To the questions of gardeners about what to do if bedbugs on tomatoes appear en masse, how to deal with pests and how dangerous they are, there are quite reassuring answers. The invasion of bedbugs on tomato bushes is a temporary phenomenon, and insects cannot cause too much harm. But it is necessary to carry out protective measures, since the pests will soon scatter around the site and begin to attack those crops on which they are most used to parasitizing.
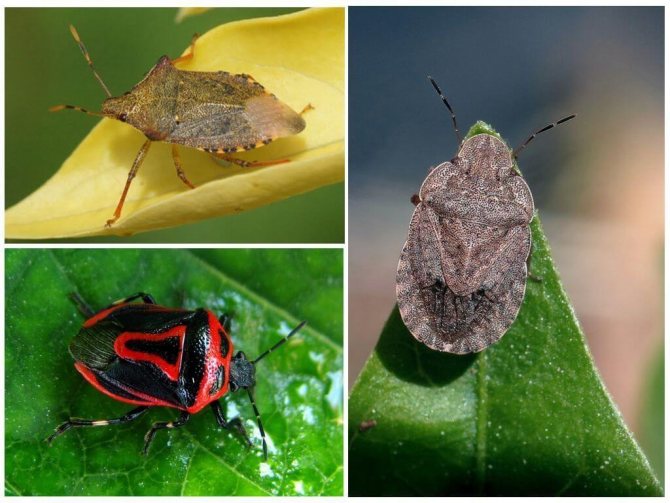

There are many ways to deal with tomato bugs.
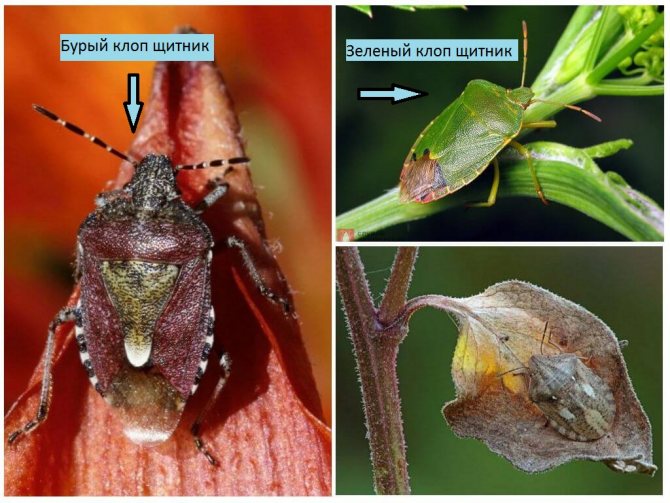
Description of garden bugs and types
In a large number of species of herbivorous bugs, 2 families are distinguished, which is almost impossible for a non-specialist to distinguish between representatives. They are called shit bugs and turtles. Most representatives feed on plant juices, although there are predatory species that prey on Colorado potato beetle larvae.
Most of the harmful species are brown or green in color, which helps them to camouflage against the background of foliage and plant bark.
But there are also variegated, brightly colored representatives, for example, cabbage and line bugs, parasitizing on cruciferous garden crops and eating flowers of umbrella plants.
Tips from experienced gardeners


Considering how many diseases can threaten tomatoes when growing, it is best to try to avoid problems by looking after and caring for the plants. Those who have been planting tomatoes on the site for more than one year have accumulated their secrets and are ready to share them:
- It is better to prepare the soil for seedlings in the fall and keep it in the cold so that it freezes thoroughly. This contributes to the death of pathogenic flora.
- A week before transplanting into the ground, the seedlings need to be treated with Bordeaux liquid, and the day before planting, shed with a manganese solution.
- Starting from the second half of June, in the morning on tomatoes, 2-3 leaves should be removed every week until you reach the first ovary. This is necessary in order to reduce the load on the bush and prevent the outbreak of fungal diseases. Old leaves are no longer needed by plants.
