Powdery mildew
Description

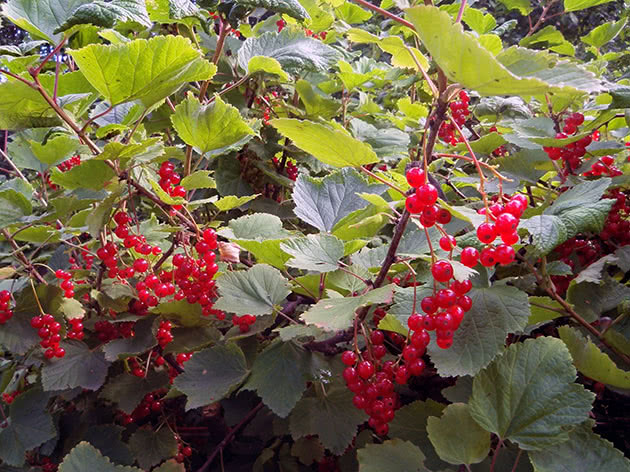
Black currant berries
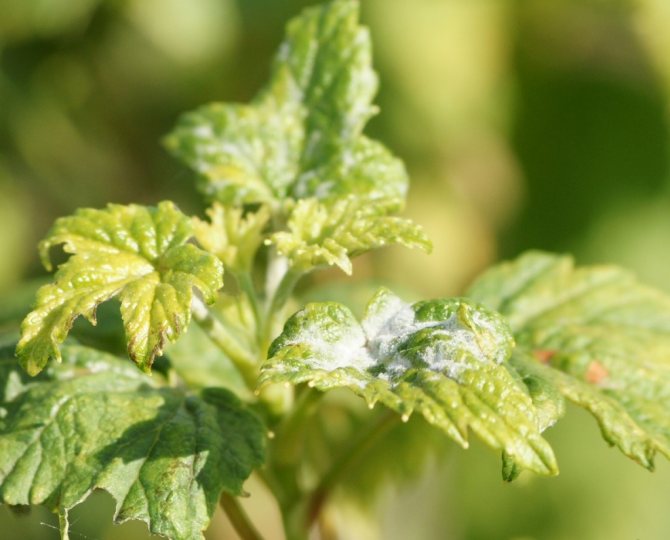
Fungal disease, which appears on young shoots and leaves in May, grows throughout the summer, hibernates in fallen leaves. As a result, the currants stop growing, the leaves dry out, their tips twist, and the berries do not ripen and fall off. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease progresses within 6 years and completely destroys large groups of bushes. The appearance is a powdery white bloom, which over time becomes dark and grows tightly to the bush, takes away strength from it and sucks out nutrients. The fungus occurs at high air humidity and prolonged high temperatures, as well as in soil oversaturated with nitrogen fertilizers. Spores are spread by insects, dewdrops and wind.


Powdery mildew
Treatment
Fresh plaque can be washed off with soapy water. This method can be used if the disease has just appeared, and the lesion is of a single focal character. In case of massive damage to the branches, they need to be cut and burned, and the bushes should be sprayed with Fundazol, Fitosporin or other fungicides. In case of group infection of bushes, 4 treatments need to be carried out: before and after flowering, after harvest and 14 days after 3 sprays. As a preventive measure, it is worth removing fallen leaves at the end of the summer season and burning them.
Diseases and their treatment
A healthy currant has many bright green large leaves of the correct shape, gives a rich harvest of round berries with a rich taste, easily tolerates winter. The infected plant loses its frost resistance, gives poor yields, and loses its greenery. Photosynthesis deteriorates, as a result, the currant dies.
Many diseases are effectively treated in the initial stages. Later, it is more difficult to deal with them. Therefore, it is important to detect the infection as early as possible. The following signs should alert the gardener:
- suspicious spots on the leaves;
- plaque on greenery, fruits and shoots;
- yellowing of leaves and falling off earlier than the autumn period;
- drying out of the bush;
- falling of fruits;
- the appearance of convex formations.
To understand why currants are sick and what to do, it is important to compare the existing symptoms with signs of disease.


