Colorado beetle

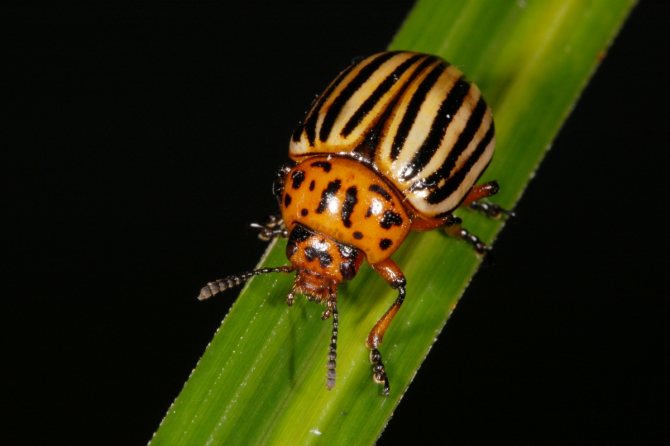
The first place in the list of "enemies" of the potato is the Colorado potato beetle. The striped orange-black insect is familiar to many summer residents for its gluttony. Having settled on potatoes, the beetle and its larvae feed on leaves and shoots of the culture, leaving behind gnawed stems.
On a note! The pest is dangerous for all plants of the nightshade family: tomato, physalis, sweet pepper, eggplant.
The size of adults (adults) does not exceed 12 mm, the larvae reach 10-15 mm. Caterpillars of orange color with a black head and two rows of black dots on the sides emerge from egg clutches in early summer. In their development, they pass through four stages (ages), then they go into the soil and pupate.
Females lay from 300 to 750 eggs per season, the number depends on weather conditions, climate characteristics. In search of food, adult larvae crawl over the plants, gradually capturing new areas of potato planting and eating healthy bushes. Thanks to their wings, beetles fly long distances in search of food.
The most active pests are during the period of budding culture, flowering. If you do not fight, then insect colonies can completely destroy the planting of potatoes. It is difficult to fight the beetle, since insects are resistant to chemicals, they can go into diapause (hibernation) for 2-3 years, going through hungry periods. Insects sense danger and at critical moments fall to the ground, pretending to be dead.
Birds, with the exception of turkeys, guinea fowls, are not interested in Colorado beetles, since a significant amount of dangerous toxins (solanine) accumulates in the cells of the pest's body. Of the natural enemies for the larvae, ground beetles and ladybugs are dangerous.
Group of gnawing pests of cabbage
Of the gnawing pests, the most common are cabbage fly, cruciferous fleas, cabbage moth, cabbage scoop and whiteworm. Do not mind feasting on flower beetles and long-legged mosquitoes on cabbage shoots.
Cabbage fly
Cabbage fly is a serious pest of cabbage. At the end of May, it lays eggs on the soil near cabbage plants. After 7-8 days, larvae hatch, whose life cycle takes place in the roots and the lower part of the stem of the culture, where they penetrate from the egg-laying laid in the soil. The damaged organs rot. External manifestation: a general wilting of the plant and the appearance of a lead tint on the lower leaves of the cabbage are noticeable.
Caterpillars of butterflies of the cabbage scoop, moths, and whiteworms cause significant harm. By gnawing holes in the leaves of the head of cabbage and polluting them with their waste, they are able to transfer the entire crop intended for the market to livestock feed.
Spring cabbage fly (Delia radicum). Janet Graham Cabbage fly larvae on cabbage roots. Andrea Babic Signs of cabbage fly infestation. rdluzen
Cabbage moth
Cabbage moth is a small gray-brown butterfly. Life expectancy is 30 days. Lays up to 300 eggs in early June (small yellow dots on the underside of the leaf) in northern regions, and from April in southern regions. After 3 days, yellowish fusiform, fast cabbage-eating caterpillars appear, intensively feeding on the pulp of leaves around the clock. Over the summer, the pest forms 5-6 generations (a new generation appears every 5-7 weeks).
Cabbage moth (Plutella xylostella). Simon Merrifield Cabbage moth larva before pupation.LDP Cabbage leaf nibbled by a cabbage moth caterpillar. agric
White butterfly
Favorite butterfly of kids, with rapture catching it with nets. It is a large mole. A distinctive feature is the black round specks on the wings. Lays up to 100 eggs on leaves. The development cycle of caterpillars from eggs is longer than that of small moths. After 8-15 days, caterpillars appear, eating up the leaves to the veins.
Cabbage, or cabbage white (Pieris brassicae). Tony Shertila clewergardendiary Cabbage butterfly caterpillar. Rasbak
Scoop butterfly
It is especially harmful in that it damages about 70 species of plants, including vegetables, fruit, garden flowers, etc. The scoop (baby owl) is nocturnal. Invisible beige-brownish, gray-brown with broken spots of light shades on the wings. Its flight is observed from the first days of May to the end of October in warm regions. The female lays up to 2700 eggs on the underside of the leaves, from which colored caterpillars (from green to brown spotted) hatch after 5-8 days. They overwinter in the form of a pupa and larva. For wintering, they deepen into the soil up to 10 cm. In the southern regions it forms 3 generations, in the northern regions - one.
Cabbage scoop butterfly (Mamestra brassicae). Peter Maton Caterpillar of cabbage scoop. k-o-ji scyrene
Fleas
Cabbage fleas damage all cruciferous plants. Small bugs with a characteristic type of movement - jumping, are distinguished by an increased appetite. If they are not stopped, they are able to completely destroy seedlings or young seedlings, damaging the young leaves. They hibernate in the soil and under various debris, including plant debris.
In addition to the pests described above, young cabbage plants suffer from bears and wireworms. Slugs that harm plants are annoying. In the heat, they hide in secluded cool places, often in the leaves of the head of cabbage, which serves as food for them at night. The eaten edges of the leaves are silent witnesses of the night feast. This whole army of pests requires immediate protection. The most practical are measures that combine soil and plant cultivation.


Cruciferous fleas (Phyllotreta cruciferae) on a gnawed cabbage leaf. Brian hall
Nematodes


The worst pests of potatoes (see photo) include the microscopic golden nematode. The worms, about 1 mm long, live in the soil for about 8-10 years. They hibernate in the form of eggs and larvae in cysts, and when warm comes, they penetrate into the root system of plants. Feeding on tissues and plant juices, they grow to adults, which, after fertilization, lay eggs inside themselves, and then die off. There are several types of nematodes:
- gallic - damages the roots of culture, potatoes in the ground;
- stem - affects the ground part of plants, manifests itself on tubers during storage;
- soil - parasitizes on the roots of potatoes.
When affected by a nematode, the bushes stop growing and turn yellow. In the flowering phase, buds are small or absent, tubers are not formed. A pest appears when agricultural technology is violated, there is no crop rotation on the site, when infected seed is planted
Preplant soil treatment
To get a good harvest of cabbage, you need to take care not only of the seeds, but also of the soil. For example, for the treatment of such a formidable disease as keela, there are no chemicals. The only way to help cabbage is to prevent the onset of the disease. To do this, you cannot do without preventive measures. Keela develops rapidly in high temperature and humidity conditions and when cabbage is grown in acidic soils. If we cannot change the weather conditions, then we can quite cope with the acidity of the soil. If you have acidic soil and you did not lime it in the fall, then 7 days before planting the seedlings in a permanent place, process the land with Bordeaux mixture (dilute 10 tablespoons in a bucket of water), and then add ash to it. You can also add 20 g of slaked lime or chalk to each hole during planting.
If you find signs of a keel, then the only thing that you must do immediately is to remove the cabbage from the garden and burn it along with the roots and soil.Spill the garden bed where diseased plants grew with a saturated solution of potassium permanganate.
Keel of cabbage - how to deal with a dangerous disease We will tell you how to get rid of keel on cabbage once and for all.
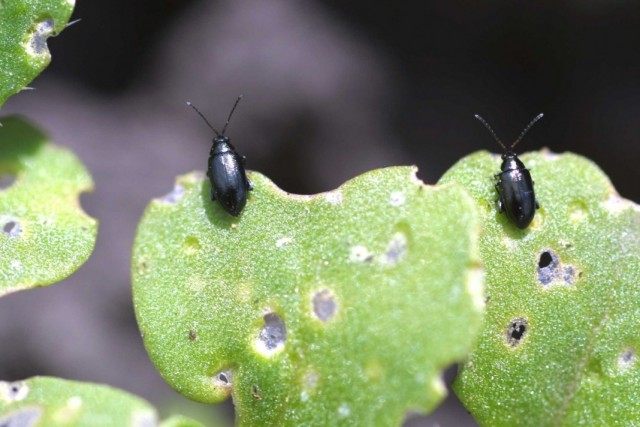
Wireworm and false wire


