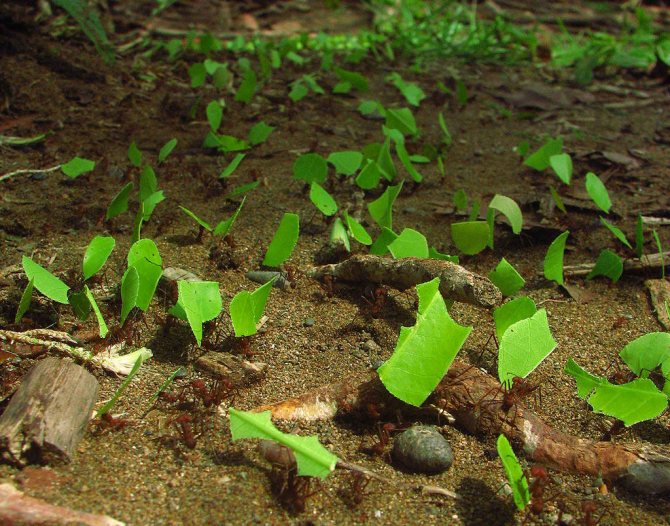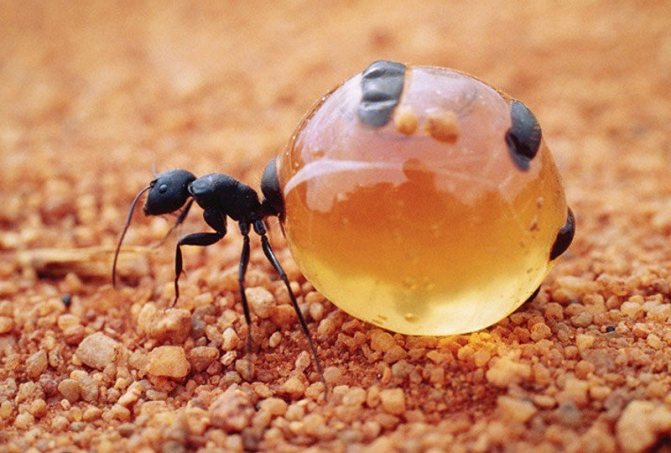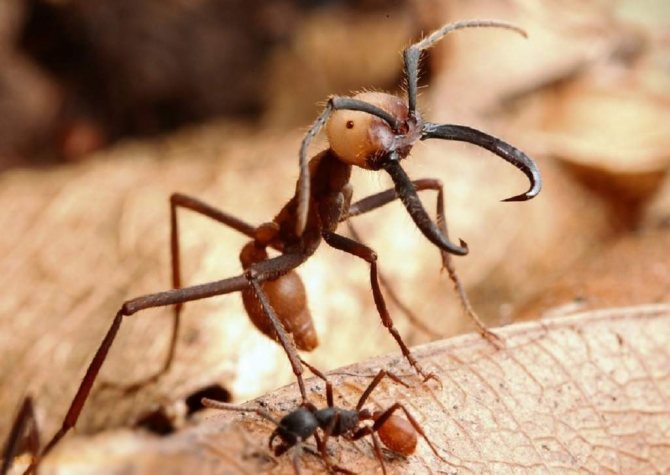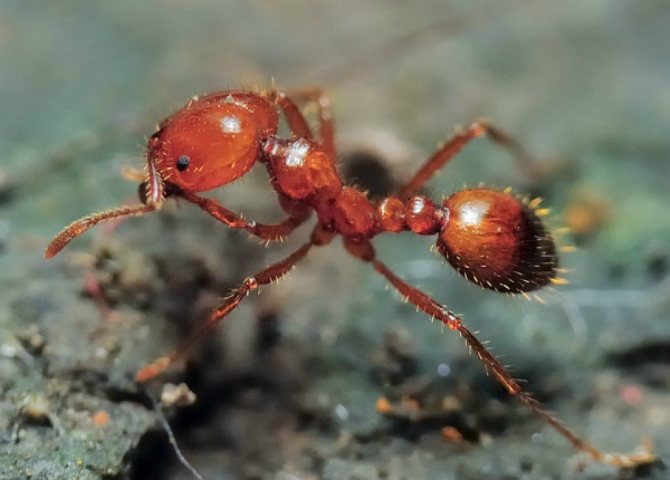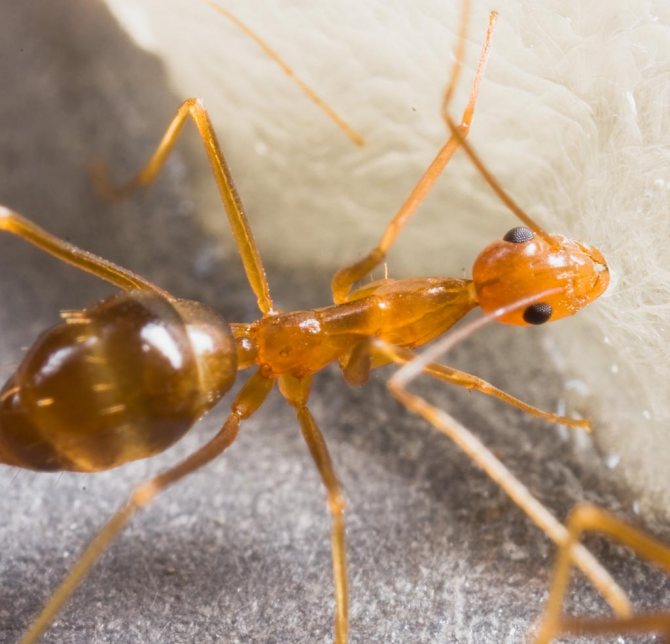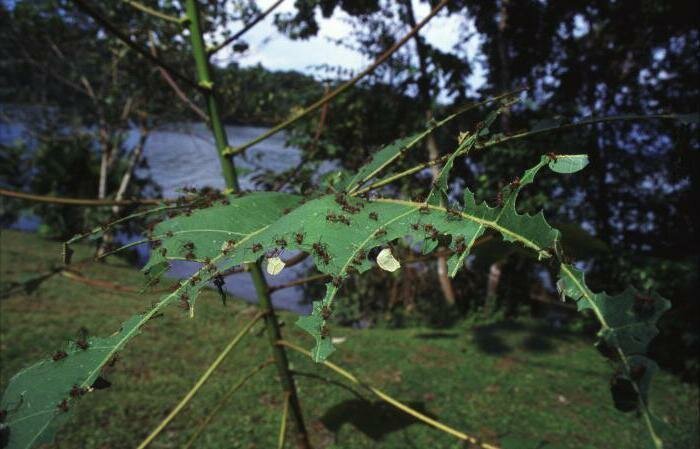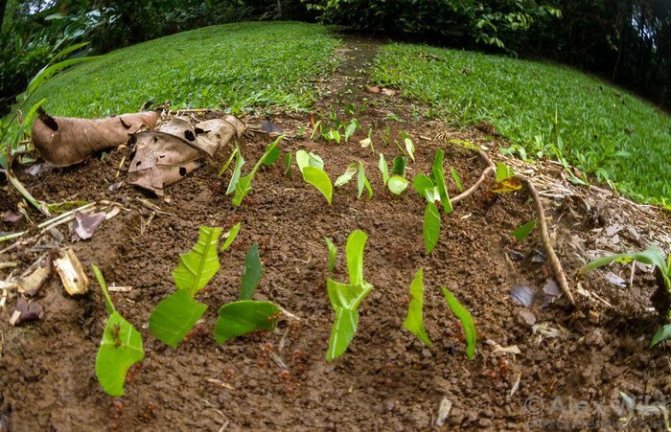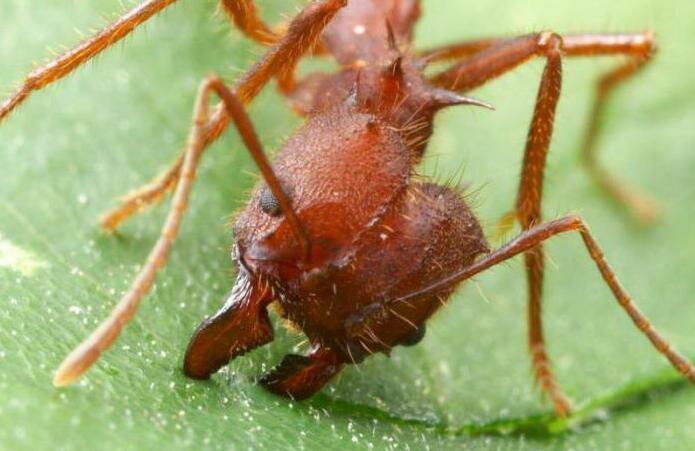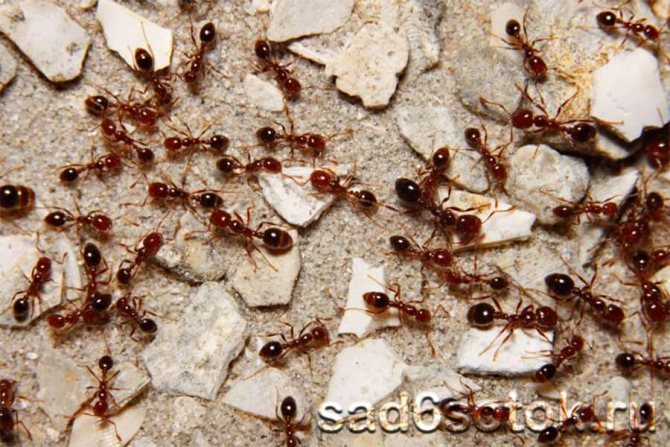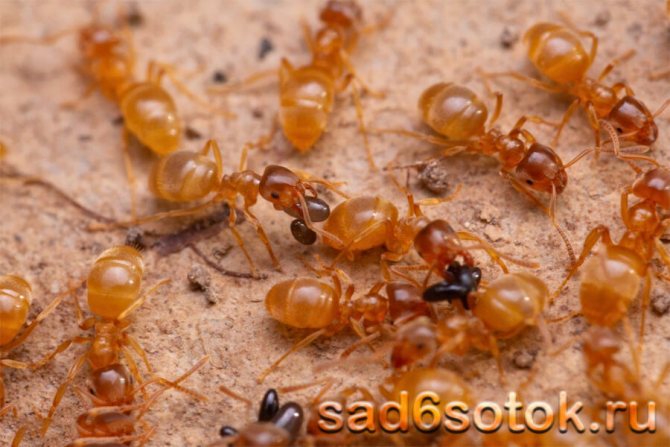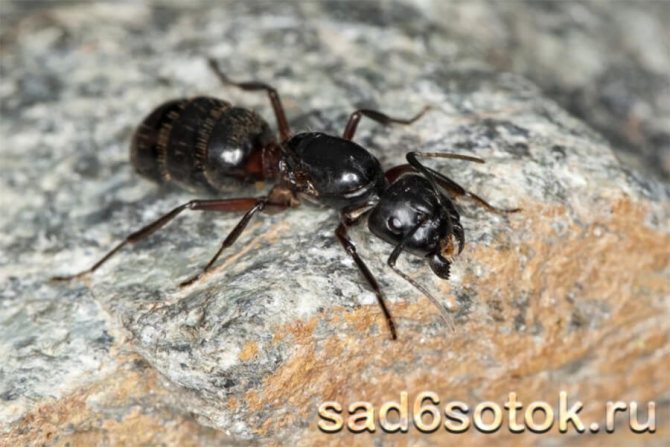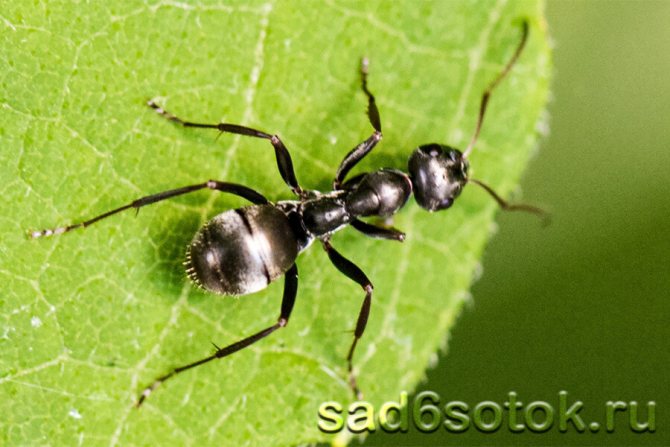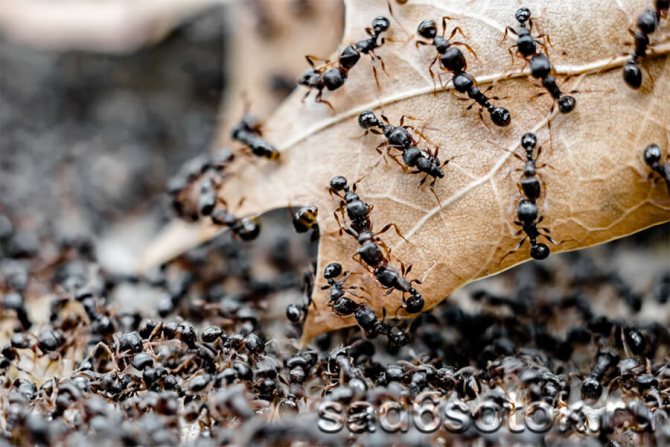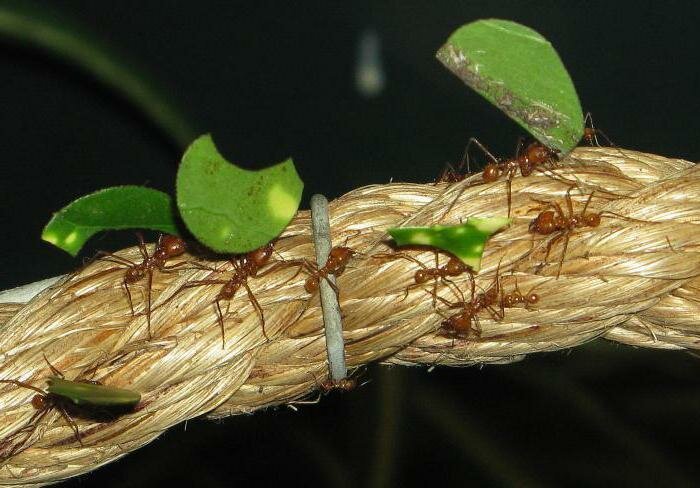
When the leaf-cutting ants first caught the eye of scientists, they decided that insects collect pieces of leaves in order to hide them in an anthill and eat them there. At the same time, even the mechanism of cutting leaves and transporting them was fascinatingly interesting and had already attracted the attention of a large number of specialists.
But then it turned out that this is only the beginning of a huge and complex process of processing and using leaves as raw materials for a real farm. And so complicated that the small leaf-cutting ant became a real sensation in science for a long time ...
What's the basic description
Leaf cutters are developed ants. Are of interest to scientists. The main characteristics, depending on the stage, are presented in the table.
