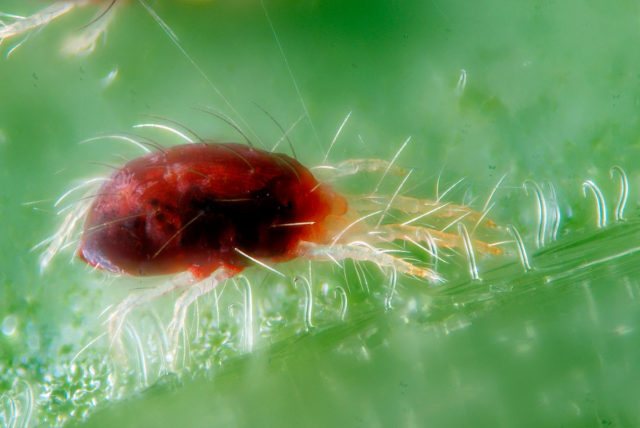
One of the most common pests affecting almost all plants with the exception of aquatic plants is the spider mite. Appearing on flowers, the aggressor multiplies quickly. It will take only two weeks from the time the eggs are laid to hatching under suitable conditions.
Despite its size, the insect is truly dangerous to flowers. He is able to destroy a culture in a short time, and then migrate to a neighboring culture. Most often, the pest gnaws the skin of the leaves, sucking useful liquid from the plant cells. Not only indoor plants, but also greenhouses, where crops are grown for sale, can suffer from a spider mite. Fighting the aggressor is not an easy task: he ignores many chemicals, keeping his offspring in the substrate.
To start actively fighting an insect at home, you need to get to know him better.
Who are ticks
Herbivorous mites belong to several families (Eriophyidae, Tetranychidae) of the order Acariformes mites, class Arachnids Arachnida.
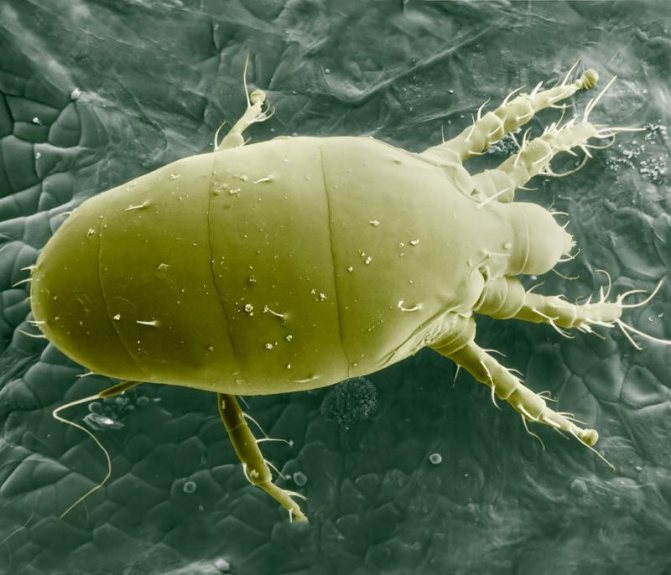
You need to understand that arachnids, and therefore ticks too, are not insects, they are arthropods. On closer examination, you can see how they look like spiders: also divided into large sections of the body (cephalothorax and abdomen), and 4 or 2 pairs of limbs (sometimes 1-2 pairs of legs on the abdomen are reduced). Moreover, the legs of herbivorous ticks have a complex claw apparatus, with the help of which they are held firmly on the leaves. The integument of the body is thin, leathery, usually covered with fine bristles, of various colors, usually light brown, dark brown, or brick red. The mouth organs are also adapted for piercing the epidermis and sucking juice.
Tick development cycle
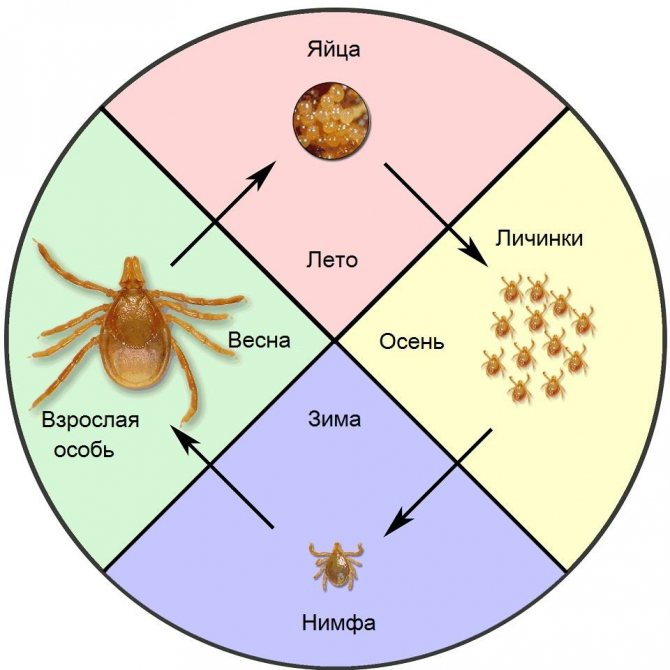
The developmental cycle of spider mites includes the phases of the egg, prelarva, larva, protonymph, and the nymph stage in the breeding phase. This process is called metamorphosis. In many species of ticks, some developmental phases are absent. For example, in the formation of a male individual, some species of ticks have only one nymph stage. Each phase occurs with a change in the cuticular layer, in other words, molting.
Interestingly, many herbivorous ticks belong to the superorder of acariform ticks; they are characterized by the completion of body segments during development to the adult stage. For example, larvae have only six legs, an adult tick has eight.
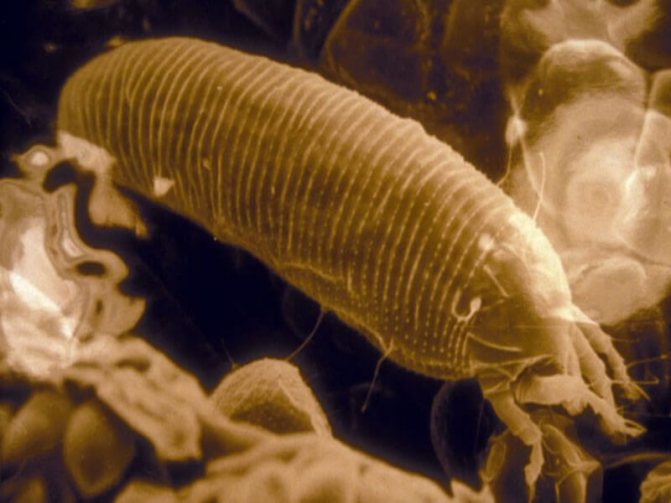
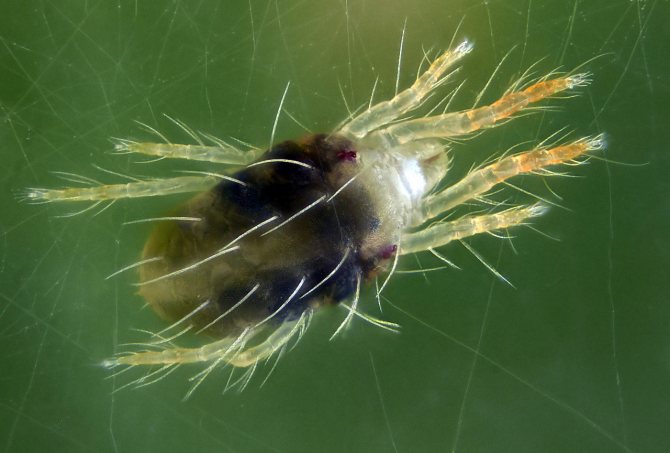
From the point of view of a grower, the anatomy of ticks, pests of flowers, is not so important and interesting - their bodies are too small, usually no more than 1 mm in length (on average 0.2 - 0.45 mm), to consider and try to distinguish one species tick from another. Therefore, we will not describe the structure of the bristles and genitals, especially since many hundreds of species differ greatly in the shape of the body, the length of the legs, etc. Let's dwell on more useful information.
