2. Chionodoxa - planting and care in the open field
2.1 How and when to plant
Chionodox bulbs are planted in late summer - early autumn - before the onset of frost, the plants will have time to get stronger and take root. When placed in the garden, it is worth considering that many varieties easily reproduce on their own, forming self-seeding.
Since the flower is tolerant to different lighting conditions. then for planting, you can pick up both a space open to the sun's rays and a shaded corner of the garden. Often these primroses decorate the tree trunks and shrubs, since flowering occurs early, when the foliage has not yet appeared on the trees.
↑ Up,

When grown on the sunny side, flowering will come earlier, since in this place the soil will thaw faster. However, when planted in partial shade, where flowering occurs later, it will last longer than in a sunny place. Flooded lowlands and places with closely lying surface groundwater are not suitable for growing chionodox - plants can rot in such conditions.
If the soil on the site is acidic, then crushed chalk is mixed into it, spilled with lime milk or dolomite flour is added. The site is carefully loosened and weeds are removed. If the site is too heavy, clayey soil, then rotted leaves are mixed into it for nutrition and river sand to improve moisture transmission capacity.
↑ Up,


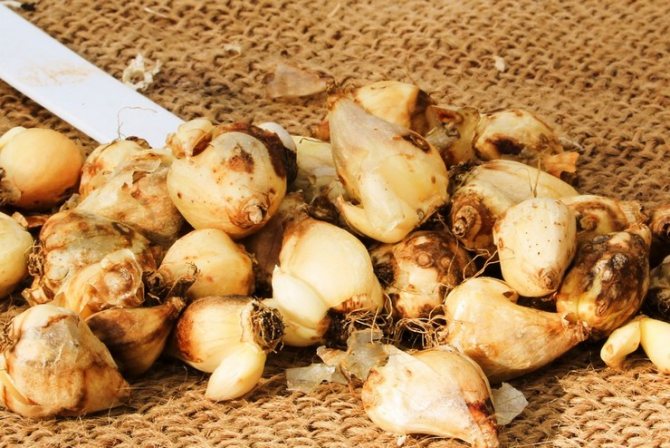
Planting holes are prepared, the depth of which will depend on the size of the bulbs. As a general rule, the bulbs are planted at a depth of 2 to 3 times their height. For a garden with dense soil, this value can be reduced, and for loose soil, plant the plants a little deeper. You can place 3 - 4 onions in each hole - in this case, chionodox will look more spectacular. Between the holes. depending on the planting scheme and the frequency of transplants in subsequent years, they leave about 8 - 10 cm.
The bulbs are dipped into the holes and sprinkled with earth, which is lightly tamped. The plantings are watered and covered with a small layer of mulch about 2 - 3 cm thick. Straw, cut grass or sawdust can be used as mulch, but they must be well rotted.
↑ Up,
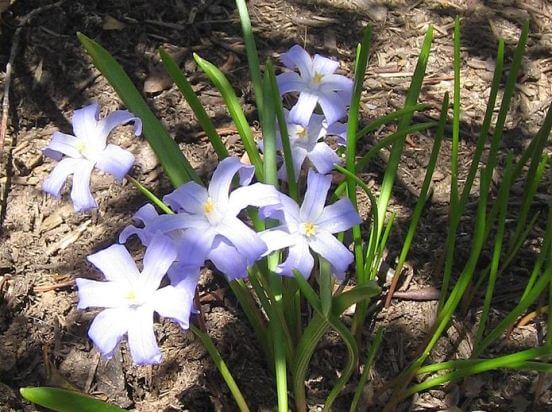


2.2 Caring for Chionodox
Further care of the flower in the garden will consist in timely watering, periodic feeding and weeding the soil. Of course, after each watering, it is worth loosening the soil to a shallow depth.
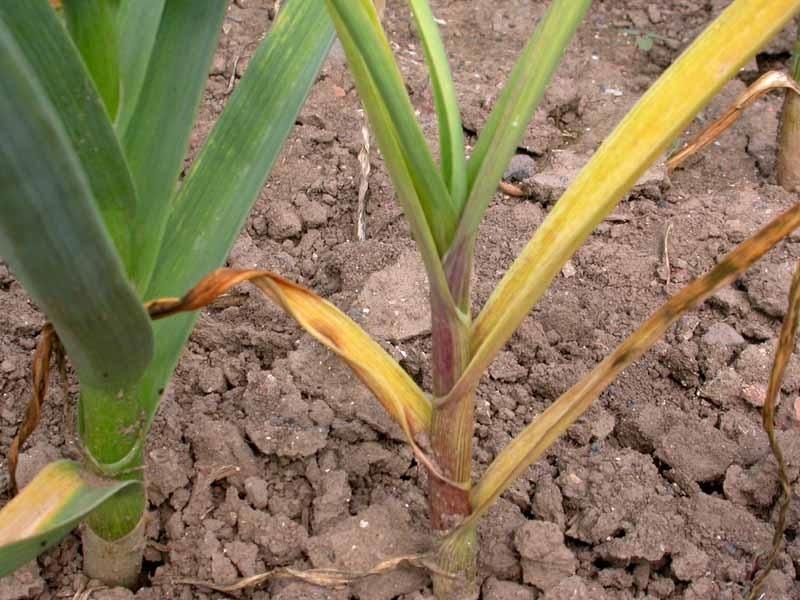
Pruning buds should be pruned. so that they do not form seeds, and the plants let all the nutrients into the bulb. When pruning, do not touch the foliage - until it dies completely, it will feed the bulbs.
↑ Upward,
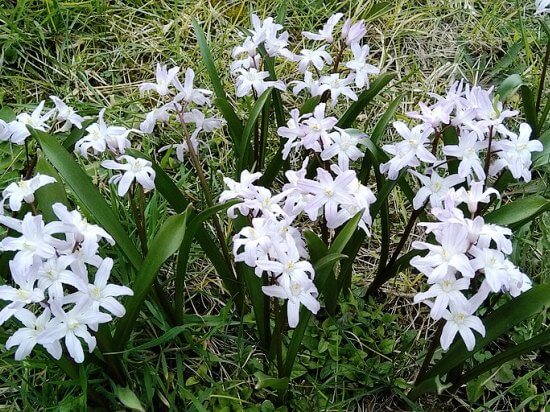


