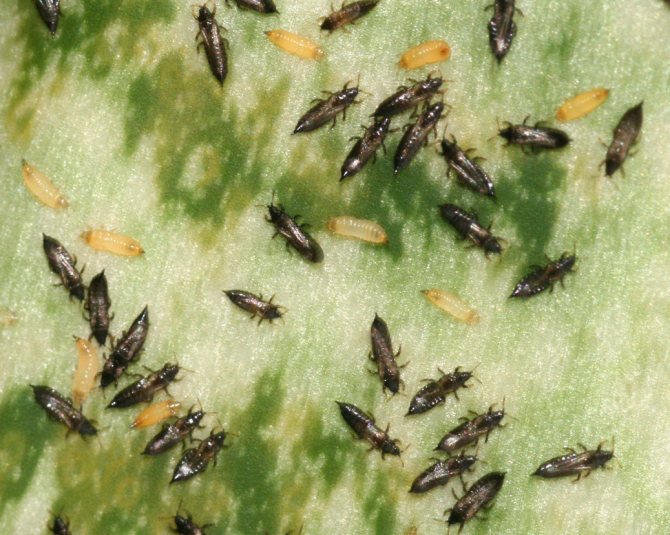
Thrips on indoor plants are quite often a phenomenon, complicated by the fact that this insect is illegible in terms of food. It successfully sucks juices from any kind, without exception. This not only negatively affects the development of the flower, but can also lead to its death.
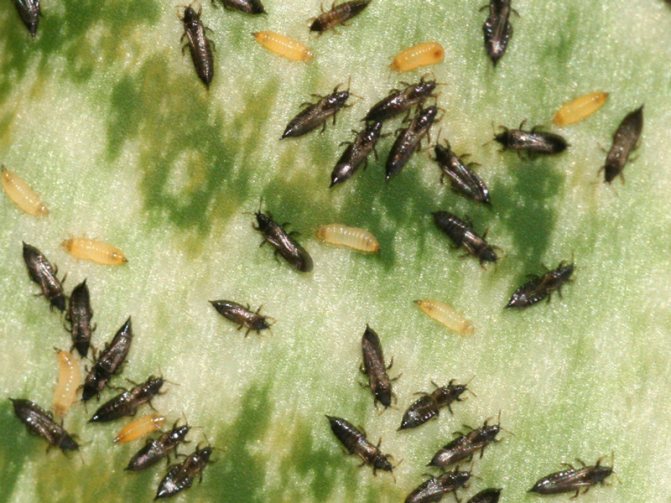

In addition, the pest multiplies quickly enough, which complicates its elimination. It is important to know about measures to combat an existing pest and how to protect indoor flowers from an invasion of thrips.
Thrips
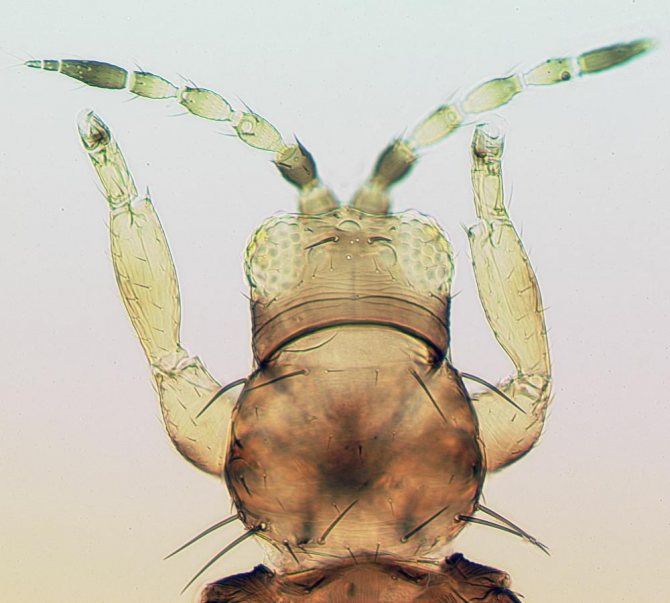
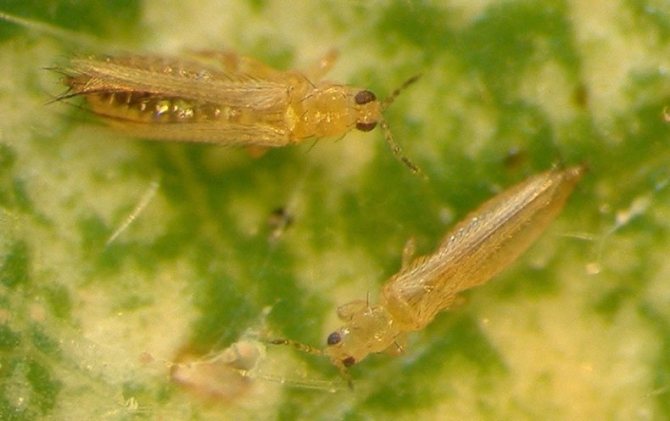
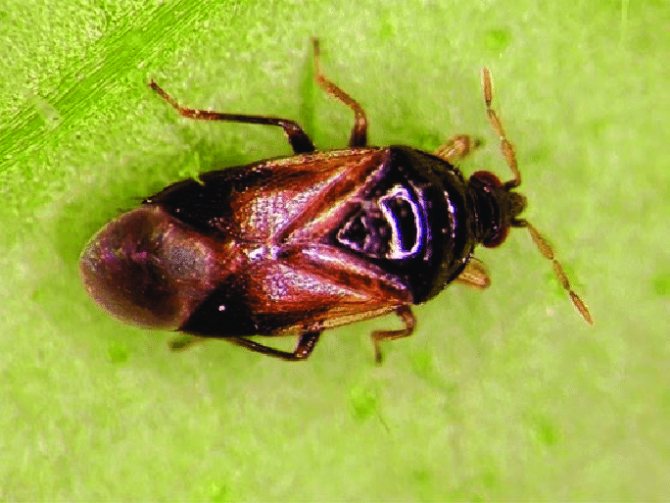
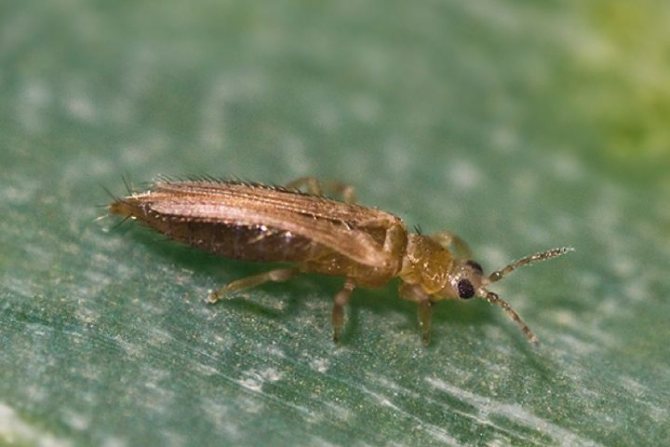
Thrips are quite famous among gardeners and gardeners, as they often parasitize on vegetable crops. They are also called Greenhouse or Bubble Legs because of their special body structure. It is due to the peculiarities of the structure of the body that thrips cannot be confused with any other insects. The body of an adult is very small in size from 0.5 to 1.5 mm and looks like a tiny midge.
