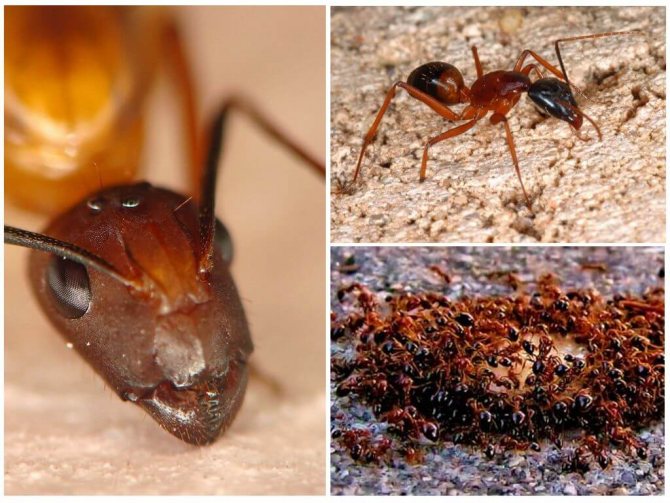
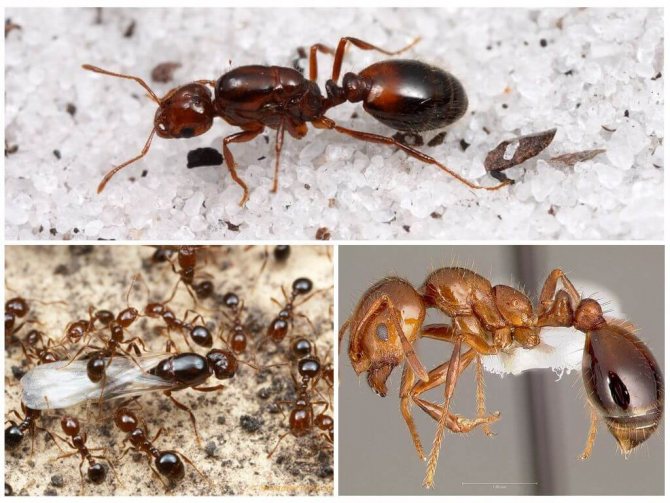
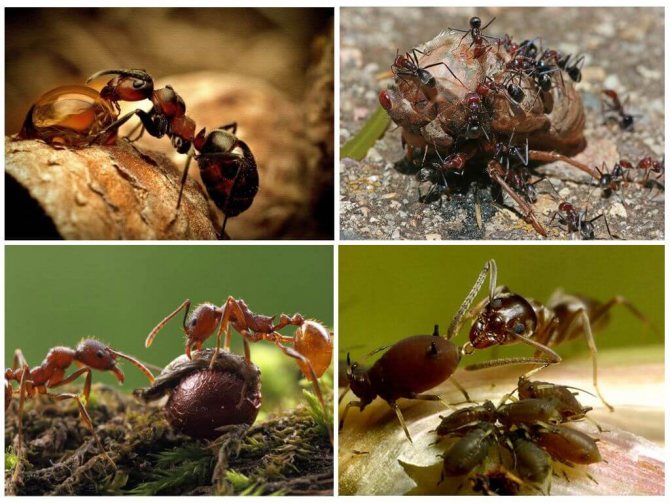
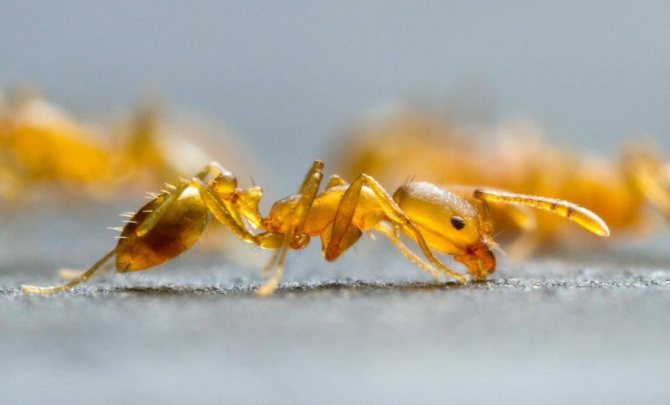
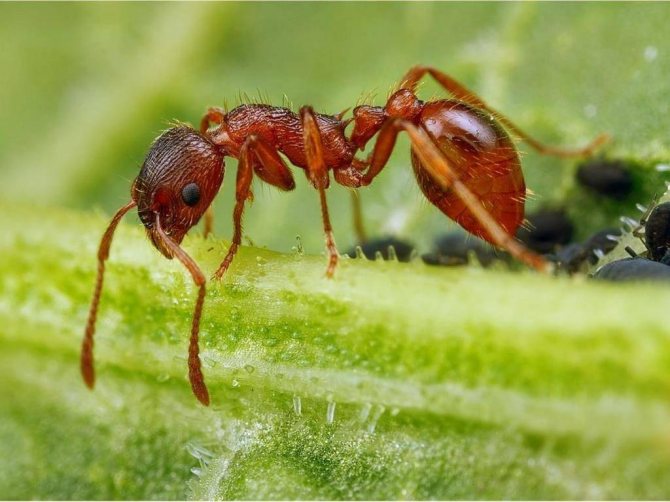
Red ants in the apartment are cause for concern. These are not at all "forest workers" who have lost their way and looked at you for a light, but dangerous domestic pests, heat-loving parasites, who are attracted by kitchen supplies. They are also called fiery red, pharaoh and ship ants.
