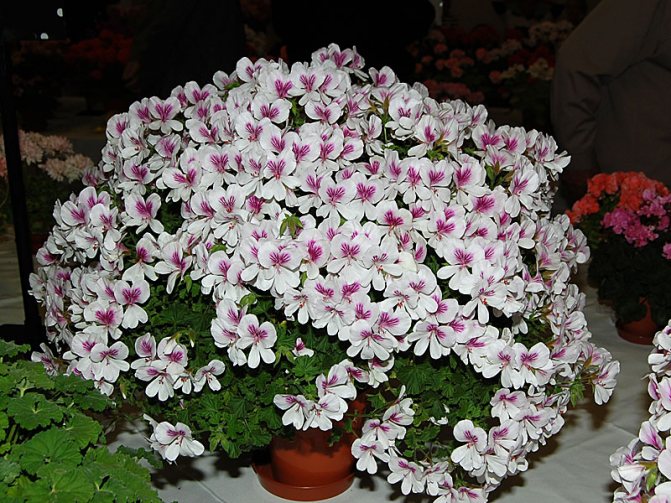
- Imperial butterfly - a variety in which the plant height is 30 centimeters. The flowers are white and the edges are pointed in fuchsia.They have a lemon scent.
- Darmsden - a variety where plants reach a height of 30 centimeters. The leaves are rounded. The flowers are bicolor: the upper petals are cherry and pink, the lower ones are white.
- PAC Angeleyes Viola - a variety that is characterized by abundant blooming of pink flowers. Crimson spots on the petals. The leaves smell of a delicate citrus scent.
And also there are such varieties as: Ann Hoystead, Askham Fringed Aztec, Georgina Blythe, Joy, Lavender Grand Slam, Rimfire, Sefton, Mona Lisa, Morvena.
Varieties with photos:
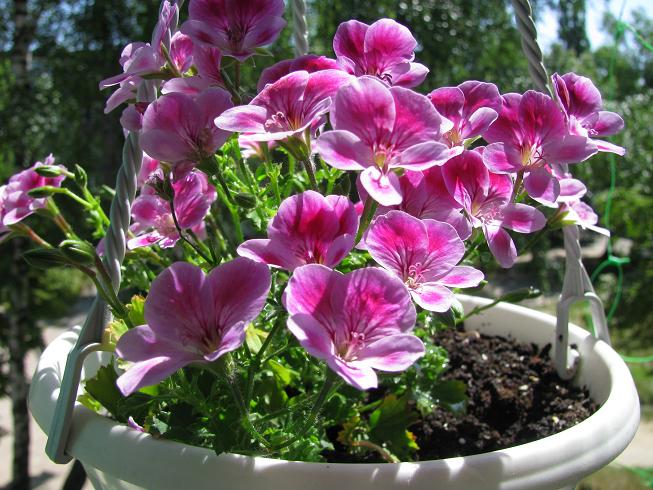


