Everyone knows that plants feed on substances removed from the soil (or other plants), they need water, light and - most of them - heat. Many people also know about the flower that eats flies, and for some reason the bulk of them are afraid of it, considering it almost a monster. Meanwhile, predatory plants are simply living organisms put by nature in such conditions that they had to survive in a non-standard way. Rather, they deserve respect for their vitality and persistence in evolution. Strictly speaking, flowers that eat flies are on the same level, for example, with tigers, who are also by no means vegetarians. Besides, most of the plant predators are amazingly beautiful.
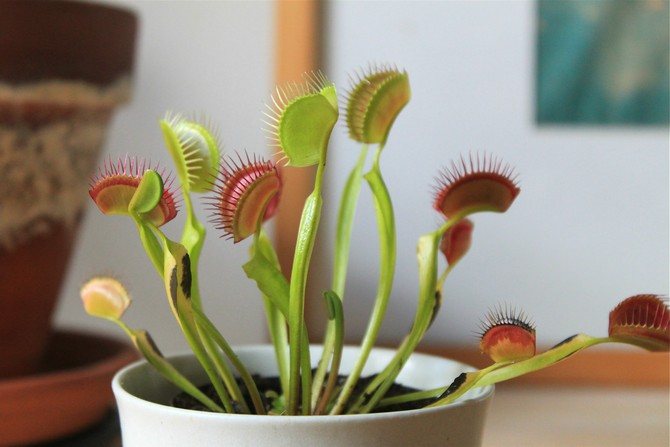
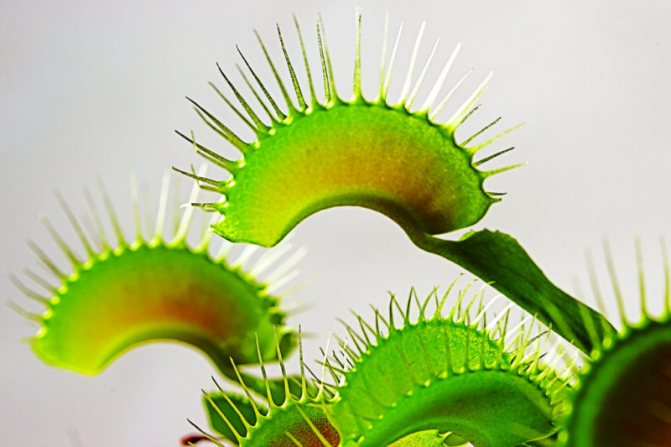
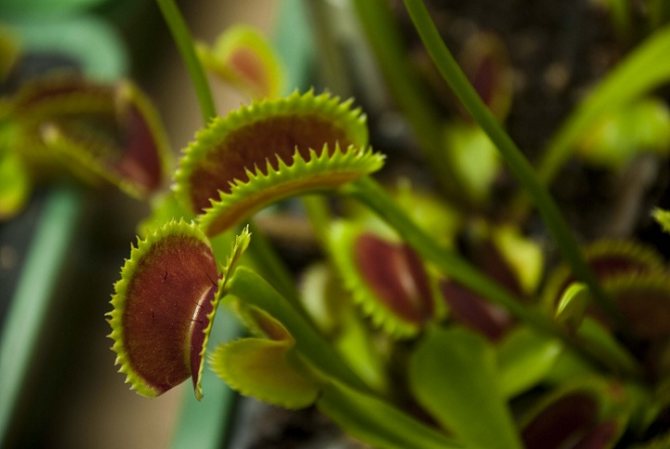
Conditions for keeping the Venus flytrap
In nature, these plants live in places saturated with water, with constantly high dampness. The best way to keep the soil moist at all times is to place the pot in a tray and add water periodically. If local conditions force the soil to dry quickly, you can periodically immerse the entire vessel in liquid.
When watering, it is best to avoid wetting the leaves. Distilled or settled rainwater is used for the flycatcher. In very dry climates, placing the pot in a transparent, tall container with an open top will help. Thus, condensation on the walls will provide additional moisture. You can grow the plant directly in the terrarium, then you should ensure the presence of ventilation and the absence of stagnant water.
The soil should be very acidic, poor, devoid of fertilizers. Dionea has the ability to digest insects and use them to obtain nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus, as well as other trace elements and minerals. Therefore, you do not need to fertilize it and water it with tap water, since an excess of seemingly useful substances can provoke the death of the plant.
