Strawberry pests, as well as strawberry diseases, can significantly affect the harvest. Excellent weather conditions, an abundance of green mass, fruits - all this is the best fit for insects to destroy entire plantations of shrubs.
To avoid the loss of the strawberry crop from pests, it is necessary to carry out preventive protective measures. They will help reduce the likelihood of pests, especially those that live in the soil.
The spectrum of strawberry pests includes a sufficient number of such individuals. The main ones are presented below.
Strawberry pests - Strawberry whitefly
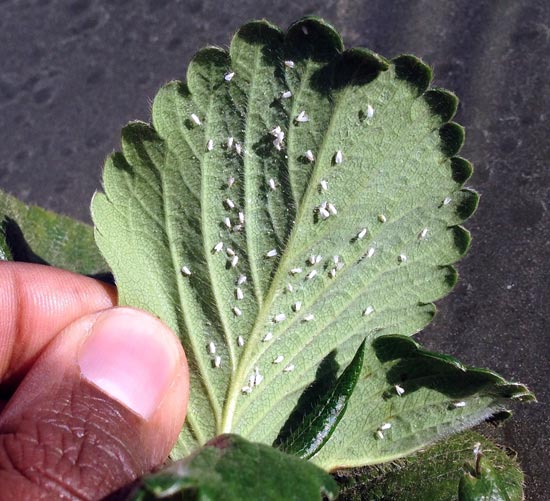

Whitefly strawberry or aleurodid strawberry - Aleurodes fragariae
Strawberry whitefly or strawberry aleurodid - Aleurodes fragariae
The whitefly that damages strawberries is very small. It looks like a micro white butterfly, less than 1.5 mm long and only 0.3 mm wide. The wings of the whitefly are covered with a wax-like coating on top. There are two pairs of wings.
Whiteflies settle at the bottom of the leaves, sucking the juice out of them. Butterflies do not like sunlight, so they can be found in shaded areas.
They also lay their eggs on the underside of the leaves. Their larvae are six-legged, oval, flat. They cannot be seen with the naked eye. In search of food, they also stick to leaf plates. Over time, their limbs and mustaches stop working.
After emerging from the puparium (a type of cocoon), fully developed adults are formed. During one growing season, the crop can give up to 4 generations of whiteflies. Such a pest overwinters in plant debris and the upper layers of the soil.
To protect strawberries from this pest, they are treated with pesticides before flowering and after harvesting the berries.
The strawberries are grown on mulch to prevent the spread of butterflies.
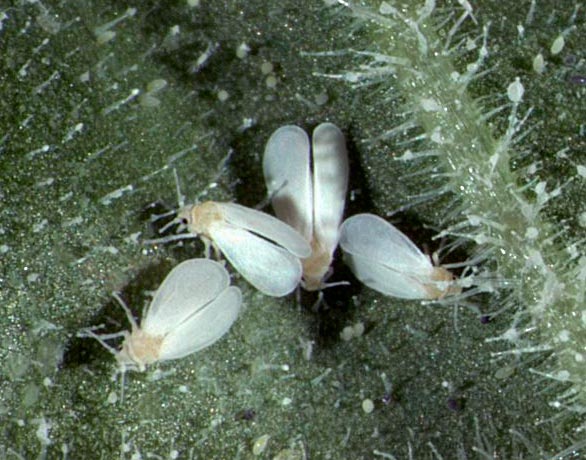


Whitefly strawberry or aleurodid strawberry - Aleurodes fragariae
Strawberry pests - Shaggy bronze
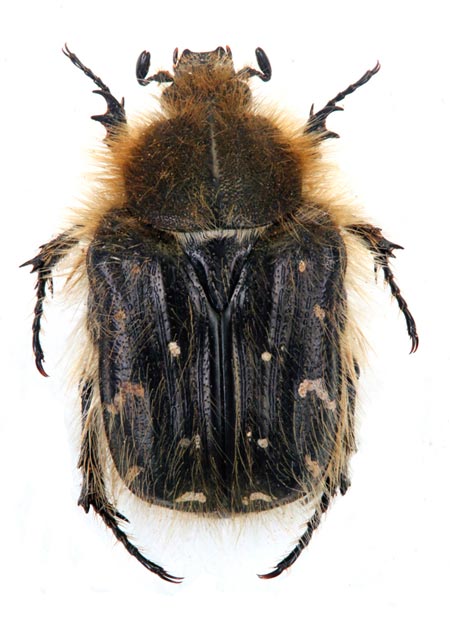


