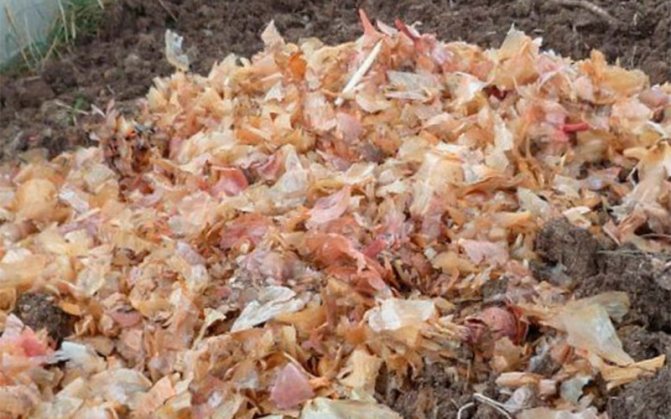
The yield of potatoes is due to many circumstances, therefore, such plant cultivation methods should be used that allow, among other things, to actively fight against pests of nightshade crops.
If the larvae of the potato nematode have settled in the soil of the site, then neither favorable weather and climatic conditions, nor the composition of the soil and the quality of its processing, nor the professional use of fertilizers and correctly selected varieties will not allow collecting a high yield.
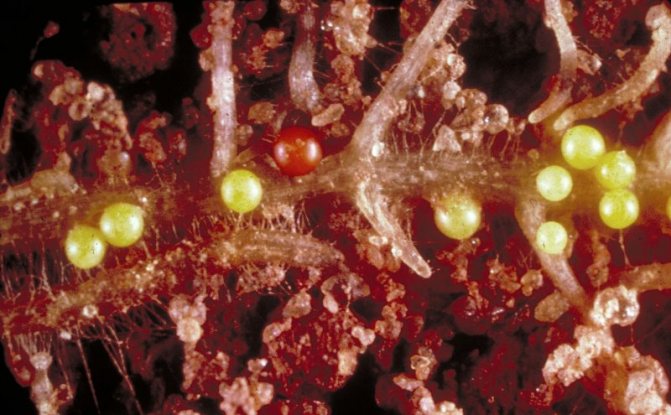
Cysts under a microscope
It is difficult to combat a phytopathogenic, but the correct choice of fungicides and the implementation of agrotechnical requirements, which are described in this article, help to significantly reduce or eliminate the harm caused to potatoes.
What is potato nematode
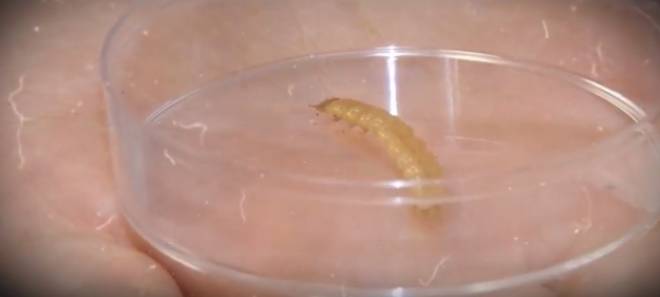
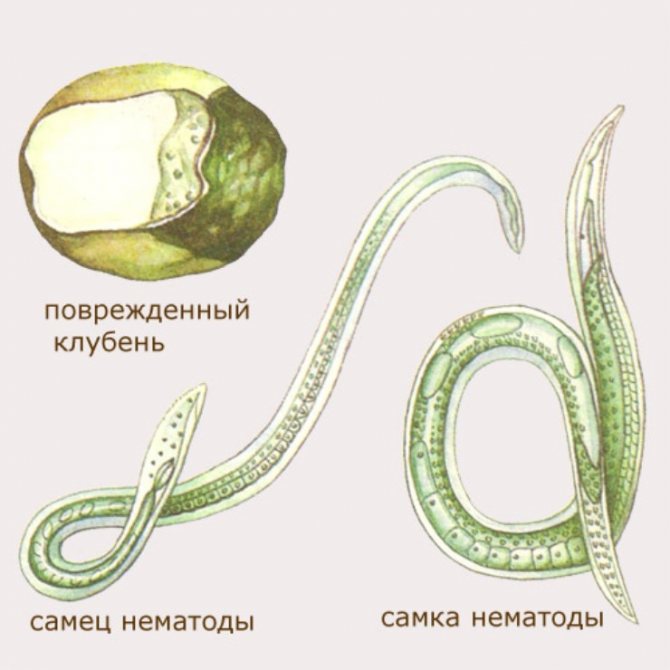
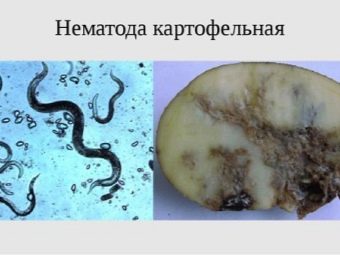
The potato nematode is a small worm that belongs to the order of roundworms. The length of his body reaches not more than 1 mm... The people consider this worm to be practically invincible, the eggs of the nematode are able to survive any winter while in the soil. The nematode demonstrates no less resistance to drought, floods, and radiation. The dose of radiation that can kill a nematode is several tens of times greater than the dose required to kill a person.


