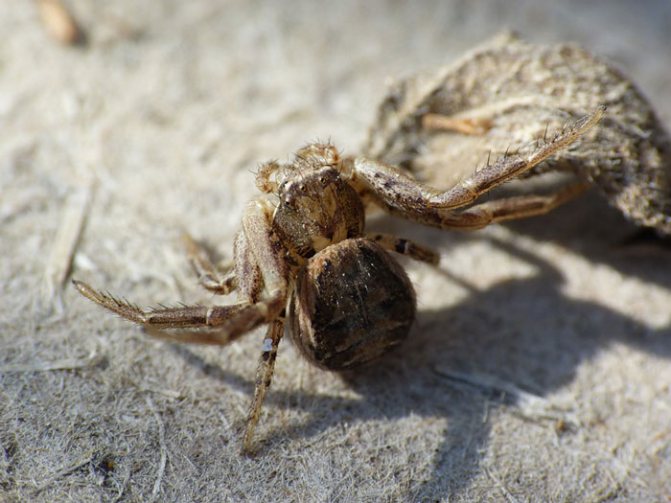
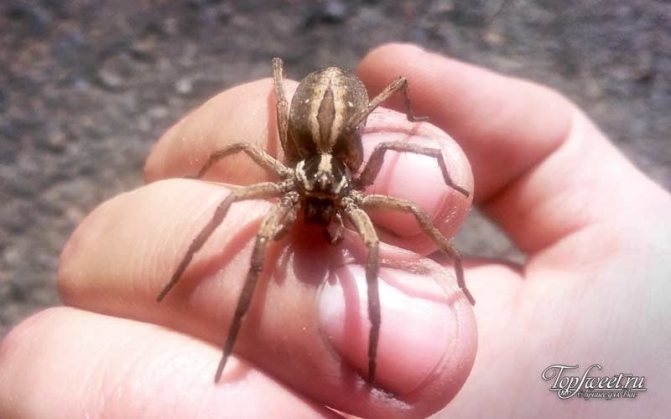
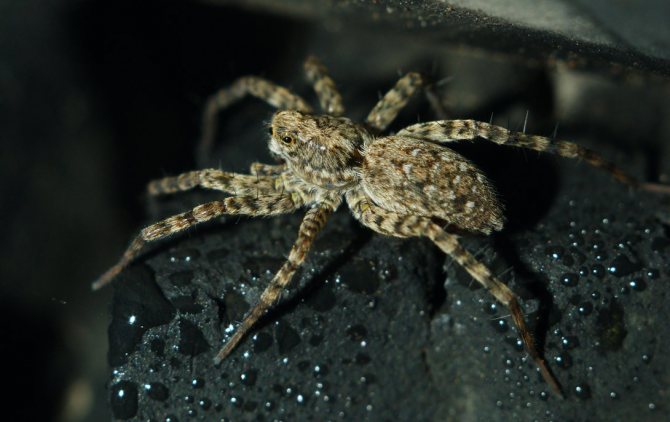
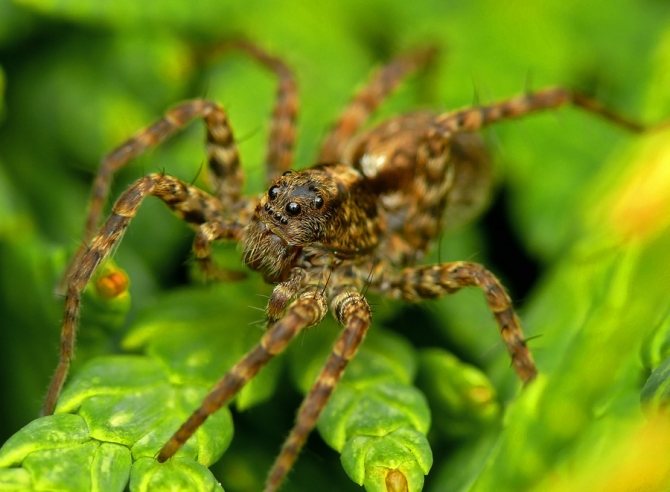
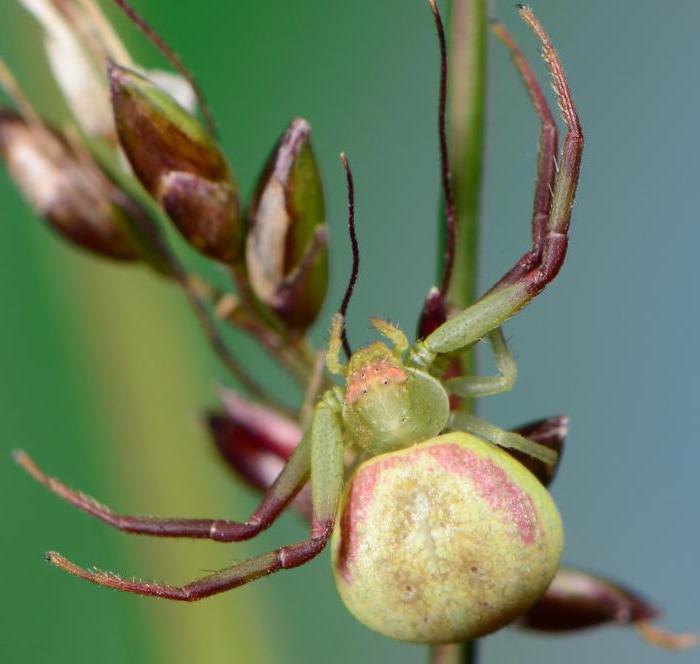
The side walker spider or crab spider is one of the most interesting species of the arthropod order.
Spider crab
Unlike his other brethren, he does not lure the victim into a web, but hunts, merging with the environment, and taking a motionless pose.
He immobilizes the victim by injecting poison into it. Eating pests, the crab spider