Features of thrips
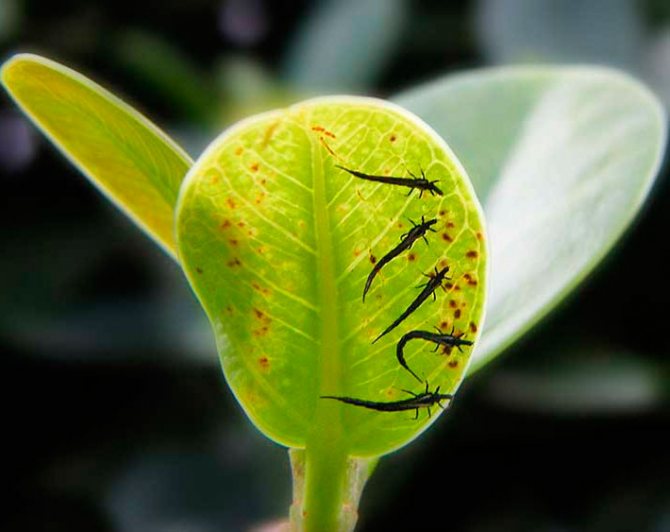

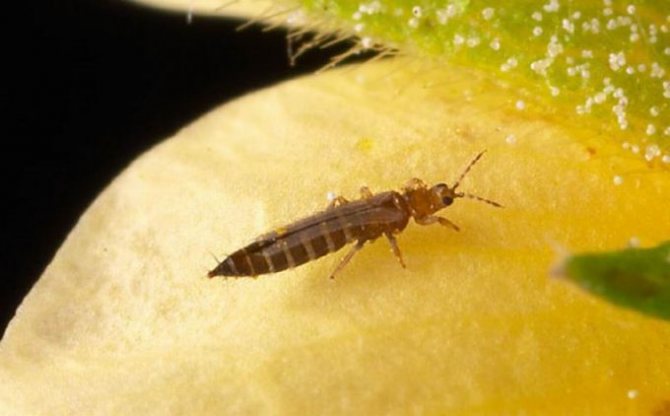
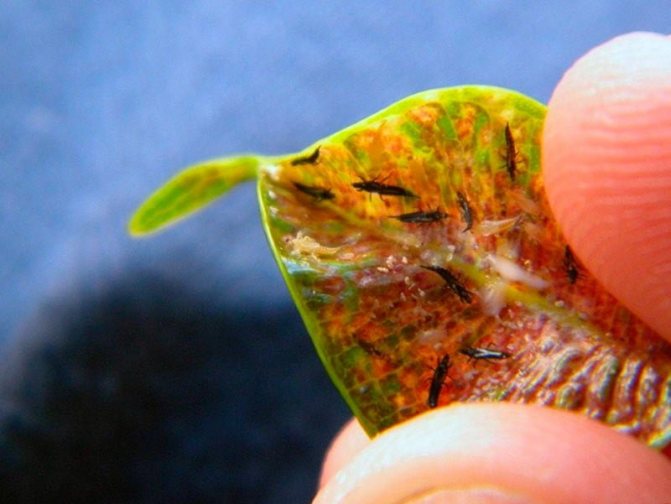
The body of thrips can be colored brown, black or gray, while its length varies from 0.05 to 0.3 cm. In some species, the body of the insect is larger - about 1.4 cm. The mouth apparatus of thrips is piercing. sucking, asymmetric, legs are running, there are no claws on the paws; instead, they have teeth and suction devices of a bubble shape. The abdomen consists of 11 segments, and there is a fringe on the edge of the wings.
The development of such an insect goes through 5 stages, namely: eggs, larvae, pronymphs, nymphs and adults. The body color of the larvae is yellowish-white or pale gray, and they differ from the imago only in that they do not have wings. Thrips are polyphages, which means that they are omnivorous insects. They are considered one of the most common harmful insects in vegetable, ornamental, agricultural, fruit and indoor crops. Indoors, thrips are the most dangerous, for example, if they appeared in a greenhouse, then it is almost impossible to exterminate them, you can only restrain their population.
It is difficult to find thrips on plants, because they are very small and lead a hidden lifestyle: they often live on the same bush for a long time, without moving to neighboring plants. Adult insects, as well as larvae, feed on sap, sucking it out of the aerial parts of the bush, while infecting it with their secretions. Initially, in the area of the bites, specks of light yellow color or discolored are formed, as well as stripes and streaks, over time they increase in size and connect to each other. The result of the life of thrips is the death of plant tissues, where there were spots, holes appear over time, wilting and flying of foliage is also observed, flowers lose their decorative effect and fade ahead of time. If the occupation of the bush is massive, then silvery areas can be seen on its aerial parts, the shoots become curved, and the flowers become deformed (as a result of injury to the flower bud). In addition, thrips are among the main carriers of viral diseases that are currently considered incurable.
Description of pests
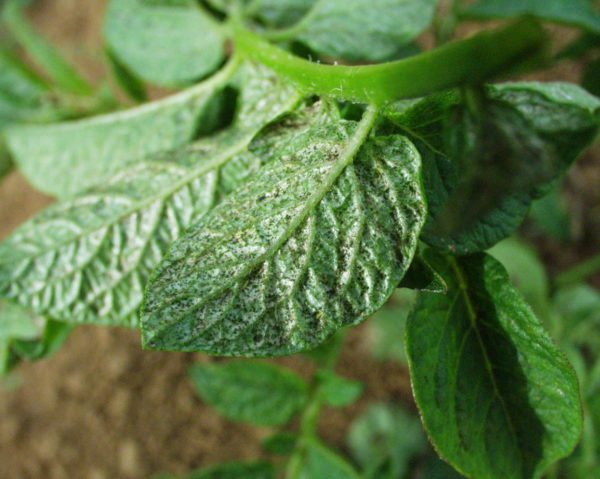


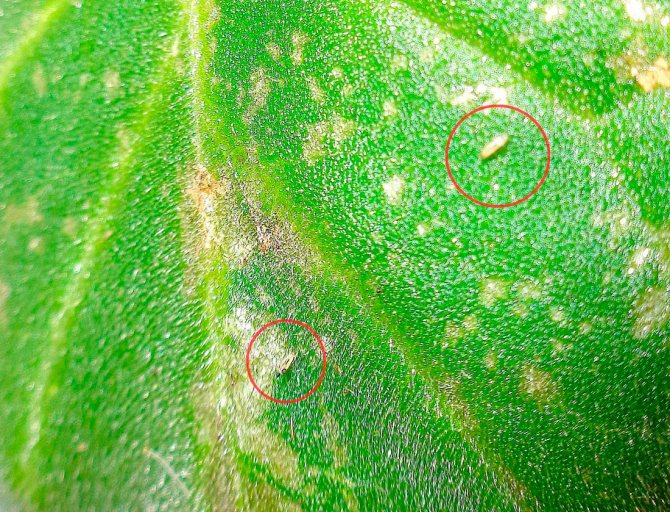
Thrips on seedlings of garden culture.
The cone-like structure of the head is distinguished by a triangular shape of the lower lip and a partially skewed frontal lobe. The tiny antennae are divided into eight segments on average. There are 3 stitching villi in the oral cavity. The bristles are able to move along the inner part of the lower lip.
The upper part of the jaw is underdeveloped. The structure of the mouth apparatus allows insects to pierce the plant. The indentations in the lower jaw form a sucking tube. The organ allows the pest to freely feed on the sap of the flowers.
Not all thrips are herbivores. There are also known categories of predators that can eat other insects and tiny ticks.
Prevention measures
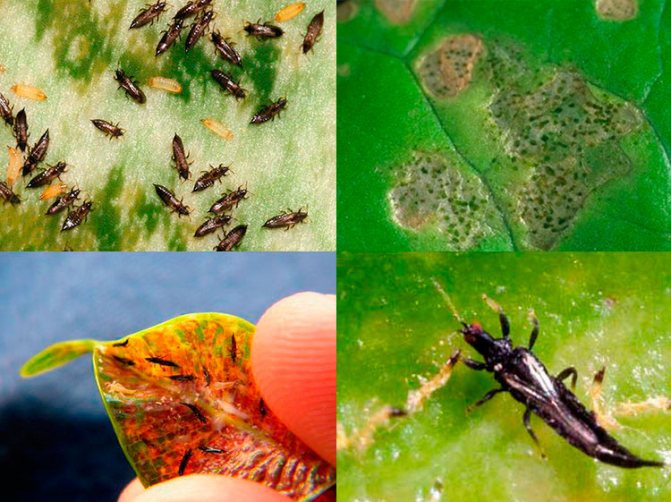