- Watering is best done in the morning at the root, so that the surface of the earth has time to dry out before the evening.
- To reduce excess air humidity in the greenhouse, mulching or covering the soil with a film will help. The building must also be regularly ventilated. Condensation must not accumulate on the walls.
- Systemic fungicides can be used outdoors, not only for treatment, but also for prevention. They begin to use them at the seedling stage, and finish 2-3 weeks before harvest. In this case, the tomatoes will be under reliable protection.
Varieties
Among the bugs crawling on tomatoes, there may be the following types:
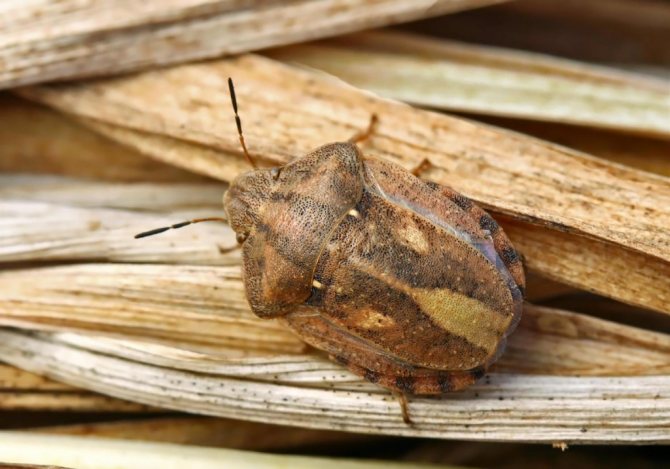
- Harmful turtle. It often feeds on cereal juices and threatens only their crops. It enters the garden with rye seeds, if it was used as a green manure, it can fly into the summer cottage from neighboring fields in the rural area. It does not harm tomatoes, but it can spoil the planting of corn, which is sometimes grown in summer cottages. The beetle is rounded, brownish-brown in color, with a masking “tortoiseshell” pattern of blurred stripes of dark and light shades.
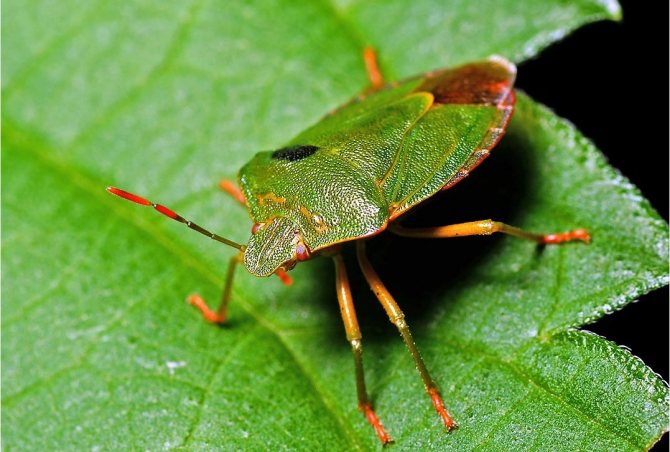
- Green bugs. The body shape is reminiscent of the previous pest.The main habitats are planting raspberries, fruit and berry crops in the garden, woody forest vegetation. Parasites pierce leaf veins with proboscis and suck the juices of young shoots, depleting plants during mass reproduction. They fall on tomatoes by accident. The main harm is the appearance on tomatoes of a characteristic unpleasant odor, which is difficult to wash off the fruit. Bedbugs give off a smelly secret in case of danger.
