The main / Flowers and plants / How to properly preserve cuttings until spring, or a second life for a rose
No wonder the rose is called the queen of flowers. This plant is so beautiful that it can decorate any garden and flower bed.
Experienced growers know exactly how to care for and breed this plant.
There are several ways to propagate this flower, but experts recommend turning to the grafting method, supposedly it is the easiest and most effective.
Indeed, it is much more convenient to plant a royal flower with cuttings.
However, this method has certain nuances, which we will talk about below.
So, if you have been looking for a step-by-step guide on how to prepare and save rose cuttings for the coming spring season for a long time, then consider that you have found it.
Choosing the "right" cutting
If you think that any shoot is suitable for breeding a rose bush, then you are greatly mistaken.

The main condition for the viability of the cuttings is the absence of damage and diseases in the plant bush.
To increase the rose's chances of future survival and abundant flowering, choose cuttings of medium diameter, much like a drawing pencil.
To make sure that the cat rose bush is ready for grafting, try breaking off the thorns on the branches, if they give in easily, then the plant is ready for propagation. For grafting, only the stem that has several buds or leaves is suitable.
Important! It is necessary to separate the shoot from the bush with a sharp tool. A dull blade can damage the stalk and cause infection.
To avoid this, before cutting the cutting, be sure to wipe the blade with an antiseptic solution or pour boiling water over it.
How to keep cuttings of garden roses in winter - answers of 7dach professionals. ru
How to keep cuttings of garden roses in winter? - Answers from 7dach professionals. Common crawl en Olya, I'm afraid that at this time the game is not much worth the candle. For three reasons. The first reason is that at the moment it is already cold and the day has begun to decline and they will not tremendously strive to take root, since at the biological level they are already falling asleep. The second reason - at + 10 degrees, they will try to germinate in January - February, and this is too early.
The best temperature is still +3 ... + 5 C. The third reason is that native-rooted roses are actually constantly developing in our strip more terribly than grafted ones, no matter what their admirers write and know. There are exceptions, but very rarely. Most often, self-rooted roses develop more terribly and more slowly than grafted ones. In the south, they develop even better and hibernate too, therefore they often take root in this way. In Ecuador and other rose-growing countries, they are only bred for greenhouses. But it is much warmer there and it is actually summer all year round. And in our area there are often snowless winters or powerful frosts in November - December, with virtually no snow.
Such roses freeze out more often than others, it has been checked more than once. But if you are extremely eager to experience, then try. Almost all readers cut the same cuttings of roses before winter. Here, in principle, these cuttings can be perfectly covered with snow and foliage, in the spring they can take root. but I would recommend asking those parents for cuttings.who gave roses, in June - July and try to root them in the summer. Or get vaccinated. taking a bud from these cuttings on a rosehip.
Most likely, those who breed and donate them will even tell you how to do it correctly.
7dach. ru
It happens that there is no time to breed roses in the autumn, or they did not manage to plant and root cuttings of roses, then the question arises of how to save them until spring. I think that seasoned gardeners have long known the answer to this question, and there are many tips on the internet. But since they began to ask me about storing cuttings of roses in the winter, I decided to write this post.
At the word read out, cuttings of almost all other plants can be stored in a similar way.
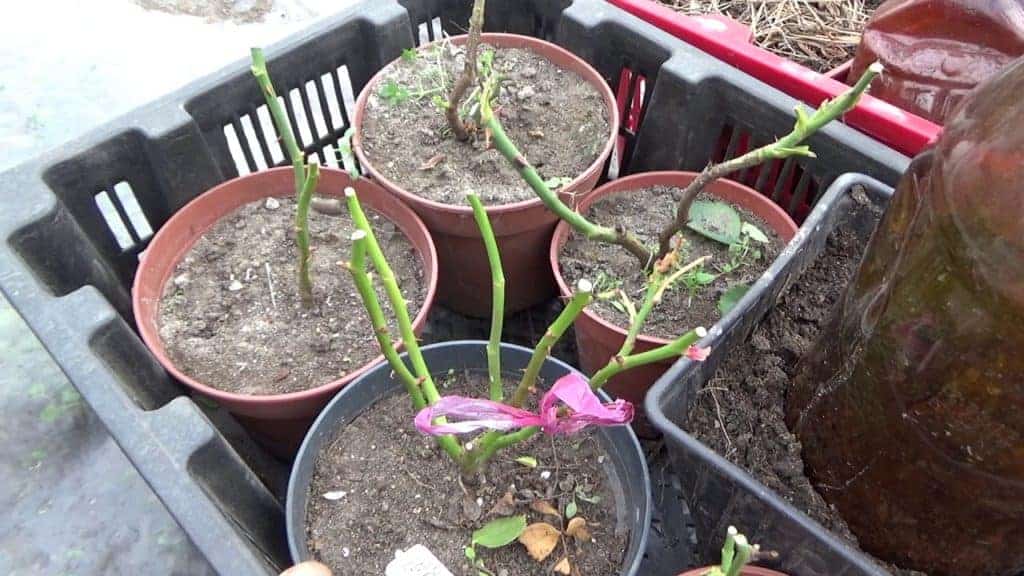
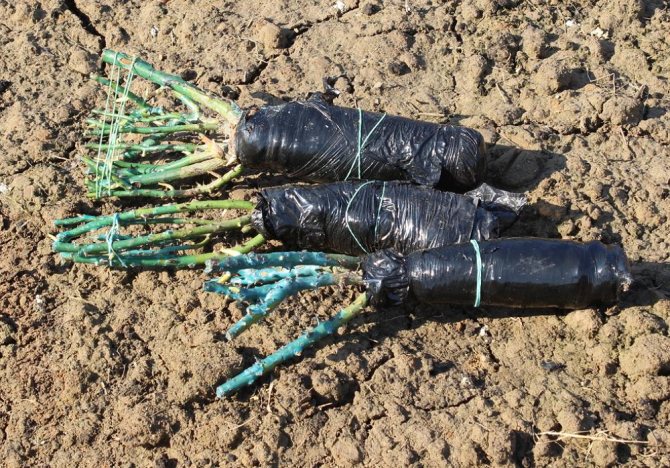
When storing cuttings of roses in winter, three conditions are needed: darkness, certain cold and humidity. The cuttings must be lignified, leafless and at least 20 cm long. The best time for cutting after the leaves fall is during the dormant period of the plant (but not in January).