Red ant - a dangerous house pest
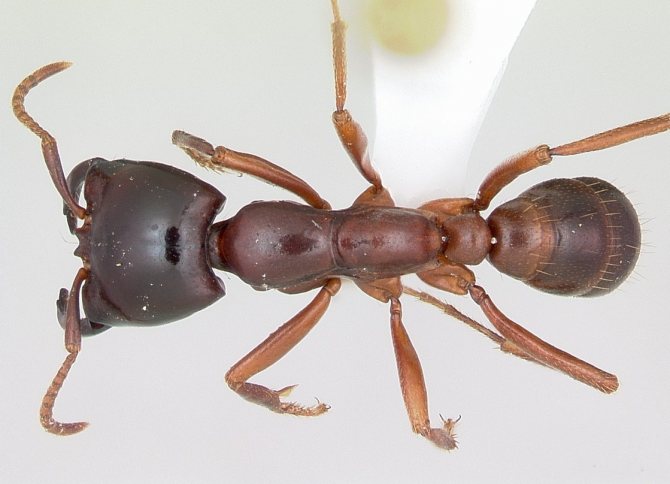
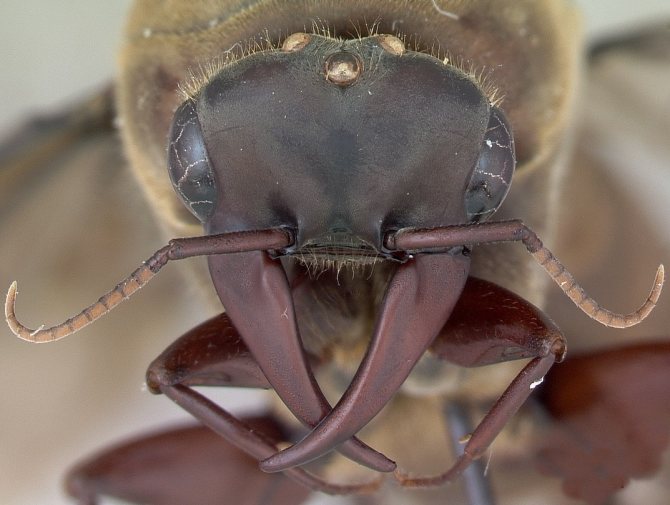
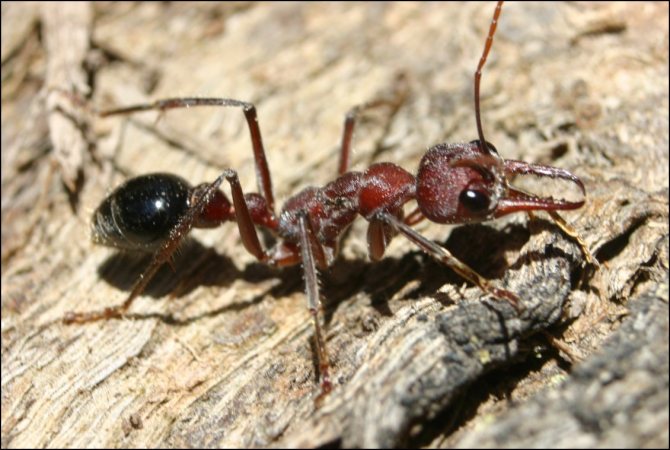
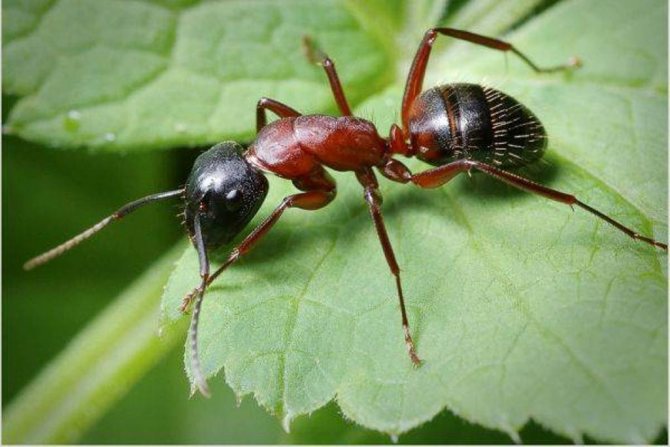
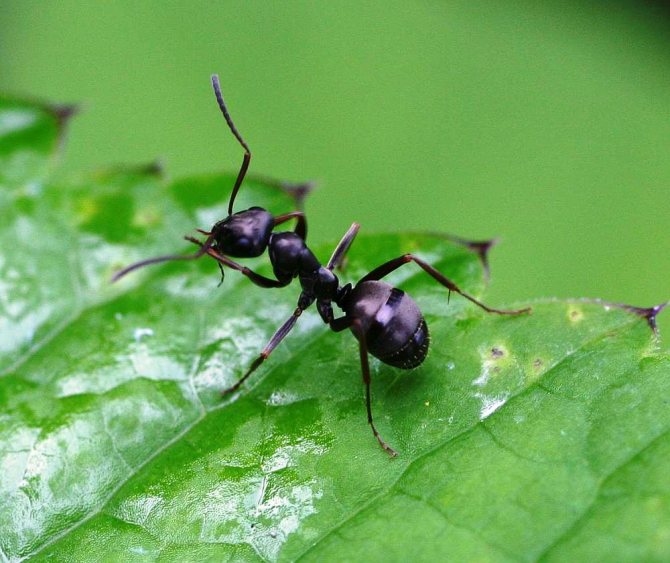
Outwardly, such a parasite differs little from its forest cousin: it has a small body about 5 mm long, a well-defined head section, chest, abdominal cavity, six legs and antennae. The insect has mandibles on its head - with their help, it transfers food and bites the victim. The antennae are the organ of smell, and the eyes of the ant have a complex faceted structure, make it easy to navigate in the dark and instantly respond to movement.