The damage caused by the wireworm is comparable to that of the Colorado potato beetle. Wireworms are the larvae of the click beetle, distinguished by their omnivorous nature and damaging all garden crops, cereals. Imagoes are not dangerous.
The larvae are caterpillars up to 2-3 cm long, with a hard chitinous cover of a brown-yellow, brown color. They live in the soil for 3-4 years, damage the roots, stolons, the lower part of plants. In tubers, the larvae gnaw out labyrinthine passages, causing potato rot and spoilage. Pests carry viruses of dangerous diseases, potatoes are unsuitable for storage and food.
On a note!
The favorite plant of wireworms is wheatgrass, and the largest reservations of the beetle larvae are located on land overgrown with this weed.
False wireworm is a darkling beetle larva, outwardly very similar to real wireworms. The differences are in the life cycle, since these pests live for about a year. Plants are harmed by adults, as well as worm larvae that eat up seed embryos, seedling roots and stems near the root collar.
Harmfulness
The larvae of the potato scoop are harmful. These voracious creatures are quite harmful to vegetables and berry crops. Crawling deep into the stem and fruit, they eat out holes in them. In addition, this parasite is able to gnaw the ovaries of berry crops, flowers and even rhizomes. As a result, the infected bush begins to wither, dry out and lose foliage.
The potato scoop is especially dangerous in waterlogged areas. As you know, moisture contributes to the development of pathogenic microorganisms, which easily penetrate the body of the affected plant. The pest gnaws the stem at the soil level, enters the tuber through it and continues active nutrition. Thus, the skin of the fruit remains intact, while its pulp is almost destroyed.
On a note! With a strong infection of the area with a potato scoop, you can lose up to 50% of the fruit!
This type of scoop eats not only potatoes. This pest often affects:
Aphid


In all regions, there is a malicious pest of potatoes - aphids. In nature, there are hundreds of species of this insect, differing in biological parameters. Potato aphid is a small insect, about 2-3 mm in size, greenish in color with a dark head. There are individuals with and without wings, each group has its own functionality (reproduction or movement).
Insects feed on plant sap, live in colonies on the underside of leaf plates. When potatoes are damaged, the upper layer of leaves begins to curl and dry out. Bushes wither, which reduces crop yield. Aphids secrete honeydew, which ants feed on, flies flock. Sooty fungi quickly form on the sheets.
This type of aphid is polyphagous, feeding on the sap of a wide variety of cultures. With a massive invasion of aphids, the threat hangs not only over the potato beds, but also over the plantings of tomatoes, eggplants, cabbage, cucumbers, zucchini, and roses. The danger of the pest lies in the fact that aphids carry a large number of various viruses, infecting healthy potato plantings.
The main types of potato pests
Certain types of insects live in the soil, they are able to stay there for several years in the form of larvae, without betraying their presence. There are also such pests that get on potato bushes in strong winds or excessive moisture. Let's talk in more detail about the most dangerous pests for potatoes and about methods of dealing with them.
Colorado beetle


Everyone knows this striped insect. The most massive and therefore the most dangerous pest of potatoes.The larvae of the beetle are especially gluttonous when eating the tops, which leads to a significant decrease in the yield of the vegetable.
Adults destroy not only leaves and stems, but also tubers. They hibernate in the ground, and in the spring, flying from one bush to another, they quickly and en masse lay eggs on the shoots as soon as they emerge from the ground. It is during this period that it is important to destroy the main population of beetles. To do this, it is recommended to use insecticides such as "Commander", "Sonnet", "Aktara". Treat the bushes three times per season, the last time 20 days before harvest.
From folk remedies, spraying the bushes with strong infusions of mint, tansy and black currant are suitable. The simplest known method, and at the same time very effective, is the manual collection of beetles and larvae. The procedure is carried out at least twice a week.
Wireworm and false wire


Yellow worm up to 3 cm long, the larva of the click beetle. Destroys leaves, tubers and even the root system of potatoes. It additionally feeds on wheatgrass, so it is better to get rid of this weed in advance.
Deep digging of the earth in autumn and spring is recommended as the most effective way to deal with an uninvited guest. Or you can put a bait between the rows of potatoes - a chopped tuber placed in the ground, and after a while remove it along with the worms. Of the chemicals, the use of insecticides "FORS" or "Hurricane Forte BP" is effective.
False wires are the larvae of the darkling beetle. They feed on tubers, roots and other parts of the plant. Lures, digging, as well as the introduction of wood ash into the soil before planting potatoes also help against them.
Nematode
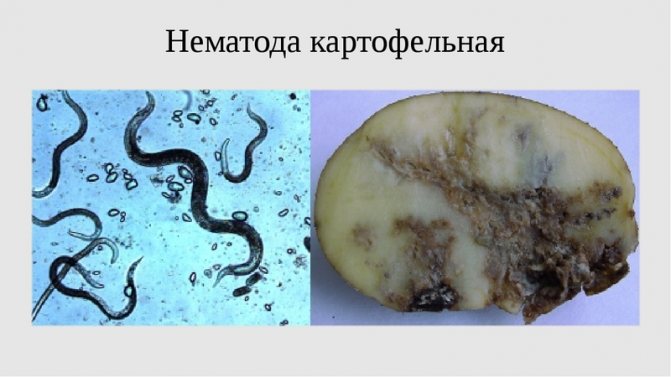

It is difficult to see nematodes with the naked eye, they are so small. They attack the stem and roots of the potato underground, destroying the entire structure. The main characteristic sign of their attack is the yellowing of the lower leaves of the tops. Nematodes can live in the ground for up to 10 years, so it is extremely difficult to destroy them, but it is possible.
Treat the entire area for potatoes with urea, and after harvesting, cover with plenty of lime... It is also advised to water the ground with a solution of chicken manure, if it is available in large quantities.
Another remedy - the drug "Bazudin Extra" - perfectly protects not only from nematodes, but also from weevils, bears, fly larvae and other parasites.
Garden moth


A small gray butterfly, whose larvae also do not mind eating all the greens and tubers of both potatoes and tomatoes, eggplants and bell peppers. Ignoring this pest can lead to the loss of the entire crop.
For prevention, deep autumn digging and processing of seed material with a strong solution of methyl bromide are suitable. Of the chemicals, the most effective against moths are Sherpa, Zolon, Arrivo.
Scoop


Ash-colored adult moths, active at night, in themselves do not pose a danger to potatoes, unlike their caterpillars. These green gluttons eat everything they can eat. They destroy stems, leaves, tubers. After "lunch" they rest in the shade of wheatgrass, winter in the same place.
The best protection against caterpillars is weed control. Against the moths themselves, laying eggs, special pheromone traps are used for this. It is advisable to use insecticides "Cymbush" or "Decis".
Cicadas


Jumping insects no larger than 3 cm, similar to a moth... During the day they live in anthills (they have interspecific cooperation with ants), and at night they drink plant juices. This leads to a slowdown in development and the death of a part of the potato bush. Leaves turn yellow and deformed, brown and white spots appear on their surface.
In addition, these pests are carriers of viral diseases, and both adults and larvae are dangerous. To protect the seedlings, the soil is treated with Tabu and Kruiser before planting.And if the leafhopper has already appeared in the garden, they use the "Karate Zeon" remedy, having previously studied the instructions.
Potato flea


Black beetle up to 3 mm long, damaging potato tops. The larvae develop on the roots and destroy healthy bushes. Adults feed on foliage, leaving pits and holes on its surface. Seedlings die.
Comfortable conditions for flea beetles are hot, dry weather or late planting of potatoes. Of the methods of struggle, the drug "Confidor" is recognized as the most effective; early planting of the vegetable is recommended for prevention.
Medvedka


