The homeland of the potato (fluorimea) is Central and South America. But today this insidious insect has captured almost the entire world, spreading along with imported potatoes (like the Colorado potato beetle) to regions with temperate and tropical climates.
Moreover, this pest affects not only potatoes, but also does not disdain tomatoes, eggplants, tobacco. At the first signs of the appearance of fluorimea, you should immediately begin to fight it.
Although the potato moth is difficult to spot at first, especially during the day, as the pest prefers to fly out mainly at night... This insect is very tenacious, easily tolerates temperature changes and can survive even in frozen tubers.
Fluorimea reproduces quite actively, so the colony grows rapidly.
Lifestyle and reproduction of potato moth
The main condition for their reproduction is warm environment... Some individuals can also overwinter, hiding in root crops that remain in the field after harvest.
The egg-laying butterfly itself has a very unpleasant appearance. Its dirty brown color makes it not particularly noticeable on the leaves of the tops. She lives from 3 to 14 days. It cannot feed itself, since the oral cavity is practically not developed. For this reason, the moth does not live long.

However, in a short period of existence, the pest lays more than a hundred eggs, the consequence of which is the larvae. It is they who do great harm to potatoes and other nightshade crops.
For fertilization and development, the pest needs special conditions. First of all, it is a warm environment. Sometimes the larvae can harm the plant faster than the crop gains sufficient growth. Individuals do the greatest harm during the formation of fruits.
Stages of development


Fluorimea.
Like all butterflies, the potato moth has 4 stages of development in its life cycle, namely:
- egg;
- larva;
- chrysalis;
- butterfly.
In the warm summer period, the entire cycle usually lasts for a month, and in winter its duration can be as long as 3-4 months.
Potato moth eggs
One female potato moth can live up to 4 weeks, and during this period of time it is quite capable of laying up to 200 eggs. The appearance of the eggs of the potato moth laid by an adult is not much different from the clutch of other insects. They are very small, oval in shape, about 0.7-1 cm long, 0.4 cm wide. They are white with a dark embryo of an insect larva inside.
You can find clutches on the underside of a nightshade plant leaf, usually on veins, as well as on stems closer to the leaf area. Usually one clutch does not exceed 10-20 eggs.
Pest larva
Usually, the larvae of these insects mature in the egg shell for 7-14 days, after which the already formed small caterpillars are born. Newborn larvae do not exceed a few millimeters in length. They have no protective cover, completely naked, have a pale light shade of the body and a darkish head.
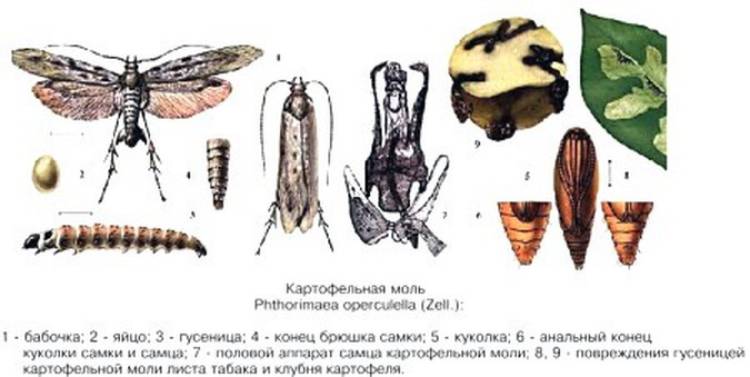

Over time, the already matured caterpillar is covered with rare dark hairs. Its pale color changes to a gray-green hue.A light longitudinal strip appears, going through the whole body, the head becomes even darker and three pairs of dark legs and a clearly pronounced segmentation of the body can already be seen. In length, an adult caterpillar can reach 1-1.3 cm.
The life span of the potato moth at the larval stage is 10-50 days, depending on climatic conditions.
Chrysalis stage
The next stage of metamorphosis in these insects is the most passive. When ready to transform into a chrysalis, the caterpillar usually looks for a safe haven to complete its life cycle with transformation into a butterfly.
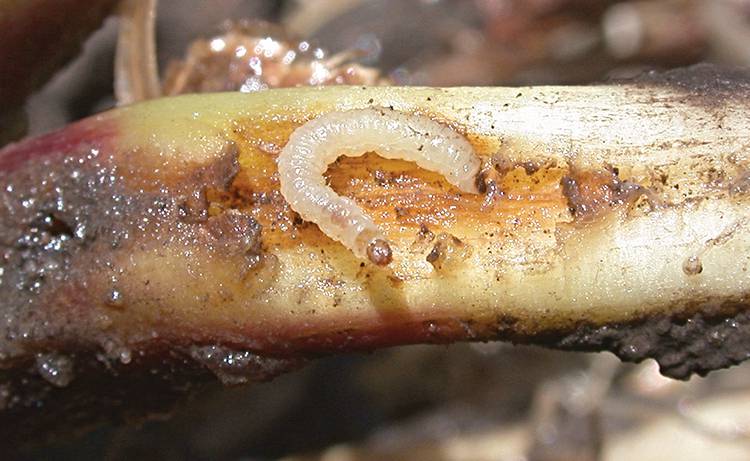