With the onset of the first spring days, fertilizing is carried out with fertilizers for flowering plants, scattering granules directly over the surface of the melting snow. Since the bulbs contain a supply of nutrients, you should not overfeed the flower. The second feeding can be carried out after complete flowering, preparing the bulbs for the dormant period.
Plants will need additional shelter for the winter only in regions with severe and little snowy winters. In such areas, planting chionodoxes before the onset of freezing is covered with pine or spruce spruce branches or fallen dry leaves.
↑ Up,


4.Transplantation and reproduction
Chionodox reproduces by small daughter bulbs and seeds.
When grown outdoors, the flower is dug up and divided every 5 to 6 years. The fact is that under the ground in each mother, in just one year, another 2 - 4 daughter bulbs are formed, which develop and begin to take more and more nutrition from the adult plant. Of course, this situation negatively affects flowering. Such large nests are dug after flowering, but until the foliage dies off - otherwise it will be problematic to find a chionodox in the garden.
↑ Up,
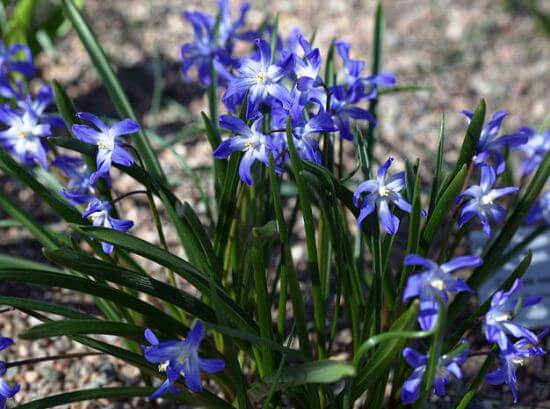


Since the planting is carried out in late summer - early autumn, and before planting it is stored in a dry and cool place at a temperature of about 15 degrees. Nests are divided into several parts by hand right before planting in open ground and only strong and healthy planting material is selected. Rotten or diseased bulbs are destroyed, and healthy ones are pretreated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or a fungicidal preparation.
↑ Up,
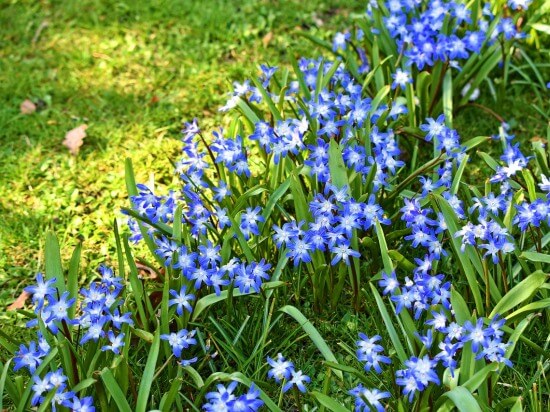


The flower is easily grown from seed and is often self-seeding. For sowing, you can use seeds of your own collection - it should be carried out in good, warm weather. The seed pods are pruned when fully ripe and the seeds are removed. prepare planting grooves with a depth of about 2 cm and carry out sowing. After sowing, the area is watered with plenty of water.
Planting a flower should be protected from ants that like to taste the planting material and are able to get the seeds and transfer them to another place.
At first, it is better not to touch the flower and do without transplants. To grow a flower from seeds, you should be patient, the first buds will appear on such plants only after 2 - 3 years - after flowering, the bulbs can be planted in the right place.
↑ Up,
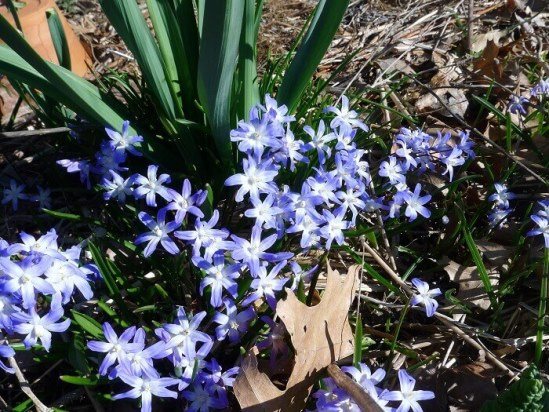