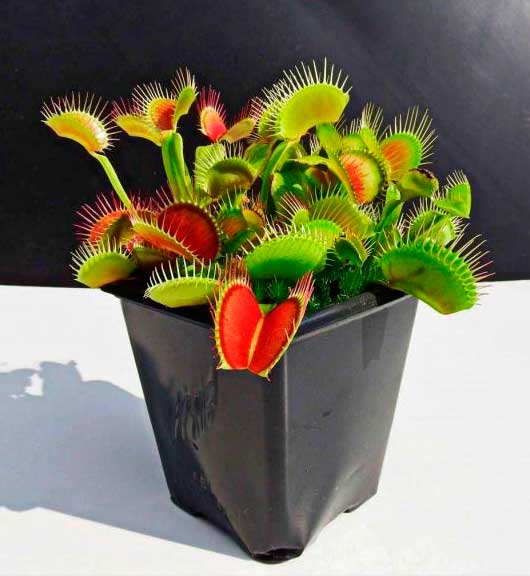

When preparing the soil, it is important to recreate the natural conditions: a mixture of sphagnum with peat (pH 2.8-4) and a little perlite, this will create an acidic soil, soft and light - the latter will provide free circulation of air and moisture.
Flycatchers love bright spots in the sun, even for many hours a day. But sunlight, especially in summer, causes moisture to evaporate quickly, which must be compensated for by more frequent watering during the hottest months. The air temperature in summer is 20-30 ° C.
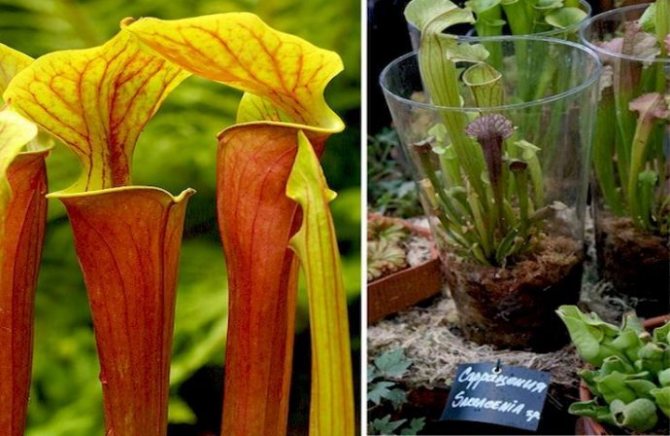
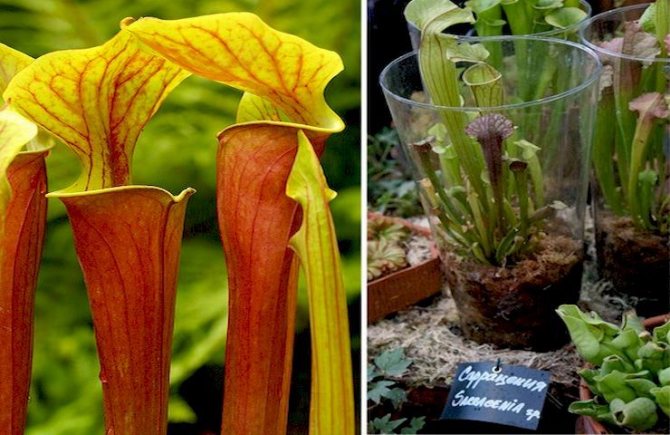
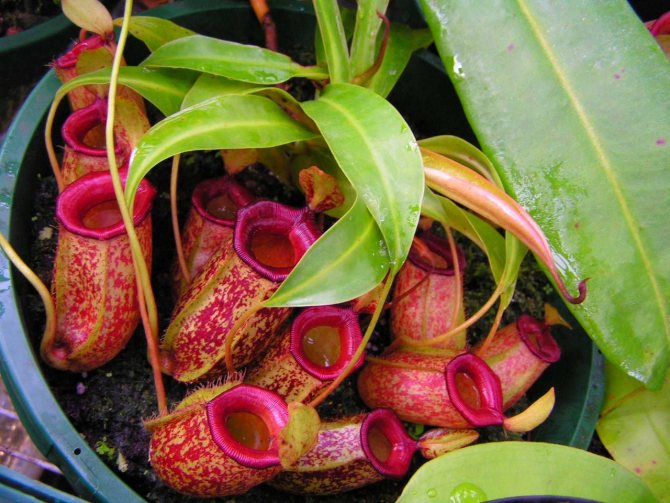
Pitchers
Plants with some leaves that look like bright, pitcher-shaped flowers. But even these plants cannot be said to use trap flowers. They also have tubular leaves as traps, at the bottom of which liquid accumulates. Flies fly to the bait and drown in it. Since in fact it is a concentrated digestive enzyme.
The pitchers are painted in various bright colors, while the real flowers of the pitchers are small and inconspicuous.


Predatory Plants: Nepentes, Sarracenia and Stapelia
Nepentes
Inhabitant of humid tropical regions. The length of the nepentes, depending on their type, is 2.5-50 cm. The largest ones can catch and digest a small mammal. Or enter into symbiosis with an animal. The large Nepenthes lowii, in addition to insects, uses the droppings of mountain tupai as a source of organic matter. And the animal feasts on nectar.
Interesting!
