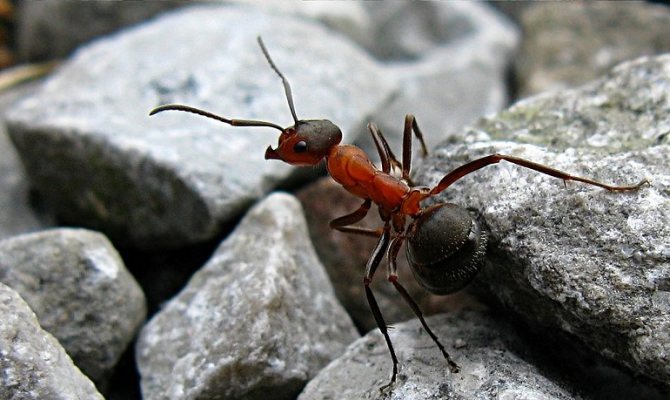
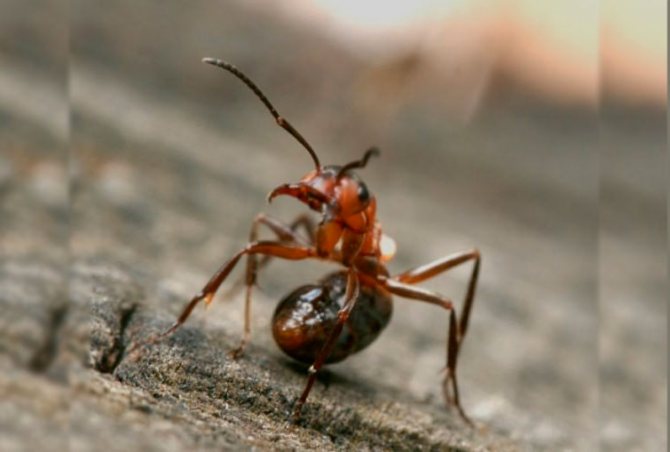
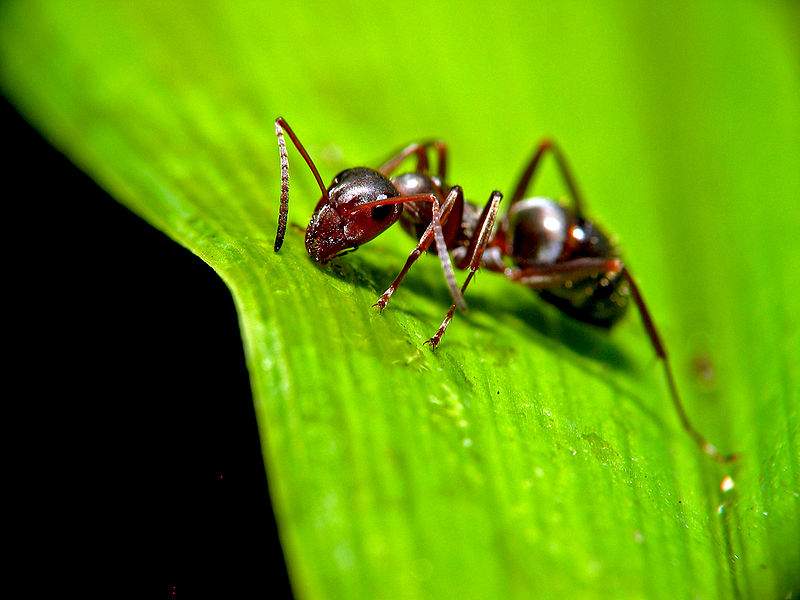
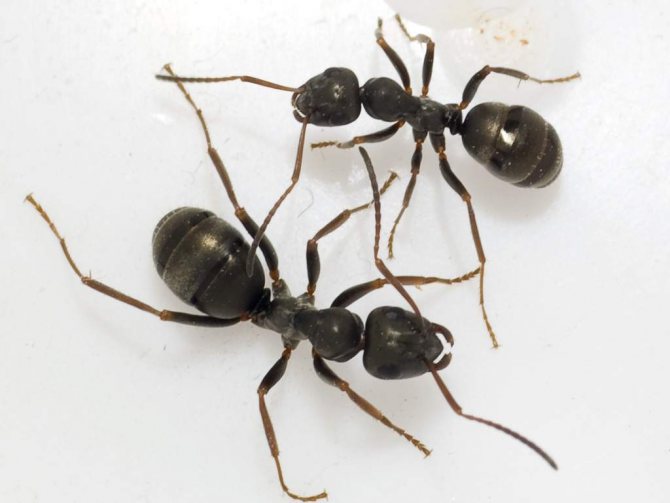
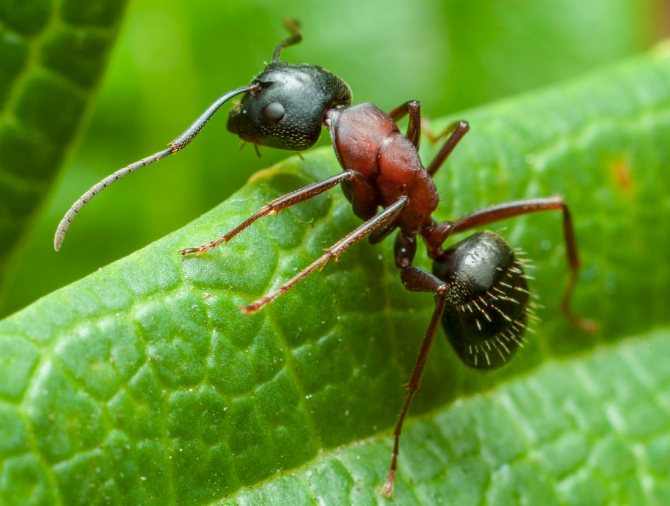
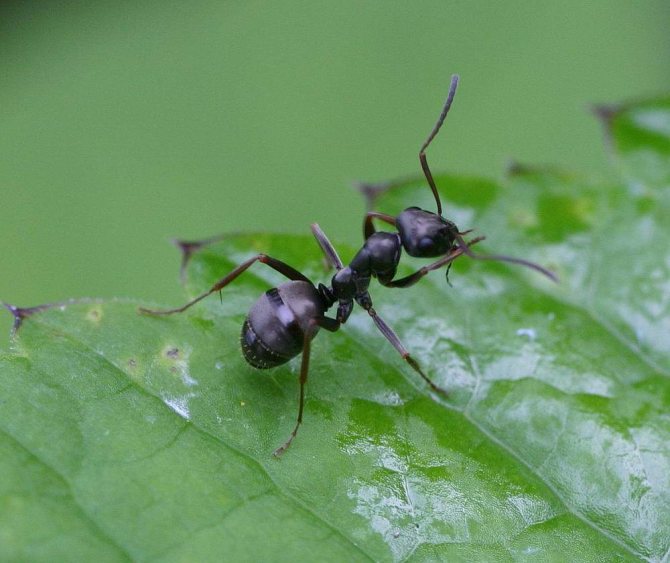
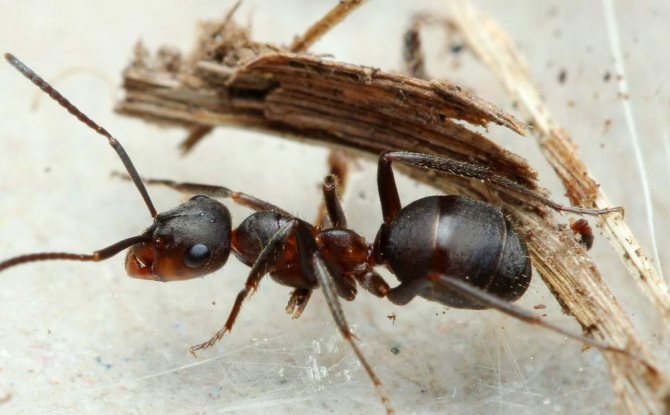
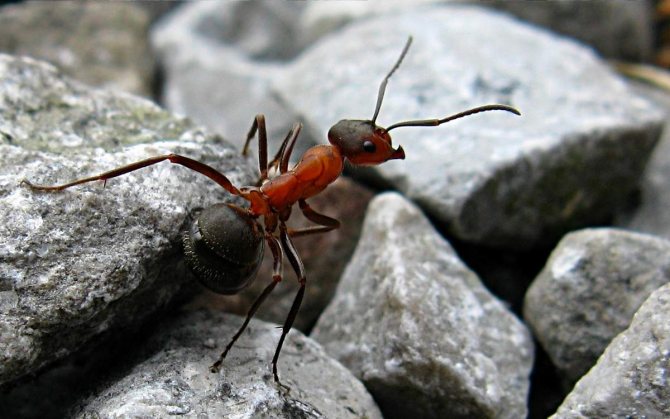
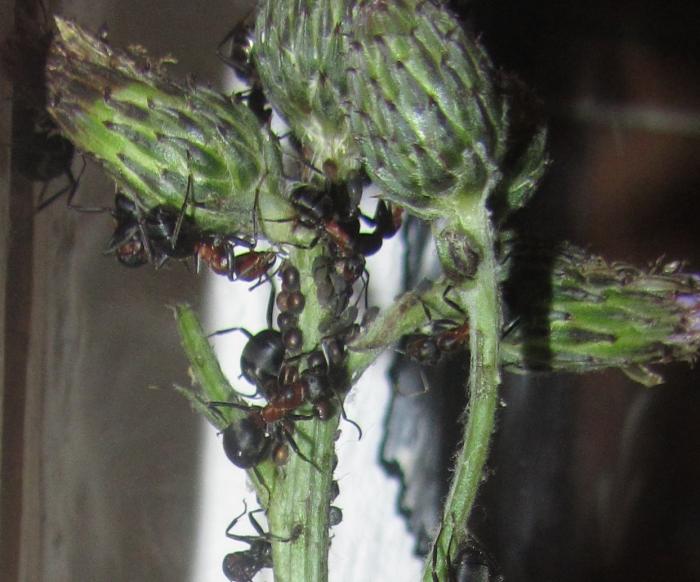
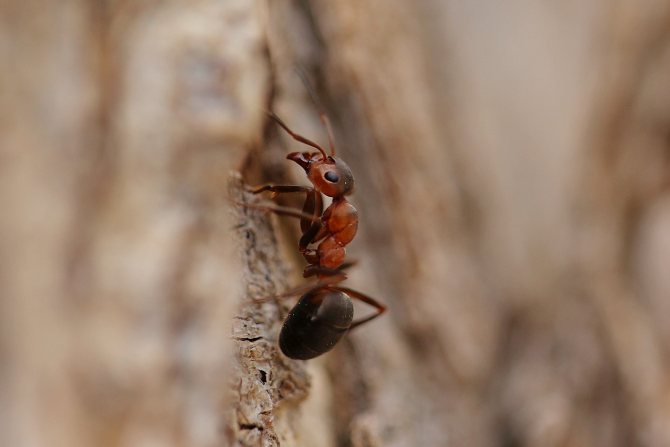
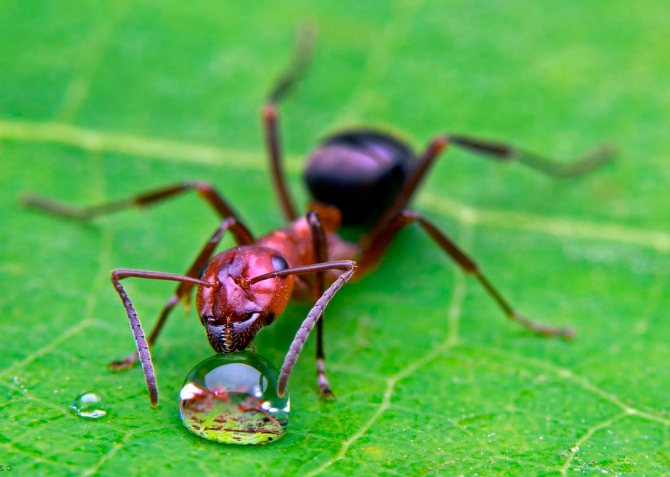
