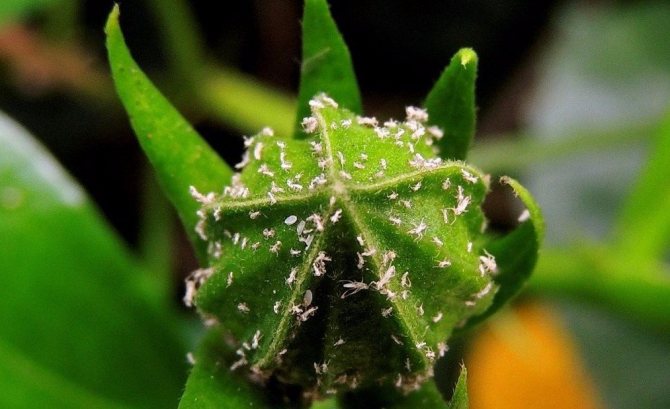
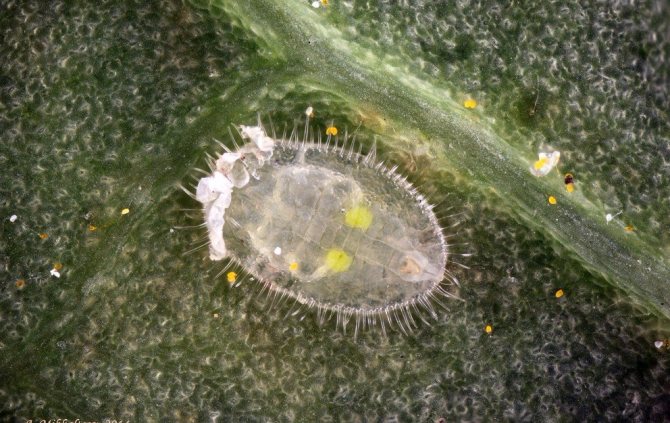
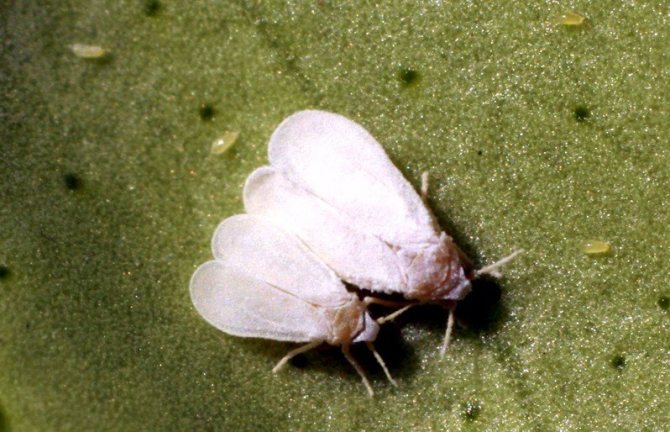
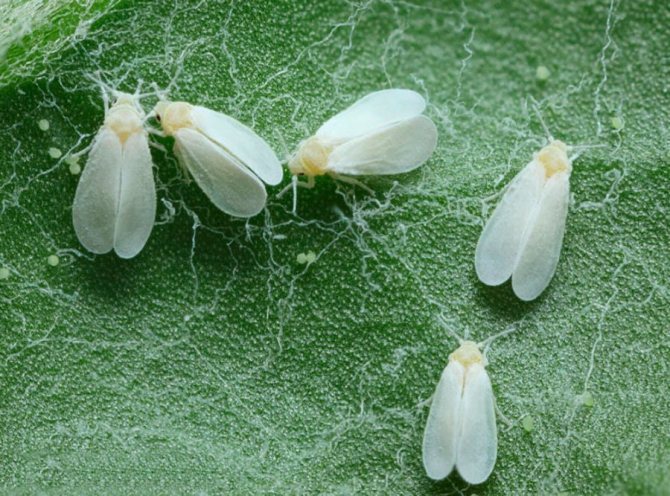
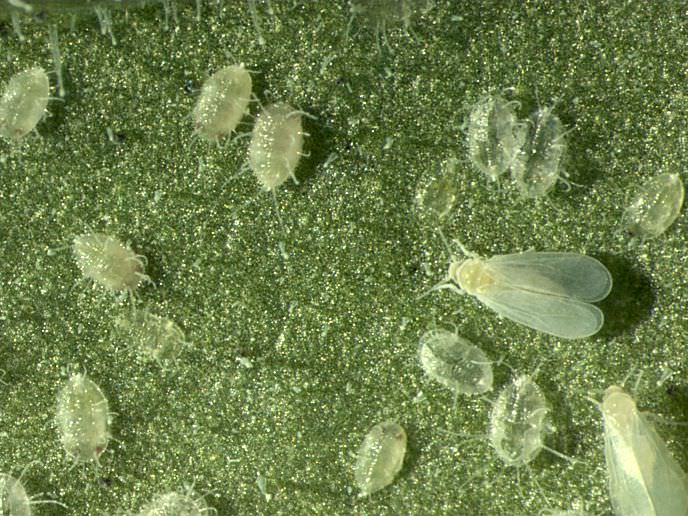
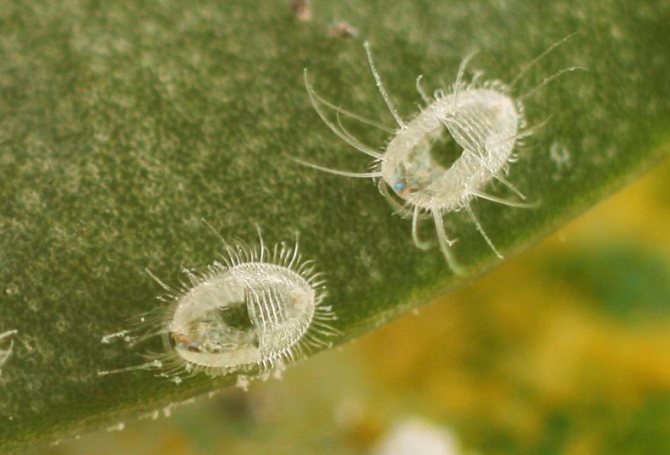
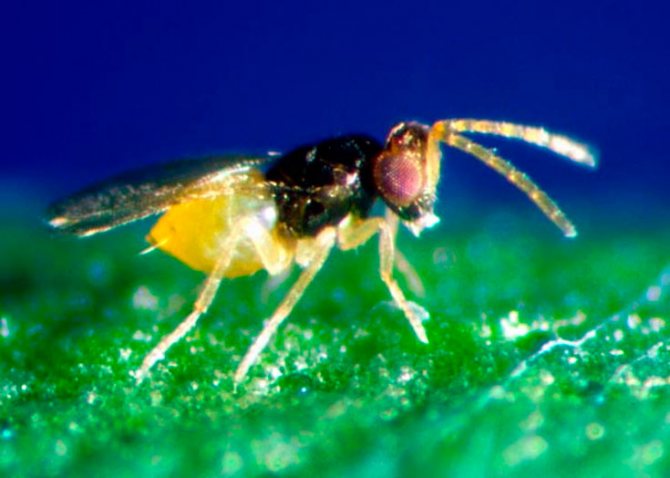
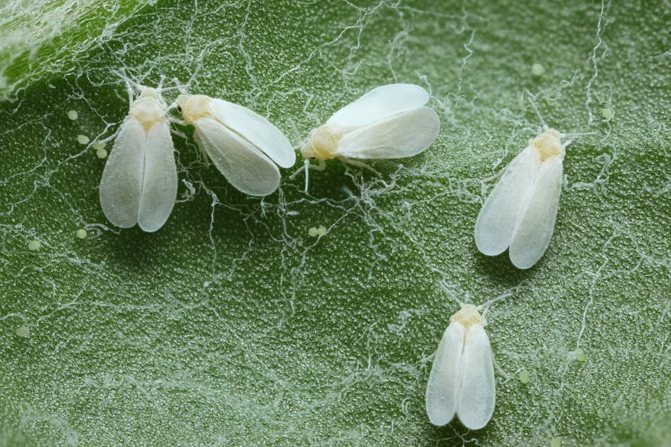
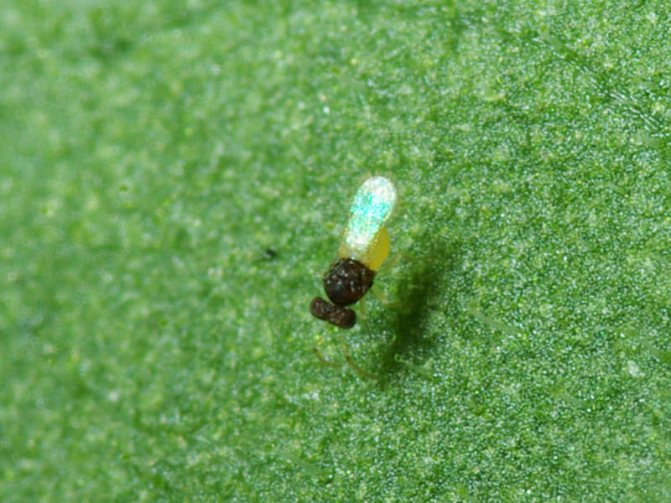
The whitefly is a small, yellowish-white or white insect that looks like a very small moth. In length, this garden pest is only 1-1.5 mm. The larvae of this insect are flat and oval in shape, and their color is pale green. Larvae are no more than 0.3 mm in size.

Insect on the leaves
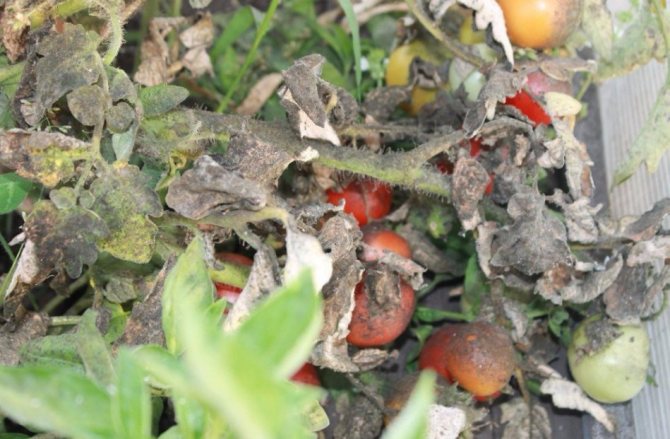
These pests are dangerous to plants. They feed on their sap, as well as aphids, which leads to disease and the plant dies. The consumption of plant sap exceeds the need of insects, so they excrete the excess in the form of dew. A