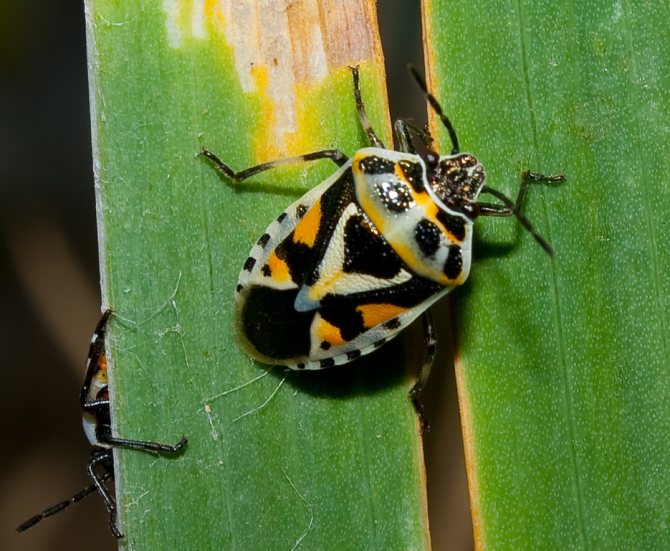
- Cruciferous, or cabbage. The pests resemble a soldier bug: the alternation of red and black spots creates a different pattern, but at a quick glance, the insects are similar. In addition to the red form, there is a yellowish one, with a less bright color. On tomatoes they parasitize slightly, they are more attracted by the sweet juice of cabbage, beets, etc. Sometimes horseradish leaves are also severely damaged.
- Marble bug, or stinker. It has a color corresponding to the name, grayish-brown, with light shades of stains. It is considered a tropical species, but in 2006 it has already spread to the southern regions of Russia. It penetrates into the middle zone of Russia with vegetables and fruits from the Krasnodar Territory, it is able to acclimatize if the regions keep warm winters. Virtually no harm to tomatoes, but it can damage the shell of young fruits, leaving punctures.
- Perillus. This variety can also be found in tomato beds. The insect is specially imported to combat the Colorado potato beetle and its larvae. Perillus plants are attracted to all nightshade crops by the characteristic plant smell. Guided by it, predators expect to find prey in the form of parasitic beetles. They do not eat vegetable juices. You can distinguish it by the red stripe on the back in the form of the letter V or U (red on a dark background) and 2 round spots on the front of the shield (resembling black eyes on a red background).
What harm do insects do
While extracting food, the parasites attacking tomatoes pierce the cells of the plant with a long, narrow proboscis, drawing juice from them. At the same time, they inject enzymes that increase the viscosity of the liquid.
Bacteria enter through the puncture, the site of the bite darkens, and necrosis of the fetal tissue begins. As a result, the plant quickly dies, becomes lethargic, stunted.
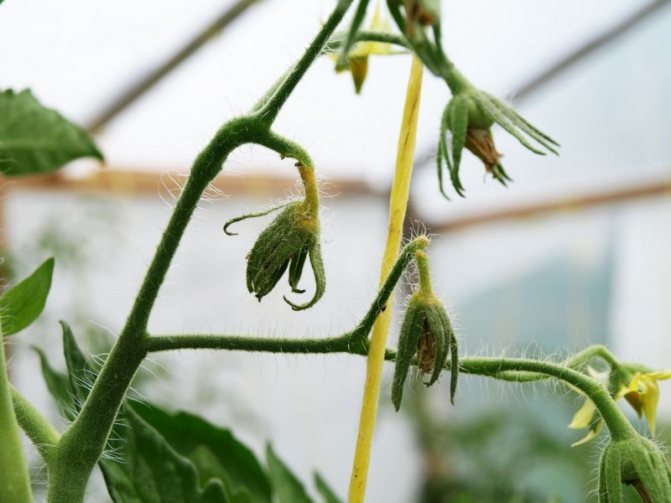


Single insects will not harm tomato fruits, they may not even be noticed right away. The first sign of the appearance of these parasites is yellow, whitish spots that appear on the skin of tomatoes. By cutting a tomato at the bite site, you can see a brown, dense tissue.
If there are many such spots, there will be no other methods of treatment, except for the cardinal removal of parasites.