Orthoptera insect up to 5 cm in length, dark brown in color. It has wings, strong jaws, mustache and powerful legs, and knows how to dig deep into the ground. An adult bear equips a nest underground, where it hatches hundreds of 2-3 mm larvae. Their growth and development takes several years.
The insect is a danger to all plants it encounters. Loves potatoes, cucumbers, beets, cabbage and many grains. Medvedka completely eats up potato tubers, and its larvae gnaw through the stem and destroy the tops.
You can get rid of the parasite by using chicken droppings - the insect cannot stand its pungent odor. Coriander, marigolds, garlic, calendula, chrysanthemums and mint are planted along the perimeter of the site and between the beds. The specific smell of these plants also scares off the bear.
Natural enemies of insects are lizards and hedgehogs: do not drive them out of your territory if they inhabit it. Using chemistry, remember that you can also destroy beneficial insects, so try to choose gentle drugs, for example, "Medvetox".
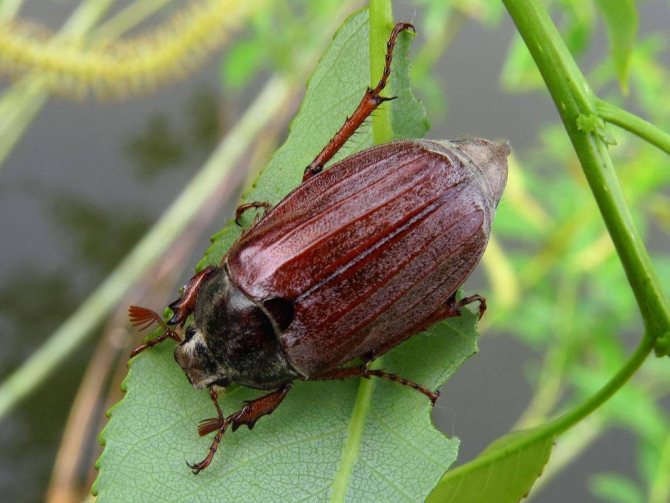
Khrushch


He's a May beetle. The harm is caused by its larva. It looks like a coiled, thick yellow-gray caterpillar. The beetle itself is not dangerous for potato crops, but its larva can spoil the tubers and roots of the plant.
At the end of April, the female May beetle lays its eggs in the ground to a depth of about 40 cm. The larvae live for several years, during which time they are capable of causing enormous damage to the crop. One such individual is able to damage several dozen potato tubers in two weeks.
It is possible to determine that a vegetable crop is affected by the larva of the May beetle by the leaves: if they dry, turn yellow and wither for no particular reason, it means that the larva of the beetle has settled in your beds. Destroying it is not easy. Autumn deep digging is obligatory. Some plants, for example, lupine, elderberry and all cruciferous plants, repel the insect. Of the chemicals used "Antichrusch" or "Bazudin".
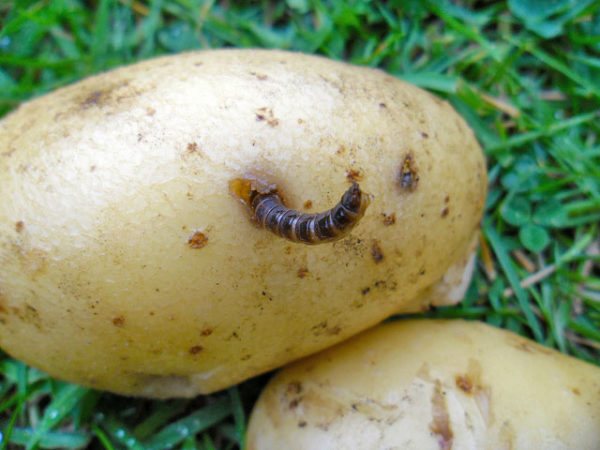
Potato aphid
Small insects, elliptical, no more than 3.5 ml, white-green color, can fly. In dry weather, they reproduce most intensively, sucking the juices from plants, leaving behind a characteristic sugary discharge.
Ash or crushed chalk will help to eliminate parasites; these mixtures are densely sprinkled on the affected plants and the soil under them. If the infection is massive, it is appropriate to spray the chemical agent "Aktara" or "Tiara".
Slugs


Naked slugs rarely attack potatoes, but in times of famine they do not disdain planting. They are active mainly at night and where it is damp and humid. Both leaves and tubers are affected, leaving bare stems. Slugs are carriers of many fungal diseases. After them, the damaged potato bush often becomes ill with late blight.
The most harmless way for the surrounding plants and humans to eliminate slugs is to pour a fine fraction of eggshells or coarse table salt on the beds: they cannot move on such a surface.
Redhead spank


Black beetle with white stripes and a red head. Body size up to 20 mm long. Harms potatoes by damaging leaves and flowers. Beetles are poisonous - eating an insect along with the grass, the animal can get severe poisoning, it can even be fatal.From accidentally touching the paws of a beetle, purulent abscesses form on the skin of a person, and if the poison gets into the eyes, you can lose your sight.
If you decide to eliminate the spanko, first get rid of the weeds on which the pests live, and then apply the Akarin or Calypso chemistry. Wear gloves when weeding.
Bedbugs


Cruciferous bugs often attack cabbage foliage, but they will not refuse tops of potatoes on occasion. Plant sap is the main food for bedbugs. It is not difficult to see them on landings, they have a bright red and black color. They spread with particular speed in hot weather.
The most effective method of dealing with this pest is prevention. These include: early planting of a vegetable, observance of crop rotation. Tansy and wormwood will help, their smell scares away bedbugs.
Rodents


Some rodents, for example, mole rat and earthen rat happily eat potato tubers, and those that are no longer able to eat are dragged into their burrows. Moles, like moles, leave passages in the ground, and small earthen mounds on the surface.
It is preferable to scare off such large pests, rather than destroy. Special repellents are sold in garden stores. If it was possible to find a mink or rodent passages, put a cloth soaked in gasoline or kerosene in their path. This simple folk remedy will help drive the animals out of the garden.
Cicadas
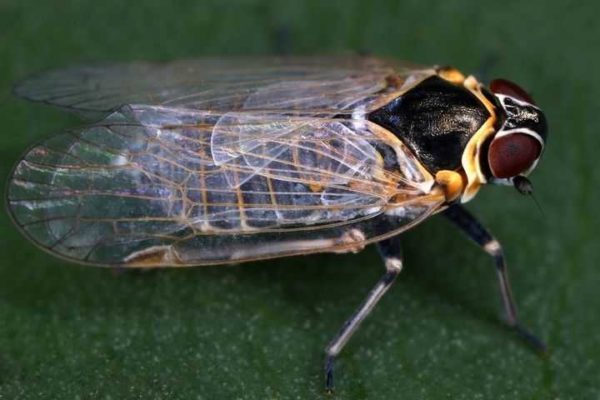


Most leafhoppers live in the southern regions of the country. Insects look like aphids, but have well-developed hind limbs. Thanks to their legs, tiny leafhoppers jump, and their wings allow them to fly over the entire site. They switch to potatoes from weeds (bindweed, thistle), feed on the juice of the leaves of the culture.
In the south, potatoes are affected by the following types of leafhoppers:
- white;
- green;
- bindweed.
The main danger lies in the transfer of various diseases by leafhoppers, including the insidious mycoplasma infection - potato stolbur.
Features of the life cycle of the scoop
On potatoes and tomatoes, 3 types of scoops parasitize:
- winter (gnawing) scoop, Agrotis segetis;
- potato (marsh, or purple) scoop, Hydraecia micacea;
- common (medullary) scoop (Gortyna flavago).
Outwardly, these scoops are very similar: their wings are painted in gray-brown, brown, dark sandy colors. Having folded its wings like a "house", the scoop becomes almost invisible on the tops of potatoes or tree bark. The wingspan of the winter moth is 35–50 mm, of the potato moth - 28–40 mm, and of the common moth - 33–42 mm.
Potato spank
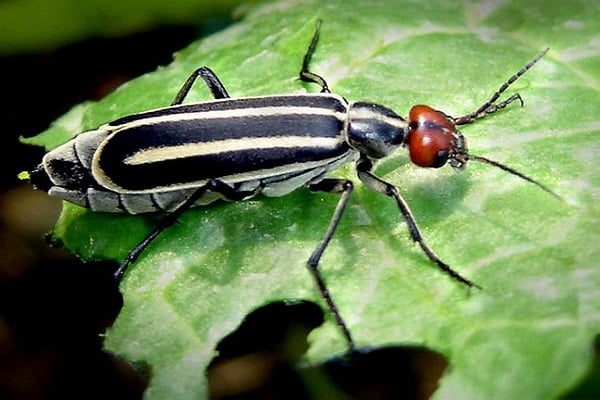