How do they look
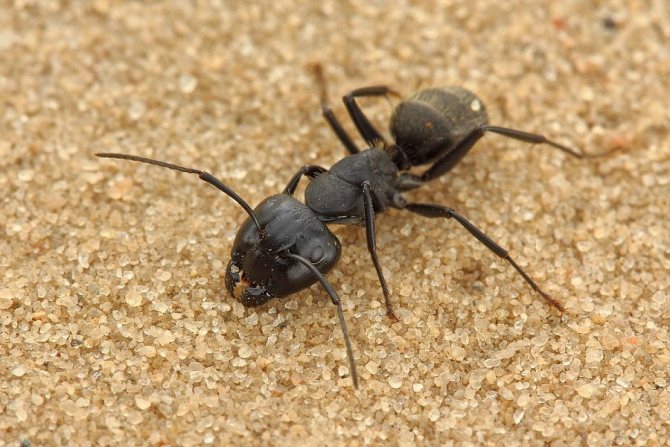
The bodies of mature individuals are divided into three parts: the head, chest, abdomen with three pairs of legs and a pair of antennae. Fire ants can be distinguished from others by their copper-brown head and body with a dark belly. Workers are blackish to reddish in color. The size varies from 2 to 6 mm. Ants of different sizes are present in the nest at the same time.

Solenopsis spp. identified by three body features: A leg with two nodes. Unarmed propodeum. Antennas with 10 segments plus a two-segment baton. Fiery ants bitespray formic acid. The bite is irritating. They have a special venom in the sting that injects an alkaloid as well as a jaw to bite.
Behavior
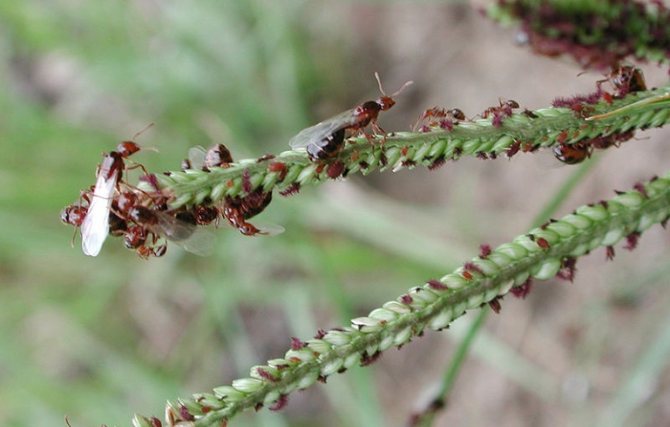
A typical fire ant colony creates large mounds in open areas. It feeds on young plants and seeds. They attack small animals and can kill them. Unlike many other species, which bite and then spray acid onto the wound, fire ants only bite to grab, then sting (from the belly).
A toxic alkaloid poison called solenopsin, a compound of the piperidine class, is injected through the sting. For humans, it is a painful bite, a burning sensation (hence the name). Subsequent exposure to the poison can be fatal to sensitive individuals.


Fire ants are more aggressive than most native species, so they pushed others out of their local habitat. For example, the bees are parasitized by Euglossa Imperialis through orchid species. They enter the hive from below and plunder the contents of the cells.
These ants are known for their ability to survive in extreme conditions. They do not hibernate, but can survive cold conditions.
With other insects
Red fire ants are known to form reciprocal relationships with several species of butterflies, Lycaenidae and Riodinidae. In Lycaena rubidus, the larvae excrete a liquid with a high sugar content. The ants return the larvae back to the nest and protect the pupal stage in exchange for feeding on liquid. For the larvae of Eurybia elvina, soil shelters are built on the inflorescences.
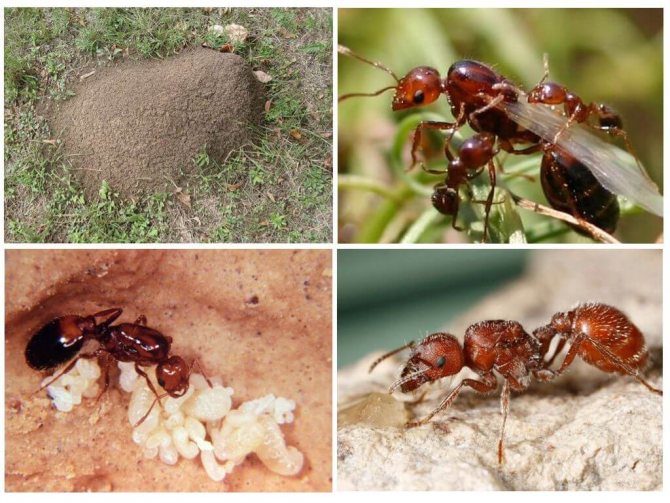
Fire ants nest in the soil, near wet places, such as river banks, ponds, lawns, highways. Usually the anthill is not visible, since it was built under wood, logs, stones, bricks. If there is no shelter, domed mounds are built.
They can only be observed in open spaces such as fields, parks, lawns. These mounds reach a height of 40 cm, higher on heavy soils -1.0 and 1.5 meters in diameter.Colonies are founded by small groups of queens or singles.


Even if only one queen survives in a month or so, the colony is thousands of individuals. Some are polygynous (have several queens per nest).
Insects are resilient and can survive floods. During Hurricane Harvey in Texas in 2020, clusters of fire ants known as rafts were observed on the surface of the water. Each cluster had as many as 100,000 individuals that formed a temporary structure until they found a new permanent home.