PAC Angeleyes Viola


Darmsden


Imperial butterfly


Imperial butterfly


Spanish angel
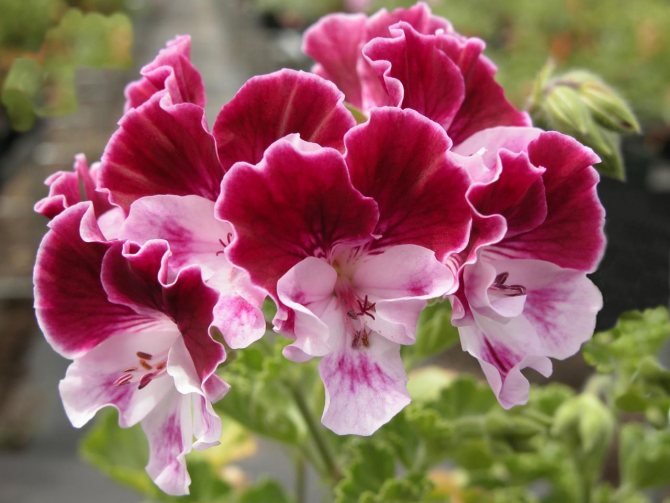


Camdared
The best varieties of zonal pelargonium: photos, reviews
- Raphael. The plant is distinguished by beautiful, compact, well-branched, strong, dense and dense bushes. Lush and beautiful balls have a very rich color palette. The hybrid grows quickly and easily from seed. The first shoots begin to appear after 1-1.5 weeks. Pelargonium zonal Rafaella grows both as an indoor potted flower, and on well-lit balconies, and as an annual in garden flower beds. The plant has good resistance to heat, tolerates short-term temperature drops well. Planting zonal pelargonium for seedlings is carried out in January-March.
- Chandelier Mix. A magnificent perennial compact plant with large flowers collected in spherical inflorescences. The leaves are rounded. Flowers of a wide variety of shades. Pelargonium zone Chandelier Mix prefers sunny places and loose, fertile soil. It grows well both at home and in the open field.
- White. A very delicate and beautiful plant that can add lightness and charm to any garden. White zoned pelargonium is a short plant, the stem of which is only up to 30 cm. It grows well at home in pots and in flower beds.
Pelargonium zonal reviews received the most positive. This is a real decoration of apartments and front gardens.
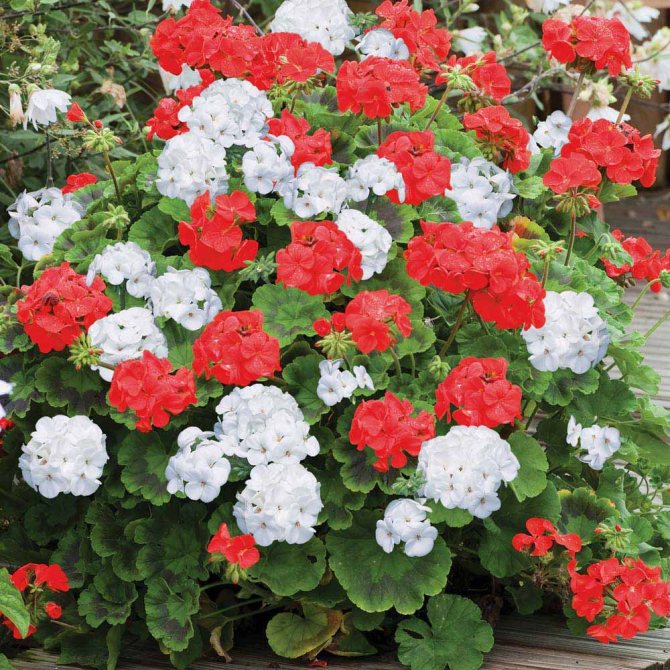


Planting large-flowered pelargonium
Alpine violet flower care at home
Pelargonium large-flowered is very demanding in terms of care and conditions of detention. Therefore, novice growers need to take this into account. Failure to comply with the basic requirements of the culture can lead to the absence of buds throughout the season.
For the plant, it is necessary to select small pots with drainage holes, the volume of which will be 2 times the root system.