sooty fungus subsequently appears on this dew, which also harms the plant. It starts to stick, and a black coating appears on it. The plant loses its ability to breathe normally and carry out photosynthesis. In addition, whiteflies carry various diseases that are dangerous to plants. Insects can harm dozens of plant species both in greenhouses and outdoors. There are various preparations and insect control agents. Let's take a closer look at how to eliminate the whitefly and what methods are best to use.
What is this insect
In nature, there are about 200 varieties of whiteflies. Previously, these insects lived only in warm regions. Today they are found everywhere, parasitizing on vegetables, greenhouse and indoor crops. They are miniature butterflies 1.3-3 mm long. The body and wings are covered with a whitish waxy coating. The female lays about 300 eggs per month.
The whitefly develops from the egg stage to the adult in several cycles (on average, 1.5-3 months):
- Laying eggs on the underside of leaves.
- Brown or black caterpillars emerge from eggs. They are localized on the lower part of the leaves and feed on the sap of the plant. The caterpillar stage lasts 7-11 days.
- Caterpillars turn into motionless larvae (nymphs).
- Within 1-2 weeks, the nymphs increase in size, remaining motionless.
- A black oval pupa is formed from the larva.
- An adult butterfly hatches from the pupa.
The most common types of whiteflies are:
- greenhouse (greenhouse);
- tobacco;
- citrus;
- strawberry.
Favorable conditions for the development of the pest are warm air and high humidity. Therefore, whiteflies often parasitize indoor and greenhouse plants.
Whitefly harm
Larvae cause the greatest harm to plants. They feed on the sap of stems and leaves. While butterflies form from the larvae, they can damage up to half of the plant.