Sliced blanks are collected together in 10-12 pieces. If you have few of them, then you don't need to tie them into one bundle.
- For example, you can store them in the refrigerator on the bottom shelf, in the basement or cellar.
The main condition will be temperature plus 2-4 ° C and humidity 65-70%. Tie the cuttings together, wrap them in moss and newspapers, slightly spray the bundle with water and put it in a plastic bag.
Check it every two to three weeks. The branches should not have mucus and rot, and the bundle should not be very wet or completely dry.
In this case, wrap the cuttings with burlap or non-woven m, pack in cardboard or other thick paper, a box. Dig it near a berry bush or in a greenhouse. Do not forget to throw snow into the greenhouse from time to time on the place of the "cache", and mark the place of digging with a beacon and cover it with spruce branches and lutrasil.
- I saw (sorry, I didn't take a photo) how the cuttings are stored in the adjoining area like this: they choose a place higher, dig a trench 60 cm deep, put a board 150-200 mm wide on the bottom.
Batches of cuttings of 8-10 pieces of various plants, including roses, are placed across these boards.


The cuttings are not connected to each other. Then they again put boards on them and only later fill the trench with earth. The place is covered with spruce branches. In the springtime, they dig out, select the favorites, some are cut into two parts. If callus has not formed, then they treat the bottom with Kornevin and put it on a spread wet newspaper, and cover it with a wet layer of newspaper and polyethylene on top; so left in a cool greenhouse for two to three weeks. During this time, the cuttings come to life and are planted in the soil.
I store the packaging in a cardboard shoe box, which in turn is placed on the floor between 2 corridors.
Unfortunately, I do not have detailed photos of the work given to us, but what I found, you can look at the extreme picture.
In the spring, I plant the cuttings first in disposable paper cups and only later in the garden.

She wrapped the prepared twigs with a thick layer of newspapers and laid them horizontally so that above and below them there was an approximately uniform amount of space filled with consistency. I wrapped the whole structure with an old blanket, and on top also with a film. I kept it like this until the temperatures above zero, then removed the film. In late winter and early spring, and at a temperature in the loggia itself, approximately from + 5 ° C and above, I removed the blanket.In mid-April, I took out the entire container to the dacha and left it in the greenhouse. I planted it on a separate bed and covered it with lutrasil already on the May holidays.
Prepare the garden bed by digging it to a depth of 13-14 cm. Or use a homemade cuttings that can be installed in any corner of the garden under the shade of the bushes. Before budding, you plant cuttings in it for growing with an interval of 10-15 cm, leaving 2-3 buds above the surface. It is necessary to look after the plantings and compact the earth, if the cutting suddenly sticks out of the ground or staggers - this often happens during the spring thawing of the soil.
When copying the text, please indicate the address of our website.