In order to protect indoor plants from thrips, do not forget about certain preventive measures:
- Maintain an optimal level of humidity in the room.Remember that thrips, like spider mites, prefer low humidity, so install an electric humidifier in the room or systematically humidify it with a fine atomizer.
- Conduct a systematic inspection of indoor flowers, pay special attention to the seamy surface of the sheet plates. As soon as the larvae or adults are found, give the plants a warm shower as soon as possible.
- Experts advise, at least once every 30 days, to arrange a shower for home flowers, this will help rid the plant of dust, adult insects and pest larvae.
- Place or hang glue traps between the flowers: you can use fly strips or yellow or blue paper strips to which the glue is applied. In this way, you can not only understand whether there are thrips on plants, but also significantly reduce their number.
- Flowers brought from a friend or bought in a store are recommended to be quarantined for 15–20 days, that is, they should be kept away from other plants and observed.
Reviews and advice from experienced florists
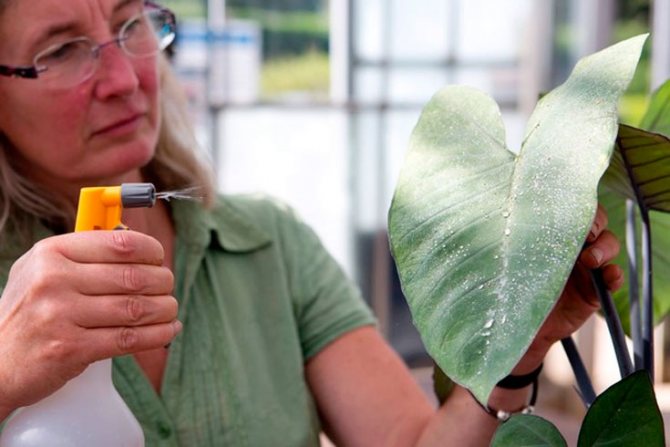
The most effective remedy that can cope with thrips is Actellic or Aktara. Observing all the standards for processing plants and the premises where they are located, you can get rid of pests from the first application.
You can get rid of thrips on indoor plants both by spraying and by immersing the plants in the prepared solution. This method works well for small potted plants.
The main thing is to remove all buds and flowers from diseased flowers. Otherwise, after a few days, a new generation of thrips may hatch from the eggs laid in them, and the processing will have to be repeated.
Violet flowers are not particularly fond of moisture, so it is often impossible to spray them. Sticky traps and anti-fly tapes can help deal with flying pests.
How to get rid of thrips on houseplants
Orchids
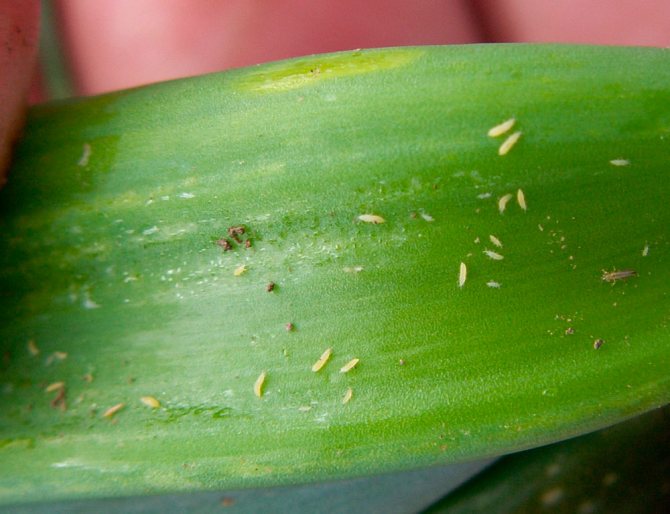


If a silvery film has formed on the foliage of the orchid, and small dots and strokes on the seamy surface, then this indicates that thrips occupied it. These lesions are very similar to those that remain after spider mites, but in this case, the bite marks are more pronounced. Thrips are quite difficult to detect, because even with a small threat they quickly hide in the soil mixture. They can also easily move from one flower to another with the help of their wings.
As soon as you notice the first signs of thrips presence, immediately rinse the bush thoroughly under a warm shower. After that, with a sharp sterile tool, cut out all the affected areas to healthy tissue, and then treat the cut sites with charcoal powder and moisten the bush from a sprayer with Actellik or Fitoverm solution. The bush is processed only 3 times with a break of 1.5 weeks. Until you completely destroy all thrips, the flower is quarantined. If there are few pests on the plant, then you can, if desired, replace pesticides with folk remedies, for example: oil water or garlic or onion infusion.
Violets

As a rule, the florist realizes that thrips have settled on the violet even when most of the bush has suffered. However, there is a method that will help get rid of this harmful insect very quickly. When there are two or three days left before processing, water the flower abundantly. Immediately before processing, it is necessary to wrap the container with a plastic bag, which will help protect the substrate during processing from the ingress of solution. First, dust is washed off the plant with a stream of water, which should be warm. Then the plant is lowered “upside down” into a deep container, which is filled with the following solution: one ampoule of Fitoverm is dissolved in 5–6 liters of warm water, and 25 to 30 milligrams of animal shampoo against fleas is also added.During the mixing of the solution, due to the shampoo, foam forms on its surface, all of it should be removed. The remains of soap flakes on the surface of the solution are removed with toilet paper. Remove the bush from the solution after 10 seconds, try to glass as much water as possible from it, for this they turn it over very slowly. Do not shake the flower or twist it, trying to shake off the liquid drops from it. Then the bush is placed on the table and the package is removed from it, after which the soil mixture in the pot is abundantly spilled with a solution of Fitosporin-M or Aktara (it must be prepared according to the instructions). After the violet has been processed, it is quarantined for a while in order to understand whether you managed to destroy the thrips the first time or not.
How to recognize thrips in the house
It is difficult to recognize thrips on indoor flowers early on. They are almost invisible, because most of the time they live on the back of the leaves. Due to the fact that they drink juice from domestic plants, visible changes occur in the structure of the leaves, and in general their condition worsens:
- pale stripes appear on the surface of the leaves, they are located in a chaotic order;
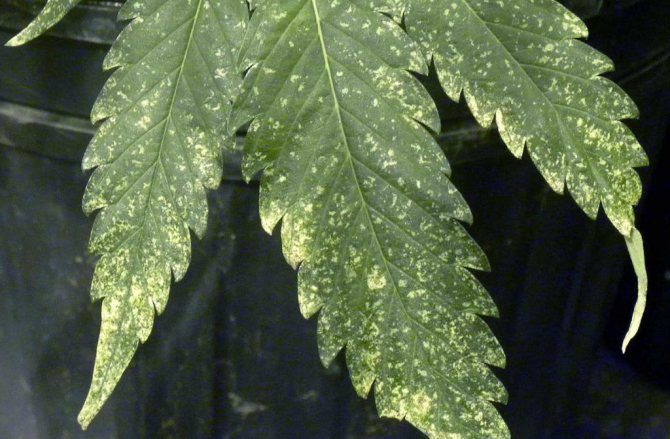


