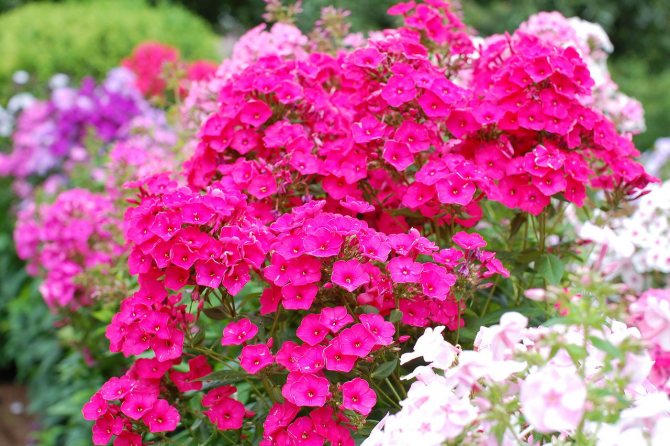
Terry, two-colored, star-shaped - all this is about phlox varieties that bloom in early July and dazzle in the garden until autumn. Perennial and annual representatives of the species do not require intricate care. They only need to be fed with fertilizers, watered on time and renew (divide) the bush every four to six years. Unfortunately, flowers are susceptible to viruses, nematodes, caterpillars, flea beetles and other pests. This undoubtedly spoils their appearance and often leads to the withering away of the culture. Phlox diseases with photos and their treatment are described in detail in this article. The selected material will help not only identify and eliminate the cause of the disease, but also tell you how to save flowers in the future.
The history of the origin of phlox begins in North America. Then in the wild there were several types of spherical pink flowers. Today biologists have more than 80 species. Among them are white, blue, lilac, red, multicolored, orange, blue and purple plants, striking in brightness and beauty.
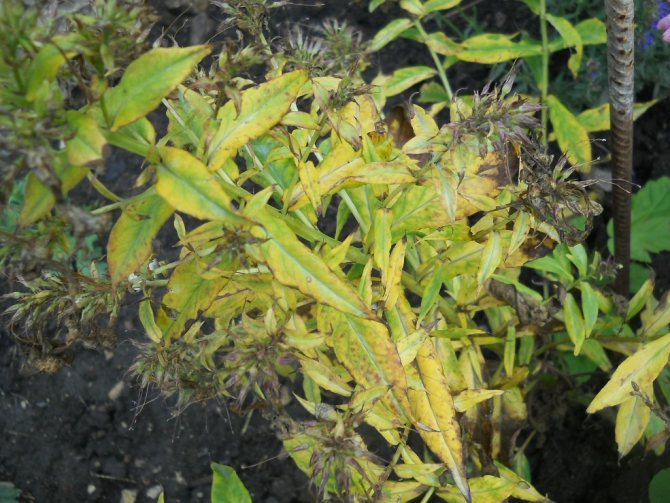
The reasons for the drying out of the lower foliage
The list of reasons can be huge, so the most commonplace of them must be excluded from the outset. Often the root of the problem lies in improper care of the plant, which suffers from:
- insufficient amount of moisture in the soil;
- nutritional deficiencies;


All these factors can cause yellowing and drying of the lower leaves, therefore it is necessary to ensure regular watering and feed the plant well. If it grows in a place too exposed to sunlight, transplant to a shaded area. Flowers are given maximum care, but phloxes still dry, what to do in this case? Look for third-party reasons:


- viral diseases;
- fungus;
- mycoplasma diseases;
- pests.
The symptoms for each of these ailments are similar, but there are differences that need to be discussed in more detail.
Variegated
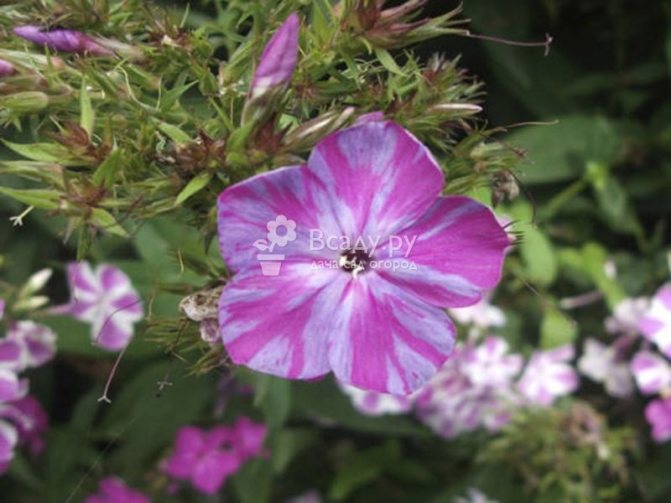
Variegation is the most undesirable phlox disease, capable of destroying an entire collection in one day. The causative agent of variegation is a virus. The virus changes the color of the petals, affecting the synthesis of coloring pigments, causing the petals to become covered with radial stripes of light color.
When variegated, the pattern is asymmetrical, uneven, located in sectors. The strokes are wider at the ends. The disease completely destroys such a varietal trait as color, and then leads to the degradation of the entire plant.
The affected bush is the source of the infection. The virus is carried by sucking insects, sap, pollen and seeds. Soil nematodes spread the mosaic virus, but through the roots.


You can recognize variegation in a recently acquired and first-bloomed specimen by comparing the color of flowers with photographs of a similar variety.
The virus can be detected with 100% accuracy only in a professional laboratory. Unfortunately, amateurs are deprived of the opportunity and can only rely on observation.
Read also: How to choose plants for a hedge, design and practicality of the solution
It is difficult to detect variegation on white varieties without an eye. If the variety is "with an eye", then the disease manifests itself as a heterogeneity of the borders of the eye.Close inspection reveals whitish abrupt strokes on the light part of the petal.
Recently, new, unusual varieties of phlox have begun to be sold on the market. Before buying a new variety, do not make inquiries in the literature or on the Internet whether it really exists and what it looks like. Unscrupulous traders can pass off plants that have changed color under the influence of viruses or high doses of radiation as a new variety.
Such, for example, is the widely advertised variety "Russian Souvenir". Its crumpled and deformed petals suggest a viral disease. More suspicious is the assertion of the inductor of this variety that "Souvenir" does not reproduce by cuttings - only by dividing the bush, because, as you know, viral diseases impede vegetative reproduction.
There are varieties, the diversity of which does not have a viral cause - it is genetically incorporated in them. These are variegated Darwin's Joyce, Elizabeth, the famous "Dragon" with strokes on the petals.
You can distinguish genetic variegation from acquired by the nature of the strokes. In the first case, the strokes are not widened towards the end, discontinuous, symmetrical, like a speck.
Do not confuse variegation and petal defects caused by bad weather. Virus-infected plants have distortions already in the buds, and bad weather affects the color of only the opened petals. To stop worrying, it is enough to pick and open a few buds with your fingers. If there is no color distortion on the petals, then you can relax.
There is only one measure to combat the variegation virus: the plant is dug up and burned.
Viral diseases
In order for a plant to become infected with a virus, it needs a carrier. Most often, this role is played by ordinary insects or already sick plants that have been transplanted from one place to another. The most common ailments:
- mosaic virus razuha;
- variegation.