is a welcome guest on farmland. Scientists are greatly interested in the appearance of the sidewalk spider and the life cycle of a small predator.
Body structure
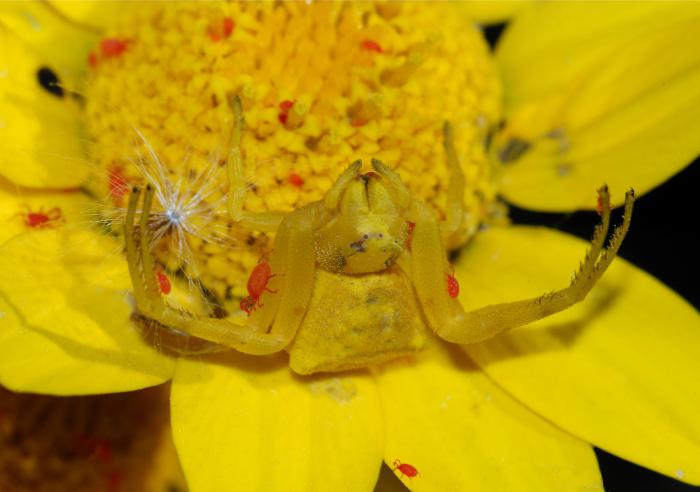
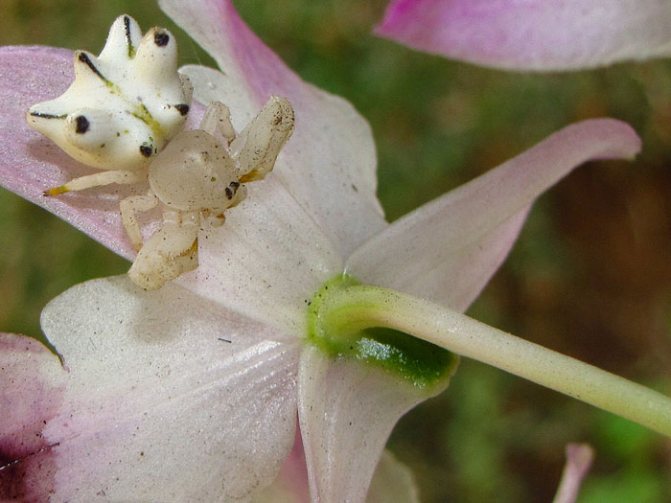
It is easier to analyze the structural features of the body by the floral yellow sidewalk spider (Misumena vatia). The name of the subspecies is explained by the habitat. Misumena is most commonly found on mushrooms and yellow flowers. These plants are an excellent camouflage from predators.