Hairy bronze - Tropinota hirta
Shaggy bronze –
Tropinota hirta
Shaggy bronze damages the generative organs of the plant.
It is a black insect, matte. Length approx. 12 mm. This is a typical representative of the lamellar beetle, which indicates its soil development. Bronzovka winters in the ground. From the end of May to the end of June, bronzovki cause the greatest harm to strawberries - they feed on flowers, periodically and young leaves.
All stages of beetle development are associated with soil, as already mentioned. This is what makes it difficult to remove pests from a certain area. In areas where intensive agricultural technology is used and constant plowing of the soil, the number of Bronzes is steadily declining. But not everyone can afford such expenses. Even in garden plots, not everyone works the land intensively.
The best recommendation to prevent the spread of shaggy bronzes is to dig up the soil, remove the larvae (suitable for small areas). It will not be superfluous to set fire to straw and leaves to scare away beetles. Some use female bait. As a last resort, beetles can be collected from plants by hand.
Since the bronzovka begins to act actively during the flowering period, treatment with chemical preparations is automatically not allowed.
The only insecticide suitable is Calypso. It can be used during any growing season.The effect is manifested after 3 hours.
Stages of strawberry processing
To prevent the spread of pests, several processing steps are required:
- spring - before the beginning of flowering strawberry;
- autumn - after harvest.
Chemicals are most effective against insect pests of strawberries. However, most of them are not allowed to be used during the growing season of plants. The drugs are used strictly in accordance with the instructions.
Folk remedies have a more gentle effect on strawberries and are used to disinfect soil and soil.
Important! Alternative methods are allowed to be used before the berries appear.


The plantings are processed by watering or spraying. For the procedure, the morning or evening period is selected, when there is no wind, rain or direct sunlight.
The following methods will help in the question of how to protect strawberries from insect infestation:
- purchase seedlings from trusted producers;
- disinfect the soil and seedlings before planting in a permanent place;
- timely fertilize;
- remove the topsoil where most insects spend the winter;
- prevent waterlogging of the soil;
- trim mustache and old leaves.
What to plant next to strawberries to repel insects? Pests bypass marigolds, calendula, cucumber grass, tansy, tobacco. Onions and garlic are planted in the garden every 30 cm.


Strawberry Pests - Green Peach Aphid


Green peach aphid - Myzus persicae
Green peach aphid - Myzus persicae
The green peach aphid inhabits the generative organs of plants, namely the petioles and flower stalks. As a result, the plants weaken and die off.
Chemical means of control are absolutely the same as in case of damage by other pests.
To protect strawberries from aphids, the gall midge aphidimiza, which is a predator, is used. These gall midges are grown in biological laboratories, laid out in a cocoon per square meter at the first appearance of aphids. If the aphid has already greatly multiplied, the number of entomophage cocoons is increased to 3 pieces per 1 m2.
Strawberry disease and treatment
Pests bring a lot of different problems to the garden:
- the risk of developing various diseases increases;
- frost resistance decreases (it does not tolerate winter well and may die);
- tangles weaken;
- the plant dies.


To prevent this from happening, every gardener, even an amateur, must take care of its further prosperity before planting a plant, protect strawberries from harmful factors affecting it.
Very often, gardeners use traditional medicine to combat various insects, which do not contain substances harmful to the human body. But before proceeding with the consideration of folk remedies, it is necessary to deal with the parasites that "attack" strawberries, there are a lot of them, and for each individual case a different approach is needed.
Strawberry pests:
- weevil;
- aphid;
- strawberry whitefly;
- mite;
- bear;
- slugs.


Let's take a closer look at each of the types of pests, how they form, develop and, of course, how to deal with them using folk methods.
Strawberry pests - Strawberry leaf beetle
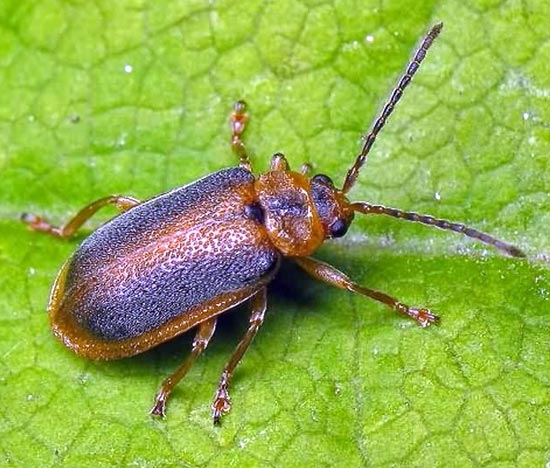