These diseases mainly occur in the midst of flowering and are manifested by the following symptoms:
- light radial stripes appear on the leaves;
- later these formations turn purple;
- flowering is rapidly suppressed.
Over time, the lower leaves of phlox begin to dry out, and the scale of the disease only increases. It is extremely difficult to fight the virus. In most cases, it is impossible. If it was detected in a timely manner, and the bush is not completely infected, then you can resort to cutting off individual shoots. If you tighten it up, there will be no other way out but to dig up the phlox along with the earth and destroy it.
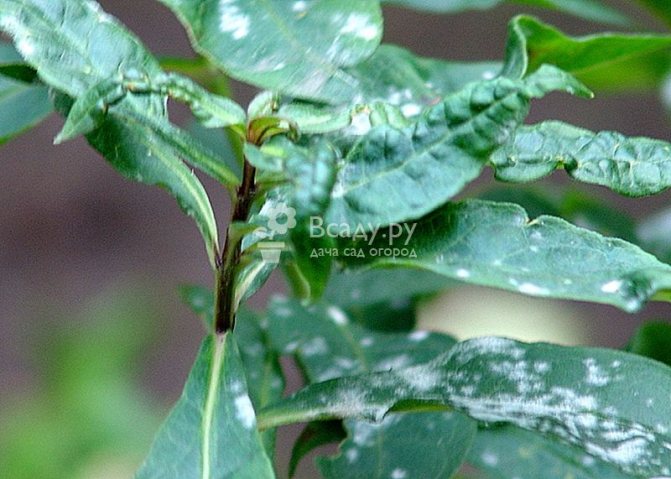
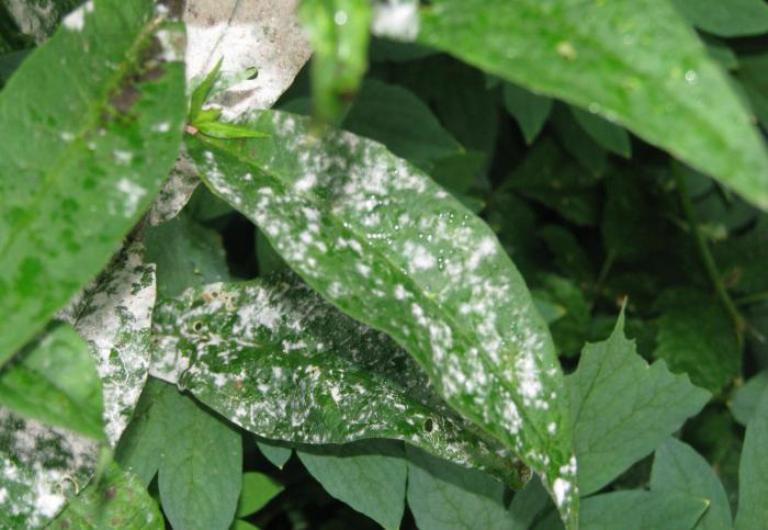
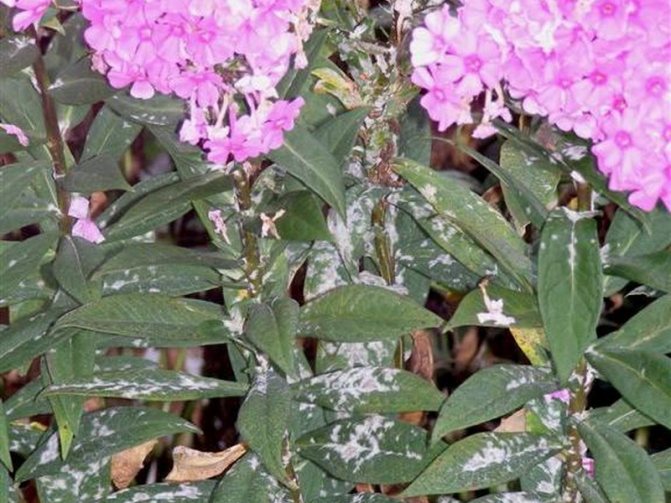
Powdery mildew
The main symptom of this disease is the appearance of white, powdery spots on the affected leaves. Powdery mildew also causes yellowish brown discoloration at some stage on the leaves. The color change usually occurs after the appearance of white spots.
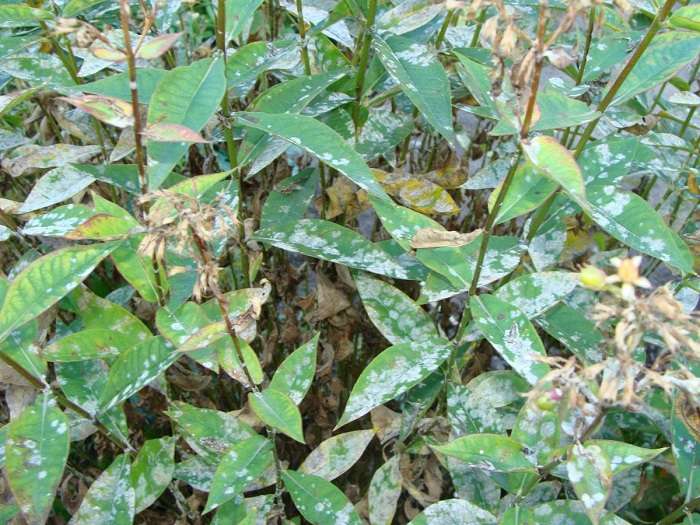


If the fungus that infects the plant remains undisturbed, it can cause the foliage to fall off and prevent the flower buds from opening. Fungal spores appear only in places with high humidity. Therefore, maintaining abundant moisture at ground level is unacceptable. Water the plants only in the morning to help prevent the growth of fungus.
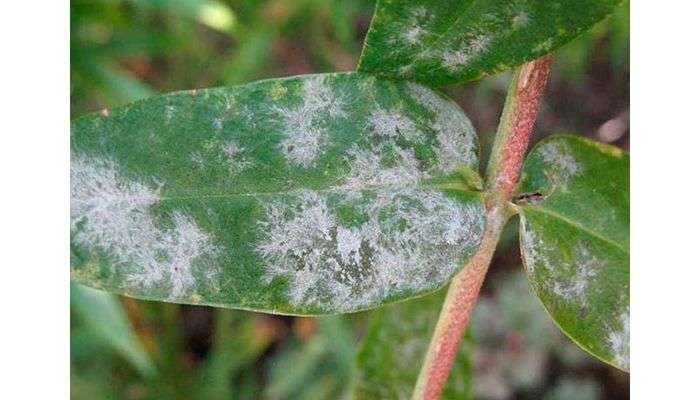


If the leaves of phlox turn yellow, then how to treat this disease? Various horticultural oils can help you get rid of the disease if it has already infected phlox, but has not had time to develop much. If powdery mildew appears annually, the use of a sulfur fungicide will stop its appearance and further development.
Fungal diseases
The most famous fungal disease is the so-called powdery mildew, which most often develops during the hot season. Her colleague in the shop - peronosporosis, on the contrary, overtakes flowers in excessively wet, cold weather. This is the reason why phlox withers.Both infections make themselves felt with the following symptoms:
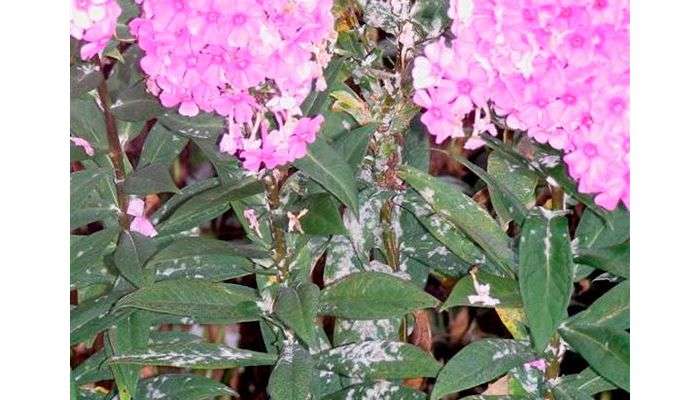


- a whitish bloom appears on the foliage;
- the lower green mass fades and gradually dries;
- over time, the leaves fall off.


If the lower leaves of phlox dry out, fungicide treatment gives a very positive result. Some growers resort to processing the entire bush with a furacilin solution. Take 20 tablets of this drug and dissolve in 10 liters of water. The resulting mixture must be sprayed several times on the plant, carefully processing the root zone. Leaves affected by the fungus can be sprinkled with soapy water or 300 grams of ash diluted in a bucket of water. In the fight against rust or brown spotting, Bordeaux liquid helps well, which can be used systematically for preventive purposes.
What to do to prevent phlox infections
To prevent the occurrence of various diseases, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures:
- it is imperative to divide the bushes and transplant flowers;
- dig up the soil around the plants;
- remove weeds and dead leaves;
- to prevent infection with nematodes, plant bait plants - parsley or peas (parasites accumulate in these plants and do not harm phlox);
- carry out preventive spraying in early spring with Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate;
- spray the acquired planting material with a fungicide and do not plant immediately on a flower bed with other varieties.
Pests
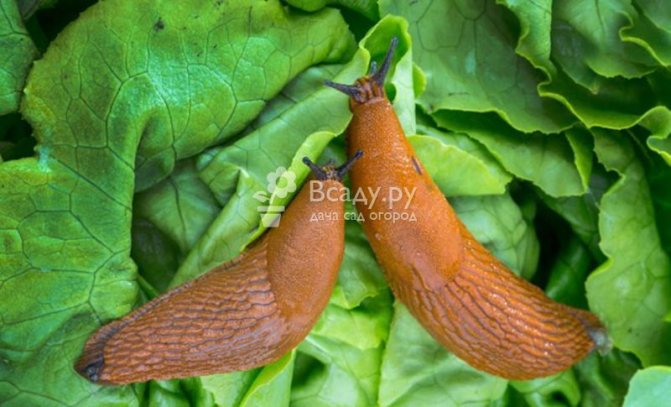
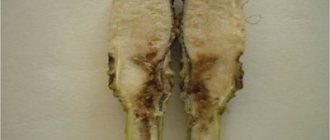
Among the phlox pests, slugs, a slobbering penny, a variety of larvae that somehow damage the bush are distinguished. But the damage they do is not so serious. The most dangerous pest is the nematode. It is a microscopic worm invisible to the naked eye. It multiplies rapidly and, with the invasion of a large number of individuals, quickly depletes the plant. Nematodes overwinter in the roots and in the lower part of the stems. Waking up in the spring, they begin their activity - that is why phloxes dry from below. This pest can be spread by water jets, plant parts or non-disinfected tools.
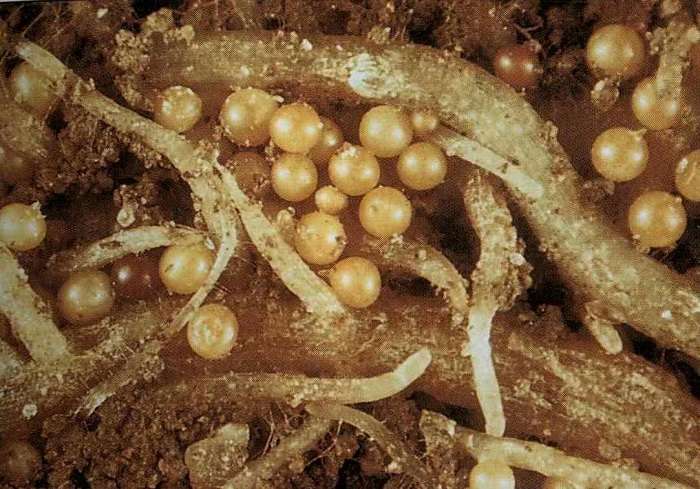