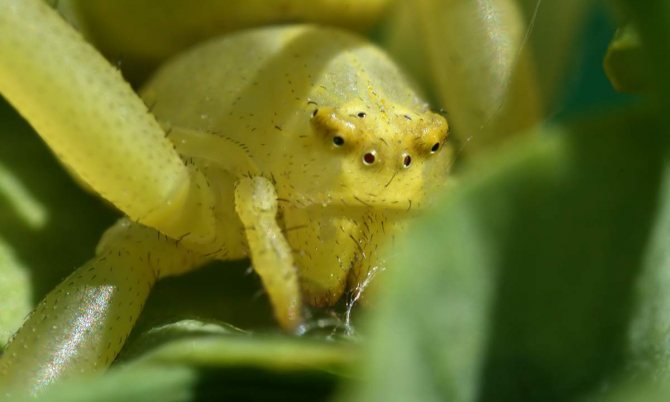
The body of a predator can be conditionally divided into two parts, connected by a small tube. The back row of eyes is wider than the front. Hind eyes set wide apart. The jaw is vertical, the segments are flattened and closely spaced.

Chelicerae claws are small but thick. Large venom glands occupy most of the cephalothorax and end behind the brain. Spider warts are found on the underside of the belly.
The body of the male is usually covered with silky protruding hairs. The knees are long, but thinner than the thighs. The shins are almost cylindrical. The front pairs of legs are equipped with two rows of large ventral spines and smaller spines at the edges of the limbs.
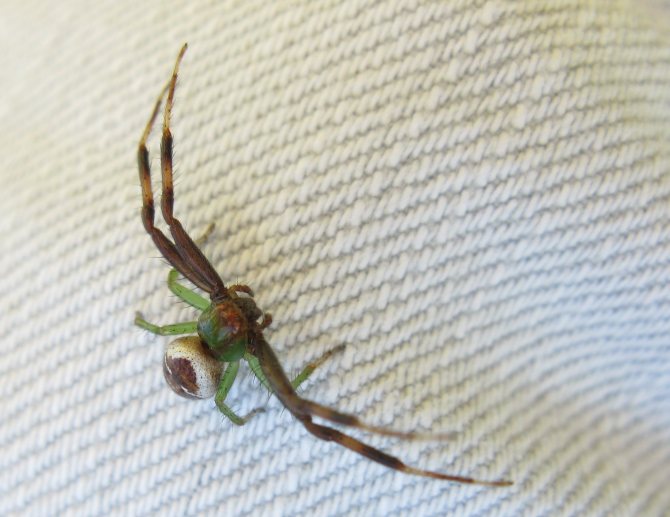
Most of the representatives have a smooth body. Individuals are called "crabs" because of the characteristic limbs that help to move not only forward, but back and sideways.
The body is distinguished by the following features, characteristic only for this species:
- the head and chest are located separately from each other.
- Two pairs of limbs are adjacent to the head. They have claws with poisonous glands.
- Leg tentacles are formed from six members.
- On the frontal part there are 2 main eyes, 6 additional ones.
- The ability to move sideways is determined by the front pairs of limbs turned upward.
- All organs are located inside the oval-shaped belly, under which the genital opening is located.
- The front legs are 4-5 times longer than the rest.
- The body is very small, not exceeding 1 cm in females, 0.5 cm in males.