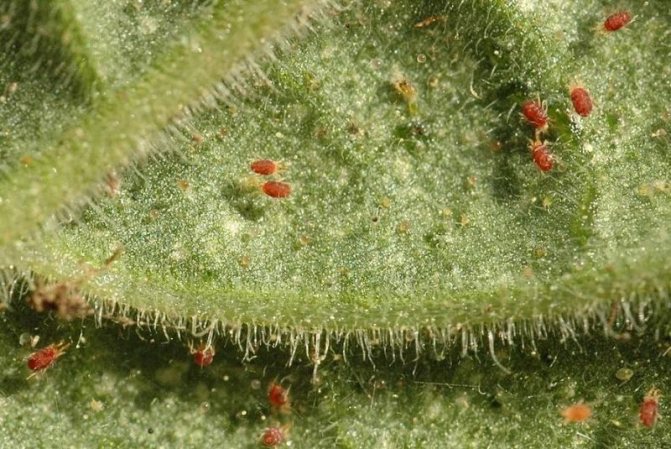
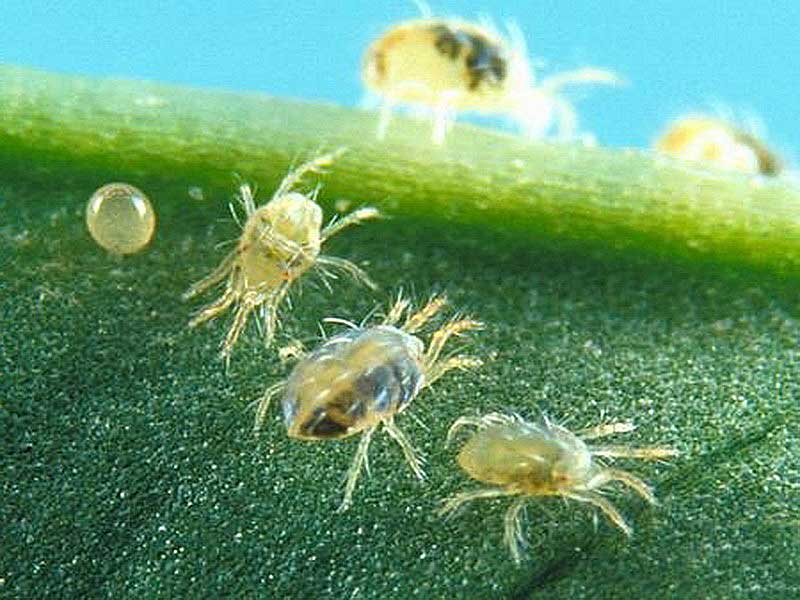
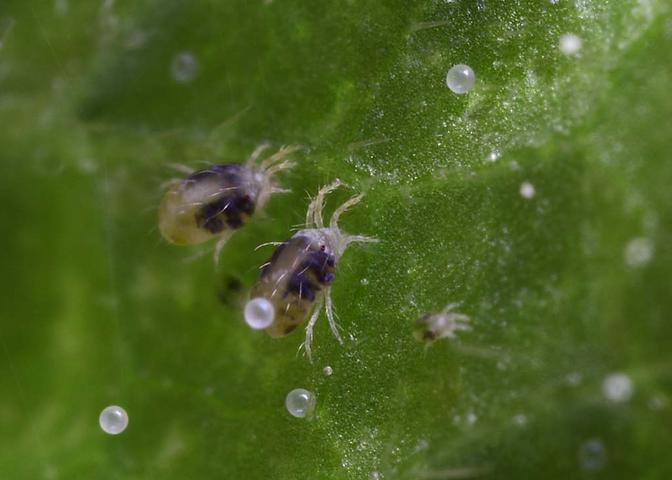
At good magnification, a colony of mites is visible on the back of the leaf.
When the plant dies, ticks can be seen even with the naked eye, but there is already no one to save.
Point punctures are visible in the lumen of the leaf - the places where the mites suck the juices from the plant.
There are several types of herbivorous mites worth focusing on.
The most common are the superfamily of Tetranychoid ticks Tetranychoidea.These include the Tetranychidae Spider Mites and Tenuipalpidae Squid Mites. The frequency of their reproduction differs, it depends on the time of metamorphosis, but in general, this process is ongoing. The duration of metamorphosis (periods between molts) depends primarily on the temperature and humidity of the air. Thus, tropical species of herbivorous mites develop almost without interruption, forming about 15-20 generations per year. In temperate climates (or, for example, when growing plants with winter dormancy in cool conditions), ticks have time to form only a few generations. During the cold period, eggs, or fertilized females, overwinter in a state of diapause.
Among the spider mites and flat beetles there are polyphages - they feed on the sap of a wide variety of plants and leaf, and conifers, and cacti; monophages who prefer one genus of plants; and oligophages, who like gourmets, feed selectively on certain plant species.
Views
Of the hundreds of species of ticks, indoor crops most often infect only a few of the most common ones.
Ordinary
One of the most common and dangerous species, as it is phenomenally omnivorous. It affects most types of crops, only conifers are not affected. The common mite is harmful to indoor plants.
Tetranychus urticae grows up to 0.3-0.6 mm, has a green-yellow color of adults and eggs. In a year, it gives several offspring, which eat crops at the root.
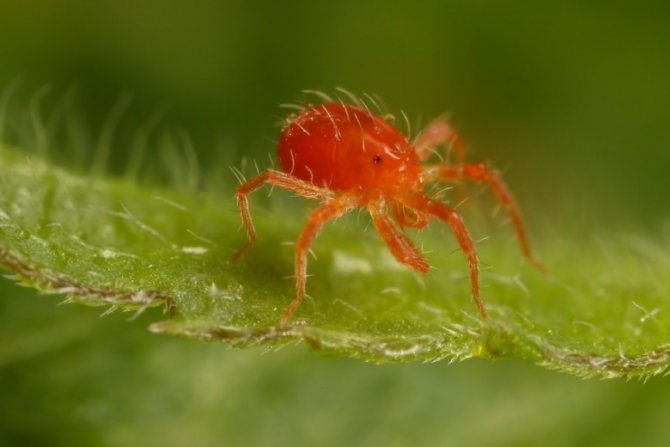
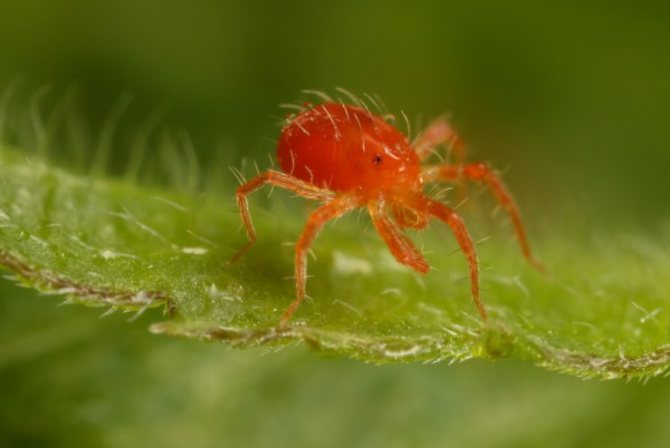
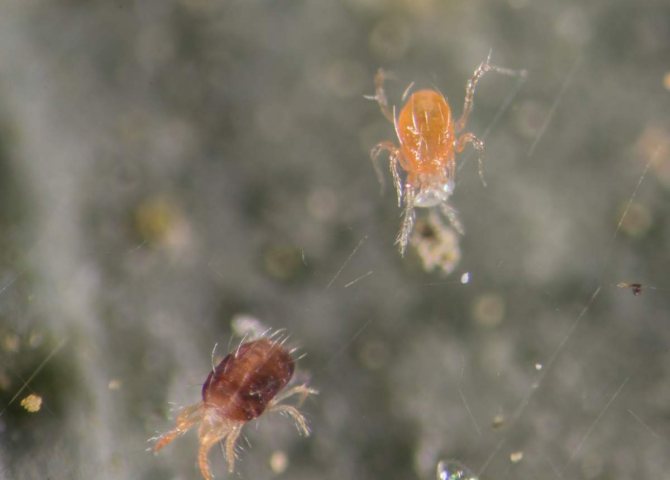
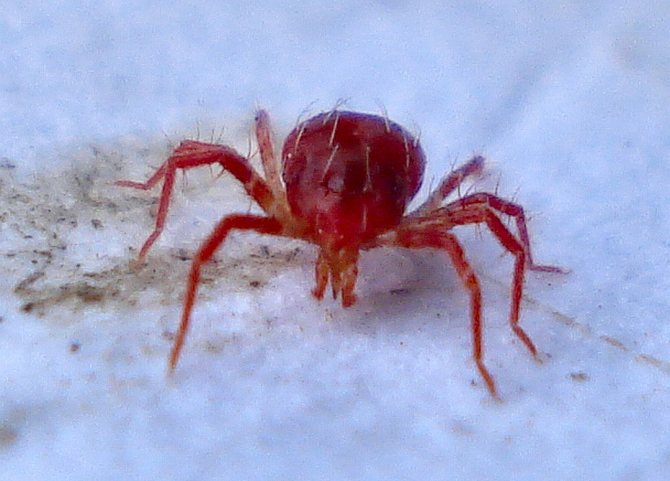
Red
Red pests often infect indoor flowers, especially roses, orchids, calla lilies, and lemons. Tetranychus cinnabarinus loves warmth and reproduces well on indoor plants. The female tick has a brighter red color.