Fighting nematodes is incredibly difficult. They are very tenacious and do not completely die under the influence of even the most powerful drugs. There are two ways out. The first is to destroy the bush completely along with the earth. And the second, if the variety is too expensive, and it looks like the plant is not completely infected, then you need to carefully remove all suspicious parts of phlox and leave only healthy ones. In the spring, cut off the remaining shoots, rinse under running water and plant in open ground under a film or glass jar. In this case, it will at least be possible to preserve the variety.
Although all varieties of phlox (Phlox stoloniferais or paniculata) have quite bright green leaves, you may not notice them throughout the summer: during the flowering of most species, the carpet of buds will simply cover all the leaves. When the flowers disappear, foliage appears, and quite often these are not fresh greens, but sluggish yellow processes.


Various pests, multiple diseases and uncontrolled watering in most cases can cause discoloration of the leaves, which gradually turn yellow, and then dry out and fall off altogether. The most dangerous are incurable viruses, faced with which you will have to part with several bushes of plants.
Phlox are very beautiful flowers and a welcome sight in the springtime when the weather is warm and the garden comes alive. The brightest species are presented in white, pink, red and blue, while they can grow both in sunny areas and in shady areas. Let's look at the main reasons why phlox leaves turn yellow and how to deal with it.
FLOXES:
Paniculata phlox is one of the most popular and beloved crops. Their presence in the garden is so familiar that it seems that it has always been so.However, the introduction of phlox paniculata (Phlox paniculata) and other closely related species of the genus Phlox - phlox spotted and carolina (Ph.maculata, Ph. Carolina) began only in the 18th century, i.e. relatively recently. Three hundred years - is this a period compared to the thousand-year history of gardeners' love for lilies, tulips and roses! But even during this short period of time from the point of view of history, a lot has been done. The rules for caring for phlox paniculata follow from the growing conditions of its wild ancestors in nature. The habitats of these plants are wet meadows, clearings and forest edges, river banks in North America. These places are distinguished by fertile soils, humid and mild climate. Accordingly, in the garden, it is necessary to provide the phlox with a well-lit place and take care of sufficient nutrition and abundant watering. The agrotechnology of paniculate phlox is simple, but it is still worth following some rules in order to give the plants the opportunity to appear in all their glory. Modern varieties often have very large flowers and large inflorescences. For a plant to develop a powerful vegetative mass, it requires a lot of nutrients and moisture. Phloxes are very responsive to care, and will thank you for your care with a true transformation from Cinderella to the queen of the garden.Pick-up location
For planting phloxes, choose a flat, lit area for most of the day. Light partial shade is quite acceptable, and even desirable for fading varieties. In partial shade, phloxes will bloom a little later. It is worth considering the fact that with partial shading, the plants will slightly elongate. If water stagnates on the site, drainage is necessary, with a close occurrence of groundwater, raised ridges are arranged. Strongly blown areas are not suitable, because in summer in such places, the soil dries out quickly, and the plants suffer from thirst, and in winter the snow is blown away, which can freeze phloxes.
The soil
Planting is desirable in nutrient-rich, loose, moisture-retaining soil with a slightly acidic or neutral reaction. Heavy clays, as well as poor sandy soils, are not suitable. If your site is located in a dry pine forest on sand, then drastic measures will be needed - a complete replacement of sand with fertile soil. In this case, the bottom of the planting pit (or the bed of the flower garden) is better to lay with a layer of clay. In less extreme cases, the soil can be improved: we add coarse sand, peat, organic matter to the clay, and clay and organic matter to the sandy one. Well-rotted manure, leaf humus, mature compost are used as organic matter. The soil should be cultivated to a depth of at least 30-40 cm. Acidic soils are limed during digging, and alkaline soils are acidified. Phloxes prefer neutral or slightly acidic soils. When improving the structure of the soil, one should strive to ensure that it is moisture and air permeable.
Landing
To plant a seedling, we dig a hole 30x30 cm, place the roots freely, cover it with earth, press it with our hands and water it abundantly. The stem should be 2-3 cm deep. A deeper planting is undesirable, because provokes the development of the second layer of roots, which slows down the development of the plant. A shallower planting is also dangerous - the buds of renewal will be at the very surface of the soil, and in winter the bush can freeze out. The best dates for planting are early May or late August. Phlox develop well if ash and vermicompost are added to the planting pit. The introduction of a complete mineral fertilizer is also encouraged. The first time after planting, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the plants, keeping the soil moist. The planting distance depends on the variety. For tall varieties, at least 50 cm should be left between the bushes, undersized varieties can be planted denser - after 35-40 s
Natalia Sapegina
For me, phlox is autumn. An unusual smell: exciting and sad, always announced that it was time to go to school. Herbaceous perennial plants native to North America belong to the cyanotic family, which includes more than 65 species. Phlox is one of the few delightful flowers that adorn our garden from early spring to late autumn. Translated from the Greek ‘phlox’ means flame and is given to plants for the bright red flowers of some species.Phlox used in floriculture can be divided into 2 groups: undersized, often with creeping shoots, blooming in early spring, and tall, with erect stems, blooming in summer and autumn.
Spider mite
Unlike their larger spider cousins, small spider mites can wreak havoc on your garden's plants, and phlox is no exception. They predominantly feed on leaves, first causing imperceptible stripes of light tones, and then completely sucking out all the juice of the green cover.


As the mite populations continue to grow, their activity becomes more evident: the leaves begin to curl up, yellowing is observed with a rare hint of red discoloration. Ultimately, the leaves from the phlox completely fall off. Spider mites systematically destroy all available plants, bush by bush.
If the lower leaves of phlox turn yellow, then what to do in this case? Insecticidal oils and soaps work best against these parasites, but only if they are applied directly to the insects. You can also use these remedies as a preventative method by spraying a mild solution on the flowers 1 to 2 times a month. Many gardeners, with experience in dealing with these pests, advise using carbaryl sprays to combat ticks.
Jaundice
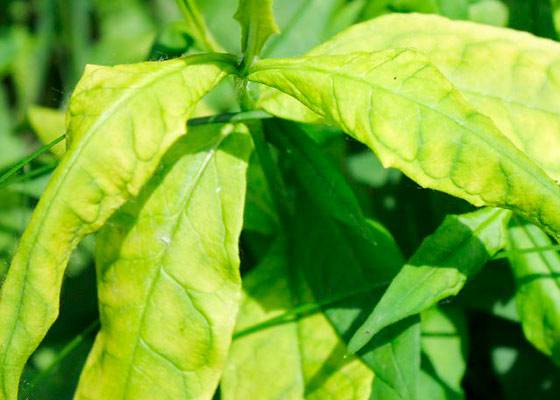


Quite a rare, but still occurring phlox disease. Spores of the fungus are transmitted in this case with the help of insect pests, usually through aphids or cicadas. The symptoms of jaundice are the following: a slow growth of a flower, a change in the color of its foliage to yellow. It is interesting that the inflorescences, on the contrary, acquire a green tint.
It is not fungi or viruses that excite this disease, but mycoplasmas - something in between, between the two above microorganisms. Age phloxes more often catch jaundice, young plants rarely get sick. Mycoplasmic diseases, like viral ones, are not cured; only competent and timely prevention can help from them.
What to do
Unfortunately, a flower infected with jaundice cannot be saved: it must be dug up and destroyed away from the garden. However, preventive measures can help: spraying in the spring with Fundazole, competent care, transplanting every 4 years with indoor growing phlox.
Viruses
When it comes to virus attacks on plants, phloxes suffer primarily from tobacco mosaics and neurotic spots. Both viruses share similar symptoms, which include yellowing of the leaves, often in the form of rings or irregular spots. Phlox leaves turn yellow and dry, sometimes they take the form of burnt paper. Young plants become stunted, old bushes finally stop their further development. The leaves may look lethargic, curled up, or simply misshapen.
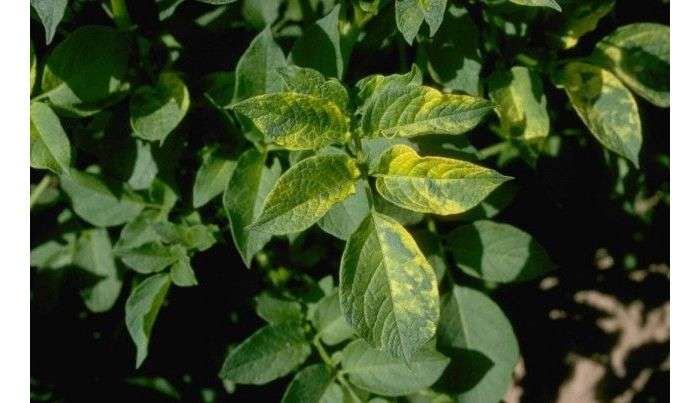