Adult whiteflies leave their waste products on the surface of the leaves. After a while, the affected areas begin to deteriorate, the plant gradually dies. Also, insects can carry viral infections. As a result of infection, the stems are deformed, the leaves curl, spots and yellowness appear. The plant stops growing.


Whitefly species
More than 100 species of this parasite are known, found in many regions. The greatest harm is caused by:
- Tobacco. Omnivorous, even feeds on medicinal herbs. It differs in the inclination of the wings of a butterfly.
- Greenhouse or greenhouse. Fertile, resistant to bad conditions. The body of an adult is yellow.
- Citrus. The butterfly has an icon similar to Y.
- Silky. The larvae are black with a white fringe. Distributed to citrus fruits.
- Cabbage.In its absence, it develops other vegetable beds.
- Bordered. Lives on cotton and melons. It has a gray body and black stripes on the wings.
- Strawberry. Prefers berry plants (strawberries, raspberries, etc.).
- Giant. The largest butterfly is up to 5 mm. It is found on roses, tomatoes, trees and ornamental shrubs.
- Honeysuckle. The front winglets are speckled. Lives on grapes.
- Iris. It also prefers gladioli. Switches to other flowers if they are missing.
- Ash. The caterpillar on the body has a small fringe with wax droplets at the ends. Harmful to trees and shrubs.
- Crowned. The larva is black with a waxy crown at the head. Lives in oak and chestnut groves.


How to recognize: signs of infection
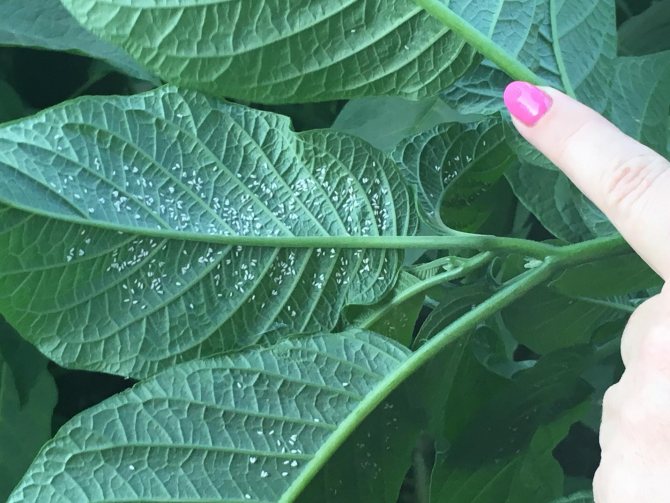
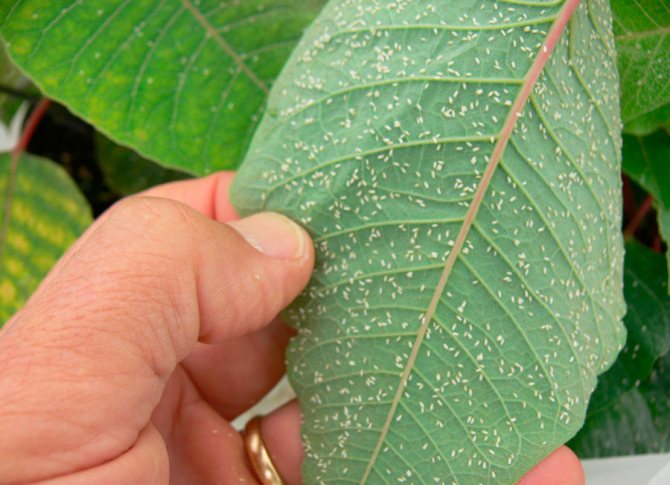
The presence of whitefly on indoor crops is indicated by characteristic signs:
- A swarm of adult insects flies up from touching the plant above the pot.
- A sticky, shiny bloom (pad) appears on the outer surface of the leaves.
- On the underside of the leaves, in addition to adults, larvae and eggs can be found.
- Deceleration of plant growth.
- Gray and black spots on the leaves are signs of a sooty fungus, which is triggered by the presence of insect excrement.
- Yellowing, curling and falling of leaves.