Atlantic
This mite (Atlanticus) reproduces rapidly in high humidity and high temperature conditions. Body size - 0.4 mm, color - yellow-green. From home crops, he prefers citrus fruits and palms.
False
Finding a false tick is difficult due to the lack of cobwebs. Body size - 0.2-0.3 millimeters, usually colored green or red. Harmful to orchids, palms, citrus fruits.
Cyclamen
This type of tick chooses certain crops, the main preference is cyclamen, in their absence it will eat geranium, gloxinia, balsam. Loves heat and moisture, often infects greenhouses. Small bodies (0.1-0.2 millimeters) are almost invisible on the leaves, clusters of mites look like dust.
Wide
The wide tick rarely dwells on the street, it prefers premises. The eggs are poorly hidden, so it's easier to deal with it. Food preferences of this species are cacti, citrus fruits, ficuses, oleander.
Cactus flat
The florists have the name of the flattender. This mite does without cobwebs, so it is especially difficult to spot it. Succulents and citrus fruits are affected to a greater extent by flat heifers.
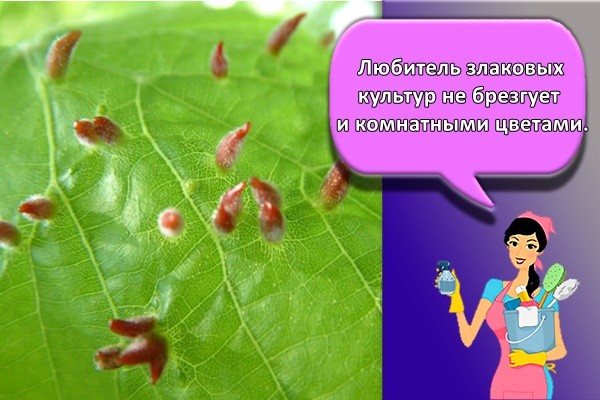
Clover
A lover of cereals does not disdain indoor flowers. Due to its long legs, it is easy to move and can quickly infect a large area. Ficuses, pereromia, euonymus suffer from this type of mite.


Spider mites
Tetranychus telarius form a cobweb, but the grower cannot always see it right away. Sometimes it is so small and thin that it is clearly visible only with a huge accumulation of mites, or when the plant has already completely dried out. Therefore, if you find suspicious spots on the leaves, do not seek to look for cobwebs, look for the skins that remain from the molts - they are usually gray or almost white, you can see them on the back of the leaf, they look like fine dandruff. This is due to the fact that the common spider mite lives mainly on the back of the leaf, and weaves a cobweb between the veins, if you look closely, you can see it with a magnifying glass along the central vein. But if nothing was found, this does not mean that there are no ticks.
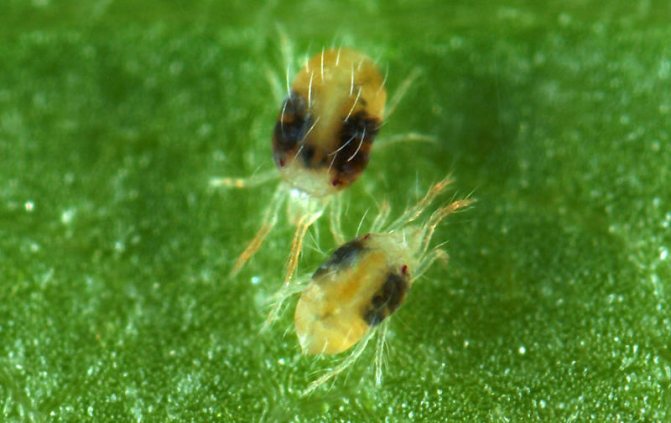
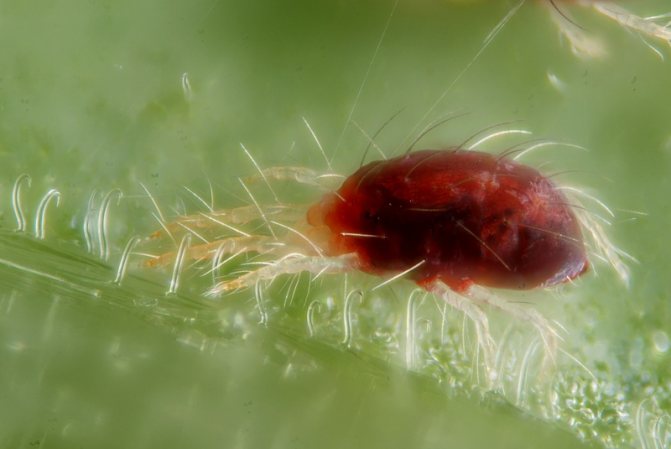
Common spider mite under a microscope.
The cobweb is visible between the leaf plate and the central vein.
The skins on the back of the sheet are white.
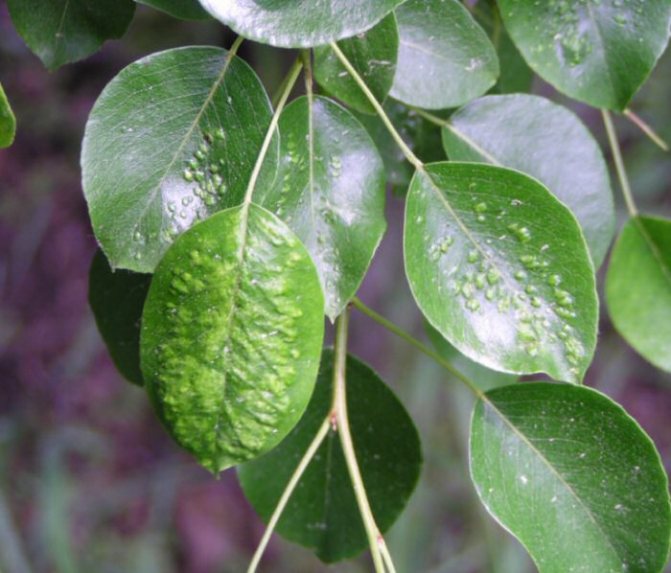
Typical signs of damage: point punctures, whitish or yellowish, are visible in the lumen of the leaf. At first there are few of them, but gradually they merge into spots. The leaves turn pale, acquire a grayish or pale yellow tint. Then the leaves dry out, completely lose their color. This is a typical picture, but in some cases, the leaves turn red or take on a bronze tint. In some plants, the leaves do not change shape even when the spots are large, in other cases they are strongly deformed, curled.
Keep inspecting the plant every day, as ticks multiply rapidly under favorable conditions. The female lays over 150-200 eggs during two to three weeks of life under favorable conditions. The duration of generation is 2-3 weeks, at the same time all stages of development are present on the plant: eggs, larvae, nymphs, females and males. The entire path of metamorphosis (from larva to adult tick) at an average temperature of 20-24 ° C, usually takes no more than 10 days, at temperatures above 32 ° C, the rate of regeneration is reduced to a week. The rate of "maturation" of a tick egg is 1-3 days.
Sexually mature individuals have a greenish color, are hardly noticeable on the leaves. With a decrease in daylight hours (from August), in dry hot weather, females appear, preparing for winter. They stop feeding on plant sap, acquire a reddish-brownish color, and look for more discreet places where they can hide (in the upper layers of the soil, under fallen leaves, in cracks in the bark). At the same time, females secrete a large amount of cobwebs, this is especially noticeable on garden roses - in a few days they become entwined with cocoons of cobwebs. If the temperature does not drop below 10-12 ° C, then the spider mites will not hibernate, but will continue to actively reproduce (this is the minimum temperature at which the vital activity of the mites is still ongoing). It is sad that even prolonged freezing does not kill spider mites. Mite eggs can survive in soil or other secluded places (for example, in straw, compost heap, window frame crevices) for years.