For the sake of tupai convenience, the entire structure of the jug leaf is reinforced to support the additional weight.
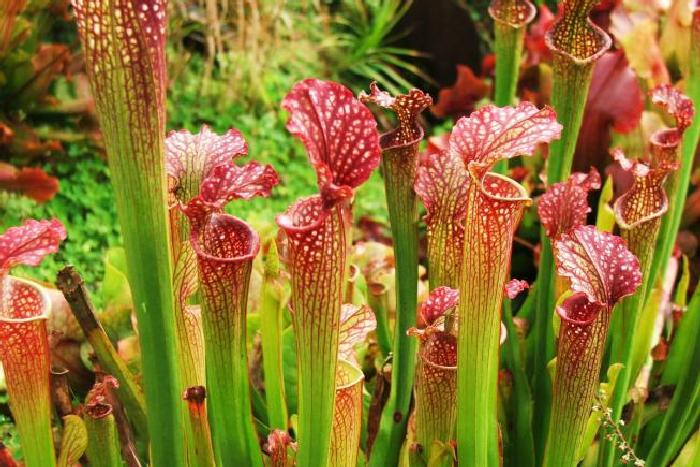
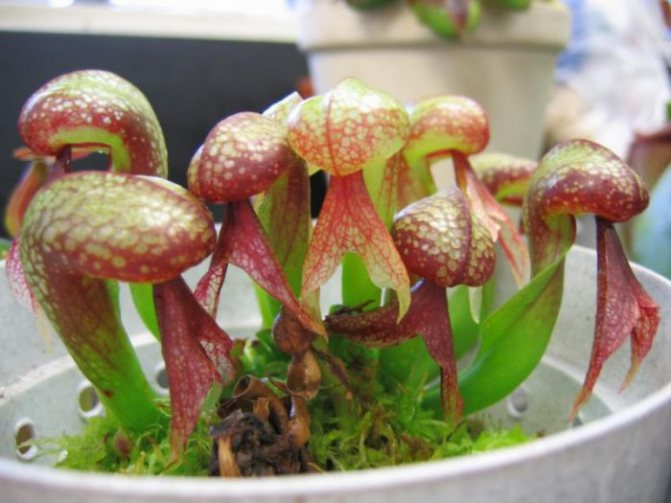
Sarracenia
The family consists of 10 species. A fly trap is a twisted, funnel-shaped leaf that grows from the root. The plant is native to North America. Sarracenia was grown as a houseplant in pre-revolutionary Russia. It grows well in pots.
Breeders have already developed new cultivated varieties of sarracenia that can be grown indoors. With good care, you can achieve blooming sarracenia.
Is it possible to get rid of flies in an apartment with the help of a plant?
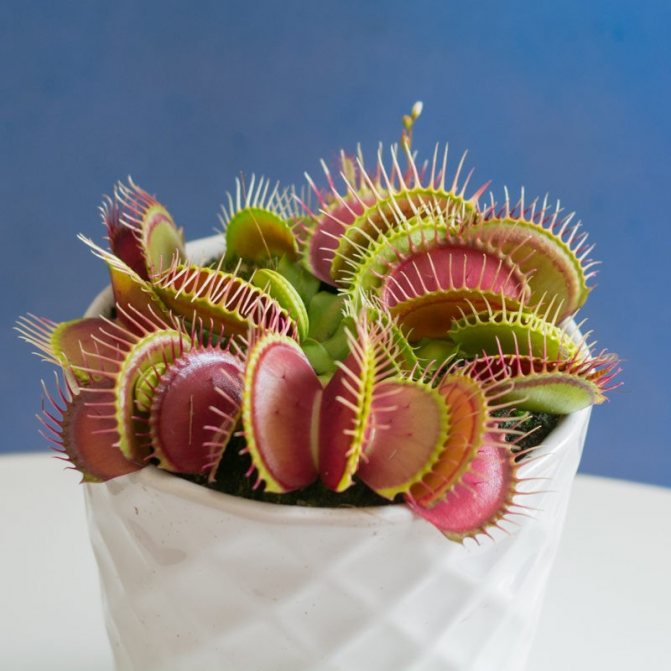
Some naively believe that purchasing a flycatcher plant will completely rid them of flies in the house, because the plant feeds on them. For example, in August, flies begin to actively reproduce and buzz boringly in the apartment. The plant is not able to eat all the flies that have flown in, it will be content with one fly in the trap, the trap will close and open only after the prey has been digested. Venus flytrap is more of an ornamental plant than an insect hunter. You will most likely have to feed him flies yourself.
To get rid of flies, it is better to purchase adhesive tape and mosquito nets on the windows, the result is guaranteed.
Reason for appearance
Flowers that eat flies did not immediately appear in the form we see them now. They evolved due to lack of nutrients and nitrogen in the soil. They needed something to feed on, and so they adapted to feed on animal protein obtained from insects. He completely replaced the necessary minerals and nitrogen.