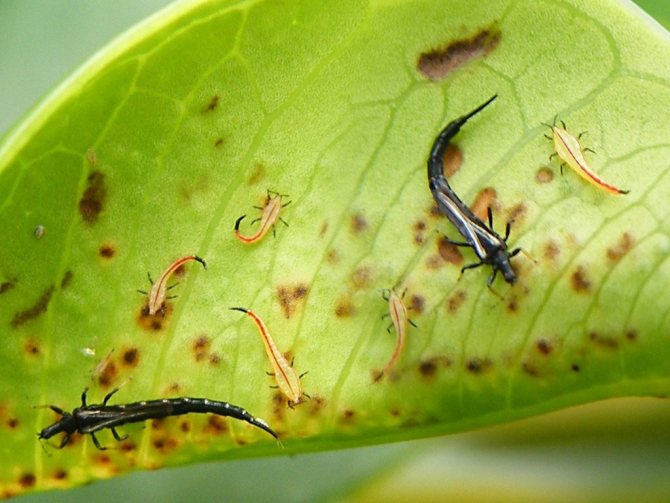


The main food of thrips is plant juices, on which they parasitize. There is a suction tube in the mouth through which the insect drinks. Thrips can fly from one bush to another with the help of a pair of long and narrow wings. Nature forces them to change their location. They move in search of fresh food and places to lay eggs. The small size and poor development of the wings do not allow them to make long flights.
The name Bubblepods came from the small bubble-shaped suckers on the hind legs, thanks to which the insect is securely fixed on the leaf. Females are strikingly different from males and look larger, can be with small wings and without them at all.
There are several types of thrips:
- Variegated;
- Decorative;
- Rosanny;
- Tobacco;
- Western floral or Californian.
Habitat
Site about a garden, a summer residence and indoor plants.
Thrips are distributed throughout the globe (prevailing in tropical and subtropical zones) where there are plants. This is the source of their food and place of residence. Today, there are up to two thousand species of thrips in the world, and only 230 of them are in the countries of the former Soviet Union.
You can meet thrips in flowers and inflorescences, where their entire life cycle passes. Here, between the stamens and petals, they crawl to find food for themselves. They feed on either nectar or the juices of any part of the plant.
Other representatives of thrips live on leaves, and it can be both the leaves of a tree and a herbaceous plant. Bark, sub-bark of trees and stumps, lichens and moss, fallen leaves - these are all favorite "flats" of thrips.
Signs of the appearance of thrips
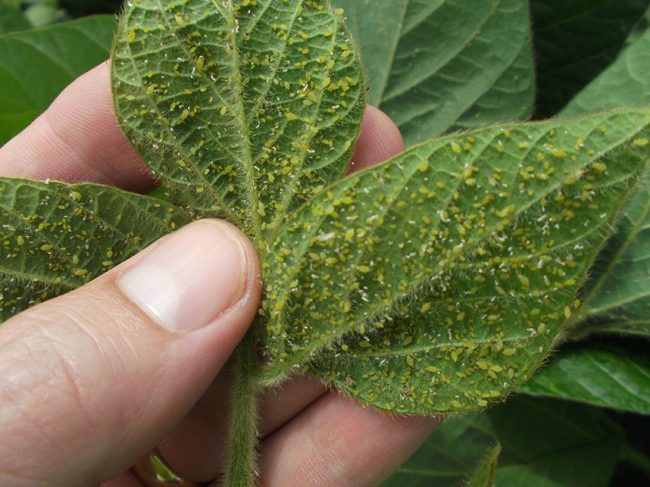
The most dangerous are western flower thrips and tobacco thrips, as they can infect a large number of different plant species, which include agricultural, fruit and ornamental crops. Tomatoes, cucumbers, strawberries and wild strawberries are especially affected. Thrips are difficult to detect at a cursory inspection, as they hide well. But when the plant begins to lag behind in development and wither, only then can we suspect something was wrong. Signs of thrips on a plant are:
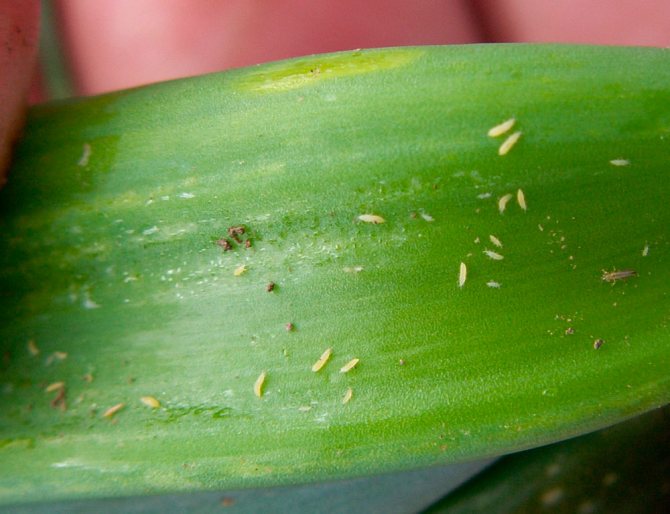
- The silvery streaks on the leaves are damaged cells. Later they dry out and holes form in these places.
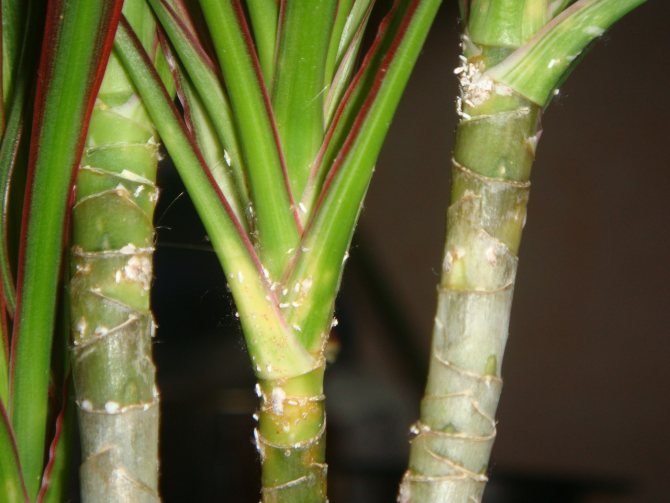
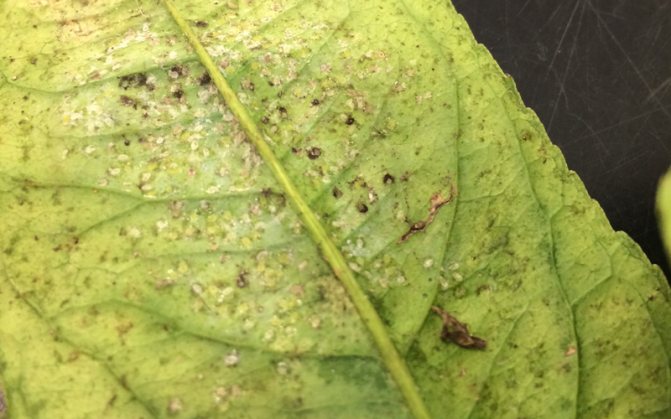
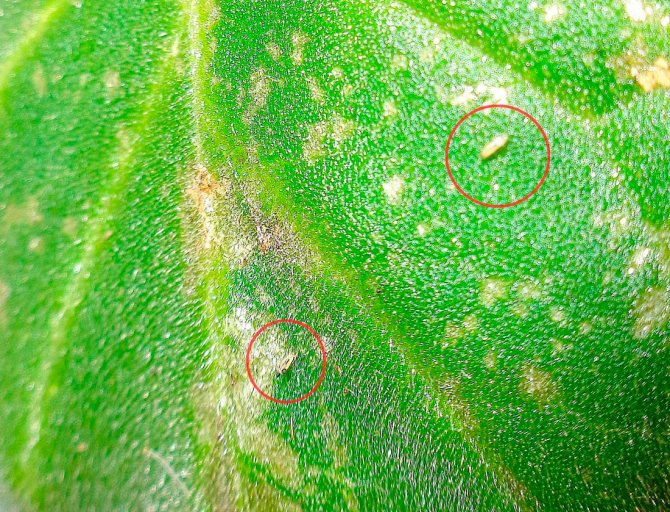
- Accumulation of excrement of dark-colored larvae.The photo shows the damage to the sheet
- Yellow and colorless spots.