On plants with dense leaves (citrus fruits), only vague yellow spots are visible on the outside.
On plants with more delicate leaves (balsam in the photo), the leaf is translucent, the traces of a tick are visible through and through.
Ticks love roses especially, we can say that the concept of "rose" and "tick" are inseparable. There is nothing to heal here.
Six-legged ticks
Phytoptipalpus paradoxus, another subfamily of tetranychid ticks, differs in that they have only three pairs of walking legs. These species of herbivorous mites have evolved over time. The fact is that the formation of the cuticle and hatching from the egg in ticks occurs at a time when the fourth pair of legs is not yet developed in the embryo. A six-legged larva with a shortened abdomen hatches - the last segments and genital valves are underdeveloped. As a result of mutations during evolution, in some adults, the abdomen developed normally, but the last pair of legs did not develop. As a result, the trait was fixed, and a subfamily of six-legged spider mites was formed. All three pairs of legs they have are very short, and the body is much wider than that of an ordinary spider mite, almost round. Six-legged ticks lack the prelarva stage in their life cycle.
Signs of the appearance on the plant
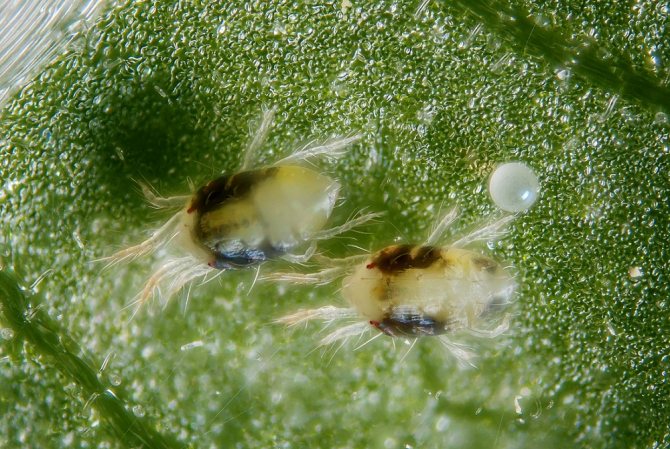
The body size of the animal (this is not an insect, belongs to the arachnids) is from 0.2 to 1.2 millimeters, rare species reach 5 millimeters. In most cases, it is difficult to notice a pest that has appeared; it is usually identified by a changed plant species. Ticks are dangerous with a short life cycle, it lasts only 8-40 days.Within 7-8 days, an adult develops from the egg, ready to reproduce. Adult ticks have 8 legs, body color varies from whitish and yellow to reddish-brown in different species.
The female makes clutches on the lower part of the foliage, in the ground, on the walls of the pots. She covers them with cobwebs. The eggs are well protected by a smooth shell; under unfavorable conditions they do not die, but slow down development, retaining their viability for several years. Nature has created an ideal pest - it multiplies quickly, goes into diapause under unfavorable conditions, eats everything. A spider mite infection can be identified by the appearance of the affected plant.
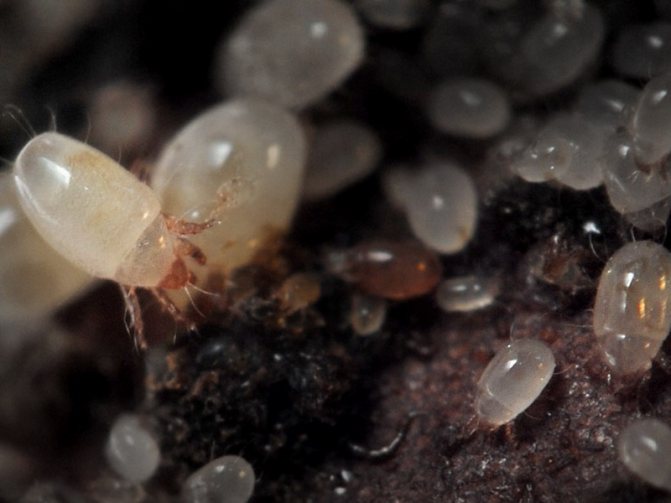
Eggs
It is difficult to notice the eggs of ticks, their size is less than a millimeter. They are white or translucent, covered with a dense shell. The female lays them out in small groups (1-3 pieces), braids with cobwebs to protect and create favorable conditions for development. Larvae appear after 3 days.
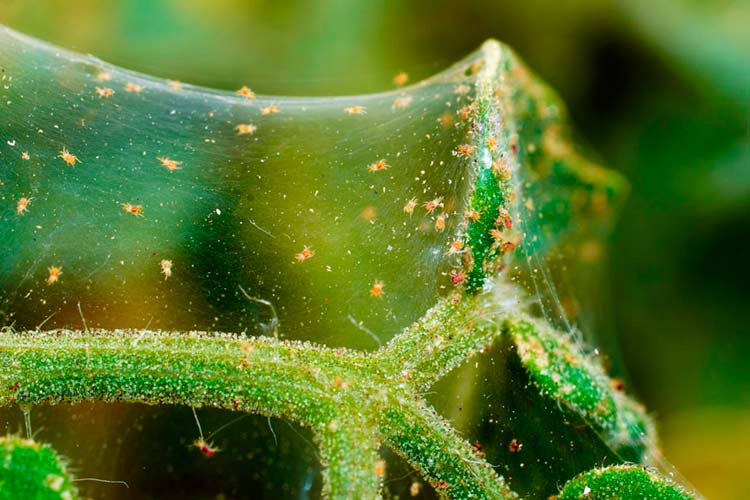
Thin spider web
The main sign of the appearance of a tick is a cobweb, which is massively woven by adults in the lower part of the foliage. Colonies of eggs, larvae and ticks are hidden under its clusters. Some species of these arachnids hardly weave a web.
With a strong infection, the plant is all shrouded in the finest nets, on which dust and excrement of small arachnids (black dots) accumulate.
Yellowing of leaves
The tick feeds on plant sap, sucking it from anywhere on the ground. A small white speck forms at the puncture site, best seen on the leaves. Cells cease to function normally, photosynthesis slows down, the conductivity of intercellular structures is disrupted.
Small specks grow, the leaf dries up in separate areas, turns yellow, becomes lethargic, loses turgor and elasticity. The houseplant takes on an unhealthy appearance - the leaves are yellow and sluggish, entangled in cobwebs.
Falling and dryness of leaves
Loss of foliage is the last stage of infection. Separate spots on the plates join, the sheet dries and falls off. When photosynthesis is disturbed, the defenses of plants are reduced. Large colonies of ticks literally suck all the strength out of the flower. They attack ovaries and buds, deform even strong stems. One skeleton remains from the flower.


Flat heifers
Squat beetles Tenuipalpidae - or false spider mites (not to be confused with the flat beetle Cucujidae), the genus Brevipalpus Brevipalpus and Tenipalpus Tenuipalpus. In size and shape, they are very similar to spider mites, they also sit on the underside of the leaves, and move slowly. Their sizes are very small, from 0.1 to 0.4 mm.
If these images are not enough for you, you can see another spider mite photo.
In many species, colonies consist only of females, which hatch from unfertilized eggs. Development takes place in three stages: larva, protonymph and deutonymph. Maturation from egg to adult tick is 12 to 24 days. The eggs of some types of flat beetles can be seen with the naked eye and appear as reddish-orange clusters. The larvae of flat beetles are six-legged, orange-red, translucent, nymphs are opaque, dark spots appear on the body. Adult mites are brown, eight-legged with a flattened body. Adult females live for 5 to 6 weeks, producing 6-10 generations per season. Many flat beetles have a pause (dormancy) of 1-2 days between molts, at this time they do not feed, they remain motionless on the leaves.
Squat beetles are brown, but very small, similar to brown grains.
Puncture points where flat beetles stick are dark dots.


Cobwebs do not form flat heifers. They do not suffer from high humidity.
Plants affected by flat plants differ in the nature of the spots. The fact is that most flat beetles have toxic saliva, which, when it enters the tissues of the plant, causes necrosis. Therefore, brown or gray-brown spots appear on the upper side of the leaf.First, small, punctate, 1-2 mm, then increasing in size. The leaves are often deformed, and in plants with dense fleshy leaves (Saintpaulia, Gloxinia), the edges of the leaves begin to tuck inward.