The plant uses unusual traps to catch its prey. Having a bright color and emitting a sweet aroma reminiscent of nectar, it attracts insects, which soon turn out to be its lunch.
Dionea's rest period
The dormant period is very important for the Venus flytrap, it lasts from about November to February, and must be strictly observed. The air temperature gradually drops to + 10 ° C, but not below zero. If the house has a balcony or veranda that does not freeze in frost, then you can settle the plant to winter there.
After the onset of cold weather, the soil remains slightly moist, watering decreases, while the water should not be warmer or colder than the air in the room. At this time, its daylight hours decreases, attention is also paid to the timely removal of blackened leaves. During the winter months, only a few leaves with small traps are produced.
If it is not possible to arrange for a flycatcher to winter in the house, as a resting place, a refrigerator with a positive temperature of up to 5 ° C is suitable. But the plant is pre-prepared for several weeks, for example, at a slightly open window. Immediately before placing it in the refrigerator, it must be treated with a fungicide and placed in a ventilated bag. In such conditions, light is not needed, but the substrate is moistened monthly with distilled water.
Species diversity and abundance
Most carnivorous plants are perennial grasses, but there are several species that are subshrubs and even shrubs. They are classified as species with narrow adaptation to environmental conditions. Usually such species are distinguished by the unusual and bizarre adaptive reactions.


Bibles giant
- The giant in the world of predators is the giant biblis. It is in the world of small predators, he is a giant, and among ordinary shrubs, biblis is not large - no more than 50 centimeters. This predator grows in Australia. Since Biblis is indeed a giant among his fellows, he has a corresponding prey. He catches not only insects and molluscs, but also frogs and lizards.
- Nepentes are woody tropical lianas. It is not entirely correct to classify them as predators.However, these plants are so unusually adapted to extract nitrogen from outside the soil that it is worth mentioning a similar invention of evolution. Some nepenthes use nectar not to attract insects for pollination, but to be used by small mammals. However, the main reward for the flower is not pollination, but excrement, which can be left by some mouse or monkey. There is a lot of nitrogen in excrement, which is absorbed by the terrestrial part of the plant.
- Rosolist is a plant large enough for a group of green predators. This is a semi-shrub, reaching a height of 30 centimeters. Grows in the Pyrenees and North Africa. He catches flies like sticky paper, which is why the local peasants love him.


Mosquitoes stick to dew leaves like sticky paper
Top dressing of Dionea
It is important to understand that the Venus flytrap is a plant, not an animal, so it needs more light and water, and then only living creatures. If she is on the street or balcony, where insects can penetrate, then you can not worry about her diet. In indoor conditions, one or two times a month it is required to feed an insect to a flycatcher, half the size of its trap. It is desirable that it be a black fly, a spider or several mosquitoes, as larger or harder ones can harm. Food is preferably given live, stale food can cause illness. A recently killed insect will do, but you need to wiggle it a little with a needle so that the sensitive hairs work and the shutters slam shut.
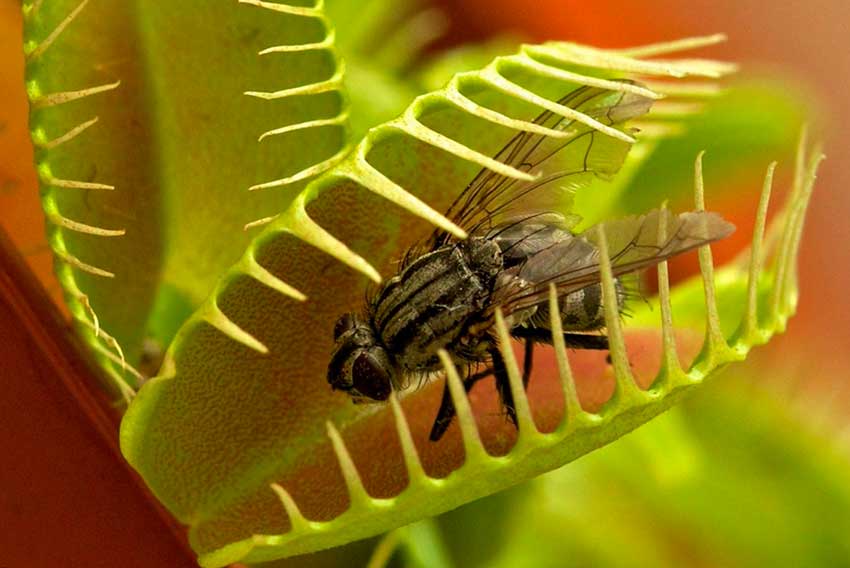


You should be careful about flycatcher traps, as its functioning is limited. After a certain amount of food digestion, it loses its ability to hunt and dies off. Therefore, if an inedible object got there or the slamming occurred due to an accidental provocation, it will open in a day, reducing its capabilities by one time. Do not give the plant meat or other food products - this will ruin it.