General information
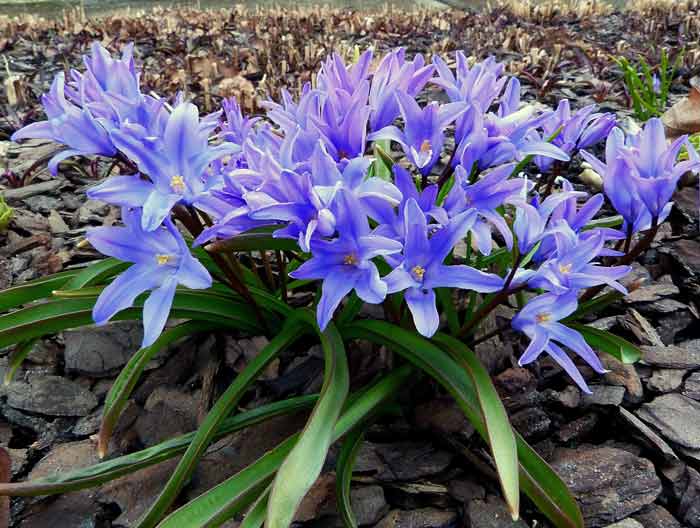
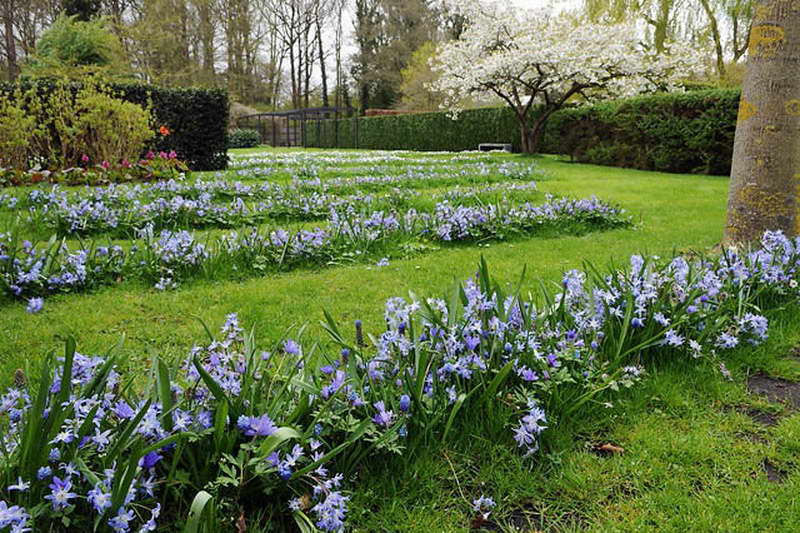
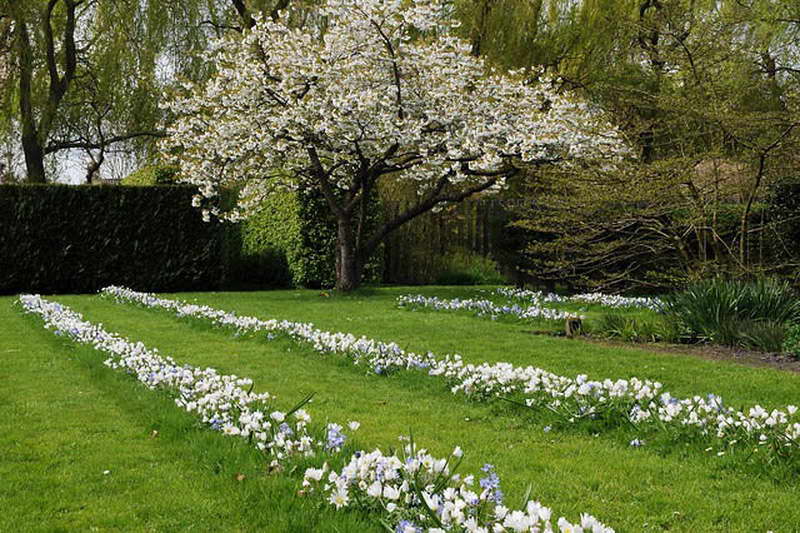
Due to its unpretentiousness, chionodox is widely used in the creation of spring beds, very often it can be found in rockeries or on an alpine slide. It goes well with almost all early spring flowers.
Planted under trees together with other bulbs, such as muscari, it will overcame in a spring garden.