Fire ants dig tunnels efficiently, using about 30% of the anthill's population, thereby avoiding congestion in the tunnels.
Reproduction
Their natural habitat is natural conditions, but this does not prevent them from coming to living quarters and settling in colonies there. Regardless of where they decide to settle down, scouts ants first examine the territory.
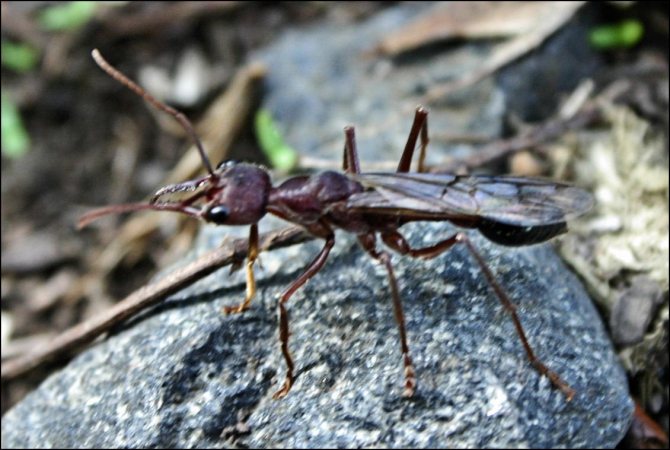
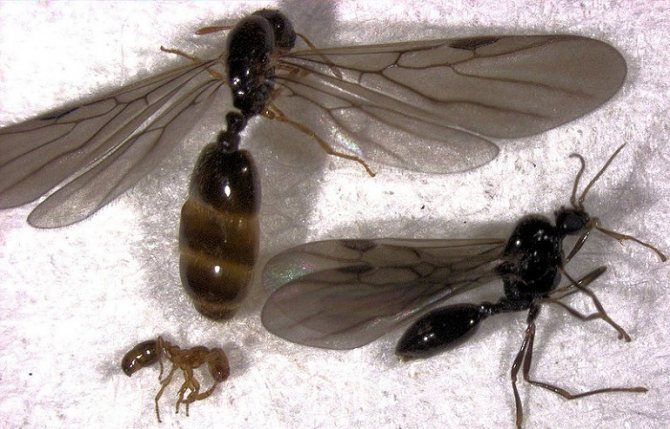
Their task is to check the conditions for arranging the nest and check food sources, these are the main criteria for finding a habitat. When the territory approaches, the old colony begins to move. The main individuals of the colony are the male and the female, which have wings; they fly to a new nest almost first.
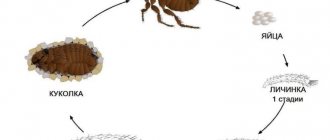
This species has a unique ability, reproductive individuals can reproduce offspring on their own, if necessary, to replenish the ranks of working ants. The uterus is engaged in the replenishment of the offspring, she reproduces females and males. One uterus can lay 250,000 eggs in its lifetime.


Not all representatives of this species spend time arranging their homes and building anthills. For example, in Argentina, goose bumps can choose a reptile nest for their colony, they drive out caimans and occupy warm housing.
But they do not stop there, the offspring of reptiles, which remain in the nest, are doomed to perish. Ants eat eggs, not giving the slightest chance of development and survival.
Regarding their own offspring, larvae appear from the eggs, which outwardly resemble worms. Individuals at this stage of development are absolutely helpless, they are not able to feed themselves, develop, and even more so survive without the help of working individuals.
The larva must go through several molts, with each molt, its body weight increases and its size increases, then it is reborn into a pupa. She is also cared for by working goosebumps, when it comes time to move to the next stage, they help her get out of the cocoon.
Roles
Queen
Fire ant queens, reproductive females, are the largest. Their main function is reproduction. The queen seeks to found a new colony after a nuptial flight. In a new location, she uses a special poison to paralyze intruders, in the absence of workers to protect.


They live up to seven years, produce up to 1600 eggs per day. Their nests contain up to 250,000 workers. Young, virgin queens have wings (like males), but shed them after mating.
Males (drones)
The main purpose of males is to mate with queens during the mating flight. After the male successfully fertilizes the queen, his goal is fulfilled. He is not accepted back to the mother colony and dies outside the nest.
Other roles
There are other types of roles that are performed by employees. The main ants are known for their larger size and more powerful mandible jaws, commonly used for maceration and food storage.
Learn more Two-tailed in the human ear: can it bite?
Small ones perform normal tasks (caring for eggs, larvae, pupae, cleaning the nest, obtaining food). Solenopsis daguerrei has no workers - they are considered social parasites.
Distribution history
The homeland of red ants is Ethiopia.Thanks to the development of trade relations and the colonial seizures of African lands, these insects came to the European continent. Accustomed to the warm, humid climate, they began to settle in people's homes, where there were optimal conditions for their habitation and reproduction. This was facilitated by their small size, which made it possible to penetrate into cracks and tiny holes in walls and floors.
Now the favorite places of residence of ants are:
- cracks under skirting boards, window sills and plumbing fixtures;
- bags with cereals, dried fruits, breadcrumbs and other products.
They can be found in the cavities of sockets and switches, among the pages of books, in the trash can, under the refrigerator and even in the hood, where particles of fat accumulate, which serve as a treat for these "invaders".
How to eliminate the source of fire ants
Most fire ant species do not bother humans and are not invasive. Solenopsis invicta, known as the red imported fire ant (RIFA), is an invasive pest in many areas of the world: USA, Australia, China, Taiwan.