Nutrition of carnivorous plants
Most feed on insects (these are sarracenia, sundew, nepentes). But aquatic representatives, for example pemphigus, consume even small crustaceans.
There are larger representatives of carnivorous plants, whose diet includes toads, fish fry, newts, lizards. So, mice and rats sometimes become prey of nepentes.
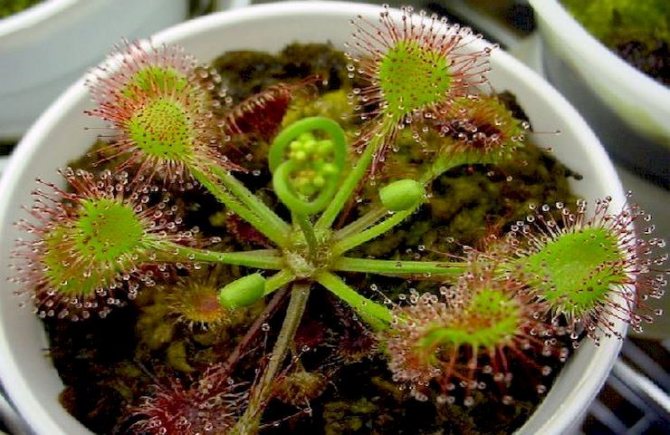


Sundew is a species that feeds on insects
Features of caring for the Venus flytrap
The Venus flytrap must be transplanted so that excess salts and minerals do not accumulate in the soil. This is also done if it has grown out of its previous container or to separate the bulbs when there are too many of them. You need to know a few rules:
- Deep pot. Since Dionea has a strong root system, the volume of the pot must be twice as large for the entire plant.
- You can transplant the Venus flytrap only in the spring, usually, these are the first days of March. It is advisable to carry out the procedure once every two years.
- During transplantation, protect the roots from unnecessary injuries, cleanse them as much as possible from the old soil and remove all non-viable leaves and traps.
- The plant in a new pot is sprinkled with soil, including the whitening legs of the leaves.
Where green predators are common
The distribution area of insectivores is quite wide, they can be found in different ecosystems in which flowers can grow, from the tropics to the Arctic zone, in wetlands and desert areas, in the alpine mountain belt. Most often found in countries with warm, tropical climates.


On the territory of Russia there are:
- sundew of two types;
- water bladder Aldrovand;
- representatives of fat women;
- several varieties of pemphigus.
Flycatcher bloom
It blooms in spring and until mid-summer.Flowers begin to appear at the end of May and are similar to those of strawberries, but with more elongated petals and longitudinal furrows on them. If the plant is young, then in order to maintain vitality, it is better to remove the shoot. In mature, sturdy plants, only strong stems with many buds should be left.


Such a stem should grow tall so that the flowers on it can be pollinated without risking a flycatcher for lunch. In indoor conditions, pollination is carried out with a brush, for which you need to carefully transfer the pollen from the stamens to the pistils. It is believed that for better offspring, it is advisable to do cross-pollination, that is, from a different flower. Within a month after pollination, bolls will begin to form, and when the boll is completely dry, its seeds can be used to breed new plants.
Types of insectivorous flowers
Biological scientists have counted about 630 species of carnivorous plants from 19 families.
The most famous flowers that catch and eat flies:
- Venus flytrap;
- zhiryanka;
- sundew;
- slipway;
- genlisei;
- sarracenia;
Video description of predator plants:
The Venus flytrap, or dionea, is the most recognizable flower that eats insects. He is a favorite on the windowsill of many gardeners. This flower is native to North America. Its main habitat is swamps, but it can easily adapt to indoor conditions. Flycatcher leaves have denticles along the edges. As soon as the insect lands in the "mouth" of the flower, its blades immediately slam shut, like the mouth of a predator. The digestion process takes place hidden for 10 days. Then the leaf opens, gets rid of the empty shell and waits for the next prey.
Zhiryanka is considered one of the most beautiful plants that eats flies. It got its name from the mucus covering the leaves. The surface becomes shiny as if it were greased. The fatty plant emits a sweet scent that attracts insects. The leaves completely cover the digestive glands that digest the prey.
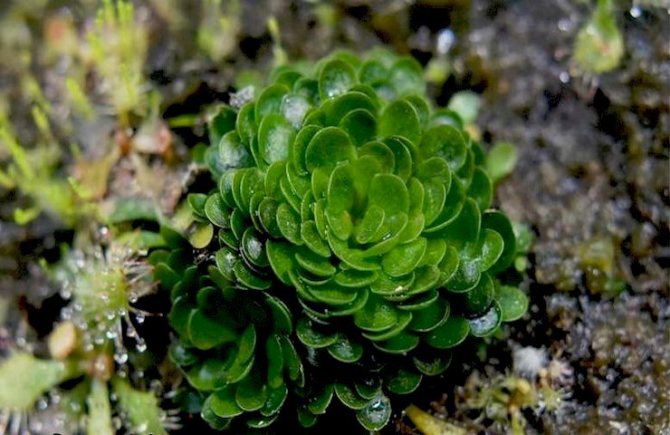


Despite the predation, Zhiryanka is one of the most beautiful plants.