At present, botanists have disbanded the genus Chionodox and attached it to the Proleski, but amateurs still call this flower by its former name.
If chionodox and redwoods grow in the garden at the same time, hybrids of these plants will appear very soon and sometimes the result is very interesting.
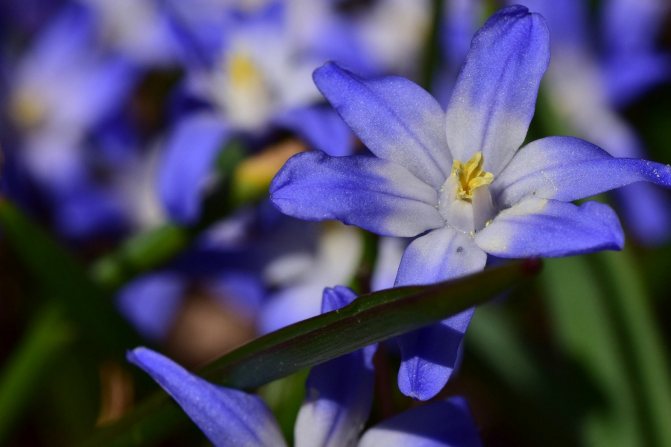
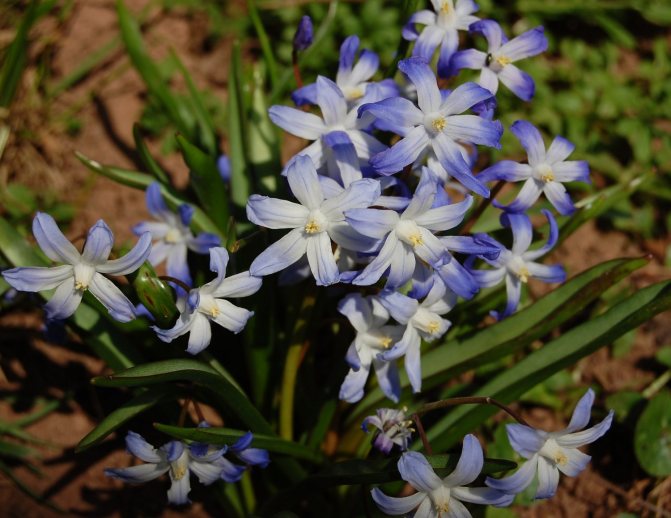
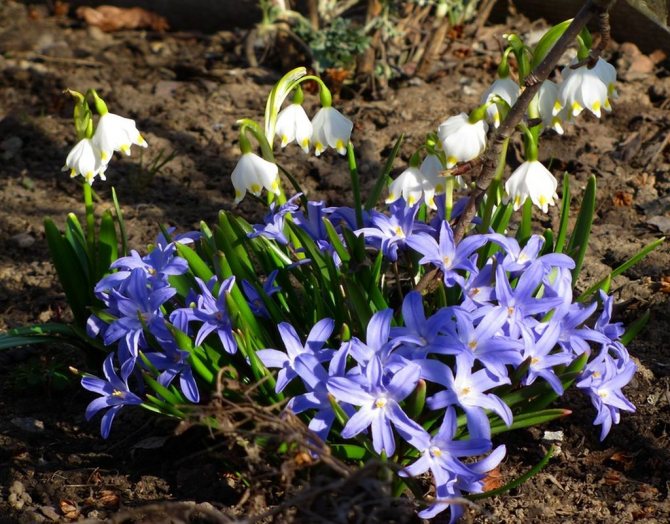
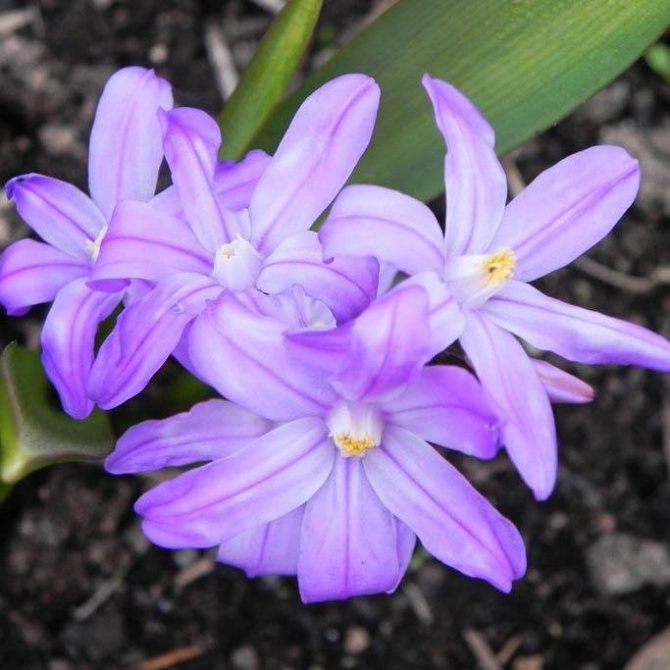
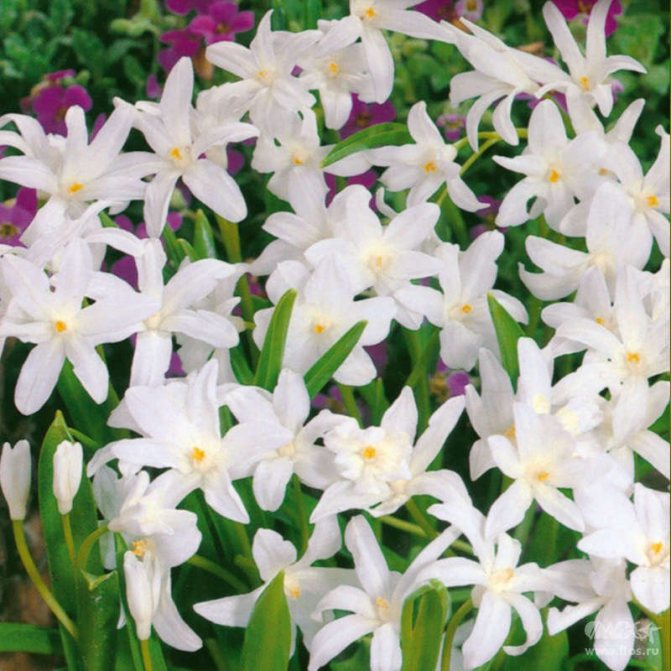
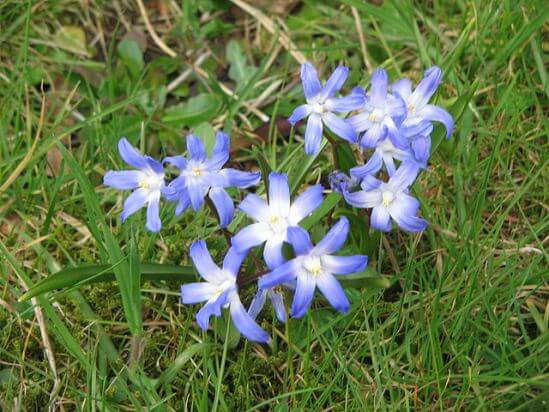
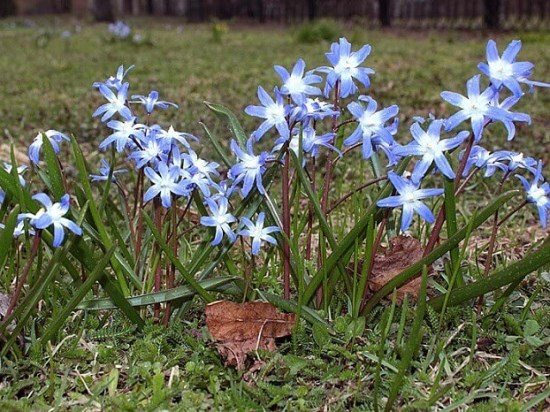
The flowers of Chionodoxa are mostly blue; at the peak of flowering, they completely cover the foliage. One of the most spectacular blue chionodoxes is the chionodox Lucilia (aka Forbes).
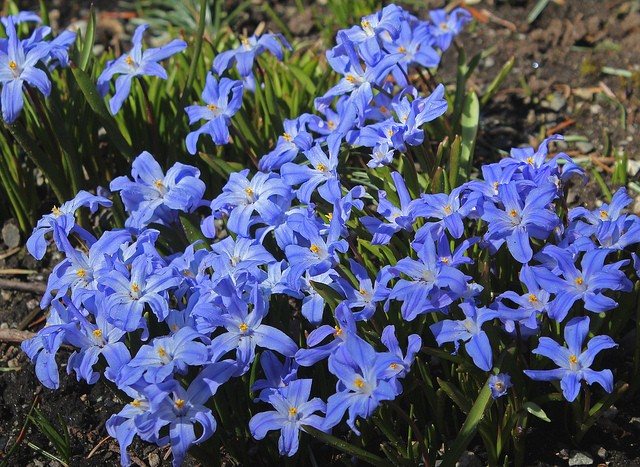


