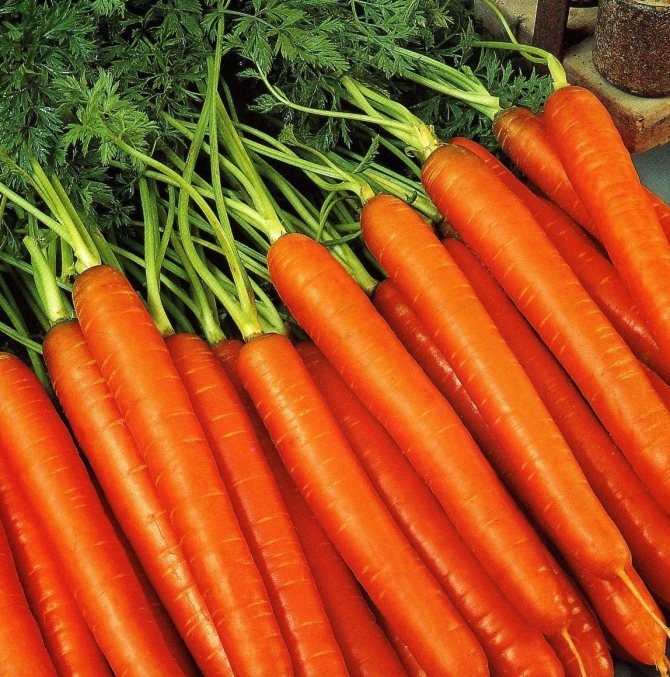
Carrots (Latin Daucus) represent the Umbrella family. The name itself was born in the Proto-Slavic language. In America, New Zealand, Australia, the Mediterranean and Africa, this root crop can be found in the wild. On personal plots, cultivated and sowing carrots (Latin Daucus sativus), which have varieties of fodder and table, are grown. For 4 thousand years, a huge number of carrot varieties have been bred.
Initially, only greens and carrot seeds were used in cooking. In Europe, carrots appeared in the 10-13th century. n. e., but in Russia the first mention of it arose in the 16th century. n. e.
Planting dates for Carrots
You can plant carrots in open ground with seeds in both spring and autumn, depending on the type of plant. In autumn, only those that cannot be stored in winter are planted. The seeds of such carrots have passed the stage of Vernalization and the harvest can be used immediately for food and for processing.
The time when you need to plant carrots in the open ground in spring comes immediately after the snow melts, when the soil is saturated with moisture as much as possible. Planting can take place at a soil temperature of +5 degrees, and an air temperature of +15. In different latitudes of Russia, the landing time will be different. So in the Volga region it will be April, in Siberia and the Urals it is better to plant carrots in May.
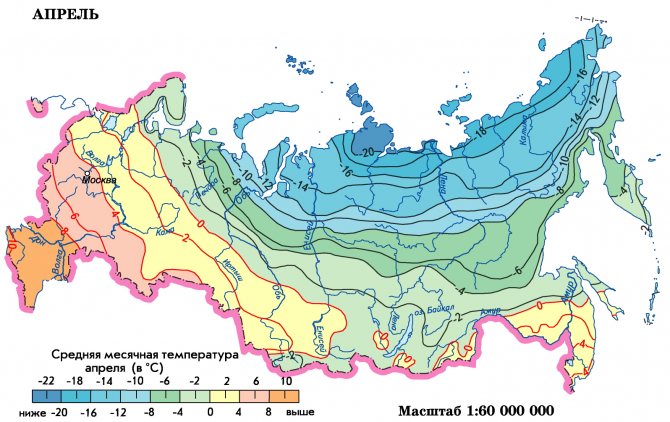
Average monthly temperature in April in Russia
You should pay attention to the landing time according to the lunar calendar.
The moon has a significant effect on plant growth. The roots develop well in breadth in the waning moon, so it is recommended to plant carrots in this phase. However, in the growing moon, the plants grow well, they will be longer, but less massive.
To get a good harvest of carrots, it is not recommended to plant them during the full moon and new moon. At this point, the plant is weakened and is unlikely to sprout well and give a good harvest.
The best varieties of carrots for open ground
When choosing the best varieties of carrot seeds for open ground, one must imagine what to expect from the harvest: fresh juices from only harvested fruits or preserving the harvest in the cellar.
All varieties of carrots for open ground are divided into groups according to the same parameters: the size of the carrot (length-diameter, shape of the fruit).
Carrot varieties in Russia:


Amsterdam, Touchon, Amsterdam, Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a fruit with parameters 150 mm x 25 mm, covered with the thinnest skin, which does not need to be removed.
This sweet fragile fruit ripening in the first half of summer is not suitable for transportation and will not be stored, but it is used for making baby vegetable food and vitamin juices.