The tobacco mosaic virus is soil-borne (i.e. it may appear in your garden with new plants). Many phlox breeding experts do not know a reliable way to combat viral diseases, but they suggest taking certain measures to prevent the appearance of a disease in the garden. Firstly, it is necessary to soak gardening tools in 20% bleaching solution for five minutes when pruning between different plants or species to avoid transmission of the virus from the soil or affected plants.
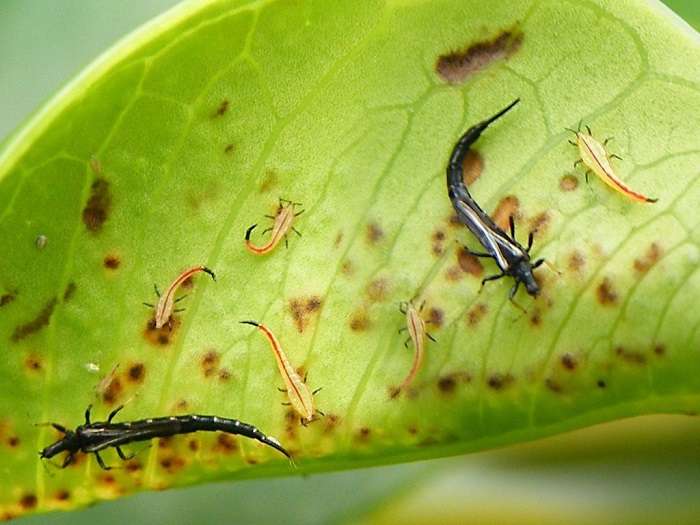


This virus is also carried by small insects - thrips. Therefore, monitoring the population of these pests is also very important. This is guaranteed to provide your entire garden with healthy flowers of all kinds. For prevention, you can use garden oils, periodically spraying your phlox.
Advice from summer residents and gardeners
Powdery mildew on cucumbers
The main recommendation for protecting phlox from powdery mildew is that it is required to strictly follow all agrotechnical recommendations.This includes aspects such as:
- selection of a resistant variety;
- adherence to the recommended landing pattern;
- choosing the best place for growing phlox;
- timely control of pests, weeds and other diseases;
- sufficient, but moderate watering, etc.
There are a number of different ways to combat this disease. Their effectiveness is the higher, the earlier this or that method or means was applied. In this regard, it is necessary to carry out regular daily visual inspection of the plantings for the presence of symptoms.
Knowing what to do with white spots on phlox, and owning ways to combat powdery mildew, you can easily defeat this harmful disease. This will allow you to keep intact not only phlox, but also other cultivated plants in the garden or on the plot.
Deciduous rot
"Leaf spot" or "leaf rot" (Botrytis) causes pimples on the affected leaves, which usually consist of a mixture of yellow and brown pigments. The disease is caused by many types of fungi, but they all appear and thrive exclusively in wet conditions.
When phlox leaves turn yellow and dry, as is the case with powdery mildew, do not overflow the plants. Phlox, which grow in large groups (bushes), can also suffer from high levels of moisture.
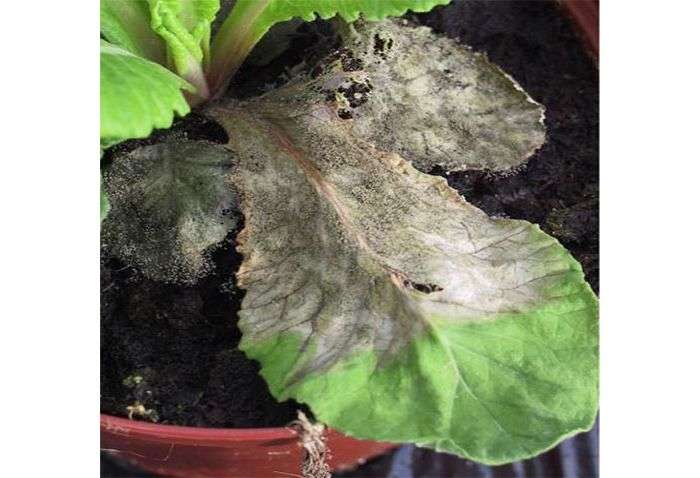


The spread of Botrytis causes the leaves to turn yellow, partially or completely. Flower buds appear discolored, gradually die, or may not open at all. The leaves eventually turn black and the stems dry out completely and die off.
Providing good air circulation is one of the best preventive measures to prevent deciduous decay. Constantly monitor the soil moisture level and the number of plants that are close to each other. If the disease has not had time to develop, remove the affected leaves and burn.
Phlox diseases: treatment and prevention
Florists do not pass by phlox indifferently. Flowers fill the garden with a light aroma, burn with a bright flame, and attract the eye thanks to the iridescence in the shades of petals and inflorescences. It is customary to attribute these flowers to unpretentious plants. But experienced florists know that unpleasant phlox diseases often occur, the treatment of which does not always lead to a positive result.
There are several varieties of phlox. It is subulate, spread apart, paniculate. Given the varietal characteristics, phlox can be planted in such a way that flowering lasts all summer. The variety of colors and the breeding of bright hybrids makes florists acquire new varieties.
But if you do not recognize phlox diseases in time, ignore the focus of the disease, the florist risks losing a whole collection of beautiful flowers.
Phlox flower diseases are transferred to a clean garden with the arrival of a new specimen. An outwardly healthy plant can carry spores of fungi, infect nearby growing flowers and gradually, instead of beautiful strong bushes, there are dried out from below, with dark spots on the leaves and poorly flowering inflorescences of the plant. Viruses and fungi cause terrible phlox diseases. They will have a long, not always effective treatment.
The reasons
Weather conditions (humidity, cold dew), thickened planting of plants, carelessness of the gardener and untimely prevention lead to the multiplication of fungal diseases.


There are enough of them in our gardens. Spores are spread at high speed from woody plants, vegetable beds, weeds.
Varieties of phlox diseases
The most common and dangerous diseases of phlox, the treatment of which is belated, can infect the plants growing nearby.
Types of fungal diseases:
- erysiphe cichoracearum, or powdery mildew;
- septoria phlogis Sacc, or septoria;
- uredineae, she is rust;
- phoma phlogis, or phomosis;
- verticillium arboatrum, otherwise verticillous wilting of stems.
Types of viral diseases:
- variegation;
- ring spot;
- curliness;
- mosaic.


Mycoplasmosis is dangerous because it spreads, albeit slowly, but if it gets caught, you need to say goodbye to the plants. While this is a rare disease. How do phloxes tolerate diseases that have been treated for a long time? Steadfastly, whenever possible, they try to console the gardener with flowering. But the appearance of the plant betrays the presence of the disease.
Viruses - what is the danger
Viral diseases are spread by garden pests: aphids, ticks, cicadas, roundworms. Plants infected with the virus cannot be cured. Florists must constantly monitor the situation, inspect their flowers, be aware of the signs of disease and fight for the survival of healthy plants.
So, with variegation, light, randomly located stripes appear on the opened flowers. The usual appearance of phlox changes, they become faded and stunted.
Ring spotting deforms the entire plant in the last period of the disease, and at first innocent light circles on the leaves give out a viral disease.