| Larvae | The larvae are legless and eyeless. For full development, a representative needs a comfortable temperature regime and a specific level of humidity. Unfertilized eggs turn into males. Depending on the conditions, uterus or infertile females emerge from the fertilized eggs. In the absence of the opportunity to create new offspring, the representative will act as a worker and take care of the anthill. Mushrooms act as food for the larvae. |
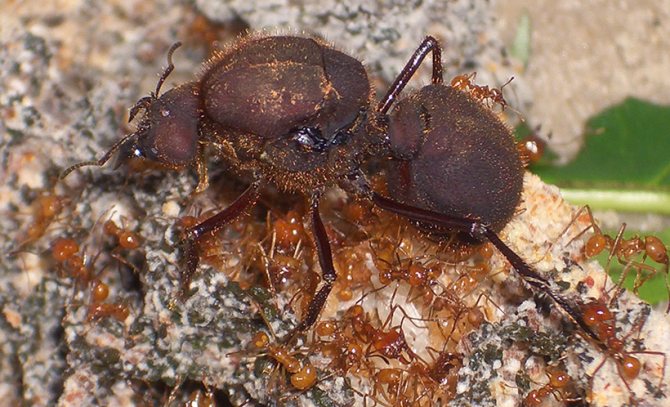
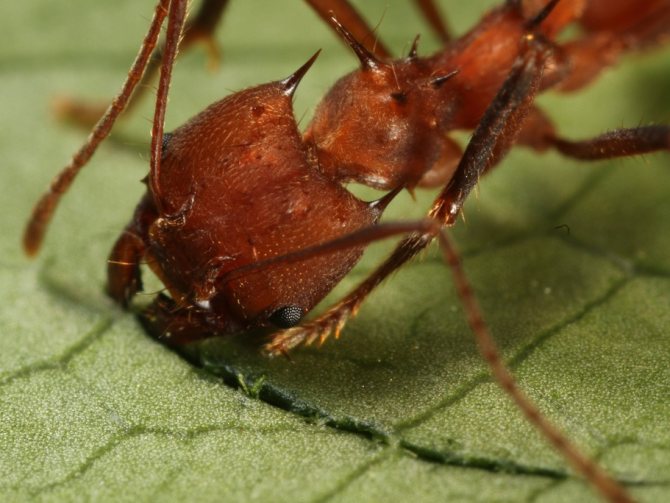
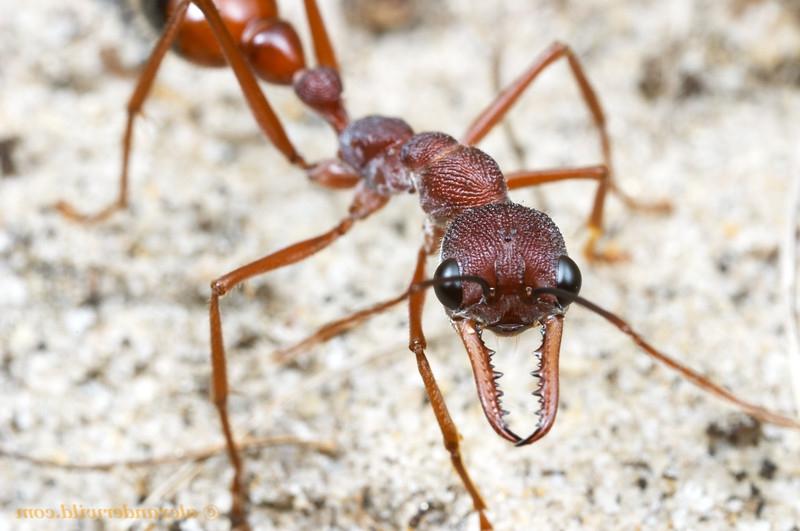
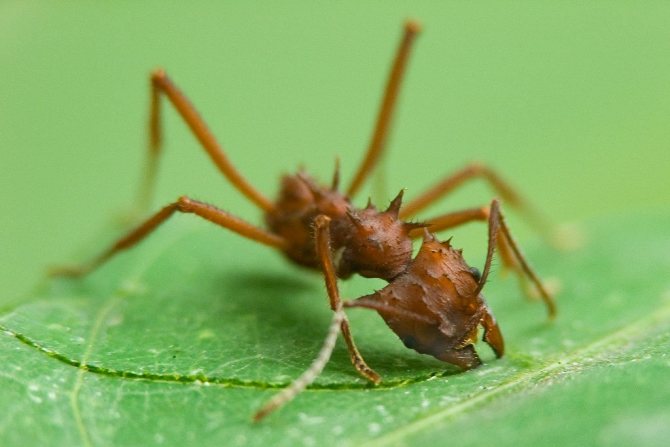
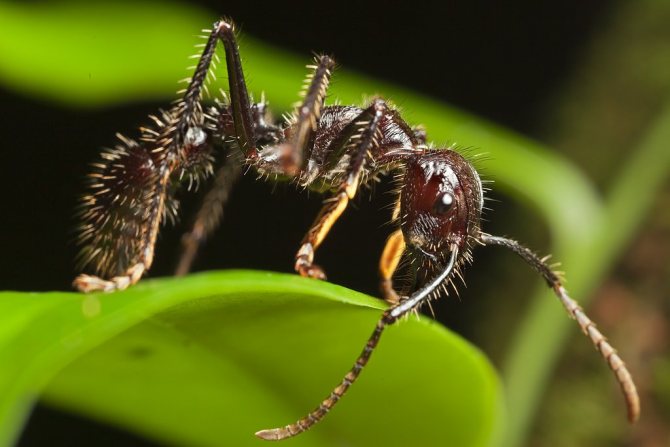
| Adult ants | Working ants with a body length of up to 20 mm. The size of the legs directly depends on the caste of the insect. A characteristic difference is the presence of a powerful hooked jaw. This is for easy cutting of dense foliage. The ant has a large head. A well-developed sting is present. There is a special pocket on the lower part of the head. This is necessary in order to make a stock of mycelium. The uterus has wings. However, they are gnawed off before the direct formation of the colony by the most fertile female. |
Insects are divided into 7 castes. Among the sheet cutters there are:
- uterus;
- males;
- soldiers;
- foragers;
- builders;
- gardeners;
- small workers.