Usually this pest lived in the southern regions of the country, but due to climate warming, it was increasingly found in the middle zone and in the southern regions of the European North. The elongated beetles reach a length of 1.5-2 cm, fly over the site, damaging the foliage of various crops. On a potato bush, up to 10-15 bugs are usually collected, completely eating up the aerial part of the plant. For 2-3 days, only the stems remain from the bush.
The period of activity of shpanki falls in the middle of summer, when it is hot in most of the country. The larvae do not bring harm, the danger is posed by adults that devour the tops of potatoes. Pest collection by hand is not practiced, since the body contains a caustic toxic substance - cantharidin. When in contact with the skin, it causes redness, abscesses, sores. If the poison enters the bloodstream through wounds and damage, it causes poisoning.
Prophylaxis
Pest control is time-consuming, it is much easier to prevent the appearance of dangerous insects in the garden. The procedures and techniques are simple, but effective:
- soaking potato tubers before planting;
- use of quality healthy seed;
- observance of agricultural practices of culture: hilling, loosening, weeding, watering, feeding;
- processing potato plantings with various infusions and decoctions to prevent the appearance of insects;
- alternation of crops on the site;
- obligatory digging of the soil (twice a year, in the fall - preferably before frost);
- disinfection of garden equipment;
- selection and cultivation of varieties resistant to pest infestation;
- careful preparation of tubers for storage;
- study of information on pests of culture, since modern truck farming requires a competent approach.
Not everyone succeeds in growing a good harvest of potatoes. Not only full care is important, but also timely prevention of diseases, prevention of the appearance of pests. If dangerous insects have chosen your planting, then, without delay, they begin to destroy enemies.
Natalia Severova
Tags: fight, potato, shovel
About
«Previous post
Potato garden moth


The small gray-brown butterfly lays its eggs in the soil, on the back of the leaves, in stores, from which voracious larvae then emerge. It is they who pose a danger to potato tubers, and on plantings - to leaves and shoots of the culture.
The larva is yellow or off-white, about 1-1.5 cm long, eats potatoes in the ground. Gnawing into the tubers, it leaves numerous twisted passages, as well as excrement. You can detect potato moths by a number of signs:
- eaten leaves of tops;
- withering tops of the bushes;
- dry or wet rot;
- moves in potato tubers.
On a note!
Potato moth also damages tomatoes, eggplants, bell peppers.
Spring Cabbage Fly - Delia radicum
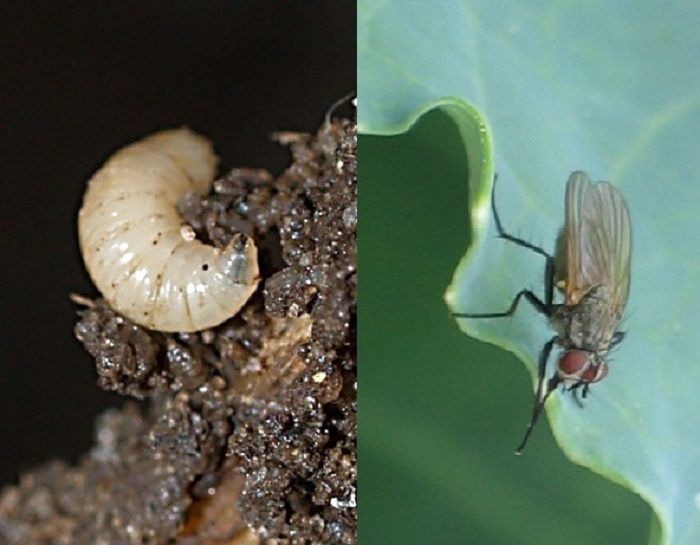


During the flowering of lilacs, females lay eggs, and after a week larvae appear. And these larvae feed on young roots, gradually rising higher to the stem.
Preventive measures for spring cabbage fly
- Deep digging in autumn.
- Early planting of seedlings.
- Crop rotation and mixed planting. Garlic, marigolds, mint, cumin, onion, dill, tansy, coriander. They will scare away pests with their smell.
- Phyto top dressing, organics help to resist these pests. Since this increases the overall health of the culture.
- Covering material without holes.
- Weeding cruciferous weeds:
zerushnik, beetroot, sverbigu, shepherd's purse, field yarok. - We attract real enemies of cabbage flies:
Ground beetle; - Cleanliness on the site. We incinerate all waste.
Effective drugs against spring cabbage fly:
- "Decis"
- "Aktara"
- "Actellik"
- "Engio
If, nevertheless, the larvae appeared, then:
200 gr. salt per 10 liters. water. Pour this solution over the cabbage and sprinkle with ashes.
Folk remedies:
- Laundry soap solution. 300 gr. on a bucket of water.
- Ash. Pour water in a ratio of 1: 3, leave for 2 days, add laundry soap. Spray.
- Dandelion. Leaves and roots. 500 gr. on a bucket of water. We pass through a meat grinder. Add soap.
- Potato tops. 4 kg. 10 liters of water. We boil. Dilute 1: 1
Tomatoes are the same. - Sagebrush. Infusion. You can add garlic gruel.
- Ammonia. 20 gr. on a bucket of water.
- Vinegar. 9% 1 glass per 10 l. water or 2 tablespoons of essence.
Spider mite
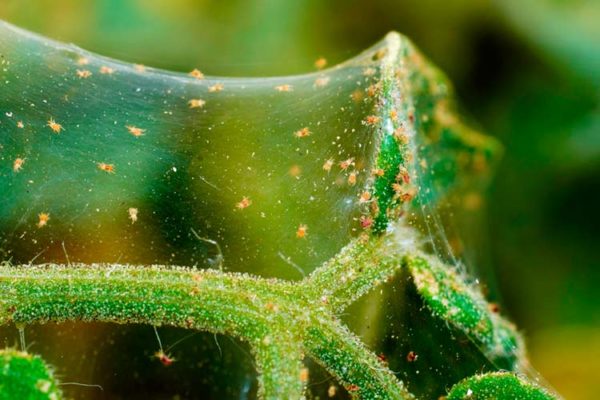


A very tenacious insect, reaching sizes of about 0.6-0.8 mm. It feeds on plant sap, lives on the underside of leaves. Under normal conditions, it gives one generation per season, but in shelters where seed potatoes are grown, up to 4-5 generations of the pest come out.
The leaves damaged by the mite are covered with yellow or brown specks, the tops wither and dry out. A characteristic sign of the presence of a tick on a potato is a silvery small cobweb that braids the underside of the leaves, flowers.
Why does the scoop appear on tomatoes
In everyday life, the scoop is also called the moth butterfly. This insect belongs to the order Lepidoptera and in appearance is very similar to the common moth. Pests spend all autumn, winter and spring in the pupa phase, hidden in the upper layers of the soil. With the onset of summer, a butterfly appears from the pupa.
The main reasons for the appearance of this pest on the site include:
- lack of autumn digging of soil, as a result of which many insect pupae survive;
- a large number of weeds in the garden, which serve as food for the larvae;
- lack of soil disinfection before planting tomatoes;
- the remains of last year's plants in the soil - they can also store the pupae of the pest;
- improper disposal of plants and fruits damaged by larvae.


The insect is small and gray in color, the wingspan does not exceed 4.5 cm. 5 days after emergence, the butterfly lays eggs on the leaves of tomatoes, from which small caterpillars hatch after about a week. Their length does not exceed 3 cm, and the color is predominantly green, but there are also pink or brown types. It is the caterpillars of the scoop that cause irreparable damage to tomatoes and other vegetables in the garden.
After reincarnation from a caterpillar to an adult butterfly, the process is repeated from the beginning.
There are several main types of scoops in nature:
- linseed (gamma)- the butterfly has a characteristic pattern on the wings in the form of the Latin letter of the same name, caterpillars are green with yellow stripes on the back. Gamma moth larvae eat not only the leaves of decorative and cultivated plants, but also the foliage of bushes and trees;