- small circles are formed on a sheet with holes, from which thrips drank juice;
- black contaminated areas are easily visible on the leaves - pest feces;
- damaged leaves and flowers wither and fall off;
- the young shoots of the infected flower are bent.
Thrips reproduce rather quickly, one individual is capable of laying up to 300 eggs.
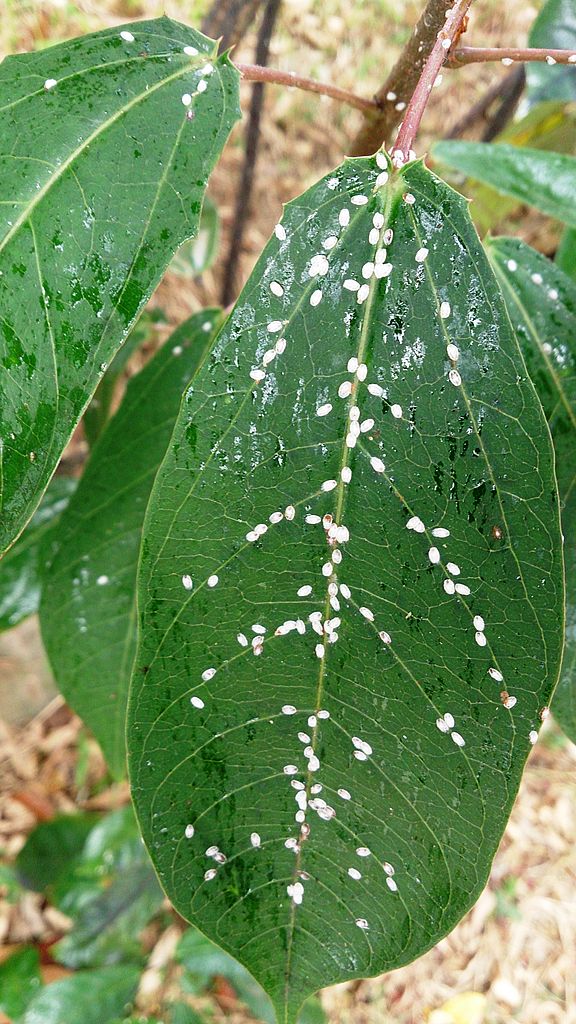


The sooner you can apply the remedy for thrips on indoor plants, the more chances that the plant will not die. There are ways that can help you recognize pests on plants:
- A white piece of paper is taken, and the leaves of the flower are gently shaken off above it. If the plant is infected, adults or larvae will end up on the leaf.
- A visual inspection of the plant is recommended with a magnifying glass. This method helps to recognize pests at an early stage.
Treatment with anti-thrips agents on indoor plants should be carried out in time, without giving a chance for further reproduction.
Set traps for thrips. They are made from a colored sheet of paper with a layer of glue applied to the top side of the sheet. They need to be placed close to flowers, no higher than 1 m above the ground. Blue or yellow paper works well for traps.
Thrips on horticultural and horticultural crops
Cucumbers
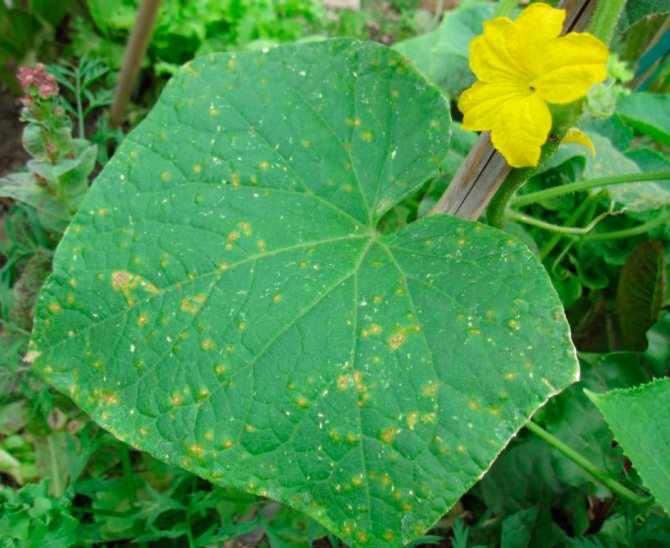


Thrips are most commonly found on greenhouse cucumbers. They can be found on the seamy surface of young leaf plates, where they suck the juice from the plant. This leads to a slowdown in the development and growth of the bush. In the area of the bites, you can see spots of light color, while they are located very densely. Also, areas of a silvery color are formed on the foliage - this indicates that air has entered the leaf plate. These pests differ in that they multiply very quickly, in this regard, as soon as the first signs of the presence of thrips on cucumbers are found, it is necessary to immediately begin to combat them. If the insects have not yet had time to multiply strongly, then an infusion made from celandine, garlic or onions can be used for processing. If there are a lot of pests, then folk remedies will be ineffective, so without wasting time, spray the bushes with pesticides, for example: a solution of Avertin N, Aktara or Imidacloprid (prepare the solution in accordance with the instructions). Be sure to wear rubber gloves, a respirator, and goggles before proceeding. In order to get rid of this pest completely, you will need more than one treatment.
Onion
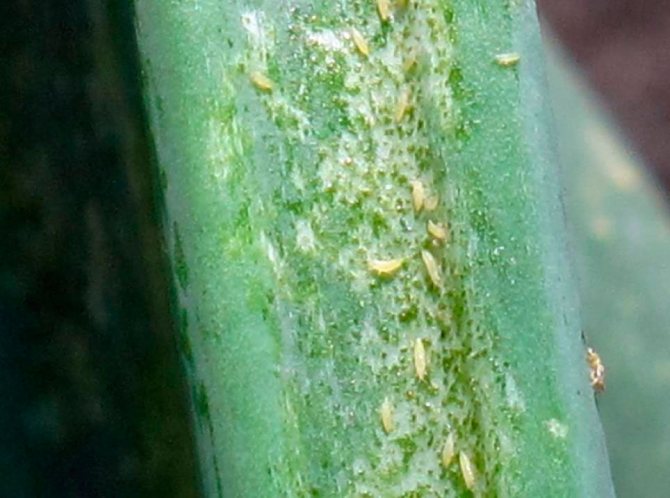


The onion is home to tobacco onion thrips, which damages both the bulb and the feather. But at first glance, it is very difficult to determine that plants are suffering from thrips.Examine the bush carefully, if there are very small black dots on its surface, and there are light specks in the leaf sinuses that outwardly resemble drops of mercury, then this indicates that the bush is occupied by thrips. Over time, yellowing of the foliage is observed, and it begins to turn yellow from the top. Then the foliage dies off. The development of the bushes slows down and they form small bulbs. Garlic is least often affected by thrips from onion crops, and shallots are also highly resistant to insects. This insect can inflict the greatest harm on onions.
In order to protect onions from pests, be sure to follow the rules of crop rotation. In the area where garlic or onion was grown, it can be planted again only after at least 4 or 5 years. After the crop is harvested, remove all plant residues from the area and destroy them. Also, in the autumn, they must dig up the soil on the site, since thrips hide in the ground for wintering to a depth of 70 mm. If the onion was grown in a greenhouse, then after harvesting, it is processed with Karbofos. Remove all weeds from the site in time, and do not forget to disinfect the planting or sowing material before planting.
If the pest is found, then the storage, where the set and the onion are located, are necessarily fumigated; for this, sulfur gas is used: 1 kilogram of sulfur is enough to process one square meter of the room. To exterminate thrips in the garden, they use Aktar, Fufanon, Spark of gold, Vertimek, Aktellik, Mospilan, Fitoverm or Karate. In recent years, gardeners are increasingly using the Spintor insecticide to process onions (treatments are carried out regularly at a frequency of 1 every 10 days). Together with treatments with pesticides, sticky traps are also used. If there are not very many insects, then you can fight them with the help of herbal infusions (tobacco, onions or celandine) or a decoction of zest.
Gladioli trips
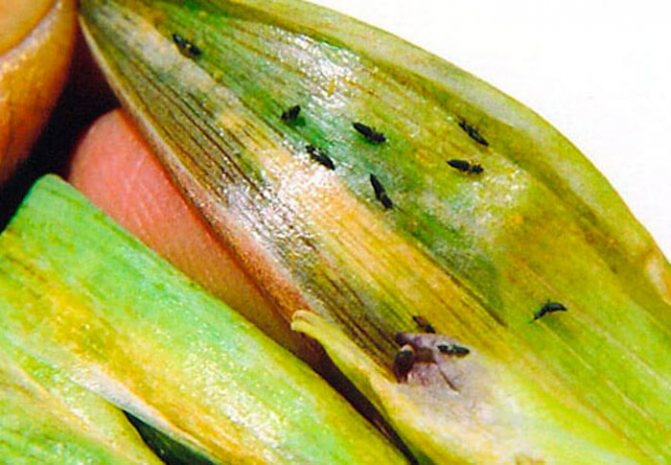


Gladiolus thrips are very dangerous for gladioli. When the weather is dry and hot, the reproduction of the pest occurs fastest: within one season, it is able to give up to 7 generations. Insects can greatly harm the opening inflorescences, the larvae and adults, once in the bud, begin to suck the juice from the delicate petals. After the rain has passed, the damaged buds turn brown, as if burnt. Those buds that are very injured dry up without blooming. In those bushes on which thrips have settled, the replacement bulb is formed very small and weak, and if you put it in storage, it will die. In autumn, the pest is buried in the ground and settles on the bottom of the bulbs. By storing such corms, you bring thrips to storage.