Parisian carotel - rounded fruits of about 100 mm - a storehouse of carotene.
Alenka and Polar Cranberry are popular among summer residents.


Nantes. This group of varieties is presented in all categories of harvest dates (early, middle, late).
In long (300 mm), strong (40 mm in diameter) fruits, a very small, relative to the total diameter, core, enclosed in the pulp of excellent taste.
- "Berlikum" - 25 cm cones with a diameter of 50 mm abound in carotene.
The fruits are suitable for storage for many months.
The most popular varieties in this category are Lakomka, Berlikum Royal, Bangor F1, Darina, Bastia F1, Emperor.
- "Flakke", the second name is "Valeria".
Late-ripening fruits for storage throughout the winter. Fruits in the form of a long, more than 200 mm, cone with a base of 50 mm.
Cons - the core is too large, and there is very little carotene.
- Mini. Miniature fruits for pickling and freezing whole. "Khibiny greenhouse".
- "Shantane" - cones with parameters 120 mm x 60 mm, have excellent keeping quality, keeping the juiciness of the sweet pulp for a long time.
In addition to all kinds of variations of "Shantane", this category includes "Darunok F1", "Abaco", "Krasa-maiden", "Red Heart", "Cascade F1", "Moscow Winter", "Katrina", "Canterbury F1", "Abledo".
Early ripe
The varieties with the earliest ripening period are planted in mid-April-early May, and the harvest is harvested in the first half of July.


Early ripe fruits are not laid in cellars for the winter, since they do not have good keeping quality, they are eaten fresh in summer, juices are squeezed out, and children's vegetable purees are prepared.
The rating of the earliest varieties of carrots for the Moscow region is headed by
- "Parisian carotel"
- "Laguna F1", a high-yielding variety, rich orange fruits, resistant to cracking, very small pith and rich in carotene;
- "Dutch" ripens in just three months.
Mid-season
In terms of sowing and harvesting, it is closer to early maturing.
These vegetables, ripe in summer, arrive fresh on the tables of gardeners.
In this category, representatives of the "Nantes" group are in the lead.
In addition to those already mentioned, varieties are popular:


- "Vitamin 6", does not crack, keeps well for many months;
- "Tip-Top" - very tasty conical fruits;
- "Losinoostrovskaya" - rich in carotene, sweet and bright cylindrical fruits, demanding watering.
Mid-late and late varieties
Such carrots are sown when stable warm days are established and night frosts can not be expected, in June.