Worst of all, flat beetles are the main carriers of viruses (mosaic and annular spotting). But even worse is that the ideal conditions for the reproduction of flat beetles are a temperature range of 25-30 ° C and a fairly high air humidity, at least at 70-80% of air humidity they feel comfortable, while spider mites with such humidity inhibit development ...
Temperature dependence of the tick metamorphosis rate:
- at an ambient temperature of 15 ° C: eggs ripen for about 2 weeks, about a week more for each subsequent stage: larvae, pronymphs and deutonymphs, only 33-36 days from egg to adult.
- at an ambient temperature of 20 ° C: eggs ripen for about a week, about 3 more days for each subsequent stage: larvae, pronymphs and deutonymphs, only 2 weeks from egg to adult.
- at an ambient temperature of 30 ° C: eggs ripen for about 3 days, about 1.5 more days for each subsequent stage: larvae, pronymphs and deutonymphs, just a week from egg to adult.
Prevention of infection
Flower lovers should constantly monitor the condition of their pets in order to notice the appearance of the pest in time. Most often, a tick enters an apartment with a new plant. The newly arrived replenishment is sent to quarantine, separating it from the bulk of the flowers.
Help: quarantine measures last 3-4 weeks, you can carry out preventive treatment with folk remedies.
Regular inspection
The entire collection of flowers should be inspected regularly. A tick can be brought in by a stream of air from a window, the soil into which the plant is transplanted is infected. The pest can appear in a random, undefined way.


When inspecting the bushes, you need to arm yourself with glasses and a magnifying glass, lift branches and leaves, pay special attention to the lower part of the plates. Sick, dried parts of plants are removed.
Compliance with the microclimate
Dry warm air in apartments, especially in winter, contributes to the comfortable life of ticks and the rapid growth of the population. Flowers often stand on windowsills near heating radiators, which dry out the air in winter.
It is important to maintain moisture by placing containers of water or using a humidifier. Pests do not like direct sun, drafts. Rooms need to be ventilated, in the absence of the sun, illuminate flowers with ultraviolet lamps.
Spraying
Regular irrigation from a spray creates uncomfortable conditions for the pest, washes away the cobweb. For crops that do not like moisture (violets), you need to be especially careful.
Flushing
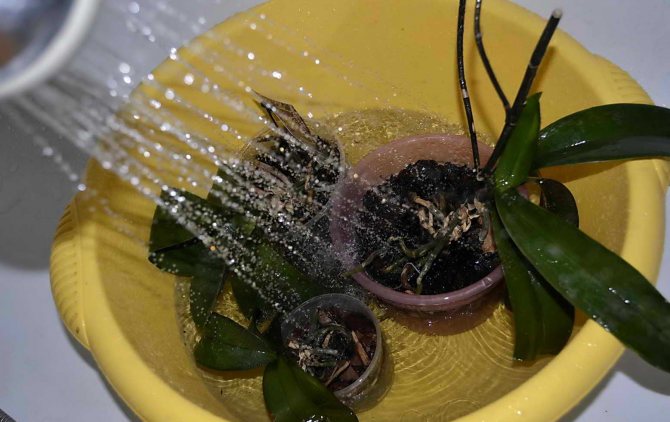
Flowers need not only be sprayed, but also washed under running water. This procedure is carried out monthly. The ground is covered with a film and the bush in the bathroom is irrigated with a gentle stream from the shower. The water temperature is 25-35 °.
Spider mite on orchids and cacti
Flat mites are common pests of cacti.
Without treatment, cacti die.
And again a tick - characteristic spots at the bottom of the stem and on the crown.
Among the flat beetles and spider mites, there are specific species that harm indoor plants of certain families, especially cacti and orchids - these are the cactus flat beetle Brevipalpus russilus, the greenhouse flat beetle Brevipalpus obovatus, the oncidium flat mite Brevipalpalpus oncidii. But these same mites are happy to eat other indoor plants, especially citrus fruits, ferns, fuchsias, roses, Saintpaulias.
Symptoms
How can a grower know that a flower has been attacked by a spider mite? There is a complex of symptoms that indicate defeat.On the reverse side of the leaf plates, spots of brown or light color appear, which eventually merge into one huge spot. As a result, the leaves deform, curl, curl, dry out and fall off. The flower stops growing and developing, the buds wither.
A thin, barely noticeable cobweb appears on the plant, on which you can see the tiny bodies of arachnids. A severely affected flower is completely entwined with cobwebs. A large number of parasites gather at the bottom of the leaves, which are actively moving and preparing to move to a new plant.
Spider mite - how to deal
If you have already found a tick on indoor flowers, do not rush to run for chemistry. This is because ticks are incredibly resistant to chemicals. With the enormous rate of generational change, after a month, repeated treatments will not bring success. And it makes no sense to apply the same pesticide more than twice. This is especially true of flowers newly purchased in the store (they are often processed at the base).
What to do? Firstly, the decisive factor for the rate of reproduction of mites is the microclimate, or rather the temperature and humidity of the air. Spider mites love when it's warm and dry. On hot days in summer, they multiply at a breakneck speed. Therefore, our task is to increase the humidity of the air. Unfortunately, spraying, even twice or three times a day, does not make the situation easier. Moisture evaporates quickly from the leaves. Imagine how much water you sprinkle on the leaves, half a glass at most (more will simply drain to the ground) and these half a glass will dry in 15 minutes. The only way out in the case of spider mites is an air humidifier, wide trays of water, tabletop fountains, and hanging the batteries with wet sheets in winter. But increasing humidity by these methods will not kill the mites, but will only slow down the rate of their development.
Therefore, if allowed, plants need to arrange a hot shower. Most of the plants on our windowsills can handle hot showers for a short time. But the shower washes away the mites from the leaves and scalds them, including the flat beetle. The shower temperature can be around 45-48 ° C (at temperatures above 40 ° C, the development of mites stops). In this case, one must try to ensure that the jets of water fall not only from above, but also to the reverse side of the leaves. If the plants are planted in loose soil with drainage and holes at the bottom of the pot, then they are not afraid of moisture from the shower, just leave the pots without trays so that the water glass. And before the next watering, touch the ground with your finger and make sure that it is dry in the upper third of the pot (or completely dry if the pots are in the room at temperatures below 16 ° C). Watering time is approximately 2-5 minutes. Some plants tolerate hot showers very well, even with temperatures up to 52 ° C, for example, monstera, ficus benjamin, hibiscus.
There are plants that cannot be wetted on the leaf, for example Saintpaulias (and the rest of the Gesneriaceae), some other plants. Basically, these are indoor flowers with thin delicate leaves, easily prone to decay at the slightest dampness. But they can also be worn in the bathroom, just not under the shower, but in the steam room. In this case, you turn on a very hot shower (maximum possible), but do not direct it at the flowers, but leave it pouring into the bathroom. After 10 minutes, the bathroom will be filled with thick steam, and it is advisable to leave the shower for 15 minutes. Do not open the door to the bathroom until the wet steam has evaporated. Then you can repeat the procedure. And so to continue, as long as financial considerations and a water meter will allow.
You need to repeat a hot shower every 3-5 days. You can do without chemicals altogether if you rinse the plants in the shower about 3-4 times weekly, and then once every 3-4 weeks. You can increase the effectiveness of a hot shower if you first wash the leaves with soapy foam. Suitable detergents include green soap, tar soap, laundry soap and, at worst, regular shampoo.Green or tar soap should be applied to the leaves with foam and left for 5 minutes. Then rinse off. Shampoos can be washed off immediately. However, do not forget that ticks are extremely tenacious and hot showers are not a panacea! It's just a safe way to try first.
If you have plants infected with a mite that cannot be transferred to the shower (very large tubular specimens), there is no shower, or the plants do not tolerate hot water, we have to fight spider mites with chemical remedies.
Remember that drugs that kill ticks are not called insecticides, but acaricides - they are drugs against arthropods. As a last resort, there are drugs that work against insect pests (thrips, aphids) and against ticks. They are called insectoacaricides (for example, phytoverm). Each drug must have an instruction, indicating the consumption rates. If a mite is not mentioned among the indicated pests, then this drug will not help, do not even try, just breathe in toxic substances once again. Very often they try to kill the tick with a common actar - this drug does not work on the tick. If it seemed to you that after spraying there were fewer ticks, then the point is not in the preparation, but in the very fact of spraying with water.