To protect these majestic flowers from thrips, do not forget about preventive measures:
- in the autumn, remove from the site all plant residues that are destroyed or laid in compost;
- carry out a mandatory digging of the site;
- before removing the bulbs in the storage, they are sorted out, removing all specimens with punctures, mechanical injuries and bites;
- healthy bulbs before harvesting for storage are immersed in a solution of Karbofos for 30 minutes, then they are washed under running water, thoroughly dried and placed in storage (the temperature should be no more than 5 degrees, this contributes to the death of the pest);
- in the spring, before planting the bulbs, they are again treated in a solution of Karbofos.
From mid-June, they begin a cycle of flower treatments with insecticidal preparations, and they must be alternated.For example, you can treat the bushes twice with a solution of Actellik or Karbofos, and then the plants are sprayed with Decis. The first 2 times gladioli are treated with a break of 7-12 days, and the third spraying - 25-28 days after the second treatment.
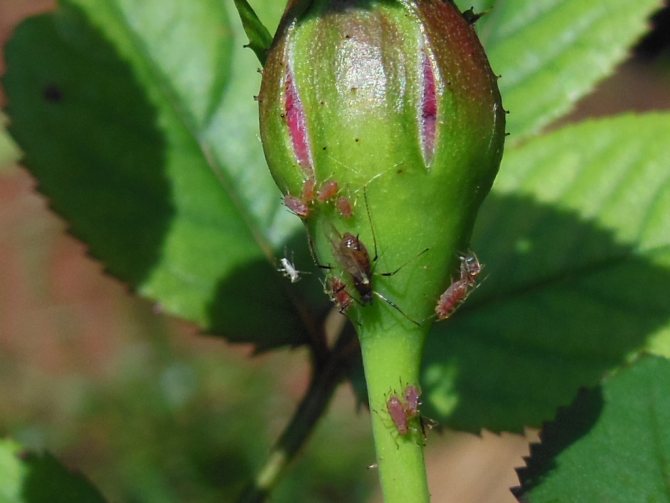
Thrips on roses
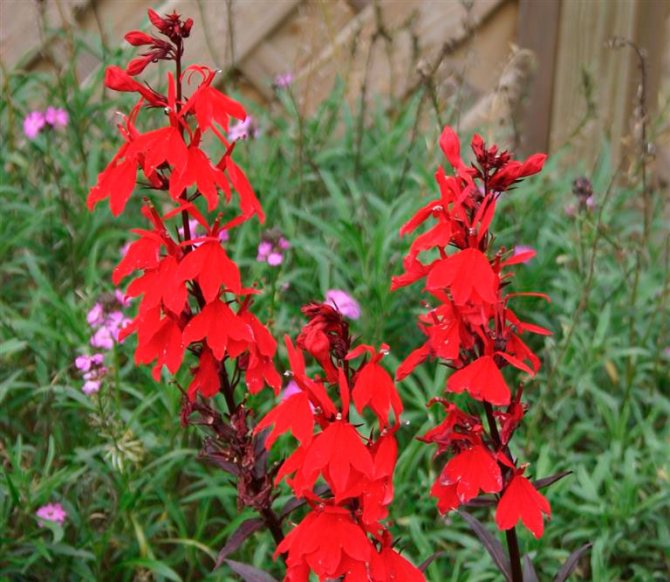


Most often, thrips on garden roses settle in buds, where they suck the juice out of them. As a result, buds damaged by the pest may not bloom and dry out quickly. Since such an insect multiplies very quickly and rapidly spreads through the bush, it is capable of destroying all roses in a short time. Therefore, it is necessary to begin to fight it immediately after the first symptoms of the presence of thrips are detected. Both in the garden and at home, roses from such a pest are treated with a solution of Aktara, Inta-vira, Fitoverma or Commander. With a solution of one of these insecticidal preparations, the soil around the plant should be shed regularly once every 15 days. To make the product more effective, it is recommended to pour in a little zoo shampoo or add green soap crushed on a grater. To treat the bushes themselves, pesticides are not used, as this can cause the death of bees. Those buds that are already damaged by the pest are cut off, because they can no longer be saved. However, you can keep healthy buds from being hit by thrips.
origin of name
The name of the fringed insect was due to the peculiar structure of the aircraft. The wings are elongated, narrow. Fringed cilia are densely located along the edges.
On the wings of thrips, a small number of veins are formed (several transverse lines and one longitudinal). Insects can move freely between plants to reproduce or in search of new food.


The body structure allows thrips to move between plants.
The flight duration is usually short. In some subspecies, colonies move in massive groups. This category also includes bread thrips (Limothrips cerealium).
Some pests have a shortened version of the wings. Rare insects exist without wings. Depending on the environmental conditions, there are different forms of the same subspecies. For example, wingless (forma aptera), short-winged (forma brachyptera) and long-winged thrips (forma macroptera).
The name Physopoda, which in translation means vesiculate, arose after studying the features of the formation of the structure of the legs. The limbs are represented by a thickened femoral part. The paws contain only two segments. Miniature claws are connected with plates. A small bubble-shaped suction cup is located between the parts. With the help of the apparatus, the insect can move its muscles.
The design of the legs allows thrips to move with lightning speed over leaves and stems. On the substrate, the insect can completely fix the tiny body at the moment of rest. Some fringed wings are capable of high jumps. Insects repel with the help of the abdomen.
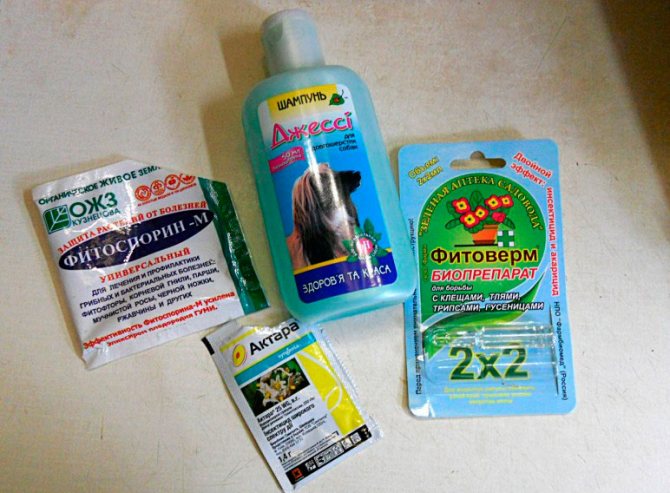
Thrips remedies (drugs)


