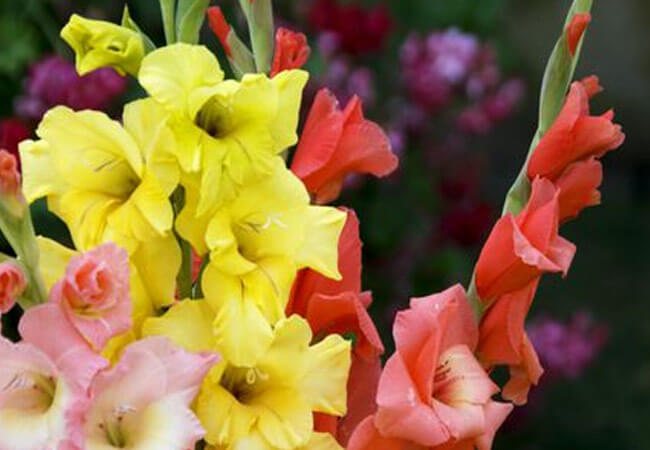
Gladioli are flowers of the bulbous family, native to Africa and the tropical Mediterranean. They create a festive atmosphere, decorate decorative lawns and flower beds in gardens and parks. The flower growers' collections showcase a fabulous variety of gladiolus varieties and colors.
But, unfortunately, this splendor can be destroyed by a large army of insect pests.
Fungal diseases of gladioli
To catch a fungal "sore" gladiolus is as easy as shelling pears. Spores of fungi are carried by wind and water, they live well in the soil. And the damage they inflict on the plant is noticeable in all its parts. Fungal pathologies of gladioli are also called rot. There are five of them:
- Dry rot or fusarium;
- Dry black rot or sclerotinia;
- Gray rot or botrytis;
- Solid rot or septoria;
- Blue rot or penicillosis.
However, there are two more slightly less common fungal diseases of gladioli bulbs:
- Courvularia;

Courvularia
- Smut.


Smut
How often gladioli are exposed to diseases
Crop plants are often exposed to diseases and pests, and gladioli are no exception to this rule. Most diseases are caused by microorganisms that inhabit the soil, and they penetrate into the flower through the roots or spores brought from a diseased plant. Weed infestation is also possible. Additional risk factors are unfavorable weather conditions and neglect of the main agrotechnical methods of growing this crop.


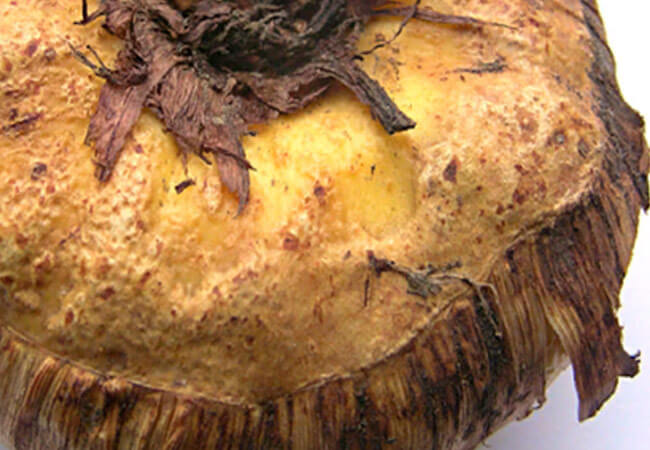
Fusarium - dry rot in gladioli
Fusarium oxysporum soil fungi belong to the Fusarium genus. They are able to live in absolutely any type of soil. For these fungi, the soil temperature is 28 ° C, high acidity and humidity above 60% is a fertile environment for development. On cool days, when the air does not warm up enough, fungi begin to migrate to the underground parts of plants.
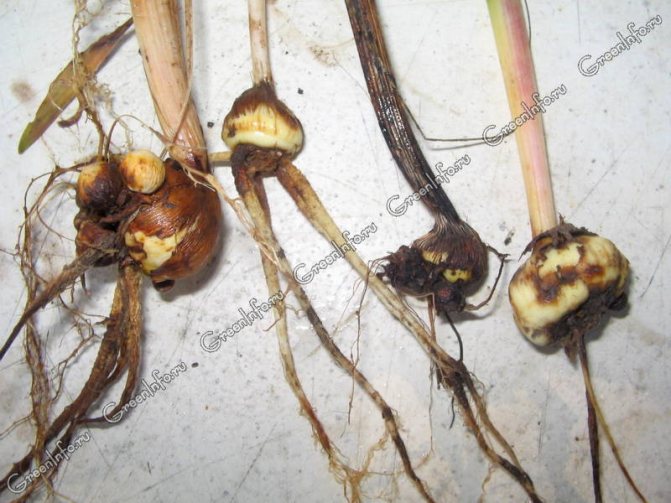
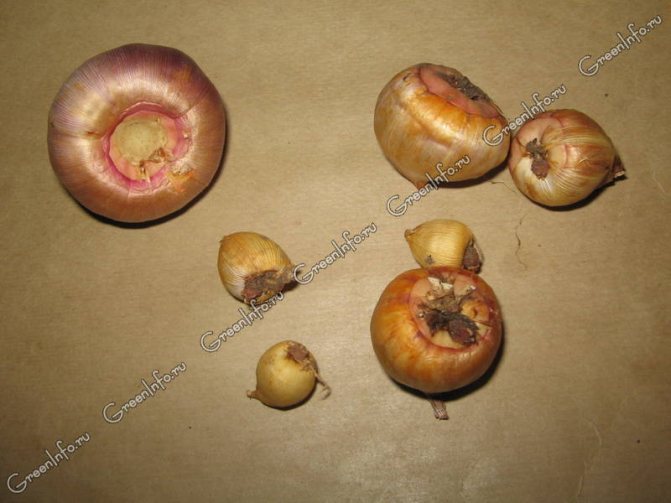
The most dangerous in this fungal infection is that the disease affects the bulbs of gladioli (see photo), but its obvious signs on the outer part of the plant at the first stages will not be visible. Unfortunately, to date, breeders have not yet developed varieties of gladioli that are resistant to fungi.


Fusarium - dry rot in gladioli
Fusarium can be considered favorable conditions for fungal infection of gladioli by fusarium:
- High soil moisture. This is not only about over-watering, but also about the climate. Abundant dew and precipitation play an important role.
- Summer weather with a temperature of 25-33 ° C.
- Sour heavy soils (above 6.5pH).
- An abundance of nitrogenous nutrition, for example, the same fresh, unripe manure.
- Frequent and dense planting of flowers.
Most often, flowers planted at the wrong time are affected. Either late - into the already warm soil, or too early - into the still cold soil, and thus the plants weaken. Bulb trauma and viral infections also reduce the defenses of flowers.
The ways in which flowers are infested can be different:
- Through an infected onion to tubercles - children;
- Penetration of fungal elements (spores, mycelium) from another carrier or from the soil into a healthy bulb. Usually mushrooms germinate into the corm through the bottom.
- Through damage to corms by pests or mechanically.
- Non-observance of the rules for storing the bulbs: poor drying of the material, laying the bulbs in several layers, high humidity, temperature over 8 degrees.
Symptoms
Symptoms of this disease of gladioli in the early stages of development only concern the bulbs. Reddish-brown depressions will be clearly visible on them. The line between rot and healthy tissue is clear. In humid conditions, a pinkish-white mycelium can be found on the bulb. Subsequently, the bulb dries up and is mummified.
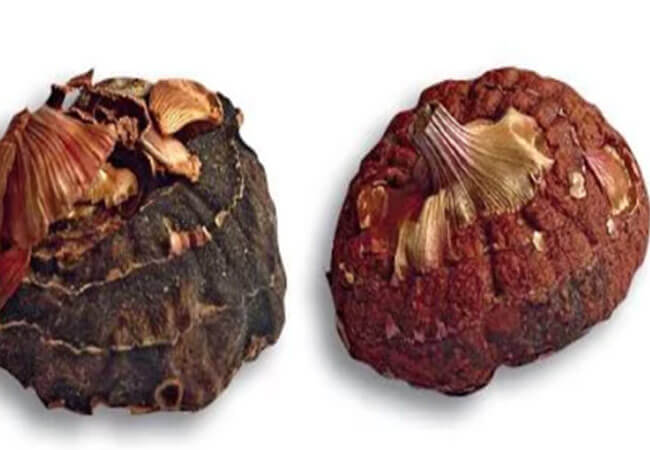


Fusarium
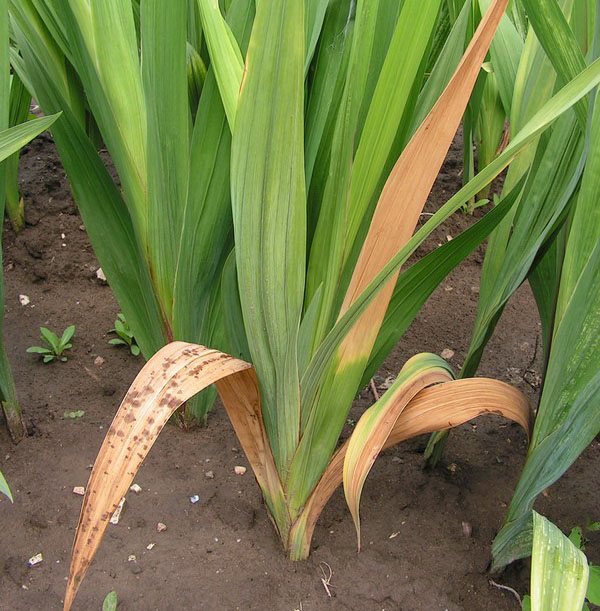
The mycelium of the fungus spreads throughout the plant, affecting the vessels. As a result of this, the lower leaves of the plant begin to dry out first from the tips and throughout the entire area. Leaf spot is not typical for this disease.
The only thing that can create the illusion of spots on dried leaves that still retain veins.
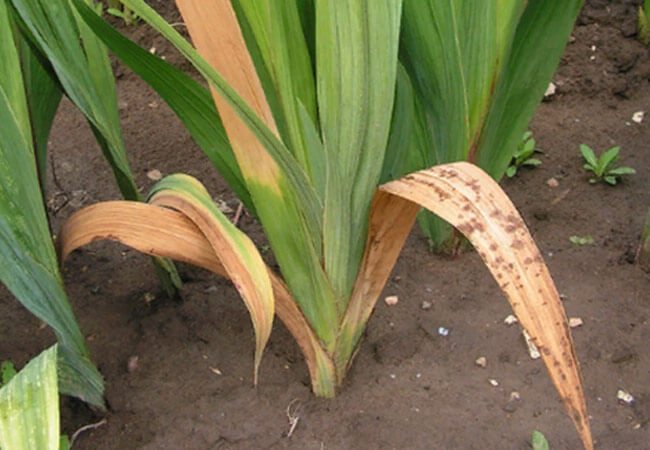


Dry rot of gladioli
Diseased bulbs lose their germination. Or they grow poorly, release defective, undersized shoots, twisted and bent.