It was believed that RIFAs were accidentally brought into countries through shipping crates. They were thought to be in the Philippines, but they are most likely confused with Solenopsis geminata.
The FDA estimates that 30-60% of people living in infected areas get bitten every year. RIFA are found mainly in the subtropical southeastern states of the United States:
- Florida;
- Georgia;
- South Carolina;
- Louisiana;
- Mississippi;
- Alabama;
- parts of North Carolina;
- Virginia;
- Tennessee;
- Arkansas;
- Texas;
- Oklahoma;
- New Mexico;
- California.
Current national control or eradication programs are not particularly effective. The insects have adapted - now they have longer legs and new behavior that helps to avoid danger.
Natural enemies
The forid flies, Phoridae, are a large family of small, humpback flies, somewhat smaller than the vinegar flies. Two species of this family (Pseudacteon tricuspis, Pseudacteon curvatus) are parasites of the red fire ant in South America.


About 110 species of Pseudacteon have been described. Pseudoactones multiply by laying eggs on the ant's ribcage. The first instar larvae migrate to the head, then develop, feeding on hemolymph, muscle, and nervous tissue.
After about two weeks, they cause the insect's head to fall by releasing an enzyme that dissolves the membrane that holds the ant's head to the body. The fly pupates in a severed head capsule that appears in two weeks.
Flies, pseudoactones, are an important ecological limiter for Solenopsis. They are introduced throughout the southern United States.
Plants
The Venus flycatcher, a carnivorous plant, is found only in North and South Carolina in the United States. About 33% of the Venus flycatcher's catch is ants of various species. They lure prey with sweet juice.


As soon as the insect has entered the trap, touched two or three "trigger hairs", the bristles on the leaf surface cover the prey. They restrict it behind the "teeth" around the perimeter, and digest it. Other carnivorous plants such as the sundew (Drosera) also trap insects.
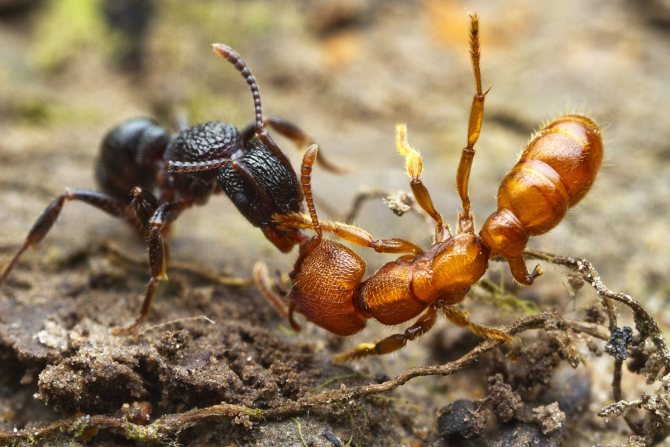
The main natural enemies of fire ants are other ant species that attack queens during the nest foundation period, when there are no workers to protect the emerging colony.
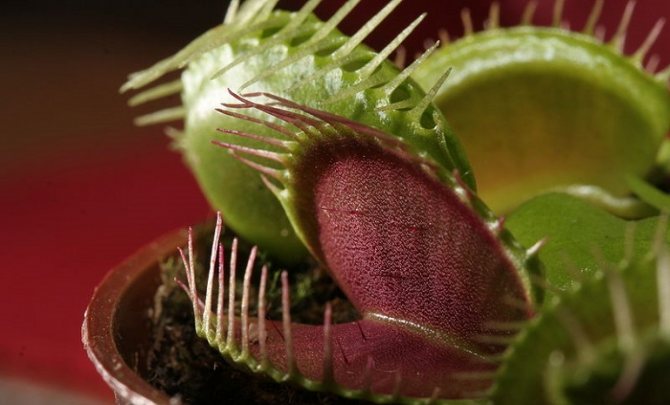


A number of entomopathogenic fungi are natural enemies. For example, Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae. The latter is commercially available for biological control (i.e., pesticide-free) of various insect pests. New technology has increased its lifespan and effectiveness against fire ants.
The lifestyle of the most dangerous insects
Ants are considered insects that can cause considerable surprise.You can start with the fact that these creatures, which do not have a developed brain, act quite clearly and orderly when protecting the family and obtaining food. They also surprise with the structure of their community. The most dangerous insects, fire ants, live in an anthill built on their own, and their reproduction takes place there. Reproductive individuals have the ability to reproduce by cloning, mating only to hatch sterile workers. Throughout her life, the queen gives birth to numerous offspring (about a quarter of a million ants).