Chemicals are the most effective in the fight against thrips. The following insecticidal preparations will be described that are used in the fight against this pest:
- Agravertine... This enteric biological agent is used for the extermination of sucking insects and is highly effective. Preparation of the solution: 10 milligrams per 1 liter of water.
- Aktara... Such a drug with an intestinal action is highly effective and is very quickly absorbed by plants.
- Actellic... An organophosphorus preparation of a wide spectrum of contact-intestinal action, it is used in the fight against ticks, sucking and leaf-gnawing pests. Solution: one ampoule for 1 liter of water.
- Vertimek... It is an insecticidal acaricidal agent, characterized by an enteric action, which is used to protect crops in the greenhouse, as well as indoor flowers. Solution: 2.5 milligrams per bucket of water.
- Decis... A broad-spectrum contact agent, which is effective in the fight against sucking and leaf-eating pests, and it exterminates both larvae and adults.
- Imidacloprid... This drug is able to exterminate various pests. It is used as an active ingredient in the manufacture of various modern drugs.
- Inta-vir... The tool is used to destroy various pests in garden and horticultural crops, both in the open field and in the greenhouse. It is not dangerous for humans and pets. Solution: one tablet for 2 liters of water.
- Spark of gold... Such a highly effective drug is used in pest control.
- Karate... This highly effective contact agent is excellent at killing pests. Solution: 2 milligrams per bucket of water.
- Karbofos... The pesticide, which is characterized by moderate toxicity, is used in the fight against pests of vegetable and fruit crops, grapes and citrus fruits. Solution: for 1 liter of water 7.5 milligrams.
- Mospilan... This systemic tool acts very quickly, it is capable of exterminating pests at any stage of development.
- Spintor... This biological agent has a unique mechanism of action against many pests.
- Fitoverm... Such a biological agent, made on the basis of the vital activity of soil microorganisms, is used to protect indoor flowers from harmful insects. Solution: for 100 milligrams of water, 1 milligram of the product.
- Fufanon... A broad-spectrum organophosphorus drug is distinguished by intestinal, contact and fumigate action.
Reproduction of insects
Thrips lay rather large eggs. The larvae emerge through the transparent shell.
Small representatives of insects have a similar body structure to adult thrips. They are distinguished by a springy cover, a complete absence of wings and a smaller number of antennae. They can have a yellow, milky or scarlet hue. The larva goes through several stages of molting. At the second stage, the first signs of wings appear.
The life cycle of thrips occurs at a fairly fast pace. The egg is able to develop within two days. In the form of a larva, fringed pterans exist no longer than a month.
The next stage (pronymphs and nymphs) will take about two months. Depending on the subspecies, thrips are capable of reproducing several generations in one year.
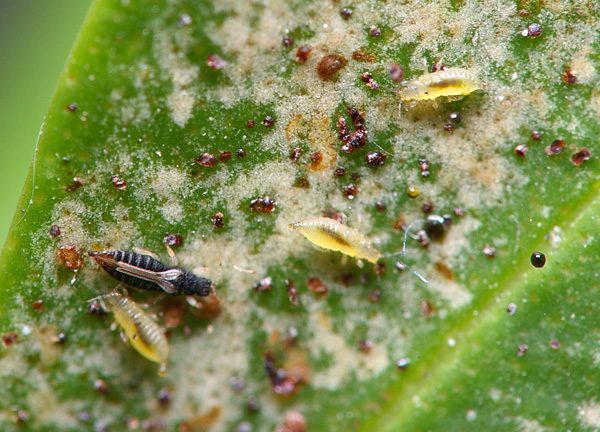


Stages of development of fringed wings.
Thrips are among the most dangerous crop pests. Insects not only feed on healthy plant sap. Parasites leave harmful secretions in various areas and carry dangerous infections.
It is impossible to detect thrips at the initial stage. Pests can hide for a long time. As a rule, a massive development of larvae occurs on one plant.
It is very difficult to independently determine the belonging of fringed-winged wings to a subspecies. Its tiny size and ability to mutate helps thrips survive in all conditions.
Fighting thrips with folk remedies
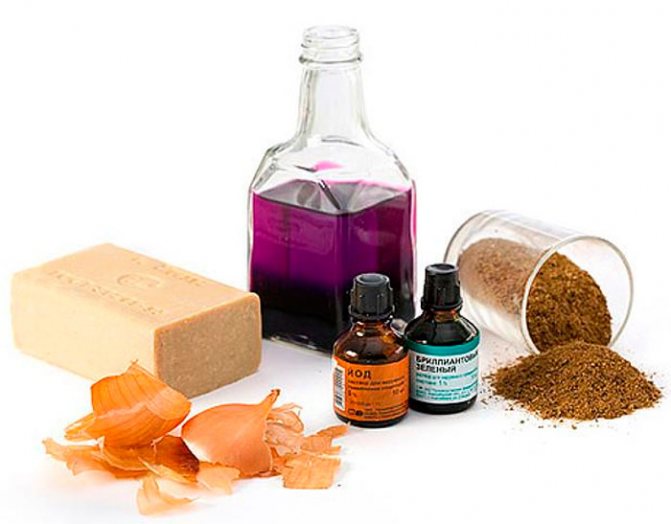


Despite the fact that folk remedies are not as effective as compared to pesticides, they are less toxic to bees, domestic animals, humans and birds. In this regard, if there are not very many thrips on the plants, you can try to get rid of them with folk remedies. They are also often used for preventive treatments.
Folk remedies:
- 1 tbsp. combine water with 1 tsp. onions or garlic, which is pre-chopped. The infusion will be ready after 24 hours, it will remain to drain and you can start processing indoor flowers.
- A 0.5 liter jar is filled with dry marigolds and so much water is poured in so that the container is full. After two days, the finished infusion is filtered and the culture is treated with it.
- 1 liter of warm water is combined with 50 grams of fresh roots or dandelion foliage.After 3 hours, the infusion is filtered and used to treat plants with thrips.
- Add 100 grams of pharmacy chamomile to a liter of water, mix everything well and leave for 12 hours. In the strained infusion, dissolve 5 grams of green soap crushed on a grater, after which the bushes affected by the pest are sprayed with it.
- A liter of water is combined with ½ tbsp. tobacco dust or crushed dry tobacco and leave for 24 hours. Pour another liter of water into the composition, mix everything thoroughly and use to spray plants from thrips.
- In 1 st. water add 50 grams of dry tomato foliage. The infusion will be ready after 3 hours, it is filtered and the volume is brought to one liter with clean water. Various cultures are processed with it.
- 100 grams of dried or 50 grams of fresh (crushed shoots and foliage) celandine is combined with a liter of water, the product will be ready after 24 hours. Then it is filtered and used to spray bushes from thrips.
- Finely chopped garlic is poured into a small container or turpentine is poured in, then it is placed directly in a flower pot to an indoor flower affected by thrips. After that, the bush is covered with a plastic bag for three hours.
Types of thrips
It was already mentioned above that there are many species of thrips in nature, and most of them are omnivores. However, the following species most often harm indoor, garden, garden and greenhouse crops:
Common thrips (Frankliniella intonsa)
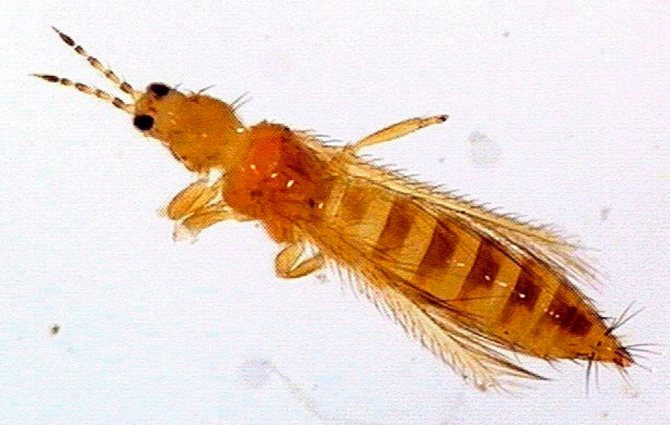


The length of the dark brown beetle is up to 0.12 cm; it is a wide polyphage that can settle on various cultures. It sucks the juice from flowers and ovaries. Berry, vegetable, decorative and fruit crops can suffer from it. The species can be found throughout the Palaearctic.
Floral western thrips
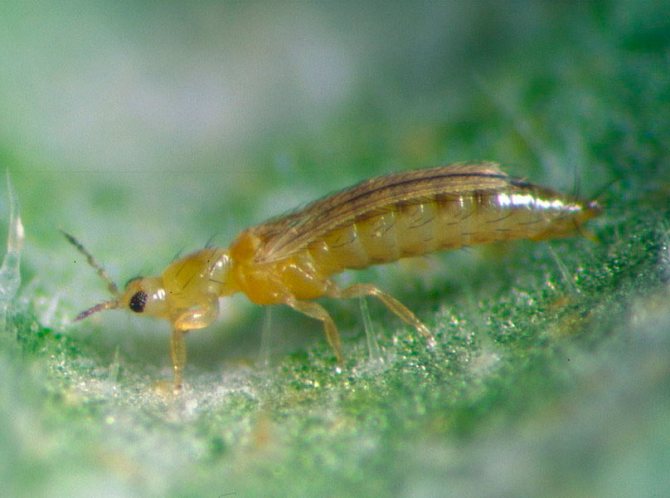