Diseases of gladioli
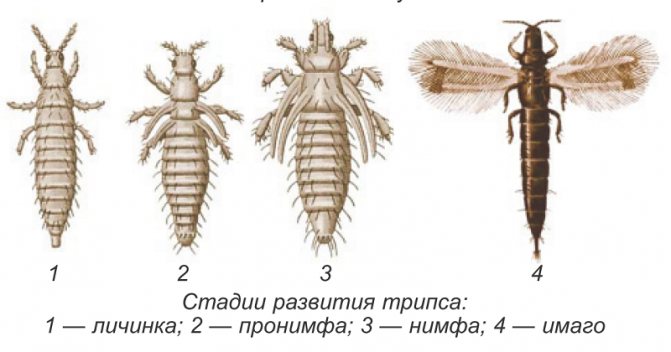
Gladiolus bulbs affected by thrips. Thrips and how to deal with them
Now any gardener can purchase small-flowered Dutch gladioli and large-flowered Russian ones. But along with the purchase of gladioli in joint ventures and stores, we can get problems. I am not afraid, but I will tell you about the most terrible pest of gladioli - thrips, because whoever is warned is armed. I must say right away that I copied a lot from the Internet, almost all the photos are also not mine, but my own comments and recommendations, tested by years of bitter 
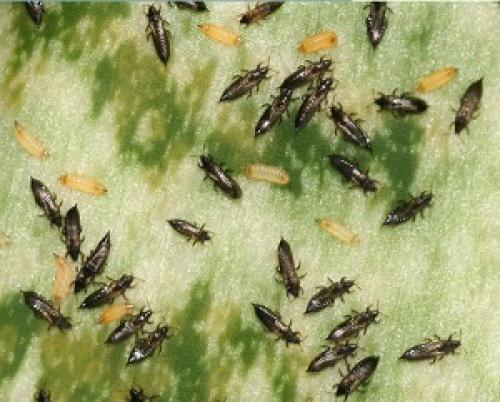



The female lays over 20 eggs. In warm weather above 10 °, one generation develops in 15-20 days. During the season, 5-6 generations of the pest can develop, and in hot dry summers up to 9 generations.
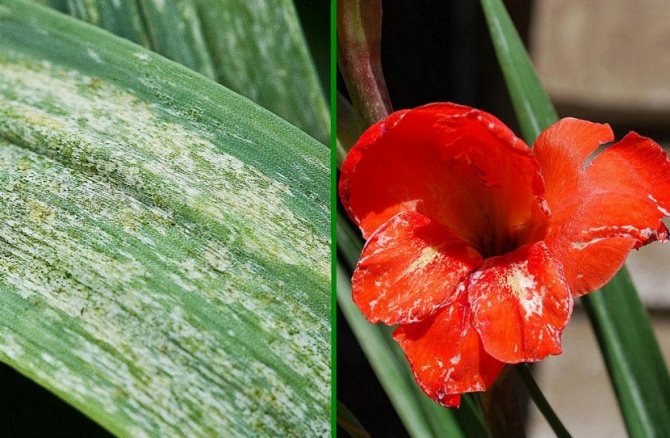
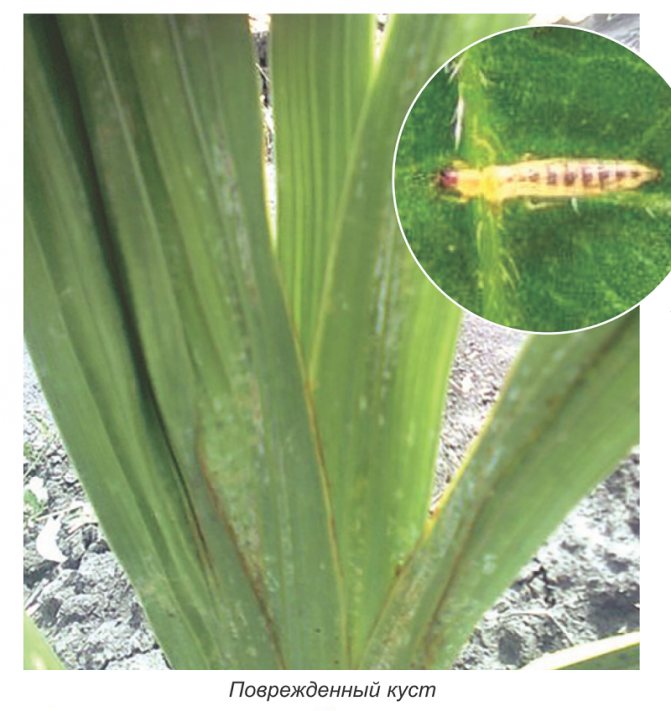
Here are the changes that occur with thrips: Stage 1 - egg. Eggs are sensitive to drying out and die en masse. Do not flood gladioli. Their roots go deep enough. Therefore, rare good deep watering and mulching are useful for them. Eggs are not affected by poisons even with a direct hit! Stage 2 - larva. The larva begins to feed 2–3 hours after emergence from the egg. A day later, at a temperature of + 27C, molt sets in. Stage 3 - after 3 - 4 days, the larva reaches the size of an adult, stops feeding and goes to a depth of 4-6 cm into the soil mixture. The larva molt and transforms into a protonymph. It stays in the protonymph stage for a day (at a temperature of +27 C) or for four days (at a temperature of +15 C). Then it turns into a nymph, after 2 - 3 days - into an imago. After 24 hours, thrips begins to fly, which ends the formation cycle. Before laying eggs, the female ceases to go out to feed and lives underground, therefore this creature, as well as the laying of eggs, is almost impossible to destroy. Life expectancy is from 25 to 45 days. When gladiolus is affected by this pest, whitish spots appear on the leaves, then the leaves dry out. During the appearance of buds, thrips penetrates inside and affects the flowers, which at the same time seem to discolor, and small holes are clearly visible along the edges of the petals after rain. Flowers heavily affected by the pest may not open at all. This is how the bulbs, leaves and flower of gladiolus, which have been visited by thrips, look like.
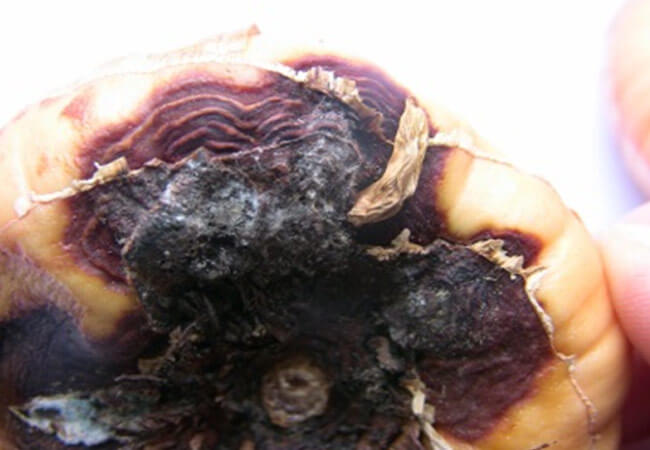
Sclerotinia - dry rot of gladioli
From August and closer to September, when summer rains become cool and more frequent, the soil fungus Sclerotinia gladioli, which infects gladioli, often announces itself. This disease is called sclerotinosis.However, often in the northern regions, especially on acidic, heavy and rotten soils, sclerotinosis can manifest itself at the beginning of the growing season.
Dry rot can persist in the soil for even more than five years. The disease can be transmitted from the mother's bulb to the children, or during storage. Complicating the diagnosis of this gladioli disease is that externally infected corms appear healthy. And even the storage period may not cause severe damage to the planting material, and in the new season, a diseased onion can be planted.
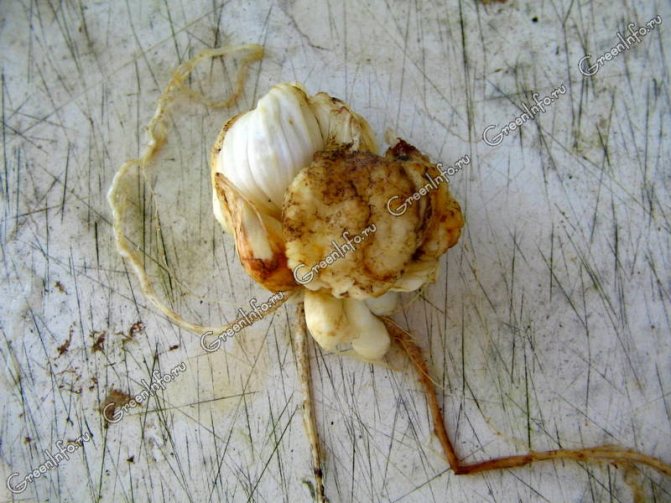
The fungus settles on the scales of the bulbs and creates there fruiting bodies in the form of dark dots. The first signs of the disease appear 1.5 months after the first shoots. The stem and lower leaves begin to acquire a brown-purple color, and then dry out.
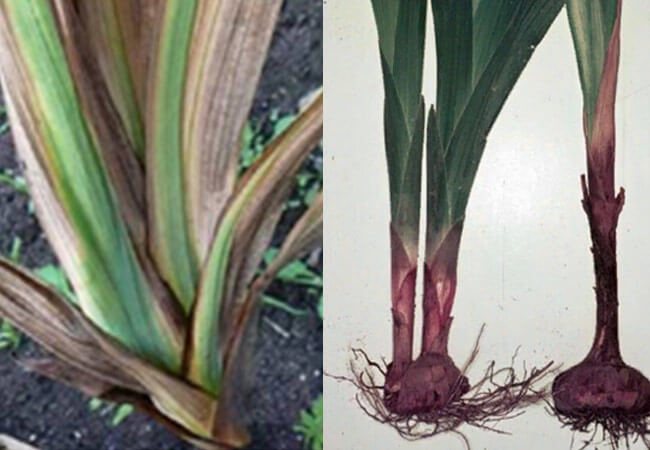