The crop is harvested in September-October, and laid in cellars and vegetable stores.
In addition to the varieties described above, you should pay attention to one of the latest achievements of breeders - "Perfection" - high-yielding, full maturity of fruits in 125 days, very undemanding to care for.
"Karlena" - a vegetable with a high level of natural sugar - a joy for children, but unacceptable for people suffering from diabetes.
How to care for carrots after planting
Growing and caring for carrots outdoors is a rather troublesome process. Carrots require constant attention, weeding, fertilization and pest control. The most difficult period in carrot ripening is seed germination. At this stage, the main thing is to break the crust of the earth formed at the place of seed germination. It is best to do this in moist soil and very carefully. To avoid this, you can cover the ground with peat.
Watering and humidity
Carrots are very moisture demanding. She does not like her excess, however, she also dislikes dryness. At the beginning of its growth, during the formation of greenery, the carrots need to be watered more often, then, with the growth of the fruit itself, the moisture should be reduced so that the carrots do not crack. Water the carrots so that the moisture makes its way to the depth so that the fruit grows straight down. It is best to water a lot, but not often. In hot weather, when moisture quickly evaporates from the soil, water the carrots 3 times a week.
Top dressing
If we have prepared beds for carrots since autumn, then growing large carrots can be done without feeding.
However, the carrots will be grateful for the fertilization and during the entire growth period.
The first feeding is best done after a month when the first shoots emerge.
In the second period of the growing season, it is better to apply fertilizer from ash (for 10 liters of water, 1 liter of ash infusion).Ash is a potash fertilizer, many plants love it very much, moreover, it protects the plant from pests.
Loosening and weeding
The first loosening of carrots should be done after the first shoots appear. This should be done very carefully so as not to damage the young, delicate leaves. It is better to do this after rain, or after watering.
Loosening is often accompanied by weeding; it is necessary to pull out the weeds so that they do not interfere with the development of the fruit.
Thinning and how to avoid it
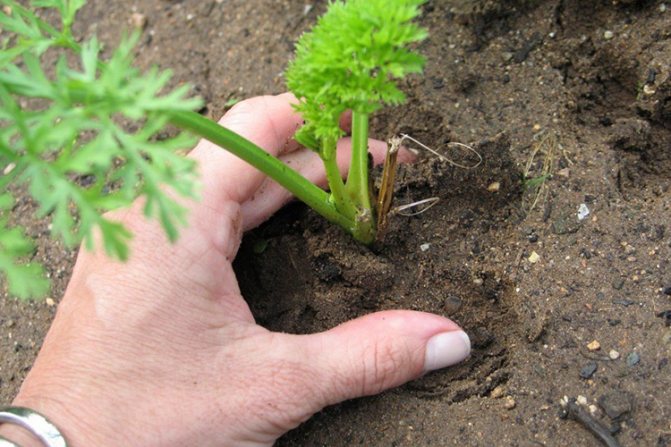
Thinning carrots is a necessary stage in their growth. Even when planting with ribbons or capsules, there is a chance that the seeds will grow too close to each other, leading to abnormal development of the fruit. Correctly thin out the beds for the first time, it will be at the first appearance of real carrot leaves, leave a distance of 5 cm between the carrots.
The best conditions for carrots
Carrot beds are allocated areas in direct sunlight: a lack of light will ruin both the shape and taste of the fruit.
Antecedents, useful and unwanted
Crop rotation is half the success in growing a sweet root crop.


Every year, a new territory is selected for planting carrots in open ground: for the second year in the previous beds, the vegetable will be sick, pests will overcome it - such a crop will not be stored.
It is possible to return this culture to its old place no earlier than four years.
Carrots will feel great after cabbage beds, potato plantations, cucumber bushes, zucchini, green crops, onions, garlic and legumes, siderates.
It is dangerous to keep carrots in the ground where relatives in the family grew, susceptible to the same diseases.
Delicate dill and aromatic parsley, cumin with coriander, celery with parsnip are the worst continuity options for carrots.
Soil preparation for sowing
Taste, shape, size, storage capacity for the prescribed period depend on the quality of soil preparation for sowing.
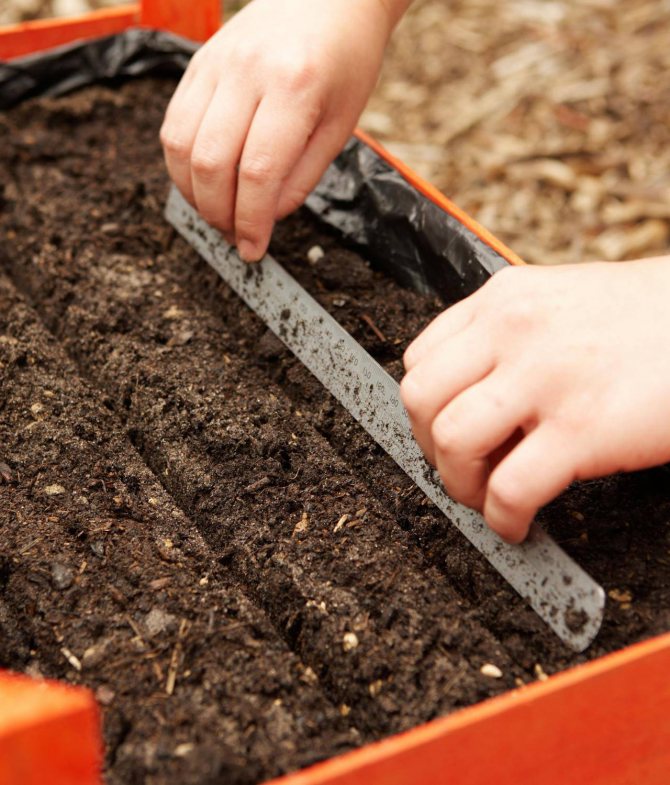