Strawberry leaf beetle - Galerucella Tenella
Strawberry leaf beetle –
Galerucella Tenella
The beetle is brown. It reaches 3-4 mm in length. It feeds on leaf plates. The name speaks for itself - leaf beetles eat up holes and holes in strawberry leaves.
The female lays eggs on the underside of the leaf or on the petioles. Masonry can be single and group.
The larvae are reflected after 2 weeks. They feed in the same way as older beetles. The larvae of the leaf beetle are yellow with a brown head. Their length is up to 5 mm. On their back there are spots and sparse short hairs.
With a strong spread of the strawberry leaf beetle, the leaves dry out, and the fruits remain in small quantities and are strongly deformed.
Beetles hibernate in the ground under plant debris. Based on this, the optimal control measures are agrotechnical. Of the chemicals, Nurell D, Sharpey, Karate and Zolon are allowed. They are used during the period of active life of the pest.
Signs of pest damage
Growing strawberries is challenging. First of all, you need to talk about the need for regular care, which consists in the correct planting of seeds or seedlings, high-quality and sufficient watering, loosening the soil, and fertilizing. Also, one should not forget about taking preventive measures aimed at reducing the risk of plant diseases or the appearance of all kinds of parasites on them.
Strawberry pests differ in their diversity, and for each individual species, you need to apply your own methods of elimination.
A distinctive feature of strawberry pests is that even in small quantities they are capable of causing irreparable damage to the crop, at the same time significantly worsening the quality of the berries.
Nobody is safe from the fact that a lovingly grown garden will not become the object of attention of certain parasites. Gardeners must be alerted to signs such as curling leaves, changing their color, the appearance of spots on the vegetative system of the plant, the formation of cobwebs and other third-party tissues, a visible slowdown in the growth of berries. This indicates that not everything is in order with the strawberries, and there is a high probability that pests have started on them.
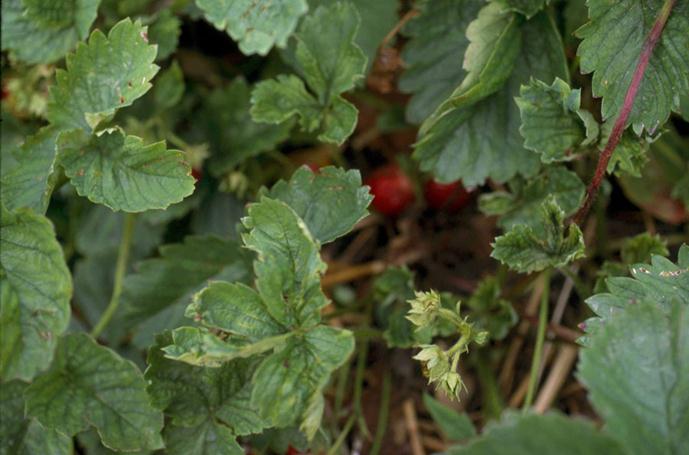


Gardeners must be alerted to signs such as curling leaves, changing their color, the appearance of spots on the vegetative system of the plant, the formation of cobwebs and other third-party tissues, a visible slowdown in the growth of berries.
The sooner you start fighting them, the more effective it will be. For each individual type, it is recommended to use various products, both homemade and purchased in specialized stores.
Strawberry Pests - Strawberry Nematode
Symptoms of Strawberry Nematode - Aphelenchoides Fragariae
Strawberry nematode –
Aphelenchoides Fragariae
Nematodes harm all vegetable and berry crops, without exception. Their harmfulness is extremely high. Therefore, their appearance in the vicinity of a field or garden is highly undesirable. The level of the obtained crop can drop to half.
This nematode is a round worm, up to 1 mm long. The body is in the form of an elongated cylinder.
Worms settle in the buds and axils of the leaves. Nematodes cause deformation of buds, flowers and ovaries. They become ugly, twisted. Bushes stop growing. With severe nematode damage, the bush may not produce berries at all. A few ugly bushes at best. Strawberry varieties Krasavitsa Zagorya and Rannyaya Makherauha lose up to 70% of their production when damaged by these pests. The Festivalnaya variety is relatively stable.
As befits most insects and various pests, nematodes can be in the soil for a long time. Therefore, the best prevention method is to perform all agricultural operations correctly and on time. You need to adhere to crop rotations, return strawberries to their original place after a certain number of years. The destruction of weeds and various plant residues is also among these actions.
If strawberries show signs of nematode infection, diseased plants are removed immediately, and then the soil is treated with a 5% solution of ferrous sulfate.
Before planting seedlings, I use thermotherapy. In addition to removing nematodes, this will also save you ticks.
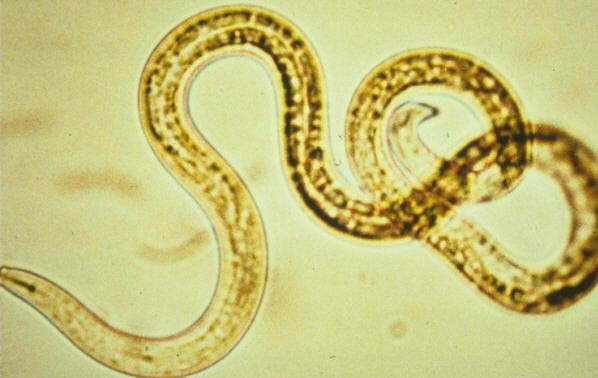

Strawberry nematode - Aphelenchoides Fragariae
How to determine if aphids
These insects can be white, black, greenish and even pink in color. They settle in the lower part of the stem, closer to the soil, and also on the back of the leaves.They crawl into secluded places in flowers and ovaries, they can crawl over the petioles, and then migrate to other cultures.
Aphids can be detected visually by the following external signs:
- leaves gradually wither, lose their elasticity and shape;
- after watering, the leaves do not recover, they continue to lose strength;
- a large ant colony was found next to a strawberry bed;
- on the plant itself, a sticky, viscous liquid with a sweet taste;
- bushes grow slowly, their tops are deformed;
- extraneous formations appear on the stems.
Affected plants look much worse than healthy ones and lose their growth rates. Therefore, the strawberry bed must be inspected regularly in order to destroy pests even at the stage of colony initiation.
Strawberry pests - Nettle leaf weevil
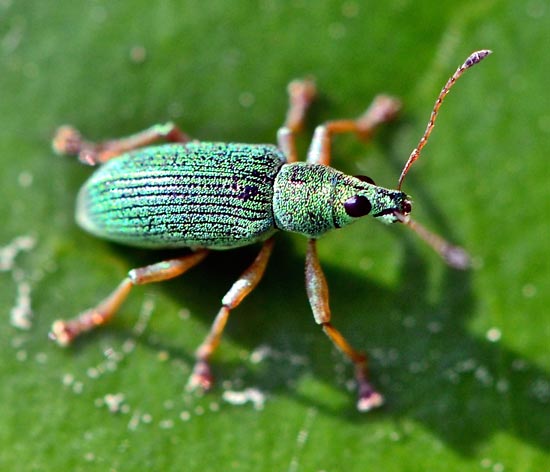