Floral western thrips, or California thrips (Frankliniella occidentallis). This pest is also a wide polyphage that affects a variety of crops grown both in the greenhouse and in the open field.
Ornamental thrips (Hercinothrips femoralis)
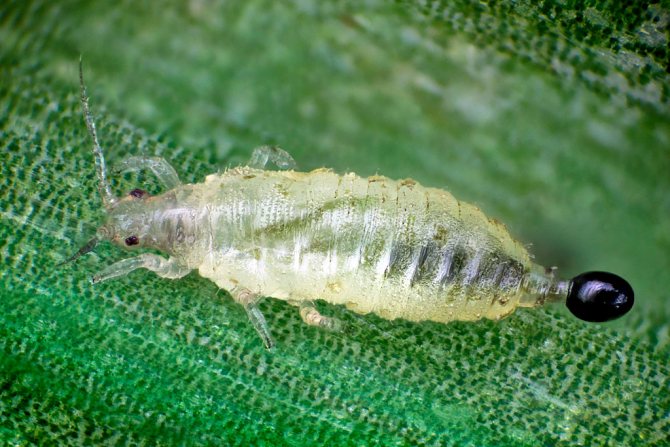


The color of such an insect is dark brown, and in length it reaches about 0.17 cm, it prefers to settle on all ornamental crops: on orchids, gardenias, cacti, calla lilies, dracenas, chrysanthemums, crotons, begonias, coleus, palms, and also on commeline and bulbous plants. In mid-latitudes, as well as in regions with a cool climate, this species is most often found indoors.
Dracene thrips (Parthenothrips dracaenae)
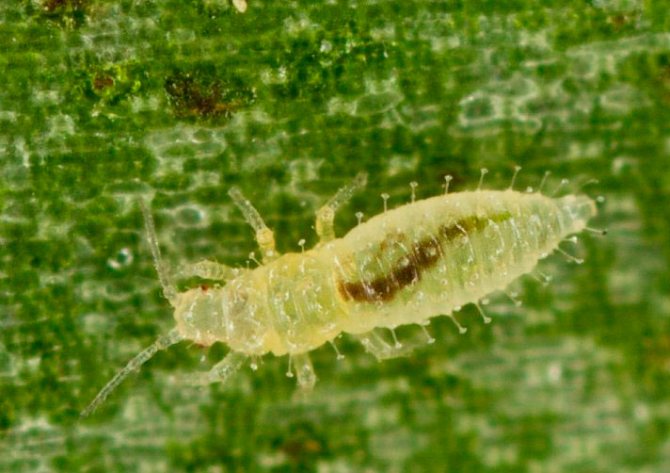


The brownish-yellow females of this species reach about 0.12 cm in length, while the males are lighter and smaller. Such insects settle on aralia, ficus, hibiscus, and also on commeline and aroid plants. Other cultures can also be damaged by them. In nature, they can be found in areas with tropical and subtropical climates, and in areas where the climate is cooler, they damage crops in closed ground and indoors.
Rose thrips (Thrips fuscipennis)
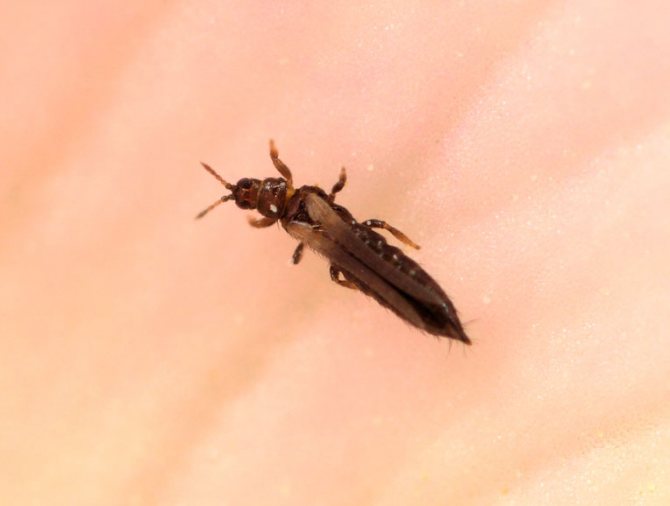


The length of the brown body in this species, which is a wide polyphage, is about 0.1 cm. This insect prefers to settle on rosaceous plants grown both in open and closed ground. They can be found in buds and flowers.
Tobacco thrips (Thrips tabaci)
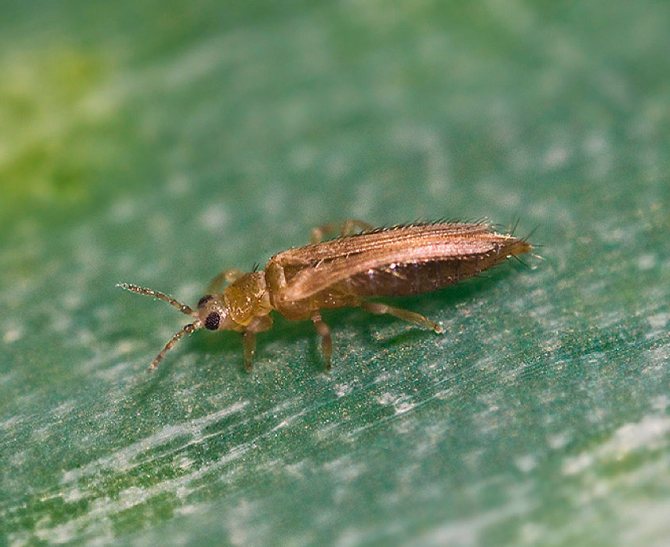


This insect can harm many crops, while most often it settles on umbrella and nightshade plants. The female's color can vary from brown to yellowish. The length of an adult is about 0.1 cm. In nature, such pests can be found in Ukraine, in the southern part of Russia and in Central Asia. In the north, such thrips are found indoors and in greenhouses.
Bulbous thrips (Liothrips vaneeckei)
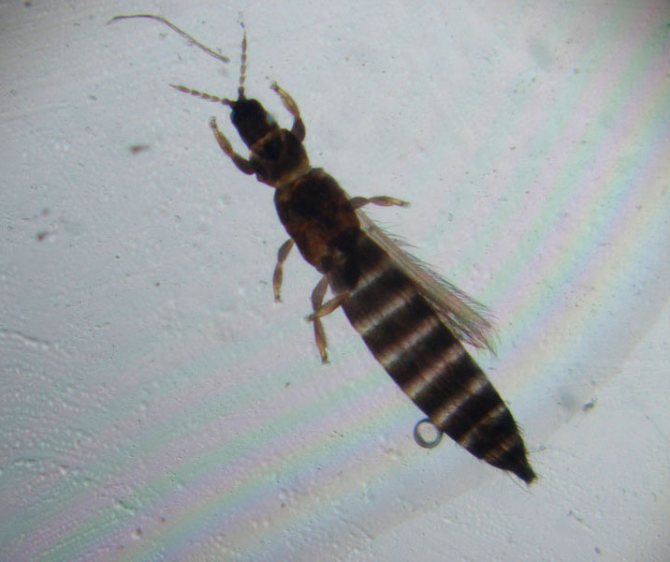


This widespread insect has a dark brown body, which reaches a length of about 0.2 cm. It settles between the scales of the bulbs.
Wheat thrips
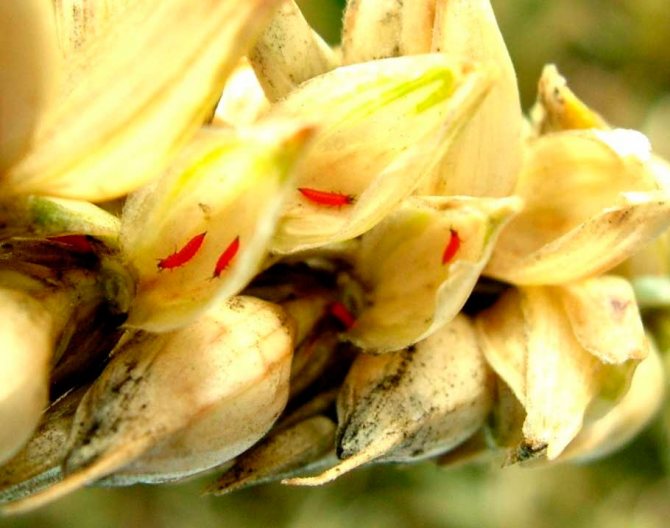