Tuberculariosis
Tuberculariosis is a fungal disease that causes the branches and leaves of a plant to dry out. The development of the disease is facilitated by a high level of moisture and mechanical damage to the bushes.
The infection manifests itself as follows:
- red tubercles form on young shoots;
- the infection spreads to other branches and enters the bark, forming red lumps;
- already in July, the leaves dry up, curl and fall off;
- the affected branches die.
To get rid of tuberculariosis, diseased branches are removed. Places of cuts are sprinkled with ash and greased with garden varnish. The bush is sprayed with preparations containing copper.
Anthracnose
Anthracnose is a fungal disease. The plant becomes infected with it in the spring, but the first signs appear after 1.5–2 months, in the summer. The epidemic usually occurs in July.
The affected plant quickly loses its leaves and fruits. Its winter hardiness decreases, photosynthesis worsens.
Important! The fungus is not afraid of frost and hibernates in plant debris.It is activated during prolonged rains, with excessively abundant watering, the presence of a large number of weeds next to the currants.
Signs of anthracnose:
- on the leaves of currants, first red or brown spots are formed, then swelling;
- gradually, the affected areas expand and merge into one large burgundy blister;
- the leaves dry up and fall off.
It is easiest to treat bladder disease in the initial stages. All affected greens are cut off. Healthy leaves are sprayed with one of the following preparations:
- Bordeaux liquid made from 100 g of the product and 10 liters of water.
- Folk: 1 kg of ash and 1 piece of laundry soap are dissolved in a bucket of water.
- Chemical when other methods are powerless. One of the most effective means is "Alirin-B" (for 1 liter of water 2 tablets).
Processing is carried out 1 time in 7 days, in dry weather.
All types of currants are ill with anthracnose, but most often the infection affects the red one.
Septoria
Septoria, or white spot, is considered a disease of black currant, but it affects other plants as well. It is caused by a fungus that is activated in summer.
The causes of the development of the disease are thickening of the planting, high humidity, lack of sunlight, poor air exchange.
Recognize white spot by the following features:
- angular brown spots with a diameter of 2-3 mm are formed on the leaves;
- over time, they turn white with a dark border;
- the disease spreads to the fetus;
- the affected leaves and berries fall off.
Before treating the disease, all the affected parts of the bushes are cut off, the weeds are carefully weeded. All collected vegetation is burned.
For the treatment of septoria, the following are effective:
- Bordeaux liquid (100 g of the drug per 10 liters of water);
- fungicides: phthalan, "Kuprozan", "Captan".
It is interesting:
How to cure cucumbers in a greenhouse from white rot.
How to get rid of top rot: proven drugs and folk remedies.
Sclerotinosis
Sclerotinosis, or white rot, is a fungal infection that affects all parts of the plant and leads to the death of the bush. The fungus lives in the soil, is activated at high humidity and weakening of plant immunity.
Signs of white rot:
- brown weeping formations appear at the base of the shoots;
- leaves wither;
- spots begin to rot, a white bloom appears, resembling cotton wool;
- parts of the currants over the infected areas die off.
When the first symptoms are found, the affected parts of the bushes are removed, the cut sites are treated with garden varnish. The entire shrub is sprayed with fungicides. If signs of the disease appear again, the affected plant is dug up and burned.
Important! If the diseased plant is not removed, the infection will spread to neighboring shrubs.
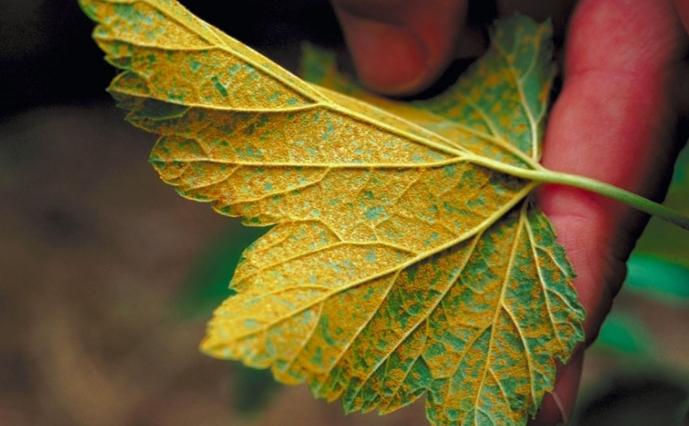
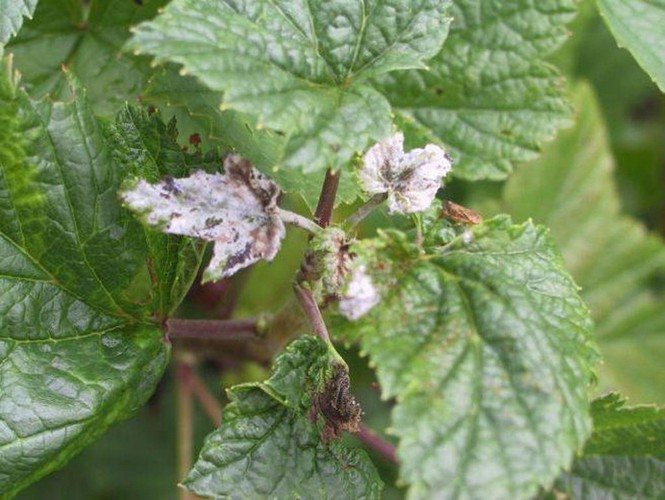
Powdery mildew