The roles in the nest are very carefully separated
The workers are responsible for caring for new offspring. They carry out work on the mushroom beds. The body does not grow more than 0.5 cm. Larger builders. The body length of some representatives can reach 2 cm. The head is powerful and large.
The largest uterus. The weight of the female is several times the weight of conventional leaf cutters. There is a powerful and large chest. All ants of this species have 3 pairs of long limbs.
Lifestyle
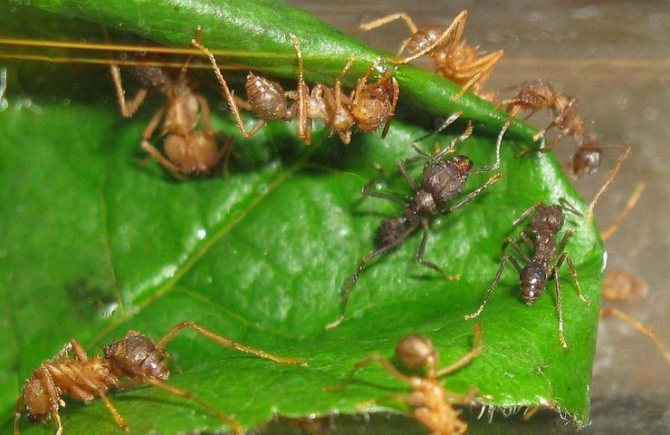
These are quite developed insects, the colonies of which represent a rather complex system of relationships. One group is divided into seven castes. Each caste has its own work, performs and is responsible for it. This, in turn, affects the development of the insect and its appearance. There are the smallest ants that do the job of caring for the eggs, larvae, and queen bees. Their dimensions do not exceed 5 mm, it is worth mentioning that they never leave the nest.
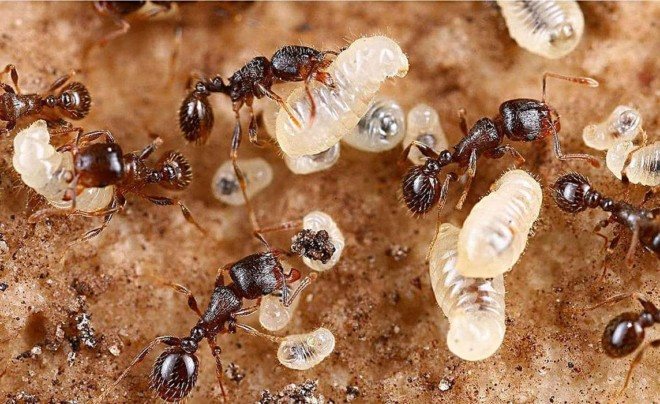