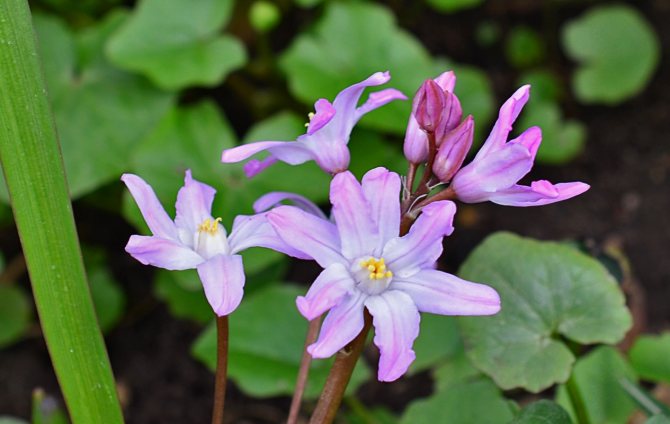
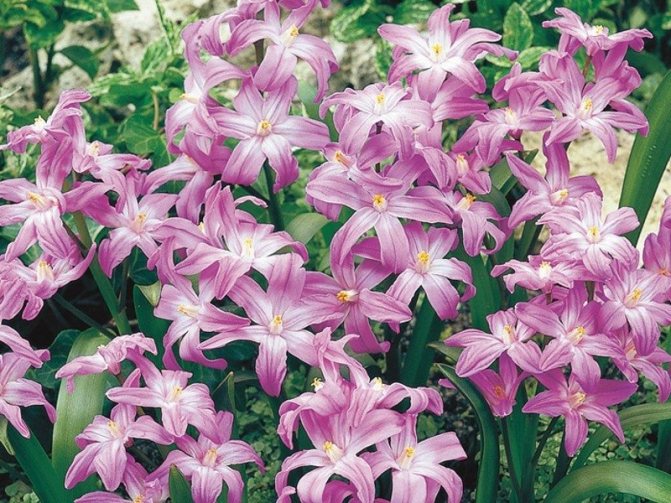
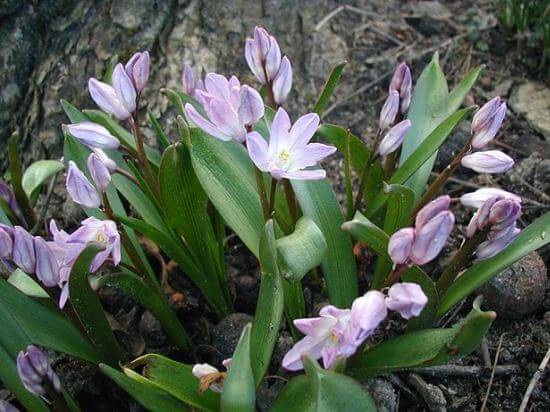
Garden forms of the plant can have other colors. The flowers may be pink.
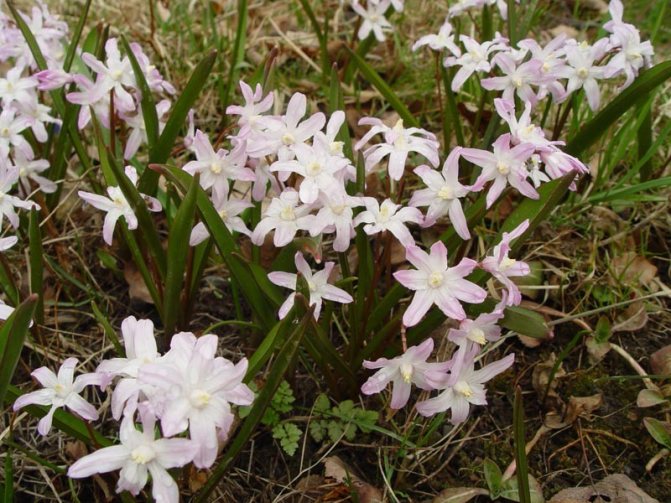