In the summer, the place of ripening of the future butterfly most often becomes cracks in trees and houses, or the same plants that served as a food base for the voracious larva. Usually, in conditions of heat, pupa maturation occurs within 12-20 days.
In winter, pupae of these pests can be found in cellars, where they can mature for 1-3 months under acceptable temperature conditions.
Butterfly
Then, the potato moth butterfly is born. An adult lives only a few days. Its natural function is to participate in the reproduction process of the species. After mating, the female lays eggs, give a new generation of pests a chance to live, while she herself soon dies.
Signs of moth infestation in potatoes
Signs of infection of potatoes are the moth - fluorimea, which shows its liveliness from 8 pm to 11 am. You need to pay attention to the leaves of the plant.
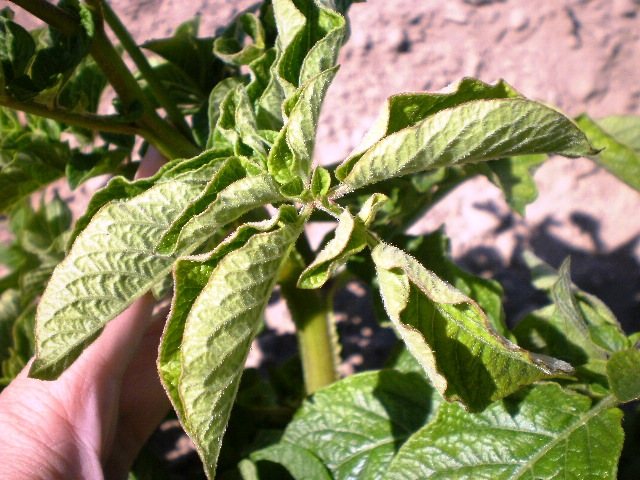
You can recognize the presence of infection by the central skeletal thread of the back of the leaf. On it, as a rule, there is a cobweb and pest feces, and the plants acquire an anemic appearance.


Caterpillars grow from the larvae of the potato moth, which eat the seamy side of the leaves. However, on a potato crop, this is not noticeable much, as for tomatoes or other nightshades, a bright trace of damage is expressed on their leaves. Moving caterpillars from one sheet to another is quite fast.
When the leaves of the potato are completely dry, the caterpillars successfully move into the tubers. In the areas where they crawled, you can find cobwebs and their excrement. Pests penetrate through cracks in the ground and the eyes of the root crop. At the moment of complete drying of the tops, the risk of harm increases several times.
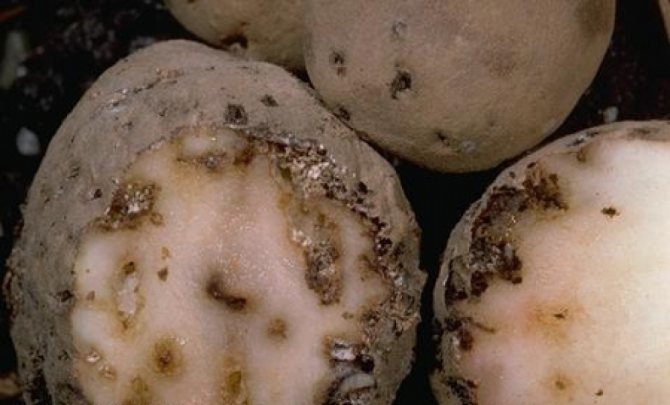
If pest secretions are found on the surface of potato root crops, they should not be used for cooking. Moreover, the fruits are changed in appearance. Brown spots appear on them, and thin small labyrinths form in the tubers.
Careful examination of root crops must be carried out to preserve the crop for the winter, otherwise infected tubers will contribute to its complete damage.
Homeland of the pest
The original habitat of these butterflies is the countries of Central and South America, however, its unpretentiousness to habitat conditions and the ability to migrate over long distances led to the widest spread of this most dangerous agricultural pest throughout the temperate zone of the globe, where the average annual temperature does not drop below 10 degrees ...
In general, more than 80 countries of the world, including the United States and China, today are forced to spend a lot of money annually to combat this pest.
The greatest distribution of these butterflies is noted in the countries of Africa (Egypt, Kenya, Tunisia), Asia (Iraq, Iran, Syria, UAE), North and South America, as well as in Australia and New Zealand.
In the CIS countries, this insect appeared in the 80s of the last century in the Crimea. Since then, the potato moth has been very widespread in the southern regions of Russia, as well as in Ukraine, Kazakhstan and other southern republics of the former USSR, especially in the countries of Central Asia, where climatic conditions are most suitable for all stages of the life of this pest.
What harm does a moth do to potatoes?
Let's summarize the damage caused to the potato crop by the fluorimea butterfly and its larvae:
- damages leaves, bushes weaken significantly;
- reduces the volume of the crop;
- damages tubers, making holes in them and leaving poisonous excrement, such potatoes cannot be eaten;
- harms yields next year if infected tubers are planted in spring.