Sclerotinia - dry rot of gladioli
Slerotinosis affects the vascular system of the plant. If the bulbs are seriously affected by the fungus, then soon the leaves and stem begin to dry out. Sometimes, seedlings from a diseased bulb may not be at all. Or the flower grows defective: the stem breaks, gets wet, breaks down into fibers.
When examining with a magnifying glass, you can see fungal bodies at the base of the plant - black dots.
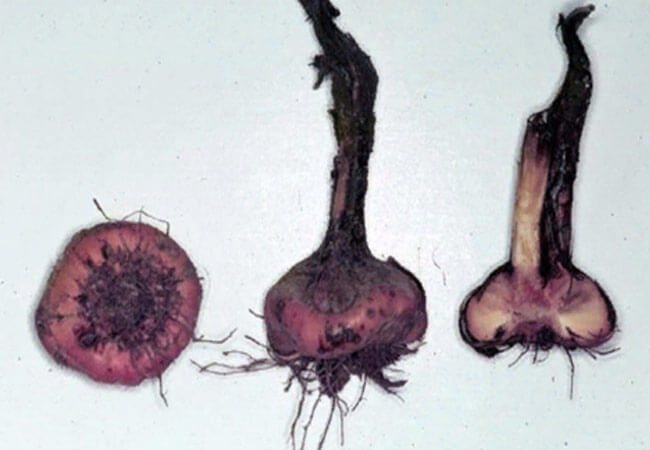


Slerotiniosis
On the bulbs, the disease manifests itself in the form of dark brown spots. They are located mainly on the edge of the scales. At first, the specks are small, in the form of dots with a match head.
Then they combine to form large, recessed spots of a dark brown color. Further, the roots die off, the bulb dries up.

There is no cure for sclerotinosis. The only way out is to destroy the diseased material and carry out preventive and disinfecting measures with the soil and other plantings, planting materials.
- Do not plant gladioli in shaded areas.
- You should avoid nitrogenous fertilizers, fresh manure.
- Coarse sand for planting flowers can solve the problem of high soil moisture.
- Bulbs should be harvested in a timely manner for the winter.
- It is necessary to reduce the acidity of the soil, for example, with lime.
Thrips on gladioli, how to get rid of. Thrips and how to deal with them
Now any gardener can purchase small-flowered Dutch gladioli and large-flowered Russian ones. But along with the purchase of gladioli in joint ventures and stores, we can get problems. I am not afraid, but I will tell you about the most terrible pest of gladioli - thrips, because whoever is warned is armed. I must say right away that I copied a lot from the Internet, almost all the photos are also not mine, but my own comments and recommendations, tested by years of bitter 

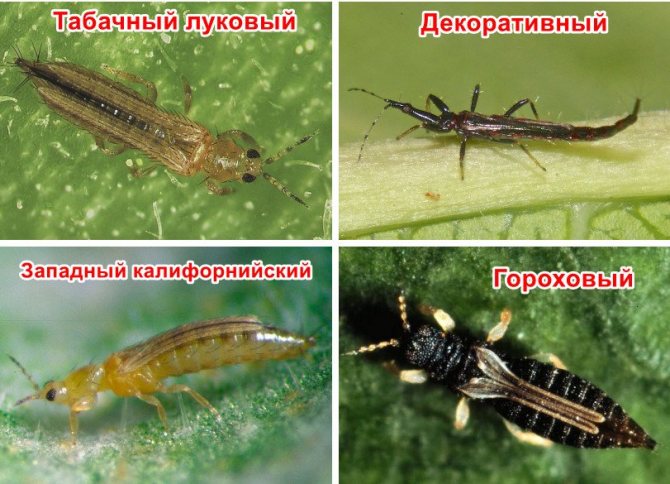
Meet thrips is a small 1.5-2 mm winged insect of dark brown color. Thrips larvae are transparent white at the beginning of development, then light yellow. Both adult insects and larvae pierce the tissues of gladioli and suck the juice from the leaves, stems, and corms.
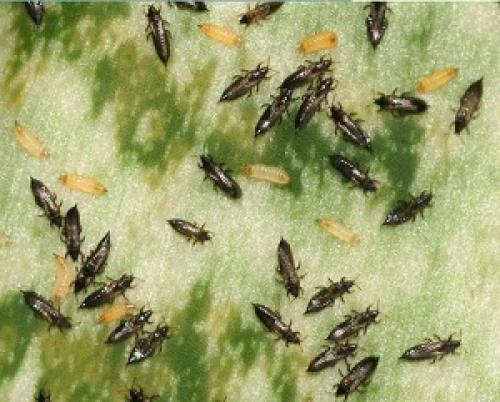


The female lays over 20 eggs. In warm weather above 10 °, one generation develops in 15-20 days. During the season, 5-6 generations of the pest can develop, and in hot dry summers up to 9 generations.
Here are the changes that occur with thrips: Stage 1 - egg. Eggs are sensitive to drying out and die en masse. Do not flood gladioli. Their roots go deep enough. Therefore, rare good deep watering and mulching are useful for them. Eggs are not affected by poisons even with a direct hit! Stage 2 - larva. The larva begins to feed 2–3 hours after emergence from the egg. A day later, at a temperature of + 27C, molt occurs. Stage 3 - after 3 - 4 days, the larva reaches the size of an adult, stops feeding and goes to a depth of 4-6 cm into the soil mixture. The larva molt and transforms into a protonymph.It stays in the protonymph stage for a day (at a temperature of +27 C) or for four days (at a temperature of +15 C). Then it turns into a nymph, after 2 - 3 days - into an imago. After 24 hours, thrips begins to fly, which ends the formation cycle. Before laying eggs, the female ceases to go out to feed and lives underground, therefore this creature, as well as the laying of eggs, is almost impossible to destroy. Life expectancy is from 25 to 45 days. When gladiolus is affected by this pest, whitish spots appear on the leaves, then the leaves dry out. During the appearance of buds, thrips penetrates inside and affects the flowers, which at the same time seem to discolor, and small holes are clearly visible along the edges of the petals after rain. Flowers heavily affected by the pest may not open at all. This is how the bulbs, leaves and flower of gladiolus, which have been visited by thrips, look like.
Botrythiasis - gray rot of gladioli
Botrytis gladiolorum is a fungus that causes botrythiasis, which gladioli often suffer from. This fungus infects the flower completely. He does not choose a specific period to attack the plant. This can happen at any time during the life of the flower. This is his cunning. But still, most often, botrytis activity is noted in cool weather with high air humidity.


Botrythiasis
By the way, this fungus is extremely selective and, depending on the region, it can attack the plant from different directions. In northern latitudes, the bulb is primarily affected. In the south of the country, botrythiasis of gladioli begins with inflorescences.
Symptoms
- Small brownish-red spots with bright edging appear on the leaves. Gradually, the spots increase in size, changing the color of the leaves. With complete defeat, the foliage dies off.
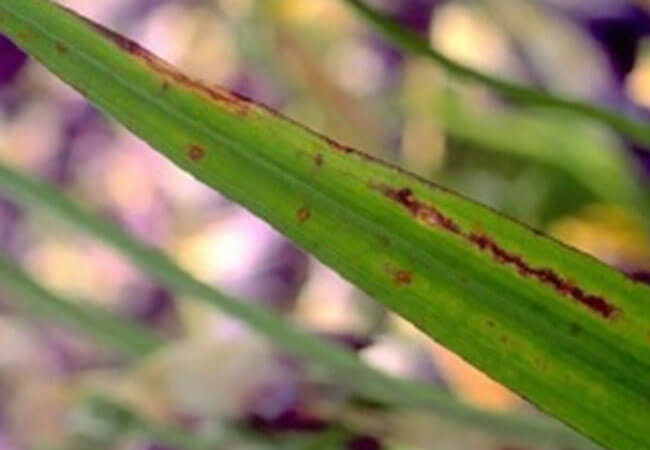


Botrythiasis - gray rot of gladioli
- With abundant dew, fog and precipitation on the leaves, you can notice a characteristic fluff, like a bloom.
- Grayish specks form on the flowers - fungal spores.
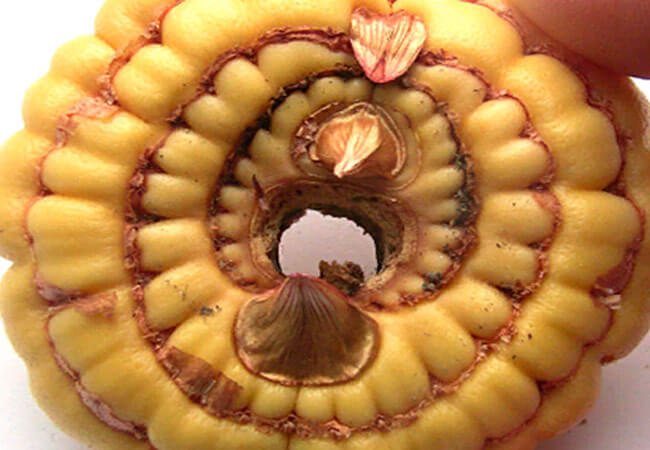
- Penetrating into the stem, the fungal infection makes it rotten and fragile. Gray rot may appear on the neck. The stem breaks and the rot moves on to the bulb.
- The affected area of the bulb becomes brown in color. The lesion site has distinct contours. Rot appears. The corm begins to dry out.
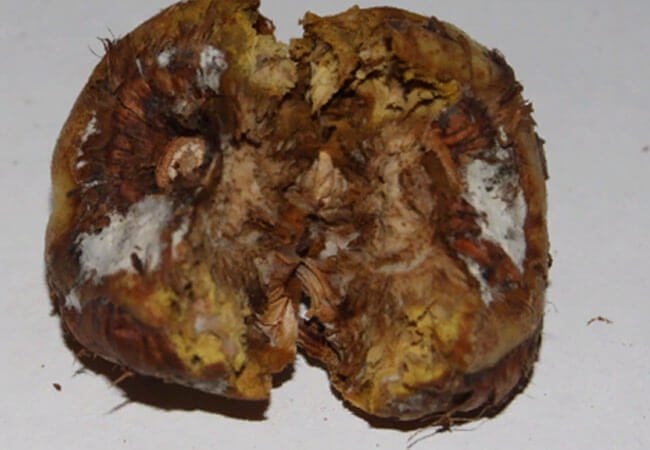