- Curvature of the stems.
- Underdeveloped buds.
- Slow kidney development.
- On roses, darkening of the edges of the petals.
The main reason for the appearance of thrips on a plant is the increased humidity of the air, which promotes the development of larvae. The rapid spread of midges is associated with close planting of bushes. Thrips are a frequent visitor to greenhouses, since greenhouse conditions are the best suited for the reproduction and development of these midges.
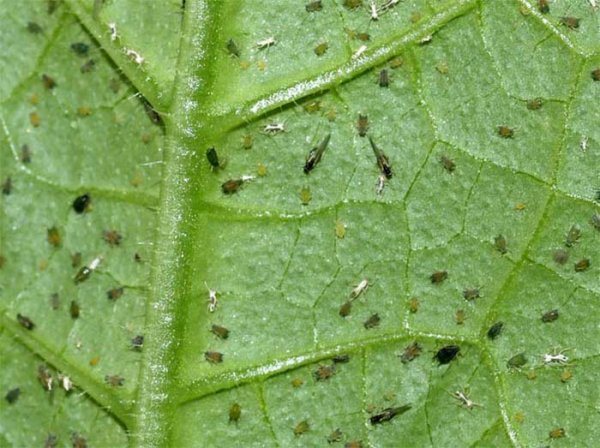


Detection of thrips on indoor plants
Since getting rid of thrips on indoor plants is not easy, it is important to see the pest in time. This is quite difficult to do, since they are well disguised. And this is despite the fact that they often live in large colonies.
At the first signs of a drooping flower, you should examine the entire plant in the house with special care.
The main food for the pest is sap, therefore, first of all, brown-brown areas are formed on the foliage, which are concentrated on the back side of the leaf plate. Brownish spots form on the edges, a sticky layer on the green part, and silvery spots with yellowish stripes on the outside.


If the plant is flowering, then, first of all, the bud and flower suffer, and only then the foliage. The stem is also attacked. Such a depressing action requires an immediate fight. Otherwise, the flower will die.
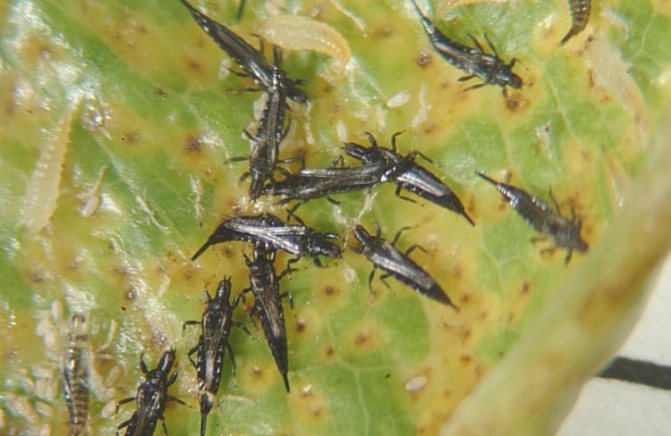
The insects themselves look like elongated larvae with a sharp tail, have an oval shape. Thrips are collected in whole colonies, grouped on the inside of the leaf or on the stems.
Preventive measures
To prevent the occurrence of flower, Californian, tobacco or any other greenhouse thrips, special measures must be taken:
- Prevent the spread of weeds that interfere with the growth of flower and vegetable crops;
- It is necessary to destroy all weeds and plants after harvest;
- In the fall, it is necessary to dig up the soil;
- Decontaminate the bulbs before planting. For this, a solution is prepared with a drug against insect pests, the bulbs are soaked in it, dried and then only planted.
- When storing bulbs during the winter, check them periodically for thrips. If found, sprinkle the bulbs with chalk or ash.
- You should not plant the same culture in the same place several times in a row.
- In the case of a large number of thrips on one bush, it is better to burn it than to try to treat it.


Prophylaxis
- Do not allow dry air, arrange a shower for indoor flowers.
- Quarantine new plants for 10-14 days.
- Conduct regular inspection of leaves, buds, flowers.
- Do not place shop and garden bouquets next to home flowers.
- After treatments, replace the top layer of soil in the recovered plants.
- Place sticky traps next to the pots to help spot the parasite in time.


Control methods
Gardeners have learned how to get rid of greenhouse thrips using various methods. Among them are chemical ones with the help of insecticides and folk methods. Traditional methods are best used for fruit and vegetable crops such as cucumber, strawberry, strawberry, etc. Since the likelihood of accumulation of poisons in the fruit is quite high. However, following the instructions and safety measures, you can avoid poisoning.
You can hang glue-coated traps. These are used for catching flies. It is very simple to prepare a sticky trap with your own hands. Castor oil, honey, petroleum jelly and rosin are taken, mixed and spread on plastic or thick cardboard. The smell attracts gnats and they stick to the surface. By replacing the tape regularly, you can achieve a significant reduction in the population of gnats. Traps are effective in greenhouses and on windowsills.
A little disaster for big plants
The winged insect itself is small, one might even say tiny: the body is only 1.5 mm long, although some specimens can reach 2.5 mm. It is omnivorous. It moves along the plant by crawling, leaving behind sticky stripes of a silvery color. The accumulation of a group of parasites on the lower part of the leaf, flower petals in a matter of days can ruin a completely healthy, well-developing plant, if you do not start to fight the aggressors in time. The ideal conditions for their existence and reproduction are high temperature in the apartment and low air humidity. In such a microclimate, parasites reproduce all year round.
The ability to disguise, hide clutches of eggs in the axillary zones of leaves, on the stem, does not immediately detect pests. Characterized by point lesions of black color, which, in a very neglected state, turn into silvery-brown stripes on the leaves. Then, the leaf blade becomes like a gauze surface.
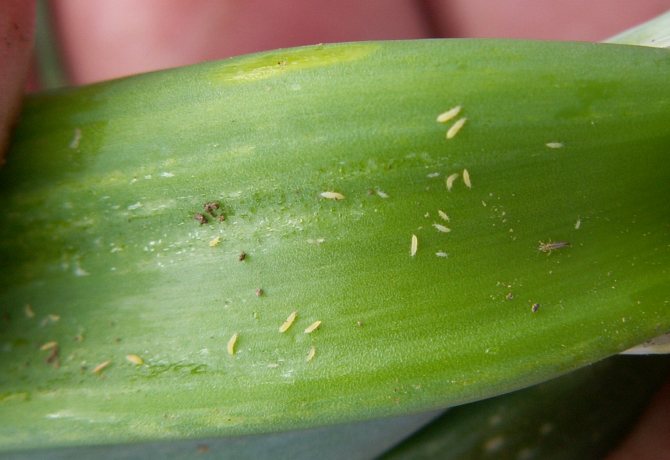
A striking example of common plant damage is thrips on orchids. Parasites, feeding on the sap of flowers, can hide in the substrate. That is why the presence of insects becomes known after the pollen from the orchid begins to crumble, the leaves wither, and the root system is affected. The release of a sticky secretion provokes a plant disease with a sooty fungus. Low air humidity, the proximity of a diseased flower increases the risk of damage to the plant.
Thrips - photo of the affected plant
Parasitic bugs, no doubt, do great harm to the greenhouse on the windowsill. Only some plants get sick in a mild form, in others the degree of damage is stronger. It all depends on the type of pest. The most dangerous are the ornamental California thrips. The parasites harm both the leaves, the root system and the fruit. In addition, they are a carrier of viral diseases dangerous for plants, they pollute the soil in a pot or flowerpot with their secretions. Thrips pierces the sheet plate, leaving a mark in the form of numerous puncture points.