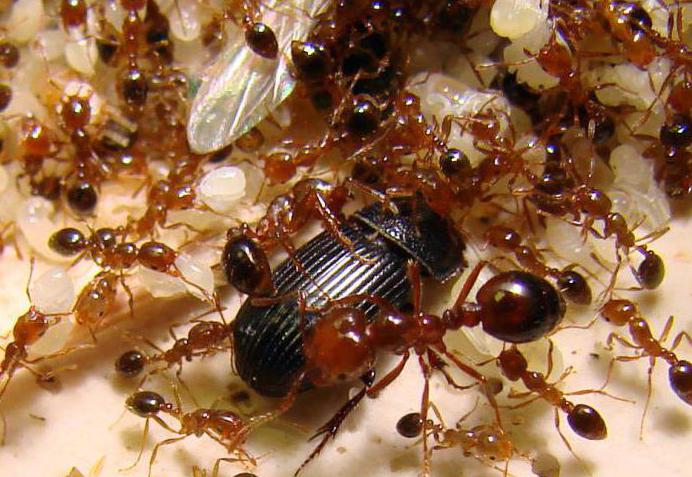


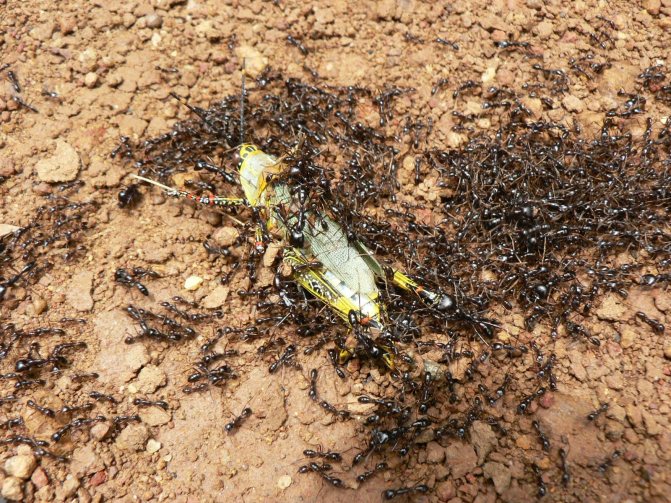
The diet of these ants consists of plant and animal food, they do not distinguish it and eat both species with pleasure. Basically, insects with addiction eat sprouts of herbal plants, shoots of small shrubs. The diet includes different types of insects, larvae, caterpillars. Fire goosebumps often attack even mice, frogs and snakes, do not disregard the corpses of large animals. During an attack on a prey, ants in a large group climb their legs on its body. They dig into the skin with the mouth apparatus and inject a sting. This is how a considerable dose of poison enters the animal's body, which is toxic. At the site of the bite, the skin begins to burn strongly, unbearable painful sensations arise.
Red imported fire ants
The red fire ant (Solenopsis invicta) is native to South America, spread across Australia, New Zealand, Asia, and the Caribbean. United States of America (USA). The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has named them one of the most invasive species in the world.
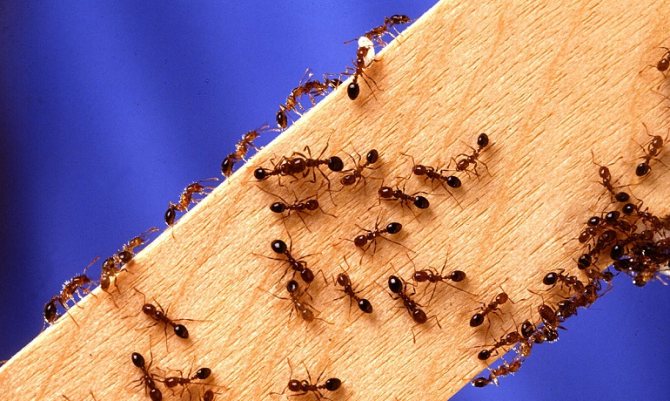


Impact
Insects are a serious problem as they cause significant environmental, social and economic damage.
Ecological
Fire ants are very aggressive, greedily feed on land animals such as insects, frogs, reptiles, birds, mammals. Displace or destroy local animals.
They pose a threat to local plants, because they eat and damage seeds and seedlings. These impacts cause serious damage to ecosystems over time.
Social
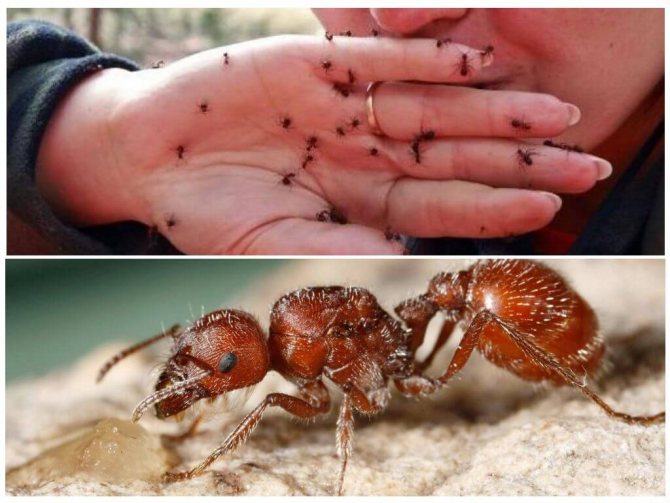
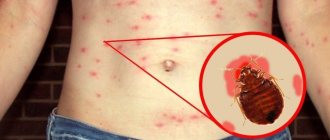
Fire ants pose a serious threat to human health due to their bite, which causes a painful burning sensation. They swarm to attack and sting repeatedly.
Bites can be fatal if a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) occurs. There is a risk of secondary infection if the blisters or pustules from the bite are damaged.
Everyday activities such as barbecues, picnics, sports activities are not possible in highly contaminated areas. Pets can also be bitten and injured, have allergic reactions, or are blinded by poison.
Economic
Insects kill farm animals and crops, and newborn animals are especially vulnerable. Fire ants pierce the eyes, mouth, nose, causing blindness, swelling, and suffocation.
They penetrate the food and water reserves of animals, do not give food, which leads to starvation and dehydration. They damage crops, eat seeds, and pass through roots and stems.
Learn more Formicaria for ants, features of keeping and feeding
They protect some of the harmful insects that produce powdery mildew. The increased presence of these pests affects the quality of products and contributes to the spread of diseases.
In the United States, fire anthills have destroyed equipment such as irrigation systems and damage equipment during harvest operations.
Anthills are a problem on lawns, sports fields, golf courses. Ants damage roads, paths, expensive electrical equipment, often seriously.