Some drugs, acaricides are described separately, with detailed instructions and consumption rates, see Acaricides, see Insectoacaricides.
When using acaricides, pay attention to the hazard class (not everything can be used in an apartment), and, if indicated, at what stages of the tick this drug acts. For example, biological products usually kill only adults, but do not affect eggs and larvae. In addition, many intestinal acaricides become simply useless at the moment when the mite is in a dormant stage before the next molt and does not feed on plant sap. In this case, it is better to repeat the reprocessing after 3-4 days, when the undetermined larvae enter the nymph stage, but do not yet form adults to lay new larvae.
- You can alternate spraying with acaricide and hot showers. By the way, when it comes to spraying, the wettability of the leaves should be as good as possible. Therefore, for some plants, for example, ficus benjamin varieties with curly and twisted leaves, it is better not to spray, but to immerse the crown in a solution with acaricide for 1-2 minutes (in a bucket with a solution).
With a large tick infestation, it makes sense to alternate drugs from different chemical groups. For example, Apollo (clofentesine) and Bi-58 (dimethoate), or neoron (bromopropylate) and actellic (pyrimiphos-methyl).
Remember that ticks are carried at a distance by the breeze of the wind, the slightest movement of air, so if a tick appears on one plant, all plants on the windowsill, and possibly in the apartment, must be processed. It is not necessary that plants living in another room will be infected, but prevention will not hurt. I have had cases when mites appeared on only two plants standing on a balcony completely covered with flowers. Incredibly, nevertheless, if you isolate the infected in time (at the slightest yellow spot), you can avoid long tedious procedures.
Also, do not forget that ticks can be on the frames, the surface of the windowsill, the walls of the pot and other surfaces. Therefore, while the plants are being processed, the window or shelf must also be wiped clean. Preferably soapy and then alcoholic solution (boric alcohol is sold at the pharmacy).
When transplanting plants, it is better to desenify the earth. The best way is in the microwave for 10 minutes (slightly moisten the ground). True, there will be a smell of rotten earth throughout the apartment. And this does not guarantee that the mite will not appear during the spring-summer season during airing. By the way, ticks fly to the high floor (even 14 or 16).
Where do they come from
Ticks enter homes and infect healthy crops in several ways:
- After the appearance of a new plant at home, affected by a tick. It is difficult to find small pests; a newly acquired flower often hides eggs or adults in the crown. All newly arrived plants must be quarantined for a period of 2-4 weeks.
- Contaminated soil. When transplanting and rejuvenating home flowers, you can infect them with a mite from the ground. Even purchased land can contain pests.
- Placing home flowers in gardens, balconies and loggias. A lot of ticks live in vegetable gardens and summer cottages.
- A light small pest can be brought in by a tailwind from the street, from open transoms and vents. Most flowers are on windowsills or just near windows.
See also
TOP 15 best products for cleaning parquet at home
Often old pots taken from pantries become hawkers. A person can bring a tick into the house on things and clothes.
How to deal with spider mites on orchids
Orchids differ in that they cannot be soaked for a long time in any solutions, sometimes it is impossible to allow water to enter or retain in the leaf axils. Very often, after treatment for a tick, orchids get sick with rot - from waterlogging of the soil, leaves, and the root zone. But oddly enough, orchids are resistant to chemicals, phytotoxicity is not expressed. Therefore, if you deal with mites on orchids, then develop a method that allows you to get rid of pests at one time. The easiest way is to prepare a solution of acaricide and completely immerse the orchid in it together with a block or pot for 2-3 minutes. Then let the solution drain, thoroughly dry all the sinuses of the leaves, with a piece of toilet paper folded in a cone (it absorbs moisture better than cotton swabs). If the orchid is in the bark, it may smell out of the pot for a while. Do not rush to rinse the bark, mites may be hiding inside. Place the orchid in a draft-free area (even a window in the warm season). In the next watering, add phytosporin-m to the water: 5 g of powder per 500 ml of water.
You can wipe the leaves of orchids (phalaenopsis, dendrobium, miltonia, etc.) daily with a soft cloth dipped in boiled water. Without insecticides, gently wipe each leaf on both sides (within 3-5 days). First, you will erase the eggs and larvae that have survived on the leaves, and secondly, the new ones will not have time to settle. And most importantly, after treatment for ticks, isolate orchids from other indoor plants until everything is free of pests.
Orchids tolerate tick treatment well with such agents as actellik, neoron, apollo, envidor, orthus. These funds are most effective, unlike other acaricides (fitoverm).
Outdoor control measures
The most effective method for dealing with spider mites in the open field is watering under pressure from a hose. This is an emergency measure to wash off adults and larvae from shoots and leaves. The pest stops multiplying, although it does not die. Further measures should be aimed at destroying the colony.
First you need to collect, take out of the site and burn diseased plants. Then the planting should be treated with insecticides. After that, it is recommended to feed the weakened crops with phosphorus fertilizers. In the fall, after harvesting, the soil must be dug up so that the female ticks are on the surface. Spring digging will also not be superfluous: it will destroy the overwintered pest.
To protect the planting from infection, experienced gardeners plant calendula along the edges of the beds, the smell of which scares off the spider mite. Control measures that include the use of chemicals are necessary if calendula does not work. For example, in dry years, it is more difficult for a pest to get food for itself, it becomes more active and settles on plants, not paying attention to unpleasant odors.In such a situation, only potent drugs will help.
Folk remedies for tick control
The most common way to fight leafy plants is with onion infusion. One of the members of the forum (YaSolnce) prepares it like this: she cuts half a medium onion, pours it with warm tap water into a half-liter jar, covers it with a lid and insists for 5-7 hours, filters and sprinkles the flowers. Here you need to add that if the water in your area is hard, then the infusion should be done only in boiled water. In addition, one large onion can be used for half a liter of water, this is a more concentrated solution, but it will not get worse.
An even easier way to get rid of a tick is with garlic water. 1 clove of garlic must be crushed, preferably in a mortar or finely grated, pour a glass of hot water and strain. Spray plant leaves with fresh solution immediately.
Acetone and alcohol against mites
Victor Serbin recommends this method of disinfection of cacti: 2 parts of 97% alcohol and 1 part of acetone. In a spring transplant, the plant is cleaned of the old substrate with a thin stick, then immersed in a solution of alcohol and acetone for 5 seconds. Then it is laid out on the newspaper to dry. The plants dry out very quickly, due to the volatility of the components (for this reason, you cannot change alcohol for vodka or moonshine, and acetone for a nitro solvent). This solution kills eggs, larvae, and adult pests, any insects at any stage of development, regardless of structure and species (alcohol-acetone solution is also effective against scale insects and worms). No addiction arises. Burns of the roots and body of the cactus - too. Even seedlings can be dipped in the solution.
In general, an alcohol solution, even without acetone, can be effective for wiping the leaves of some plants. First of all, those who have leathery wide leaves (monstera and other philoderndrons, adeniums, alocasia and other aroids, calatheas and other arrowroots with hairless leaves). But alcohol cleans the leaves from pests only in the place where you wiped them. And ticks, as you know, hide in secluded places, for example, in the axils of leaves, where it is difficult to reach even with a brush. Therefore, simply rubbing the leaves with alcohol cannot guarantee a 100% result, as in the case of dipping the entire plant into a solution, as in Viktor Serbin's.
In addition to pure alcohol, some flower growers are trying to use various tinctures, for example, calendula infusion. This is all well and good, and the alcohol solution works, but it leaves a sticky film on the surface of the leaf. Firstly, it clogs the stomata, which makes it difficult for plants to breathe, and secondly, soot or other fungi easily settle on sticky surfaces. Therefore, such infusions need to be washed off a day or two after spraying.
Natalia Rusinova
Destruction of the phytophage in the greenhouse
Indoor buildings have all the conditions for nutrition, life and rapid reproduction of ticks. In warm, high humidity, a colony of adults and larvae very soon sticks to all plants. Insects can get into the nursery with soil, on shoes, as well as with infected seedlings purchased at the market or grown in a room. It is difficult to get rid of the pest, so it is better to prevent it from entering the greenhouse or greenhouse.