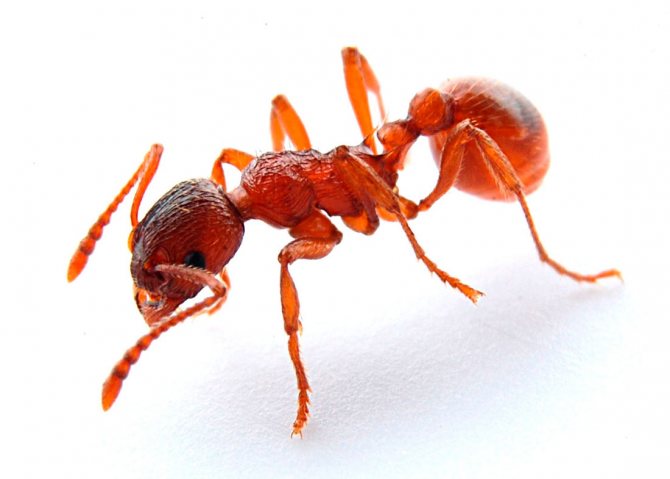
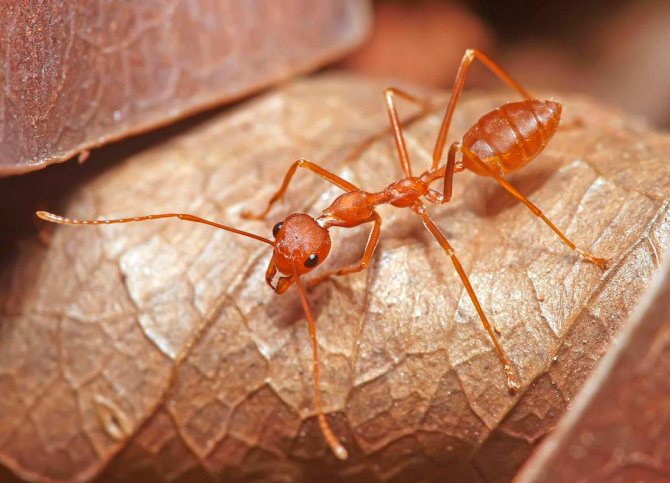
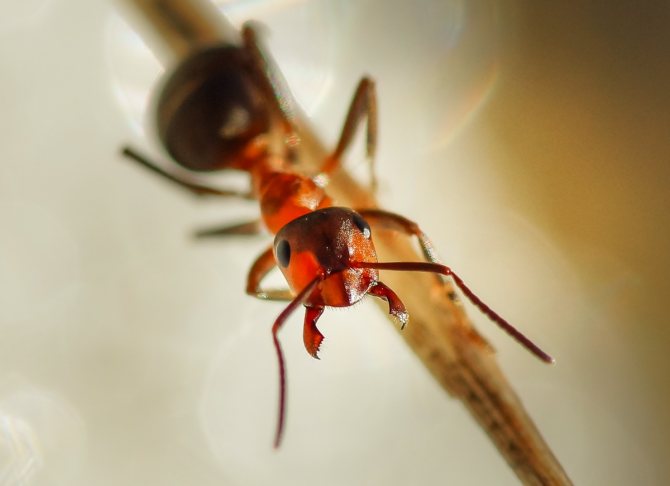
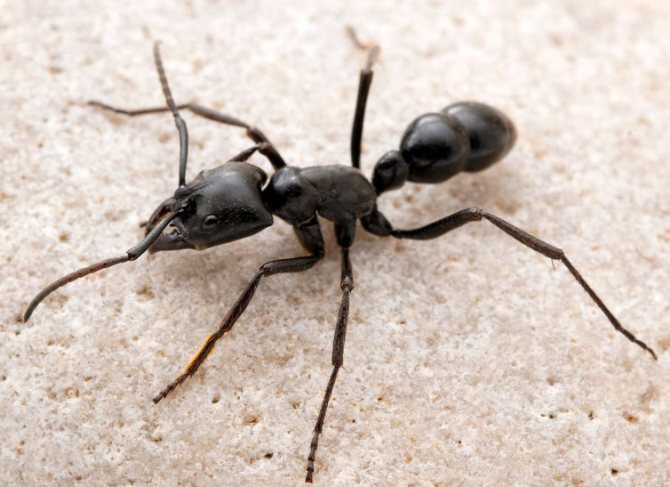
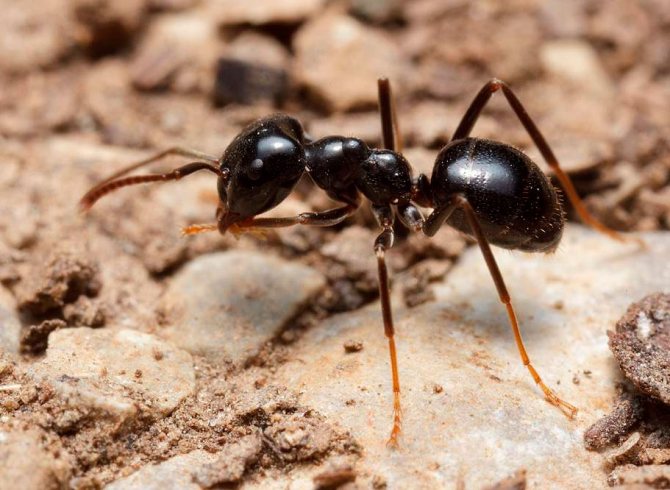
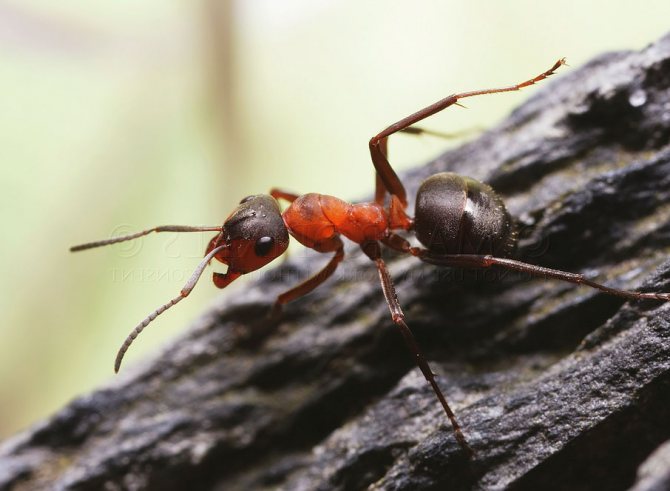
The ginger forest ant lives throughout European territory. Individuals of this species are also found in Asia and North America.... Perhaps, red ants were met by everyone