Inhabitants of our country
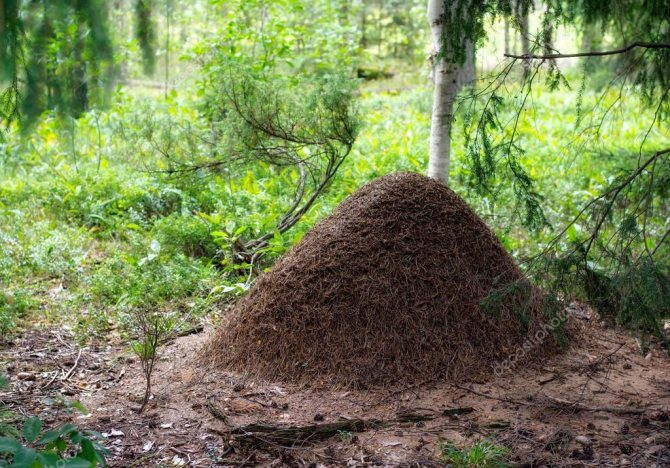
If we talk about the territory of our country, then this species is quite rare, since such living conditions are not quite suitable for them.Our territory is inhabited by red ants, which are fiery among the people. Compared to the fiery ones, you cannot call them aggressive, but on the contrary, against their background they look very peaceful.
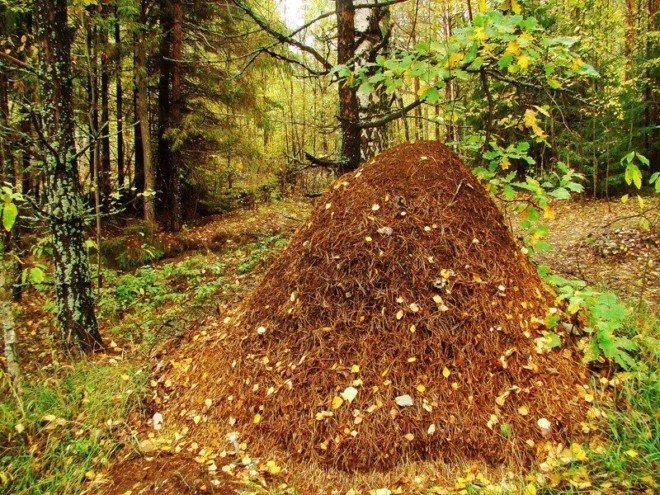


They live in natural conditions, they prefer to equip anthills in coniferous, deciduous forests. They belong to very useful insects, since they are directly involved in the formation of a nutritious soil layer for plants, in addition, they are forest orderlies, since they destroy pests. For humans, they do not pose any danger.
European view
Myrmica rubra, known as the European fire ant or common red ant, is from the genus Myrmica. Found throughout Europe, invasive in parts of North America, Asia. It is red in color with dark pigmentation on the head.
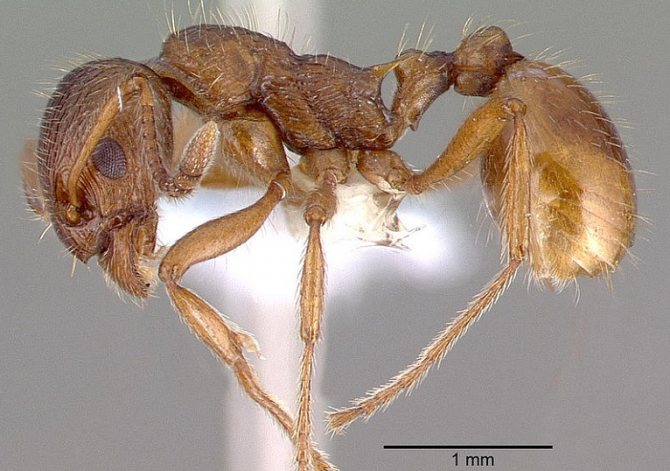


Lives under stones, fallen trees, in the soil. Aggressive, often attacks rather than flees, can bite, although does not have the ability to spray formic acid like Formica.
It is found in the region from Portugal to Eastern Siberia (up to Transbaikalia), from northern Greece to the forest-tundra zone in the north. In Japan, North America, it is considered unpleasant and aggressive.
Anthills are polygynous, have up to one hundred queens per nest. Queens get together after the mating flight, form a nest, lay eggs.
The species is polydomic, with many nests per colony. Queens live up to fifteen years. Mating flights in Europe run from late July to mid-August. Hundreds of young winged insects rise into the air to mate.


After that, the males die and the queens shed their wings to create a new nest. They do not fly in North America, but only male swarms have been recorded in Newfoundland, Canada.
They are very common in Europe, live in meadows and gardens. They feed on powdery mildew secreted by aphids, insects, invertebrates.
Fire ant venom is relatively well understood.
They attack any creature that interferes with their nest, but are not as aggressive as the imported red fire ant. They also eat pollen, a phenomenon rarely seen in temperate ants.
The larvae of the butterflies Phengaris alcon (Alcon blue) and P. teleius (rare large blue) use M. rubra as their main host.
Fire ant venom
Poisonous substances play an important role in the biology of fire ants, used to capture prey, protect, antimicrobial action. Newborns contain little to no supplementation, but workers who are only one day old produce 1.17 mcg / day.
Upon reaching the age of 15 days, the amount decreases to 0.3 μg. The poison is secreted and stored in a bag. When used, it is thrown through the main channel of the tip The capacity is 20 - 40 nl, depending on the size of the insect.
American entomologist Justin O. Schmidt called it "sharp, sudden, slightly disturbing." Scored 1 for the Schmidt Bite Pain Index, a scale that measures the intensity of pain from an insect bite from 0 to 4.