Carrots require a loose, breathable, moisture-absorbing substrate without the formation of a superficial crust.
Acidity - neutral, composition - loam, sandstone.
Carrots, which need to fulfill all of the listed requirements, suffer most from heavy caked soils, that is, looseness is the most important quality of the soil.
In heavy soil, the germination of carrot seeds is fundamentally lower, and the fruit is deprived of air: oxygen deficiency affects all qualities, the plant is susceptible to fungal diseases.
For sowing seeds of early-ripening carrots, the land is prepared in advance, in the fall of the previous season, and for the rest of the planting dates for carrots - in the spring, when the soil thaws.
To grow carrots in the country, a deep, at least one and a half bayonet of a shovel is required, digging with the introduction of compost, humus, rotted manure, removal of weeds, roots, stones.
Sand added to heavy soil gives looseness, lightness, rotted sawdust is useful for the same purpose, and ash is a source of potassium.
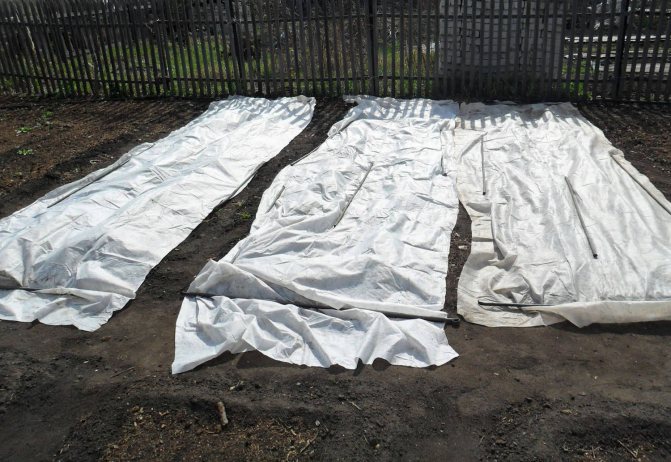


A few days before planting, the carefully dug, loosened beds are leveled with a rake, every 15 cm they make furrows 2 cm deep.
Furrows are spilled with boiling water and hidden under a film.
Hot water vaporization under the film will prevent the soil from drying out and crusting.
Important to remember! In no case should fresh manure and sawdust be introduced for carrot crops: the fruits will be branched and tasteless. Nitrogen fertilizers - in a strictly specified proportion. Overdose is fraught with the accumulation of nitrates in the vegetable.
Seed preparation
Like most members of the umbrella family, carrot seeds, containing essential oils to reliably protect the embryos from moisture, hatch for a very long time, at least three weeks.