Gray rot
- The bulb becomes soft, the bottom falls through. For this disease of gladioli bulbs, the shape of a bagel is characteristic (see photo).
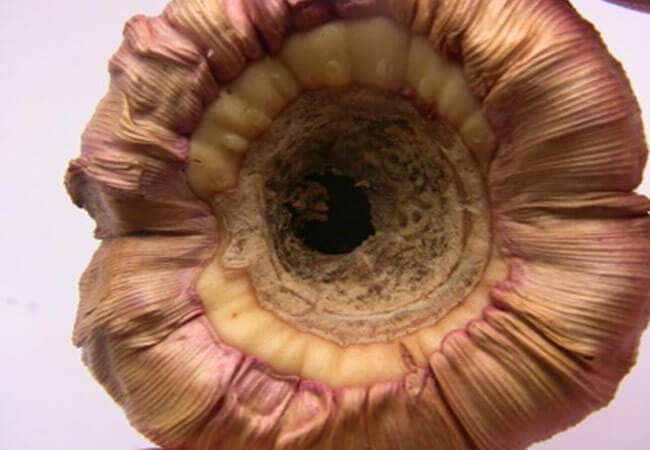

Donut shape
This disease develops very intensively. The fungus only needs a few days of favorable conditions (humidity, coolness) to infect all flowers.
Preparations against thrips
In the fight against gladiolus thrips, chemical preparations are used to completely destroy a wide range of insect pests, their eggs and larvae. Such pesticides have proven themselves well: "Karate", "Karbofos", "Confidor", "Inta-Vir", "Fitoform", "Aktelik". The most effective drug for today is "Decis".
To avoid stable addiction of thrips to insecticides, they need to be alternated. Spraying in the early morning is especially effective in warm, calm weather. On cool, cloudy days, the benefits of such treatment are minimal, because thrips does not appear on the surface of the leaves.

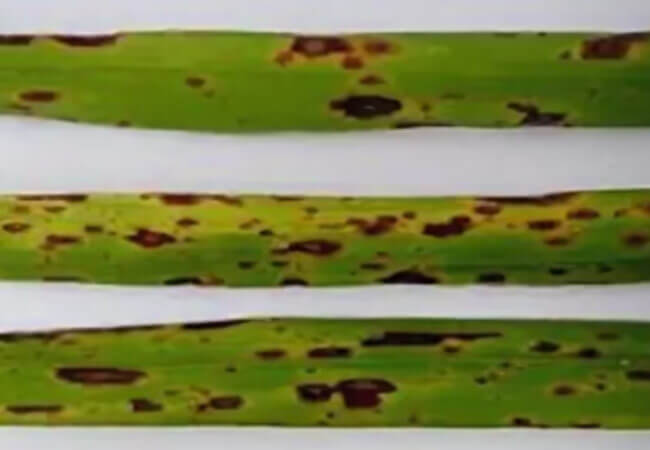
Septoria - hard rot of gladioli
The causative agent of septoria, the microscopic fungus Septoria gladioli Pass, can infect a plant both through the soil and through the air, waterways. The fungus enters the soil with infected bulbs.
The septoria can maintain their vital activity for up to four years, calmly transferring wintering. Septoria spores, carried by wind and rain, can settle on the leaves of gladioli and begin their destructive work.
The situation is aggravated by unfavorable growing conditions for plants:
- High humidity;
- Sour, heavy, barren soil;
- Abundance of peat and acidic fertilizers;
- Cool.
In such an environment, gladioli are weakened and do not have the ability to fully resist fungal infection. In addition, even during the winter storage of corms, fungi continue to develop inside the infected planting material and infect the rest of the bulbs.
Symptoms
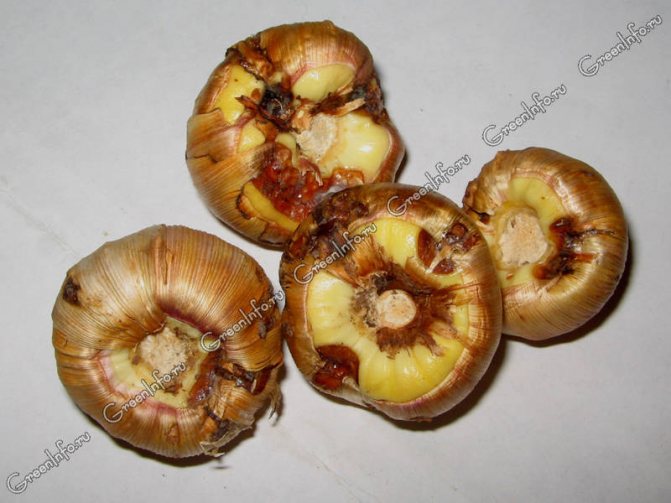
The first symptoms of septoria appear in late August - early September. External manifestations may be similar to other fungal diseases of gladioli. The defeat of the bulbs is similar to sclerotinosis:
- Spots of burgundy-brown color appear.
- Over time, the spots grow and turn black.
- Bulb tissue necrosis leads to the formation of dents. They merge into large lesions and, as a result, the bulbs are mummified.
- Even if the bulbs are not fatally affected, they do not germinate when planted or give defective shoots.
Leaf damage during septoria is identical to botrythiasis:
- The appearance of reddish-brown spots with a light center and a clear border.
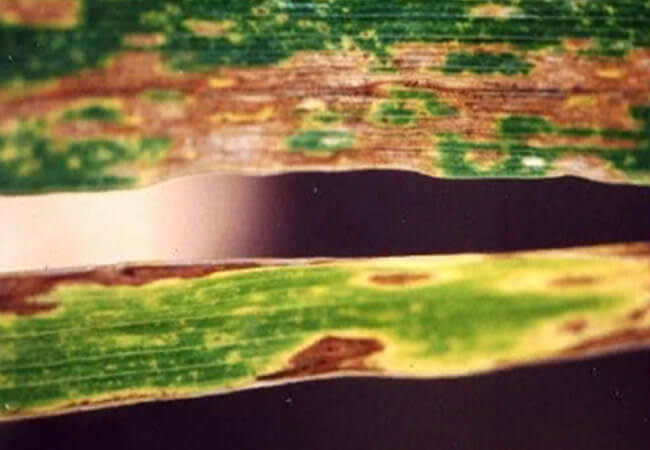

The appearance of reddish-brown spots
- In the center of the spots, over time, fruiting bodies of fungi are formed in the form of black convex dots.
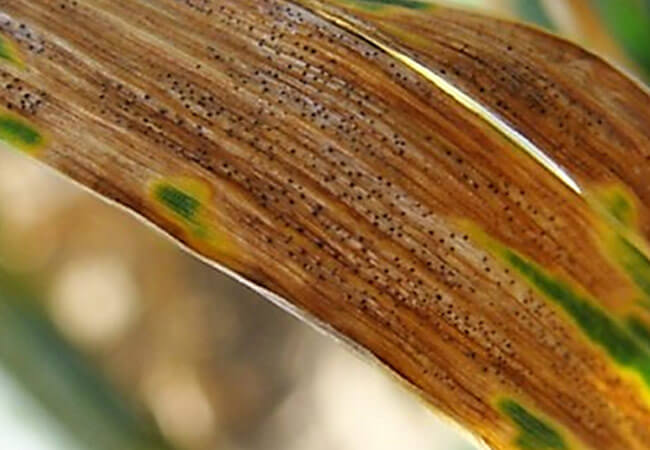


Septoria - hard rot of gladioli
- The leaves are completely dry.
My flower garden!
Registration from 07.02.2019


Gladiolus is a noble plant. It is also called the sword flower. The fact is that, according to legend, the gladiolus grew up in the arena of the Colosseum, at the place where the swords of two gladiator friends who refused to kill each other for the amusement of the nobility were thrown. Gladiators were executed, and Gladiolus, or Gladíolus, became a symbol of loyalty. There is a lot of information about this beautiful plant, and in this material we will tell you in detail about gladiolus diseases... It is better to see a hundred times than hear once, so we will not limit ourselves to just a description, we will definitely post their photos taken from the atlas-determinant of diseases of ornamental plants.
Fusarium gladiolus
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus Fusarium oxysporum (Fusarium oxysporum)... The disease can manifest itself both during the growing season and during the storage period of corms. The fungus infects the roots and corms. Before flowering, the leaves begin to turn yellow from top to bottom, then the leaf blade turns brown, and the plant dries out.
A dead plant is easy to pull out of the soil, because its roots completely rot. On the affected tissues of the stem and on the underside of the corms, a pinkish-white sporulation of the fungus (fluffy bloom) can be seen.
During storage, reddish-brown spots are initially formed on the corms, if the humidity is high, then a fluffy bloom of sporulation is formed, then the corm finally dries up.
Since the fungus infects the vascular system of plants, then from the mother corm, it also enters the daughter baby bulbs. There he remains in a latent form for some time. In addition, the infection spreads with contaminated plant debris in the soil.
HOW TO FIGHT FUSARIOSIS
It is necessary to use both agrotechnical and chemical control methods.
- removal of affected plants from the site along with a clod of earth,
- removal of all plant residues,
- annual replacement of the site for planting crops (crop rotation),
- maintaining an optimal storage regime for corms in winter,
- optimal conditions for winter storage,
- processing of planting material before planting and laying for storage by immersion in a 0.2-0.4% solution with an exposure of 30 minutes of the drug Maxim and subsequent drying. For industrial cultivation, dressing of corms before planting in a 0.2% solution Fundazola... You can also use biologics: Trichodermin, Fitosporin, Glyocladin, Alirin.
Brown heart rot
The causative agent of this disease is gladioli mushroom Botrytis gladiolorum (Botrytis gladiolorum)... Brown heart rot can affect all parts of the plant, but is more often based at the base of the stem.Brown spots appear there, yellowing and drying of the foliage begins, a grayish bloom of sporulation can be seen on the peduncles and stems.
The fungus makes its way deep into the tissue of the corms, damaging the very core (hence the name), which rots, dries up and loses color.
If the planting material is stored at high humidity, then the corms gradually dry out, and a smoky-gray bloom of fungal sporulation remains on the surface. The spores dissipate, and the disease spreads to neighboring corms. The infection persists in plant debris and in the affected corms.
HOW TO FIGHT BROWN HEART ROT
Control measures are similar to those against fusarium.
Solid rot, or septoria, gladiolus
The causative agent of the disease is a mushroom Septoria gladioli... Initially, numerous angular irregular spots of a red-brown hue can be seen on the leaves. Feature - clear dark brown border around the spots... Gradually, the spots merge, small dotted fruiting bodies develop on them. This is the hibernating stage of the fungus.
As for the corms, creamy-brown rounded spots appear on them in the fall, gradually they deepen, become angular, dark brown in color. The disease progresses strongly when stored in humid conditions, the spots deepen and expand both from the upper side of the corm and from the bottom, the affected tissues harden, and the corm is mummified. The infection persists in plant debris and in the affected corms.
HOW TO FIGHT SEPTORIOSIS
The same as with Fusarium. The named fungal diseases have pathogens similar in morphology and development, therefore, the control measures are the same.
You can see the listed diseases of gladioli in the photo below, click on it to enlarge.