At the stage of pregnancy and laying eggs, the female takes care of the offspring on her own, she cares for and feeds him, which gives her the opportunity to regulate the number of individuals in the caste. One clutch is about 60 eggs. The entire colony consists only of female goosebumps, which do not have the possibility of conception. Males are born from unfertilized eggs, fertilize females and die immediately.
Their dwelling is a huge underground anthill, the diameter of which reaches 10 meters. This whole structure resembles the shape of an egg, in the very center are the queens and offspring. The rest of the area is divided into separate chambers, this is a kind of farm where the ants grow their own mushrooms on their own. It's hard to believe, but one anthill can number over a million individuals. Such dwellings have a lot of exits, they serve not only as convenient passages, but also perform a security function.
These ants are in excellent contact with other types of insects, and some of them live in their nests. But this is not hospitality at all, but just a mutually beneficial relationship. For example, a cockroach is a fairly frequent visitor and resident of such anthills, namely the Texas maravielyub. As you can tell from the name of the cockroach, he really loves goosebumps. The fact is that this cockroach feeds on the remnants of food that is on the ants, eats it and thereby cleans the ant. It is a beneficial relationship that allows two species of insects to exist together.


In addition to cockroaches, leaf cutters cooperate with other species, for example, dung beetles and predatory ants. In this case, they play the role of guarding the anthill and the entire colony. Regarding dung beetles, they can do just fine without leaf cutters, but since ants depend on them, they can forcibly attract dung beetles to their home.
Unfortunately, there are those who pose a great danger to the colony. For example, nomadic ants can attack a colony, which leads to the destruction of the anthill and quite serious losses. They attack to take away food, in this case mushrooms. Despite the fact that the leaf cutters are large enough, the sting and the caste of fighters, the so-called soldiers, they lose in battle, since they are rather weak individuals.