Appearance and lifestyle
The size of bugs of different species and in different stages of development varies within 0.5-2 cm. The shape of the body of garden parasites is rounded, in adults it is oval, sometimes with a narrower rear part. It is possible to distinguish larvae from adults by the presence of wings in the latter. In any phase of development, insects move actively, crawling over the leaves and fruits of tomatoes.
Only adult specimens hibernate. When the first shoots of greenery appear, they wake up and fly to places rich in fodder plants. At the same time, the breeding period begins.
After mating, the female lays eggs, from which the larvae of the first period hatch within 1-2 weeks: small bugs of greenish or brown color. They grow actively, feeding on plant juices. The larva molts 5 times, and then turns into an adult, capable of reproduction and flight. A large accumulation of larvae on tomato bushes is most often caused by the presence of plants in the beds on which bedbugs feed: weeds or other suitable grasses.
Most bugs avoid the pungent smell of tomatoes and rarely settle on them. But in the absence of suitable nutrition, the larvae are able to suck juices from young shoots or tomato fruits. At the same time, small puncture points appear on them, surrounded by dried tissue.
In rainy weather, spores of pathogenic fungi that cause diseases (late blight, fusarium, etc.) can penetrate into such punctures. The main harm from bedbugs is most often only this.
Preventive measures
The main measures for preventing the appearance of bedbug larvae on tomatoes and other plants are cleaning the territory of the garden or greenhouse in the fall. So adult pests will not have the opportunity to winter on the site, and they will leave the garden in search of fallen leaves and other shelters.
In the garden, on open ridges, all tops and weed residues are collected and burned. If possible, the soil should be dug up: larvae of other pests and weed seeds will die. In the greenhouse, the remains of the plants are collected and taken out. All surfaces are treated with solutions of Karbofos, bleach or sulfur bombs are ignited.
Previous BedbugsHow to find out if there are bedbugs in the apartment Next BedbugsHow to choose the most effective and inexpensive remedy for bedbugs
How to detect?
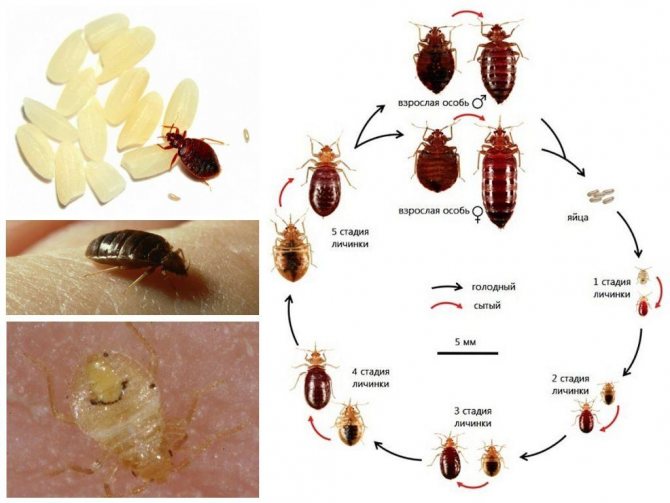

Stages of bedbug development.
The insects are large enough to be seen on any part of the bush: they crawl through foliage and unripe tomatoes.
Varieties with a green color are almost invisible if immobile, and they can be detected when picking tomatoes or caring for plants, accidentally disturbing the insect: it emits a liquid with a strong unpleasant odor.
Black and white and brownish larvae do not blend well with the background and attract the attention of the gardener.
What will happen if you do not get rid of pests
Are you ready to give pests part of your crop? Surely, you were not pursuing such goals when, on dark winter evenings, you warmed and illuminated the just-risen tomato seedlings. Leaving everything to chance and not fighting pests is an inexpedient and dead-end path. for those who count on results.


It is imperative to get rid of the "saboteurs" so that:
- the harvest of the current year was not affected;
- the soil did not become unusable for planting in the next season.
How to deal with them?
With a small distribution of larvae and adult insects, it is easiest to collect it by hand, shaking it off the branches into a jar.
After they should be destroyed, so that they do not move to those plants that can damage more.