Diseases of gladioli
Dry rot of gladiolus
The causative agent is another mushroom Sclerotinia gladioli... At the base of the stem, blurry dark brown spots appear, then the leaves turn yellow, brown and dry out. Typically, in a diseased plant, the stem softens and may break.
On the corms, dry rot manifests itself as follows: numerous, yellowish-cream spots appear, over time they turn brown and are depressed, they are best seen along the line of connection with the scales. Affected corms harden and dry up, a dense white mycelium first develops on the affected tissue, and many small black sclerotia of the fungus form in it, thanks to which the fungus can persist in the soil for more than 5 years.
HOW TO FIGHT DRY ROT OF GLADIOLUS
The same as with fusarium.
Gladiolus Penicillus Rot
The causative agent is a mushroom Penicillium gladioli (Penicillium gladioli)... During storage, rounded, wrinkled, slightly depressed spots of a yellow-brown hue form on the corms.
Then a grayish-green bloom develops on the damaged tissues, apparently, many have seen similar to moldy bread. The disease is spread by spores and is transmitted with contaminated planting material.
HOW TO FIGHT PENICILLOUS ROT
The same as against fusarium.
Heterosporia gladiolus
Another fungal disease caused by Heterosporium gracile The course of the disease begins with the appearance of elongated, rounded-elongated spots on the leaves, which at first have a yellowish tint, and then dry up, become light brown with a brown border.
If you do not take any measures, the leaves will turn completely yellow and dry out. Sporulation plaque is dark in color. The infection persists in plant debris.
HOW TO FIGHT HETEROSPORIOSIS
Collection of plant residues, annual replacement of the planting site, spraying of plants during the growing season with copper-containing preparations Hom, Oxyhom, Abiga Peak or other fungicides - Skor, Horus, Tiovit Jet.
Alternaria gladiolus
The causative agent of Alternaria fungus Altemaria tenuis (Alternaria tenuis)... Symptoms appear on leaves and peduncles, usually in weakened plants growing in inappropriate conditions. At the end of summer, vague dark spots appear on them, which are then covered with a dark brown or black bloom of sporulation. The affected plant parts dry out. The disease manifests itself especially clearly on peduncles, in which the lower flowers dry out prematurely and are covered with bloom. The infection persists in the soil in plant debris.
HOW TO FIGHT ALTERNARIOSIS
Control measures are similar to those against heterosporiosis, that is, spraying with fungicides during the growing season.
Gladiolus scab
The causative agent is a bacterium Pseudomonas marginata (Pseudomonas marginata)... Initially, the disease is localized at the base of the leaves and manifests itself as reddish-brown elongated or irregularly shaped depressed spots. If the weather is humid, the affected areas will rot.
On corms, spots are more often visible from the lower side. Initially, they are roundish yellowish-beige, about 5 mm in diameter. A transparent sticky liquid (exudate) is released on their surface. Gradually the spots turn black and sink inside, dry up, crack. The causative agents of infection persist in the soil in plant debris and in infected corms.
HOW TO FIGHT WITH A GUY ON GLADIOS
Agrotechnical measures are similar to those in the fight against fungal diseases: collecting plant residues, culling heavily affected corms, changing sites. Chemical methods include etching in a solution of the drug "Maxim" or in a red solution of potassium permanganate. Watering Fitolavin.
The following photo shows the described diseases of gladioli: white bloom with fusarium, tissue loss with pith rot, gray rot, septoria, or hard rot.
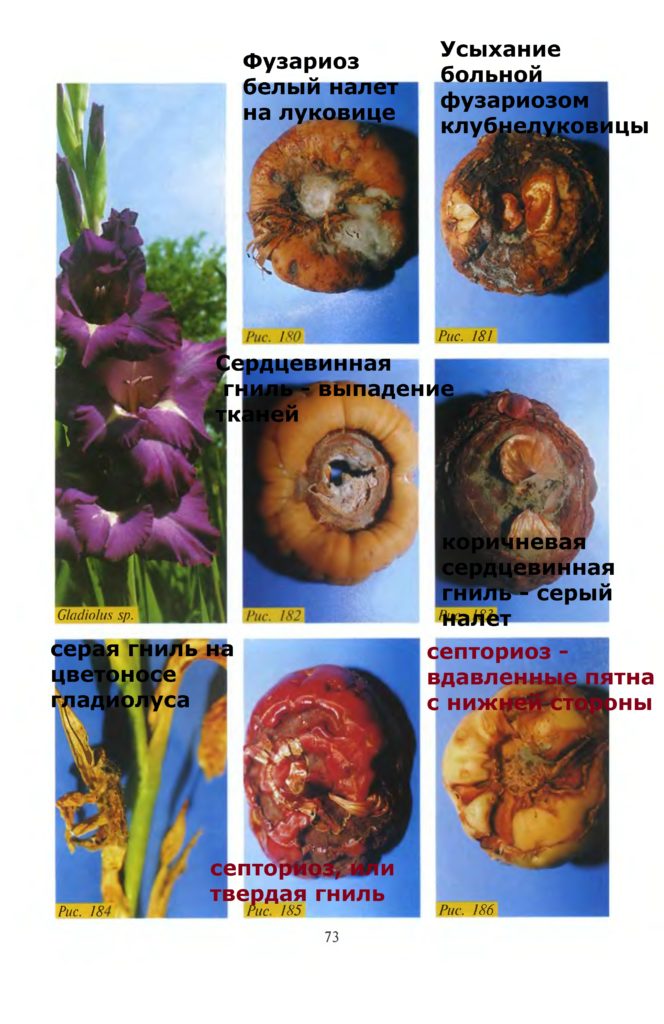

Corm diseases
Gladiolus jaundice
A dangerous phytoplasmic disease that is currently not amenable to treatment. Pathogen - phytoplasmas (formerly mycoplasma organisms).
The infection persists in plant debris and perennial weeds and is transferred from plant to plant by sucking insects - leafhoppers, leaf beetles... The leaves of sick gladioli turn yellow, become chlorotic (as if discolored), then turn brown and dry. The stems are also deformed: bent and thinner.
HOW TO FIGHT YELLOW GLADIOLUS
If you see a specimen with signs of this disease, discard and destroy it without regret (do not put it in compost). To prevent the spread of the disease, it is necessary to spray the plantings with insecticides against sucking insects (Fufanon Nova, Aktellik, Inta-vir, Fitover, Alatar).
WHITE DESTROYING MOSAIC GLADIOLUS
The causative agents of the mosaic in gladioli can be various viruses: cucumber mosaic virus Cucumis mosaic cucumovirus (CMV), tobacco rattle virus (TRV), Bean yellow mosaic vims virus (BYMV)... They are carried by aphids and other sucking pests.
Viral diseases have typical manifestations: variegated petals twisted inward in flowers, deformation of flowers and their inhibited development, yellow-green stripes and specks on the leaves, which can later dry out and acquire a bronze tint.
HOW TO FIGHT THE WHITE DESTROYING MOSAIC IN GLADIOLES
Control measures are the same as against jaundice.
MAIN PESTS OF GLADIOLUS AND THEIR PHOTOS
Ordinary earwig
Common earwig (Forficula auricularia) - an elongated rather large insect 20 mm long, with an abdomen ending in ticks. Adult insects and their larvae gnaw leaves, peduncles, buds, and eat petals.
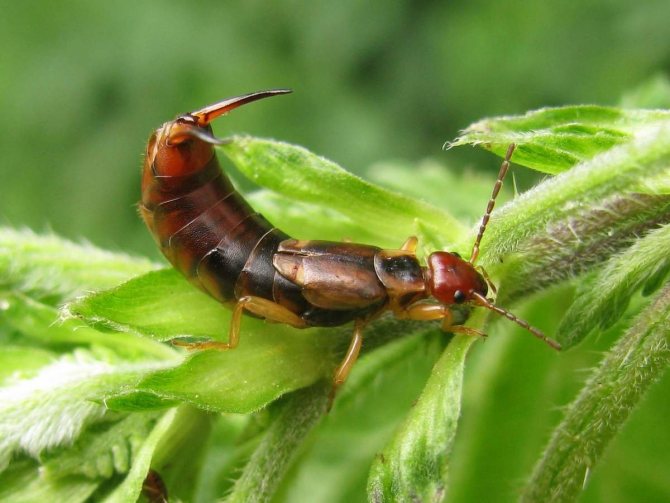


Common earwig (Forficula auricularia)
A gnawing mouth apparatus, two pairs of wings, leathery anterior elytra are often underdeveloped or absent altogether - these are the main morphological features of the earwig. Two solid appendages are visible at the end of the abdomen. The larvae are similar to adult insects, but smaller in size. Earwigs are nocturnal, hiding under the bark during the day. They feed on plant debris, gnaw buds, leaves, young shoots of deciduous trees and shrubs.
HOW TO FIGHT WITH HAIRDRIVERS
With a strong reproduction of the pest, spraying with insecticides is carried out - Senpai, Fufanon... Prevention is weed control and deep digging of the soil.
Slugs
The field slug (Agriolimax agrestis) and the net slug (Agriolimax reticulatus), the well-known gastropods without a shell, eat gladioli with pleasure. With a large number, they cause irreparable damage to all flower crops, not just gladioli.
HOW TO FIGHT SLIMES
Catching slugs under shelters made of cardboard, boards. With a large number of sprinkling tracks with superphosphate (5-8 g per 1 sq. M), the use of drugs based on metaldehyde (Thunderstorm, Slizneed).