Therefore, leaf cutters share their home with ants of the species Megalomyrmex symmetochus, which cannot be called peaceful and harmless at all. They belong to those individuals that rob anthills, but leaf cutters voluntarily share food, which allows them to exist peacefully. These predators are much smaller, but in battle they are very dangerous.
What is the agricultural activity of insects
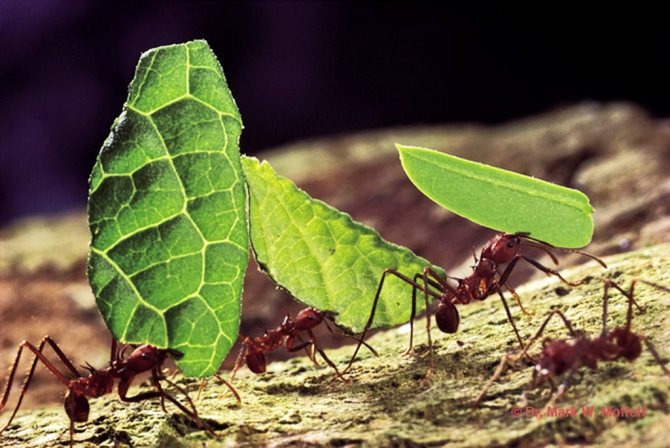
You might think that leaf cutters are harvesting foliage for food. This opinion is wrong. Ants are unable to digest tough plant fibers. The collected leaves are chewed by a specific caste of insects. The resulting plant mass is stored in specially designated places in the anthill, where favorable conditions are maintained.
A fungus begins to grow on the plant mass, which is food for insects. The ant does not eat the fruit bodies of mushrooms. Only the mycelium is required.
The ant bites off the fruit bodies at the initial stage of their development. For insects, this is a waste of resources that does not represent any nutritional value. The saliva of the leaf cutter contains a number of antibacterial substances that help to destroy harmful microorganisms that pose a danger to the mycelium.
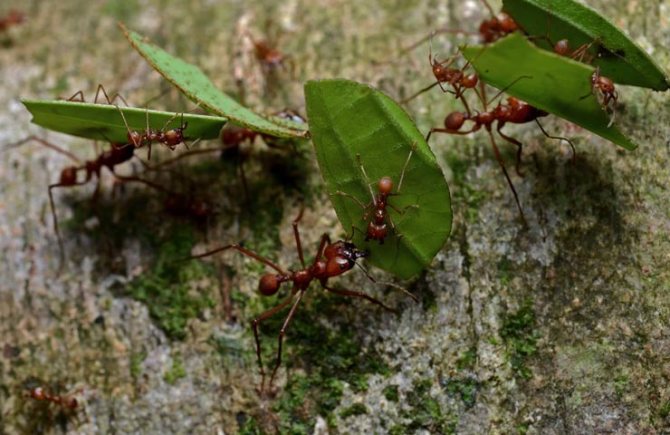


There are a huge number of types of sheet cutters
In total, there are about 200 species of ants in the world that grow mushrooms. Some of them are done on dead animals or faeces. Sheet cutters use the most affordable and simple material. Leaf cutters are considered pests. In places of residence, they are able to destroy all foliage on trees and shrubs.
Benefit or harm
Ant colonies can very densely inhabit the territory chosen for habitation. To minimize the harm caused by leaf cutters, they use not only chemical protection means,