Bushes infected with the curl virus twist the leaves into a spiral, but such phloxes will no longer please with flowers. The death of the plant is inevitable.
The mosaic "decorates" the leaves with irregular spots, plant nutrition deteriorates, a lot of energy is wasted, phlox gradually dies in an unequal struggle.
Fungal diseases - we will treat
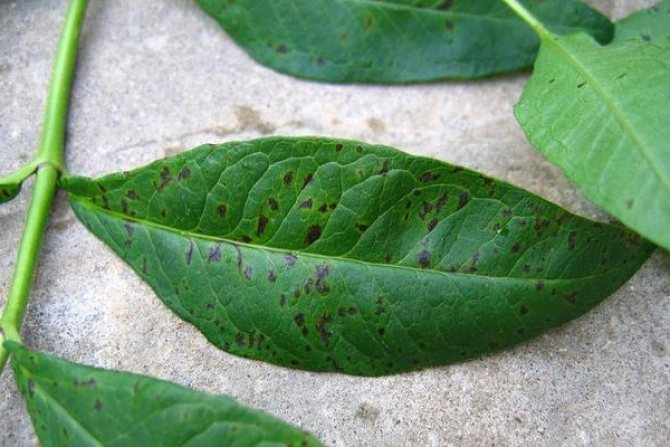
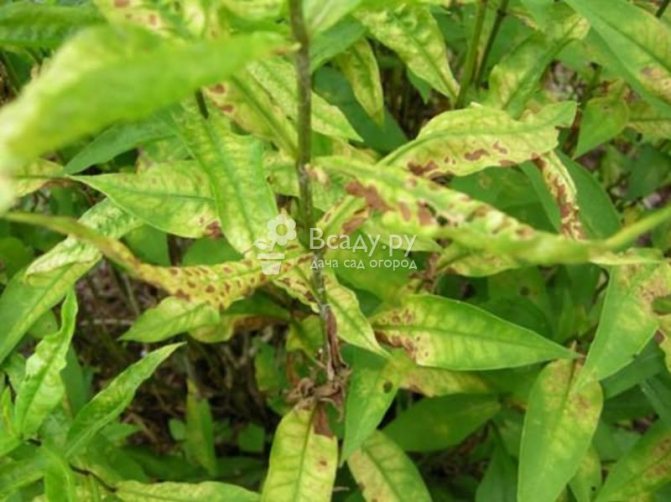
White spot and rust differ only in the color of the spots. White, gray-brown or bright brown irregular spots that appear on the leaves of phlox paniculata, gradually deplete the bushes, the lower leaves dry out. The disease progresses rapidly, spreads to other specimens. The fight can be effective, it is enough to process the bushes with Bordeaux mixture once every 7 days. Florists study phlox diseases and their treatment. Photos of affected flowers often help in the diagnosis of viral and fungal diseases.


Gardeners call verticillary wilting of stems (wilt) "lightning". Wilt affects plants during flowering, the leaf dries very quickly, the bush does not look aesthetically pleasing. The stems are resistant to the disease, and the root system is covered with a white or brownish bloom. If you are late, the disease will destroy the entire flower bed. The fungus, the causative agent of wilting, enters the soil with sour sawdust, dung soil. It thrives on acidic soils. Liming and ash treatment will prevent the development of wilt. But if this has already happened, you should remove the plant from the ground, cut the bush and rinse the roots in a disinfectant solution. Any drug against fungal diseases is suitable, for example, "Fitosporin".
Phlox are picking up buds, be careful
Almost all phlox diseases are actively progressing during the budding period. Phomosis is no exception. The plant changes its appearance, the leaves dry out, and the stem is covered with cracks. The fungus penetrates the tissues, the twigs turn brown. The disease recedes if 1% Bordeaux liquid is applied to the soil in late autumn and early spring. Fomoz can be introduced into the soil with moldy manure, untreated sawdust. The fungus quickly infects the plant. Phlox disease is hard to survive.
The treatment, fortunately, works. The upper young leaves are seen to be healthy.
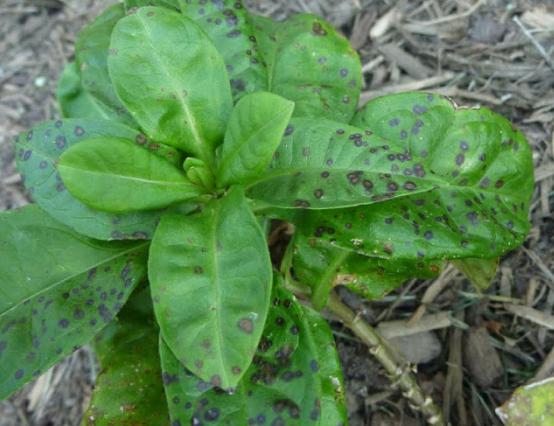


Brown dots and spots on the leaves appear from septoria. Phlox turn yellow, leaves are framed by a brown or purple border. The trunk is bare, the sight of a sick bush is not happy. But the disease will weaken from the therapeutic spraying of a mixture of milk of lime and copper sulfate diluted in water. Three sprays at intervals of 7-10 days are enough for the disease to go away. Miss the chance, cut out the affected stems and burn them. The ground is watered with a copper-containing lime 1% solution. If phloxes receive care, the diseases will recede, and no hardships will interfere with the beautiful flowering.
Insidious white dew
Everyone is used to thinking that powdery mildew affects the tender and juicy leaves of peppers and cucumbers.Phloxes, although they have a hard stem, cannot withstand this insidious fungus.
White bloom appears on plants in the form of scattered flour carelessly. It grows very quickly. The color of a dense, suede coating changes. It turns brown or gray, it oppresses the plant. The leaves begin to dry out, the respiration of the plant stops. Plants are often affected during wet summers. Infected flowers are sporules of the fungus Erysiphe Cichoracearum. All parts of the plant located above the ground suffer from the disease.
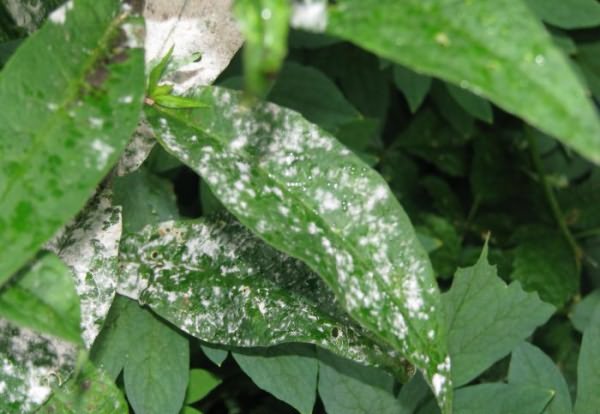


The spread of the disease is facilitated by overfeeding plants with nitrogenous fertilizers in the spring. Pampered bushes are not able to fight such a scourge. Any diseases of phlox are dangerous. Powdery mildew is the most dangerous of these.
Care
When creating phlox mixborders, the first step is to prepare the soil for planting. These flowers prefer loose, neutral, nutritious, breathable soil. Filling it with fresh manure is strongly discouraged. Only well-rotted, three-year-old manure is suitable for these handsome men. Top dressing during the summer in the doses indicated on the fertilizer package strengthens the paniculate phlox bushes.


The benefits of fertilizing with mineral fertilizers are obvious: when plants receive timely nutrition, they get sick less. Elimination of excessive soil acidity, drainage from flower beds in rainy seasons and watering in dry seasons, give plants a chance to avoid insidious diseases.
Prophylaxis
Processing with Bordeaux mixture twice a year will prevent fungi from spreading. Spraying with "Epin" will strengthen the immune system. A good result is obtained by pruning the tops during the rainy season. This postpones the flowering period. If the florist conducts timely treatment for phlox disease, powdery mildew will not be able to harm.
Any suspicion of the development of the disease requires preventive measures. Treatment with ash, Bordeaux liquid, antifungal drugs will help prevent the disease.


In the fall, the branches break off and are burned, the bush is mulched, earthed up with earth. Frost-damaged roots of phlox sticking out of the ground can damage the health of the flower.
Treatment or goodbye
Even the best and most experienced grower has periods when preventive measures are not enough, and diseases win. Intensive, systematic treatment preserves some of the plants. Fungal diseases can still be treated.
If there is room, it is better to plant the bush by transshipment, and treat it for 3 weeks. Does the treatment fail? Destroy the plant without regret and do not risk your whole collection of flowers.
We noticed that the culprit of phlox disease in the flower garden is a virus - a plant on fire. Why is the recommendation so categorical? There is no other way. Neither the fence, nor in the compost, nor to the neighbor can carry the infection. She will return to your flower bed very quickly.
If fungal diseases of phlox are found, the treatment will be sparing. Flowers heal successfully with proper care. The main thing is to find the hearth and destroy it, to disinfect the soil.
Abundant humidity
Another of the most common culprits for the yellow appearance of phlox leaves is its primary survival resource - water. In general, most phloxes require moderately moist soil for productive growth and abundant flowering, but too much water prevents the plant from getting enough nutrients because the roots become waterlogged and deprived of oxygen. Eventually, the roots start to rot, but before this stage the leaves turn yellow and then fall off.