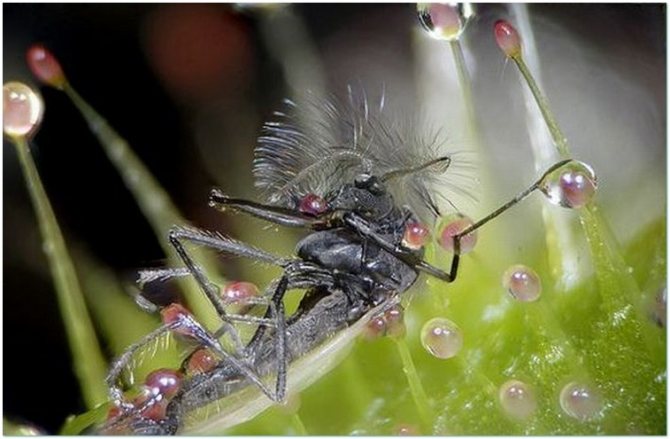
The most common flower that catches flies is the sundew. Grows in mountains, swamps and sandstones. The leaves have long hairs that give off a sweet, aromatic liquid similar to dew. When a fly touches a viscous syrup the leaf of the flower folds and digests the insect... A large sundew can even catch a dragonfly. English sundew and round-leaved sundew are common in Russia.
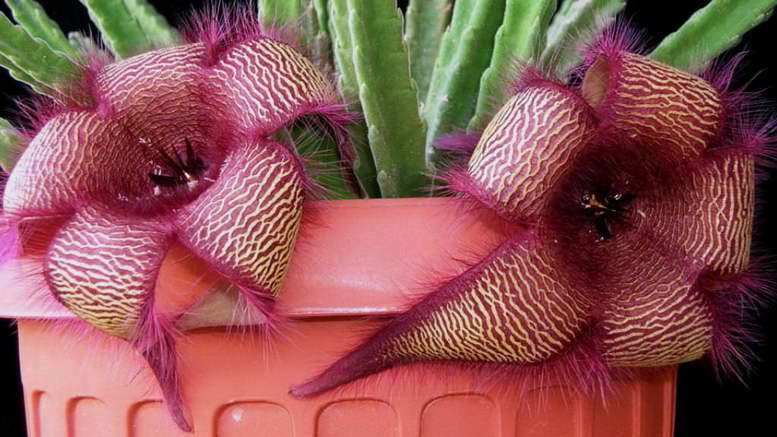
Stapelia is another houseplantthat eats flies. It is often confused with a cactus, with which it has nothing to do. Staple flowers give off a rotten meat smell that attracts flies. They lay eggs in flowers. But the flower lives only for a day, which means that the larvae die with it, never having time to hatch.
The genlisea flower looks very cute and delicate. But this is only at first glance. It has hollow tubes containing a fragrant and sticky liquid that attracts insects. Climbing into the tube, the insect cannot get out and dies on the spot. The flower grows in Central and South America, as well as in Africa and Madagascar.
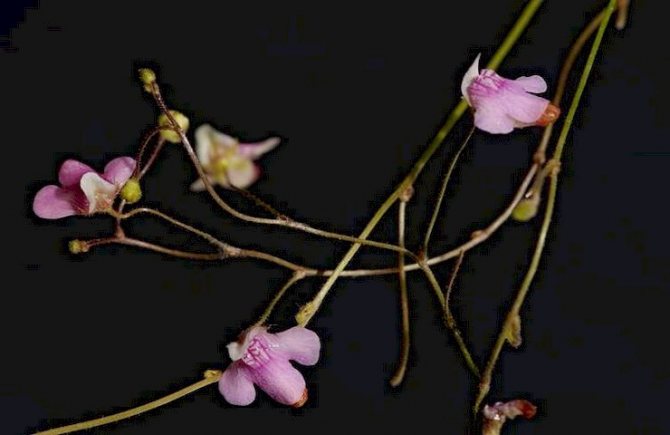


Genlisea looks like a gentle and safe plant, but it's deceiving.
Sarracenia is another flower that eats flies. Its name is unusual. This funnel-shaped plant came from North America and is well established in Russia as a house potted flower that eats flies. The sarracenia funnel is filled with sweet nectar, and its walls are very slippery.
When a fly climbs into a flower to feast on, it can no longer get out and dies under the influence of digestive enzymes.