Step-by-step pruning process
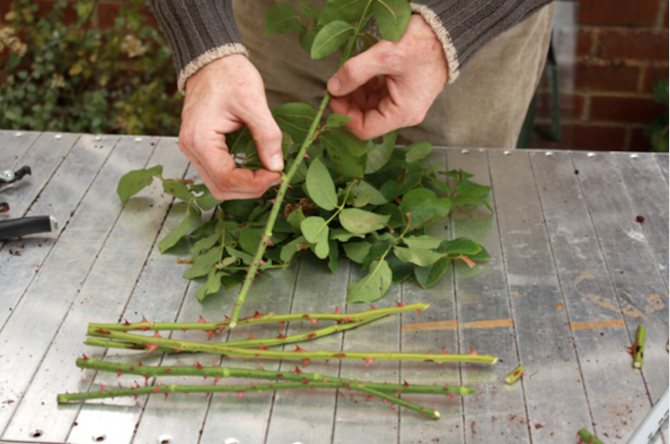
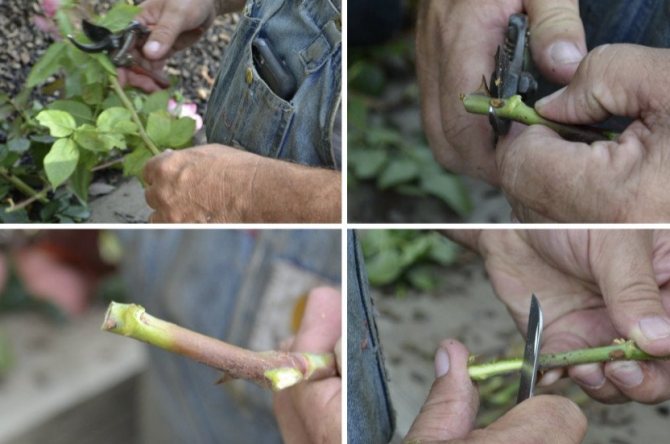
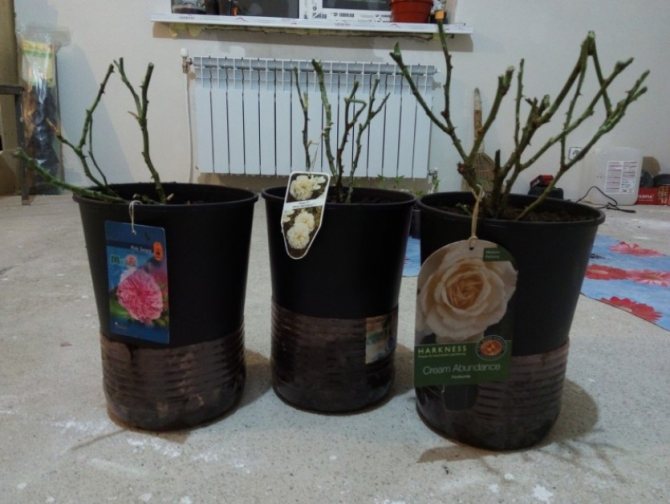
Choosing a shoot with a diameter of 0.4-08 cm and a length of 14-16 cm, carefully cut off the stem.


The top cut should be straight and the bottom cut at a 45 ° angle. Then, tear off all the thorns and leaves on the branch, leaving only a few buds or leaves.
The next step is to stimulate the rooting process. To do this, the stalk is dipped into a solution from Heteroauxin or Kornevin.
If they are not there, then you can use your own preparation. To do this, you will need to mix 200 milliliters of pure water with 0.5 teaspoonful of liquid honey.
Advantages of roses grown from cuttings
- cuttings do not give wild root growth and if for some reason it was not removed, then they will not turn into rose hips;
- plants from cuttings have good winter hardiness, but even if the aboveground part freezes, they are able to recover from dormant buds, in contrast to grafted roses;
- they are durable, growing and blooming for decades.
Small-leaved varieties of roses - miniature, climbing and semi-climbing, with small flowers, ground cover ones - take root most easily during grafting.
Large-flowered climbing, park and remontant rooted poorly, so it is better to graft them.
Time to prune roses
The best time to prepare cuttings is summer. June and July are considered to be the most favorable.


However, if you did not have time to carry out the pruning, then you can reschedule the work in the fall, at the time of seasonal pruning.
Such an early harvesting of cuttings guarantees a high resistance of plants to low temperatures and pests that the flower will encounter next year.
Winter storage of rose bushes
Florists from Siberia, the Urals and other regions with severe winters resort to this method of storage. Every autumn they face the question of how to preserve roses in winter, so that next year they can again please with their flowering.
In winter in Siberia, the air temperature can drop below -35 °, and the spring can be protracted with late return frosts. Therefore, garden roses, especially climbing roses, will not be able to hibernate in the open field under such conditions. Experienced flower growers prefer to dig them up in the fall and place them for further storage in the cellar or basement of a house or summer cottage. Below is a detailed answer to the question of how to preserve roses in winter in Siberia.
We create ideal storage conditions
The secret of whether the cuttings will take root after planting lies in the optimal conditions for storing the workpiece.


First of all, what is worth paying attention to is the temperature regime. It should be stable in the region of + 3 ° to + 5 ° Celsius.
If the temperature drops below, then the cuttings may freeze, the higher temperature will contribute to the awakening of the planting material.
At the same time, the humidity in the storage location should fluctuate within the range of 65-70%.
To prevent the rose twigs from becoming moldy, they must be ventilated once a month, i.e. take out to another room with a different temperature regime.
To exclude the possibility of damage to the shoot, it is necessary to protect it from the possibility of freezing, drying out and sudden changes in temperature and humidity.