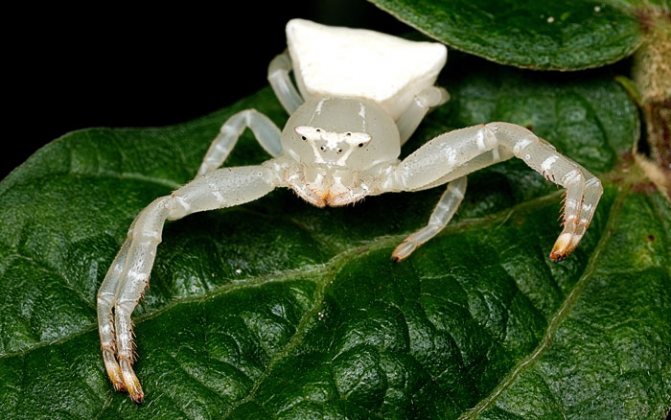
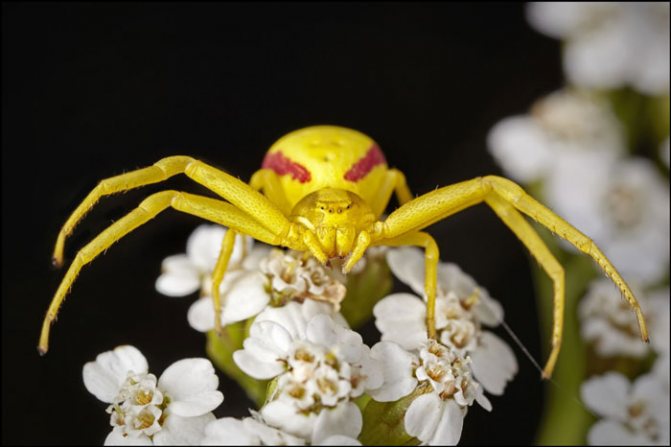
- It can change its color according to the principle of a chameleon.
The structural features of the body help deftly and imperceptibly wade sideways between leaves, flowers, penetrate into a crack in a tree or run across to another surface.
Sydney funnel spider


This is one of the most aggressive representatives of arachnids. Lives on the Australian continent. He prefers to settle in humid forests, on the coast under rocks or not far from people - in gardens and parks. The length of the spider usually does not exceed 5 cm. The color is dark brown or black, sometimes with copper stripes on the legs.
The atrax bite is painful, and thanks to its powerful chelicerae, it is able to bite through a leg even through leather shoes. Not every spider attack ends with the injection of poison, but if he did it, then the person could face death.
Food
Despite their body size, these arthropods are predators. They do not twist spider webs to catch prey. They only need the web for comfortable movement.
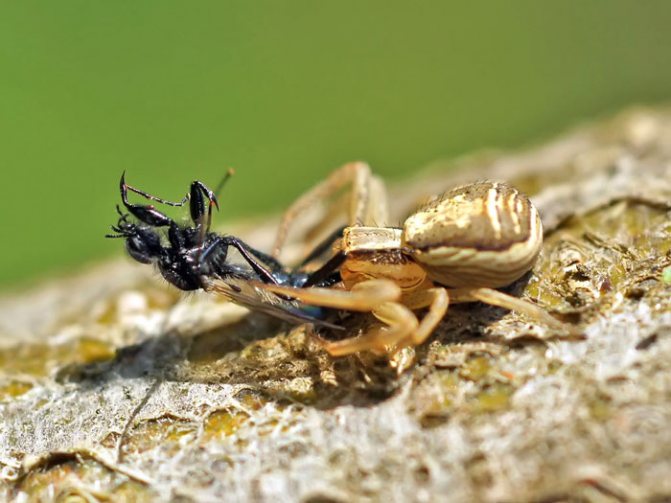
Small predators merge with the environment, waiting for their prey. They can be absolutely motionless for a long time. They attack not only small insects - those whose size is larger than the hunter also turn out to be prey.


During an ambush, cunning predators disguise themselves, spread their forelimbs wide apart, preparing to attack instantly. If prey is nearby, the arthropod approaches the victim, injects poison.
Poisonous substances affect the victim's nervous system, immobilizing it for a long time... This aggressive behavior is explained by the fact that the front legs of the spider are equipped with claws, which contain a powerful poison that paralyzes prey.
When the victim is immobilized, the arthropod sucks out all the vital juices from it. Due to its weak jaw and small size, the side walker does not absorb its food entirely. Bumblebees, locusts, bees, flies serve as food.