In the photo: Chionodoxa Pink Giant
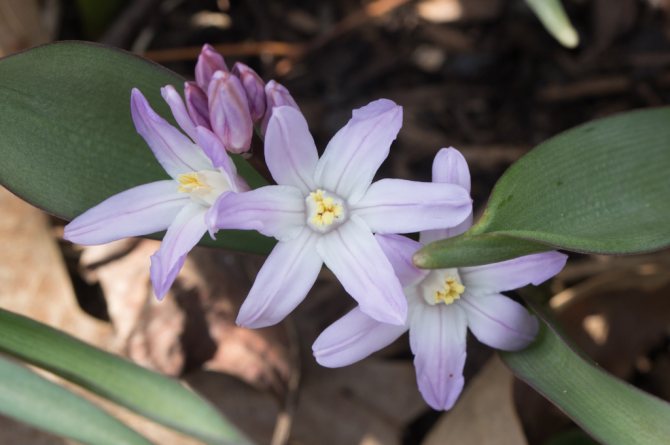
You can see the Blue Giant in the title photo of the article. There are also white varieties known as "Alba". Today, this word is often called any white varieties of Chionodox, apparently because the Alba variety was bred in 1885 and it suffered the fate of the word "Xerox", which became generic from the name of the brand. On the net called alba, you can also see varieties such as below.
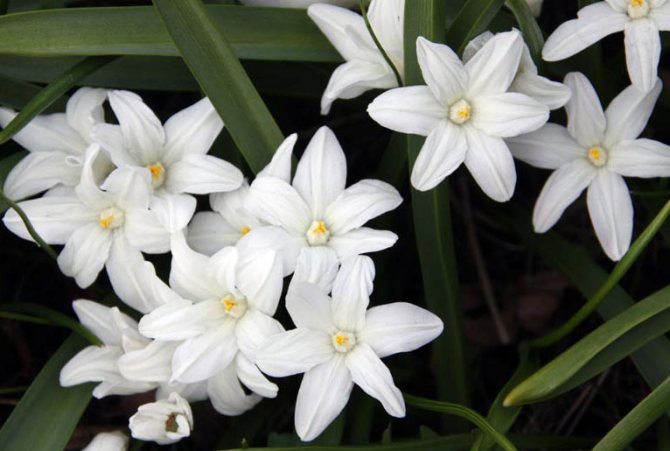


Photo: Chionodoxa Lucilia, Miss Alice cultivar
5 chionodox at home
Unfortunately, chionodox bulbs bloom in a pot culture for 1 season, after which they are dug up and kept cool for several months - until signs of new growth appear. After flowering, the leaves will turn yellow and dry - do not remove them, they continue to nourish the bulb.
↑ Up,