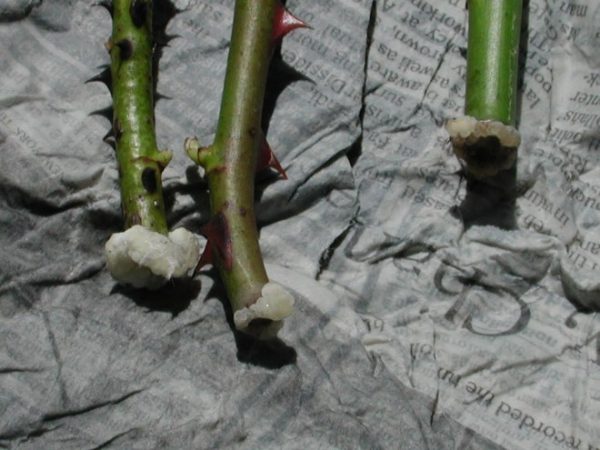
If, however, signs of mold appear on the handle, be sure to rinse the branches in an iodine solution or a product based on copper sulfate. Such disinfection will protect the rose from rotting and the spread of fungus.
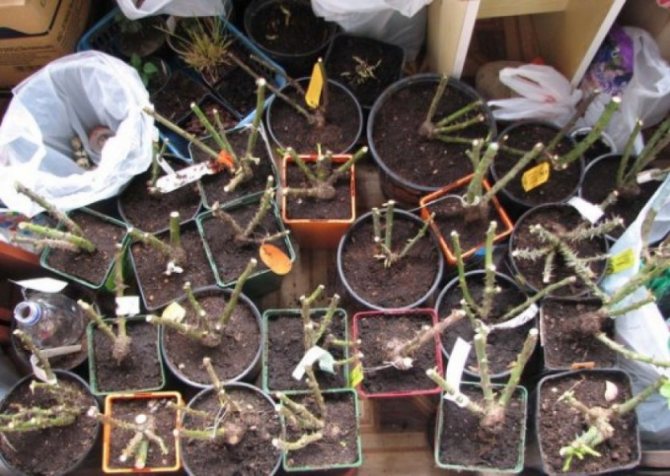
Storage preparation
In order for the cuttings of roses to be well preserved in the cellar until spring, they must be properly prepared. The shoots from which it is planned to cut the planting material must be carefully examined. They must be of good quality and fully ripe. If the core is well defined on the cut of the branch and the subcrustal layer is completely lignified, while the brownish or dark green bark is well separated, then such rose shoots are suitable for cuttings.
The stems must not have:
- young immature shoots and fresh leaves that continue to grow;
- insect pests;
- traces of disease;
- signs of drying out.
Competent preparation before laying rose cuttings for the winter in the basement consists in the following actions:
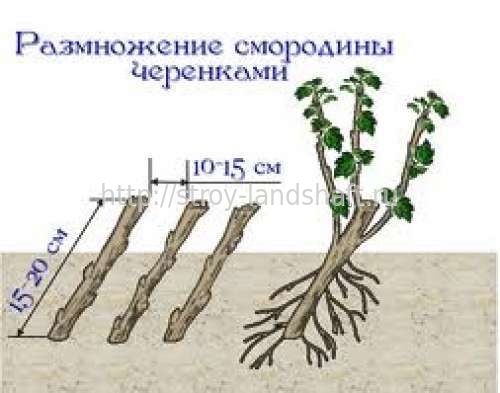
- Planting material is harvested from shoots at least 4-5 mm thick. Sapling length - from 20 cm. It is better to use the middle part of the branch.
- The lower cut of the cutting is made below the last bud at an acute angle (about 45 °). The upper incision is made straight and 2-3 cm above the kidney. A rose seedling should have at least 3-5 healthy buds.
- All work is performed with a sharp tool (knife), which must be pre-disinfected (boiled or wiped with vodka, alcohol, etc.).
- All leaves are removed from the branches.
- It is recommended to treat the cuts with liquid paraffin in order to avoid the germination of shoots and reduce the evaporation of moisture from the surface. At an air temperature within + 2 ... + 5 ° C, they will not start growing.
Cuttings of roses that were planted in summer are also dug up, since their root system is still too weak and they can freeze out in winter. The storage conditions for these seedlings are the same as for fresh cuttings. If the local climate allows, then you can leave them in the ground.


Rose varieties suitable for storage
It is important to choose the right variety of roses for grafting and storage in the cellar, because not all varieties of this culture reproduce well in this way.
Ground cover and miniature, climbing and semi-climbing varieties, as well as polyanthus and hybrid-polyanthus types of roses, which have small flowers, take root best. Their survival rate can reach 90-100%.
When propagated by cuttings of a floribunda rose, no more than 50% of seedlings survive. It is quite difficult to root a large-colored rose of hybrid tea and park varieties with this method, since their cuttings take root extremely poorly.
Where to store the cuttings?
Experienced gardeners offer several options for storing rose shoots. The most popular ones are:
- In the snow. Dig a hole 20-25 cm deep in your garden plot. Cover the bottom with a cotton cloth, put the cuttings on top and cover with another layer of material. Then fill the hole with soil and wait for spring;
- On the balcony. If you live in an apartment and there is no basement nearby, and there is no desire to go to the dacha, then use your balcony.