How to get rid of potato moths?
At the first detection of parasites in the garden, you should immediately start fighting moths in the potatoes. It is not an easy exercise, since it is quite difficult to visually detect fluorimea.
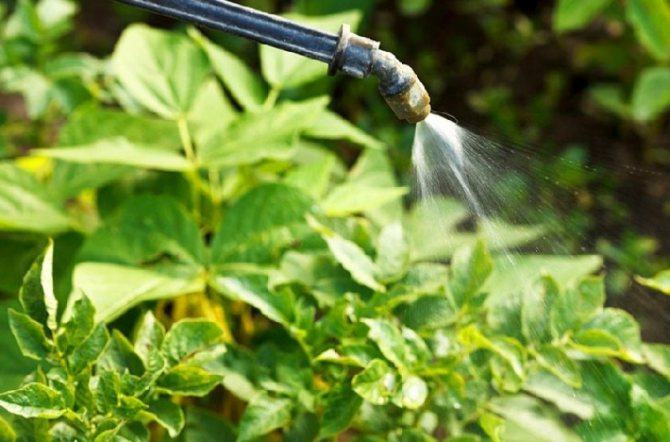
However, you should not give up, as there are many ways and methods to prevent the death of the crop. A variety of chemicals used to control the Colorado potato beetle are also very well suited for the extermination of potato moths. In addition to chemicals, special traps can be used. This method is quite effective.
Biological way to control potato moth
The biological method does not harm the crop, I leave the products biologically pure, this includes the preparations Dendrobacillin (in powder), Lepidocid, Enterobacterin, Bitoxibacillin. Treatment with these drugs does not harm the plant, fruits and humans.


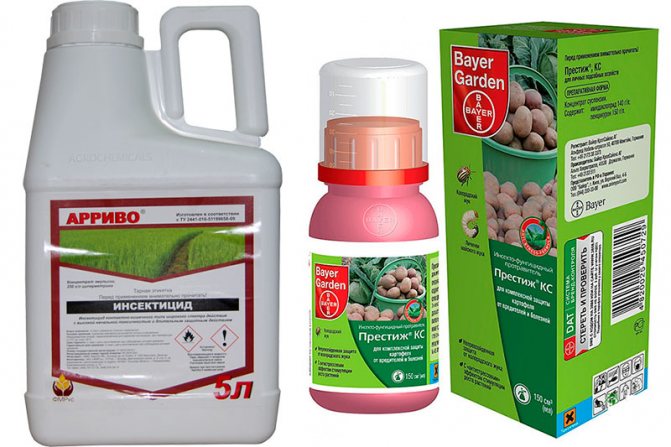
A chemical method for dealing with potato moths
The chemical method is more effective, but it can contain substances toxic to humans, albeit in small quantities. The most famous chemicals for the destruction and prevention of the appearance of moths in potatoes are Arrivo, Sherpa, Zolon, Prestige KS, Decis, Danadim.


Agrotechnical way to control moths
Agrotechnical method implies the following factors:
- correct sowing of potatoes;
- regular hilling;
- planting good, not infected potatoes;
- busting of seed, destruction of bad seedlings;
- setting the tubers to the correct depth;
- timely and regular weeding of the garden, weed removal.