Integrated control combines a chemical method (for example, Phosphamide), agrotechnical (includes measures to destroy places of probable wintering) and scare away. For the latter method, tomato stepchildren and leaves are often used if the bugs eat other cultivated plants. It is easy to ward off the parasites from the tomatoes themselves with the garlic and onion aroma.
Tomato processing rules
When choosing agents for chemical treatment, it must be remembered that stink bugs are almost insensitive to pyrethroids (deltamethrin, permethrin, cypermethrin). To get rid of them, they use products with phosphate compounds (they often contain a part of "phos" in the name). Most of these agents are classified as highly toxic compounds for humans.
When processing tomatoes, spraying times must be observed:
- it is safe to process before the formation of tomatoes;
- it is undesirable to spray when the fruits begin to ripen;
- the last use of pesticides must be made at least 20 days before harvest.
Tomatoes sprayed from bedbugs should be rinsed well in running water before use.
Chemicals
When choosing insect repellents in the garden, you need to carefully read the information on the package. To remove shield bugs from tomato plantations, preparations against sucking varieties are suitable.
Available means for treating the garden from bedbugs:

Mixing karbofos solution.
- Chlorophos aerosol: it effectively destroys pests, but is considered toxic to humans. Processing is carried out only at the beginning of summer, when a large number of larvae begin to appear on young bushes. Spray on the top and bottom of the leaves. It is undesirable to carry out processing during the flowering period: bees also suffer from the poison. Brushes with small ovaries are treated prophylactically in order to destroy the larvae if the bugs have laid eggs somewhere.
- Other household aerosols (Dichlorvos, Karbofos, etc.) are also quite effective against bedbugs, they are used as analogues of Chlorophos.
- In addition to aerosols, these drugs are also produced in powder form. It can be dissolved in water according to the instructions (20 g per 10 L of water, unless otherwise specified) and spray the plants with a spray bottle or garden sprayer.
- Phosphamide is a liquid agent in ampoules. 10 liters of working solution will require 2 ampoules of the drug.
- Aktara is a granular preparation from the group of neonicotinoids. It is effective not only against bedbugs, it is also capable of destroying other sucking and leaf-eating pests. Applied both by application to the foliage (spray bottle) and by simple watering under the root (solution of 8 g of the drug per 10 l of water). With the latter method, it remains toxic for up to 60 days, getting not only in the leaves, but also in the fruits. When spraying, it works for 14-20 days.
- Inta-Vir is a tablet preparation that can be easily diluted in water (2 tablets per 2 l). The composition includes cypermethrin, which is ineffective in direct contact with the body of the scutellor, but is absorbed when sucking the juice. It is not necessary to process the solution with bugs and their larvae, but spray the foliage and ovaries, where the parasites will feed.
Folk ways of fighting
Popular methods include the use of deterrent measures, and the use of means for baiting insects. The main method of getting rid is mechanical.
By collecting and destroying young and adult pests, you can effectively get rid of them for the entire season (while the larvae are small, they will not fly from other places).
To prevent adult parasites from visiting the garden, they use plants with strong odors that drive away bedbugs: garlic and onions. The infusion is prepared from 2 heads of garlic in 10 liters of cold water. Infusion lasts 3-4 days, then tomato plots and other ridges are sprayed with the product. Instead of heads of garlic, flower arrows of the plant are often used, cutting them off when they appear. For 10 liters of infusion, you need about 0.5 kg of chopped arrows.
Onions are used both in the form of onion gruel and in the form of a husk. The gruel is poured with cold water and infused like garlic. A strong decoction is prepared from the husk (0.5 kg of husk per 2-3 liters of water) by boiling it for 15 minutes. The finished liquid is cooled and sprayed on the plants.
A cimicifuga (black cohosh) planted around the perimeter of the garden can also scare off pests.