who has ever been in a real forest. This type is the most common. However, it should not be confused with house ants of red color, as these are completely different types of insects.

Description
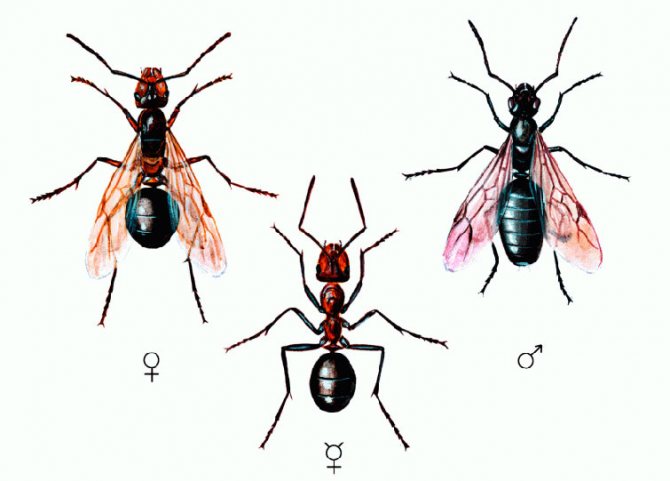
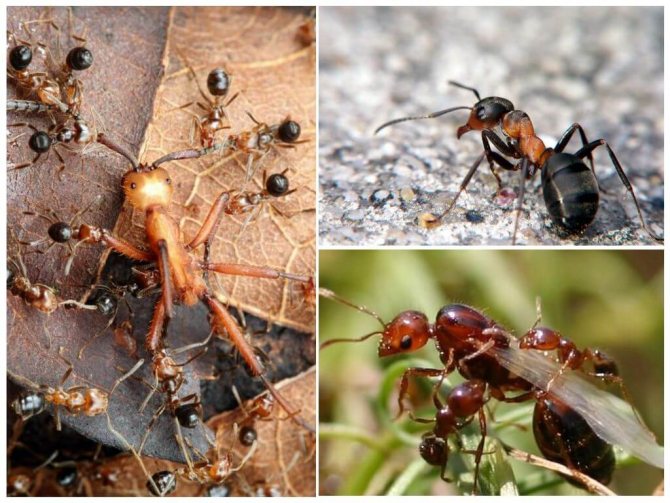
Forest ants have a large body, the length of which reaches 1.5 cm. The head is disproportionately large in comparison with the small chest. Long antennae are localized on it, which are necessary for touch. The males of these insects are visually very different from the females.
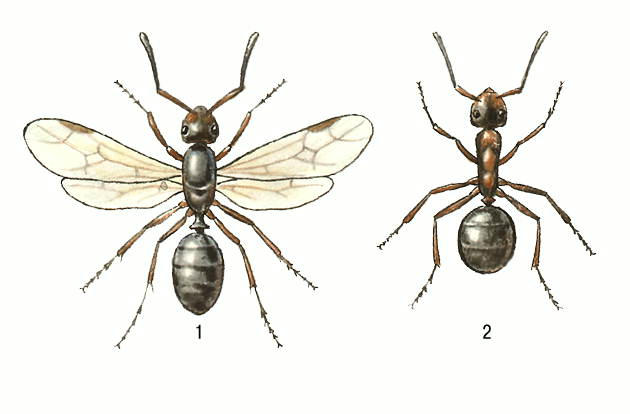

Male forest ants have a darker body and red or yellow legs.... They also have wings. In forest females, a smaller body is red-brown in color.
They have wings only during the mating season, and then they gnaw them off. Workers are also reddish-brown and without wings.