but also mechanical methods. A fairly effective method of dealing with leaf-cutting ants is the direct destruction of their nests.The most effective were metal or plastic fences, as well as the use of water barriers. The harm caused to horticultural crops is practically not felt in the selva. The activity of leaf cutters in wild natural conditions not only contributes to the enrichment of soil layers, but also accelerates all metabolic processes occurring in the ecosystem.
Large individuals of leaf cutters have long been food in some countries. Residents in South America collect this species of ants and eat them fried.
The seven-spotted cow destroys aphid colonies, which greatly helps farmers. The lacewing is a very beautiful fragile, but at the same time, a predatory insect that preys on aphids. Read the full description of the insect in this article.
The gray blowfly lays its larvae both on various insects and on the bodies of mammals. How to deal with this insect, read the link.
What are the features of reproduction
Reproduction of leaf cutters is similar to other types of ants. The larvae are raised by a caste of workers. Representatives, together with food, give special substances for accelerated development and puberty.
Males and females, adapted for reproduction, additionally have wings. Years begin as soon as the number of the column reaches critical values. Representatives begin to actively mate and create a new ant society.
When the only uterus dies, working representatives are engaged in reproduction. The female mates with several males at once. This is necessary to obtain a sufficient amount of seed. After fertilization, male representatives die. Workers appear one month after the ovipositor.
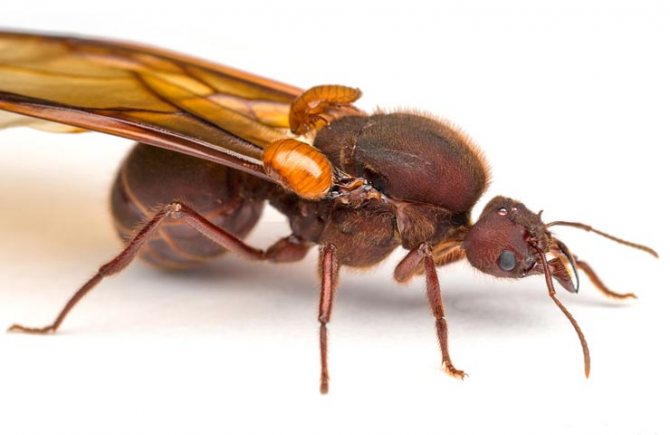


Females are large and have wings.
Behavior
Basidiomycete mushroom serves as food for leaf-cutting ants. It is grown in special chambers that are inside the anthill. The nests are built in such a way as to create optimal conditions for maintaining the necessary humidity and creating ventilation for growing the mushroom.
Insects carry pieces of plants from everywhere, which, after chewing and fermentation, become a breeding ground for the fungus.
As the anthill grows, it is clearly divided into groups of soldiers, workers and gatherers. Individuals are allocated from each group, which are engaged in specific operations.
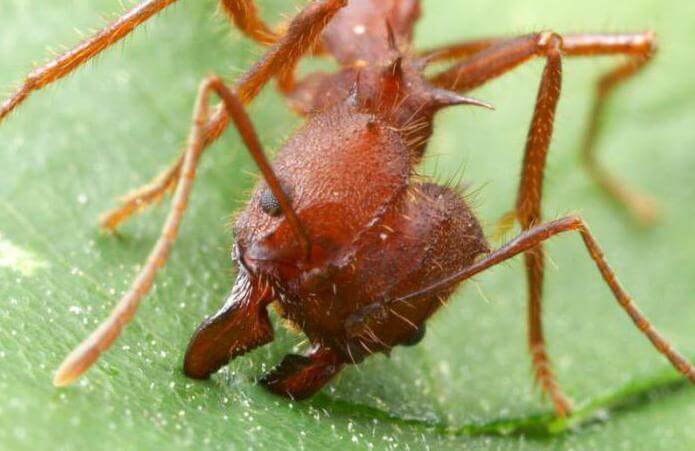


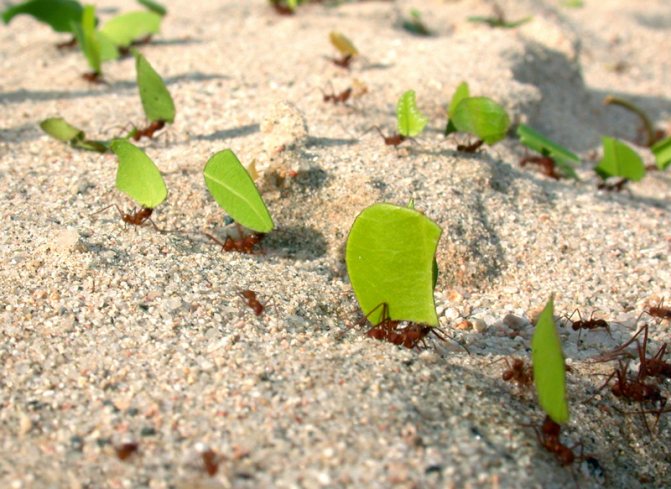
Over time, castes are formed, whose members can be very different from each other in appearance and their purpose. Small specimens of gatherers bring pieces of plants from nearby places, and large ones, on the contrary, from more distant ones.
Having found a suitable plant, the insect with the help of mandibles separates it from unnecessary fragments and takes it to the nest. Work ants often ride on pieces from above and drive away parasites. They also carry out work in the internal chambers.
The protection of the nest and its population is carried out by large and strong soldiers. Large workers crumble the brought greens, and small ones chew into even more miniature pieces and fertilize the mycelium with them. Very small worker ants prepare mushroom food for the queen and other ants.
What does the insect eat
Ants gnaw at the grown mushrooms at the base. The insect drinks all the drops that have appeared on the surface. The mushrooms themselves are like a sponge loaded with nutrients. After the ants gnaw the fungi, solid formations are formed that cover the entire surface of the nutrient substrate. It is the main food for insects.
The weight of one formation can reach 500 g. Each colony may contain about 100 such fungi.
Only ants from the guard caste are distinguished by the ability to gnaw the dense leaves of tropical plants. The rest of the representatives choose softer leaves.
Ants are the source of life and protection for other creatures
The species of bugs Acanthaspis petax is surprising in that its representatives, feeding on ants, do not throw their corpses, but construct a shield from them, which they wear on their backs. This shield protects against