The germination rate of planting material also causes a number of problems: the seeds must be fresh, not older than two years, and the germination percentage should be two-thirds of the total.
The stores sell carrot seeds in granules that have passed all stages of processing and hardening.
But no one guarantees the quality of the planting material, and there are more and more claims to the germination of carrot seeds every year.
This encourages growers to cull and prepare their own seeds.
Rejection occurs at the end of ten hours of soaking in warm salted water.
Non-vegetative seeds float on the surface, so they are easy to pick up and discard.
High-quality planting material - swollen seeds lying at the bottom - are suitable for the next stage of preparation.
There are several ways to treat seeds:
- The seeds, washed under running cold water, are wrapped in clean material, immersed in hot, at least 600 water, for 15 minutes.
After rinsing again in cool water, dry it for a day, after which you can sow.
- Stratification is the most popular method for stimulating germination and strengthening the plant's immunity.
Selected seeds are wrapped with a damp cloth or napkin, placed in a closed container in a refrigerator for three days.
Before stratification, the seeds are soaked for 24 hours in an ash (spoon per liter of water) or for about two hours in a weak manganese solution, the temperature of which is not less than 300, renewing the liquid several times.
After - washing, drying and sowing.
- The planting material is kept in a tablespoon of hydrogen peroxide diluted in a liter of water for 24 hours.
Liquid temperature + 400.
- Hardening and stimulation with contrasting immersions: the wrapped seeds are heated in + 500 water for 15-20 minutes, after which they are cooled for about three minutes in cold water
- A damp cloth with seeds is dropped into the ground for a week and a half.
During this time, the seeds germinate, they can be planted.
Typical planting and grooming mistakes
The first mistake when caring for carrots, this is too abundant watering. It leads to rotting of the carrot fruit. The fruit affected by rot should be removed immediately after detection, otherwise the rot will spread to the rest of the fruit.
Second mistake - insufficient watering. With insufficient watering, many roots (hairs) appear on the carrots. So the carrots are trying to take at least a drop of moisture from the soil.
Third mistake - these are strong differences between dryness and excess moisture. This error leads to the fact that cracks appear on the fruits of the carrots. This is not the most dangerous mistake, however, the fruits become not beautiful and are not suitable for long-term storage.
The fourth mistake - this is the introduction of fresh fertilizers into the soil. This leads to an excess of nitrogen and nitrates, to a subsequent change in the chemical composition of the fruit, causing curvature, thinning, deterioration of sugar content.
USEFUL PROPERTIES OF CARROTS
This sweet orange root vegetable is a treasure trove of vitamins and nutrients. It contains all the vitamins of group B, vitamins A, C. E, K, PP, beta-carotene; trace elements - iron, manganese, potassium, sodium, cobalt, molybdenum, magnesium, copper, boron, selenium, phosphorus, chromium; glucose and various sugars, essential mineral salts and other nutrients.
However, with the introduction of increased doses of mineral fertilizers, carrots, like all root crops, are able to accumulate them in huge quantities, then filling our body with them. That is why it is better to grow this unique vegetable without chemicals in your garden, and not buy it in stores.
She needs very little space. For a family, it will be enough to allocate one not very large garden bed for carrots.


Diseases and pests of carrots
Closer to the ripening period of carrots, the fruits can infect diseases and parasites, attracted by the sweet smell and taste.
One of the diseases of carrots is rot. It can be white, gray, felt and dry.
White Rot caused by the fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. It spreads easily and can cause great harm to the crop during the storage stage.


White rot
Signs: Carrot fruits are covered with a white bloom, with black dots on top and mucus on the bottom.
Recommendations for treatment and prevention:
- using proven, healthy seeds;
- fertilization of carrots with potash and phosphorus fertilizers to increase their immunity;
- harvesting in dry weather;
- weed out injured fruits (they are most susceptible to infection), as well as fruits with signs of damage;
- disinfection of the storage of carrots before storage with a sulfur checker;
- storage of carrots at 1-2 degrees.
Dry rot or Phomoz Is the fungus Phoma rostrupii Sacc. It affects already almost healthy fruits and, upon subsequent storage, spreads to the entire crop.
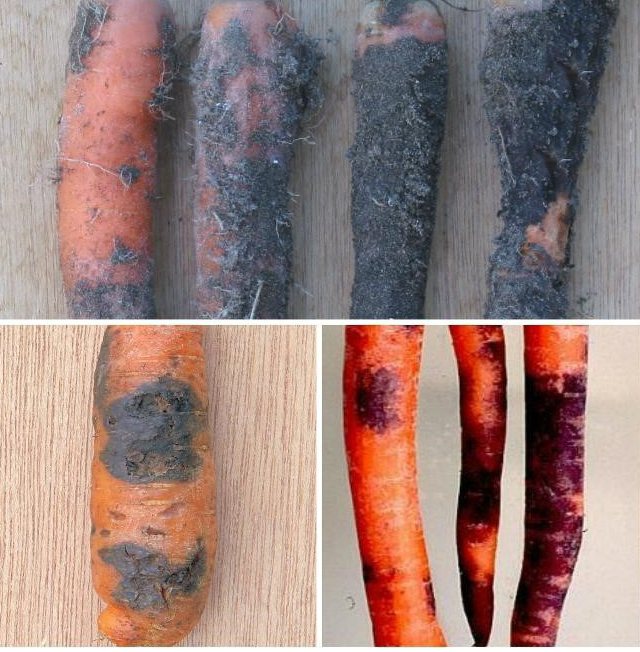


Dry rot (phomosis)
Signs: elongated, dark spots appear on the leaves, and on the fruits dark, depressed spots with black dots at the top are fungal spores.
Recommendations for treatment and prevention:
- destroy fruits with signs of disease before storage;
- disinfection of the storage of carrots before storage with a sulfur checker;
- storage of carrots at 1-2 degrees.
- to collect and destroy the tops before storage;
- fertilization of carrots with potash and phosphorus fertilizers to increase their immunity;
- compliance with crop rotation.