This insect can damage both ornamental and cultivated plants, but cereals most often suffer from it: rye, barley, oats, corn, and also buckwheat, cotton and tobacco. And also this pest settles on weeds. It is a dark-colored beetle, the body length of the male is about 12 mm, and the female is twice as long.
In the fight against thrips, it should be borne in mind that scientists have discovered elements of social behavior in them.This insect, like bees or ants, can gather in large groups to guard larvae and clutches, and it has also been noticed that they pave odorous paths for group coordination.
Morphology and biology of the pest
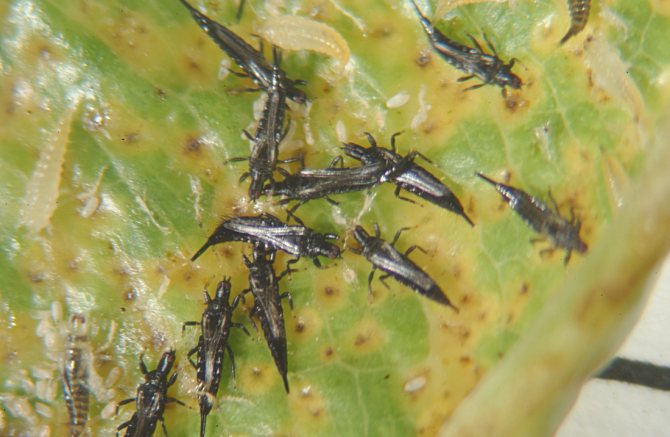
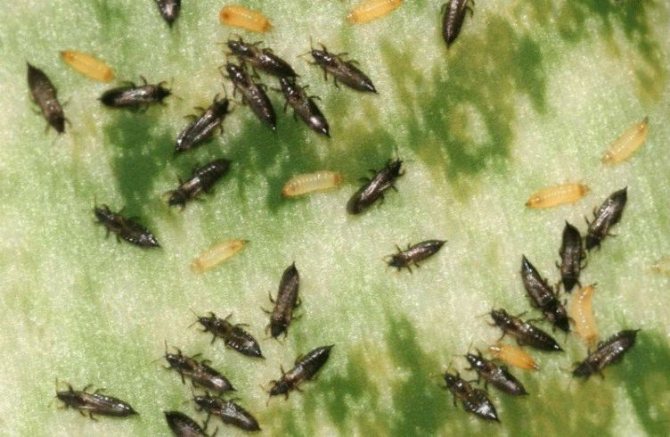
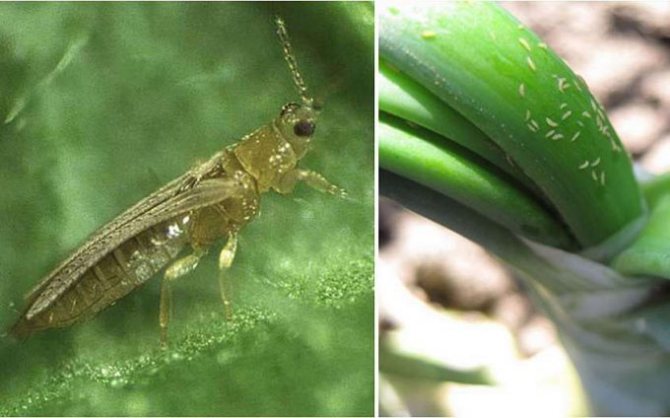
Recognizing thrips is not that difficult. They look like small insects, which have an elongated body up to 2 mm long, light yellow, black or dark brown. In adults, two pairs of wings with long hairs are usually found.
The larvae of the pest have a light yellow body, and do not exceed 1 mm in length. An additional clue about the presence of thrips can be the nature of their movement: adults move very quickly, often making sharp jumps with the help of their belly.
The difference between males and females is that the former have a slender, but not so long body. They are also painted in different colors.
Thrips can also be distinguished by their wings: in some species they may be rather short, in others they may not be at all. Thrips are one of the many pest groups that include over 2,000 species. We have about 200 species in our country.
Their main habitats are leaves, flowers and buds of indoor plants. They feed on the nectar and sap of the leaf tissue. Thrips are dangerous because they multiply very quickly. As a place for laying eggs, leaf tissue or flowers are used.
After 10 days, new offspring appear from the eggs. However, it takes one month for the larvae to develop into adult insects.
At this moment, a great threat appears to plants, since as a result of the activity of pests, they lose their attractiveness, they begin to be affected by viral diseases. Over time, when insects drink all the juices from one plant, they move to others located in the neighborhood.
So what is flower thrips? As we have already said, this is a small insect, the length of which is usually one and a half millimeters, but there are adults with a length of up to two and a half millimeters. Their wings are folded behind their backs, in a calm state they form a light, narrow strip that is barely visible.
Adults are brownish, black or sandy in color, juveniles are greenish, whitish, yellow. It is thanks to their camouflage color that these insects hide well, they are difficult to detect.
The larvae have no wings, they are small, in order to find them and destroy them, you need to make a lot of effort. Most of the insects hide among the stamens of the flower, in the axils of the leaves, so if you find the first signs of damage, inspect your plant very carefully. The sooner you take action, the better for your pet.
When deciding how to deal with thrips on flowers, you must first familiarize yourself with them and their biology in a little more detail. The biggest challenge lies in their small size, multiple developmental stages, and virtually immunity to chemicals.
A single treatment of a plant can only slightly reduce the number of pests, but it will not be possible to completely remove them at once.
Therefore, when fighting insects, it is recommended to divide the entire period into several parts, gradually destroying the pests. We also take into account the fact that during processing the eggs are not affected, since they are located directly in the leaf tissue. Therefore, it is necessary to remove the affected leaves, and carefully examine the remaining ones. Fighting thrips with pesticides may also be unsuccessful, since they adapt perfectly to any poisons.
At the larval stage, insects are generally inaccessible; they simply bury themselves in the ground at the root system, where there is no way to get them.It usually takes two to three times the concentration of insecticides to deal with insects, which are incredibly resistant compared to other pests. The most stringent measures are required here.
Common types of thrips
The first information about the existence of thrips was obtained back in 1744, when Karl de Geer discovered these pests. Today, a person has become more aware of the species diversity of these pests, among which special species can be distinguished that most often affect other ornamental plants:
The length of an adult insect is about 2 mm, the color can vary from light yellow to brownish yellow. California thrips prefer to live on buds and flowers, but the population can also reproduce on leaves.
California thrips are dangerous in that they are carriers of the tomato virus, which gives the leaves of tomatoes a bronze color. Western flower thrips are considered to be very wide polyphages.
It can eat on peppers, cucumbers, onions, tomatoes, grapes, peaches, strawberries and many other fruit and vegetable crops, as well as on numerous ornamental and floral plants: gerberas, roses, daisies, chrysanthemums, Saintpaulias, cineraria, cyclamens.
The larvae and adults of the western flower thrips suck the cell sap from the plant tissue. This causes the appearance of first yellow spots on buds, leaves or fruits, streakiness; gradually, in these places of lesions, plant tissues die off.
Damage to flower buds in vegetable and fruit crops causes deformation of flowers and fruits.
For example, severe curliness of the flowers and curliness of the set fruit of the cucumber is a common sign that thrips have settled on the plant. On roses, when populated with western flower thrips, damaged buds do not open and dry out.
This pest lives in the middle lane and southern regions of our country. Here it is found on various ornamental plants grown in greenhouses and greenhouses. The insect itself is small, reaches a length of no more than 1 mm, has a light yellow or brown color.
The most widespread is in the northern regions and the middle zone of our country. Threats to many indoor plants.
Most of all, orchids, monstera, dieffenbachia and certain types of palms suffer from this pest. It can be identified by its dark brown color, as well as a small body, which has a length of 1.5-2 mm.
Adult insects are about 1.3 mm long, females are yellow-brown in color, the male is slightly smaller and lighter in color. The larvae are white. This type of thrips is also a large polyphage and is found on the leaves of a very large number of species of ornamental plants: orchids, monsters, aralia, tradescantia, anthuriums, hibiscus, ficuses, dracenas, palms and many others.
In natural conditions, dracaena thrips is found in tropical and subtropical countries. In more northern latitudes, it is widely distributed on plants in greenhouses (in greenhouses, greenhouses).
In the conditions of industrial greenhouse farms, it is almost impossible to destroy thrips. In the best case, their number is kept at a level that would not affect the commercial quality of products (flowers, fruits, vegetables).
This is due to the fact that thrips have a very high adaptation to pesticides. This is especially true for individuals feeding on flowers.
This species is represented in most of our country. The main food for him is flowers and buds of indoor plants. It looks like a dark brown insect, reaching a length of just over 1 mm.
Its favorite habitats are rosaceous plants.A characteristic feature is a brown body, up to 1 mm in length.