Harm to indoor plants
The whitefly itself (larvae) harms houseplants by puncturing a leaf or shoot, it begins to actively suck out the juice. The plant gradually weakens, the leaves begin to curl, turn yellow and fall off. At the same time, parasites carried by various destructive viruses: yellow mosaic, jaundice, chlorosis, leaf curl. All this causes deformation of plants and a stop of their growth. And with a strong defeat, complete death.
Even more damage is caused by the sooty fungus, which is the result of the vital activity of the whitefly and can cause rotting of the plant.
The difference between a spider mite and a whitefly can be seen in the photo here.
And here is a detailed instruction on how to independently deal with the scabbard on indoor plants.
For you, we have created a step-by-step instruction on how to combat powdery mildew on roses.
Control methods
Whiteflies reproduce quickly and can fly. This creates certain difficulties in quickly getting rid of parasites. Therefore, the fight against these pests should be carried out consistently and in stages.
General rules
Infected plants need quarantine. Move them to a cool room. When the temperature drops below +10 degrees, whiteflies die. If the flowers are unpretentious to the cold, you can take them out on an open balcony or veranda in cold weather. A weekly quarantine is enough for the insects to die completely. Wash off the remains of eggs and larvae with running warm water.
Note! It is imperative to remove all damaged parts of the plant. It is better to replace the soil in the pot with a new one. Disinfect it first. To be sure of the complete extermination of insects, you need to carry out preventive treatment of all plants in the house.
Chemicals
The most effective in the fight against whitefly are chemical insecticides. But before using them, you need to carefully read the instructions. It is important that the product is safe for the plant. When working with chemicals, it is recommended to take care of the presence of protection for the skin and hair. Among all insecticides against flower pests, several of the most popular can be distinguished.
Confidor
Complex means of contact action. Whiteflies begin to die after 1.5-2 hours after treatment with the drug. Imidacloprid is a part of Confidor. On its basis, the following insecticides are produced: Marathon, Apploud, Admir. They are all interchangeable. You can destroy insects with one treatment (watering at the root). But to consolidate the result, repeat the treatment in a week.The price of a bag of 1 g of Confidor is 30-40 rubles.
Akarin (Agravertine)
Insectoacaricide, which enters the intestines of insects through food, and they die. The drug is sprayed on all leaves and stems. It is necessary to fill the whitefly colony as much as possible, spray the solution on it. A 4 ml package costs 13-20 rubles.
Spark
The drug is available in several forms: sticks, powder, tablets, liquid. The agent is watered on infected plants. Effectiveness after treatment lasts for 25 days. More often, one spraying is enough to destroy pests.
Aktara
A potent systemic agent mainly used for watering the root system. The active ingredient thiamethoxam enters the stems and leaves. And insects, eating the poisoned sap of the plant, die. A one-time treatment of the plant with Aktara gives it protection for 3-5 weeks. In order for the parasites to be destroyed in one go, it is recommended to make a stronger solution than indicated in the instructions. If the lesions are too serious, the plant is additionally sprayed (3 times with an interval of 1 week between each). The average cost of a 4 g sachet is 100-120 rubles, a 1.2 ml ampoule is 50 rubles.
Fitoverm
Complex insectoacaricide that destroys adult insects and larvae in 1-2 treatments. The procedure is best done before flowering. The cost of a 4 ml ampoule is 15-20 rubles.
Rules for treating plants with insecticides
Nuances of using chemicals:
- The room temperature should be above +20 degrees. At lower temperatures, chemicals are ineffective.
- After spraying, you can put a transparent bag on the flower to make the product work faster.
- A single treatment gives a one-time action. It is recommended to repeat the procedure after 6-8 days in order to finally destroy the parasites.