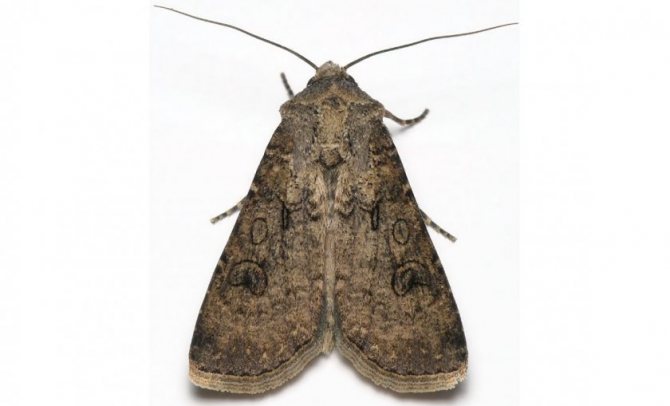
winter - the wings of butterflies have a pattern of spots and stripes, the caterpillars are gray with a shiny greenish tint. They feed on corn seeds, weeds and young shoots of plants in the garden;


grain - the wings of butterflies are variegated, they combine gray and brown colors, the caterpillars have a brown-gray color with a yellow stripe on the back. They feed on grain and perennial grasses;
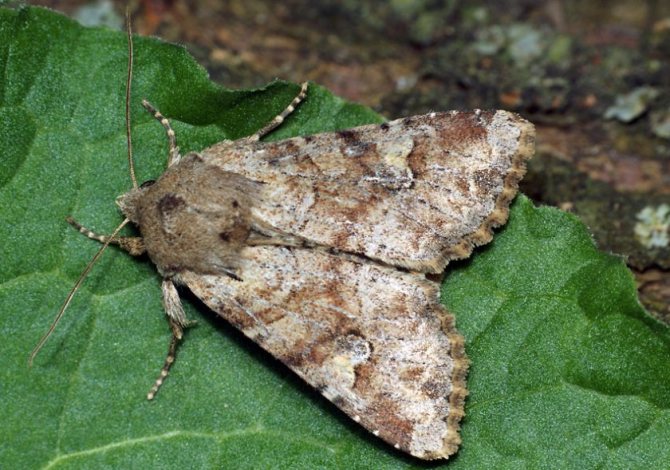


gnawing - on the wings of butterflies, a pattern in the form of an exclamation mark is clearly visible, the color is gray, brown or dark brown. Caterpillars are gray with a yellowish tinge and orange head. They feed on grains and vegetables, as well as ornamental plants;


hothouse - butterflies have a light gray color, specks of various shapes are clearly visible on the wings, the larvae are gray with a dark stripe on the back. Pests feed on the leaves and fruits of all plants in the vicinity;


cotton - butterflies are yellowish-gray with dark gray stripes and spots, larvae can be white, green, yellow or black. The caterpillars of the cotton bollworm eat all kinds of plants;


agrippina - beige or light gray butterflies with intricate patterns on the wings, green caterpillars with black spots and light stripes on the sides. The pest eats the leaves of leguminous plants;


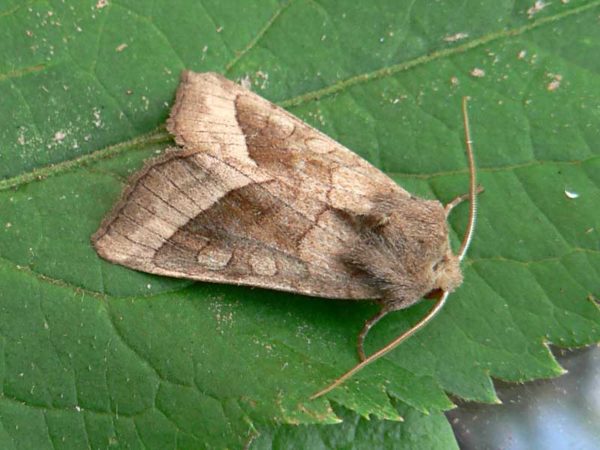
pine - butterflies have a variegated wing color (from white to brown) with spots and lines of various shapes, caterpillars are green with a wide white stripe. The larvae eat pine needles, young shoots and buds;


garden (garden) - these include tomato, potato and cabbage scoops. The butterflies are dark or gray in color, the larvae are predominantly green or gray. Leaves and fruits of cultivated plants are eaten.


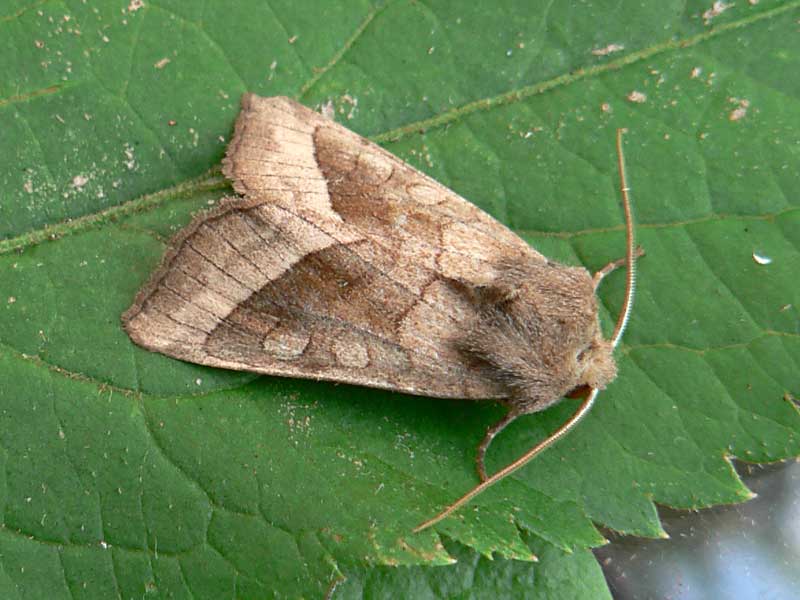
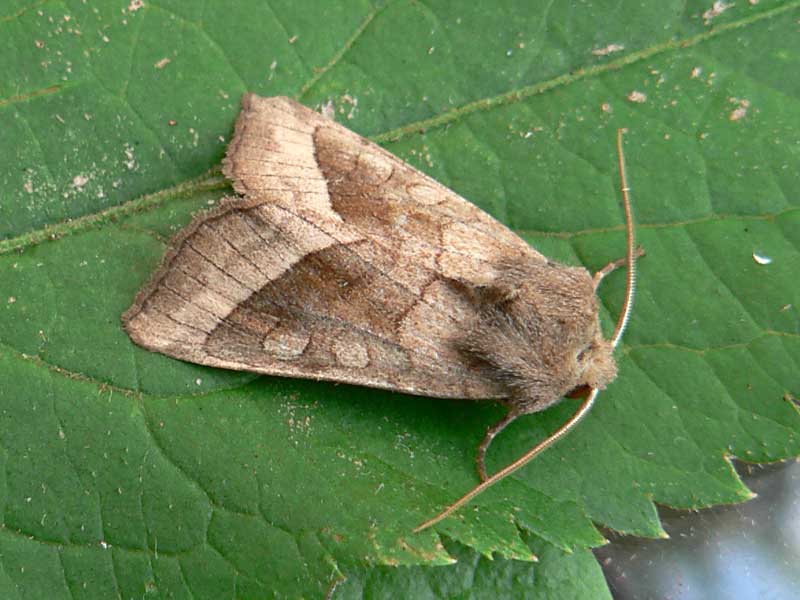
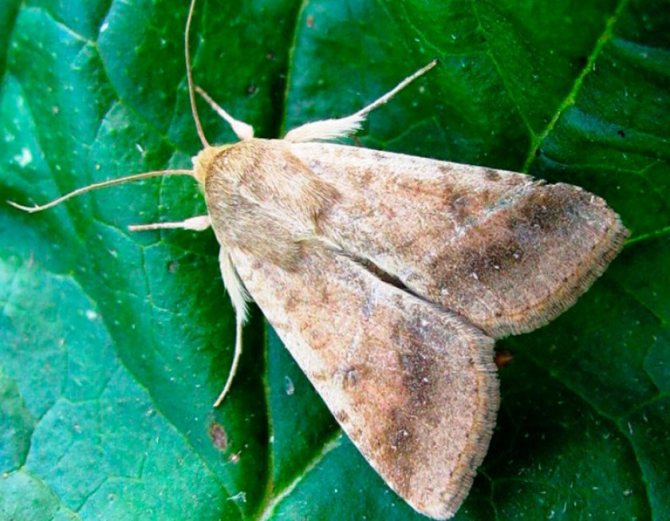
Potato scoop


A nondescript gray butterfly is capable of destroying potato plantings over a large area. Pest females lay up to 60-70 eggs, of which caterpillars appear in late spring. Potato scoop - an insect from the group of polyphages, in addition to potatoes, damages plantings of carrots and onions.
Yellow or red-brown larvae reach a length of 5 cm, penetrate into the stem of the bushes into the tubers. Due to the fact that the roots are eaten up, the tops wither, the bush quickly dies. In potato tubers, the scoop makes moves, feeding on the tissues of the vegetable and leaving excrement in the cavities. After filling the cavity, the larva moves to another tuber. Damaged tubers will rot, resulting in severe crop losses.
Harmfulness and features of life
The fight against the potato scoop is sometimes unsuccessful or the effect of the measures taken does not correspond to the funds and efforts expended.To prevent this from happening to you, you need not only to correctly apply chemical agents, as indicated by the manufacturer, but to do this taking into account the specifics of the pest's vital activity.
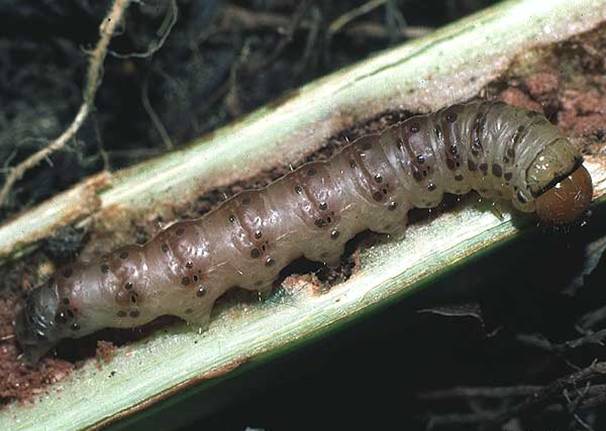