attacks by spiders and other insects. If the attack does happen, the bug drops this shield and flees.
The unique behavior of the cordyceps mushroom is one-sided. If the ant inhales the spores of this fungus, then it immediately turns into a zombie and follows to the place optimal for the development of the fungus. Usually it is a plant up to 20-30 cm tall. The ant climbs the plant and clings with its jaws to the central vein of the lower part of the leaf. A couple of days later, a pedunculate mushroom grows from the back of the head of a dead ant with hundreds of thousands of new spores. Any new ants that accidentally pass through this location will be infected and killed in the same way.
What are the features of the anthill
Ants spend most of their time in trees. An anthill is being built deep underground. Under the soil, the grown mushrooms are not afraid of temperature changes.
The nest resembles an egg. In the middle is the uterus, which is responsible for reproducing new offspring. Incubators with larvae and eggs are localized around the female. Further there are myceliums. One anthill of leaf cutters can be up to 5 meters long. From this video you will learn a little interesting about leaf cutter ants:
Brains and muscles are moldy
In the work, the results of which appeared in the article "Behavioral mechanisms and morphological symptoms of zombie ants dying from fungal infection", scientists investigated the dying behavior and morphological changes of infected Thai ants. Scientists note that, as described earlier, infected ants are characterized by "extraordinary behavior": they go where healthy insects do not stick their noses - into the forest floor, closer to the green parts of the plant, on which they die. However, solitary healthy ants also sometimes run into the forest litter, but again return to the den - into the trees, to a height of more than 1.5 meters. Entomologists note that such "migratory ants" suffer from Ophiocordyceps unilateralis, and those that "sit at home" do not face infection and do not get sick.
Infected arthropods roam the forest alone. They stumble, fall and, it seems, generally go wherever it turns out: "The ants begin muscle cramps and they cannot control their limbs," the authors of the new study explain. It is also interesting that insects prepared for death leave the anthill and begin to look for a “grave” in the morning: “Sick ants are active from 9.30 to 12.45,” the scientists concretize. "They obey the solar rhythm."
How labor is distributed among leaf cutters
The worker ants are the tiniest. The length is 0.5 cm. Such representatives are responsible for the growth and maturation of new offspring, as well as garden work. The soldiers are 3 or even 4 times larger. The main goal is to protect the anthill from strangers. Have a stronger jaw.
The uterus is 700 times heavier than workers. The thoracic region of the body is pronounced.
Soldiers are not present in every anthill. The guards live only in large nests, where there is an opportunity to feed the defenders. In smaller columns, all residents take over the security functions in order to make up for the lack of an army.
Danger of a bite to humans
When a forest ant bites, formic acid is released, which is a poison. In small quantities, it is not very dangerous for people, it often causes only a local reaction. It is manifested by swelling of the affected area, severe itching and redness of the skin.
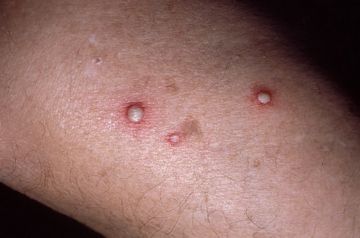

With multiple bites, there is already a general reaction of the body in the form of dizziness, sweating, pain in the chest, and nausea.
In people allergic to this substance, the throat and face swell, itchy rashes (urticaria) appear on the skin, speech becomes slurred, blood pressure decreases, and in severe cases, coma or anaphylactic shock may develop.
It is dangerous if formic acid gets into the eyes and mucous membranes, it corrodes them and causes chemical burns.
To reduce the harmful effect, ice or a cold compress is applied to the bite site, treated with any alcohol-containing agent.In the case of a large number of bites, antihistamines should be taken, for example, Suprastin, Claritin, Histamine.
Varieties
Lasius niger
This is the most numerous species. Distributed in Europe and central Russia. Found in Siberia and Mongolia. The color of adults is black or dark brown.


The nests are more often placed in the ground. They can be seen by their characteristic mound. Less often, a colony of black ants settles in tree bark or under stones. Young females establish colonies on their own, without the help of worker ants.
A characteristic feature of the species is the long life of the queens. According to some reports, they live up to 2 years. The queen is always alone in the colony. Reproduction takes place from early summer to late August.
This species of ants feeds on the sweetish secretions of aphids. To provide themselves with food, adult insects diligently protect pests from attacks by other families of ants. And if necessary, they even transfer aphids onto whole leaves of plants so that they can reproduce successfully.
For the winter, a few aphids must be taken to the nest. And next year a new "farm" is being bred with their help.
Lasius flavus
Distributed throughout Eurasia. Found in Japan, North Africa and North America.


The color of adult yellow ants is light brown with a yellowish tinge. The body is devoid of small hairs and looks translucent.
The size of females is up to 7 millimeters, sometimes more. The nests are placed in the soil, making mounds above them. Most often, large colonies are found in flat areas and in gardens overgrown with dense grass. They practically do not come to the surface of the soil. They lead a secretive, underground lifestyle.
They feed on the secretions of root aphids, which are bred as needed.
Lasius alienus


Lives in Europe. It is also found in the Caucasus. The body color of pale-legged ants is light brown. The head has large eyes - this is a characteristic feature of the species.
They prefer to settle on lawns, pulling out small craters in them. They also nest under sidewalks or large rocks. Lead a secretive lifestyle.
They feed mainly on dead insects. Less commonly - by aphids that parasitize flower beds. They reproduce actively in summer, damaging lawns.
War of annihilation