Slug on salad
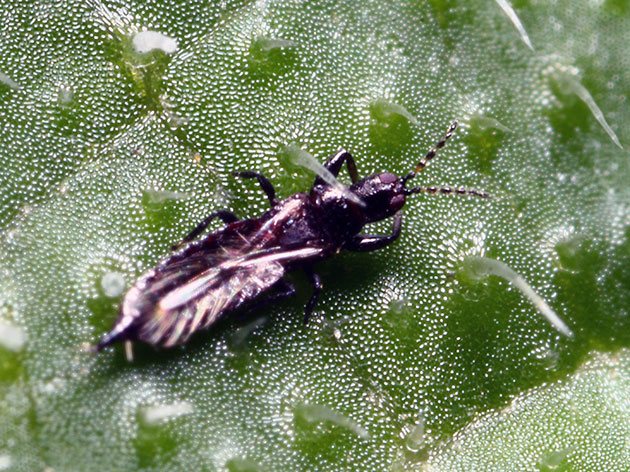
Gladiolus thrips
Gladiolus thrips (Taeniothrips simplex) - small insect 1 - 1.5 mm in size, oblong, dark brown in color with fringed wings. The larvae are yellow-orange. Adult insects and their larvae feed on tissue sap. Flowers and leaves become discolored and strongly deformed, buds do not open, corms dry out completely.
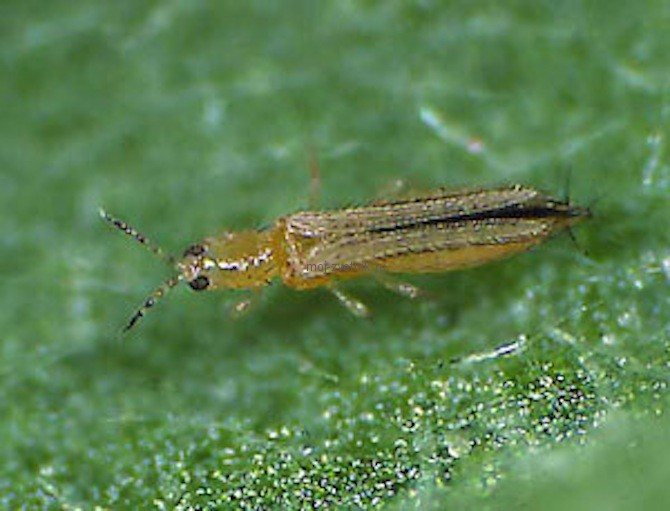


Thrips
HOW TO FIGHT TRIPS ON GLADIOS
Treating corms before planting in an insecticide solution (Fufanon, Biotlin, Fitoverm, Aktara or Inta-vir). Spraying plants before flowering with the same preparations. With a large number of pests, dressing of corms immediately after digging.


Diseases and pests of gladioli
Root onion mite
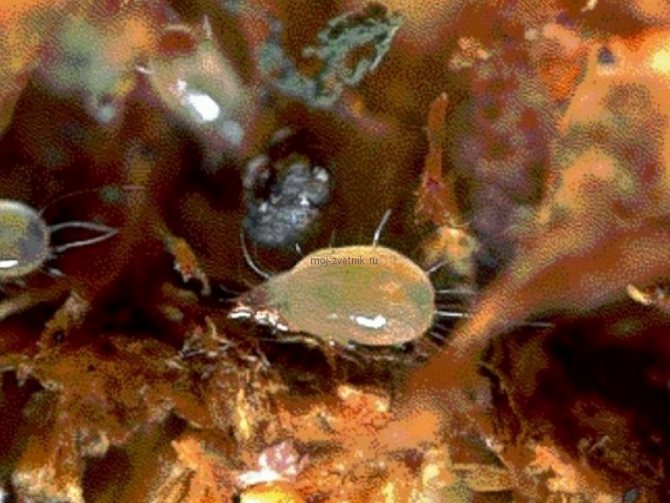


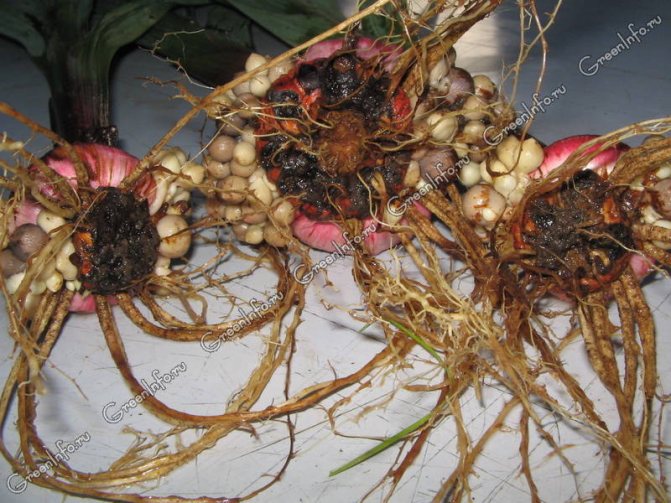
Root onion mite (Rhizogliphus echinopus) - a very harmful small sucking pest. Ticks and their larvae feed on corms and bulbs, grind the bottom, suck the juice from the scales and buds.
With severe damage, the bottom rots, the plants do not bloom and die. Damage is often noticeable on the upper side of the corm in the form of small brownish necrotic areas. At low temperatures and low humidity, the pest forms the hypopus stage and remains in it.
HOW TO FIGHT ROOT MITCHES
Be sure to pickle the corms in a solution of any acaricidal preparation (Fitoverm, Fufanona, Actellika).


Root onion tick on gladioli
We have listed all the main diseases that you may encounter when growing gladioli. Now, thanks to the photo and description, you will know them by sight. However, we hope that you will not need this material and that all your plants will be healthy and strong!
Did you like the article? Share with your friends
РќСЂР ° вится
Ornamental plants diseases and plant pests
- ← What is the name of a herringbone-like houseplant
- Tomatoes of an unusual shape and color →
Penicillosis - blue rot of gladioli
This disease affects the bulbs of gladioli during their storage period. The main reason for the occurrence of blue rot is non-compliance with storage rules.
As a result of high humidity and poor ventilation of the premises, the fungus Penicillium gladioli Mc Cull appears in the storage facilities. et Thorn. It easily penetrates the wounds on the corms and infects the planting material.
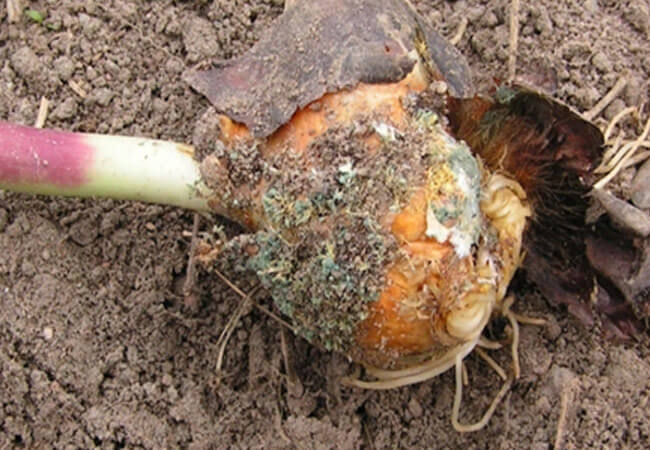


Penicillosis - blue rot of gladioli
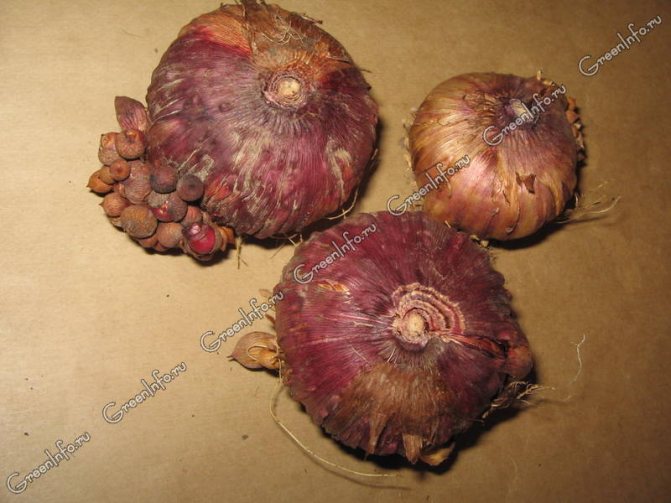
It is not difficult to identify penicillosis in gladioli bulbs:
- Brownish dents are formed near the bottom.
- Over time, they become rough and change color to yellowish gray.
- At a storage temperature above 20 ° C, fungi sporulate and the bulbs become covered with a bluish-green bloom.
- Light brownish or creamy small spherical formations with a diameter of no more than 0.1 cm appear inside the corms. These are sclerotia - mycelium during the wintering period, characteristic of parasitic fungi.
Penicillosis can be avoided by properly preparing the material for storage and observing the wintering conditions for planting material:
- Dry the bulbs well after digging;
- Do not injure the bulbs;
- Store planting material in a dry, ventilated place.
- You can pickle the bulbs after digging in fungicide solutions.
Etching gladioli bulbs. Cleaning and storage of gladiolus bulbs


Everyone loves gladioli, but many gardeners do not want to burden themselves with storing their bulbs in winter.
Harvesting, processing, drying and storage of gladioli planting material are very important stages in the technology of growing this crop. The harvesting time of the bulbs depends on the weather conditions and the climatic zone. Experienced gardeners do this in late September or early October in dry, sunny weather before severe frosts.
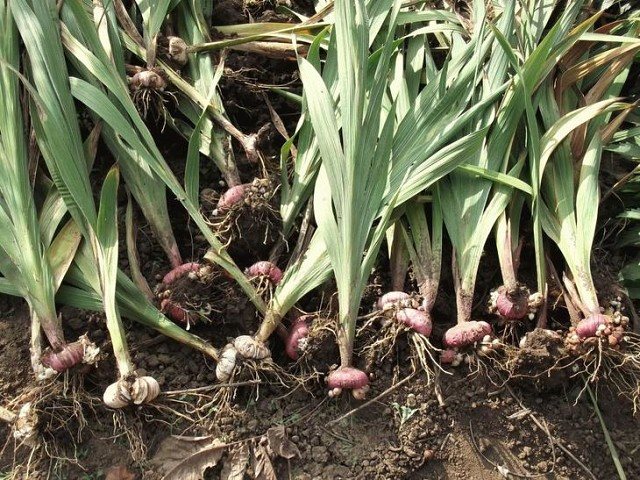
The corms are harvested in the following order: first, the varieties of the early flowering period are dug, then the early middle, medium and so on according to the flowering period.
But dark-colored varieties (cherry-red, purple and lavender-blue) are dug out primarily among equal flowering periods, since they lose their natural immunity to fungal diseases earlier than others and can be severely affected by them. Bulbs grown from tubers (children) are the last to be harvested. If the flowers were not cut, then the peduncles must be carefully broken off immediately after the end of the flowering of the upper flowers.
Dig up the corms with a shovel or pitchfork, gently shake off the soil from them, carefully collect the well-separated baby (ripe covered with a dense shell).
Immediately after digging out, the stems and roots should be cut off from the bulbs, leaving a stump no more than 0.5-1 cm. You should not leave more stumps, since by the fall the common pest of gladioli - thrips gathers on the bulbs closer to the base of the stem. And by doing short cutting of the stem, we reduce the possibility of damage to the bulbs during their winter storage.
In adult corms, the old maternal corms and roots must be removed immediately, because this prevents the spread of diseases and reduces the drying time of the planting material. If the mother corm is not immediately separated or is not completely separated, then after 10-15 days of drying the corms, it with the remnants of the roots is very easily separated from the replacement corm.