It affects flowers, inflorescences and tobacco thrips. It feeds on nectar and also sucks the juice from the ovary. At the same time, the picture of plant disease is very similar to that observed with a spider mite, cicada, etc. As a deterrent, you can put a pot of blooming geraniums next to the affected plant.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of fighting against midges involve the preparation of decoctions and tinctures.
- Dandelion. A decoction is made in the proportion: 60 g of dandelion roots or leaves are added to a liter of warm water. Insist for at least 5 hours.
- From crushed garlic. A teaspoon of garlic is taken in a glass of hot water. The tincture should stand for a day, then process the plants.
- From tomato leaves. The leaves are pre-dried, then crushed and brewed in a glass of boiling water 40 g. After the broth has been infused for a day, it can be diluted with a liter of water and treated with plants.
- Celandine remedy. 400 g of fresh leaves and stems of celandine are taken per liter of water. The composition needs to be infused during the day, then strain and can be used.
- The decoction contains yarrow leaves, red pepper, orange peel, a clove of garlic and ash. The ingredients are crushed, boiled, cooled and filtered. In the resulting solution, wash the plant bulbs and roots of the seedlings.
- The solution is prepared from soap, which is taken 15 g per liter of water. The leaves are washed with the resulting solution.
- A good remedy is onion broth, which is made from onion peel and water. Boil for 2 minutes and infuse. After cooling, you can water and wipe the leaves of the plant.


Protecting vegetables
Thrips suck the juices from the leaves of cucumbers, creating an obstacle to the process of photosynthesis.Most often, greenhouse plants are affected, the microclimate of which makes it possible to develop several generations of pests per season. Parasites hibernate, burrowing into the soil. With the onset of the new season, they continue to destroy the crop.
With the early detection of insects on a culture, when the extent of the defeat is minimal, you can try to use folk methods of struggle, including celandine decoctions and garlic infusion.
In other cases, you will have to use insecticides: Aktara, Avertin, Tanrek and Zhukoed. The preparations are diluted with water, following the instructions supplied.
On damaged plants, the products are applied with a spray, carefully, from all sides. A solution of Fitoverm is effectively used, one ampoule of which is dissolved in 600 ml. water. Parasites die within 4 hours after thorough spraying of cucumbers, eggplant, tomatoes.
After two weeks, the treatment should be repeated. It is very difficult to survive pests from the greenhouse, and if they are allowed to multiply, then it is impossible. Therefore, greenhouse crops should be inspected frequently and carefully. At the first suspicion of the presence of pests, you must immediately begin to destroy them.


Biological preparations
The use of biological preparations is not only effective against thrips, but also safe for humans. The best, according to many gardeners, is Fitoverm, which is diluted with 10 ml per 1 liter of water. It is necessary to spray "Fitoverm" every three weeks in order to destroy the larvae hatched from the eggs. Another excellent universal drug "Aktar", which is prepared at the rate of 1 sachet of 4 g is diluted in 5 liters of water. Processing is carried out once a month.


Find and destroy
Thrips-infested leaves of room violet
When a population is detected, a problem arises: how to treat the plants in order not only to kill harmful parasites, but also to minimize injury to your favorite flowers? After all, the danger is posed by both adult voracious bugs and larvae. A single treatment even with potent drugs such as Karbofos, Vertimek, Karate, Fitoverm and others will not give the desired effect. Periodic spraying and combined methods (watering, wiping) will significantly increase the efficiency of plant treatment. Before using chemical compositions, you can first apply a soap solution to all parts of the plant, leave the plant like this for a day, then rinse the solution. Or, insist potato tops (600 g) in water for 8 hours and spray the flower with this composition. Mospilan, Apache or Dantop (neurotoxins) are recommended for the chemical treatment of thrips. If several plants are affected, all plants in the house must be treated with an insecticide.
The most delicate flower crops should not be sprayed. Noteworthy is the broad-spectrum thrips remedy Gaupsin. It is both a fungicide and a bioinsecticide.
It not only kills the fungal formations parasitizing on the sticky secretion, but also the thrips themselves. With an almost absolute result (90-94%), the drug is removed from plants, does not accumulate in the soil, and is not toxic to humans and domestic animals.
The use of chemicals
Before using chemicals, be sure to read the instructions and adhere to all proportions. When processing plants, take precautions and protect the respiratory tract. You have to be especially careful in the greenhouse. Processing is carried out at least 2 times with an interval of 10 days.
Organophosphates include: "Fufanon", "Iskra-M", "Iskra Zolotaya", "Ditox", etc.
For pyrethroids: "Alatar", "Caesar", "Tarzan", "Fitosan", "Accord", etc.
There are no varieties resistant to thrips, but if preventive measures are taken, they can be prevented from appearing on the site or indoor plants.
How to detect a pest
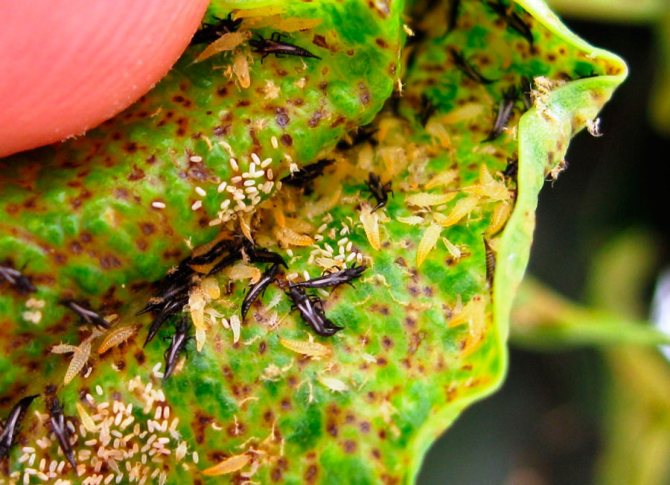


The fact that thrips have appeared on the plant is difficult to detect even for experienced flower growers.Despite the fact that they live in numerous colonies, they can perfectly camouflage themselves. Only a daily inspection of indoor flowers will help to detect these parasites at an early stage. Since they feed on plant sap, even by the appearance of some leaves, it can be determined that something is wrong with the plant. Thrips leave traces of their vital activity in the form of brown-brown spots located on the back of the leaf. In addition, a large number of brown spots can be seen along the edges of the leaves. After a while, the leaf loses its natural color and begins to fade. In addition, residues of sticky liquid remain on the sheet, as evidence of the vital activity of parasites. On the outside of the leaf, you can see spots of a silvery shade, with the presence of yellow stripes. The results of damage to the flower are visible immediately, as the flower loses its decorative appearance. First of all, the buds that have just appeared, and then the whole flower, suffer. As a rule, the affected leaves fall off after a while.
What harm is done to indoor plants?
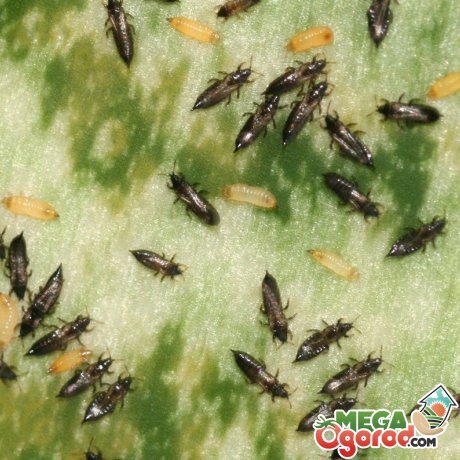


All types of indoor flowers are affected by thrips. Begonia, fuchsia, and roses are especially susceptible to the pest.