You may also be interested in:
- Anemone - a photo of a flower, planting and care in the open field and at home, the composition of the soil for growing in a pot, description, flowering time, varieties and types, plant propagation, what a perennial looks like
- Proleska - flower photo, planting and care in the open field, description of the plant, growing at home, reproduction - seedling from seeds, family, varieties, primrose transplant, flowering time, where it grows
- Poultry garden - photo, planting and care in the open field, description of the plant, medicinal properties, home care, application. flowering time, varieties and species, soil for growing in a pot, transplanting
- Ranunculus - a photo of a flower, planting and care in the open field, growing at home from seeds, keeping in a pot, description, flowering time in a flower bed and at home, description of plant varieties
↑ Up,


5.1 Containment Temperature
The planted chionodox bulbs are stored at a temperature of about 5 ° C until flower buds appear. Subsequently, moderately cool content at temperatures up to 15 ° C promotes abundant and long flowering. When kept warm, flowering may not occur at all.
↑ Up,
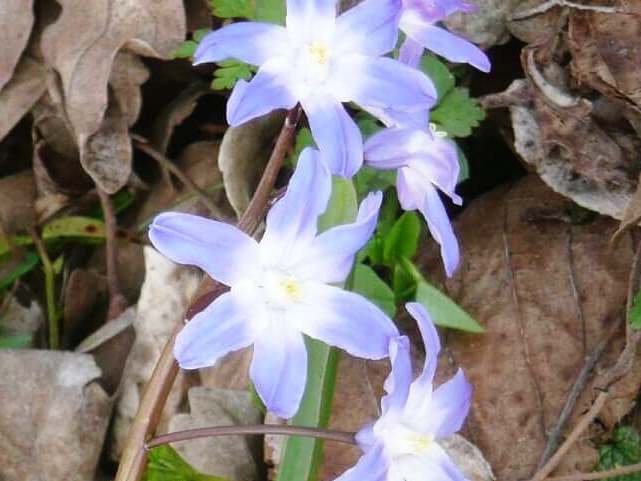


5.2 Lighting
Chionodoxa is not demanding on light conditions - it can be successfully grown both in a brightly lit place and in partial shade.
↑ Up,
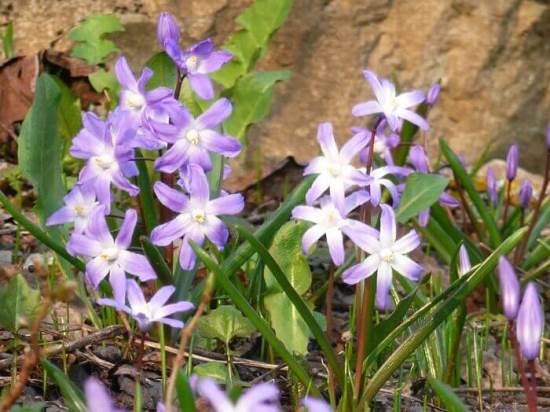


5.3 Soil
Feels great in any soil with good drainage, but prefers organic-rich nutrient substrates with a neutral to slightly alkaline pH reaction. The soil can be composed on the basis of components such as leaf and turf humus, river sand.
↑ Up,
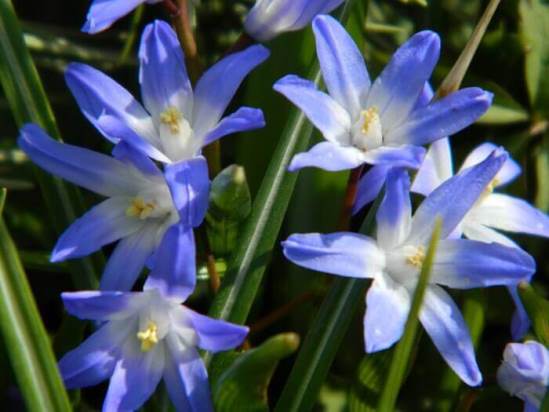


5.4 Fertilizer
With the emergence of sprouts, fertilizing with complex fertilizers begins. Enough 2 - 3 dressings per season.
5.5 Spraying
Maintain high humidity by placing the container with the plant on a tray of damp pebbles, or use a room humidifier. Spraying can be carried out.
↑ Up,
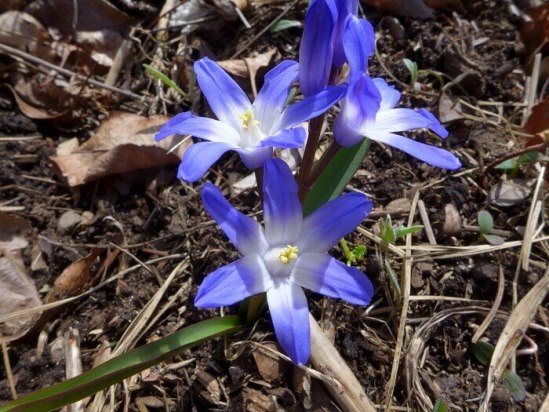