Take a box with expanded clay, pour a little soil mixture on top and moisten it with a spray bottle.
Plant the shoots treated with a special growth agent in the ground, wrap the box in polyethylene and cover with a warm blanket.
As mentioned above, open the drawer once a month and ventilate the cutting;


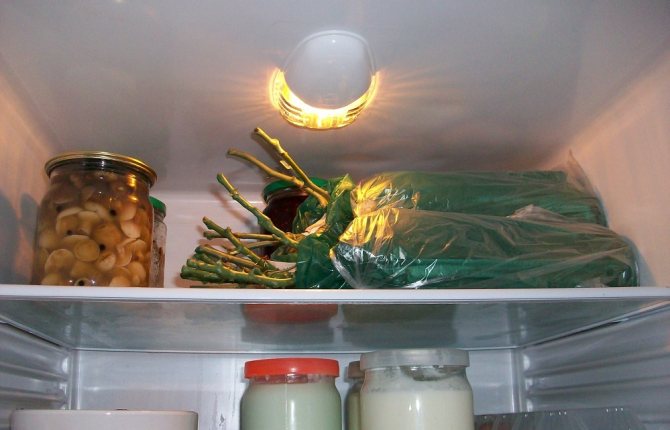
- In a refrigerator. Some amateur gardeners manage to keep rose sprigs in the refrigerator. For this, the trimmed planting material is wrapped in a damp cotton cloth, and wrapped in plastic wrap on top. The cuttings should be stored in the vegetable compartment, becausehe is best suited for the job;
- Under the rose bush. This method suggests storing shoots, so to speak, "on the spot." After cutting off the stalk, dig in it right under the bush. The whole process completely repeats the first storage option in the snow, although the hole is dug about 15 cm deep.
Wintering young roses on the windowsill
If you keep your own rooted roses in pots on the windowsill, then do not abuse it with watering in winter. Until the end of January, water them very carefully - in small doses (the soil should be slightly damp). But after increasing the length of the day, start feeding the roses and water enough.
If, before planting in open ground, self-rooted roses grow too intensively, pinch the tops to delay this process.
In the dry and warm air of the apartment, the spider mite multiplies intensively - this is the scourge of the rose. To save the rose bushes from this misfortune, souls are very useful. The ripening period of ticks at room temperature of 20 degrees is seven days. During this period, the plant is regularly treated with cold water so that it washes over both sides of the rose leaf. If you missed one day, start over. To restrain the reproduction of mites, it is recommended to carry out 4-6 treatments of the rose with a sulfur-tar emulsion during the winter (with an interval of 7 days). These pests quickly develop resistance to commercial anti-mite chemicals, but they are not addictive to soap. The emulsion is prepared from sulfur-tar soap (sold in pharmacies), a concentration of 1-2% is quite enough. Inspect the young leaves of roses wintering in the apartment more often, because the tick first of all affects them. And in the open field, due to sufficient humidity, this pest develops poorly on roses; in addition, the spider mite has many natural enemies in the garden - useful garden insects (predatory mites, lacewing, etc.).
How to root a rose shoot?
For better preservation of the branches, experts advise to root the cutting. This can be done with moss or potatoes.
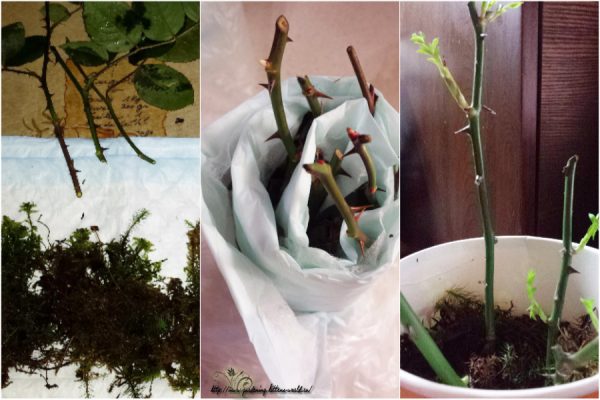
The first option involves the use of sphagnum. Don't forget to treat it with a fungus remover before use.
Then wrap the cutting in moss, wrap it in plastic and send it to a dark, cool place until spring.
When it's time to plant, unpack the branches, cut the thorns, and plant the rose in a box filled with river sand and moss.
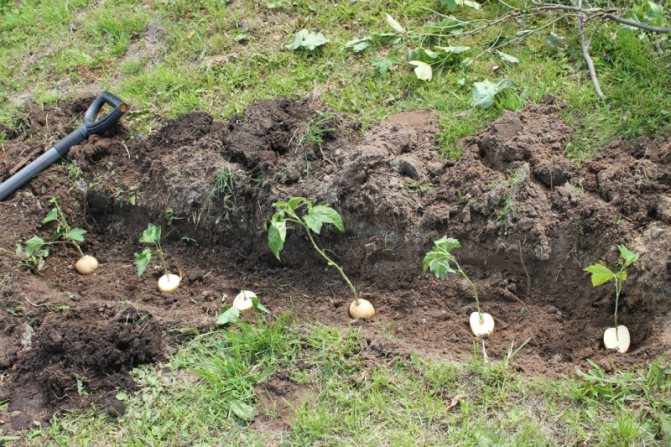
Another way is to use a potato tuber. Take a vegetable and treat it with an antiseptic, dip the stalk in a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Then make several holes in the root vegetable and stick the rose shoots into them.