Brown spot
Another disease of carrots is brown spotalso caused by a fungus.
Signs: It is expressed in dark brown constrictions on the lower parts of the stem, near the soil. Young plants die quickly. On already adult plants, the disease manifests itself during the formation of the fetus. The leaves are covered with brown spots, curl, light brown spots appear on the fruits.
Recommendations for treatment and prevention:
- fertilization of carrots with potash and phosphorus fertilizers to increase their immunity;
- planting resistant crops;
- spray the stems of the plant with celandine broth.
Alternaria or black rot, is not caused by a fungus - it is an infectious disease of the plant.


Alternaria or black rot
Signs: it manifests itself in the blackening of the stem. On young leaves, this manifests itself immediately, the leaves curl and acquire a dark color. A spot of coal-black color appears on root crops.
Recommendations for treatment and prevention:
- remove all remnants of vegetation from the beds;
- compliance with crop rotation;
- planting resistant crops;
- fertilization of carrots with potash and phosphorus fertilizers to increase their immunity;
- strengthening plant immunity with a solution of "Baikal-M" and "Immunocytophyte";
- remove damaged fruits from the site.
Another disease of carrots - powdery mildewcaused by a fungus.


Powdery mildew
Signs: it is expressed by a white bloom on any part of the plant, then, with increasing distribution, the leaves begin to turn brown and wither. The roots become hard and stop growing.
Recommendations for treatment and prevention:
- thinning the beds;
- watering with warm water;
- fungicide treatment during the growing season;
- strengthening plant immunity with a solution of "Baikal-M" and "Immunocytophyte";
- destruction of plant residues from the beds.
WHERE THE CARROTS COME FROM
It is believed that the homeland of carrots is the Middle East and Asian countries, primarily Syria and Afghanistan. Here you can still find its wild roots, colored in yellow, bright blue, green, purple, dark brown and cream colors. Some types of carrots were also used for food by the first tribes in Ancient Egypt.
Carrots came to Russia from Europe in the middle of the XIV century. Initially the best varieties were brought from Holland and France. But in the middle of the 18th century, the first domestic carrot varieties were created: Nantes, Danverskaya, Vorobievskaya.
They quickly spread throughout Russia, and by the middle of the 19th century, carrots were already growing in every estate. They began to grow carrots on peasant plots as well.
General tips for growing carrots
In short, all the tips for growing carrots can be summarized as follows:
- change the place of planting carrots every 4 years;
- promptly remove plant residues and tops from the garden;
- fertilize the soil with phosphorus-potassium fertilizer before planting;
- feeding the plant with potassium;
- feeding with nitrogen fertilizers;
- spraying with copper-containing preparations (with white rot);
- spraying with copper oxychloride (with felt rot);
- spraying with 1% Bordeaux liquid (with gray rot);
- planting disease resistant crops.
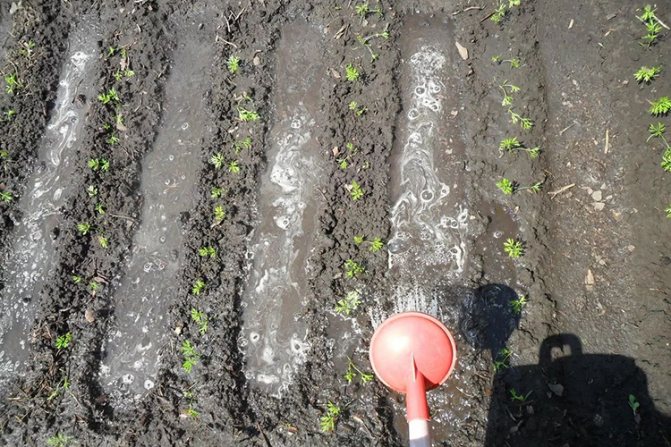
Do I need to water the carrots after planting
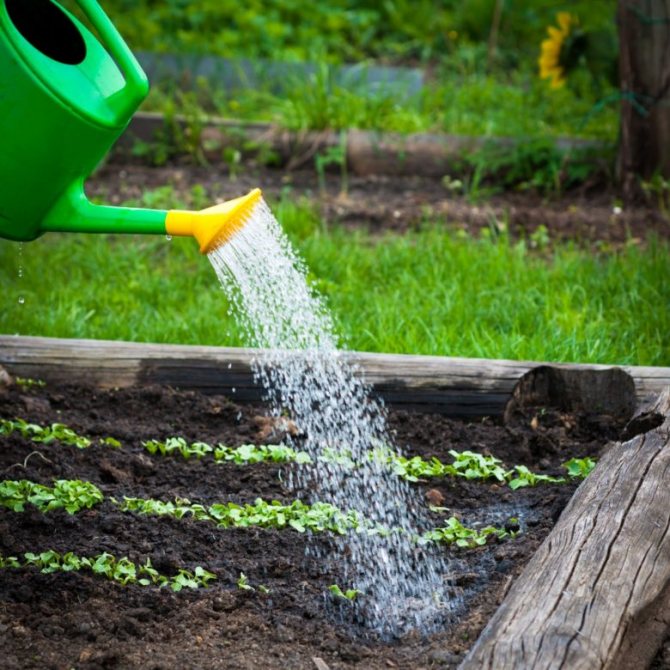