And for bulbs grown from children, the roots are only shortened well, and they are removed the next year in preparation for spring planting.
After trimming the stem and roots, the corms are washed from the soil, treated in a solution of potassium permanganate (6–8 g per 10 l of water). Then it is advisable to dry them in the open air for at least one day.
The corms by varieties are laid out in boxes (cardboard, wooden) and dried in the air for several hours (if there is no precipitation). Then they are transferred to a heated room and dried at a temperature of 30–35 ° C for 6–8 days (near heating devices, fan heaters). After that, drying is carried out at a temperature of 20-22 ° C up to 6-8 weeks after digging. During the entire drying period (especially in the first days), it is necessary to stir the bulbs (2 times a day) for even drying.
The quality of drying the bulbs depends on their condition during winter storage. Poorly dried corms, due to high humidity under the scales, often get sick, are poorly stored and die.
After drying, the corms must be carefully reviewed, the infected ones must be thrown away, and the corms with mechanical damage must be treated with brilliant greens or a strong solution of potassium permanganate and put into bags according to varieties, attaching tags indicating the variety.
Then the bags are laid out in boxes and transferred to storage. For the prevention of diseases, it is advisable to put peeled cloves of garlic in these bags, which has phytoncidal and antibacterial properties.
The bulbs should be stored in a dry (air humidity not higher than 70%) and cool (3–6 ° С) room. It is difficult to create such conditions in a comfortable apartment, so the first 1-1.5 months the bulbs can be stored near the balcony, on the windowsill, between the frames, and then stored in paper bags on the lower shelf of the refrigerator, where the specified temperature regime is maintained.
The baby of gladioli should not be overdried, because it just won't come up. Immediately after separation from the bulb, it must be put in a bag and stored on the lower shelf of the refrigerator. During the storage period, it is necessary to view the corms once a month, remove diseased ones in order to exclude contamination of healthy planting material.
To facilitate the storage of bulbs in winter, many gardeners, after drying, are dipped into melted paraffin at a temperature of 32–35 ° C, and then into cold water. In this case, the bulb is covered with a thin protective layer that protects it from drying out. These bulbs can be stored at temperatures up to 10-15 ° C. Before planting, the paraffin film is removed from the bulb along with the scales or in hot water at a temperature of 40–45 ° C.
Last but not least. The next year, the beds where gladioli grew should be used for garden crops. Once again, gladioli can be planted in their original place only after 3 years.
Based on materials from the newspaper "Ural Gardener" No. 39-2012
Smut - a fungal disease of gladioli
In hot, windy dry summers, spores of the fungus Urocystis gladioli W. G. Smith scatter everywhere, affecting crops, including flowers. However, gladioli can wait for this infection underground, because this fungal infection, when it gets into the soil with infected planting material, can persist there for a long time.
The symptomatology of smut is characteristic only for this disease of gladioli and is not similar to others:
- The leaves, scaly part of the bulbs and stems are covered with swollen black stripes. These are spore vessels, from which mushroom "seeds" spill out after a while. The affected leaves turn yellow and die off. The bulbs break down and dry out.
The danger of such a fungus lies in its massive infection of large areas of planting. This fungal infection is characteristic for the southern regions.
To reduce the risks of contamination of flower plantations, during the growing season, spraying should be carried out once every 10 days with copper chloride (3-5 g / 1 l) or Bordeaux solution of 1%.
Other processing methods
In addition to industrial insecticides for the treatment of gladioli and its bulbs from thrips, plant compositions are used that are no less effective and absolutely safe for humans and the environment.
- Before planting, the tubers can be soaked in garlic juice for 2-3 hours.
- A piece of cloth, abundantly moistened with alcohol, is placed in a container with tubers and sealed for several hours. Due to the lack of oxygen, thrips get out from under the integumentary scales and die.


- Spraying plants with infusions of tobacco dust and makhorka.
Performing simple agrotechnical techniques and methods of dealing with harmful insects, you can grow beautiful, pleasing gladioli.
Curvularia - gladiolus disease
Although this disease of gladioli is not so common, there have been cases of a real epidemic in history when the crops of these flowers were exterminated by the fungi Curvularia trifolii en masse. This pathology is also known as "leaf spot".
It is spotting that curvularia is manifested. Oval spots with black spore "vessels" cover young plant leaves, seeds and buds. This symptomatology is more typical for the southern regions.
Often, these fungi attack plants from below, starting with the bulbs.For no apparent reason and external manifestations, the flowers simply die. And only examination of the bulbs can indicate a progressive disease:
- The bulbs are covered with dark, almost black spots. Lesions are shallow and not large-scale. Usually localized around the bottom. At the slightest pressure, necrotic tissue is separated from healthy tissue.
High humidity and heat are favorable conditions for the outbreak of this fungal infection. Only preventive treatment with fungicides once every 1-2 weeks can help here.
What to do if gladiolus has thrips
If all the precautions did not bring the desired result and signs of a pest appeared on the gladiolus, urgent action must be taken. The pest, in addition to depleting the vitality of the plant, can bring a dangerous disease.
Did you know? In ancient Rome, gladiolus was considered a magical plant. The bulb of this flower was worn by gladiators on their chests for victory.
For this reason, the following steps are immediately followed:
- Provide uniform watering of flowers and row spacings, because the first foci of thrips appear in dry places.
- The plantings are treated every 7-10 days with "Karbofos" (10% solution).
- If the thrips have begun to multiply intensively and have completely infected the flower, you need to cut it off. Thus, the movement of the pest to the lower part of the stem can be prevented.


How to treat fungal diseases of gladioli
First of all, when treating flowers from fungus, you should disinfect corms and soil using microbiological agents:
- "Gamair". Every 2 weeks, shedding soil under the root during the growing season. Consumption: 1 tablet / 5 l of water / 1 m².
- Fitosporin. Soaking the bulbs in a solution (4 drops / 200 ml of water). Spilling soil under the root part of plants with 6 ml / 1 l of water / 1 m². Dip the bulbs before storage in a solution of 60 ml / 1 L of water.
- "Trichodermin" - processing of planting material, introduction into the soil. Spilling the soil with this preparation is more effective than soaking the bulbs in it.
- "Alirin". Preplant soil cultivation to a depth of 20 cm (spillage + loosening) with a solution of 1 tablet / 5 l of water / 5 m². Before planting, you also need to soak the bulbs in a solution (1 tablet / 1 liter of water).


How to process plants
Fungicides also play an important role in the fight against fungal diseases. It is recommended to process plants every 10-14 days:
- Treatment of corms with "Carbendazim" / "Colfugo Super" or "Colfugo Duplet" ("Carbendazim" with "Carboxin") before planting and after digging up with a 0.2% solution.
- Mercuric chloride (mercury chloride) also fights fusarium well.
- Good for soil disinfection: Benomil, Karbendazim, Chlorotolonil.
- To enhance the effect, fungicides are often mixed with ascorbic acid, acetic or phosphoric acid. These acids help the fungicidal substances to penetrate into the bulb faster and better.
- With "Vitaros" (2 ml / 1 l of water), it is necessary to process the bulbs for 2 hours. You can process the bulbs in this way even 10 days before planting.
- Good efficiency is shown by Fundazol treatment of planting material before planting or storage. Soak the bulbs for half an hour in a solution of 3 ml / 1 l of water. But we must not forget that mushrooms quickly get used to this drug, so it should be enhanced with Kaptan or Maxim.
- Another good contact fungicide "Maxim" for the treatment of corms. Soak the bulbs for 30 minutes in a solution of 4 ml / 1 l of water. This volume of solution is enough to process 1 kg of planting material. After soaking, the bulbs must be dried well.
You can also disinfect planting material with the following drugs:
- TMTD (1% solution / 1 kg of planting material /) for 1 hour;
- Topsin (2 ml / 1 l of water) for 2 hours;
- "Captan" (1 ml / 1 l of water) for 2 hours.
- Antibiotics have been identified by many researchers as an effective remedy for combating fusarium. These preparations increase the protection of plants and show a healing effect.Treatment of the bulbs with a solution of penicillin (0.5 g per 1 liter of water) for 1 hour.
If fungal diseases of gladioli have been detected, then the affected flowers must be destroyed. To avoid the disease, you need to regularly process plants, observe crop rotation and agricultural technology. Acidic soils must be neutralized with lime or dolomite flour. Such processing should be carried out 2 years before planting gladioli. During the growing period, the soil can be alkalized with gypsum.
Pest control of gladioli
It is important to track and fight insects - pests of gladioli, if only because they are carriers of incurable viral diseases.
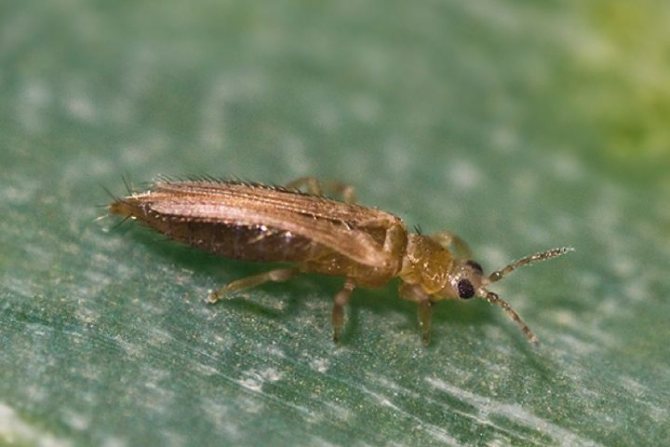
Thrips