Place the workpiece in a hole dug in the ground and cover with a glass jar. Water the cutting with warm water once a week.


As you can see, there is nothing difficult in independent propagation of roses by cuttings.
The main thing is to follow the recommendations, and very soon you will have a whole flower garden, in which the queen will be a rose.
AllaAuthor of the article
Did you like the article?
How to save cuttings of roses until spring in several ways
How to keep rose cuttings until spring: several ways
In early March, you should start rooting cuttings. They are taken out of the moss and the thorns are removed. A special box is prepared: the bottom is lined with moss, river sand is poured on top with a layer of about 3 cm. It must be pre-washed. After this, branches can be planted so that one or two buds remain above the ground. They are covered with a plastic bag, having made enough holes in it for good air circulation.
Sprouts should be placed in a warm, bright place, but not in direct sunlight. You need to look after the moisture content of the soil: if it dries out, then the package must be removed and the plant and the soil around it must be sprayed.
Rooting in potatoes
You can also root cuttings of roses in potato tubers. This is a fairly reliable method, as the nutrients and starch make them well accepted and reproduced.The tuber should be of medium size, without visible damage. It is treated with a fungicide and the eyes are removed. It is also necessary to prepare the cutting: remove a huge part of the leaves, lubricate the cut with potassium permanganate.
It is great to put in aloe juice for 12 hours: this way the plant gets drunk with moisture, and the cut remains fresh. Growth catalysts can also be used.

Then a recess is made in the potato, into which the cutting is placed.
Advice
The upper part can be sealed with paraffin by melting the candle in a water bath.
A tuber with a sprout is buried in a small opaque pot and watered with unsaturated potassium permanganate. You can also put it in a bag and hang it on the window. In a couple of weeks, it will be noticeable that the kidney has begun to grow. In principle, water the cuttings of roses often. Once a week, it is better to feed with water and sugar; for this, a tablespoon of sugar is dissolved in a glass of water. A similar procedure will provide the sprout with carbohydrates.
A month after planting, it is worth applying complex fertilizers.
Cuttings in a pot must be covered with a jar of a rather huge size so that the leaves do not touch the glass. Watering should be of high quality, it is better to choose a drip spraying method. The soil must be slightly moistened at all times. As soon as the shoots appear, the roots will begin to develop. After two to three weeks, you should start accustoming the plant to open air.
At first, the jar, which is covered with the sprout, is slightly raised and fixed in this position. The time of the procedure given for us is evenly increased. Then it is quickly completely removed, just as slowly stretching these periods. When the flower gets used to an open airy place, the jar is removed for good. It can take several days.
You should not rush to plant from a pot. This must be done in the spring, then by the fall you can get a real bush. When buds appear, they are removed.
Mschistota. ru
How to use moss
In gardening, sphagnum moss is used for many purposes. This bog plant has unique properties:
- can retain moisture in an amount 20 times its own weight;
- contains antibacterial compounds, thanks to which it can be stored for a very long time without losing its valuable qualities.
It should be noted that high moor peat consists of dead sphagnum particles, and it is considered the most breathable and fertile peat layer. As for the use of moss in horticulture, tubers, bulbs and other sowing material are perfectly preserved in peat moss. Its loose structure guarantees excellent ventilation, and its antibacterial properties prevent rotting and mildew.
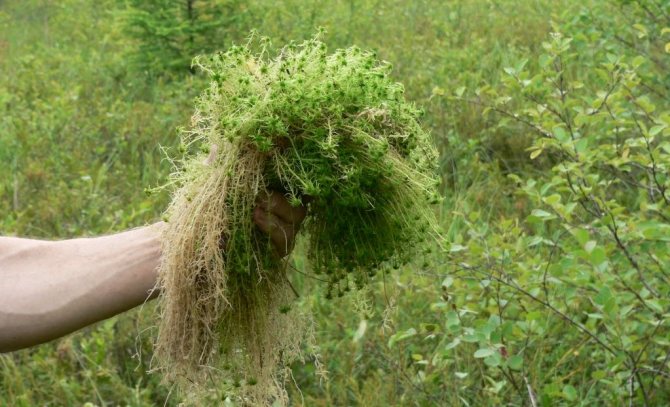


These qualities make it possible to use moss for storing rose cuttings. Before using the material, the lower cut of the moss must be treated with Phytosporin or aloe juice diluted with water in a 1: 9 ratio. Then the cuttings should be wrapped in moss, placed in a plastic bag, and put in a cold place - if there is no cellar or basement, then you can put it in the lower compartment of the refrigerator. If the moss begins to dry out, take out the bag and lightly spray the moss with water.