Undoubtedly, the most effective method in the fight against pests of potatoes and the family of nightshade crops is high-quality prevention.
Preparations for the fight against fluorimea: pesticides
They are widely used for the destruction of such a harmful insect as the potato moth, control measures. Preparations (both chemical and biological) are popular with gardeners. Moreover, since the first butterflies of the potato moth appear almost simultaneously with the overwintered individuals of the Colorado potato beetle, it is possible to direct efforts to combat these pests at the same time, since the means that destroy the beetle are also effective against the moth. We are talking about such drugs as "Arrivo", "Decis", "Inta-VIR", "Sherpa" and others.
It is necessary to do the treatment at the beginning of summer, do not wait until the butterflies lay their eggs and the voracious larvae appear. After two weeks, the treatment must be repeated. At the end of August, the Colorado potato beetle no longer poses a danger, but the number of potato moths is maximum, therefore, the fight against fluorimea is of decisive importance during this period. It is important to remember that it is not recommended to carry out the treatment with the same insecticide more than 2-3 times, and the last treatment should be carried out no later than 20 days before harvesting.
Protecting potatoes from potato moths during storage
When collecting potatoes for storage, you plan to use stocks in the winter and damage to the crop will hit your pocket. Potato moths that enter storage with tubers can continue to multiply and damage potatoes. Losses can reach 80%. What measures to take when storing potatoes so as not to feed your stocks to pests?


Clean and treat the crop storage area with special biological preparations. Try to store potatoes at 3-5 degrees Celsius. At this temperature, it does not freeze, does not deteriorate, and the pest cannot fully develop and reproduce. At -4 ºС, pests and their larvae die, but this temperature is not desirable for potatoes, it will turn black.
A biological preparation for potato moths can be prepared independently from lepidocide and planrisa... Dissolve 2 liters of lepidocide and 0.5 liters of planris per 100 liters of water. Dip the potato tubers into the resulting mixture for 5-10 minutes, then dry them. The effect of such a remedy will last for 1.5-2 years, it fights moths and prevents the formation of fungal diseases of the fetus.
Another way to protect the potato crop during storage is to use a solution of a microbiological product Entobacterin, it is harmless to humans and products, but the moth loses its activity and dies under its influence.
Before harvesting, process the storage room, be it a basement, cellar, pantry. One of the simplest and safest folk remedies is quicklime, it is used to whitewash the surfaces in the room. You can resort to using fumigants or other chemicals. Helps well for room treatment smoke bomb Gamma and FAS.
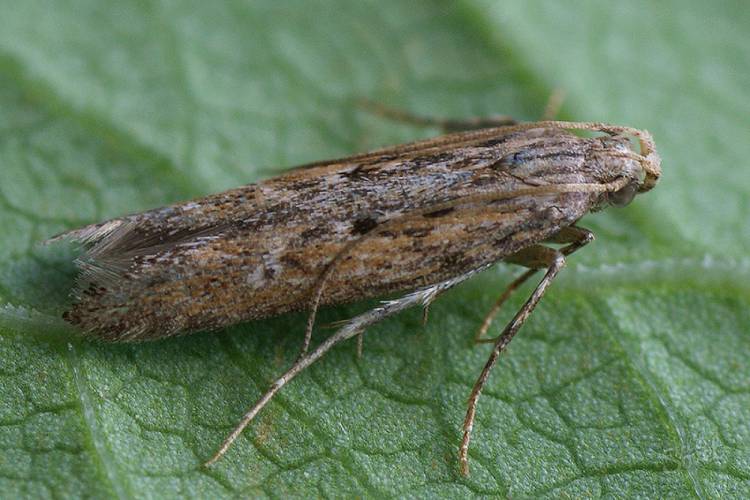
Appearance
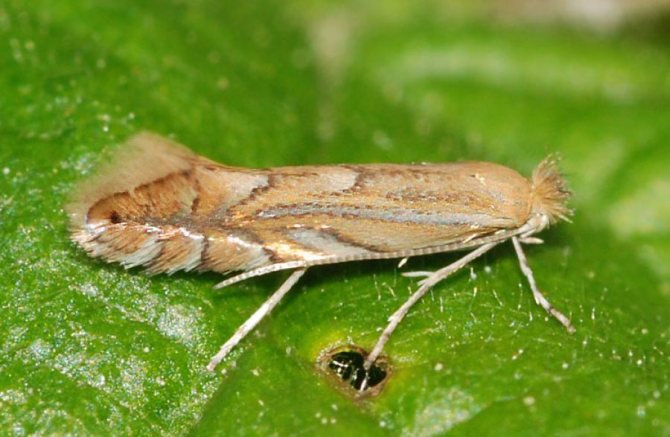
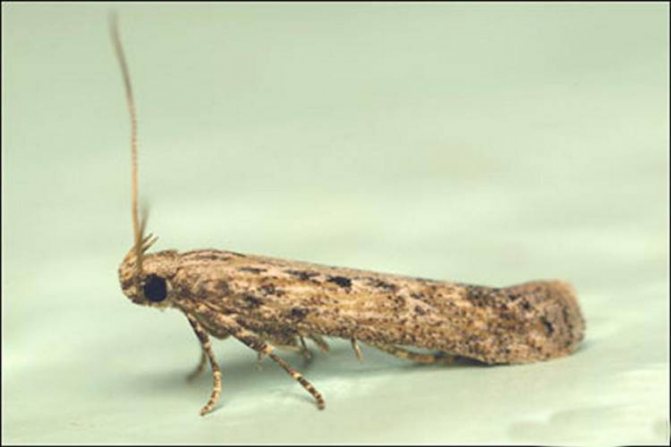
The potato moth, also known as Fluorimea, is an insect from the order of Lepidoptera or butterflies. Outwardly, this arthropod has an extremely unremarkable appearance. Like most moths, this is a nondescript gray butterfly, very inconspicuous. It has a body length of about 8-10 mm., And 10-13 mm. wingspan.
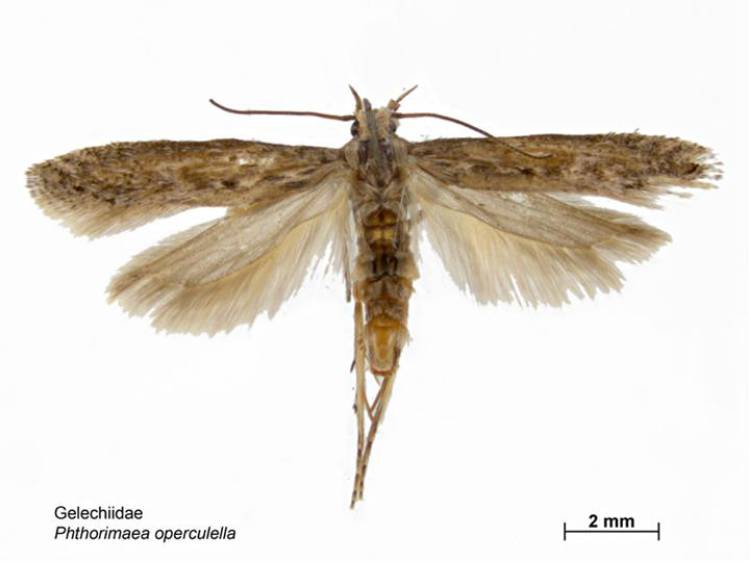