Photo of a caterpillar scoop
- The conditional harmful phase of the moth falls in the dark, and during the day their activity is significantly reduced. Therefore, it is better to carry out regular inspections if you do not live in the village permanently, it is better after sunset.
- The scoop can hide not only in potato tubers, but also in cracks in the bark of trees or between floorboards. It is quite difficult to notice an insect due to the masking color, especially if you do not look for it on purpose. Therefore, before going around the site, arm yourself with a good flashlight and be patient.
- If next to your summer cottage there is an abandoned field that was once a collective farm, the risk increases many times over. Moreover, the population may develop resistance to common insecticides, making conventional chemicals ineffective.
- Another risk factor to put up with concerns the location of your site. This potato pest "loves" shady and moist areas very much. And if the summer is particularly rainy, the area of damaged leaves and stems can reach up to 1/3.
- The most likely place for the appearance of the first signs of damage is the area just above the root collar. In dry weather, problematic plants dry out and wither much more often than healthy ones, and in rainy weather, on the contrary, they are among the first to rot.
- If you find and destroy several eggs, it is too early to calm down: one female is capable of laying almost 500 eggs, which can endure a rather harsh winter without any consequences.
Potato flea
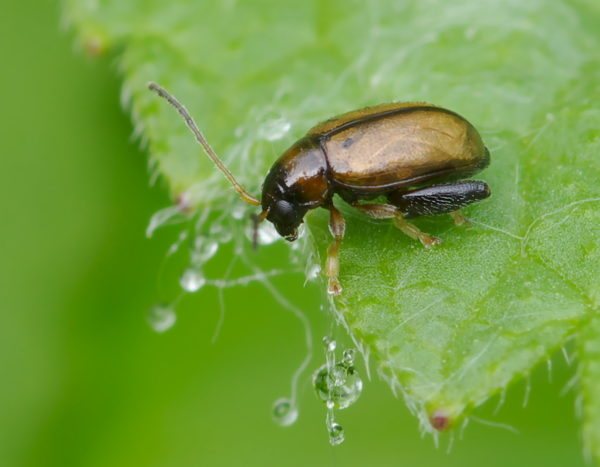


Tiny black bugs were first discovered in the United States, then they moved to other continents. In Russia, they are found everywhere, up to the Far East.
The sizes of adults are from 2 to 2.8 mm, larvae are up to 12 mm. Caterpillars of white color, emerge from eggs in underground clutches, feed on potato roots. Adult beetles - leaf beetles, eat leaf plates on bushes. After the invasion of flea beetles, the potato leaves are covered with numerous holes and look like a sieve. Plants stop growing, dry out, and yield sharply decreases. In addition, fleas carry viruses that infect weakened crop plantings.
Signs of appearance
Moths fly at night, so it will not be possible to spot them during the day. Caterpillars of the pest hide in the ground during the day and begin to eat the tops and fruits of tomatoes only at nightfall. Therefore, it can be quite difficult to detect the appearance of a scoop in the garden.
Related article: Phyto-peeling of potatoes: concept, frequency, technique
Here are some of the main signs:
- clusters of white round eggs appear on the leaves of tomatoes;
- the appearance of greenish or brown caterpillars on the leaves and stem, especially in the evening;
- small holes in the leaves, which increase over time, only large veins remain on the leaf;
- damaged buds or fruit ovaries;
- holes with eaten flesh in tomatoes.
Potato cow
The scientific name is epilyakhna, outwardly similar to a ladybug, but the body is covered with whitish hairs and the number of black dots on the wings is much greater (28 specks).
A 4-5 mm beetle makes clutches of eggs on the underside of the foliage. In one litter - up to 20 specimens, while the total number of eggs per season can be about 300-500 pieces. The larvae are yellowish-green with numerous black villi; they eat the leafy flesh. Caterpillars and adults leave only one vein of the plates, completely eating soft tissues.
Plants dry up, wither, the formation of tubers stops. The cow is a carrier of dangerous viruses, which increases the damage caused to insects to garden plantings. In addition to potatoes, it damages bushes of tomatoes, peppers, young shoots of cucumbers, pumpkins, corn.
Cabbage white (cabbage)
Damages cabbage, radish, rapeseed, mustard, mignonette, nasturtium.
The wingspan of the butterfly is 55-60 mm. The wings are white. On the top of the front wings there is a black crescent-shaped spot. The female has two rounded black spots on the front wings. Eggs are yellow, bottle-shaped, with longitudinal ribs. Caterpillar is yellow-green in color, with black spots. A yellow stripe runs along the sides of the caterpillar's body, and a light stripe along the back. On the body of the caterpillar there are sparse hairs and bristles. Track length - up to 40 mm.
The cabbage whitefish develops in 3-4 generations. Pupae overwinter on the trunks of trees, shrubs, fences, walls of buildings. At temperatures of -20 ° C and below, many wintering pupae die. This explains the low abundance of whitewater in the years after the cold winter. Butterflies fly out in April, fly during the day, feed on nectar on flowers of various plants.
Butterfly eggs are laid in groups of 15-200 eggs on the underside of the leaves of cabbage and other cultivated and weed cruciferous plants. The egg stage lasts 1–2 weeks. Young caterpillars stick together. They eat the parenchyma of the leaves from the underside, without violating the integrity of the skin (skeleton). Damaged leaves turn yellow and dry out. The grown caterpillars eat leaves from the edges, often eating the leaves entirely, leaving only large veins. The duration of caterpillar development is 2-4 weeks. Caterpillars pupate on fences, walls of buildings, on tree trunks, on the stems of large weeds. Single caterpillars pupate on cabbage leaves. The number of butterflies of the overwintered generation is usually small, and it increases in subsequent generations.
During the growing season, the abundance of white women is reduced by parasites.
Slugs
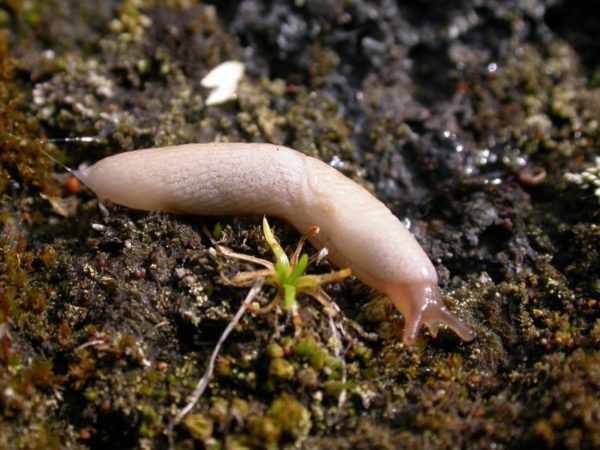