More than 95% of the components of the poison are water-insoluble alkaloids. Solenopsin has cytotoxic, hemolytic, necrotic, insecticidal, antibacterial, antifungal, anti-HIV properties. Experiments show that the average lethal dose (LD 50) for female rats is 0.36 mg / kg.
Approximately 46 proteins have been identified. They directly affect the anaphylactic reactions seen in poison-sensitive people. While these include neurotoxins and potential allergens, not all proteins are involved in venom function.
Proteins benefit the colony. Some kill bacteria, which explains why workers spray poison around the nests. Others bind pheromones, which help create chemical pathways for communication with congeners.
Symptoms and Signs
Fire ant venom (> 95%) consists of oil alkaloids derived from piperidine (Solenopsin) mixed with a small amount of toxic proteins. Stinging ant bites are painful, characterized by a local burning sensation, accompanied by urticaria. Develops into a bump, rash, or blister within 20 minutes.
The bite site swells in a few hours. Causes further pain, irritation, especially after several bites in the same place.
The bump develops into a white pustule within 24–36 hours. She can become infected by scratching. It goes away spontaneously after a few days if left alone.
The pustules are obsessive, uncomfortable during activity. If infected, it can cause scarring. The formation of pustules occurs in almost every person bitten by ants.
Medicines such as antibiotics, diphenylhydrazines, epinephrines, topical steroids do not affect pustular reactions.
Some people are allergic to poison, even anaphylaxis, which requires urgent medical attention. Hypersensitivity occurs in people with certain medical problems, such as heart disease or diabetes.
Learn more Recipe for boric acid from ants in an apartment, in the country
The use of adrenaline is recommended. It has been proven that the formation of pustules occurs from the introduction of poison alkaloids, an allergy to fire ant bites is caused exclusively by allergenic proteins.
In addition, neuropathy, seizures (without any signs of previous systemic reactions), cerebrovascular trauma, and nephrotic syndrome are associated with fire ant venom.
The neurotoxins in the venom explain why some victims experience hallucinations after being stung.
First aid
First aid for a fire ant bite includes topical treatment and oral medications. There are many home remedies of varying effectiveness, including the immediate application of a one-to-one bleach solution and water or aloe vera gel.
External, local drugs - anesthetic benzocaine, antihistamine diphenhydramine, corticosteroid hydrocortisone.
Antihistamines or topical corticosteroids can help relieve itching and local stinging reactions. Tablets are antihistamines.
Severe allergic reactions to ant bites, including severe chest pain, nausea, excessive sweating, loss of breath, severe swelling, slurred speech, are fatal if left untreated. An urgent request for medical attention is required.
Reasons for appearing in the house
There are many reasons why small red ants start up in the apartment. They like the smell of food and the warmth, so they try their best to get inside the room.
Often, red ants appear at home due to:
- a live anthill stationed in an adjacent room;
- accidental introduction of a lonely individual into the house on clothes or any object;
- rare house cleaning;
- detachment migration in search of a new home;
- the presence of a garbage chute, front door, dryer or damp basement.
Working ants are in constant search of food for the queen and, despite their small size, are able to easily travel great distances. If there is enough food in the apartment, it remains on the floor in the form of crumbs, garbage, etc., then the colony of ants will grow very quickly, and the fight against them will be difficult.
Treating fire ant bites
Epinephrine rapidly reverses the adverse effects of shortness of breath and hypotension.
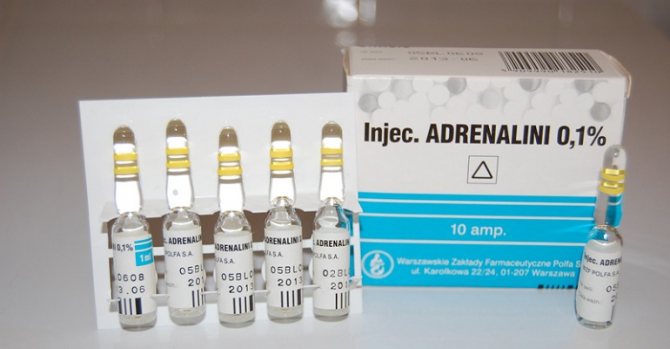

It is suggested to use a conservative approach in the treatment of bite injuries. Treatment is based on symptoms. For minor injuries with symptoms including pustule formation and pain, over-the-counter products are available to prevent infection. Ants are removed by washing the area with antiseptic soap.
Victims with signs of anaphylaxis are treated with antihistamines, epinephrine, parenteral corticosteroids. It is recommended that people who suffer from anaphylaxis use an epinephrine autoinjector (EpiPen) if shortness of breath or hypotension occurs.
Immunotherapy (WBE) has been used to treat anaphylaxis since 1973. Anyone suspected of having an allergy is referred to an allergist for evaluation. The whole body of the ant is used for treatment, not just the poison.
Unlike ant poison immunotherapy (which is sometimes used), WBE contains proteins. To reduce sensitivity, dose extracts are gradually introduced into the body. WBE is very effective in preventing systemic reactions. Not recommended for children with large local reactions, those who live in areas with severe infection are made an exception.
The recommended maintenance dose is 0.5 ml 1: 100 w / v 1:10 w / v WBE. For poison immunotherapy, a common maintenance dose is 0.5 ml of a 1: 200 dilution (w / v).
During the build-up phase, it is recommended to give the dose weekly or biweekly. Patients undergoing immunotherapy are required to receive treatment for three to five years and lifelong therapy, although there is no consensus as to how long a person should be treated.