Before planting seedlings or sowing seeds, dig up the soil as deep as possible. All parts of the greenhouse are treated with an antiseptic compound. After a while, the procedure is repeated. When the plants are planted, you need to monitor their condition, including preventing phosphorus starvation and drying out of the soil.
If there is a suspicion that the crops are contaminated, you should first increase the humidity to 80%. This will lead to the fact that most of the individuals will die. Then all the affected parts of the plants are collected and taken out. If there is no way to burn them, you need to bury them.
In order for the pest colony to die out completely, you need to place jars of turpentine or onion-garlic gruel next to the plants. This usually works. In the future, the plants need to be watered with a drip method so that the humidity remains as high as possible.
Sometimes all of the above measures are ineffective. Then proven folk remedies, insecticides and biological agents come to the aid of the gardener.
How to treat pest-free plants?
A sick, severely affected plant cannot be saved, since the pests have exhausted it, and it will not be easy for the flower to recover from the disease. In this case, there is only one way out - to burn it.
A plant cleared of ticks must be transplanted into another pot, completely replacing the soil. For treatment, you can feed the flower with complex mineral fertilizers. You should not use organics, because parasite eggs are most often found in it.
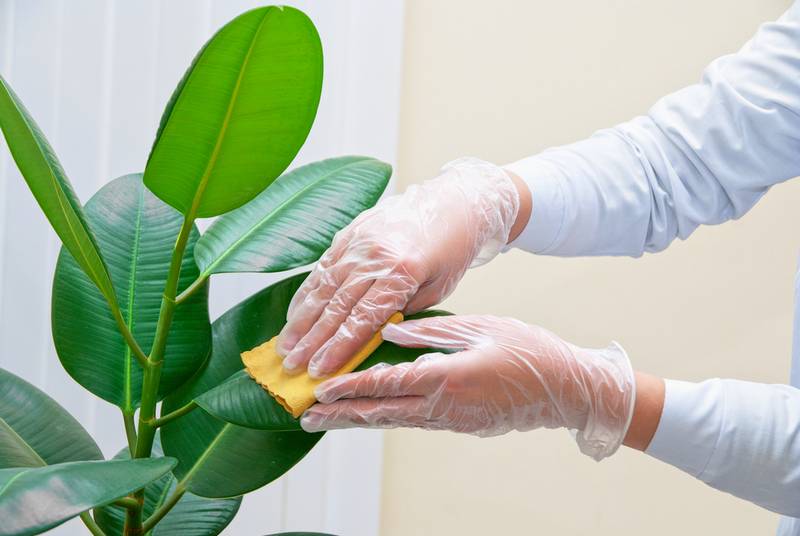
Further care consists in regular humidification of the air, removal of yellowed and dry leaves. It is important to constantly inspect the plant, paying attention to the inside of the leaves, wipe dust from them and wipe them. It is impossible to use soapy water for prophylaxis, since it does not allow the plant to breathe. Purchased plants are placed separately from the rest and kept for several weeks to make sure there are no pests.
Loading ...
What plants are affected
First of all, the spider mite settles on berry bushes and grapes. Also in the high-risk group:
- Vegetable crops - cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes, eggplants.
- Fruit trees - apple, pear, peach, plum.
- Legumes - beans and peas.
- Among outdoor ornamental plants, roses and asters are primarily affected.
Greenhouse crops are more likely to suffer, since the spider mite receives all the most favorable conditions in the greenhouse - food, humidity, high temperatures.


Start of treatment
Regardless of what means will be used in the fight against an arthropod, treatment always begins the same. If the number of parasites is small, these three steps will completely solve the problem. Otherwise, they will help get rid of the cobweb, significantly reduce the number of arthropods and simplify further therapy.
- Remove affected leaves and shoots. They will no longer recover, but part of the pest population will be destroyed.
- Make a soap wash. Prepare a strong solution of laundry soap or other detergent. To enhance the effectiveness, you can add baking soda at the rate of a tablespoon of 5 liters. Beat the foam and apply it to the leaves. After three to four hours, wash off the composition with clean water, carefully wiping each sheet. If the solution gets on the roots, the flower may die.
- Increase humidity. Until the drops of water on the flower have dried, you need to cover the pot with a plastic bag and leave to knock. High humidity is detrimental to most spider mite species. If you find varieties for which such conditions are favorable, it is not worth placing in a plant in a "steam room".
It is only necessary to wipe the outer side of the leaves with a soapy composition - on the back side there are “breathing” pores, the blockage of which can lead to the leaves die. If your plant has too small leaves to wipe each one individually, you can spray it with a fine spray with soapy water.
Optimal living conditions
The unique adaptability to the habitat and weather conditions allows the spider mite to live throughout the globe, except for Antarctica. Optimal conditions: temperature 20-30 degrees Celsius, humidity 35-55%. The active stage of activity and reproduction of the pest begins in the open air in June. In early August, ticks begin to hibernate. It is the active period that is favorable for spraying plants. It is worth using folk remedies for spider mites.Very high summer temperatures, high humidity, the onset of cold weather stop the active phase of activity, the insects hibernate, hide in the soil, in the cracks of buildings, under the remains of plants.
In the house, ticks creep under the baseboards, on the ceiling, in the cracks in the windowsills. It is difficult to apply a remedy for spider mites during this period, since the spiders themselves are not visible, and the places of their activity too - they sleep and do not eat. Visually, it seems that everything is in order, but the tick is just waiting for a favorable period.
Tick larvae and adults are transferred by humans, animals, on the cobweb. And they themselves crawl quickly. In good conditions, egg clutches remain viable for up to 5 years.
Tips & Tricks
Summing up, you can give a few of the following tips and tricks that may be useful to novice growers:
- Plants with downward leaves tolerate infection with these parasites much worse, since they cannot be sprayed with acaricides or washed with special agents, as this can cause their rotting and subsequent death. For this reason, they need to pay special attention and not forget about taking preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of ticks.
- Many people practice or advise applying soapy water to plant foliage in order to repel and eradicate pests. In fact, such a procedure is harmful only to domestic flowers, but it does not have any effect on the parasites. Such treatments clog the stomata, which disrupts the natural process of gas exchange.
- There are different types of parasitic mites that infest houseplants. They are sometimes mistaken for a spiderweb variety, although the methods for destroying such pests can be fundamentally different, so you need to decide exactly with whom the fight is being fought. Most often, confusion occurs when false spider mites appear, which deform the inflorescences and leave silvery marks on the foliage. Most often they affect citrus trees, exotic plant species, cacti or orchids. All these species differ in that they are not able to form a web.
Biologicals
The effectiveness of biological preparations is based on the fact that they enter the body of the phytophage and block important functions, causing death within 8-11 hours. Such products are harmless to people, pets and plants. They only harm insects that feed on processed greens. It is necessary to treat the plant 3-4 times at intervals of several days: during this time, the larvae are transformed into adults and also die.
Effective drugs:
- "Vertimek";
- "Agravertin";
- Aktofit;
- "Kleschevit";
- Fitoverm;
- Akarin.
Specialty chemicals
Without the use of chemistry, it will not be possible to completely remove pests. Modern acaricidal preparations are designed for indoor use. An effective method of dealing with spider mites is spraying with chemical compounds and treating the soil with them in a pot. Recommended remedies include:
Fitoverm
Plant-based bio-insecticide Fitoverm can be safely used at home. It is recommended for the prevention and destruction of pests on indoor plants. The effect of the product begins 6-7 hours after application. The period of protective action is 2-3 weeks. An ampoule of the drug (2 ml) must be brought into 1 liter of water, intensively spray the infected plants with the ready-made composition.
Aktara
A modern acaricidal drug is used not only in the garden, but also to destroy pests on flowers - roses, violets, ficus and others. The product is offered in the form of a concentrated emulsion and water-soluble granules. Small packaging in ampoules and sachets is convenient when processing houseplants. Aktara from spider mites is a systemic drug.It penetrates the leaves and tissues of plants, sucking out the juice from them, pests receive a dose of poison.
An hour after the insecticide enters their body, phytophages lose their ability to feed and die within 24 hours. The action of the drug when applied to the soil protects indoor plants for 2 months. When spraying, use a fresh solution. When working with a toxic substance, you should be careful - wear gloves, wash your face and hands after work, change your clothes.