The worm is striking in its ability to multiply very quickly. Despite its tiny size, the nematode can destroy almost the entire crop. The countries of South America are considered the homeland of the pest. Subsequently, the nematode struck other continents as well. At this stage of time, zones bordering with Ukraine and Kazakhstan are considered endemic areas. After a nematode becomes detected in any region, quarantine is urgently announced. Thanks to such measures, the spread of the worm is slowed down.
Preventive measures


Nematoda is a tenacious and persistent pest, so it is easier to prevent its appearance in the garden than to waste time and money on a difficult and not always effective fight.
- planting healthy tubers;
- disinfection of potatoes before planting;
- compliance with the rules of crop rotation. Usually summer residents have planted a crop in one place for decades, which is why bacteria, viruses, pests accumulate in the soil and the risk of catching an infection increases tenfold;
- treatment of tubers before planting with hot water;
- timely hilling, weeding, watering of the crop;
- removal of plant residues from the ridges (both during the growing season and after harvesting potatoes).
Varieties of nematodes
Currently, there are several types of nematodes that can infect plants, especially potatoes. Each species has its own characteristics in terms of vital processes, as well as external signs.
There are the following main types of pathogen:
- Golden nematode.
- Stem.
- Leafy.
- Gallic root.
Golden nematode
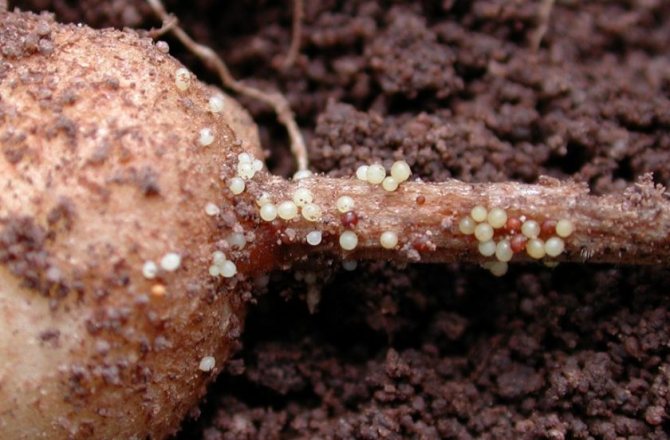
This variety affects only nightshade plants. The size of the nematode does not exceed 2 mm, which does not allow you to see it with the naked human eye. The worm has a round shape, golden or brownish color, from where it got its name. The roots of a plant are affected after the parasite attaches to them and releases a secret into the roots that can destroy cell components. After softening the cells, the worm eats them.
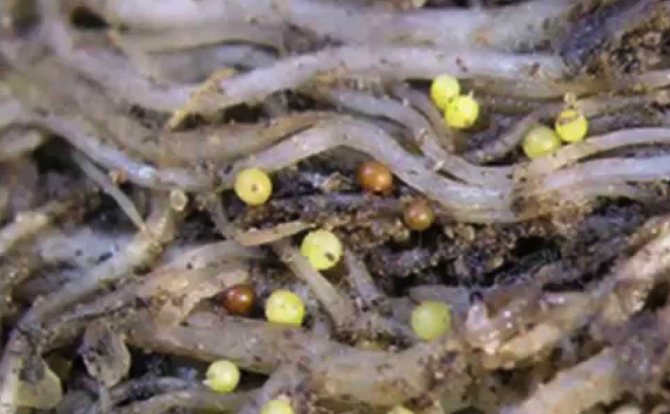


It is not difficult to determine infection with a nematode: the lower leaves of the plant dry out, acquiring a yellow color. On a potato bush, the number of stems decreases due to the fact that one part of them dies, and the other cannot grow to the required size. The bush does not bloom, tubers are not formed.
Stem form
Each type of plant has its own kind of nematode. The worm usually affects onions, garlic, potatoes, tulips, carnations and others. The size of the worm is also small, does not exceed 1.5 mm, has the shape of a thread.


The nematode enters the plant through damage to the root of the plant. When they get inside, they quickly multiply and lay eggs. A characteristic sign of nematode damage is the appearance of bright white spots, which soon become friable. Stems and leaves become deformed, and subsequently the plant dies.
Leaf form
These worms are the smallest representatives of nematodes. As a rule, the leaf form of the nematode has no color, and its size about 1 mm... A distinctive feature of leaf nematodes is the ability to quickly move around the plant. The nematode can move the virus, which will aggravate the course of the lesion.
Unlike other species, the leaf nematode parasitizes the leaves, causing the foliage to wilt. The signs of infection are the appearance of defects in the leaves, as well as various spots.
Gallic root
This type of parasite infects the roots of vegetables, is white in color and small in size. It should be noted how the worm enters the plant. The parasite has a special component in the mouth opening in the form of a needle, which makes a hole in the cage and penetrates through the hole inward.