Never water your phlox if the top 2 to 3 cm of soil is saturated with moisture. If standing water remains a problem despite reducing and adjusting irrigation, improve drainage by adding a small amount of compost and medium-sized pebbles to the topsoil. Compost decomposes and weakens the soil, facilitating drainage, and small stones will prevent it from caking and compaction.
18
EMERGENCY AID (how to help a plant to cope with diseases)
Olga, pepper and tomatoes are fed 2-3 times a month. Top dressing is combined with watering. Pepper is more responsive to nitrogen fertilization. But phosphorus and potassium will not be superfluous either - they improve the quality of the fruit. Tomatoes, however, now want everything at once, and nitrogen, and phosphorus, and potassium. Today it rains in many places. They very strongly leach nutrients from the soil. Especially potassium. So it is necessary to feed. You can take either ready-made fertilizers for feeding, now there are many different ones on sale. Or feed with fermented grass, or mullein infusion - they will give more nitrogen, ash is a phosphorus-potassium fertilizer, you can add it a little and embed it in the soil, you can make an extract from ash and water it.
Nina! Thank you for your advice and I will. (F)
Olga Moiseeva-try stimulants. Will help plants to hold out. Epin zircon and others also HB-101
Girls, please tell me - two troubles -
First, I planted onion sets on a turnip, and today I found a worm on an onion. How to be. I heard that with salt water ...
Agrotechnics of planting
Phlox diseases most often affect plants in the spring and summer. That is, it is at this time that it is necessary to show maximum attention to the health of plants. Let's decide when is the best time to plant phlox. There are no restrictions on the planting period; plants can be planted during the entire growing season. Phloxes are very tenacious, they will easily take root even planted on the hottest days, but they will bloom only the next day. If you are decorating a garden in the spring, then this can be done immediately after the snow has melted and the soil has thawed. However, if you want the plant to bloom already this year, then the following rule must be observed: planting must be done before mid-May. In this case, the flowering time is delayed by several weeks, but this is not too critical.
If planting occurs in the fall, then it should be carried out from the second half of August to the end of September. At the same time, it is impossible to pull too much with planting, because if the autumn is early and cold, then the plants may not have time to take root and will not survive the winter well. In this case, a lot depends on what winter will be like. If it comes out cold, the roots will freeze.
You can plant these flowers in the summer, but it is at this time that phlox diseases are very active. To avoid them, it is necessary to plant the plants correctly. There should be an earthen lump on the rhizome, while abundant watering must be ensured. All inflorescences must be cut off mercilessly. This is necessary so that all forces are spent on rooting. Flowering takes up a lot of resources, which can be critical for the plant.
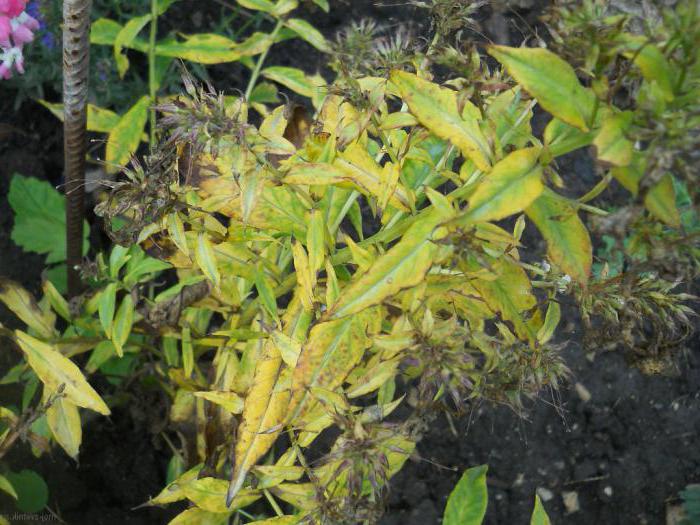


Variegated
This is the most dangerous virus that can instantly destroy a tough-looking bush. The fact that it is infected with variegated leaves is indicated by the appearance of light stripes of different widths on inflorescences and leaves.
The virus first deforms the petals, changing their color, then completely destroys them in a short period. But before dying, the flower manages to infect neighboring plants with the help of pollen, seeds, insects, tools.
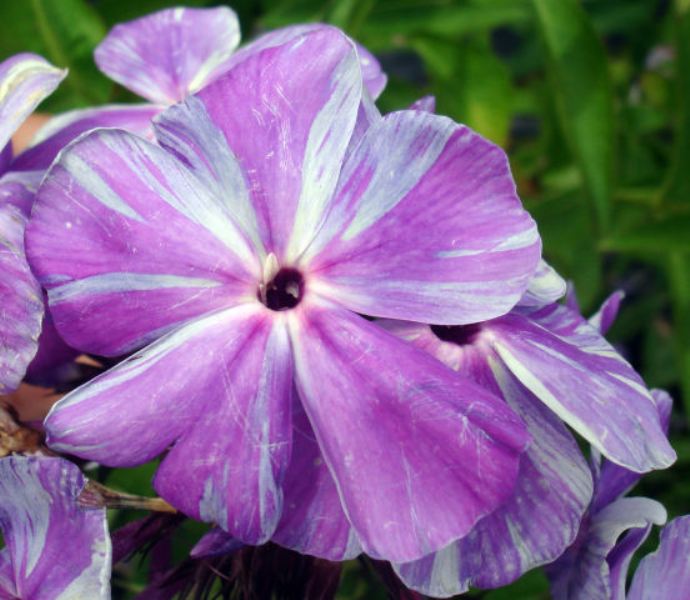


This disease can be quickly recognized by comparing the color of the greenery or inflorescence with a photograph of this variety. But only a detailed examination in the laboratory will give an accurate result.
If the petals are white, then in this case, carefully examine its peephole. In a healthy person, the eyes will have a distinct border, and in those infected with variegated leaves, the borders are erased, that is, the color of the eye merges with the white petals.
Every year, breeders release new varieties of phlox, therefore, during the purchase, it is recommended to carefully compare the color of the flower with a photograph of this variety, otherwise the risk of acquiring a diseased plant from unscrupulous sellers increases, thus ruining the entire home collection of indoor flowers.
It is especially difficult to recognize this viral disease in varieties that initially have a variegated color. In this case, we carefully look at the stripes. In the patient, they should be expanded towards the end, periodically interrupting. A healthy one has even stripes.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for this virus. It remains only to dig up and destroy the infected bush, and throw the earth away, or even better, burn it.
Then thoroughly disinfect the pot and tools. Then, for a month, it is recommended to carefully monitor other plants in this room, whether they have had time to become infected with this virus. If the flower grew on the street, then you need to carefully examine all the greenery growing around it, whether the virus has been transmitted to them.
How to transplant phlox
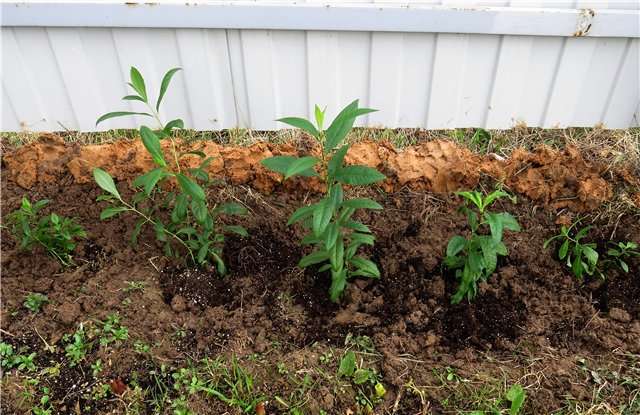


It is better to transplant phloxes at the time recommended for transplanting peonies, that is, in late summer or early autumn. This is due to the fact that in early spring, when it is still cold, their roots are already beginning to grow.
In fact, phloxes can be moved to another location even in the summer when they are blooming. Only this must be done very carefully, leaving as large a clod of earth as possible on the roots.
High-quality rooting of transplanted plants largely depends on the condition of the soil. Flowers love lands that contain a lot of organic matter. Flowers need frequent watering and this must be taken into account when choosing a planting site.


After the bush is planted, sprinkle it with soil and water it immediately so that all voids are filled with earth. From above, it is necessary to mulch the flower well with humus or compost. All weeds must be removed from the flower bed in a timely manner, the soil must be maintained in a loosened state. Top dressing after transplanting should be carried out on a regular basis for 1-2 months.
"Rodents"


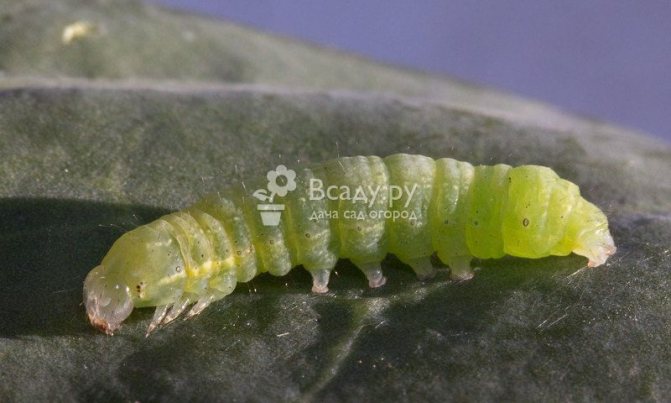
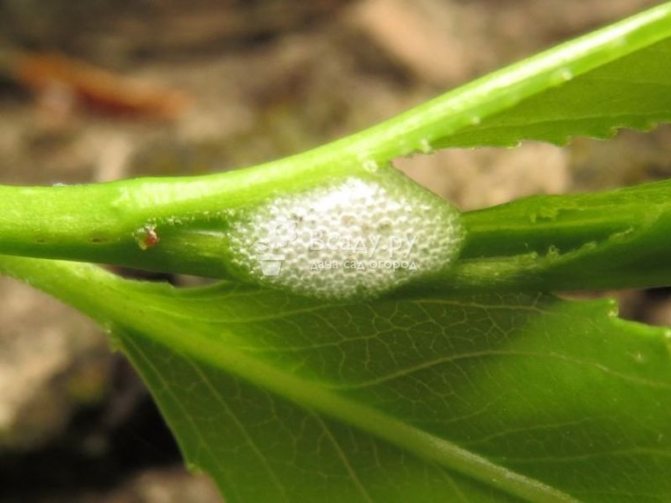
There are a number of pests that eat leaves, stems, buds and flowers from phlox, these are - slugs, snails, slobbering penny, various caterpillars... These pests are especially dangerous during the period when young shoots and seedlings are growing back.
If there are still few of them, then it is better to collect them by hand and then destroy them. Otherwise, it is worth treating the plant with preparations against sucking and gnawing insects. You can also fight slugs and snails by arranging traps for them in the form of large leaves, planks, pieces of cloth. They usually hide from the sun there during the day. You can also scare off pests from plants if you scatter around ash, tobacco dust, sawdust, metaldehyde granules. Recently, more and more phlox are harmed thrips, which are almost invisible due to their small size, but the results of their activities are quite tangible. This is most noticeable in varieties with a dark color. Indeed, feeding on plant juices, thrips damage the surface of the petals and leave ugly whitish traces in the form of blurry spots.
To destroy these insects, it is necessary to timely process the inflorescences even in the budding stage with any of these systemic insecticides: Aktar, Commander, Confidor, etc.
That, perhaps, is all that I wanted to tell about the diseases and pests of our beloved phloxes. Of course, I wish you, my dear readers, that the plants in your gardens never get sick, but as the saying goes, "he who is warned is armed."