Plant-Pin
Sticks with the active ingredient butoxycarboxyme. Spider mite remedy for indoor plants that does not require spraying. The number of sticks depends on the diameter of the pot - by 9 cm - 1, by 12 cm - 2, by 20 cm - 5-6. They are stuck into the ground at a distance of 2 cm from the plant. During watering, the active substance dissolves and enters the roots of the flower. The effect of the drug is observed after 3-7 days. It will protect against the pest for 8 weeks. The Etisso remedy has a similar effect.
Pest control methods
Many flower lovers have not encountered such a problem before, so they do not know how to deal with spider mites on indoor plants. Methods for killing the parasite depend on the degree of its spread. At the initial stage, it is necessary to use a mechanical method - to cut off the yellowed leaves, where the bulk of the pests have accumulated, and burn them. Treat the plant itself with soapy water. It is prepared at the rate of 10-20 g of laundry or tar soap per 1 liter of water.
After removing the dry leaves, the rest are wiped with a napkin dipped in soapy water on both sides. This allows you to remove adults and part of the larvae. To enhance the effect, the plant, together with the moisture foam, is placed in a plastic bag for 2 days. After 48 hours, it is rinsed thoroughly with a warm shower. The procedure is not one-time; it is repeated after a week.
Attention. Simultaneously with the processing of flowers, it is necessary to wash the window sill (with soap or alcohol), window frames, wash the curtains.
A common method of getting rid of spider mites is alcohol treatment. It should be carried out carefully, first try on one leaf so that there is no burn. Apply alcohol with a spray bottle or cotton pad. The treatment is suitable for ficus, dieffenbachia and other plants with dense leaves. This disinfection is effective for window frames. Exposure to UV lamps is recommended. It only benefits plants, and mites always avoid contact with ultraviolet light.
Should there be a spider web?
Despite the fact that the spider mite, judging from its name, is simply obliged to braid the plants with cobwebs, it does not always do this. Most species do secrete a filamentous secret, but sometimes in very small, imperceptible quantities. Only with excessive overpopulation, when there are too many individuals, they can entangle the entire plant with cobwebs.
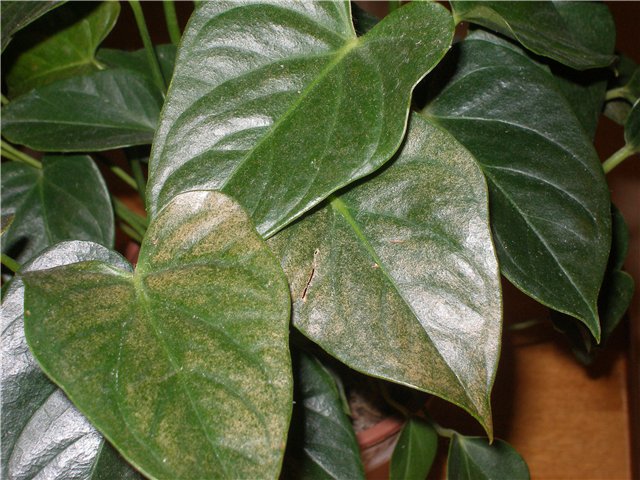


Yellow dots on the leaves of anthurium indicate the intrigues of a spider mite
Preventive measures
Simple steps can help reduce the risk of spider mite infection. In the fall, when the crop is harvested, you need to pull out or dig up the remnants of the roots from the ground, as well as remove all the above-ground parts of the crops, take them off the site or burn them. It is not recommended to compost diseased plants. For the winter, you cannot leave heaps of grass, foliage and other debris in the garden: adult phytophages winter there.
It is necessary to plant and sow crops far enough from each other. On compacted beds, pests start up more often and multiply faster, and this applies not only to the tick. If it was not possible to avoid infection, after treatment (in the fall), it is advisable to completely remove the top layer of soil and bring in a new one. It is also necessary to carry out preventive treatments using folk or chemical agents.
The main preventive measure in the greenhouse is fumigation.Ticks hibernate in heated structures, so in the spring it is imperative to do this procedure and treat all parts of the structure with a blowtorch where phytophages may be located.
During the growing season, the relative humidity in closed ground should be at least 80 and not higher than 90%, and the temperature should not be higher than 25 degrees. Such conditions are uncomfortable for the pest and prevent its reproduction.
Acaricidal chemicals
This group of drugs is also called insectoacaricides. To some of them, phytophages acquire resistance after a generational change, therefore, if one remedy is ineffective, you need to try the next, with another active ingredient. For the destruction of larvae and adult phytophages, 3 treatments are required every 3 days. Spraying is carried out in a respirator and gloves, wearing a hat and a work gown.
Insectoacaricides are poisonous and very dangerous. Store, dilute and use them strictly according to the instructions. Such potent agents are used when other methods have not been effective. The following works best (the active ingredient is indicated in brackets):
- Apollo (clofentesin);
- Flumite (flufensin);
- Oberon (spiromesifen);
- Sunmight (pyridaben);
- Nisoran (Hexythiazox);
- Floromite (biphenazate).
Physical struggle
This concept means, first of all, the creation of favorable conditions for the development of plants: watering, weed control. For indoor plants, the temperature of the content is of great importance.
The first single diseased plants must be removed immediately. Destroy torn out spoiled leaves or shoots, do not leave it just like that on the ground - this is a breeding ground for the next generations of the pest.
It would be good to irradiate indoor plants with ultraviolet light: this slows down the reproduction of the parasite.
Folk recipes
All traditional methods are based on spraying diseased plants with decoctions and infusions. They can be used in the room at any time of the day, and in the open field - only before sunrise or after sunset. Here are some recipes for spray mixes:
- 200 g of onion and garlic husks are placed in a bucket of water, infused for 12 hours, the next day, filtered and sprayed.
- 500 g of yarrow is poured with water, brought to a boil, removed from the heat, more water is added to make 10 liters.
- A pinch of dry celandine is brewed with a little water. Indoor flowers are processed.
- 400 g of calendula is placed in 4 liters of water, insisted for 4 days.
- 3 kg of fresh or 1 kg of dry dope leaves are poured into 10 liters of boiling water. Spray plantings in the garden. For indoor plants, the proportions are reduced.
Biological impact
For every predator, there is a more terrible predator. So, for the spider mite, the phytoseiulus bug is considered the enemy. Artificial colonization of plants with these insects allows you to destroy the parasite with someone else's, so to speak, teeth. Disadvantage: this method can only be used in greenhouses.
To combat the tick, biological products have been created: "Akarin", "Bitoxibacillin", "Fitoverm". How to use them correctly?
- "Akarin" is diluted in the proportion of 2 ml of the drug per liter of water.
- "Bitoxibacillin" - 80-100 g per 10 liters of water. The disadvantage of this drug is that it can cause allergies if it comes into contact with treated plants.
Both solutions are used throughout the growing season every 15 -17 days.
- Fitoverm is diluted in the amount of 10 ml per 10 liters of water. Processing is carried out every 7-10 or 14-20 days. The processing period depends on the age and size of the plant.
Another common disadvantage of biological agents is that they act exclusively on adults. Eggs and larvae are not affected. The processing period depends on this: for each generation - a new portion.
The pesticides clofentesin and flufensin are hormonal. They do not destroy all individuals at once, but sterilize the uterus. The effect of their use is long-term, but becomes noticeable after a few days.Some individuals die out, while others do not appear. If you need to destroy the tick urgently, you can mix this drug with any of the biological products.
Reasons for the appearance
In indoor plants, the reasons for the appearance are as follows:
- In winter, at home, when the heating is running, the air becomes dry.
Reference. Flowers near the batteries are watered less often, almost never sprayed and are capable of becoming infected with spider mites at this time. - Pest-infested flowers can be brought back after purchase at the flower shop. Ticks are difficult to see due to their small size.
- In greenhouses, worms can overwinter in the vegetative layer of the soil, be carried on clothes, and get in with seedlings.
- In open areas of garden plots, it is possible to accumulate under last year's foliage, and in other secluded places.
How to find?
- On the leaves you can see small yellow or white dots. It was the ticks that pierced them and sucked out the cell sap.
- If pests have been living on plants for a long time, then the leaves of indoor flowers can discolor and dry out.
- Pests can be found on the undersides of leaves and stems.
- If a large number of them are divorced, then a cobweb appears.
- On closer inspection, green and red dots can be seen on the web - these are spider mites.
- If you do not take control measures, the cobweb envelops all the leaves and entangles the shoots.