In early March, you can start rooting cuttings. They must be taken out of the bag, freed from the sphagnum, the thorns must be removed, if the sections were covered with paraffin, the paraffin must be removed. Next, you should prepare a container with a substrate in which the roses will be planted.
A thick layer of moss is placed on the bottom of a box or other container, a small (3-5 cm) layer of pre-washed river sand is poured onto it. Cuttings are buried in this mixture at a slight slope so that no more than two buds remain on the surface. Then the container with seedlings is covered with a bag with several holes (for ventilation), and placed in a bright, warm place, but not in direct sunlight.The substrate must be periodically moistened. With this method, cuttings of roses take root very quickly.
What roses require shelter in winter?
There are several types of shelter for roses in winter: dry type of shelter, digging, incomplete shelter, etc. The choice of wintering option for this plant will depend on its winter hardiness and other characteristics of the variety.
Cold-tolerant varieties do not need to be covered?
Park, species varieties and some hybrids are considered the most cold-resistant. The opinion that frost-resistant roses can winter without preparation is wrong. Even the most hardy species need special preparation for subzero temperatures.
In the middle lane and in the south of Russia, frost-resistant varieties can winter without shelter, but it is still better to spud the root system with sod soil, spruce or dry foliage. All feeding and pinching stops by September. Before winter, the bushes are treated with an antiseptic, cut off and covered (in whole or in part). Full cover is necessary for bushes that hibernate in especially harsh conditions - if the thermometer in winter drops below -30 degrees.
The most cold-tolerant varieties include: Ritausma, Golden Celebration, Pink Grothendorst, Leonardo da Vinci, Konrad Ferdinand Meyer, Hansa, Adelaide Hootles, Lavinia, Scabroza, Snow Pavel, Jens Munch, John Davis, Hansa, Peace, New Dawn, Black Magic, Black Magic William Shakespeare 2000, etc.
Wintering conditions for thermophilic roses
Climbing roses, miniature, hybrid tea and exotic varieties are sensitive to cold weather. Such varieties require special protection in the winter: they must be insulated from above, spudded, and some even completely buried in the ground.
Such varieties as Louise Odier, Souvenir de la Malmaison, Hybrid Gallica, Rosa Mundi, Fritz Nobis, Bourbon roses need a solid shelter. In a particularly cold climate, such roses are recommended to be grown in greenhouses, or in large flowerpots, which are displayed in the garden only in summer, and the rest of the year the flowers "live" indoors.
Planting roses after rooting
If the preparatory stage of grafting is carried out correctly, there are no difficulties with planting the material. Cuttings are planted in an open, well-lit area, but with a light shade, in order to prevent the sun's rays from burning young leaves. A rose garden can be laid immediately in a permanent place or made a nursery, and then transplant roses next fall to another place. A fertile light soil is chosen under the rose garden so that young roots can develop and breathe freely. If the soil is heavy, add humus, compost, turf soil, peat, sand. Landing is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Wells are made 12-15 cm deep and covered with soil mixture;
- Expose seedlings in the ground at an acute angle;
- The distance between the bushes ranges from 5 cm to 1 meter, depending on the task at hand. If the seedlings are placed only for rooting, then the distance is minimal. The cuttings are planted in a permanent place, taking into account the landscape design of the site and the variety of roses, which can grow several meters wide;
- The planted stalks are covered with fertile soil mixed with sand and peat;
- Seedlings are watered with a solution of potassium permanganate to destroy harmful bacteria and fungal spores in the soil, they can provoke rotting of the cuttings;
- A wire frame is installed over closely planted bushes and a PVC film is stretched. It turns out a small nursery for the future rose garden, which is easy to care for.
If the autumn days are sunny, it is worth shading the greenhouse or plastic containers from bright rays. But the autumn cuttings of roses are so convenient because the days are getting shorter, the nights are cooler and the sun does not burn the leaves under the cover. For seedlings, ideal conditions are created to take root and harden before the first frost.
In advance, you need to take care of the shelter of the plant for the autumn-winter period. This will save the bushes from frost.Some specimens should be excavated and stored in a cool, damp place. So roses from a bouquet will appear in the garden again and again, delighting not only the gardener, but everyone around them.
Wintering in the garden of rooted two-year-old roses
In the second year of life, young self-rooted roses can be covered more easily - only by insulating the bases of the bushes with a dry leaf or by spudding them with breathable material (peat or dry soil mixed with dried wood shavings). Such material can be stored in bags during the summer. And so that in winter the leaves or an air-dry hillock do not get wet during thaws, put pieces of polyethylene under the roses, cutting them under the stems. The main thing is to avoid contact of the hummock with the soil.
From the third year of life, mature self-rooted roses are covered like adult bushes.
Weekly Free Digest
Every week, for 10 years, for our 100,000 subscribers, an excellent selection of relevant materials about flowers and garden, as well as other useful information.