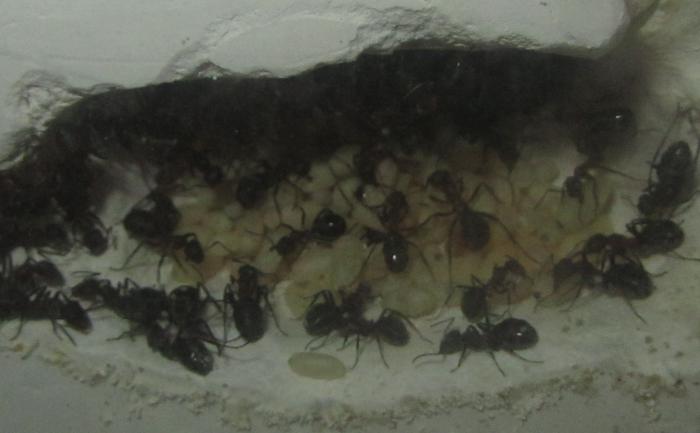
In ant larvae, the body is elongated, large, white, covered with hairs. During molting, they turn into pupae. Workers help the insect to leave the pupa. They break the cocoon, and the young forest ant becomes a full-fledged member of the community.
The meaning of forest ants
Ants secrete such a useful substance as formic alcohol... It is used in


modern medicine for the treatment of rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, hepatitis, bronchial asthma, renal failure, diabetes mellitus. Helps with hair loss.
Forest ants have a very extensive positive effect on the soil - they loosen it, enrich the soil with oxygen and nutrients, and increase the biological activity of the soil.
They are the main food for many useful for the forest zone and game birds, for example, woodpeckers, tits, black grouses, wood grouses.
They increase the grass cover in the forest, enrich it.
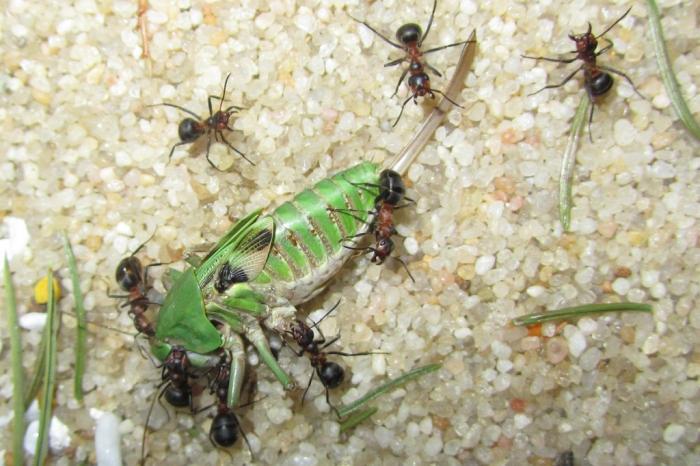
They regulate the number of harmful insects by eating any species that has begun mass reproduction. Often they completely switch to this species, suppressing further spread.
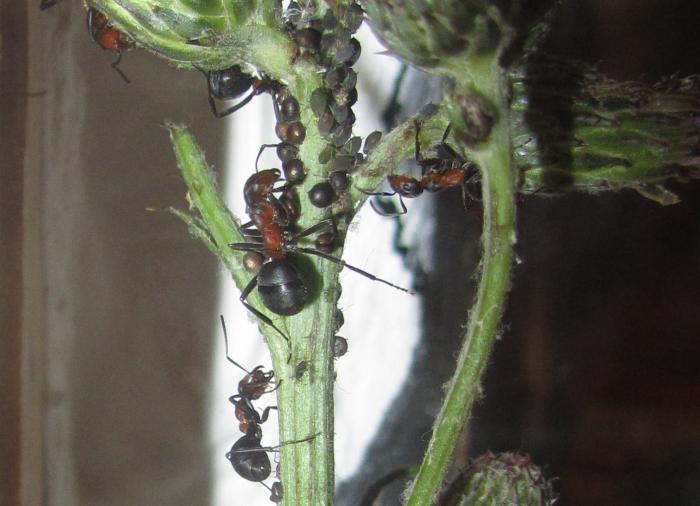
The negative influence of ants is their ability to breed and graze aphids that harm plants.
However, in the forest, this feature is much less harmful than in orchards and vegetable gardens.
The two-point cow is a real helper and friend of the farmer, as she destroys aphid colonies. Only strong families of leaf-cutting ants can afford soldiers. Read about the life of these amazing insects in this article.
The dragonfly is a predatory insect that feeds on flies and mosquitoes. Read the full description here.
Features of the


The ginger forest ant has the following features:
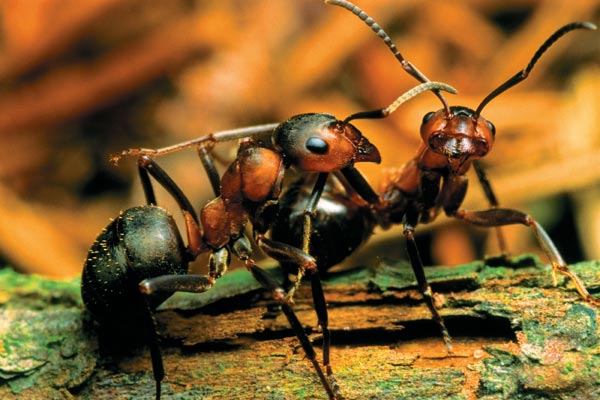
- The belly of an insect has a gland filled with a poisonous substance. Forest dwellers use it to defend against enemies. The poison is very painful. Even people feel discomfort from it. And with multiple bites, an allergic reaction can be triggered.
- Forest ants are completely deprived of the organ of hearing, so they hear nothing. In contrast, they have a well-developed sense of smell. Thanks to him, these forest dwellers are free to navigate the terrain and find their prey.
- The organ of vision in forest ants does not work at full strength.They see, but exclusively purple hues.