The harm of this inconspicuous nocturnal mollusk cannot be underestimated. Gastropods parasitize on ridges with potatoes, carrots, beets, preferring wet areas.
Slugs gnaw through the tissues of the leaf plates, leaving holes and silvery marks on the surface, damage roots and tubers. By doing this, they spoil the presentation of vegetables, reduce the quality and keeping quality of the crop. Molluscs carry parasitic worms, pathogen spores, infecting not only plants on the site, but also domestic animals.
How to get rid of a cabbage scoop?
To get rid of the pest, you can use different methods: collecting insects by hand, using pesticides, traps and decoctions. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's take a closer look at various ways to get rid of a cabbage scoop.
Mechanical methods of dealing with scoop
The easiest way to reduce pests is by hand picking.
Regularly, every week, it is necessary to inspect the cabbage leaves. All found clutches of eggs and larvae must be destroyed. The optimal time for collecting caterpillars is early twilight, when the larvae crawl out of their hiding places in search of food.
Hand picking insects is considered an ineffective pest control method. It will help reduce the number of moths on the site, but it is impossible to completely get rid of them. If you do not use other methods or miss at least a few weeks of collecting pests, then the population will fully recover, and all the work will be in vain.
To get rid of scoop pupae, it is necessary to loosen the soil to a depth of at least 10 cm before winter.
Chemical methods of dealing with scoop
To destroy pests, the most effective method is the use of chemicals.
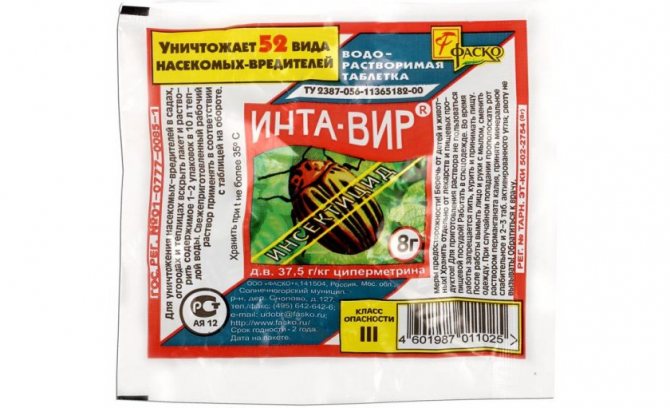
To combat the scoop, the following tools are suitable:
- Iskra-M;
- Inta-Vir;
- Sherpa;
- Kinmix;
- Fas;
- Banker;
- Zeta et al.
Insecticides should be sprayed at sunset in calm and not rainy weather. Chemicals can be used no more than twice a season.
The use of insecticides must be stopped a month before picking cabbage, otherwise there is a possibility of fruit poisoning later.
Biological ways to control the scoop
Using biological agents is a safer way to get rid of pests than using chemicals.
The following biological agents will be effective against scoops:
- Lepidocide;
- Bitoxibacillin;
- Fitoverm, etc.
Biological products do not harm humans and processed fruits. But their application has its own rules: it is necessary to finish processing with biological agents at least 5 days before the start of harvesting.
Traditional methods of dealing with a scoop


Cabbage scoop, methods of struggle
Folk methods are highly popular. They are quite effective, completely safe for humans and planting, and most often they are cheaper, since all the ingredients are either cheap or completely free.
For catching pests, you can prepare special traps. To make them, you need to take disposable cups or cut plastic bottles (the height of the container should be about 3 cm). They need to be filled with sweet liquid and hung a meter from the ground.
To prepare a sweet liquid, you need to mix a liter of water and 50 g of yeast. Then wait a few hours for the mixture to ferment. Next, add a liter of molasses and 3 liters of water. Compote, jam, syrup and other sweet liquids are suitable as bait.
From time to time, you need to add sweet liquid to the traps, and once every 2 weeks, you need to completely change the contents and throw out the caught butterflies.
Recipes for decoctions and tinctures against cabbage scoop:
- Mix a glass of ash with 200 g of tobacco waste, 30 g of liquid soap, 15 g of mustard. Pour all 10 liters of boiling water and leave for 24 hours.
- Boil for an hour in a liter of water 100 g of fresh plucked paprika or 20 g of dry pods. Strain and leave to brew for two days. Add the resulting broth to 10 liters of water.
- Pour half a bucket of burdock leaves with water, leave for 72 hours.
- Add 300-400 g of chopped flowers and stems of bitter wormwood, plucked during the flowering period, to a bucket with boiling water. Defend for 6 hours. Add a spoonful of liquid soap.
- Add a glass of baking soda to a bucket of water.
After preparing any of the above broths, pour it into a container with a spray bottle and process the cabbage.
The cabbage scoop has natural enemies. In particular, these include trichograms. These parasitic insects lay their eggs inside the eggs of the pest butterflies.
Often on the cabbage growing in the garden, you can see small green or brown caterpillars - these are the larvae of the cabbage scoop
The cabbage scoop is a pest that can destroy the crop, so it is important to detect the insect in time and immediately begin to fight it
Medvedka
A large, threatening insect (up to 5-6 cm) with a dark brown body, strong legs and powerful jaws. Medvedka lives in the soil, making numerous moves, arranging clutches of eggs. The harm is done by the imago and the larvae of the bear:
- gnaw the stems of plants;
- eat root vegetables;
- damage potato tubers.
You can find out that a bear has settled on the site, both by damaged withering bushes, and by holes with piles of earth on the soil surface (insect exits).
Description
Systematic position: order Lepidoptera, family of moths (Noctuidae).
Distributed everywhere. It damages cabbage, beets, peas, beans, onions, lettuce, corn, sunflower, lupine and many other crops - over 70 plant species from 22 families in total.
The butterfly has a wingspan of about 50 mm; forewings gray-brown with yellowish-white wavy lines and two dark-bordered spots located near the wing apex; external reniform spot; the hind wings are dark gray; in a calm state, the wings fold along the body in a roof-like manner. The egg is hemispherical, flattened at the base, whitish.Adult caterpillar up to 50 mm long, 16-legged, almost naked; color varies from light green to almost black with a characteristic herringbone pattern on the dorsal side. Younger caterpillars are greenish.
The pupa hibernates in the soil at a depth of 9-12 (up to 25) cm. For the emergence of butterflies, the onset of average daily temperatures of 14-16 ° C and the accumulation of the sum of effective temperatures of 233-283 ° C at the lower threshold of development of 10 ° C. In the Northwest and Central regions, butterflies appear in the first half of June, in the Volga and North Caucasian regions - in May. The flight of butterflies is very extended.
Butterflies lead a twilight lifestyle. They additionally feed on flowering plants. The female lays eggs in clusters, mainly on the underside of the leaf. One clutch may contain from 8 to 200 or more eggs, usually 25-60. Fertility is 700-800 eggs, maximum - up to 2500. The duration of embryonic development at 13 ° C is 9 days, at 22.5 ° C - 4 days. The hatched caterpillars first feed together, scraping the flesh of the leaf. Starting from age III, they creep over the plant and gnaw through holes of irregular shape on the leaves. Caterpillars of V-VI instars feed inside the head of cabbage, making tunnels there and contaminating them with excrement, as a result of which the heads of cabbage can rot. In cauliflower, caterpillars damage both leaves and inflorescences. The duration of development of caterpillars is 40-50 days. In most regions of Russia, it develops in one generation, in the North Caucasus region, in two.
Parasites and predators, as well as various causative agents of diseases, can have a significant effect on the number of cabbage scoops. The most common pest parasite is the trichogramma egg-eater (Trichogrаmma evanescens Westw). In years with high humidity among the caterpillars of the cabbage scoop, the development of viral and bacterial diseases is noted.
Chafer
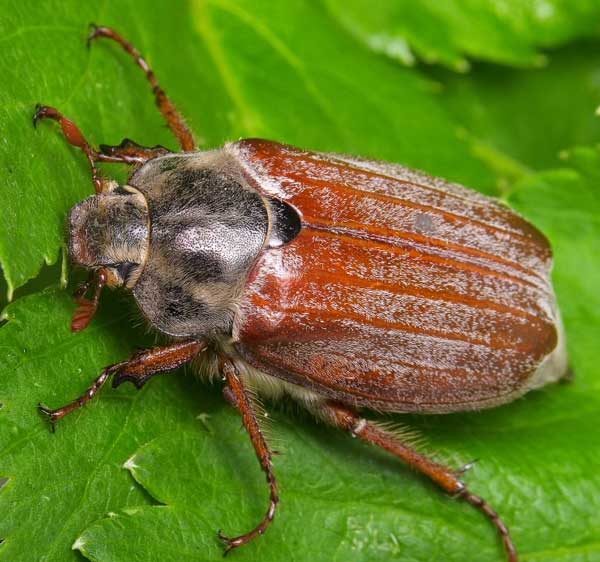