Nettle weevil - Phyllobius urticae
Nettle weevil -
Phyllobius urticae
A bright green beetle that damages leaf blades.
Not very large in size - up to 12 mm long, common in the European part of Russia and Siberia. The pest hibernates in the soil. In the spring they begin to act actively.
Leaf weevils are polyphagous, have a rather bright color - from green-blue to bronze-brown. Often, males and females often have different colors.
Most species of beetles emerge from the soil in the spring when the rosaceous plants are in the rosebud phase. They usually feed in the early morning, evening and night, as well as in cloudy weather, the buds, leaves and flowers of various woody and shrub plants for about a month. In the daytime, they are found in folded leaves, under loose bark, or in a litter under plants.
The eggs are laid in the soil, the legless white thick wrinkled larvae that emerge from them live in the upper layers of the soil, feeding on the small roots of plants. Their influence on the state of plants is insignificant. Larvae also pupate in the soil. Pupae of pale white color, with black eyes, about 5 mm long. Beetles emerge from pupae in late summer or autumn, but remain in the soil for the winter.
Before flowering, the bushes can be sprayed with 50% karbofos (no more than 30 grams is required per bucket of water). Additionally, Confidor and Decis are used.
Strawberry pests - May beetle
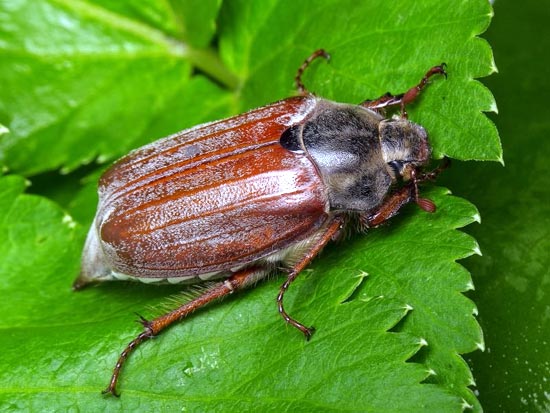


May beetle - Melolontha melolontha, Melolontha hippocastani
Chafer –
Melolontha melolontha, Melolontha hippocastani
Two species of beetles of the same genus are harmful. They are similar in appearance and harmfulness. Large enough - 22-29 mm. Black, but elytra brownish. Pubescent with fine white hairs.
They fly already in April in warmer southern regions and in May in colder ones. They are active in the afternoon, almost in the evening. Distributed in the vicinity of deciduous tree species. The flight is 20-40 days, during which they safely eat the foliage.
The female reproduces clutch at a depth of up to 30 cm. Soils they choose medium in granulometric composition, while avoiding sandy and rough. Each female can lay up to 70 eggs. After 1-1.5 months, the larvae appear. The first year of their life cycle, they feed on humus, gradually digging closer and closer under the root systems of various plants.
The beetle larva remains in this stage for 3 years. Only on the 4th year of its existence does it pupate. And, again, after 1-1.5 months a beetle emerges from the pupa, which also spends the next winter in the soil.
May beetle larvae are easily recognizable. They are very large (up to 6 cm and sometimes more), white or yellowish-white in color.
It is important to use all the same standard insecticides - Nurell D, Zolon, Sharpey and Karate during the period of active sabotage of beetles and their larvae. During the process of their degeneration and pupation in the presence of drip irrigation, Marshall, Bazudin, Aktar and Zolon are added to the nutrient solution in the required concentrations.If there is no drip irrigation in this farm, then the soil is treated with the drug Force, as well as Aktara VDG 250g / l.
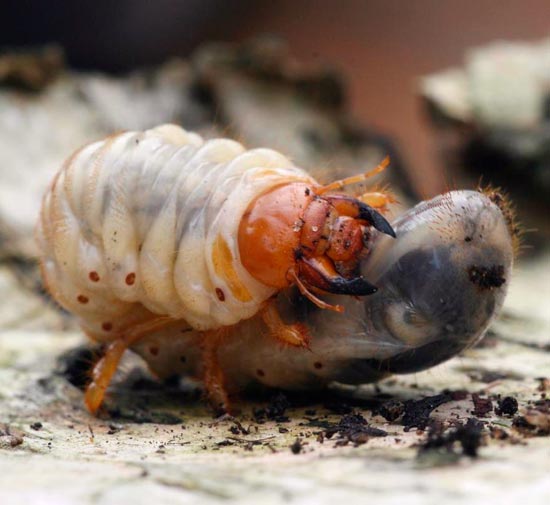