You can determine the infection with the parasite by:
- clusters of black dots on the back of the sheet
- yellow spots on flowers, buds, leaves
- rolling leaves
- falling buds
- wilting and drying of inflorescences
When a large number of insects accumulate on a plant, traces of excrement are visible on the leaf plates. Areas of silvery appear on the flowers. In addition to the deformation of the buds, the curvature of the shoots occurs.
The danger of thrips is that they are carriers of viral infections. And then the plant can die due to blockage of food intake. In two to three weeks, thrips will spread to all indoor plants, gradually leading to their death.
Causes of occurrence
Thrips enter the room in various ways, then the parasites look for an object for a meal.
Insects can enter an apartment in several ways:
- the most common way is through an open window while airing the room. Pests have strong enough wings, which allows them to move long distances in search of food, sometimes small parasites are simply carried by the wind. Often insects enter the dwelling from neighbors who are several floors below;
- you can infect the entire collection of domestic plants by purchasing an infected flower in a pot;
- A bouquet of wildflowers or house flowers brought home can also become a source of infection for house plants.
Considering the ways in which flowers are infested in the house, before buying a plant in a store, carefully examine it for the presence of pests.
Control measures for thrips in the garden
Fighting thrips on cucumbers
Most often, thrips on cucumbers can be found in the greenhouse. They settle on the underside of young leaves and feed on their sap, which slows down the growth and development of the entire plant. In places of punctures, light circles are formed, and they are located so densely that they are found upon close examination. In addition to bites, silvery areas appear on the leaves - evidence that air has entered the leaf.
Diseases of cucumbers and their treatment
Thrips multiply very quickly, so the fight against them must be started immediately. If there are few pests, then you can treat cucumbers with infusions of garlic, onions or celandine, but if the moment is missed and thrips have settled throughout the greenhouse, they resort to using drugs such as Aktara, Avertin N or Imidacloprid, from which an aqueous solution is prepared in accordance with the instructions ...Do not forget to protect yourself with rubber gloves, goggles and a respirator when processing, and tune in to the fact that you will need several such treatments to completely defeat thrips.
Onion trips
Tobacco onion thrips affects the main parts of the plant - the feather and the bulb, but it is often difficult to immediately figure out which insect is damaging the onion. If you find small black dots on the plant, and light, mercury-like spots in the leaf axils, you are probably dealing with thrips. In the future, onion leaves turn yellow, starting from the top, and die off. The plant slows down development and forms small bulbs. Of the onion crops, garlic is less susceptible to infection with thrips than others; shallots are also quite resistant to this pest. Thrips are most dangerous for onions.
- Rodents: how to get rid of and why are they dangerous?
You can protect onion plantings from thrips by organizing the correct crop rotation, that is, re-planting onions or garlic on the site no earlier than 4-5 years later, and after harvesting, collecting and burning all plant residues. Do not forget about the obligatory digging of the earth in the fall: the pest hibernates at a depth of 7 cm. After collecting the onions in the greenhouse, do not forget to treat it with a solution of Karbofos. Remove weeds in a timely manner and sow only decontaminated material.
If thrips are found, it is necessary to fumigate the room where onions and sets are stored with sulfur gas: 1 kg of sulfur is enough to treat 1 m³ of the storage. The fight against thrips on the onion bed is carried out by Aktellik, Aktara, Mospilan, Fufanon, Fitoverm, Iskra Zolotoy, Karate or Vertimek. Recently, the Spintor insecticide has gained popularity, with which onions are treated every one and a half weeks. In addition to insecticides, sticky traps can be used, and if there are few thrips on the onion, then an infusion of onions, tobacco, celandine or a decoction of zest is used to destroy them.
Gladioli trips
Gladiolus thrips are a real disaster for these majestic flowers. It multiplies more intensively in hot dry weather and can give up to seven generations in one season. Thrips cause serious damage to blossoming inflorescences: climbing into the buds, adults and larvae make punctures in delicate petals, and after rain they turn brown, as if burnt. Severely damaged buds do not open and dry out. But not only gladiolus flowers suffer from thrips: the replacement bulb of the affected plant is formed so small and weakened that it dies during storage. With the onset of autumn, thrips make their way into the soil and settle on the bottom of the gladiolus corms, and after harvesting, you bring pests to the storage.


How to protect gladioli from infection with thrips? Every autumn, collect and burn or compost all plant residues, dig up the ground, and before storing the dug corms, sort out and discard all specimens with mechanical damage, punctures and gnaws, lower healthy corms for half an hour in a solution of Karbofos, and then rinse them in clean water, dry it and only then put it in storage at a temperature not exceeding 5 ºC: in such conditions, the thrips dies. Before spring planting, gladiolus corms need to be etched again in a solution of Karbofos.
From mid-June, carry out a cycle of insecticide treatments for gladioli, alternating preparations. For example, you can spray the flowers with Karbofos or Aktellik twice, then treat them with Decis. The first two treatments are carried out with an interval of 7-12 days, and the subsequent ones - 25-28 days after the second.
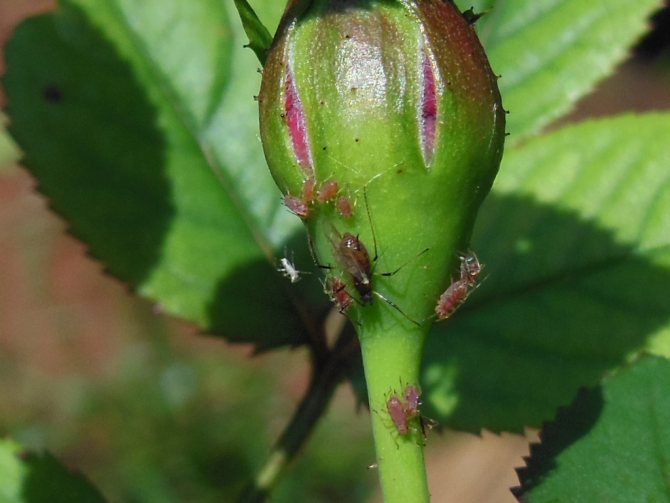
Thrips on roses
On garden roses, thrips settle mainly in the buds and feed on their juice, as a result of which the affected flowers do not open and dry out very quickly.Since thrips multiply and spread very quickly throughout the plant, you can lose all roses if you do not decisively start fighting the pest. On both home and garden roses, drugs such as Fitoverm, Aktara, Commander and Inta-vir are used against thrips. Roots of roses are shed with solutions of these insecticides once every two weeks, and experienced gardeners recommend adding a little zoo shampoo or grated green soap to the soil solution. Bushes are not treated with insecticides, as this can kill the bees. Affected buds need to be cut off: it will still not be possible to save them, but you can protect healthy flowers from pest infestation.
Harm and features of the fight
Common signs of infection:
- The formation of small dark or discolored dots on the surface of the leaves - traces of insect bites that die off after the loss of cell sap.
- Premature wilting, curvature of stems and leaves, deformation or too small size of blossoming flowers and buds set during the growing season.
- The presence of traces of the pest's vital activity - a silvery cobweb or white plaque that interferes with normal photosynthesis.
- The appearance of a streak-like mesh, connecting in solid brown or brown spots, forming dips, causing the leaves and buds to dry out and die.
Important: In addition to the direct harm caused by the parasite and its larvae, they also carry dangerous viral diseases that affect plants. ... The danger also lies in the fact that thrips multiply very quickly on flowers, and with an increase in the population, the likelihood of plant death increases.
If you do not take measures to destroy the pest in time, the flower may die, and after finishing with one, the thrips will immediately move on to the next. We talked in detail about how to deal with these insects in this article.
The danger lies in the fact that thrips multiply very quickly on flowers, and with the growth of the population, the likelihood of plant death also increases. If you do not take measures to destroy the pest in time, the flower may die, and after finishing with one, the thrips will immediately move on to the next. We talked in detail about how to deal with these insects in this article.