Watering can watering carrots
Carrots need regular watering during all phases of their growth.
After planting carrots, it is imperative to moisten the soil well so that the seeds can swell and germinate well. However, it is essential to water the carrots correctly so as not to wash the seeds out of the soil or drown them too deep. To do this, you need to gently water with a watering can with a nozzle, which creates many small drops, like a shower. Or use drip irrigation. To keep moisture in the soil longer, the garden bed should be covered with foil or mulch after the first watering. A greenhouse for carrots is not needed unless the cultivation takes place on an industrial scale. So in closed ground, with a heated greenhouse, carrots are grown all year round.
How many carrot seeds sprout
A feature of carrot cultivation is its long germination phase. In the spring, carrot seeds sprout about two weeks after planting it in the ground, the first shoots with small leaves appear. Then the first thinning of the carrots occurs at a distance of 2-3 cm from each other. After another 15-20 days, it is necessary to re-weed the carrots already at a distance of 4-6 cm from each other.
Choosing a place for a garden in the garden
It's no secret that carrots are an unpretentious root crop, but to get a rich harvest, you still need to create comfortable conditions. When choosing a place for the beds, the gardener must take into account:
- this vegetable crop is developing well on a lighted area;
- fertile loamy-sandy soil with 4% humus and neutral acidity 6-7 pH;
- previously, potatoes, tomatoes, maize and legumes were grown at the sowing site;
- do not use for growing beds where spicy herbs previously grew (dill, parsley, fennel, etc.);
- it is impossible plant a vegetable in the same area 2 years in a row.
Large, well-shaped roots grow on peat soilsthat were formed after the drying up of the swamps. And on clay soil, carrots will take on an ugly shape due to strong resistance during growth.
Before freezing, the area for vegetables must be dig up, remove roots and stones... But do not drive the shovel too deep into the ground and destroy the fertile layer. Digging should be about 0.3 meters deep. With the onset of spring, smooth and deeply loosen the surface.
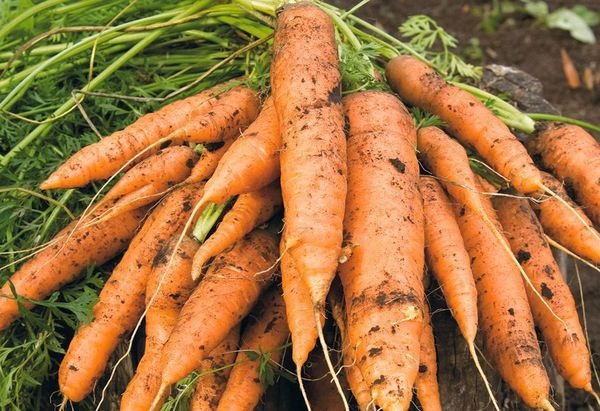


On peat soils, carrots will be large and regular in shape.