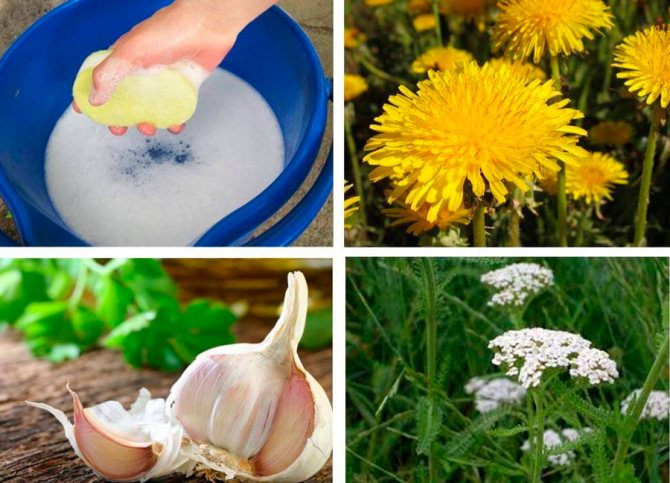
Folk remedies
If the infection is insignificant and the whiteflies have not yet had time to severely damage the plant, you can resort to using less toxic folk remedies.
Proven recipes:
- Gut tobacco from 1 pack of cigarettes. Pour 1 liter of boiling water over it. Leave the product to infuse for 5 days. Strain and spray 2-3 times a day.
- Grind 20-30 g of hot pepper. Boil it in a glass of water for an hour. Insist the remedy for 1 day and strain. Dilute 10 ml of the resulting infusion in 1 liter of water. Treat affected plants once every 14 days.
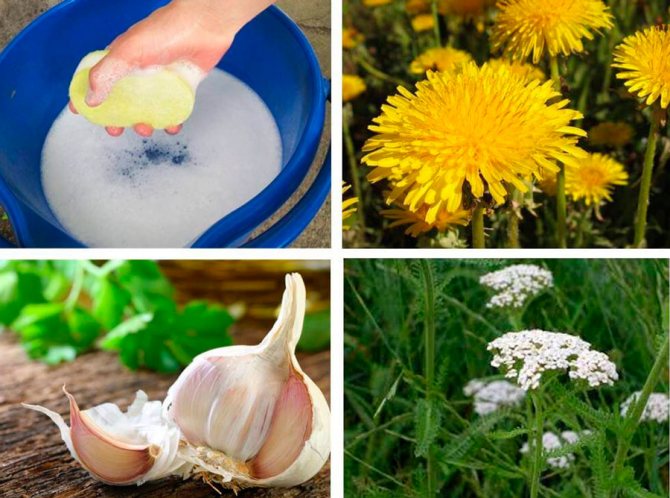
- Grind the rhizomes and dandelion leaves (80-100 g). Pour them with 1 liter of water, leave for 4 days. Spray the ready-made infusion of the plant 3-4 times at weekly intervals.
- Grate with laundry soap. Dissolve it in warm water (1 glass per 1 spoonful of shavings). Add 1 teaspoon of ammonia to the solution. Beat the product into a lather, apply to the leaves and stems of the plant. After 20 minutes, wash off the soap-alcohol solution with warm water.
- Chop 100 g of garlic finely. Pour it with 500 ml of water. Cover and leave for 5-6 days in a dark place. Before use, dilute 1 spoonful of infusion in 1 liter of water and spray the flowerpots.
- Pour 100 g of crushed yarrow leaves with 1 liter of water. Let it brew for 1 day. Spray the ground parts of the plant 2-3 times at intervals of 7-10 days.
- Dissolve 200 g of wood ash in 5 liters of water. Leave on for 3-4 hours. Pour 50 g of liquid soap into the composition. Treat infected crops. Repeat the procedure after 1 week.
Fumigator
This is a device in which a container with a poisonous insect solution is placed. The device is plugged into an outlet, the plate heats up and the solution begins to evaporate. After an hour, the fumigator is turned off. All windows and doors must be tightly closed while the appliance is in operation. It is better to leave the room.