Violet


The violet affected by the flower thrips dries up almost immediately. This is especially dangerous because, due to its structure, it is possible to detect the presence of insects already in a dying state. The violet suffers mainly from larvae that infect the anther, which leads to wilting of unblown buds and prevents the ovary of new ones.
Signs:
- leaves fall;
- traces of drying may appear;
- the edges are curled;
- from the opened buds, pollen is vigorously crumbled.
The fight against an insect attacking a violet begins with the quarantine of the infected plant.
- It is separated from others, preferably in a room without any greenery.
- After isolation, the violet is treated with an insecticide solution intended specifically for flower thrips and covered with a plastic bag.
- At the end of the day, the bag is removed, and leaving the flower in isolation, the usual care is continued.
- Two weeks later, the procedure is repeated to get rid of the possibly surviving larvae.
Ficus
On Benjamin's ficus, in the presence of thrips, the leaves begin to turn yellow, dry out over time and fall off. Without the possibility of obtaining nutrients, the plant itself dies next. To destroy the parasite, insecticides are used, which are sprayed several times on the leaves after a certain period of time.
Attention: The selection of chemicals is made strictly for indoor plants, in order to avoid the risk of getting poisoned. ... rose flower
rose flower
On roses, most often thrips settle in unblown buds, feeding on their cell sap and leading to the fact that the flowers do not bloom and dry quickly.
To fight the pest on garden roses, the root system of the plant is treated with a chemical solution once every 10 - 14 days. It is forbidden to spray the buds growing in the garden, because all insecticides are also poisonous for bees. In the case of a room rose, there are no such restrictions, and its buds are treated on a par with the roots, but the most effective way is spraying the roots. Infected flowers are also pruned, which reduces the number of insects and the rate of population growth.
Phalaenopsis
Thrips cause the same harm to orchids as to most plants. Phalaenopsis leaves become covered with a thin film, wither and die off. Flowers and roots are damaged.
- before using the poison, the orchid is “bathed” in warm water;
- remove areas damaged by the parasite;
- spray several times, repeating the steps every 10 days until the phalaenopsis recovers.
You will learn more about where thrips come from on an orchid and how to deal with them in a separate article.
Cyclamena
For cyclamen, hit by pests, along with the usual symptoms, curling of the leaves upward is also characteristic. They destroy insects, as is the case with the orchid:
- a warm shower is used;
- not only damaged areas are cut off, but also all leaves and peduncles affected by the parasite;
- after which the cyclamen is washed, dried and treated with insecticides 2 - 3 times a week.
If the cyclamen seeds are infected, the flower thrips can be transferred with them, from where they are picked at high temperatures and low humidity. Such conditions are the most favorable for their reproduction.
How to use chemistry correctly?
The processing efficiency depends on the ambient temperature. At rates up to eighteen degrees, the efficiency is greatly reduced, the optimal range is from twenty to twenty-six degrees.
After spraying with a chemical agent, you do not need to put on a plastic bag. Remember that a one-time treatment will be ineffective, several procedures are required. If the parasites were found on only one plant, preventive treatment is required for all other specimens from the flower collection.
The plant to be processed must be dry. It is best to carry out the procedure before lunchtime. Make sure that the sun's rays do not fall on the flowers after spraying.
If you are using a grade 3 or 4 insecticide, take the flowers to the bathroom or balcony. Preparations with the second class can only be used outdoors.
Protect the respiratory tract. After processing, wash your hands and face thoroughly with soap, rinse your nose and mouth with water.
Tired of pest control
Are there cockroaches, mice or other pests in the country or in the apartment? We need to fight them! They are carriers of serious diseases: salmonellosis, rabies.
Many summer residents are faced with pests that destroy crops and damage plants.
In such cases, our readers recommend using the latest invention -.
It has the following properties:
- Eliminates mosquitoes, cockroaches, rodents, ants, bedbugs
- Safe for children and pets
- Mains powered, no recharging required
- No addictive effect on pests
- Large area of action of the device
Morphology and biology of the pest
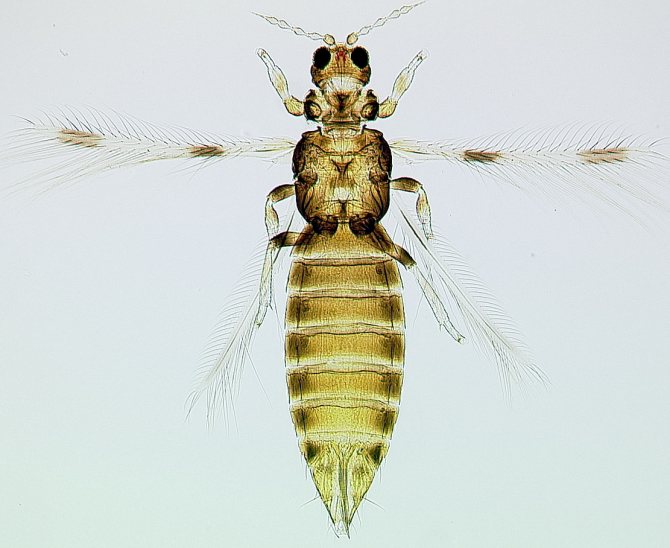
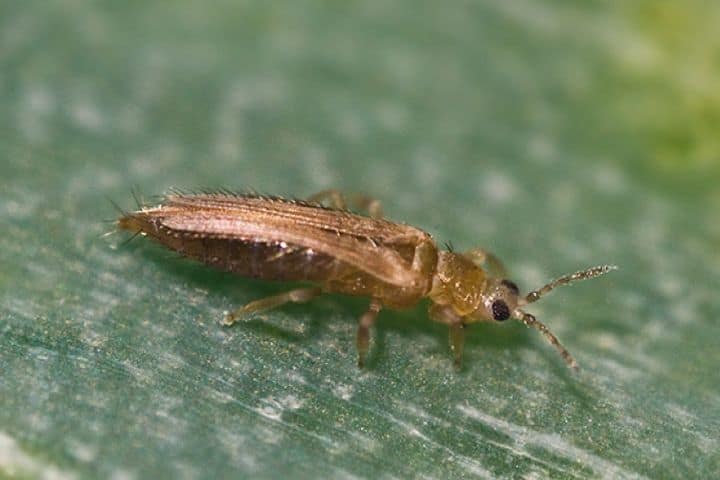
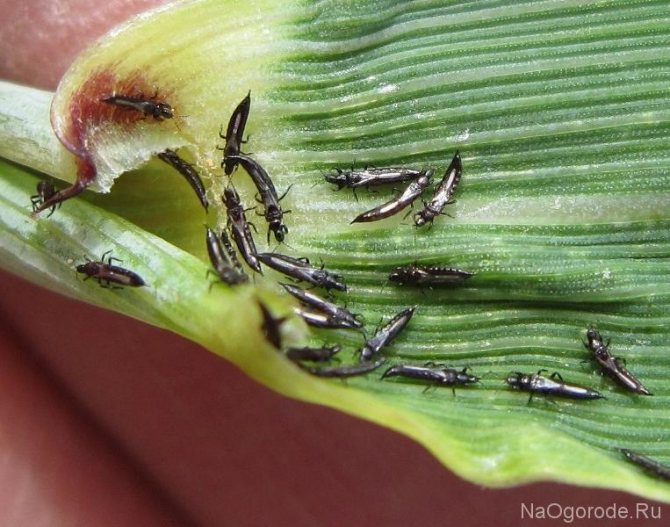
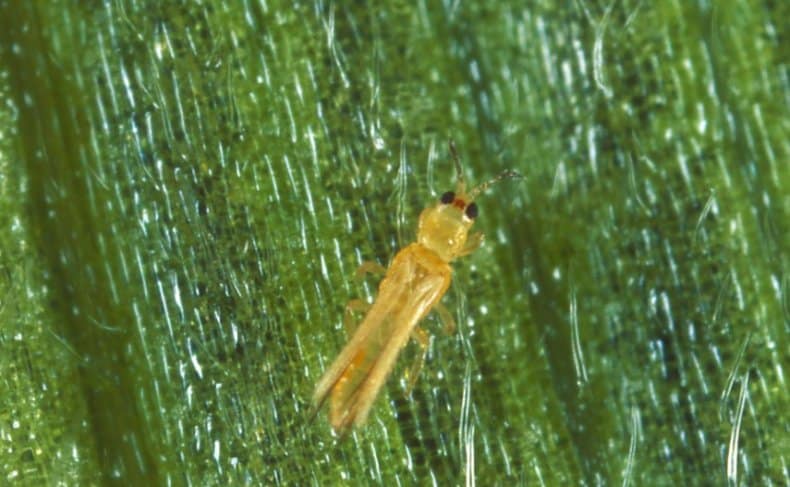
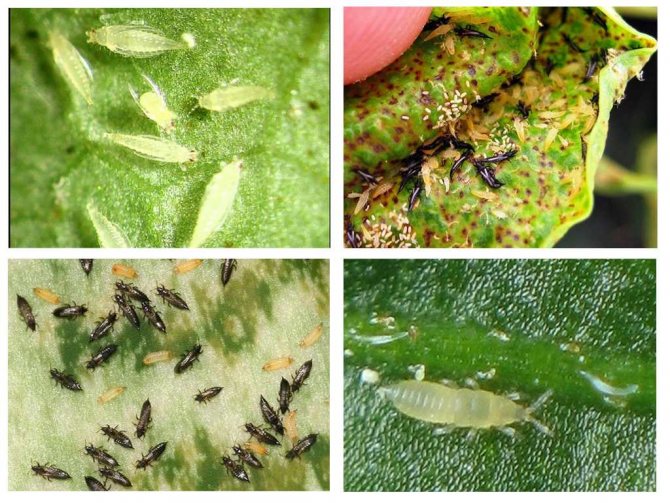
Recognizing thrips is not that difficult. They look like small insects, which have an elongated body up to 2 mm long, light yellow, black or dark brown. In adults, two pairs of wings with long hairs are usually found.
The larvae of the pest have a light yellow body, and do not exceed 1 mm in length. An additional clue about the presence of thrips can be the nature of their movement: adults move very quickly, often making sharp jumps with the help of their belly.
The difference between males and females is that the former have a slender, but not so long body. They are also painted in different colors.