May beetle larva - Melolontha melolontha, Melolontha hippocastani
Strawberry pests - Raspberry-strawberry weevil


Raspberry Strawberry Weevil - Anthonomus Rubi
Raspberry-strawberry weevil –
Anthonomus Rubi
The beetle is dark in color (gray or black), small in size - only 2-3 mm in length. Harmful mainly to young leaves, buds and pedicels.
During the period of budding and further flowering, pedicels without buds are found on the affected bushes. Sometimes the buds hang on a thin film.
The weevil is most harmful to early varieties of Krubniki. It comes out of the soil after wintering and begins to gnaw and eat up the pedicels of the first buds. It is these buds that give the largest first berries.
After eating up, the females lay the larvae in the buds. These larvae devour the contents, and after a while pupate there.
Each larva develops for 20-25 days. The next generation of weevils feeds on young leaves. They gnaw out narrow holes in them in large quantities.
Weevils hibernate traditionally in the ground at a shallow depth (up to 1.5 cm) or under plant debris.
To protect strawberries from this pest, strawberry bushes are sprayed during the life of the pests with Nurell D, Karate, Aktellik, Zolon.
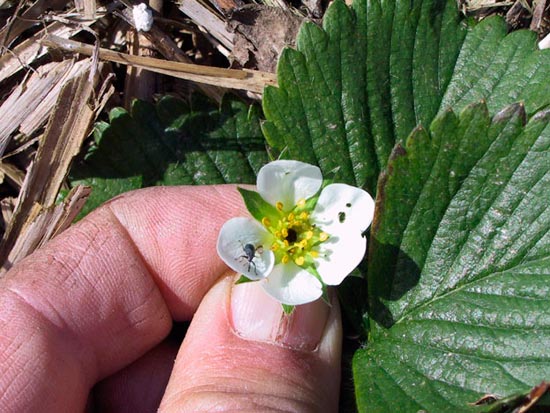


Raspberry Strawberry Weevil - Anthonomus Rubi
Strawberry pests - Medvedka ordinary


Medvedka ordinary - Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa
Medvedka ordinary –
Gryllotalpa gryllotalpa
Medvedka is a large, unpleasant-looking typically garden and field pest. The range of affected plants of this beetle is very large and is polyphagous. The presence of a bear on the site will be indicated by wilting of plants, having pulled out which the bitten parts of the root system are visible.
Medvedka is about 6 cm long. The beetle is brown. The forefeet is very large with tibiae with teeth capable of digging soil.
A very large amount of this pest occurs in fields well fertilized with organic fertilizers. In addition, high humidity is also a plus for them.
Bears overwinter in 20-40 cm thick soil. In spring, when the soil reaches a temperature of 8-10 ºС, the beetles crawl into higher layers and begin to actively gnaw at the roots. Consequently, the greatest harmfulness is manifested precisely in early spring, as well as at the beginning of summer.
Females lay eggs at a depth of 14 cm. Their maximum number reaches 400 pieces. Bears protect their offspring and hatched larvae. The larvae themselves hatch by the end of May - beginning of June.
They begin their feeding only a few weeks after hatching. They feed on plants. The bear lives in the larval stage for 2 years.
Special baits are used to fight the bear. Marshall, Hinofur and Zolon are also used for etching. Similarly with May beetles, they use the same drugs with drip irrigation and, in its absence, Force.
How to resist adversity?
Experienced farmers do not start pest control after they appear, but long before. Their war on insects is waged almost all year round. Constant care of your backyard plots helps to avoid financial and other problems when growing and harvesting strawberries in the future.
Preventive actions
So that the fight against insects does not turn into a constant war with them, it is better to do prevention when growing strawberries. For this, various repellent plants are planted, household chemicals are used, and folk methods of destroying gluttonous pests are used.
Repellent plants
Representatives of these flora species have strong and pungent aromas. They scare away insects from strawberry plantations and protect the beds from aphids.
Dill and parsley
These umbellates attract ladybirds, earwigs and lacewings with hoverflies with their scent. They destroy aphids on the strawberry plantation.
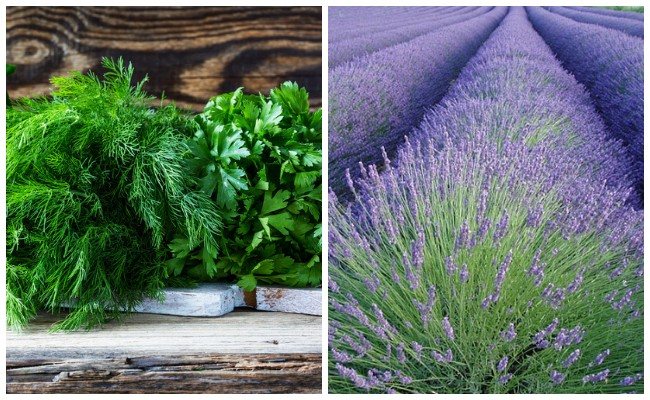