Large pots cannot be selected for the royal variety
Site selection and lighting
Royal Pelargonium needs good lighting. Therefore, it is recommended to place the flower pot on the lightest windowsill in the house with light shading from direct sunlight so that burns do not appear on the leaves.
In winter, for the full development of the bush, it is necessary to provide at least 10 hours of daylight. Therefore, phytolamps should be turned on in the evening.
Important! With a lack of light, the flower does not form buds, but its shoots stretch out.
Priming
For the royal variety, you should purchase a substrate intended for growing pelargonium. It has good moisture and air permeability and a balanced composition. In the absence of such a soil in the store, you can prepare it yourself by connecting the following components:
- 1 part - turf;
- 1 part - humus;
- 1 part - sand;
- Part 1 - peat.
Before planting, expanded clay should be laid on the bottom of the pot with a layer of 1.0 cm. And then sprinkle it with a nutritious substrate. Place the flower in the center of the container without deepening the root collar and fill the resulting voids with soil.
After planting, water the plant abundantly and put it in a shaded place for 2-3 days.
How to plant?
Florists actively practice two types of reproduction of pelargonium: cuttings and with the help of seeds.
- Cutting propagation. This is the most popular way that even a beginner can handle.At the same time, the characteristics of the variety remain the same. First, you need to cut off the upper part of the shoot by 5-15 cm. All lower leaves and peduncles are removed from the finished cutting. The site that was used for cutting needs to be air-dried for several hours. Provided that the leaves on the shoot are too large, it is allowed to cut them only in half. For rooting, it is quite possible to use an ordinary glass of water, but a mixture of peat, perlite and sand will be more priority. The prepared soil must be periodically moistened, but always monitor the stagnation of moisture and this should not be allowed. Light must necessarily fall on the roots, and the temperature must be warm. Complex fertilizers will help strengthen the sprouts. In the future, it remains only to transplant the grown culture into a pot.
- Cultivation of zoned pelargonium from seeds. If, when using a cuttings for propagation, you can be completely sure that all the maternal characteristics will be preserved, in the case of seeds this does not always work. Mostly crossed shrubs of two varieties grow. In order for a container with seeds to give shoots, it is necessary to keep it warm with a temperature of about 20-25 ° C with diffused light. Covering is not required, but be sure to periodically moisturize. In a couple of weeks, the first shoots should already appear. As soon as two pairs of small leaves are cut through them, the seedlings can be safely transferred to full-fledged pots.


Growing and care
Favorable conditions
For the growth and flowering of a plant, not so much is needed - proper watering and sufficient lighting, and your pelargonium will delight you with lush flowering for a long time.
Lighting
In order for the plant to grow and form a lush green crown and abundant inflorescences, it needs bright light 4-8 hours a day, the ideal place is the south side.


On hot days, the plant should be darkened to avoid sunburn. In summer, it is optimal to maintain a temperature of 20-23 degrees during the day and 12-15 at night.
In winter, it is optimal to keep the flower at a temperature of 12-20 degrees. Blooming geraniums must be protected from drafts and from contact with cold glass windows.
Watering
Watering should be regular and dosed, since if there is too much water, the roots may start to rot, if there is not enough water, the leaves will wither and turn yellow.


It is necessary to water abundantly only after the topsoil dries out. In winter, you can water once every half a month.
There is no need to spray the plant because it is tolerant of air humidity, and water on the leaves can lead to unsightly stains.
In winter, when the air in the apartments is dry, the plant should be placed on a tray with expanded clay, which is important to periodically moisten.
Transfer
Pelargonium zonal grows quickly enough, so periodic transplantation into a new, more spacious pot is required.


You can transplant the plant at any convenient time from spring to autumn. When kept in open ground, the plant should also be transplanted into a pot for the winter and brought indoors.
Young plants should be transplanted into slightly larger containers a couple of centimeters in diameter. Adults - in pots of the same volume, changing only completely the soil mixture, which usually includes peat, loamy soil, sand, perlite and charcoal.
Pruning
Flowers appear on young shoots, so it is important to carry out pruning in a timely manner to form the crown, if it is not carried out, the plant will stretch out and lose its decorative effect.


Since the plant grows very quickly, it is important to prune and pinch the plants regularly.
Reproduction of pelargonium
In the conditions of indoor and garden floriculture, zonal pelargonium is propagated mainly either by cuttings or by seeds.
Cuttings
Propagation by cuttings is a simple and popular method.Cutting is also a good option to rejuvenate the plant, while the young plant retains all the species characteristics of the mother.


As cuttings, you can use the shoots left over from pruning the plant. For the cutting, the tip of the shoot 5-15 centimeters with a leaf knot is suitable, it is necessary to cut it below it by 0.5 centimeters below the knot.
- From the cutting, you need to cut off all the remnants of the lower flowers and leaves, if they are preserved.
- Dry the cut of the cuttings in the air for a couple of hours and root in water or soil (a mixture of peat with sand).
- The soil with cuttings must be kept moist as it dries, but water must not be stagnant. Roots usually appear in 10-14 days.
- The hardened seedlings are fed with a complex of fertilizers, and after a while they are transferred into permanent pots.
Seeds
Growing from seeds cannot guarantee the preservation of the species characteristics of the plants. It is better to plant pelargonium seeds at the end of winter, then in spring the sprouts will gain strength and in the summer they will be able to please with flowering.