Beetles begin their summer in late April and May, laying their eggs in the soil. After about 3-4 weeks, larvae appear, which at the age of the younger stages are harmless to root crops. Starting from the second year, the insect has a chewing apparatus, and from that time on, the larvae move in search of food to potato tubers and root crops.
Caterpillars of white color with red or orange dots on the sides live in the soil for about 4 years, then turning into beetles. The larvae bring the greatest harm at the age of 3-4 years, when they need a large amount of food.
In search of food, they move 80-100 meters underground, gnawing the pulp of tubers. In a month, one adult larva can damage up to 10-15 bushes of the culture. Potato tops turn yellow, dry out, wither, tubers rot, deteriorate.
When cleanliness is really the key to healthy potatoes
- If the task is to destroy the scoop, then the first thing to understand is that the female lays eggs on the weeds. This means that the systematic destruction of weeds is not only a guarantee of a good harvest, but also a fairly simple way to prevent the pest from breeding in a potato garden.
- In order to destroy the shelter of the potato scoop, loosen the soil in the aisles more often. Do not neglect the timely hilling of plants - preferably several times per season. This will take a certain amount of time, but will significantly reduce the likelihood of a pest appearing.
- The potato core scoop will die if in the fall, even before the first frost, you carefully dig up the area around the entire perimeter.
- Remove pest-infected plants and fruits in time. This work cannot be called easy, especially if your site is more than the notorious "six acres", but you will hardly succeed in any other way.
Rodents


Of the gnawing animals, the earthen rat and mole rat damage potatoes. Rats belong to the group of vole mice, most often they live in vegetable gardens near ponds and streams. Length - up to 25 cm, the body is covered with brown-black fur.Animals eat tubers, gnaw through the roots of plants, equip whole storehouses underground where they hide potato tubers and small root crops.
On a note!
The ground rat is very prolific. Gives up to five litters per year, the number of pups in each is 2-14.
In favorable conditions, it multiplies very quickly, therefore, having noticed the animal on the site (by holes in the ground, traces of damage to plants), it is necessary to immediately start exterminating the pest.
Mole rats are large, up to 30 cm long, rodents that feed on roots and potato tubers. The animal has no eyes, instead of them there are dense folds of skin. It dwells underground, digging out complex passages with holes, arranging nests and pantries. Unlike moles, the mole rat is a herbivorous rodent, digging holes with strong teeth. Adult animals can eat as much food per day as they weigh themselves (up to 1-1.2 kg). On the site, his activity is noticeable by the earthen mounds and numerous tunnels, into which you can even stumble if you carelessly.
How to get rid of a cabbage scoop?
In order to eliminate the caterpillars of the cabbage scoop, you need to start acting as soon as possible, since this insect reproduces very quickly.
The most appropriate option would be to apply preventive measures to prevent the spread of caterpillars in the garden in advance.
- Predatory mites can be used. This method is absolutely safe and brings good results in the fight against the cabbage scoop. Ticks can be found freely available in specialized stores. However, they are quite expensive, so you will have to resort to other methods if the pests were able to settle in large areas.
- Manual collection of caterpillars. This is the simplest control measure that allows you to get rid of insects, however, it will not be able to help completely get rid of them, since most of the caterpillars are hiding among the leaves and in the ground. Gathering should be started in the evening, since it is after the heat has subsided that the caterpillars begin to leave their shelters and go in search of food. Gloves can be used as personal protective equipment.
- Chemical treatment. The use of chemically active substances will make it possible to process the territory of any area. Preparations from the category of pyrethroids, for example, ISS, are recognized as effective agents suitable for combating the cabbage scoop.
Together with pyrethroids, it is possible to use organophosphate-type agents, they show not such good results, but at the same time they are not able to poison plants and soil with toxins. The cabbage should be sprayed with a solution prepared according to the factory recipe. The best time to start treatment is in the evening, and it is desirable that the time is dry, since the product can very quickly be washed off the leaves and stems with rainwater. Remember that this procedure should be repeated once a week, since the formation of broods of larvae of caterpillars occurs at different times and, getting rid of one population, you will not be able to harm a new one that has not yet hatched.
It is almost impossible to completely prevent the invasion of the cabbage scoop on the garden, but if you approach the process of growing vegetable crops correctly and provide them with protection in time, you will be able to minimize the risk of mass spread of various types of pests in the garden.
Pest control methods
If any pests are found on the site, it is necessary to start fighting them as soon as possible. Delay threatens with crop losses, outbreaks of various infections in weakened plants.
Agrotechnical techniques and mechanical methods


Observing the rules of caring for the crop, you can prevent the appearance of pests on the site. Among the main ways:
- obligatory digging of the site in spring and autumn;
- loosening and hilling beds;
- weeding.
Such measures help to extract larvae, egg clutches, adults to the surface, where it is easier to destroy the pest.After the autumn digging, the pests on the surface will inevitably die from the winter cold.
In the fight against a number of insects, manual collection is effective. With small quantities of the Colorado potato beetle or potato shpanki, they are collected from the bushes by hand, not forgetting about gloves and accuracy.
The use of chemicals


Modern insecticides are effective means for protecting potatoes from many pests, while both universal and specialized preparations are produced. "Minus" - toxicity, therefore it is recommended to use it only with a large number of insects, strictly following the instructions.
From the Colorado potato beetle:
- from the group of pyrethroids, Decis, Karate are suitable;
- from organophosphates - Zolon;
- Novodor is used against larvae, at all stages of insect development - Fitoverm, Bankol.
For the extermination of the potato ladybug and moth:
- Inta-Vir;
- Spark;
- Tsiperon.
Vidat is used to combat the potato stem nematode, but Tagor, Imidor, Confidor extra, Bi-58 are effective against aphids.
Granular remedies have been created against slugs on potatoes:
- Ferramol;
- Storm;
- Meta;
- Anti-slug.
The granules are scattered in the aisles, but at the same time they exclude the access of pets to the site.
You can save potatoes from a bear, larvae of a beetle (May beetle), a wireworm with the help of the preparations Bazudin, Medvetoks, Antichrushch. Vallar (based on diazinon) has been created specifically against the larvae of the May beetle. The easiest way to destroy a potato flea is with solutions of Decis, Calypso, Spark, Sherpa, Actellik, Fufanon are used from the scoop.
For dressing tubers before planting, use:
- Prestige;
- Taboo.
From biological products for the protection of potatoes, Lepidocid, Bitoxibacillin, Enterobacterin have been created and have proven themselves well. They can be used at any stage of cultural development.
Folk remedies


In summer cottages, it is preferable to fight potato pests with compositions according to folk recipes that are safe for humans and the environment. These are various decoctions, infusions of herbs, mullein, ash, which are prepared immediately before use.
On a note!
Such formulations are effective against a small number of insects, as well as for the prevention of pests.
From the Colorado potato beetle (all proportions are given for 10 liters of water):
- infusion of wormwood. Pour 300 g of grass with water, add a glass of ash, stand for a day;
- infusion of tobacco. Dry stems, roots, powder are suitable. The amount of raw materials is half a kilo, soaked in water for two days;
- decoction of horsetail and dandelion. Take 200 g of each type of herb, boil for 15 minutes. The concentrate is cooled, diluted with more water (for 0.5 liters - 10 liters of water).
To destroy the bear and slugs, traps are made with beer, the wireworm is lured into "traps" with cut potatoes. After 3-4 days, it remains only to remove the caught insects that have gathered in the traps. You can get rid of potato moths, fleas, dusting the plantings with a mixture of wood ash, hot pepper and tobacco dust.
Many insects do not tolerate harsh odors, so it is recommended to plant such plants on potato ridges and along their perimeter:
- calendula;
- fennel;
- coriander;
- lavender;
- peppermint.
Thrips will not appear on the ridges if the potatoes are sprayed with an infusion of garlic cloves or arrows (200 g of raw materials are taken per liter of water, insisted for 4-5 days). A decoction of tobacco, an infusion of marigolds, a solution of ammonia (2 tablespoons per bucket), helping to get rid of aphids, scoops, flea beetles, showed themselves well on potatoes.
Liming
Using this procedure, you can not only protect yourself from scoops, but also enrich the soil with the most useful trace elements and minerals, increase the effectiveness of fertilizers and significantly reduce the amount of toxins entering potatoes from the soil and air. The recommended concentration of lime is from 0.4 to -0.8 g per square meter of soil.If necessary, it can be replaced with eggshells or wood ash, but they must first be crushed to a powdery state.


Tips for performing the procedure:
- after processing the site, the soil must be dug up on the same day;
- do not mix lime with phosphorus or nitrogen fertilizers;
- liming should not be done in windy weather and high humidity;
- Dolomite flour can be a good substitute for lime, but its cost will be slightly higher.
Do you know firsthand what a potato scoop is? Share with us your experience in dealing with this pest. You can leave your recommendations in the form of comments under the article.


The potato scoop is a small nondescript brownish butterfly. It seems that such an inconspicuous creature is incapable of causing any special harm. However, in fact, it gives a lot of trouble to many gardeners. It is quite possible to get rid of this pest, only in order for the measures taken to provide the expected result, first it is necessary to find out the characteristics of the parasite's vital activity.