- The insect has powerful jaws. Their oral apparatus performs several tasks at once: construction, protective, grabbing prey. And also with their help insects transfer eggs, larvae.
Working individuals of red forest ants live 5-6 years, and uterus up to 20 years.
Output
The forest ant does no harm to humans. Moreover, he is an orderly and protector of the entire forest. In no case should he be exterminated. As for home guests, you can and should fight with them. They do not bear great harm to a person, but the risk of catching an infection is still present.
Males die after a while. Until workers appear, the female feeds on nutrients from the remnants of the musculature of the wings. From fertilized eggs, worker ants and females are born, and from unfertilized eggs, males.
These insects are by no means harmful, of course, if they do not look out for a human dwelling for their habitat. Therefore, it is not worth exterminating them just like that: after all, an ant is an important link in the ecological chain.
Varieties
Red forest ants have the following classification:
- Lesser or forest bare-backed. Its body length is 7-14 mm, its color is red-brown. Found in the temperate zone of northern Eurasia. Large anthills are created from needles, twigs (they reach 2 m in height).
- Northern forest. Found in the forests of the temperate zone of Eurasia. Red List of Threatened Species.
- Hairy forest. The length of working ants is 4-9 mm, while females and males reach 9-11 mm. They are also listed in the Red Book.

In addition, there is a bloody ant and a black-brown forest ant.
Methods for preventing the appearance of garden ants
It is always easier to prevent the dispersal of pests on the site than to deal with an overgrown population later. All biological methods are also suitable for prophylaxis. Experienced summer residents also recommend:
- clean the areas in time from unnecessary trash and product residues;


Lack of litter on the site reduces the risk of garden ants - destroy weeds not only in the garden or in the greenhouse, but also throughout the site;


Weeds and plant debris lure garden ants - prevent the appearance of aphids;
- dig up the soil regularly.
Lifestyle
The small forest ant is often found in deciduous, coniferous or mixed forests that have been around for 20-30 years. In the summer season, insects are very active, and in the winter they go into hibernation underground. Forest representatives, like all other species of these insects, are very hardworking.
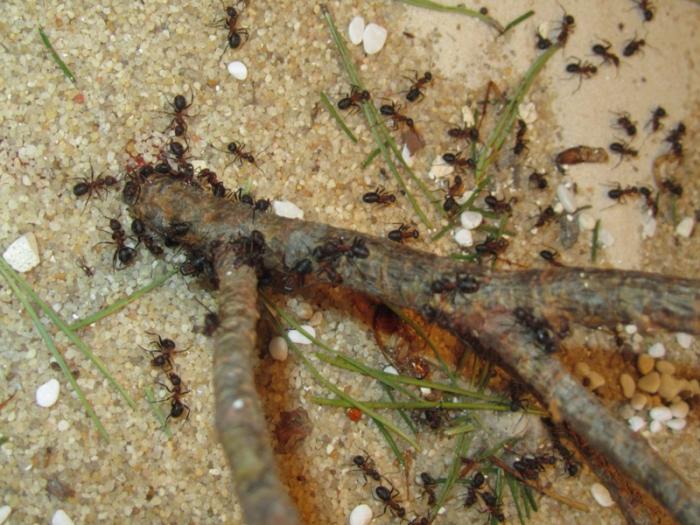
Forest ants create colonies that live in nesting anthills. They arrange them in the ground, wood, or under stones. Forest insects are well organized. All members of the family have clearly assigned responsibilities.
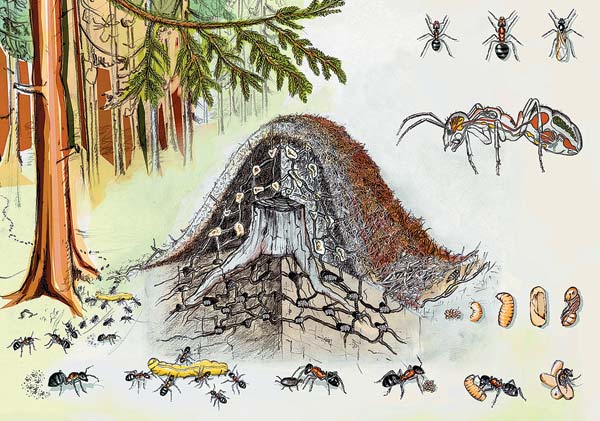


Forest ants are divided into several castes.:
- Females (queens or queens). The females lay eggs. Of these, male members of the family appear (from eggs that have not been fertilized) and females (from eggs that have been fertilized). The body of the uterus is noticeably larger than that of males and worker ants. The only long-liver of the colony is the queen.
- Males. The task of the male representatives of ants is to participate in mating. After a while, they are destroyed by other relatives from the anthill. Males are smaller than females. They have wings, but they only live 2-3 weeks.
- Foragers (workers). These are female representatives who have an underdeveloped reproductive system. They build an anthill, take care of the offspring. In their size, they are significantly inferior to the uterus. They have no wings.
- Ants are soldiers. These working members of the family have a large head and highly developed jaws. They duplicate the duties of worker ants, and also protect their nest from enemy invasions.
The female mates only once in her life.The obtained male material is enough for her to produce offspring all her life (10-20 years).
Let's say you've found a uterus. Now the fun begins.
You can't just put it in a test tube and put it in a warm place for a month - it won't grow anything and won't lay a single egg. She needs a family. The introduction of ants of the same species will also not give any positive results (tested in practice). This requires a different strategy. Naturally, it begs to implant her cocoons or her kindred species. And then there are a couple of interesting points that completely ruin the entire preparation for grafting cocoons.