See you soon, dear readers!
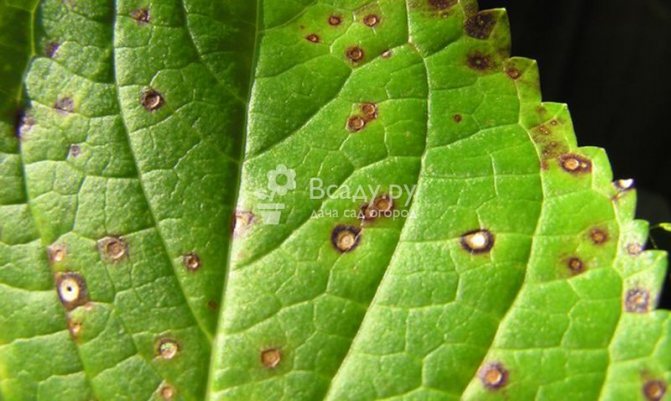
Brown and rusty spots on the leaves
If you see brown spots on the leaves, like with chickenpox on human skin, which become more every day. Over time, they merge into one large spot, which completely destroys the leaves, making them yellow, then bringing them to a state of dust.
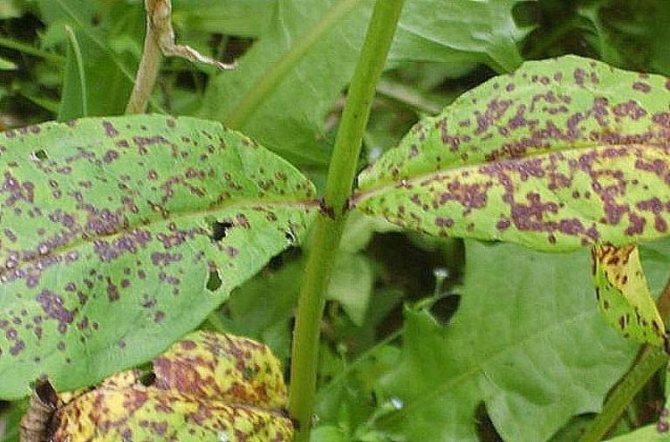


This disease occurs due to a fungus that can multiply in any weather conditions. Airborne. You can get rid of it with any copper-containing preparation by spraying the bush and soil. This procedure, as a preventive measure, does not hurt to do it every two weeks.
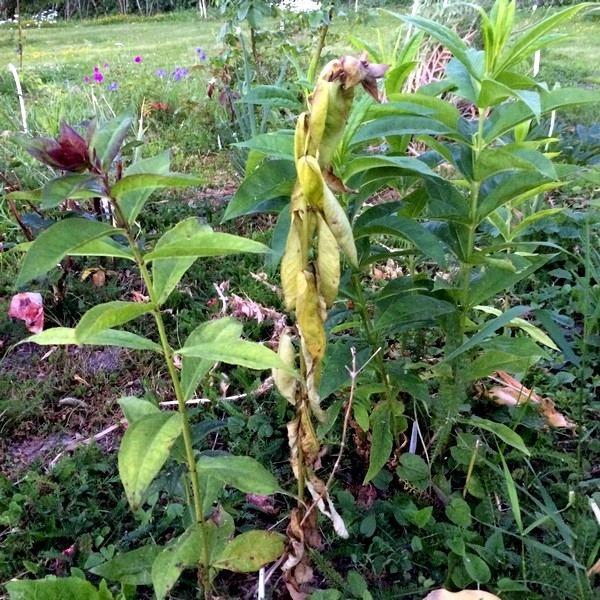
Verticillary wilting
If yesterday a blooming culture suddenly faded today, tear off a leaf from the stem and carefully examine its root. With verticillary wilting, the petiole is brown. This is a fungus that parasitizes in blood vessels.
The stem will look straight, healthy, but it will be decorated with twisted and yellowed leaves. After three months, the flower completely dies. Unfortunately, there is no escape from this fungus.
But, as you know, hope dies last. You can still try to save the vegetation. First, they dig it up. Then the roots are carefully shaken off the ground, thoroughly washed in the preparation "Maxim". For the first time it can be planted in a pot, before putting "Trichodermin" in the ground.


If you managed to notice the first signs of the disease, then immediately water the soil with the preparation "Maxim" and sprinkle with ash to reduce its acidity.
Preparing for winter
This is a very important step in preventing many phlox diseases. A photo taken by professional gardeners allows us to say that phlox, properly prepared for winter, come out from under the snow strong and strong. In order for the phlox to overwinter calmly, it is necessary to cut off the ground part at the end of autumn at the end of autumn. Most gardeners do this, leaving only low stumps, about 15 cm in height. Experts also recommend to level the plant with the ground level. This is when it will be able to winter best. In the first version, various pests and spores with diseases will be able to winter on the stumps. The second option excludes such a possibility, which is why phlox diseases and the fight against them are minimized. A photo of a flower bed, which was trimmed according to all the rules, looks much more spectacular than one that was not trimmed for the winter. Pruning is done at the end of October, when the weather is cold outside. In this case, the base of the phlox and the soil around it must be treated with agents against various diseases. After that, you will need to wait about 10 days and mulch the planting site well. This set of measures will allow the plant to winter well, and will also serve as an excellent preventive measure against various diseases.


What phloxes can hurt
This is actually a very broad topic. There are a variety of phlox diseases. A photo of an infected plant is always very different from healthy counterparts, so even a layman can easily distinguish it. Despite the fact that phloxes are considered quite resistant to diseases and pests, under bad conditions they are successfully affected by viral and fungal, as well as mycoplasma diseases. The very first sign of a disease is an underdeveloped plant species. The sizes and shapes of all parts of the affected plants change. For example, it is quite easy to recognize plants affected by mycoplasma: they have a small leaf size and chlorosis, modified parts of plants, and a different color of buds. In addition to diseases, phloxes can be attacked by pests such as nematodes, slugs, caterpillars, cruciferous fleas and pennies. Let's continue to consider the topic of how to recognize an ailment and cure phlox. Diseases, the treatment of which is possible, we will cite below, in all other cases, only uprooting the diseased bush and disinfecting the soil will help.