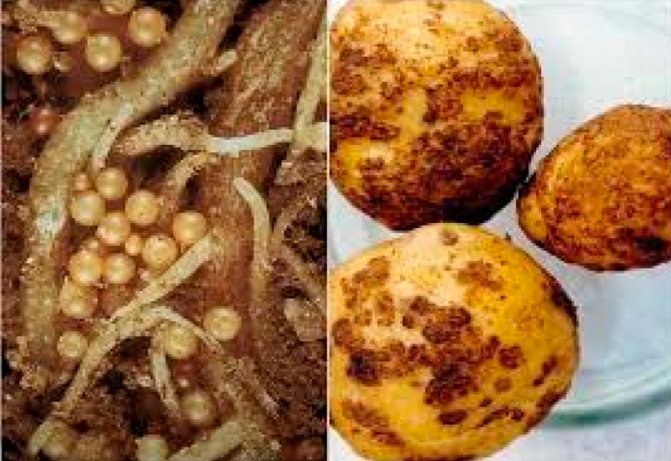
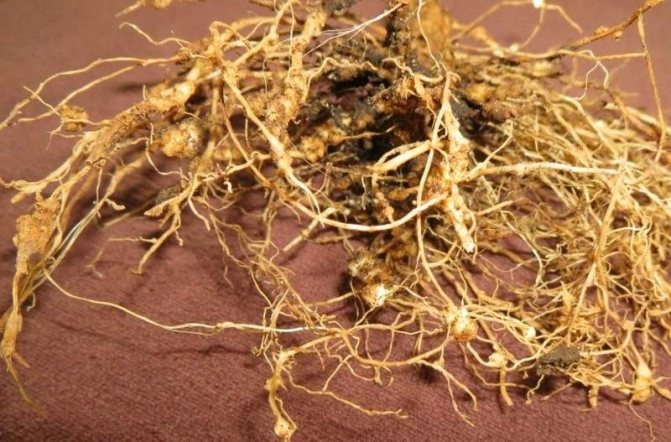
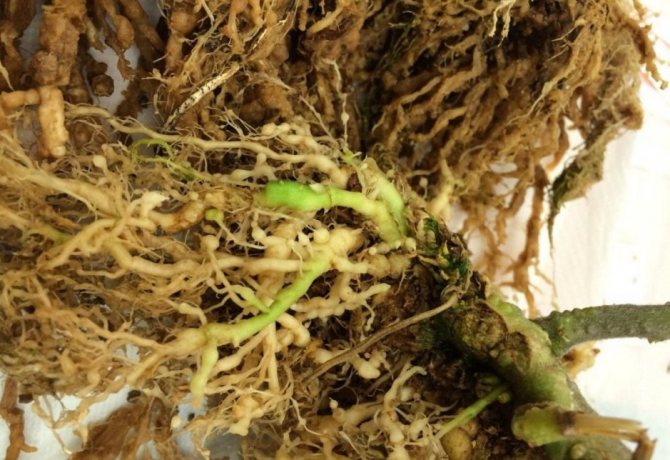
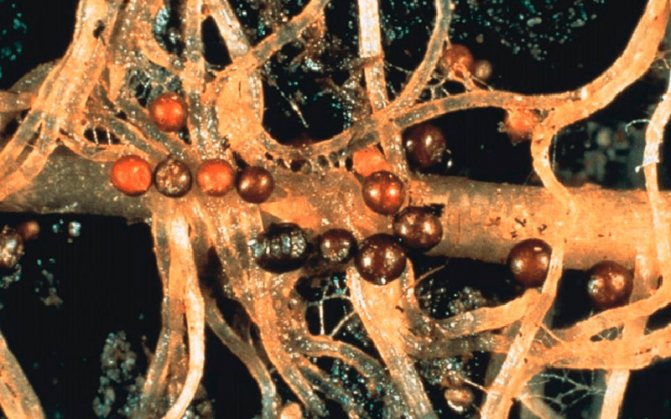
Subsequently, the worm releases toxic products during its life, which have a detrimental effect on the plant. A characteristic feature of the nematode is the appearance on the root of the plant of white growths, which are called galls. The galls contain the larvae of the parasite.
How to deal with a nematode
For the fight, the most important are two rules: compliance with preventive measures, as well as the declaration of quarantine in the event of a disease in plants.
The basic rules of the fight include the following points:
- Crop rotation must be observed. In the place where the nightshade plants grew, it is not worth planting anything other than vegetables and legumes for several years.
- Do not use greenhouse land on the plot.
- In the fall, a deep digging must be carried out without fail.
- Before planting, you must carefully inspect the seeds. Before sowing, the seeds should be rinsed in warm water.
- It is best to grow potato varieties that are resistant to nematodes.
- To strengthen the immunity of the plant, it is necessary to fertilize and introduce microelements.
- For prophylactic purposes, the site should be treated with urea before sowing.
There are aggressive techniques to kill the parasite. For this, various chemicals are used to treat the affected plants. These drugs include: Nematicide, Nemabakt, Mercaptophos, BI-58.
It should be noted that chemical preparations have some effect on the fruits of the plant, so the best option for dealing with a nematode is its timely prevention. The developed complex of preventive measures will contribute to a healthy harvest without the use of chemicals.
Potatoes are one of the most important crops grown in home gardens and farmland. Not always the reasons for low yields lie in unfavorable weather conditions, improper care. Pests contribute no less to the deterioration of the quality characteristics of root crops. The insidious and worst enemy of nightshade crops is the potato nematode, recognized as an object of internal and external quarantine.