- The queens of these species cannot do anything at all. They even feed on their own irregularly. Taking this into account, we usually believe that she will not be able to grow larvae until the moment the cocoon is woven, but we completely miss the moment that the higher ants also need outside help in order to get out of the cocoon. The uterus cannot provide such help. As a result, the ant in the cocoon dies. What to do? Get the doll yourself. This does not have to be done right before the ant hatches. You can give the uterus already pupae without a cocoon and leave them for independent development without a shell. Thus, they will not have to wait for someone to open the cocoon later. The whole problem is how to get the pupa out of the cocoon. The procedure is very difficult. The cocoon shell is torn with a needle from a syringe from the side of the pupa's head. If you tear from the side of the abdomen, then you can injure the ant, because the abdomen is quite close to the shell. "Naked" pupae are tossed into a test tube to the uterus. There is always a percentage of the dead. They either get injured while removing the cocoon, or they lack care, because the uterus does not follow the pupae.
- The second interesting point is the choice of the donor. It would seem that the best donor is an ant of the same species. Practice shows that it is not. During the development of this technique, it turned out that ants of the genus Serviformica are born with basic skills in caring, feeding, building, etc. However, ants of the subgenus Formica at the time of their birth do not have any skills at all. A freshly released ant does not know how to do anything, it is like a blank sheet of paper. The uterus, in addition to it, also has no education. As a result, having got stronger, the ants continue to climb from place to place until they die. Conclusion: we use Serviformic cocoons, but not Formic cocoons. Suitable S. rufibarbis, S. cunicularia, as a variant of S. fusca and the like.
Now we have found a uterus and received pupae of future workers. After catching the uterus, it is necessary to feed it. this is not lazius, which is adapted not to eat for a couple of months to feed offspring. You can grow this whole family in a standard test tube, followed by a transition to a small gypsum formicarium.
Also, you can not plant two queens together. Each uterus has its own test tube and its own pupae. Like other ants, one of the queens will eventually be expelled from the family.


Young donor workers Srviformica. A uterus and a dozen serviformics are already a good start. Then you should look well after them, because even after the first workers emerge from the pupae, the uterus will not lay eggs. They will appear a little later after the first donor workers hatch. What factors are responsible for this is not yet clear. Possibly temperature, possibly the presence of protein feed. In practice, it was not always possible to get the first native generation from the uterus before the onset of diapause. With the onset of diapause, the ants should be sent to winter, because in such a small colony at low temperatures, losses will be minimized.


The first native generation of rufa.
Food
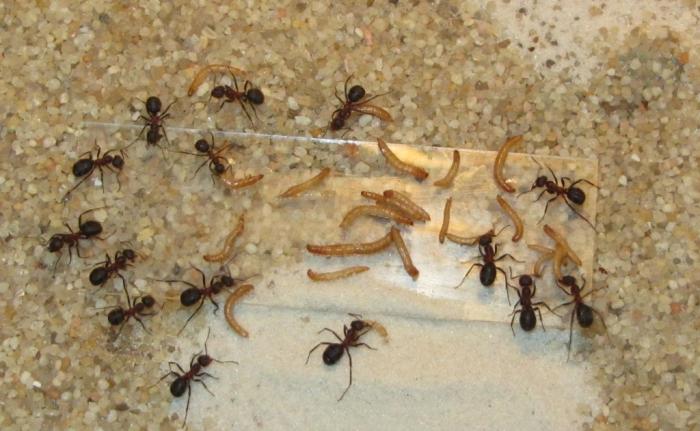
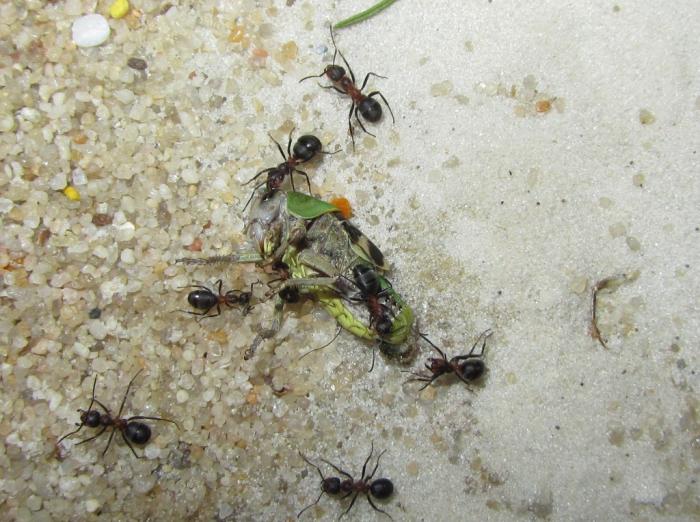
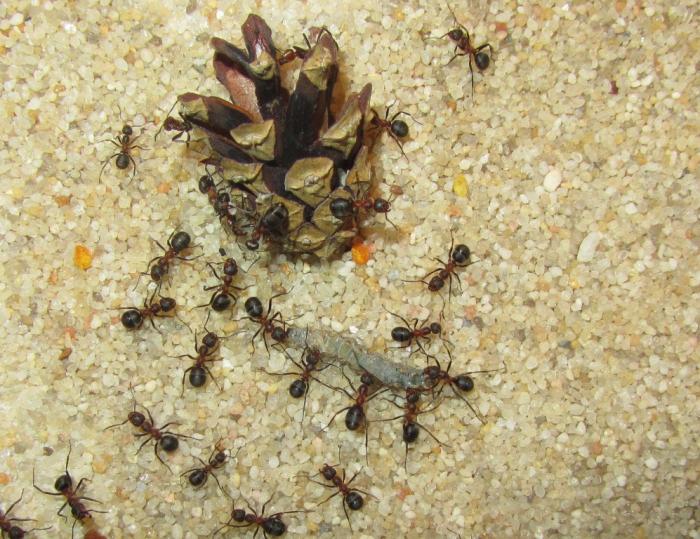
The small forest ant eats absolutely everything. Any insects and their larvae are the basis of the diet of forest ants. Therefore, all trees that grow next to the anthill are reliably protected from pests.In addition, ants love plant sap, as well as the sugary secretions of aphids.