Areal of plants
Despite their exoticism, insectivorous plants are found throughout the entire Earth. Most often these are swamps and areas with high humidity.The range of many species is limited to South and North Carolina (for example, the Venus flytrap), others grow only in Australia. In Russia, carnivorous plants are represented by 13 species, among which the most famous are sundew, fat and pemphigus. They grow in the European part, in the Caucasus and the Far East. Many species can be found not only in swampy areas, but also along the banks of rivers, lakes, on trees and stumps.
Sarracenia
Sarracenia also feeds on midges and flies, which fall into long tube-shaped trap leaves.
In our country, little is known about this plant, mainly, its habitat is Western Europe, as a rule, in open ground.
At home, he is planted in a pot of sphagnum. Care must be taken to ensure that the drainage in it is correct and the soil is loose.
Conditions of keeping at home:
- the temperature regime in the room should be slightly lower in winter;
- frequent watering with purified water;
- in the summertime it is best to put it in the garden or on the balcony (preferably in the shade).
This plant propagates with the help of seeds and rhizomes.
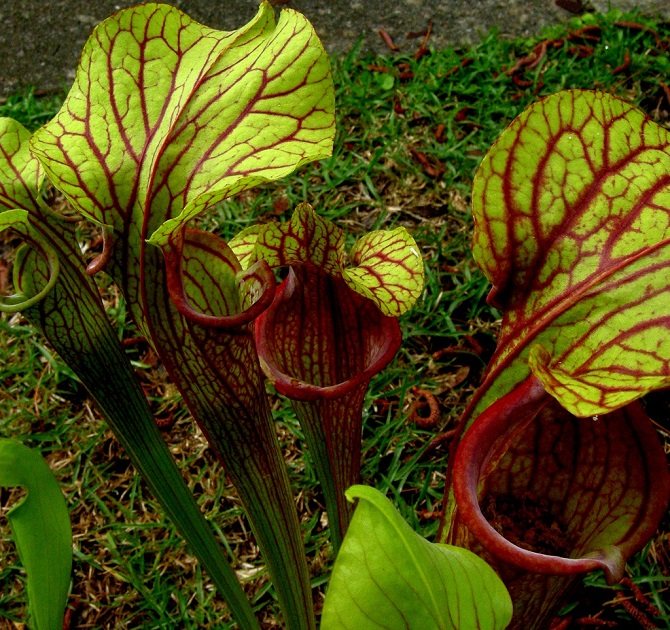


Sarracenia
Pemphigus
Pemphigus is a predatory plant whose habitat is stagnant water. Pemphigus is deprived of the roots of nutrition habitual for plants, which is why it preys on insects and small crustaceans. Fishing "bubbles" are under water together with leaves, and only its flowers float on the surface.
The “bubbles” have a kind of “entrance” that opens as soon as an insect is near. The signal about the opening of the "bubble" comes from the hairs-probes located near the "entrance". When the insect catches the hair, the "bubble" opens and it is drawn in along with the water. And at the next stage of the hunt, the digestion of food begins.
Sticky zhiryanka
Almost a complete analogue of the adhesive tape that hung from the ceiling of almost every diner just a couple of decades ago in the summer. True, Pinguicula, or zhiryanka, is much more beautiful than those dark brown spirals from the past. The bright green or pink leaves on the outside are covered with two types of cells. The peduncle glands located closer to the stem produce mucus containing glue that attracts the smell, and at the same time reliably fixes insects. This is the very Velcro. The second type of cells is the so-called sessile glands. They relate directly to the digestive system and produce protease, esterase and amylase, that is, enzymes that decompose living organisms into components useful for the plant.
For the winter, some types of ghee hide under a dense rosette, in order to bloom again in spring and continue the merciless hunt, dissolving carnivorous sticky leaves.
Genlisei
Genliseya is a plant with yellow flowers in the form of a crab claw, which serve as a trap for parasites. Small hairs grow inside the inflorescence, which retain insects.
Genliseya has two types of leaves: those that grow above the ground and those that are under it - they are the ones who catch and digest small insects.
It is worth adding that carnivorous plants themselves can become victims of parasites such as small worms and aphids. When there are too many of them on the plant, it is necessary to resort to the use of insecticides.