This species is represented in most of our country. Most often it can be found among the scales of lily plants. It can be identified by its dark brown color and body up to 2 mm long.
The insect is dark brown or brown in color, in length from 1.3 mm (males) to 1.6 mm (females). Echinotrips American prefers to live mainly on leaves, in the tissue of which females lay their eggs. This type of thrips was discovered in the nineties of the last century in Holland at one of the popular flower auctions, which bring plants from all over the world.
Thrips was first found on orchids. Now American thrips are transported from country to country on cut flowers, seedlings, ornamental pot plants.
At first, the activity of American thrips is visible by the appearance of yellow spots. The presence of ten thrips on one leaf is enough for it to begin to fade. 30-40 thrips will lead to drying out and leaf fall, which starts from the lower layer. And although thrips do not lead plants directly to death, they significantly reduce the decorative effect of flowers.
In search of food, thrips move to flowers and fruits or to neighboring plants and continue their vital activity there. Due to the fact that the American thrips population is spreading very quickly, it is highly likely to spread not only to all ornamental plants, but also to other vegetable crops grown in greenhouses.
Adult insects are about 1-1.5 mm long, dark brown or almost black in color with a brownish-brown belly and yellowish forewings. The larvae are white or yellowish, differ from adults in slightly smaller size and lack of wings.
Adult insects and black thrips larvae usually inhabit the underside of the leaves. The nature of damage to plants is practically the same as from tobacco thrips.
Indoors (in greenhouses, greenhouses), black thrips is widespread and reproduces all year round. Both adult insects and black thrips larvae cause harm, causing great harm to cucumbers, tomatoes, other vegetable and green crops, as well as pot and ornamental plants. Black thrips winters well in the topsoil under plant debris or in compost heaps.
What houseplants do insects appear on
These insects are omnivorous and live on any plants. Most of all, they prefer violets, ficuses, lemons, begonias, roses, orchids and dracaena from their indoor flowers. Thrips cause particular harm to violets, damaging flowers.
The plant stops blooming, loses its decorative appearance.
The most favorable climate for insects is warm and dry air. They can appear in any home, but they actively reproduce most often where the plants are not sprayed or rarely watered.
How to detect and signs of flower infestation
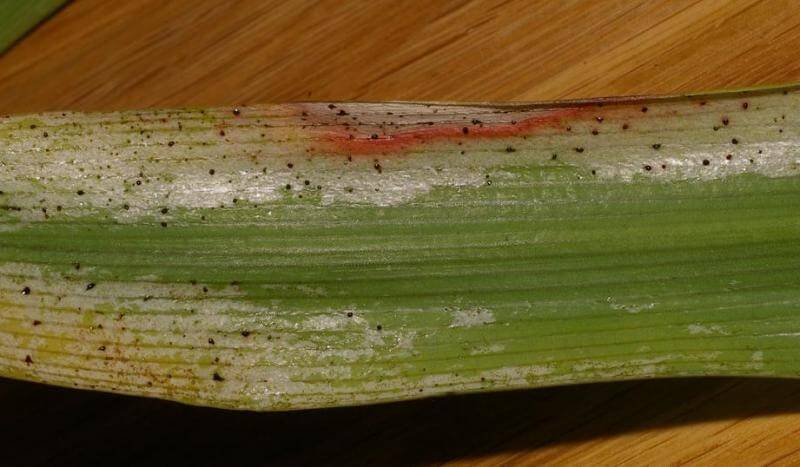
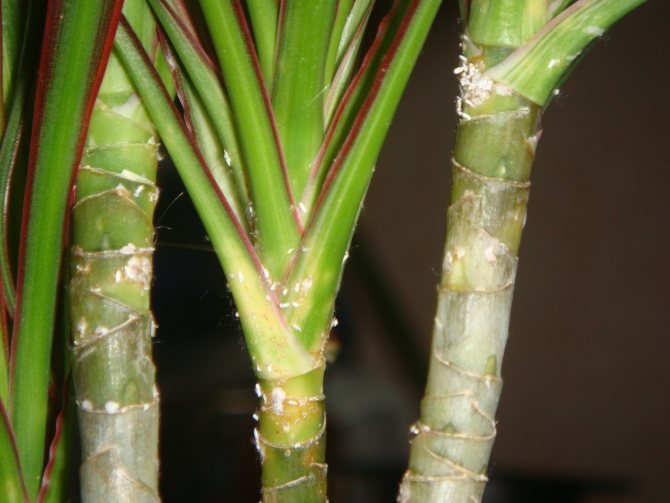
If, in the process of examining indoor plants, you find that some of the leaves are discolored, and there are also many points caused by punctures on them, then this is a clear sign that thrips are bred in your apartment. If you pay attention to the lower part of the leaves, then there you can find spots of a brownish or brown hue.
The damaged areas often turn silvery, which can be explained by the ingress of air into the cells.
If, at the first signs of thrips activity, no operative measures are taken for treatment, foliage dying off, deformation of flowers and buds subsequently occurs. Insects cause additional harm by depositing sticky secretions, which are a favorable environment for the development of a sooty fungus.
Although thrips are not picky about food, the most preferred houseplants for them are violets, begonias, roses, citrus fruits, orchids and ficuses. Violets suffer the most from thrips larvae, as they destroy the flower's anther.
At the first signs of their appearance, it is necessary to cut off all flowers and buds within the next 1.5 months, combining this with treatment with suitable preparations.
Unfortunately, the presence of insects is often detected when the plant has already died. They hide in the axils of leaves, pistils of flowers. If you look closely at the plant, you can find the following signs of infection with thrips:
- Small brown dots on the leaves are the places from which the insects drank the juice;
- Many leaves darken, die off, discolor or become covered with gray stripes, they can also be covered with an openwork mesh;
- Brown spots are visible on the underside of the leaf plate;
- Young leaves and shoots grow small and deformed;
- The flowers dry quickly and fall off.
Almost all insects that parasitize houseplants are suckers. Thrips are no exception, with their thin proboscis they penetrate the leaf of the plant and suck the juice out of it.
How to determine if a plant is infected:
Many people consider this phenomenon a sunburn and try to remove the plant away from the effects of rays. However, such a method will not bring results, since the thrips larvae are to blame for this, destroying the leaves with great speed. Plus, there are accumulations of dirt on the flowers, which are insect excrement.
In addition, thrips carries various viral diseases that pose a great danger to plants, since they can die.
Parasites are characterized by the release of a liquid substance with a sticky consistency, which is an excellent breeding ground for sooty fungus. The most dangerous among the large number of varieties of thrips are tobacco, bulbous, varivorous, decorative, dracaena, rose and floral western. It is almost impossible to determine which of them affects the flowers in the apartment.
Danger to indoor plants
If you do not start fighting insects in time, they can completely destroy the plant. Thrips not only suck the juice from the leaves, leading to their death. They are carriers of dangerous flower diseases, such as fungus. Reproducing rapidly, insects spoil the decorative appearance of the flower and, over time, completely destroy it.
The plant withers, the leaves darken, lose their shape, the flowers fall off. The danger of these pests is that it is very difficult to notice them, they hide in the axils of the leaves or between the stamens of the flower. The larvae are generally buried in the ground, therefore, many methods of processing plants do not work on them.
Detection of thrips on houseplants usually occurs after the flower begins to look depressed.
The most dangerous are decorative, Californian, tobacco, greenhouse thrips, which are capable of carrying various viral infections between flowers. The first sign of damage is pollen, which spills out from the stamens onto the petals.
But you should be careful, since this phenomenon can occur even in too hot weather, when affected by some types of ticks. It is quite easy to check, we tear off a few with a flower and shake them over black paper, after which we examine the sheet.
The degree of damage can be different, it depends on the type of pest. For example, California thrips, as well as decorative, tobacco thrips provoke not only on the leaves, but also on flowers, while the lesions are very similar to those inflicted by spider mites, leafhoppers, and flat-bodied mites.
Flowers wither, quickly deform, become covered with specks of black and white.
The surface of the leaves is similar to a cloth that has been pierced many times with a needle. Pollen is abundant on the lower leaves. Thrips pests can get into the apartment through open windows, along with bouquets brought from open ground, with infected plants. Garden flowers are also susceptible to attack by pests; even unpretentious gladioli (propagation by seeds, children) and well-known bearded irises can suffer from their harmful activities.






