Eriovixia gryffindori
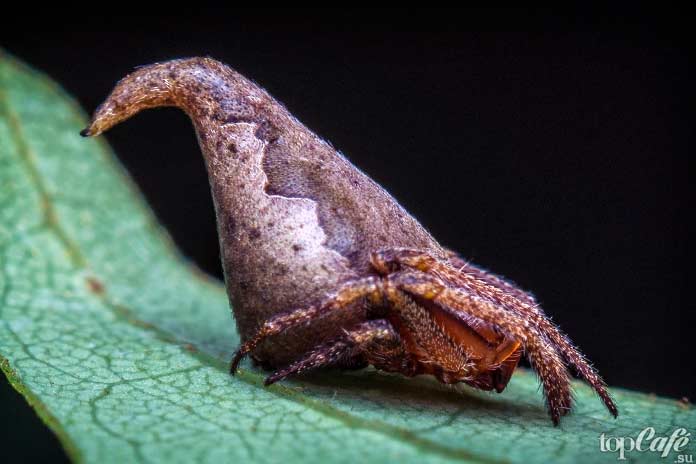


More recently, in 2020, a completely new species of small spiders was discovered in India, which got its name after the Sorting Hat from the wizarding world of Harry Potter. This baby got its name due to its appearance. As one of the members of the group that discovered this species admitted, he is very fond of the story of the young wizard, and when he saw the insect, first of all, he thought about one of the artifacts of Hogwarts.
So far, the way of life of Eriovixia gryffindori has not been studied, but its discovery indicates that our planet is very amazing and conceals with itself a lot of unknowns.
11
Habitat
Side walk spiders do not like hot or cold climates. They prefer to live in mild temperate climates. They are not found in hot deserts and in icy terrain.


Trees, flowers and even soil become the habitat of arthropods. A cocoon with larvae is placed on vertical surfaces - plant stems, flower leaves.
Some representatives of these spiders are limited to a specific area of residence. For example, the subspecies Xysticus sabulosus Hahn lives exclusively in lichens
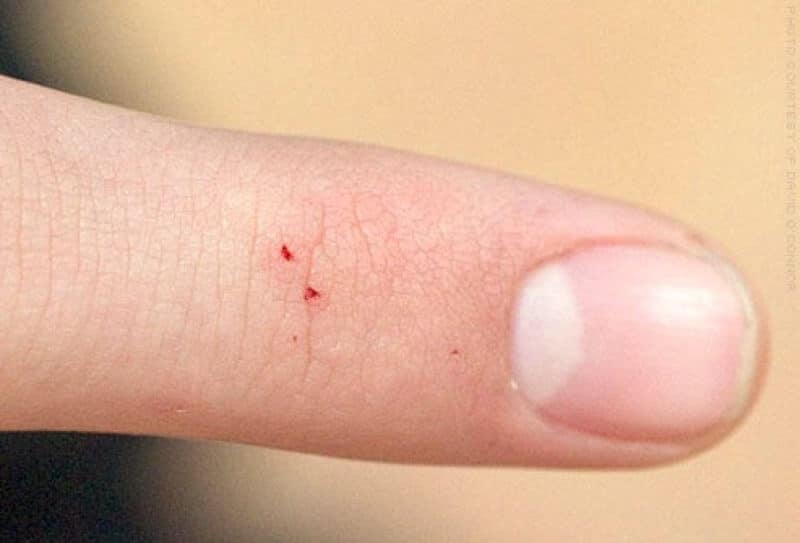
What to do with a bite
Side walk spiders are not dangerous for humans, but their bite is still unpleasant with the following symptoms:


- redness, swelling, itching and burning of the bite site;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- weakness.
With a bite of a sidewalk spider, it is enough to apply ice to the wound and take antihistamines. The bite site can be treated with Zvezda balm or Fenistil-gel.
We often mistake spiders for ordinary insects, but this is wrong. They have at their disposal poisonous glands containing toxins. All types of sidewalk spiders must be handled carefully to avoid the unpleasant sensations that are caused by the bites of these crumbs.
Features of behavior
Side walker spiders do not weave webs, but use the webs to move around. Gusts of wind can throw spiders over long distances. From the side, the illusion is created that the spider flies freely through the air.
In autumn, in one day, they are able to migrate several kilometers.... For arachnids, this is a significant distance. To stop, the side walker throws off the cobweb that clings to the plants that act as a brake.