Eliminate white plaque
To successfully defeat this infection, you can use different means and methods:
- Fungicides (Skor, Topaz, Oxyhom, Topsin, Fundazol). The disadvantage of using chemicals is that the infection quickly adapts to them and the funds cease to work.
- Infusion of hay dust: 1 kg of hay is poured with 3 liters of water and insisted for 3 days. The finished infusion must be filtered, diluted 1: 3 with water. It is necessary to spray flowers with a solution once a week, at least 3 times. For 10 liters of this ready-made solution, you can add another 5 g of copper sulfate.
- A solution of linen (soda ash) 1%. It is necessary to spray diseased plants with a solution three times over the summer, taking breaks between treatments in eight to twelve days;
- Copper-soap solution. Dissolve green soap (250 grams) and copper sulfate (20-25 g) in 10 liters of water. Spray two to three times weekly (every 8 days). It is better to prepare the solution in an enamel or wooden container: in one, a solution of green soap is made (in 5 liters of water), in the other - a solution of copper sulfate (in 5 liters of water), then both solutions must be mixed. You should get a bluish-white liquid;
- Bordeaux liquid solution. Prepare a 0.3-0.5% solution and spray it on diseased plants;
In order for spraying to give the greatest effect, it is better to carry out it in calm weather, in the late afternoon, so as not to burn the weakened plant. Solutions prepared according to folk recipes must be prepared fresh for each spraying.
Ideally, phloxes, on which white bloom has appeared, are best removed from the site. And if a certain variety in your flowerbed is constantly sick with powdery mildew, it is better to replace it with another one - more stable.
It is best to prevent the appearance of the disease, for which it is necessary to examine the flowers more often, to check what condition they are in. It is good to periodically remove fallen leaves and debris from the plant, dust the loosened soil with ash at the roots, near the stem. Fertilizers are best given to phlox complex, in the first half of summer.
Sources of information: the magazine "Favorite perennials in the garden" and the book "Caring for phlox" (Krasnova NS).
Wintering in the basement
Many gardeners who have already encountered such an unpleasant phenomenon as diseases of perennial phloxes prefer to dig them up for the winter. For this, special buckets and boxes are prepared, in which the soil is placed, and ventures and plants with a lump of earth. This process is very time consuming. It is necessary not only to dig up and transfer the bush to the basement, but also to create suitable conditions. It shouldn't be too warm or cold, damp or dry. Any of these kinks can kill your plant. Therefore, this method can be considered too complicated and difficult, it is much easier to just cover the plant well, for example, with a bucket of sawdust or humus. It is best to do this in early October, at which time the soil is still warm enough. In the spring, you will need to carefully remove the embankment from the bush.
Physiological disorders when growing phlox
It is important to know when growing phlox, pests and diseases are not the only problems that you may face. Improper soil composition, violations of agricultural technology and cultivation rules lead to damage to plants, which can lead to their death or disease. In some cases, they can be similar to fungal and viral infections.
Drying and falling leaves
Most often it is a consequence of a lack of moisture. The plant reduces the area of evaporation of moisture by shedding the lower leaves. Similar symptoms occur when phlox is transplanted to a new place in the summer. It is necessary to adjust watering, shade the plant and introduce spraying of the ground part.
Cracking stems
Often the growth of stems is accompanied by their longitudinal cracking. Then the lesions are covered with growths (callus), and the stem becomes brittle, thinner and often breaks off under the weight of the foliage. Cracking can occur due to lack of watering during hot and dry summers.
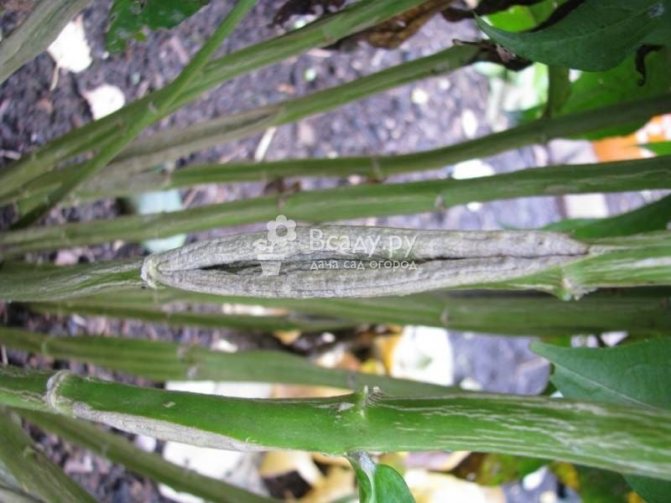


Phlox stems cracking
To avoid the problem, do not allow thickening of the plantings and an excess of nitrogen in the soil. In dry weather, water in the evenings, after the heat has subsided.Consider supports or fences for tall species of phlox.
Care
When creating phlox mixborders, the first step is to prepare the soil for planting. These flowers prefer loose, neutral, nutritious, breathable soil. Filling it with fresh manure is strongly discouraged. Only well-rotted, three-year-old manure is suitable for these handsome men. Top dressing during the summer in the doses indicated on the fertilizer package strengthens the paniculate phlox bushes.
The benefits of fertilizing with mineral fertilizers are obvious: when plants receive timely nutrition, they get sick less. Elimination of excessive soil acidity, drainage from flower beds in rainy seasons and watering in dry seasons, give plants a chance to avoid insidious diseases.
Rust


This disease appears in June as rusty brown spots. Then these spots begin to spread and eventually completely cover the entire leaf plate. The plant loses leaves, starting from the bottom of the stem, and gradually becomes bare.
For the prevention and treatment of this disease, we spray the bushes themselves, as well as the soil around them, with solutions of Bordeaux liquid, copper oxychloride, ferrous sulfate in accordance with the instructions for these drugs.
Fungal diseases
Very often phlox diseases are associated with parasitic fungi, for the development of which moisture and a certain temperature are needed. The favorable combination of humidity and temperature determines their mass development and, accordingly, the appearance of diseases. The spread of fungal infection occurs with the help of wind, water, insects, people who care for plants. The infection persists on the affected plant debris, in the soil, in sowing and planting material, as well as on perennial weeds.
With the strong development of powdery mildew in phlox, leaves dry out, as a result of which not only the decorativeness of plants, the quality and flowering period decreases - all physiological processes are also disturbed in diseased plants, which negatively affects their general condition.
It should be noted that the degree of susceptibility to various types and varieties of phlox fungal diseases is not the same.
To carry out preventive (preventive) measures, it is necessary to know the signs of the main diseases of phlox, and diseases of fungal origin, as a rule, are mainly characterized by the appearance on the leaves and shoots of plants of various kinds of spots, necrosis and plaque.
The most common and harmful fungal diseases affecting phlox are:
Verticillium wilting (causative agent - fungus Vnticillium albo-atrum)
Powdery mildew (causative agent - fungus Erysiphe cichoracearum f. Phlogis)
Phomosis (causative agent - mushroom Phomaphlogis)
Also diseases associated with leaf spots caused by a number of pathogenic fungi: Altemaria tenuis, Septoria phlogis, S. phlogina, S. divaricatae, S. drummondii, Phyllosticta decussatae, Cercospora omphacodes.
Strict adherence to agrotechnical methods for caring for plants - correct watering, the use of mineral fertilizers with increased doses of potash, timely preventive measures - increases the resistance of phlox to phytopathogenic fungi.
Verticillary wilting. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Verticillium albo-atrum. Withering of phlox shoots is associated with damage to the plant's conducting system. A soil pathogen that enters the vascular system of a plant through a root system damaged during planting or tillage (for example, cuts when loosening) or wounds caused by pests (for example, a wireworm). Then it spreads, clogs it and poisons it with its toxins, as a result of which there is a sudden wilting of leaves and shoots. The leaves turn yellow, turn brown and dry out, remaining hanging on the plants.
Species and varietal sensitivity to the pathogen is observed.The fungus can affect all or part of the vessels. The nature of leaf wilting depends on this - general or one-sided. Plants are much stunted, rarely form normal inflorescences or die.
Most often, the symptoms of powdery mildew are characterized by drooping of the leaves and tops of individual shoots on the phlox bush, which is associated with the loss of turgor by the cells and tissues of the plant. The main reason for the death of shoots is the lack of nutrients and water in the plant, which is caused by the cessation of their flow through the dead vessels. Outwardly, wilting leaves and shoots usually look healthy and the disease resembles wilting and drying out from lack of water, but darkening and vascular necrosis can be seen on the transverse sections of the shoots, and under the microscope, mycelium is found in them.
Powdery mildew is focal in nature, is especially pronounced on acidic and light soils due to their weak microbiological activity. On rich humus soils with high biogenicity, the disease manifests itself less strongly. The temperature favorable for the development of the disease is about 25 ° C, therefore, the spread of the pathogen in July and August increases, and with a cold snap, in September, at the base of the stem, sometimes new healthy shoots develop. The introduction of large doses of nitrogen fertilization also contributes to the development of the pathogen. According to some experts, the development of the disease can be provoked by waterlogging of the soil.
The primary source of infection is contaminated planting material, seeds collected from diseased plants, poorly rotted manure, compost and sawdust. It has been noticed that strawberries, nightshades and pumpkins are especially susceptible to Verticillium albo-atmm and are its accumulators.
The pathogen in the form of mycelium remains in plant debris, and in the form of microsclerotia in the soil retains its viability for up to 15 years. Distributed everywhere.
Good results in the fight against verticillosis are obtained by the introduction of the biofungicide Trichodermin into the soil during the growing season of plants at a dose of 2 g per plant or its analogues, for example - Glyocladin (one tablet is applied under one plant). Particularly valuable plants can be watered with a solution of the biofungicide Fitosporin-M (strictly following the manufacturer's recommendations), diseased plants can be etched in the same solution, after which they are planted in a new place. For dressing rhizomes, you can also use 0.2% solutions of fungicides Vitaros or Maxim.
In case of mass infection and death of plants from powdery mildew, it is not recommended to occupy these areas for phlox and other crops susceptible to this disease for 10 years.
It is necessary to collect and be sure to destroy all affected plant debris at the end of the growing season.
Choosing a landing site
Probably, it's not a secret for anyone that many phlox diseases are the result of an incorrectly chosen place or soil. That is, the conditions are unsuitable for the life and development of plants. You need to pay attention to the conditions in which phlox grow in the wild. Moreover, the most suitable climate for them is moderately warm and humid. In such places, the soil is loose and very rich in organic elements. Thus, in the garden, it is necessary to choose the appropriate conditions: fertile soil, as well as partial shade from trees or shrubs. Phloxes love the sun, but direct sunlight can be detrimental to them.