The overall color has an ashy shade, with splashes on gray wings. This color, together with its dimensions, perfectly perform the function of camouflage of this pest, protecting it from enemies and making it more than difficult for humans to find it among the foliage.
It should be noted that there are two subspecies of the potato moth. Guatemalan potato moth and tomato moth. The first subspecies attacks both growing potato bushes and stored tubers. Tomato pests mainly on stored stocks of nightshades.
Preventive measures
- Weed the soil thoroughly twice a year: in the fall and in the spring.
- Purchase planting material from trusted manufacturers.
- Plant with healthy tubers, at a depth of at least 15-18 cm.
- Before planting, root vegetables should be germinated in a warm room.
- Throughout all stages of growth, it is worthwhile to conduct a visual inspection of the potato tops and all nightshade crops.
- It is necessary to carry out weeding, as overgrown with grass, especially one that belongs to the nightshade family.
- Carry out hilling once or twice during the growing period, so that the roots are completely covered with soil.
- Harvest before the tops are dry.
- Many gardeners mow the tops, which is not at all necessary. If, however, such an event is carried out, then no later than a week before the harvest.
- You can also treat the planting material with synthetic preparations before planting and laying the tubers for storage.
- During the growing season, follow the rules for treating plants with chemicals.


Potato moth on the territory of our country belongs to pests that cannot be destroyed or restrained by other insects. For such purposes, as a rule, a quarantine is introduced, which prohibits the export, send by parcels of all planting materials of the family of nightshade crops.
Quarantine measures


To prevent the spread of potato moths, special measures are taken. They are aimed at limiting the movement of the insect. All potatoes are exported outside the sanitary zone only with permits and certificates.
To eliminate the focus of infection during planting, only clean, pre-treated tubers are used. The next time a new planting site is chosen. It, like the place for winter storage of the crop, must be at a distance of at least 1 km from the field where the infection occurred.
Fields during the growing season are promptly treated against pests at least once every 10 days.In this case, all wild plants from the Solanaceae family are destroyed. Before digging potatoes, the tops must be cut and burned. Harvesting is done correctly. Potatoes must be processed before being placed in storage. Harvests from different sites are stored in separate places.






