Pest control methods
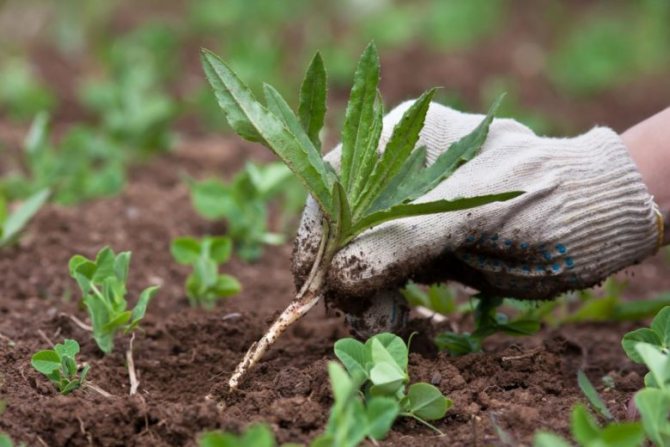
How to deal with insects will depend on their species. For example, stem worms can be harvested by hand. They usually affect not only potatoes, but also some types of flowers, including carnations and tulips. You can prevent the spread of the pest over the site by removing the infected plants from it along with the roots, followed by burning.
If the bulbs of crops are infected, you can try to solve the problem by heat treatment. To do this, they are immersed in hot water, where they are kept for at least 10 minutes, after which they are cleaned, dried and planted in the soil. Do the same with pots or any other container where the bulbs will be planted.
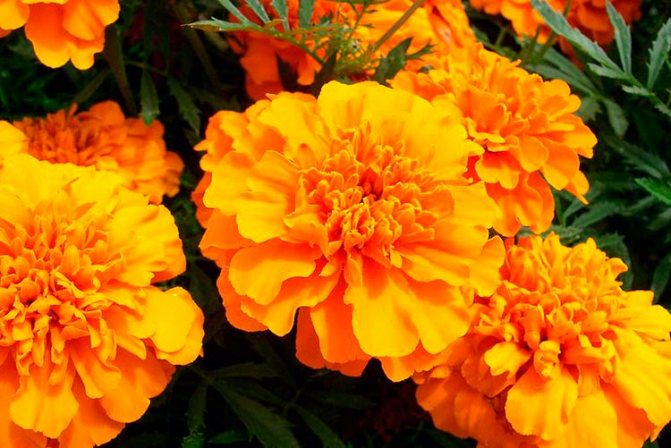
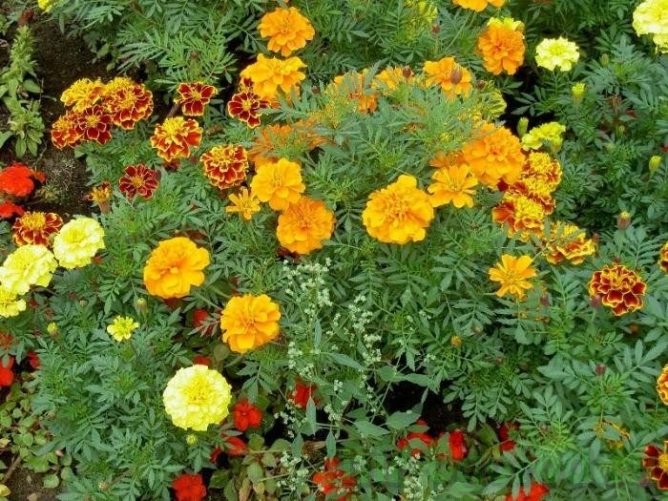
Not everyone knows that the golden potato nematode is afraid of some plant species, which in this case act as defenders of the plot in the garden. Planting such crops will help get rid of parasites and improve plant growth. We are talking about strong-smelling marigolds, as well as the root system of rudbeckia, coreopsis, Gaillardia. All of them repel the nematode and protect garden crops without harming the plants.


The solution to the problem of the appearance of nematodes in the soil will be preventive measures. When planting plants, you need to use only disinfected tools. In addition, it is recommended to set aside a separate pot for each bush during quarantine.
It is important to regularly treat the soil with hot steam for 40 minutes, check the plants for infection as often as possible, and from time to time rinse the rhizomes with a solution of fosdrin.
If traces of a nematode were seen on potatoes, despite preventive measures, it is worth immediately contacting the control authorities, whose representatives can take measures to solve the problem. Bushes affected by worms must be removed and destroyed.
It is believed that an effective remedy for the nematode is percalcite, which affects not only adults, but also eggs. They use it a week before planting potatoes - 200-300 g / cm2, immersed in the ground to a depth of 15 cm.Also, as an option to combat the parasite, carbamide, introduced into the soil a month before planting potatoes, at the rate of 100 g per m2 ...