Lavender and fennel
Thinning phytoncides (aromatic substances), these plants are able to drive away aphids with a diffused odor. These crops are advised to be located near the beds. Better to plant them in the aisles or at the borders of the strawberry planting. You can use lavender with fennel throughout the garden or vegetable garden, planting them in small islands.
Nasturtium
Along with mallow, petunia, nasturtium is an attraction plant. Their task is to distract harmful insects from the desired plantings. These flowers are planted far from the protected beds, protecting the cultivated plants from the invasion of pests. Then the affected plantings are disposed of.
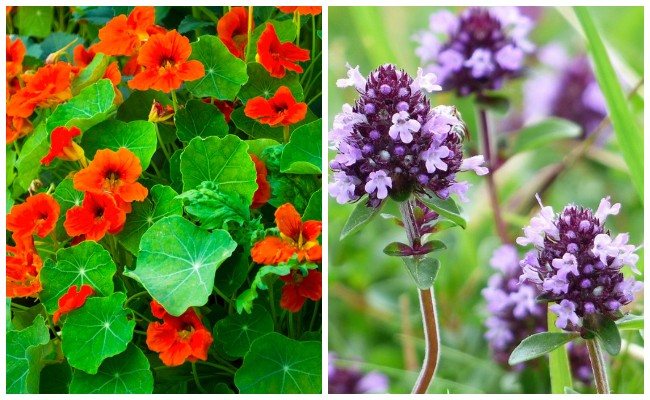


Thyme
A herb with pronounced insect repellent properties. Like lavender and fennel, thyme emits an aphid-intolerant fragrance. Essential oils are produced from this plant. The use of extracts from such herbs leads to good results in the fight against aphids.
Compliance with content rules
Knowing and observing certain conditions will help to better protect the berry plantations. The chances of getting a good harvest will increase.
Wood shavings
Sawdust or wood shavings are often used to protect the backyard. In the fight against insects, shavings are used as follows. Sawdust pots are placed on the territory of the site. Earwigs willingly settle in them. They do not mind eating aphids and protect the crop from destruction.
Sawdust is also used for soil mulching. Along with loosening, this creates comfortable conditions for strawberry ripening.
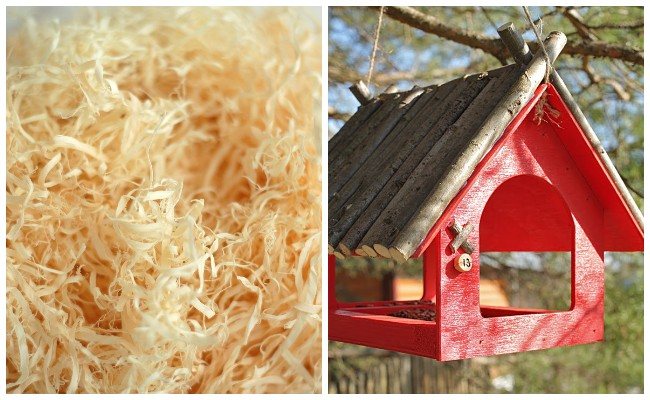


Bird Feeders
You can get rid of aphids on blooming strawberries by attracting birds to protect your garden plot. Small birdies destroy aphids and eggs laid by them. To attract birds, you can make and place several feeders in the garden area.
On a note! If bird assistance is used, the use of pesticides should be limited. This will save the life of the feathered helpers.
Top dressing
As a rule, aphids attack weak plants that are not able to fight it. To increase the resistance of strawberries, they need to be properly cared for. It includes soil plowing, mulching, timely moistening of the beds. Potash and phosphate fertilizers will increase the hardiness of the strawberries.
Strawberry pests - Strawberry mite
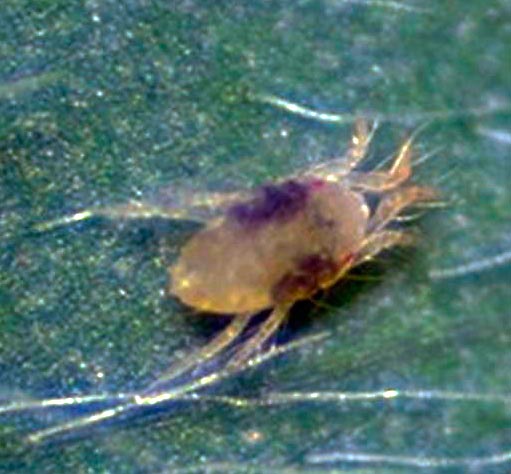