Destruction of ants
If methods for scaring off ants have proved ineffective, there is only one way to save the garden from their destructive activities - to try to destroy them. Considering the peculiarities of ants' life, both physiologically and socially, this is a very difficult task. However, mankind has been successfully using the methods of war against insects for more than one hundred years.
Using poisonous baits
The choice of funds is quite varied and they are quite effective. The main components of such baits are substances that are deadly to ants, such as borax, boric acid or yeast.
To hide the smell of these substances, the baits use components that the ants love (sugar, honey, meat, and so on).
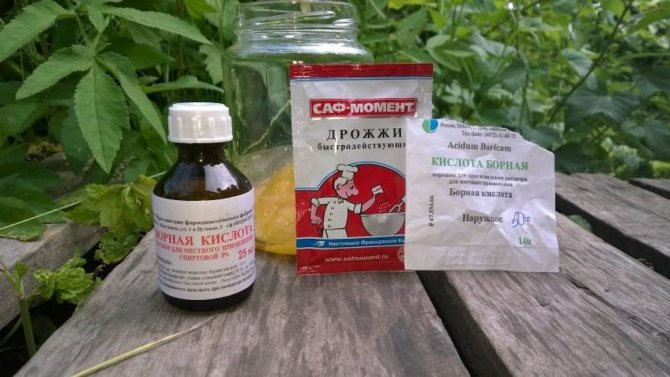

Lure Components
Eating such baits, the ants will die after a while. And by bringing them to the anthill, they will ensure the spread of the poison throughout the colony.
The bait recipes are as follows:
- 20 ml of hot water, 15 g of sugar, 3-4 g of borax mix and cool, add 5 ml of honey; the bait lays down near the anthill
- 8 parts sugar, 2 parts honey, 9 parts water, 1 part borax; everything is thoroughly mixed and laid out in small containers near the entrance to anthills and on ant paths
- 20 g minced meat and 5 g borax
- a tablespoon of yeast is mixed with water to a state of gruel, a teaspoon of jam is added to the resulting mixture; the resulting composition is applied to a sheet of cardboard and installed in places where ants accumulate


Lures ready to be laid
The baits are renewed at intervals of 4-5 days.
The more baits are placed, the more effective will be the fight against ants.
PROS:
- ease of implementation
- effective result
MINUSES:
long implementation time
Destruction of anthills
The essence of the method is simple: the destruction of ants and their homes. The main thing is not only to destroy the anthill, but also to destroy the queen, larvae, eggs and the maximum number of working individuals.
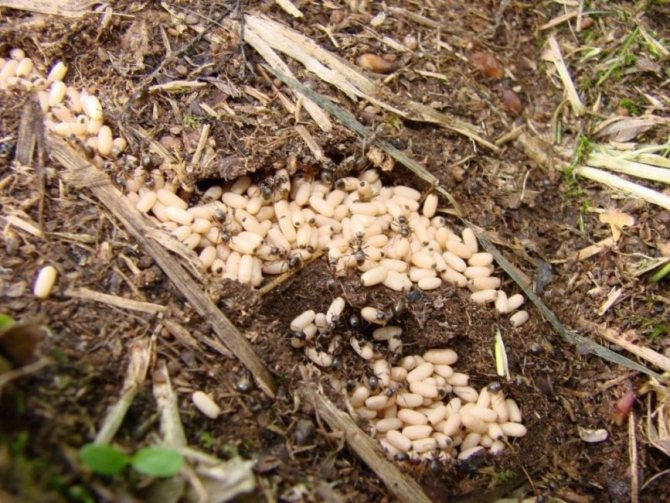


Burst chamber with eggs
This is accomplished in a variety of ways:
- flooding anthills with some active or poisonous liquid: boiling water, kerosene or infusion of nightshade tops
- stir up the anthill and cover it with hot ash or coals
- dig out an anthill, pour kerosene and set fire to
- etc
PROS:
speed and efficiency
MINUSES:
- possible soil contamination
- low efficiency for large anthills
Use of chemicals


Ant chemicals
This method is an extreme measure, and is used when other means have proved to be ineffective, and the condition of the site is very poor. Ants are highly resistant to insecticides, so you will have to use the most powerful means, such as Muratsid or Thunder.
PROS:
the fastest way with guaranteed results
MINUSES:
- many other insects are destroyed;
- soil contamination with toxic substances;
- possible damage to plants
Biological control method
A very simple method from the point of view of an idea, but quite complicated as an implementation. However, it is increasingly used to effectively solve the "ant" problem.
Its essence lies in bringing to the site any natural enemies of garden ants, which would not disturb the balance in the ecosystem of the garden.
The only enemy that can effectively cope with this task are ants of another species, for example, red forest ants. They are perfectly capable of living in a garden and can replace their garden predecessors as fighters against all kinds of garden pests.
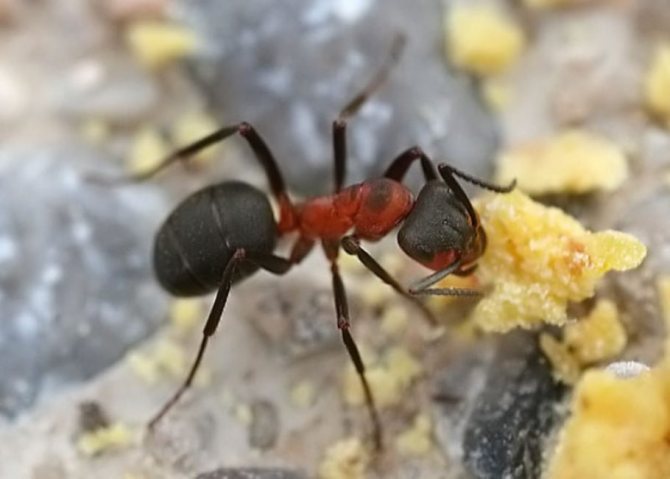


Ginger forest ant
In order to bring forest ants to the site, you must use a large bucket with a tight lid. In the forest there is a small anthill, it is torn apart with a shovel to the chamber where the larvae are stored, placed in a bucket and brought to the garden plot, where it simply spills out in a sunny place.
In order not to destroy the anthill in the forest and at the same time ensure the efficiency of their life in a new place, it is enough to bring about a third of the forest anthill to the garden.
Then everything will happen by itself. Forest red ants will destroy not only garden ants, but also the aphids that they raise.
PROS:
- guaranteed result
- replacing ants in the garden with those that do not protect aphids
MINUSES:
- complexity in implementation
- forest anthills are harmed as it takes energy to restore them
- the survival rate is low; in 80% of cases, the brought anthill will not survive the winter


