Urea
Using aggressive control methods, you can get rid of the nematode in the soil without the help of specialists. Suitable drugs such as "Nematicide", which can disrupt the development of cysts, if you add it to the soil a few weeks before planting potatoes, or "Nemabakt" - a particularly effective drug against cysts, capable of destroying them from the inside.
For spraying infected plants, you can use Bi-58 or 0.2% mercaptophos solution. Plants are treated every five days for a month. When working with drugs, you should observe safety measures. Getting on the skin and mucous membranes, Bi-58 poses a real danger to humans, damaging unprotected areas.
In conclusion, we note that it is easier to prevent contamination of crops in the garden than to fight parasites on your own. Even if there are no traces of a pest on the site or in the greenhouse, you need to remain vigilant and take measures to prevent its appearance.
Anyone who begins to regularly dig up the soil in the fall, observe potato crop rotation, monitor the cleanliness of the tool and the quality of tubers for planting will not have to learn what a fight in the garden against a nematode is.
It is believed that the most resistant to harmful insects potato varieties are Agria, Vital, Alvara, Latona, Prior and some others. It is they who should be given preference, not forgetting about the plants that protect the site from parasites and disinfect the soil.
Harm of the golden potato nematode
In the early stages of infection, it can be extremely difficult to identify the pest. The following signs indicate the appearance of a potato nematode:
- plants are very lagging behind in growth;
- rapid dying off of the lower leaves;
- the green mass fades prematurely and begins to turn yellow;
- the stems are curved;
- little or no flowering;
- death of bushes, small tubers;
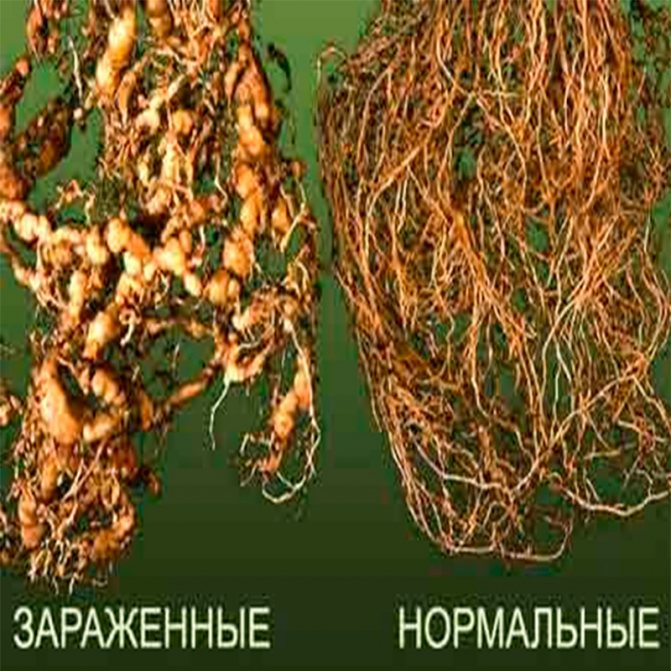
- the roots turn brown.
If chaotically located areas with underdeveloped plants appear on a potato field, this can become a signal of nematodosis. As a rule, symptoms become clearly visible 40-50 days after planting the tubers.
The danger to humans of the golden potato nematode lies not in the infection of the person himself when eating root crops, but in a decrease in yield, which can reach 80% and the absolute unsuitability of the site for planting nightshade crops for 10 years.
Where does the pest come from and how does it infect plants?
The soil, as well as plants, are affected by the pest as a result of getting it on the site by a mechanical method. It happens as follows:
- during planting of infected crops;
- when storing infected potatoes healthy in high humidity;
- when working with an infected tool (not cleaned after contact with soil where nematodes live).
Infection can also occur if crops are planted in the soil where pest-damaged potatoes once grew, but only if the number of pests exceeded 1000 individuals per 100 cm3. In this case, it is recommended to take a break between plantings - at least one year.
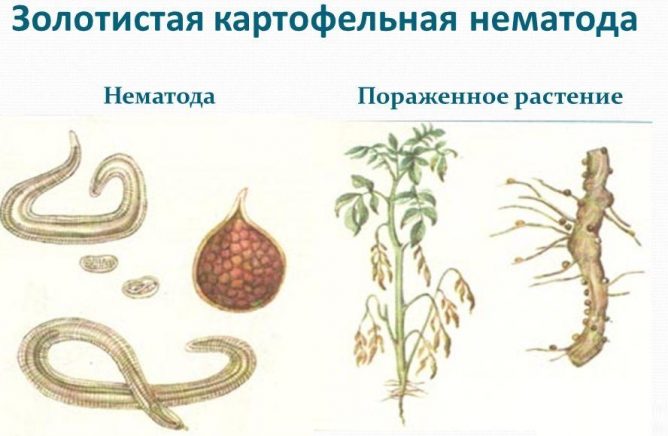