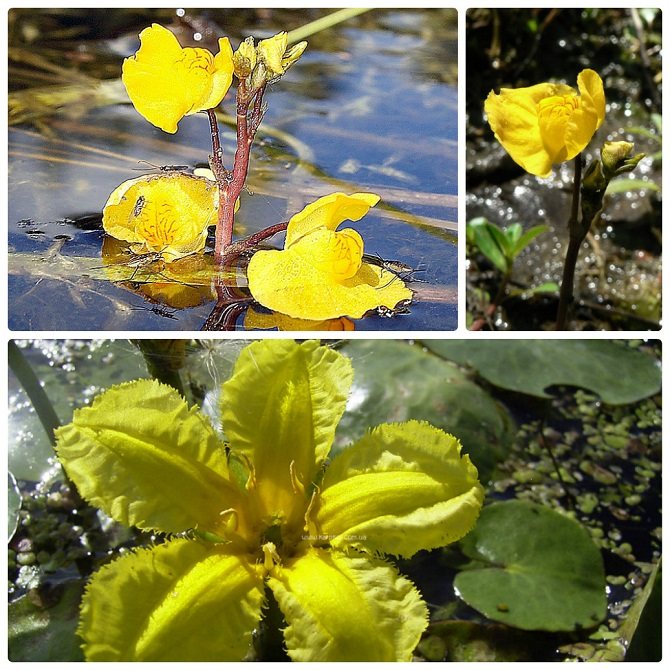


Genlisei
Round-leaved sundew
The round-leaved sundew is a representative of insectivorous plants in Europe and the CIS countries. Most often it can be found in the middle climatic zone of Russia, growing in swampy areas, in places deprived of useful minerals - "acidic soils".
In the summertime, a blooming sundew can be recognized by its small white flowers growing on a long peduncle stem. The sundew itself, a rather inconspicuous marsh insectivorous grass with leaves on the ground, strewn with hairs.The fluid secreted by the hairs is very similar to dew, but in reality it is a deadly glue for insects, as well as an enzyme for digesting prey.
The victim, attracted by the smell of "dew", sits down on a leaf and sticks to it. The hairs press the unfortunate creature to the surface of the leaf, and the enzyme begins the process of dissolving food, and the leaf itself, meanwhile, curls up, depriving the prisoner of all chances of salvation. The remains, which the sundew did not digest, fall to the ground, the leaves take their usual form, the hairs are covered with "dew" beads and a new hunt begins.
Trap leaves, covered with red tentacle hairs (from 20 to 30 pieces per leaf), play their role no more than five times. They then dry out and fall off, replaced by freshly grown ones.
Some, especially large, sundew species can catch even unwary frogs or small birds. Science knows about 130 varieties of this plant. And in the days of Ancient Russia, the Slavic peoples used sundew to prepare decoctions for colds.
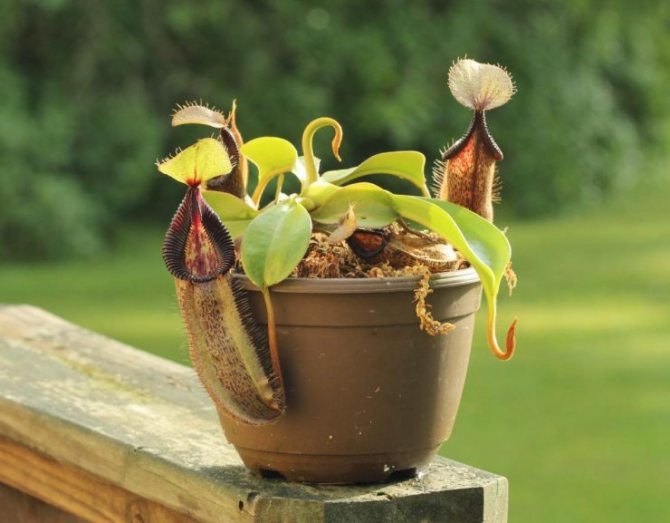
Nepentes
This plant, although very beautiful in appearance, is dangerous for winged small pests: it catches them with the help of its leaves in the form of "jugs" with a lid, inside which is a digestive enzyme.
The nectar formed along the edges of the lid attracts parasites - they sit on the edge and cannot leave the "jug", as they roll down and find themselves "trapped".
You can grow nepentes-"flies" in your home greenhouse or in a closed aquarium, constantly airing it.
The plant feels comfortable:
- at a temperature of 20 ° C;
- in good light conditions;
- with regular fertilizing with mineral fertilizers;
- in constantly moist soil. Watering nepentes is necessary only with soft purified water.
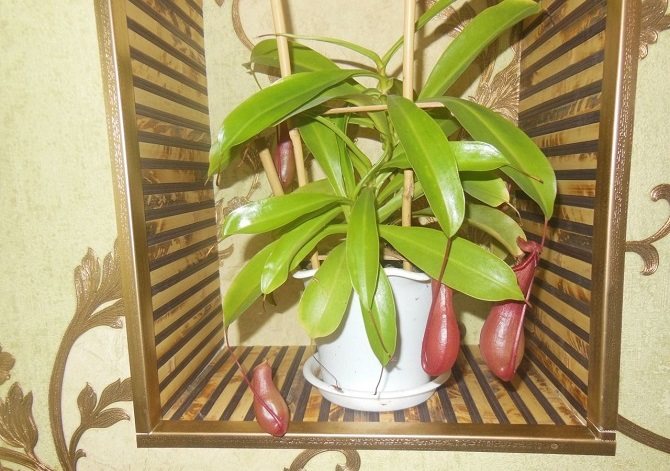


Nepentes