5.6 Watering Chionodox
Chionodoxa requires abundant and regular watering during the growing season. After flowering, watering is gradually reduced.
You may also be interested in:
- Primrose - photo, caring for a perennial plant, planting in open ground, home care, varieties, flowering, growing from seeds, when to transplant a plant
- Crocus - planting and care, flowering, growing in the open field, a description of when to plant, propagation of domestic crocuses by seeds, when and how to transplant
- Narcissus - photo of a flower, planting and care in the open field, flowering, varieties, description, transplanting, pruning home plants, growing in a pot
- Eukomis or pineapple lily - a photo of a flower, planting and care in the open field and at home, a description of the plant, growing in a pot, reproduction - eukomis from seeds, family, varieties, transplant, flowering time, where it grows
↑ Up,
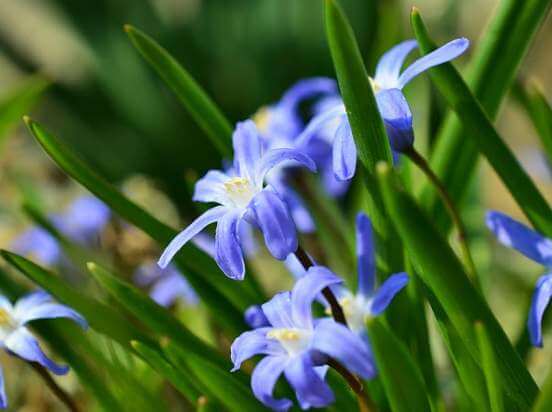


5.7 Transfer
Every year, the bulbs are planted in fresh soil in such a way that they are only slightly covered with the substrate.
↑ Up,
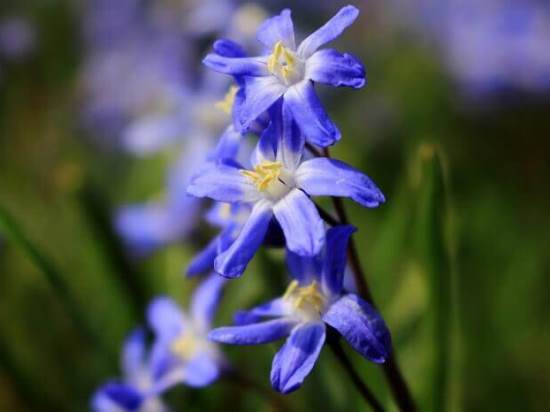


8. Varieties:
8.1 Chionodoxa Forbes - Chionodoxa forbesii
A perennial bulbous herb, reaching a height of 15 - 30 cm, has a very delicate flowering and belongs to primroses. Each bulb forms 2 - 3 dark green, belt-like, glossy leaves, slightly folded along the central vein. Peduncles 15 to 25 cm in height bear an inflorescence on the tops - a loose brush, consisting of 4 - 10 pale blue flowers with 6 oblong petals. The tips of the petals are bright blue, while the center of the flowers remains white.
↑ Up,
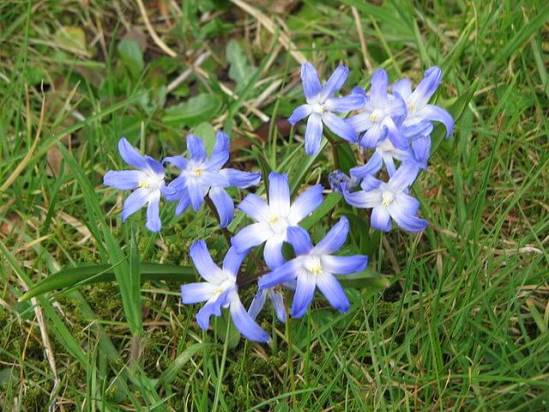


general characteristics
Chionodoxa is a plant belonging to the genus Scilla in the asparagus family. In total, the species has 6-8 representatives. The first mention of the flower appeared in 1877.The plant got its name in honor of the wife of a naturalist from Switzerland Pierre Emond Boissier Lucille.
The height of the bushes is from 10 to 20 cm. Each flower has 2 lance-shaped leaf plates. The length of the leaf is up to 12 cm. The shade is dark green, saturated.
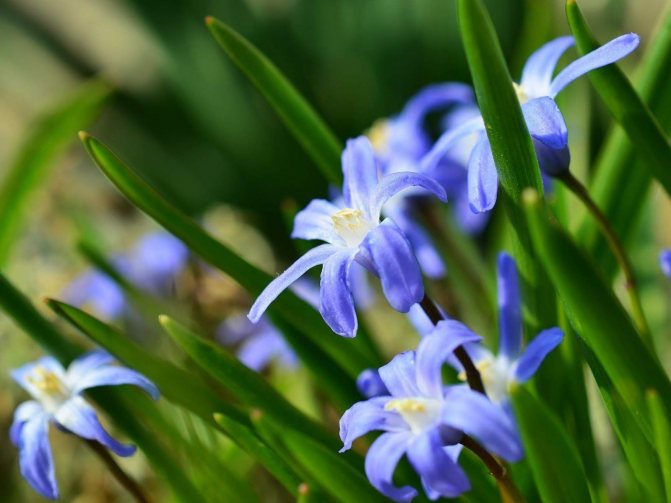


Chionodox
Each bulb produces a peduncle, at the end of which a cluster of 3-5 buds is collected. The average flower diameter is 4 cm. The color of the buds depends on the variety. Basic shades: blue, deep blue, white, lilac, lilac and pink.
After flowering, the plant bears fruit - boxes with seeds. Flowers are propagated in a bulbous way.