How the golden potato nematode spreads and how to control it
Despite the fact that the nematode belongs to quarantine objects, its habitat is constantly expanding. Cysts from contaminated soil are transferred:
- through the wind;
- on shoes, tools;
- with rainwater;
- with planting material.
When signs of parasitic worms are detected, the question of how to deal with a potato nematode that has settled in the soil becomes relevant. Alas, even such a potent drug "Tiazon" cannot completely eradicate the problem, because cysts are weakly susceptible to the effects of poisons. All measures are aimed at containing and reducing population growth:
- After harvesting, the soil is sprinkled with lime in an even layer, during digging it is mixed with the soil.
- During the planting of tubers, a handful of ash mixed with 1 spoonful of bird droppings and 3 handfuls of dry manure is added to each hole.
- To destroy the larvae at the end of planting, you can treat the soil with a solution of bird droppings. To do this, liquid chicken manure is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:20. For 1 sq. m is consumed from 5 to 10 liters of the finished solution.
- In early spring, to stimulate the release of larvae from the cysts, a tincture of potato sprouts is prepared. One kilogram of shoots must be crushed, you can use a meat grinder, pour 10 liters of water and insist throughout the day. Urea is added to the soil, and then the finished solution (one bucket per 10 sq. M).
- During hilling, mineral fertilizers are applied between the rows at a distance of 5-6 cm from the stems.
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to observe crop rotation and cultivate legumes or cereals after potatoes. The inventory must be disinfected and cleaned. You can plant potato varieties that are resistant to nematodes:
- Aspia, Pomegranate;
- Pushkinets, Lukyanovsky;
- Early Zhukovsky, Picasso, Frigate;
- Prolisok, Latona, Crystal;
- Belarusian, Karatop, Prior.
Control measures
The most reliable way is to prevent nematodes from entering your area. But if this was not done, then the following should be adopted potato nematode control measures:
- As seeds for the next season, it is necessary to select only healthy tubers, without the slightest signs of disease.
- Better to use potato varieties that are resistant to nematode infestation. These are Nida, Romano, Kristall, Prigozhiy 2 and others.Choosing from their own seeds, preference is given to early and mid-early varieties, the duration of the growth and maturation period of which is 60-80 days.
- Care must be taken to ensure that contaminated soil does not enter arable land.
- The crop rotation method is used. Dill, peas, clover, mustard and other nematode-resistant plants are not planted on the infected sites. After five years, the previous varieties of potatoes can be planted in this area.
- Dug out diseased plants must be burned without fail. The same is done with the tops left after the autumn harvest. It must not be left on the field.
- All equipment and shoes are recommended to be disinfected at the end of the work.
- The introduction of finely crushed bark of coniferous trees (spruce and pine) into the soil will help to reduce the number of nematodes. Mix them in equal amounts and add them in the early spring on the site.
- Using organic fertilizers (manure, chicken droppings), you can achieve not only a decrease in the population of a dangerous pest, but also strengthen the immunity of plants.
Stem nematode development on potatoes
For a long time, the pest was mistaken for a stem onion nematode, and only 60 years ago the differences between the two related species were described. The parasite is ubiquitous, in almost all countries of the world.
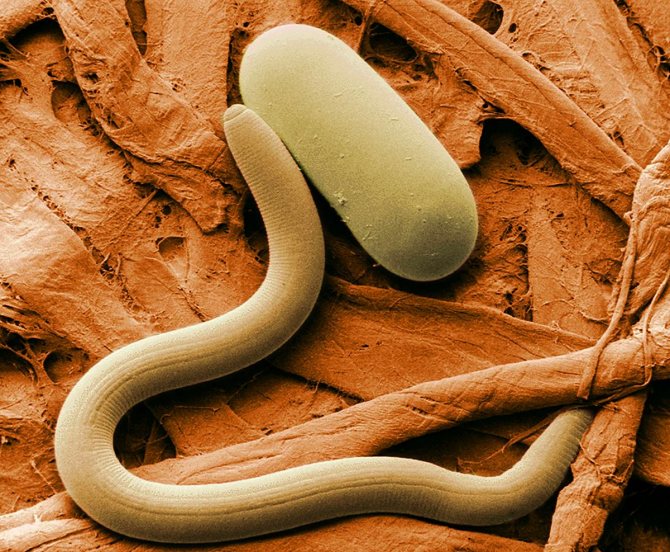
This type of nematode infects tubers during the growing season and during storage in vegetable stores. In addition to potatoes, it can parasitize on other crops: beets, cucumbers, tomatoes, legumes, pumpkin seeds. The potato stem nematode is characterized by a microscopic size of 0.7-1.4 mm, a thin long and slightly curved milky body. The larvae differ from their parents in smaller dimensions and an underdeveloped reproductive system.
Mostly infection occurs from the uterine tuber during the growing season. The nematoda penetrates through the underground parts of the bush into the formed tubers. The possibility of the invasion of the worm from the contaminated soil, in which the larvae from previous crops remained, is not excluded. Eggs of stem nematodes withstand low temperatures and do not die when the soil freezes.
The larvae undergo 4 molts and become sexually mature individuals. A fertile female lays up to 250 eggs inside the tuber. At an optimal temperature regime of + 20-24 ° C, the development of one generation takes from 20 to 25 days. The temperature range at which the female is capable of reproducing offspring is very wide: from + 3 ° C to 37 ° C. High humidity, rainy and damp weather favorably affect the development and reproduction of potato stem nematodes.
Description of the pest


In the wild, there are more than 20 thousand species of nematodes - roundworms, most of which are parasites. They were brought to Europe from South America, and for more than a century in European countries, farmers and gardeners have been fighting this scourge.
In our country, the first pests were noted in the middle of the 20th century, now the nematode is found in all regions.
Ask and get useful advice from professional gardeners and experienced summer residents. >>


What is a nematode? This is a microscopic worm that infects the roots, stolons, tubers of potatoes, penetrates the stems, which slows down and stops the growth of the bushes. Most nematodes are dioecious, not hermaphrodites. Females usually have rounded bodies in which eggs accumulate.
At the end of summer, females die, forming a cyst with a strong shell, from which larvae gradually emerge. The life cycle of worms depends on the species; soil infection with the parasite occurs over several years.
Tubers rot, they cannot be eaten or stored. The nematoda is a carrier of various viral diseases, which aggravates the damage done to it.These types of roundworms are not dangerous to humans.
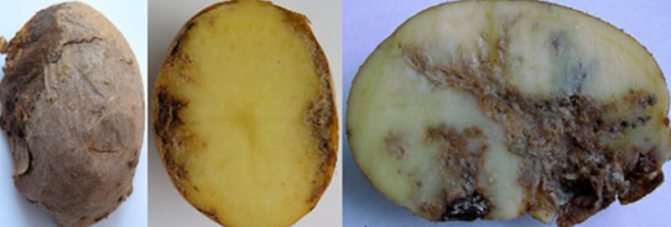

It is difficult to fight it, since worms show resistance to common insecticides, parasitize mainly on the underground part of plants, which makes it difficult to timely diagnose.
Gall nematode
The nematode species affects plants both outdoors and indoors. It parasitizes on various types of crops, including potatoes. It is localized in the root system and in tubers. Females lay eggs directly in the roots. Of all types of potato nematodes, they lead in fertility - up to 2000 eggs, as a result of which neoplasms - galls - are formed on the infected places.
Damage blocks the flow of water and nutrients into the plant, which in turn leads to a lag in growth, development and, accordingly, affects the yield.
- Compliance with crop rotation and rotation of pest-resistant crops.
- Soil treatment with steam or preparations from the Avermectin group, which are a double complex of biological components and chemical compounds.
- Disinfection of planting material, inventory.
Lack of moisture provokes the development of the population and reproduction of root-knot nematodes, therefore, in dry years, their greatest distribution is recorded.
In our country, nematodes were identified at the end of the forties of the last century. For seventy years, this parasite has spread throughout the country from south to north. In total, there are more than twenty thousand species of nematodes in nature, these parasites are steadily expanding their range, becoming the cause of problems in agriculture in different countries. The most dangerous nematodes for potatoes.