In general, seeds can be planted at least all year round.
The seeds of the plant themselves are large enough, oblong in shape and have a dense shell.
Therefore, before planting, it is better to carry out the scarification procedure - to grind the planting material with a file or sandpaper, soak the seeds in water at room temperature.
This will speed up the germination procedure by 10 times. If you buy seeds in a store, then you can skip the preparation, they already sell processed material for planting.
Seeds should be sown on a mixture of peat soil and perlite, which must first be sterilized. And sprinkle on top with a layer of a couple of millimeters.
For rooting, the seeds should be kept warm, with diffused lighting, regularly watered with a spray bottle with water dissolved in it Biohumus for seedlings.


The first sprouts hatch in a couple of weeks. Young plants should dive into separate pots after the appearance of two pairs of leaves.
Germination devices
Good for seed germination regular cotton pads... To create the necessary structure for germinating seeds, it is necessary to wet one disk well with water, put the seed on it, and cover it with another cotton pad.


Place this device in a container with a lid and transfer to a warm place. Periodically, you need to ventilate by opening the lid of the structure, and daily check for hatching seeds. As soon as a sprout appears from the seed, it should be planted in a previously prepared substrate.
Subtleties of lighting and temperature
In no case should there be a lack of light for this beauty. Otherwise, it will leave you without flowers and will delight you with a half-empty stem with small leaves. To get the opportunity to observe the chic hat and fragrant flowers, you need to pick up the pot in the brightest place, for example, the south side of the house. But, if, after some time in the sun, faded yellow spots began to appear on the leaves, then you must definitely add shadows. In winter, small lamps are suitable for good lighting.
The heat is harmful for a little beauty. She will not stand the 30-degree heat. The standard for pelargonium zonal F1 is stable +20 degrees, maximum +25. Drafts and cold glass are also enemies for the plant.


Transplant and fertilization
Due to the accelerated growth of zonal pelargonium, it is necessary to immediately take care of the possibilities of transplantation. From spring to autumn is the most optimal period for this. If the culture is grown outdoors, then in the cold season, starting in autumn, you will have to transplant it into pots and keep it until summer, until the soil and air are sufficiently warmed up.
In fertilizers, pelargonium is not particularly picky, so a universal complex of fertilizers for tomatoes or flowering plants is quite suitable for it. The only thing that needs to be checked in the composition is a low content of substances such as phosphorus and potassium, and a minimum of nitrogen. After transplantation, it is not recommended to fertilize the culture for another 1.5 months. In the cold season, it is enough to fertilize the soil about once a month.
Botanical description and history of origin
Pelargonium Grandiflora is a small bush that, during flowering, is completely covered with lush buds. Sometimes, the variety is called English, although to this day, it is not completely known where it came from. In England, the flower is known as the "royal" variety or "exhibition", and in the USA it is called "Lady Washington".
The plant is very much appreciated by flower growers all over the world. Most of all are attracted by large, immediately striking flowers. The scent does not come from the buds, and the flowering period does not differ in its duration, only about 3-4 months.
Diseases and pests
Even if pelargonium has grown to its full potential and began to bloom, sooner or later pests may begin to attack: ticks, worms, aphids and other insects. Then you need to immediately save the flower with the help of special preparations. The main thing is to notice the damage in time. The most common pest that attacks pelargonium is white butterflies, which are called whiteflies. They lay the larvae on the underside of the leaf, so it is difficult to notice them at a glance. Soapy water is a great weapon. To do this, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the flower and wrap it in plastic for several days. If the damage is too strong, and it is no longer possible to cope with it with improvised means, you can use "Aktar", but only strictly according to the instructions.
The black leg is the trouble with most young plants. It arises due to the fact that the conditions of care were not followed. For example, too frequent watering or low air temperatures may well contribute to the development of this disease. The same unpleasant disease is mold. The most important thing is to take rescue measures in time: remove all damaged leaves and flowers to prevent the spread of infection. And a solution of fungicides will help to destroy the infection.