Thrips can also be distinguished by their wings: in some species they may be quite short, in others they may not be at all. Thrips are one of the many pest groups that include over 2,000 species. We have about 200 species in our country.
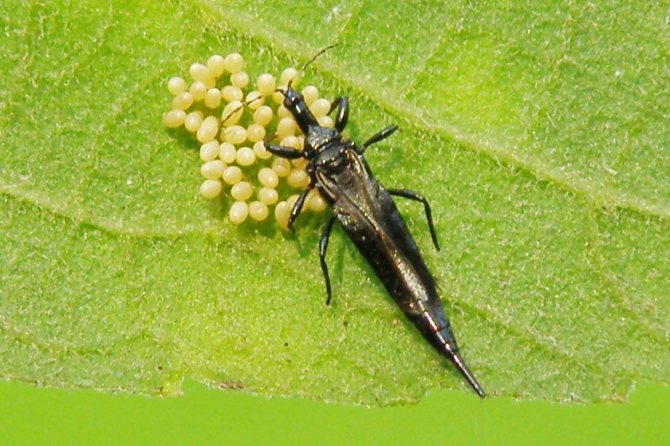
Their main habitats are leaves, flowers and buds of indoor plants. They feed on the nectar and sap of the leaf tissue. Thrips are dangerous because they multiply very quickly. As a place for laying eggs, leaf tissue or flowers are used.
After 10 days, new offspring appear from the eggs. However, it takes one month for the larvae to develop into adult insects.
At this moment, a great threat appears to plants, since as a result of the activity of pests, they lose their attractiveness, they begin to be affected by viral diseases. Over time, when insects drink all the juices from one plant, they move to others located in the neighborhood.
So what is flower thrips? As we have already said, this is a small insect, the length of which is usually one and a half millimeters, but there are adults with a length of up to two and a half millimeters. Their wings are folded behind their backs, in a calm state they form a light, narrow strip that is barely visible.
Adults are brownish, black or sandy in color, juveniles are greenish, whitish, yellow. It is thanks to their camouflage color that these insects hide well, they are difficult to detect.
The larvae have no wings, they are small, in order to find them and destroy them, you need to make a lot of effort. Most of the insects hide among the stamens of the flower, in the axils of the leaves, so if you find the first signs of damage, inspect your plant very carefully. The sooner you take action, the better for your pet.
When deciding how to deal with thrips on flowers, you must first familiarize yourself with them and their biology in a little more detail. The biggest challenge lies in their small size, multiple developmental stages, and virtually immunity to chemicals.
A single treatment of a plant can only slightly reduce the number of pests, but it will not be possible to completely remove them at once.
Therefore, when fighting insects, it is recommended to divide the entire period into several parts, gradually destroying the pests. We also take into account the fact that during processing the eggs are not affected, since they are located directly in the leaf tissue. Therefore, it is necessary to remove the affected leaves, and carefully examine the remaining ones. Fighting thrips with pesticides may also not be successful, since they adapt perfectly to any poisons.
At the larval stage, insects are generally inaccessible; they simply bury themselves in the ground near the root system, where there is no way to get them. It usually takes two to three times the concentration of insecticides to deal with insects, which are incredibly resistant compared to other pests. The most stringent measures are required here.
Common types of thrips
The first information about the existence of thrips was obtained back in 1744, when Karl de Geer discovered these pests. Today, a person has become more aware of the species diversity of these pests, among which special species can be distinguished, which most often affect other ornamental plants:
The length of an adult insect is about 2 mm, the color can vary from light yellow to brownish yellow. California thrips prefer to live on buds and flowers, but the population can also reproduce on leaves.
California thrips are dangerous because they are carriers of the tomato virus, which gives the leaves of tomatoes a bronze color. Western flower thrips are considered to be very wide polyphages.
It can eat on peppers, cucumbers, onions, tomatoes, grapes, peaches, strawberries and many other fruit and vegetable crops, as well as on numerous ornamental and floral plants: gerberas, roses, chamomiles, chrysanthemums, Saintpaulias, cineraria, cyclamen.
The larvae and adults of the western flower thrips suck the cell sap from the plant tissue. This causes the appearance of first yellow spots on buds, leaves or fruits, streakiness; gradually in these places of lesions plant tissues die off.
Damage to flower buds in vegetable and fruit crops causes deformation of flowers and fruits.
For example, severe curliness of the flowers and curliness of the set fruit of the cucumber is a common sign that thrips have settled on the plant. On roses, when populated with western flower thrips, damaged buds do not open and dry out.
This pest lives in the middle lane and southern regions of our country. Here it is found on various ornamental plants grown in greenhouses and greenhouses. The insect itself is small, reaches a length of no more than 1 mm, has a light yellow or brown color.
The most widespread is in the northern regions and the middle zone of our country. Threats to many indoor plants.
Most of all, orchids, monstera, dieffenbachia and certain types of palms suffer from this pest. It can be identified by its dark brown color, as well as a small body, which has a length of 1.5-2 mm.
Adult insects are about 1.3 mm long, females are yellow-brown in color, the male is slightly smaller and lighter in color. The larvae are white. This type of thrips is also a large polyphage and is found on the leaves of a very large number of species of ornamental plants: orchids, monsters, aralia, tradescantia, anthuriums, hibiscus, ficuses, dracenas, palms and many others.