Solutions of potassium permanganate, saltpeter, applied not under the root, as with top dressing, but sprayed onto the leaves, also help to fight insects:
- Dissolve potassium permanganate in a separate bowl, and then mix with water until a dark pink solution is obtained;
- potassium nitrate is diluted in water at the rate of 5 g per 10 liters of water.
Prevention methods
It is easier to prevent than to cure later. This truth is also true in the gardening business. If you take preventive measures, then the likelihood of pest damage to tomatoes will decrease significantly.
How to prevent pests:
- Carry out pre-planting soil cultivation before planting tomatoes. Spill the earth with boiling water or a solution of copper sulfate (1 tablespoon of the drug is taken per liter of water). It is advisable to dig deep into the soil throughout the entire area.
- Immediately remove plant residues from the area to avoid the spread of pests.
- Observe the crop rotation of the soil.
- Select varieties and hybrids of tomatoes that are resistant to pests and diseases for growing on the site.
Interesting on the topic:
Secrets of planting and caring for tomatoes
How often to water tomatoes in the heat to get a good harvest
What to do when tomatoes grow poorly
How to grow and tie tall tomatoes
How to feed tomatoes during flowering in a greenhouse and fruiting
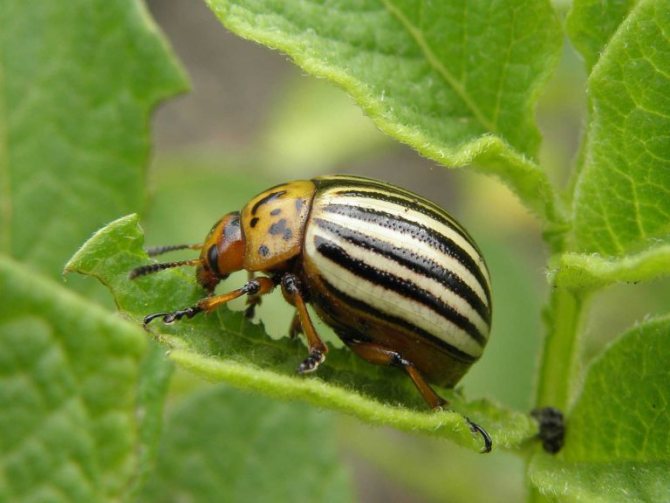
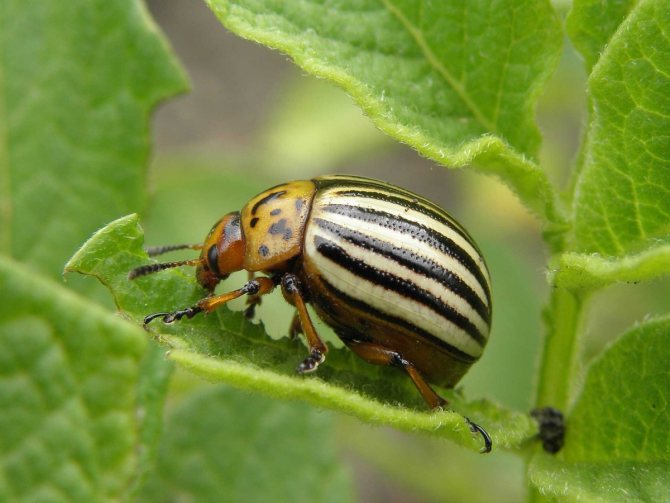
What is the danger of the Colorado potato beetle on tomatoes?
When the Colorado potato beetle appears on tomatoes, it does a lot of harm.
The danger of such an invasion lies in the following factors:
- favorable conditions contribute to the activation of the insect and its reproduction;
- the appearance of larvae leads to the rapid eating of greens;
- the pest successfully adapts to different climatic conditions;
- the beetle is tenacious and gluttonous.
The parasite is extremely quickly able to adapt to insecticides, developing resistance to these substances, so it is difficult to get rid of the Colorado potato beetle reliably using folk remedies or other methods. Dealing with it is quite problematic.