The food suppliers in the nest are senior workers.... More aggressive members of the family are engaged in hunting. Attacking the victim, the ant paralyzes it with a special acid.
Then he drags the immobilized victim into the anthill. There it is divided into pieces and distributed between adult relatives and faces.


A hungry relative can get food if it knocks its antennae on the forager's head. He will immediately give him a small portion of food. After satisfying his hunger, he takes the rest of the food deep into the nest, where he feeds other ants, as well as their larvae.
If the forager breaks the rules and does not bring food to the anthill or does not want to share, then they do not stand on ceremony with him for a long time and eat them.
Among the workers, there are nannies who care for eggs, larvae and nymphs. They deserve a good portion of food. They spend a lot of energy on dragging the offspring from camera to camera in order to provide them with suitable conditions for development according to age characteristics. Forest ants also collect the sweetish secretions of aphids. In one season, they manage to harvest up to 20 kg of such food.
How to deal with ants in the garden
The most annoying ants are while they are in the garden. If you want to learn how to kill ants, take on board several proven methods:
- to scare off ants, place a rag soaked in kerosene under each fruit bush. Near the plantings of currants and gooseberries, you can sow calendula - it attracts a ladybug, which actively eats aphids;
- tie the tree trunk with cotton wool or wool soaked in a carbolic solution. Also create a palm-wide "protective ring" of soot and linseed oil;
- attach bottles of sugar water to the branches and lubricate their necks with syrup or anise oil;
- if ants have settled at the roots of a tree, use lime or bleach. Sprinkle quicklime on the heaps of ants and pour water over them. A 20% solution of carbolic acid will also make insects flee;
- indirect strikes against ants must be applied while fighting aphids. Dip the ends of the branches into a bowl of soapy saline or soapy ash solution and rinse there. Such a "shower" eats away at the skin of aphids and it becomes unviable.
To prevent ants from running through the trees, use trapping belts soaked in kerosene
Reproduction
New individuals of the male and female genders from the eggs laid by the uterus are born in the spring. On a warm day after rain, females and males with wings leave the nest.
Having flown 30-40 meters from the anthill, they land and start mating. After that, the female bites off her wings, forms a new colony, or returns to her previous home.


After intercourse, all male ants die. A new uterus lays 10 eggs every dayc. And working individuals take care of the offspring. Nymphs produce a special liquid that forms thin cobwebs in the air. Cocoons are spun from them. After 1.5 months, a young forest ant appears.
In young insects, the body is soft, the chest is light red, and the head and breast are gray. After 2-3 days, the chitinous cover gradually hardens, and the ant acquires a color, as in adults. At this stage, the teenager loses the guardianship of older relatives and begins to work on an equal basis with everyone.
The queen rules her colony, and the ants recognize each other thanks to special pheromones. When forest ants from different colonies are encountered, it is difficult to avoid a fight.
Strangers bite each other and bombard each other with formic acid. And they also attract relatives to help. There are even massive battles lasting 2-3 days in a row.
Reasons for the appearance of ants on the site
Insects are constantly exploring territories in search of food. On the backyard, garden ants are attracted by:
- the presence of unplowed land, where it is convenient to arrange dwellings;
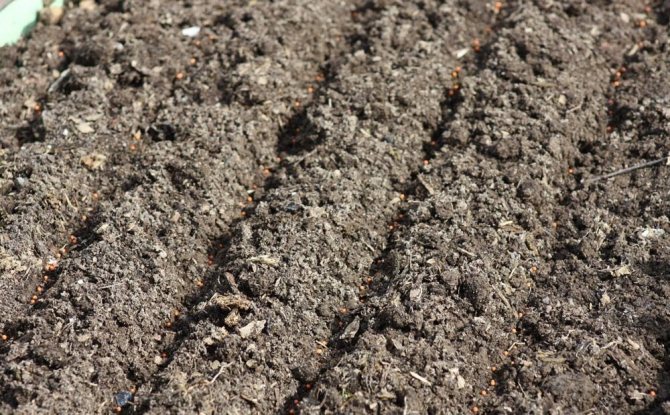


Ants will not be able to build an anthill on cultivated soil. - aphids: the main reason why ants take a liking to sites.
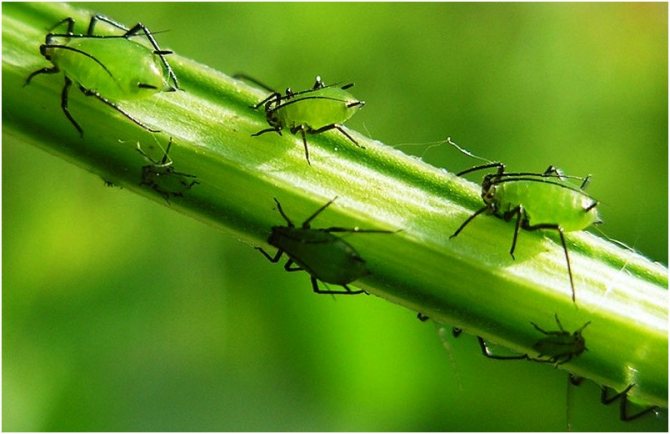


Aphids give off a sweet substance that ants like very much.
Populations of ants usually spread from neighboring areas or nearby woodlands.
For ants, aphids are a source of carbohydrate-rich food. Areas without it are of no interest to insects.