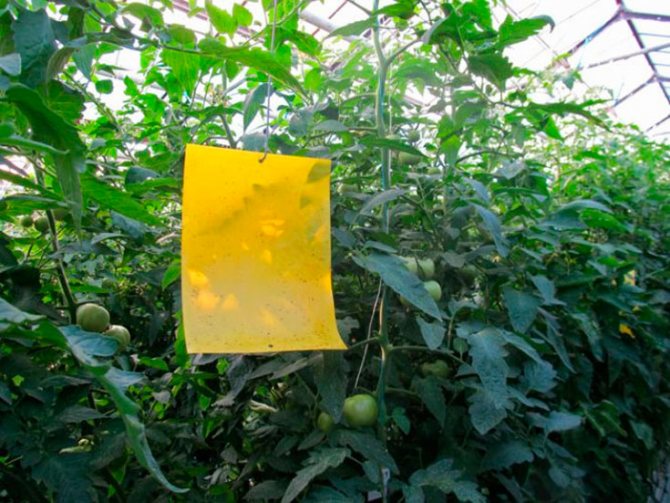
Traps
These devices are used to kill adult whiteflies. You can buy pre-made sticky traps or make your own. Take a piece of cardboard, apply odorless glue to it, which dries for a long time.To attract insects, you can paint the trap with a bright color. Instead of glue, petroleum jelly or castor oil will do. Hang the finished trap over the flowerpot with a thread / wire or set directly in the pot.


Ready-made traps can be bought at the store. Famous manufacturers:
- Pheromone;
- ARGUS;
- Bona Forte.
Whiteflies quickly stick to traps, even with a light touch. But it should be borne in mind that these devices can be used as an additional measure of insect control. They are powerless against larvae and eggs.
Preventive measures
Fighting a whitefly is not so difficult; for this you can use 1 or more of the tools described above. To avoid the appearance of very large colonies, it is necessary to take care of the destruction of pests in advance. For this, experienced summer residents use certain preventive measures:
- In the fall (mid-September), it is recommended to thoroughly dig up the soil in the greenhouse, and no fertilizers or insecticides can be added at this time. If there was a strong infestation in the summer, it is advisable to carry out the treatment with a sulfur checker. For every 5 m3 of volume, 300 g of active ingredient is enough.
- Also, in the fall, you need to take out all the tops from the greenhouse and burn the remnants of the crop. It is in plant waste (leaves, stems, inflorescences) that the whitefly lays its eggs. If there is a composter on the site, it should be placed as far as possible from the greenhouse and from the garden in general.
- In winter, with the onset of frost, the greenhouse is opened for 2-3 days. The eggs left by the whitefly will freeze and die. This can be omitted if the design allows you to remove the sheets from the frame.
- If no treatments were carried out in the fall and winter, in the spring you can dig up the soil by adding 1-2 glasses of ash for each 1 m2 of area.
- Before transplanting, it is advisable to treat seedlings with any insecticide (Decis, Karbofos, Aktara, Karate) and fungicide (Tattu, Profit, Topaz, Bordeaux liquid). Do not be afraid that these are chemical preparations: they will not harm the plant, and besides, it is still very far from harvesting the fruits.


One of the most effective preventive measures is to freeze the greenhouse in winter.
Pest prevention
The fight against whitefly is quite laborious. Therefore, it is better to pre-protect indoor plants from infection, to create conditions under which insects cannot reproduce and parasitize.
It is necessary:
- Avoid stagnant water in the sump.
- Do not put flowerpots very densely, close to each other.
- For a week after purchasing the plant, keep it isolated from others.
- Remove dried and rotten leaves and stems in a timely manner.
- Ventilate the room regularly.
- Before planting indoor crops, disinfect the soil with a fungicide or potassium permanganate solution.
- From time to time, bathe plants in the shower or wipe them with a damp cloth, with the exception of crops for which water procedures are contraindicated.
- Do not fertilize the soil with tea leaves or other food debris.
- Use growth stimulants (Epin) and top dressing. They increase the immunity of plants, strengthen them.
Whiteflies are insects that can destroy many indoor plants in a short time. The fight against parasites should be started immediately after their detection. It is necessary to destroy these pests to the end, without leaving not only adults, but also eggs with larvae.
You can learn more useful tips and ways to combat whitefly from the following video:
Causes of whitefly damage
It is rather difficult to determine how the pest got on the plant. It can be brought in by a person on clothes, along with purchased seedlings, through an open window, etc. If there are favorable conditions in the room, then it immediately begins to multiply. He needs warmth and high humidity, which is especially typical for greenhouses and hotbeds.
In the open field, active reproduction of the parasite begins in the second half of summer, when hot weather sets in. It is mainly suitable for dense plantings, where air movement is difficult. The high reproduction rate of this pest requires periodic inspection so as not to miss its appearance and to start treatment in a timely manner.