Strawberry mite - Tarsonemus fragariae
Strawberry mite -
Tarsonemus fragariae
The mite is transparent and small. The size of the female is 0.2 mm, the male is 1.5 times smaller. It is impossible to detect this tick with the naked eye. At the initial stages of development, mites are whitish-transparent. As they grow older, they turn yellow or brown. Bushes heavily affected by strawberry mites are always dwarf. Their yield is extremely reduced.
The mites suck the sap from the young leaves. After that, the leaves curl, become waxy yellow in appearance and die off. Those that survived remain shriveled.
Most of all, the effect of ticks on strawberry bushes is noticeable in the second half of summer.
Strawberry pests such as mites prefer waterlogged regions and places with warm temperatures. The pest is widespread everywhere. But the harmfulness increases from southern and dry areas to humid and warm places in the north.
Can be found in greenhouses.
To protect strawberries from this pest, only clean and healthy seedlings should be used before planting. The drug Keltan (0.2% solution at the beginning of leaf growth) can partially destroy the tick. An alternative to it is Karbofos (0.3% solution). This spraying is repeated, if necessary, after harvesting and harvesting old leaves.
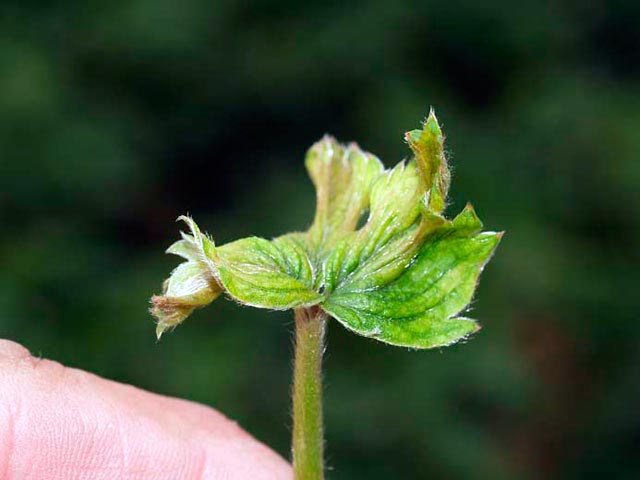


Strawberry mite symptoms - Tarsonemus fragariae
Strawberry pests - Spider mite


Spider mite - Tetranychus Urticae
Spider mite –
Tetranychus Urticae
Such mites envelop the entire bush with a thin cobweb. After some time, the bush dries up completely.
On this cobweb in good light, you can see those very spider mites. They are very small - 0.5 mm, whitish. Therefore, they are not easy to spot in the shade and on leaf blades. They populate the undersides of the leaf blades. The initial signs are visible, on the contrary, from the top of the sheet. These are small light points.
In the spring, spider mites develop on weeds, after which they directly infect the strawberries themselves. The maximum number of pests falls on the second part of fruiting.
For prevention, you need to adhere to all, without exception, the rules of cultivation. When a spider mite appears, a predator, phytoseiulus, is bred on plantations. Fitoseyulus is also a mite that feeds on a spider mite. It is grown on an industrial scale in biological laboratories.
The following acaricides are used: Actellic, Sunmight, Omite, Flumite and Ortus.
Strawberry Pests - Slugs


Slugs on strawberries
Slugs harm strawberry crops in any growing region. Best of all, they tolerate temperatures from +15 to +17 ºС. In this case, the air humidity must be absolute. That is why they do the most harm precisely in a humid climate and under appropriate conditions for crop cultivation.
They hibernate in the ground. But mostly in areas remote from the cultivation zone. Overwintered individuals lay eggs in June, and those that hatch from eggs in spring - in July-August.
Slug clutches are prepared under lumps of earth in damp areas.
Harm the fruit. They eat the flesh of the berry, starting from the bottom - where the berry comes into contact with soil or a wet object. In the centers of the leaf plates, slugs gnaw round holes. Less commonly, they use the edges of the leaves for this. During the day, slugs do not climb to the surface. They actively harm it in the twilight time. Depending on the species, the slug can live up to 4 years.
To protect strawberries from slugs from chemical remedies, Slimax is effective at a concentration of 5-7 kg / ha. Also, the aisles can be sprinkled with metaldehyde (8-10 kg / ha). Before planting, the soil is treated with formaldehyde. In addition, you should control the humidity in the area occupied by strawberries, adhere to the rules of agrotechnical soil cultivation.
Testimonials
Decis from thrips does not help much. I worked on flowers with Dichlorvos in the form of an aerosol, the result is instant. In general, pest control is a complex process and it takes a lot of experimentation to develop your strategy. I'm talking about what. For example, Dichlorvos helped me with thrips, but he killed both predatory thrips and predatory mites - insects that destroy thrips, as a result, there were fewer thrips, but its enemies became smaller, the remaining individuals can quickly restore their population in even more comfortable conditions ... I am more for something natural, such as spruce mulch from slugs or marigolds from nematodes, but I have not yet come up with an effective method for thrips.
Thrips add a headache to gardeners, but timely prevention allows you to quickly identify the pest and take measures to destroy it. Unfortunately, at the present time, without the use of remedies, it is almost impossible to grow garden strawberries. In order not to poison yourself with chemistry, it is better to use any of the biological products. For example, Fitoverm or its Ukrainian analogue Aktofit will perfectly cope with a complex of pests at once, only there should be several treatments: at least 2-3 with an interval of 5-7 days.
Strawberry pests - Tobacco thrips