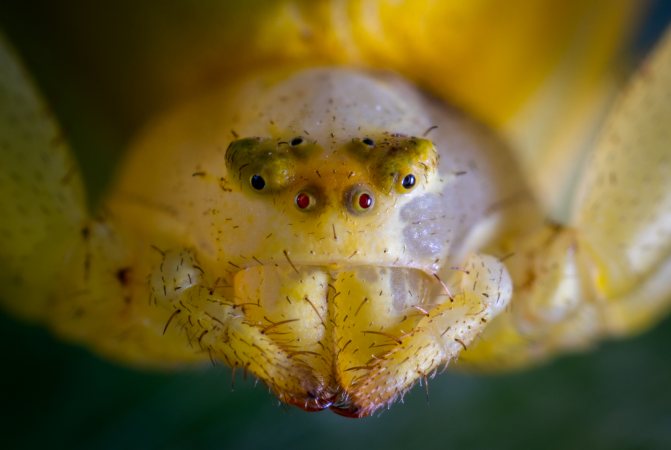


At the sight of prey, the hunter spreads his front paws, preparing for a deadly embrace. A specific subspecies of Thomisidae sidewalkers are born actors. Sensing danger, they fall with their feet up and pretend to be dead, deceiving their rival.
The side walker is capable of attacking an insect several times larger than it. An arthropod eats four medium-sized bees in 1 hour.
The reproduction of these spiders has a number of interesting features. Most males of this species are stenochronous; have one copulation period per year, while females are eurychronous - they reproduce throughout the summer.
Males search for females in different ways. Some groom the female, while others sneak up on her. The fact is that the eyesight of females is much worse than that of males.
Anyone who approaches her runs the risk of becoming her dinner. But even if the spider likes her beau, she will still taste him. A large proportion of spiders, after copulation, become food for females. While the female is busy, the male can quickly fertilize her and escape.
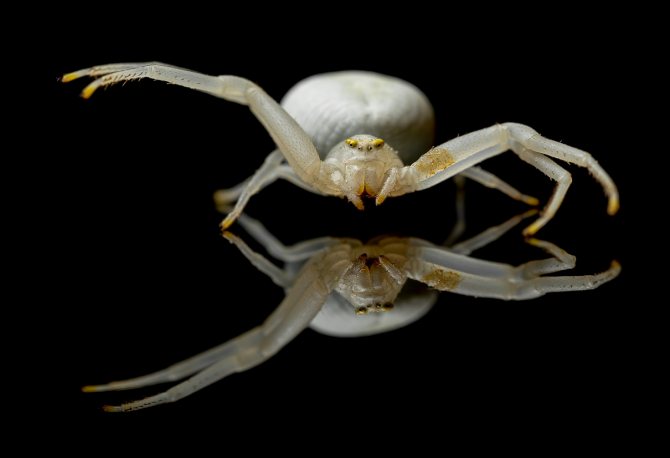


Before the birth of offspring, the spider carefully guards its larvae. After birth, babies are not independent - they are still guarded and fed by their parents.
Males have even developed a technique by which they fertilize the female in such a way as to have time to escape from her. Arthropods block the partner's front legs with cobwebs in order not to be paralyzed by her venom.
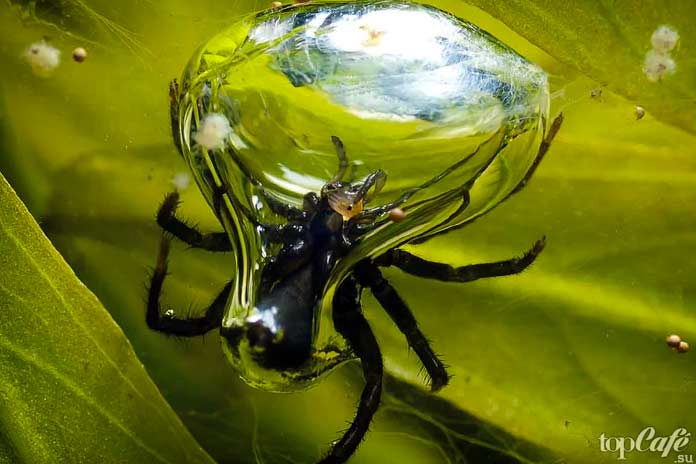
After fertilization, the eggs are hidden in cocoons. The spider carries cocoons with it or attaches to a flower or tree bark.