In natural conditions, dracaena thrips is found in tropical and subtropical countries. In more northern latitudes, it is widely distributed on plants in greenhouses (in greenhouses, greenhouses).
In the conditions of industrial greenhouse farms, it is almost impossible to destroy thrips. In the best case, their number is kept at a level that would not affect the commercial quality of products (flowers, fruits, vegetables).
This is due to the fact that thrips have a very high adaptation to pesticides. This is especially true for individuals feeding on flowers.
This species is represented in most of our country. The main food for him is flowers and buds of indoor plants. It looks like a dark brown insect, reaching a length of just over 1 mm.
Its favorite habitats are rosaceous plants. A characteristic feature is a brown body, up to 1 mm in length.
This species is represented in most of our country. Most often it can be found among the scales of lily plants. It can be identified by its dark brown color and body up to 2 mm long.
The insect is dark brown or brown in color, in length from 1.3 mm (males) to 1.6 mm (females). Echinotrips American prefers to live mainly on leaves, in the tissue of which females lay their eggs. This type of thrips was discovered in the nineties of the last century in Holland at one of the popular flower auctions, which bring plants from all over the world.
Thrips was first found on orchids. Now American thrips are transported from country to country on cut flowers, seedlings, ornamental pot plants.
At first, the activity of American thrips is visible by the appearance of yellow spots.The presence of ten thrips on one leaf is enough for it to begin to fade. 30-40 thrips will lead to drying out and leaf fall, which starts from the lower layer. And although thrips do not lead plants directly to death, they significantly reduce the decorative effect of flowers.
In search of food, thrips move to flowers and fruits or to neighboring plants and continue their vital activity there. Due to the fact that the American thrips population is spreading very quickly, it is highly likely to spread not only to all ornamental plants, but also to other vegetable crops grown in greenhouses.
The adult insects are about 1-1.5 mm long, dark brown or almost black in color with a brownish-brown belly and yellowish forewings. The larvae are white or yellowish, differ from adults in slightly smaller size and lack of wings.
Adult insects and black thrips larvae usually live on the underside of the leaves. The nature of damage to plants is practically the same as from tobacco thrips.
Indoors (in greenhouses, greenhouses), black thrips is widespread and reproduces all year round. Both adult insects and black thrips larvae cause harm, causing great harm to cucumbers, tomatoes, other vegetable and green crops, as well as pot and ornamental plants. Black thrips winters well in the topsoil under plant debris or in compost heaps.
What houseplants do insects appear on
These insects are omnivorous and live on any plants. Most of all, they prefer violets, ficuses, lemons, begonias, roses, orchids and dracaena from their indoor flowers. Thrips cause particular harm to violets, damaging flowers.
The plant stops blooming, loses its decorative appearance.
The most favorable climate for insects is warm and dry air. They can appear in any home, but they actively reproduce most often where the plants are not sprayed or rarely watered.
How to detect and signs of flower infestation
If, in the process of examining indoor plants, you find that some of the leaves are discolored, and there are also many points caused by punctures on them, then this is a clear sign that thrips have started in your apartment. If you pay attention to the lower part of the leaves, then there you can find spots of a brownish or brownish tint.
The damaged areas often turn silvery, which can be explained by the ingress of air into the cells.
If, at the first signs of thrips activity, no operative measures are taken for treatment, foliage dying off, deformation of flowers and buds subsequently occurs. Insects cause additional harm by depositing sticky secretions, which are a favorable environment for the development of a sooty fungus.
Although thrips are not picky about food, the most preferred houseplants for them are violets, begonias, roses, citrus fruits, orchids and ficuses. Violets suffer the most from thrips larvae, as they destroy the flower's anther.
At the first signs of their appearance, it is necessary to cut off all flowers and buds within the next 1.5 months, combining this with treatment with suitable preparations.
Unfortunately, the presence of insects is often detected when the plant is already dying. They hide in the axils of leaves, pistils of flowers. If you carefully examine the plant, you can find the following signs of infection with thrips:
- Small brown dots on the leaves are the places from which the insects drank the juice;
- Many leaves darken, die off, discolor or become covered with gray stripes, they can also be covered with an openwork mesh;
- Brown spots are visible on the underside of the leaf plate;
- Young leaves and shoots grow small and deformed;
- The flowers dry quickly and fall off.
Almost all insects that parasitize houseplants are suckers. Thrips are no exception, with their thin proboscis they penetrate the leaf of the plant and suck the juice out of it.
How to determine if a plant is infected:
Many people consider this phenomenon a sunburn and try to remove the plant away from the effects of rays. However, such a method will not bring results, since the thrips larvae are to blame for this, destroying the leaves with great speed. Plus, there are accumulations of dirt on the flowers, which are insect excrement.
In addition, thrips carries various viral diseases that pose a great danger to plants, since they can die.
Parasites are characterized by the release of a liquid substance with a sticky consistency, which is an excellent breeding ground for sooty fungus. The most dangerous among the large number of varieties of thrips are tobacco, bulbous, varivorous, decorative, dracaena, rose and floral western. It is almost impossible to determine which of them affects the flowers in the apartment.
Danger to indoor plants
If you do not start fighting insects in time, they can completely destroy the plant. Thrips not only suck the juice from the leaves, leading to their death. They are carriers of dangerous flower diseases, such as fungus. Reproducing rapidly, insects spoil the decorative appearance of the flower and, over time, completely destroy it.
The plant withers, the leaves darken, lose their shape, the flowers fall off. The danger of these pests is that it is very difficult to notice them, they hide in the axils of the leaves or between the stamens of the flower. The larvae are generally buried in the ground, therefore, many methods of processing plants do not work on them.
Detection of thrips on houseplants usually occurs after the flower begins to look depressed.
The most dangerous are decorative, Californian, tobacco, greenhouse thrips, which are capable of carrying various viral infections between flowers. The first sign of damage is pollen, which spills out from the stamens onto the petals.
But you should be careful, since this phenomenon can occur even in too hot weather, when affected by some types of ticks. It is quite easy to check, we tear off a few with a flower and shake them over black paper, after which we examine the sheet.
The degree of damage can be different, it depends on the type of pest. For example, California thrips, as well as decorative, tobacco thrips provoke not only on the leaves, but also on flowers, while the lesions are very similar to those inflicted by spider mites, leafhoppers, and flat-bodied mites.
Flowers wither, quickly deform, become covered with specks of black and white.
The surface of the leaves is similar to a cloth that has been pierced many times with a needle. Pollen is abundant on the lower leaves. Thrips pests can get into the apartment through open windows, along with bouquets brought from open ground, with infected plants. Garden flowers are also susceptible to attack by pests; even unpretentious gladioli (propagation by seeds, children) and well-known bearded irises can suffer from their harmful activities.
How to recognize a parasite infestation
The thrips themselves are not always immediately detectable. They are quite secretive and prefer to manage on individual plants, gradually moving to others.
The discoloration of some leaves should raise suspicion in the grower. Also, in flowering plants, pollen is intensively poured from the stamens onto the petals (the same phenomenon can be observed during heat and as a result of an attack by a spider mite).
If during the examination many small punctures are recorded (like from a needle on a tissue), then thrips made them, therefore, they drank the juice from the plant.
On the lower part of the leaf blades, brownish or brown spots can be seen. These are damaged areas. When oxygen enters plant cells, they often acquire a silvery color. Also on the leaf you can notice a sticky mark and brown-black dots (thrips feces), which contribute to the development of such a disease as sooty fungus.
A late sign of an attack by thrips (unless rescue measures have been taken) are falling leaves and flowers, as well as a curvature of the trunk.