Symptoms of the disease
The first signs of the disease are detected on crop seedlings. Affected plants are delayed in development, chlorosis of the leaves is clearly manifested, spreading to the entire potato bush.
Signs of damage to potatoes
First of all, roundworms harm the root system. It is difficult for plants to provide nutrients with water from the soil, and then a large number of small tubers are formed. In everyday life, this state of potatoes is called "bearded". In drought and insufficiently fertilized soil, plants die.
What it is?
The cause of many troubles for agriculture can be a gluttonous parasite - a nematode. It does not pose a danger to humans, but a potato nematode, for example, can completely ruin the crop.
The worm is microscopic in size, but the description of indirect signs of infection is quite simple:
- plants slow down growth;
- leaves turn yellow and dry up;
Nematodes can enter a plant in a variety of ways that are difficult to track. Microscopic worms can be carried by summer residents through untreated tools, they are also transferred to shoes, spores can be carried along with moisture and wind.


Soil contamination: how to avoid


One of the reasons for the spread of the disease is soil contamination, which leads to infection of the root system and stem. It happens trivially - as a result of mechanical transfer:
- planting infected tubers;
- joint storage of healthy and diseased fruits;
- using untreated garden tools (or shoes) after "contact" with contaminated soil;
- during harvesting, the capsules, with the nematode larvae separated from the root, remain in the ground;
- incorrect crop rotation or lack thereof;
- others.
Varieties
Potato plants are attractive to these types of nematodes:
Golden
Especially dangerous is the golden nematode, which has been terrorizing Europe for more than a century.
And also this parasite is also called a soil nematode. Mainly affects plants:


The parasite has a body measuring 0.2-1.4 mm, the worm at an early age has a white color, in a sexually mature state it casts a golden color.First of all, the roots suffer, from which nematodes suck out all the useful substances. A pregnant cyst-forming female nematode increases in size two to three times, becoming like a ball covered with a caramel-colored shell. One female can give birth to up to two hundred offspring at a time (sometimes this number can reach half a thousand).
In early spring, the parasites attack plants and eat the roots. In one season, up to two generations of these dangerous worms can change. Fighting nematodes is not easy; their larvae are well protected and hardy, they are not afraid of:
- frost;
- floods;
- high temperatures;
- radiation;
- toxins.
Golden nematodes are able to stay in a state of suspended animation for ten years.


Stem
The stem nematode has a length of 0.9 to 1.9 mm. Females lay up to 350 eggs. Up to 5 generations can change in one year. Potato stem nematode is one of the brightest representatives of phytohelminths. It feeds on root systems:
Potatoes suffer the most from stem nematode. The development of generation takes place from three weeks to two months, much depends on the ambient temperature. Wintering takes place in the form of an egg or larva. There is no anabiosis.
The stem nematode is very fond of high moisture content in the air, if the summer is rainy and there is little sunlight, then the parasite reproduces exponentially. Huge areas of useful crops can be destroyed in a short time.

Pale
The pale potato nematode is a cyst-forming parasite of the heteroderite family. In addition to potatoes, it also affects:
Reproduces bisexually. Loves the climate of the middle zone. Fertility up to 450 individuals, size 375-532 microns.
The male does not feed for one week, he fertilizes the female and dies. The larvae emerge from the eggs in the spring and penetrate the roots. After a short time, they are destroyed.
The range of the pale nematode (affects potato tubers) is the same as that of the golden relative. Such "kids" are able to completely eat the harvest. Infection is possible from seedlings or soil. The eggs of the parasite are not afraid of low temperatures; the female lays them directly in the tuber itself. The incubation period lasts about three weeks.
Up to 90% of the crop can die when such a scourge appears. After the appearance of the nematode, it is not possible to plant any crops on such soil. It will take years of reclamation and processing of such a site, sometimes the terms can be delayed up to ten years.
Another harm that the nematode brings to the plant. The action of worms is a kind of battering ram, pathogenic microorganisms, a fungus, which “eat up” the remains of the culture, attack a weakened plant through a punctured "gap".
Signs of appearance
It is possible to detect nematodes when there are obvious signs of its appearance on the leaves and stems of plants. This happens most often after 6-7 weeks after planting. Signs of nematode infestation:
- slowing down the growth of the plant;
- yellowness of the leaves, which are located closer to the ground;
- twisting of the stems;
- faded flowering;
- general underdevelopment of the bushes;
- the roots are painted in a dark brown color.
When the growing season lasts, nematodes cannot be detected, just one "fine day" they suddenly appear everywhere everywhere. An indirect symptom may be thickening of the stems, as well as the fact that the bushes become too "curly". Another clear sign is the appearance of white spots on the tubers and the loosening of the tuber structure. And brown spots may also appear, which quickly increase in size.