The benefits of this type of arthropod for the countryside are known. They eat many pests, while trying not to bite people.
The main diet of the side walker is flies, which often act as pests for people, carriers of a large number of dangerous bacteria.
Garden pests turn out to be food: Colorado potato beetle, moths, bedbugs. Spider venom is sometimes used as a pesticide.
A side walk spider is deadly to humans - true or myth?
These members of the arthropod family secrete a very toxic poison that immobilizes the victim almost instantly.
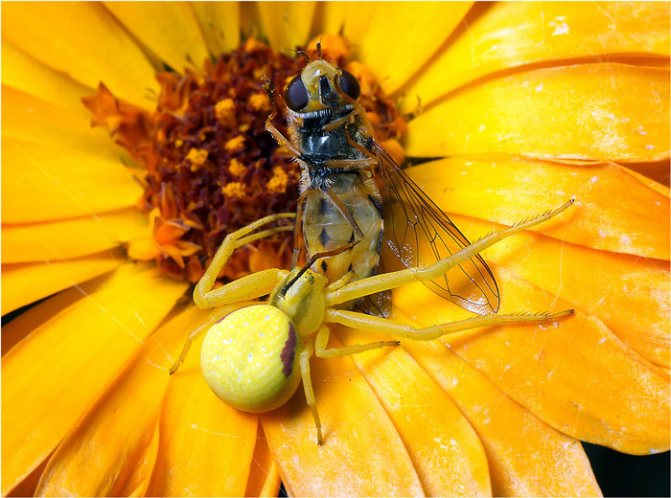


Spider-side walker on the hunt
And here a completely logical question arises: "Is the sidewalk spider dangerous or not for humans?"
The arthropod is not dangerous to humans for several reasons:
- it does not attack people:
- the concentration of poison in such a scanty creature is even scanty;
- this amount of poison is not even enough to paralyze a pet.
Only small representatives of the animal world (hamsters, mice, rats, etc.) are able to feel its influence.
Conclusion
Looking at the photo of the side walker spider, you can appreciate the whole variety of these representatives of the fauna.
Body coloration, merging with the habitat, leaves them invisible not only to potential victims, but also to the human eye.
And since the food for the predator is mainly pests of garden crops, crab spiders bring undeniable benefits to mankind.
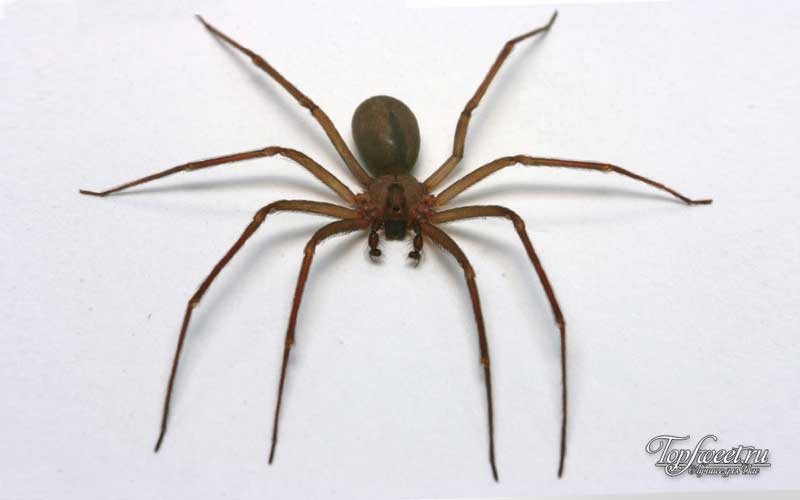
Black Widow
You can meet this spider in South and North America. A striking distinguishing feature is an hourglass-shaped spot on the insect's belly.