One of the most vicious pests, giving a lot of difficulties to gladioli. Thrips are very small in size, up to 1.5 mm in length, brown body with a black head. The larvae are light yellow, up to 1 mm long with a tubular process at the end of the body. Thrips suck the juice from gladioli and carry viral diseases.
The first sign of defeat by thrips is the appearance of silvery-colorless spots and black dots on the perianths and leaves of gladiolus. If the plants are heavily affected by thrips, the buds will not open at all. But they will be filled with yellow larvae from the inside. Pests reproduce especially well in dry and hot weather.
Closer to autumn, insects move to the corms and hibernate there.
At the very first signs of the appearance of thrips, gladioli are treated with powerful insecticides, such as Confidor or Aktara, at least 3 times per season. They also try to cut the peduncles early so that the thrips do not have time to move to the lower part of the plants. Before laying for storage, the corms must be treated with insecticides again.
Wireworm
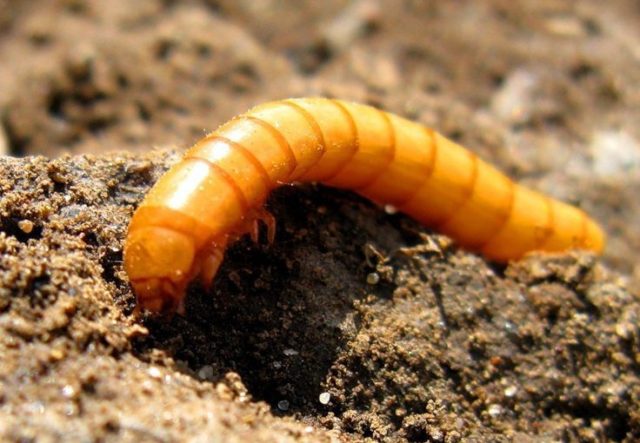


The wireworm, or the larva of the click beetle, is capable of eating the corms of gladioli, making holes in it. By itself, this can cause the death of flowers, and through the holes of the bulbs they can become infected with fungal infections living in the soil.
Wireworms are very fond of settling in the roots of wheatgrass, therefore, the site for planting gladioli must be carefully freed from weeds. It is not recommended to plant gladioli after carrots and potatoes. But legumes, tomatoes and garlic will be good predecessors.
Advice! To protect against the wireworm, metaphos powder can be embedded in the soil at the rate of 8 g per 1 sq. m.
Slugs
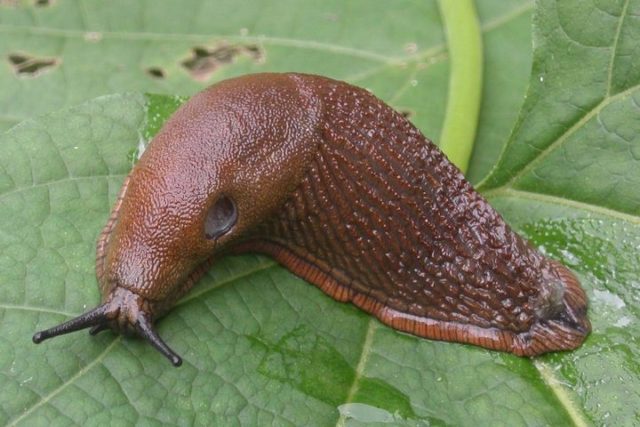


Slugs love to make holes in the green foliage and buds of gladioli. With a large number, they can destroy all young shoots of gladioli in a short time. It is necessary to remove weeds in time, collect slugs by hand and set special traps for them. The aisles are sprinkled with wood ash or superphosphate.
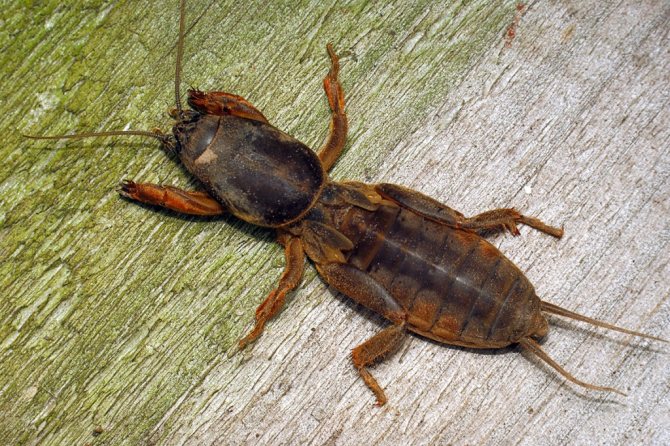
Medvedka
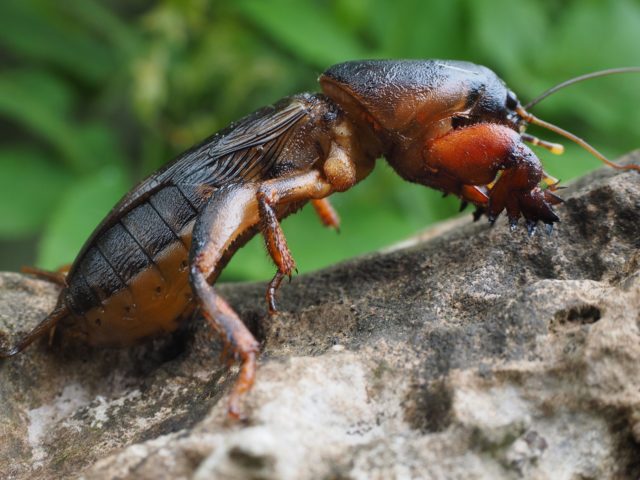


One of the largest underground insects. It feeds on all the roots and bulbs it can find in its habitat. For corms, gladioli can pose a serious threat. He is especially fond of moist soils enriched with manure.
To combat it, they usually dig deeply into the area for the future planting of gladioli. In this case, all the passages and holes of the insect are destroyed. Before planting corms, karbofos is introduced into the soil.
Root mite


A common pest that affects many bulbous plants. Having a small size (up to 1.1 mm) and a light yellow color, they penetrate through the bottom into the corm of gladiolus, settle between the scales and lay eggs in the same place. The larvae suck sap from plant tissues. Ticks thrive especially well in high temperatures and high humidity.
As a result of their activity, the growth of gladioli slows down, the leaves wither. The mite is capable of damaging the corms during storage.
Agronomic and chemical methods are used to protect against root mites:
- gladioli are not planted after other bulbous plants;
- in the fall, carefully remove all plant residues;
- clean the planting material from scales before storing it and carry out its disinfection;
- spraying with special acaricidal preparations is used;
Non-communicable diseases
| Lack of micronutrients The reasons:
Symptoms:
Treatment methods:
Prevention:
|
| Chlorosis The reasons:
Symptoms:
Treatment methods:
Prevention:
|
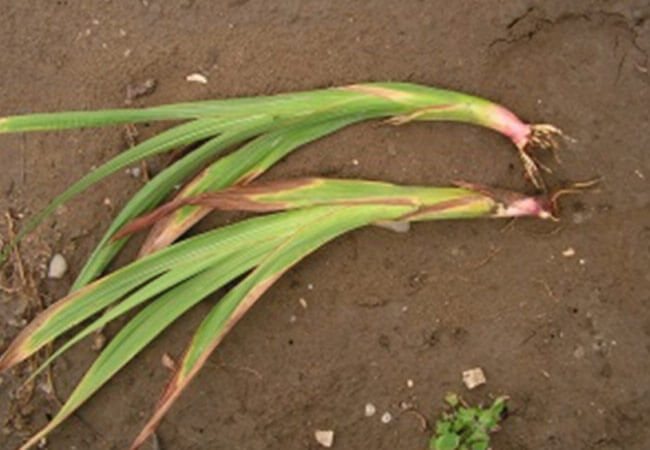
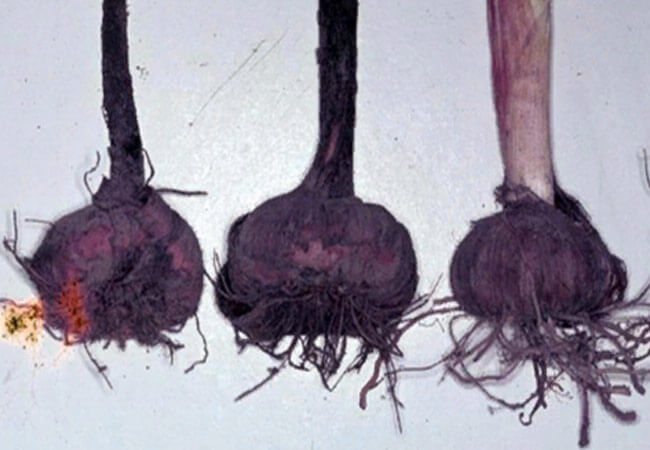
Bacterial scab: treatment
The causative agent is a bacterium that is constantly in the soil and is activated under certain conditions. Most often, plants planted in areas with high groundwater levels or on clay and peat soils are exposed to infection (Figure 4).
The symptoms of bacterial scab are expressed this way:
- Reddish-brown spots appear on the lower parts of the leaves, which turn into rot in wet weather.
- The resulting reddish or blackish spots on the scales lead to the appearance of red-brown sores on the corms under them, oval in shape with raised edges and a varnished surface.
In the initial stages of infection, damaged areas of the bulb can be simply cut out and sprinkled with crushed coal. However, such planting material will not have a marketable appearance, and it will only be possible to use it on its own site.


Figure 4. Signs of bacterial scab on the bulb and leaves
In order to prevent the spread of bacterial scab, it is necessary to improve the soil conditions at the site: carry out a deep digging, apply fertilizers or make drainage. Before planting, the corms are treated with hot water and a solution of copper sulfate.