Rosa is a majestic and slightly capricious inhabitant of the garden. Today we will tell you how to cover roses for the winter. Many varieties winter well even without shelter, while their other brethren require special wintering conditions. The homeland of this wonderful flower is Ancient Rome, where winters are not as severe as in Russia. The minimum temperature in the homeland of roses does not drop below 3 degrees Celsius. And the Siberians would not have seen roses if the experts had not come up with ways to shelter them for the winter.
Winter on the balcony
Saving cuttings of roses in winter is also possible on the balcony. This method is especially relevant for residents of city apartments.
- After the first autumn frosts, cuttings with two or three buds are pruned. Their size should be about 20 cm.
- It is necessary to pour expanded clay into a plastic bucket in a thick layer, then - earth for roses. It is useful to mix it with Perlite.
- The prepared soil should be slightly moistened.
- Each cutting must be cut into water, then into powder to stimulate growth. Then place it in a pre-dug hole.
- Next, you need to wrap the bucket in cellophane and secure it on top with clothespins. Then the bucket should be wrapped in warm blankets.
- Now the entire structure can be taken out onto the balcony and placed in the warmest and brightest place. If the floor is cement, then foam plastic or boards should be laid under the bucket.
- You don't need to water your plants often. In good sunny weather, you can let them breathe a little: remove the clothespins and spray with water to which Epin has been added. Close the bag only after complete drying.
- In case of severe night frosts (below 20 degrees), it is better to bring the sprouts indoors.
- When spring comes, the resulting seedlings can be planted in the garden. You need to get out of the bucket with a tablespoon so as not to damage the neighboring stalk.
To grow roses, you have to tinker. But true connoisseurs know that the opportunity to enjoy the beauty and scent of the queen of flowers is worth it.
Winter on the balcony
Shelter cuttings or seedlings of roses on the balcony is important for city dwellers who have only a glazed loggia or balcony from cold rooms. With this method, cuttings are prepared and processed in the same way as before storage in soil. To preserve the planting material, you need to select unnecessary boxes or buckets. Pour a drainage layer (expanded clay) into these containers, and on top of it, earth mixed with perlite.
Before planting, the soil mixture should be well moistened, and the cuttings should be soaked in a growth stimulator. Next, make small holes in the soil and deepen the cuttings there. If the winters in your area are not cold, the cuttings can be wrapped in paper, wrapped in plastic bags, and simply packed in cardboard boxes. It is clear that with the onset of frost, even on the glazed balcony, there is a threat of freezing of the planting material, so it is important to know how to cover the cuttings of roses for the winter.


A bucket (container) with cuttings must be wrapped in a plastic bag and secured on top (clothespins can be used for this purpose), and the bucket itself must be wrapped with something warm, for example, an unnecessary blanket. In this form, the structure is taken out onto the balcony. Cuttings should not be watered often. In sunny weather, the film cover can be removed for a short time, and the cuttings can be sprayed with water. In case of severe frosts below (-10-20 ° C), it is better to bring the cuttings indoors.
Florists who grow roses at home in pots will be interested in knowing how to preserve rose seedlings between flowering periods. Pruned seedlings in pots, perfectly stored at temperatures from +3 to -4 ° C. Such conditions can easily be created on a glazed balcony in winter, where the plants, being in a state of sleep, will be perfectly preserved, and in the spring they will grow with renewed vigor.
Growing roses with potatoes
Novice florists can easily cope with this technology. Its essence is to plant the cutting not in the ground, but in the tuber. From it, the plant feeds the necessary substances (starch, vitamins, phytohormones and moisture). In addition, the plant will not freeze or dry out while it is in the potato, and pests will not get to its root. This method works 85% of the time.
To root roses in potatoes, you will need:
- prepared cuttings;
- medium to large potatoes;
- growth stimulant for roots.
You should approach the choice of a tuber responsibly: the potatoes should be healthy, juicy, without damage and eyes. A sluggish, unhealthy potato will rot in the soil and infect roses. Therefore, it is necessary to disinfect the tubers in potassium permanganate and dry them well. One vegetable is used for one cutting. Make a blind hole in it and insert the plant into it with the bottom cut.
Tip: the lower part of the cutting must be dipped in a growth stimulator, this will help the flower to take root.
Potatoes with seedlings should be placed in a container 15 cm deep. Its bottom is covered with a layer of sand (5 cm), tubers are placed, and sprinkled with earth on top. In this case, the upper kidney should remain above the ground. Water the plants with water and cover with something transparent (like plastic) to create a greenhouse effect.
Tomato seeds Siberian Garden catalog with a description Lunar calendar for planting peppers in March 2020 Diseases of strawberries photos and their treatment How to feed cucumbers in a greenhouse to have a good harvest
After that, it remains only to monitor the condition of the soil. Abundant irrigation, as well as excessive dryness, will be detrimental to the development of roses. When the first shoots are formed in internodes, start airing the seedlings. After 14-17 days, the protective film is completely removed.


