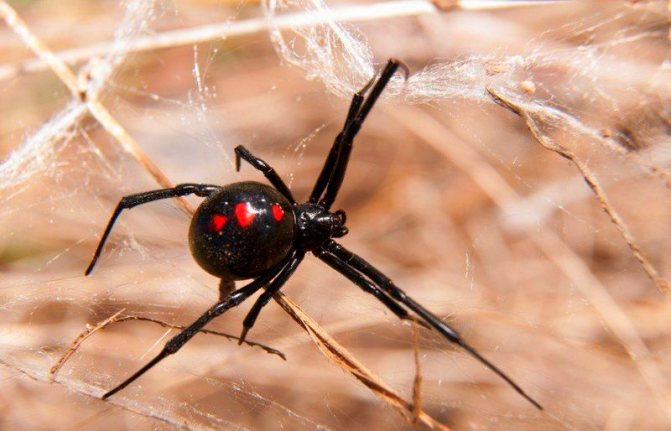


The widow devours males after mating, so the number of females is incredibly large. However, it is important to know that this species is not aggressive and only attacks when it understands that it is in danger.
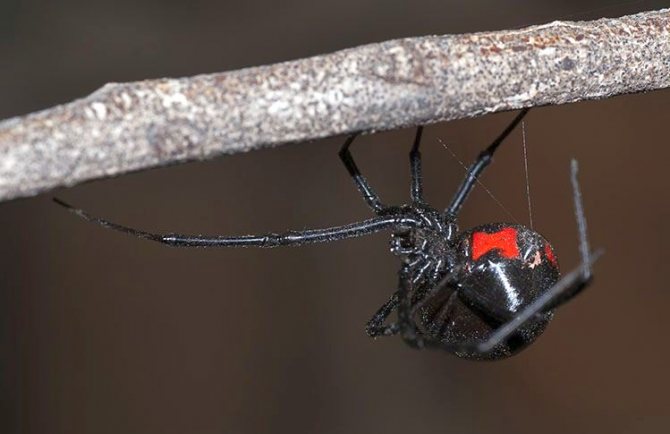


The consequences of a bite are severe pain, convulsions, bouts of nausea, difficulty breathing. For healthy adults, a black widow bite will bring minimal damage, but children and the elderly are at risk.
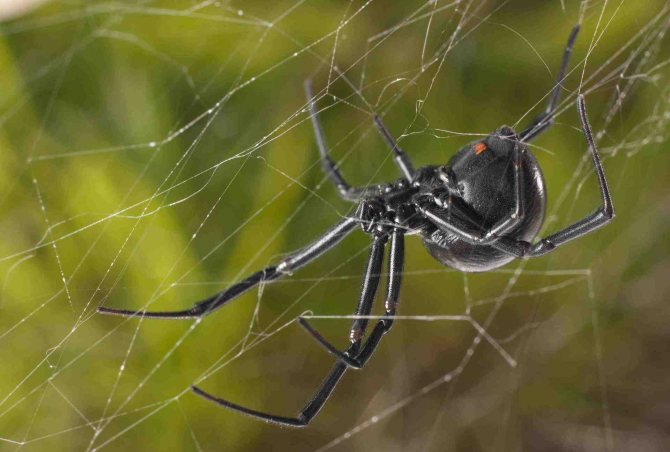


Reproduction
After spring courtship and mating, the female lays three or four flat cocoons, which she attaches to the back of the leaves of shrubs and tall grass. And sometimes a spider incubator is located on the walls of outbuildings. Depending on the air temperature, but on average - after a few weeks, small "crabs" are born and immediately scatter in search of game - the most delicate leaf beetles and springtails. During the year, the young will grow, and after hibernation, spring courtship will be repeated again.
Hunter tactics
Despite their size, spiders are not afraid to attack larger insects. As real hunters, they can sit in ambush for a long time, waiting for the victim with open legs. As soon as a butterfly or a wasp sinks onto a flower, they instantly grab them and bite into vulnerable spots.After injecting venom, the flower spider begins its meal.
However, if a hunter has not eaten for a long time, then his behavior changes dramatically. He restlessly runs through the leaves, looking out for the victim and wiggling his legs in anticipation of dinner. At the sight of an approaching insect, the spider freezes with legs wide open. From the side it seems that he opened a friendly embrace. Thanks to the coloring, they manage to remain unnoticed, and the tactics bring the desired result.