Prophylaxis
Measures that can be effective are compliance with all crop rotation conditions.There is a high probability of the appearance of this parasite in those areas where potatoes are grown from year to year for a long period. It is better to plant potatoes after legumes (or grains), give the soil a rest and resume planting after four years.
After harvesting, the site should be well cultivated, removing half-rotten roots from the ground. Thoroughly wash and disinfect garden tools, often even a formalin solution is used for these purposes. In no case should you plant tubers if there is even the slightest suspicion of their "ill health". Treat seedlings with antiseptics, rinse the tubers in warm water just in case. Strengthen the immunity of seedlings by processing them:


Plants must have adequate nutrition, which also contributes to an increase in their resistance. Necessary trace elements such as:
It is recommended to grow potatoes that have good nematode resistance. All these standby measures can reduce the risk of infection with this terrible parasite by nine-tenths. Special potato varieties that are not afraid of nematodes:


If the larva enters such tubers, then where it has penetrated, the potato tissue dies, the parasite dies of hunger. But it should be remembered that it is forbidden to plant the same varieties, there is a threat of the development of immunity in nematodes. Potato varieties should be changed every four years.
Bushes that have been attacked are immediately dug up and burned, this is the only way to protect themselves from the parasite. The infected plant should not be shaken, cysts can easily scatter throughout the area; in this case, a large area will be affected, especially if the weather is windy. Plants affected by the nematode are often placed in a pit and watered with chlorine solution. The nematode should be fought non-stop, it is a very insidious pest, its elimination is possible only with the help of complex systemic measures. In late autumn, the areas where potatoes are supposed to be grown are processed with lime. In early spring, each hole is placed:
- manure (two handfuls);
- wood ash (one handful);
- bird droppings (one teaspoon).
This method allows you to protect yourself from nematodes and feed the plants.
Poultry droppings effectively destroy the larvae of the parasite. A solution is made in a consistency of 1: 20 and the potatoes are poured over with this composition. On average, one square meter can take up to one bucket of this solution.


But you can also use urea or mineral fertilizers, they also prevent the reproduction of this parasite. Nematodes "love" annelids. If you treat the area with organic fertilizers in early spring, then you can thus attract the appearance of worms in large quantities. There are special preparations containing annelids ("Nemabakt", "Protection"). Along the perimeter, you can plant plants that scare off nematodes, releasing irritating substances:
If the area of the site is infected, then it is sown with winter rye. This usually happens after the first week of September, then the plants will have time to develop before the cold weather. With the appearance of the first snowflakes, it is cut off, laid on the soil and finely crumbled with a bayonet shovel. The resulting mass is sprayed with the composition "Baikal EM" (the solution is made one in a hundred). After it gets warmer in the spring and the snow melts, the mass is interfered with the ground, dug up.


It is recommended to use chemicals only in case of severe damage, when there is no other chance to get rid of the pest. Substances are powerful toxins, therefore, safety precautions should be followed, and they should be handled in accordance with safety standards.
Non-malignant varieties are very popular in our country. There are more than seventy positions in the register of the Russian Federation. If taken as a percentage, then this is more than 30% of the total number of crops used.
The best results are observed in such varieties as Impala and Rocco (77% and 78%). Penetrating into the tuber of such a potato, the nematode larva does not find enough nutrition in it, the parasite does not develop, and it dies.


Agrotechnical measures
The disease is easier to prevent than to cure after it. The results in preventing the spread of nematodes are clearly visible in the technology of crop rotation on the site. The greatest effect is obtained after sowing legumes in a potato field.
After harvesting the potatoes, the land must be dug to a considerable depth. All suspicious soil fragments are treated with hot water. At temperatures above 40 degrees, most of the larvae and eggs of the nematode die. This is the minimum that can be done, it is safer to completely destroy a piece of soil if it is small.
Potato treatment methods
The chemical compound "Bazudin" helps to get rid of nematodes quite well, it is a rather effective remedy that also solves the problem with the wireworm, which kills the roots of plants and potato tubers.
It should be borne in mind that toxins themselves can only be a help, the fight against this dangerous parasite should be carried out by all methods according to the developed strategy. Just "pouring and forgetting" with chemistry will not work, it will not solve the problem.
Nematodes should be controlled by supervisory authorities, in case of their appearance, it is imperative to inform the official organization - phytocontrol. Experts will be able to give practical advice on how to deal with this scourge.


It is important to carry out preventive measures, which are an effective tool in the fight against this harmful parasite.
For information on how to protect potatoes from nematodes, see the next video.
Harmfulness
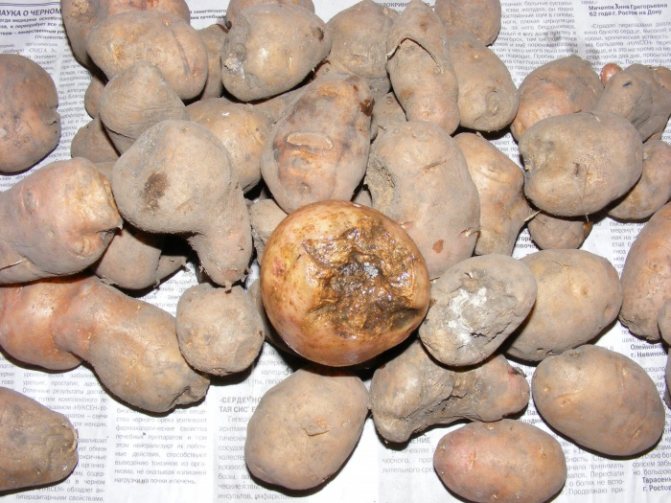
The potato nematode cannot harm people, it does not pose a danger to humans. The greatest harm to plants is caused by the larvae of parasites, which absorb most of the nutrient juices during the development period. Outwardly, this is expressed in the oppression of the tops and the low development of tubers. The lower leaves of the plant die off first, the whole bush dies by autumn. Tubers in the ground are absent or grow small.
The larvae do not stop their activity even after the harvest. Having penetrated inside the tuber, the nematode destroys it from the inside, turning the root crop into a loose mass. And during winter storage, the entire crop can die.
We all fight against agricultural pests. Not everyone knows how to deal with potato nematode. There are simple but effective measures to prevent the spread of the pest.