Thrips tobacco - Thrips tabaci
Thrips tobacco –
Thrips tabaci
This type of thrips is ubiquitous. Harmful to many crops, both vegetables and berries. The size of thrips is traditionally small - adults reach up to 1 mm. The color of thrips is yellowish and brown. The larvae are light. Thrips overwinter in plant debris or at a shallow depth in the ground.
In early spring, they feed on weeds. The pest is extremely fertile - the female forms 70-100 eggs per clutch. Larvae appear within 5 days.After another 10 days, the larvae deepen into a 15-centimeter layer of soil, and after a week, adult insects appear. During the growing season, thrips form a maximum of 5 generations.
Spray in the same way as in previous cases.
Additional tips and tricks
Using folk methods of repelling insect attacks, farmers use not only solutions, but also dry substances. Shredded tobacco, wood ash, its mixture with makhorka is used to treat aphid-infected areas.
Many people use tar soap, ammonia solution, Coca-Cola, mustard. Infusions containing vodka and just alcohol, other improvised substances are used.
The processing of the territory with the help of folk methods is carried out in the evening. Sunlight quickly neutralizes the effect of natural drugs. Subsequent protection of the beds is carried out after 3-5 days. It is advisable to do this with other solutions.
As you can see, there are a lot of means to help destroy aphids. What to use, folk methods or household chemicals is your choice. But one rule must be followed by all. Aphids should be removed by any available methods. It is better to alternate methods of plant protection. A cared-for garden and berry beds will delight you with a good harvest of healthy and tasty fruits more than once.
Strawberry pest control methods
The best way to deal with anything is to prevent the appearance of a pest, or pathogen. With the right approach, you can generally prevent damage to your site by any of the pests.
Agrotechnical methods of protecting strawberries from pests
- compliance with crop rotation;
- destruction of weeds and plant residues;
- plowing / digging the soil;
- air humidity control (for greenhouse conditions);
- controlled amount of watering.
Biological methods of protecting strawberries from pests
In this case, they assume the cultivation of predatory insects that are able to feed on some types of pests. These are entomophages of gall midge aphidimiza - against aphids and phytoseiulus - against spider mites.
Chemical methods of protecting strawberries from pests
- Apollo, c.s. (a.i. clofentesin, 500 g / l) is a contact acaricide that destroys spider mites. The second treatments are carried out during the growing season with a drug consumption of 0.3-0.4 l / ha.
- Zolon, c.e. (a.i. fosolone, 350 g / l) - it exhibits a wide spectrum of action on strawberries. Used during the growing season before flowering and after harvest. Consumption rate 0.6 l / ha.
- Karate, μs (a.i. lambda-cyhalothrin, 50 g / l) - suitable against aphids, ticks, leaf beetles and other pests. To prepare the solution, take 4 g of the drug per 10 liters of water.
- Actellic, c.e. (ae pyrimiphos-methyl) - on this berry crop, the insecticide can destroy almost all pests, including beetles and aphids. Sprayed twice during the growing season with a flow rate of 0.6 l / ha.
- Aktara, century (d.v. thiamethoxam 250 g / kg) - applied at a rate of 2 g / 10 l of water per hundred square meters. Two treatments. The first spraying before flowering, the second spraying after harvesting. Intavir, vrt (a.c. cypermethrin, 37.5 g / kg) - effective use against weevils on strawberry plantations. Sprayed 25 days before picking berries with a consumption of 1.5 liters per 10 m2.
- Karbofos, c.e. (d.v. karbofos 30%) is an insectoacaricide that fights against aphids, beetles, weevils, moths and ticks. Spraying is carried out one month before harvest. Consumption of 10 liters for 10 strawberry bushes, and one solution requires 8 liters of water and 60 g of Karbofos.
- Metaldehyde, g. (d.v. metaldehyde) - a typical remedy for slugs. Scattered onto the soil surface. The approximate consumption is 4 granules per square meter.
- Shar Pei, m.e. (a.i. cypermethrin, 250 g / l) - used against beetles and often other pests. The consumption rate ranges from 0.15 to 0.3 l / ha.
- Nurell D, c.e. (d.v. chlorpyrifos 500 g / l + cypermethrin 50 g / l) is a broad-spectrum insecticide. The consumption rate is 1-1.5 l / ha.
- Force, city (d.v.tefluthrin) - strawberry plantations are treated in the absence of drip irrigation once at a working solution concentration of 10-12 kg / ha.
Folk methods of protecting strawberries from pests
- Tobacco dust - can be used against aphids, flea beetles, ticks. Take 1 kg of dust per 10 liters of water, insist for a day. Then it is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 3 and 40 g of soap per 10 l of solution are added. Sprayed 2 weeks before harvest.
- Mustard powder - pollinates the soil to prevent slugs. In addition, it eliminates bedbugs and thrips (100 g per 10 liters of water must also be insisted for 2 days, strain, add 40 g of soap). Treatments are carried out 20 days after flowering.
- Honey - acts as a bait for the bear.
- Salt - Common table salt will keep the ants out of your strawberry planting.
- Sunflower oil - diluted in water has the same effect as salt.
- Apple cider vinegar - sprayed with plants against aphids.
Prevention measures
In order to prevent the spread of thrips on strawberry plantings, you need to follow the following simple recommendations:
- water the plants regularly to maintain a moderate air humidity;
- periodically inspect strawberry bushes for signs of infection;
- keep strawberry seedlings in quarantine for 1-3 weeks in order to reject infected plants even before planting in the ground;
- place special traps over the plantings: colored (yellow or blue) sticky strips of paper, they will help to timely detect the appearance of pests on strawberry bushes.
To scare away pests from strawberries, you can spray the bushes with herbal infusions every 2-3 weeks; marigolds, garlic, yarrow, tobacco, celandine and other odorous plants are suitable for their preparation.




