Powdery mildew is another fungal disease. The fungus is most active in the middle of summer.
The disease is dangerous for the plant: it affects all parts of the shrub, causing the leaves and fruits to fall off, and the shoots to dry out. Photosynthesis is impaired, and the chances of the plant surviving the winter frosts are reduced. For several years, the culture completely stops growth and dies.
The reasons for the development of powdery mildew are dry soil, high air humidity, soil oversaturation with nitrogen. Currants are infected through the ground, infected planting material and weeds.
Signs of illness:
- a dry translucent whitish bloom forms on the leaves and shoots;
- over time, it becomes denser, in places it turns brown, to the touch it resembles felt;
- the affected shoots are deformed, stop growing and die off;
- the berries are covered with bloom, darken, fall off without ripening.
The sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of dispensing with serious chemicals. Before spraying the plants with special preparations, all diseased parts are cut off.
Treatment methods:
- Copper preparations. Currants are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate.
- Folk method. Take 1 bottle of 5% iodine and 2 liters of milk on a bucket of water. Plants are treated 2 times with a break of 4 days.
- The bacterial method. Chicken droppings are diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. The resulting composition is sprayed on the bushes.
- Purchased substances. If folk remedies and preparations with copper do not help, use fungicides - "Topaz" or "Fundazol". In this case, the fruits cannot be eaten.
Rust


The causative agent of rust is a fungus. Usually, the plant becomes infected in mid-summer or autumn. As a result, leaves and berries fall off.
Important! Spores of the fungus sedge, conifers, weeds are transferred.
There are two types of currant rust - goblet and columnar. The first is expressed like this:
- orange spots appear on the inside of the leaves;
- over time, they transform into yellow bubbles filled with spores;
- the affected areas increase and lead to the drying out of the entire leaf plate;
- leaves and berries fall off.
Columnar rust is no less dangerous. Its manifestations:
- the outer side of the leaves is covered with small yellow dots;
- red growths with spores are formed on the seamy side;
- the growths take the form of hairs, to the touch the leaves resemble felt.
All diseased leaves are removed before processing. For treatment are used:
- biological product "Fitosporin";
- Bordeaux liquid diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 100.
Striped mosaic
Currant mosaic is a viral disease that causes drying and falling of leaves and leads to the death of the bush.
The main signs are:
- yellow-orange patches appear on the leaves;
- lesions begin to dry out, spreading over the entire surface;
- leaves fall.
The mosaic cannot be cured. Affected plants are removed from the site. To prevent the disease, the bushes are treated with insecticides, since they carry the pathogen of aphids and ticks.


Curly leaves
Both a virus and a fungus cause curliness. Both infections are spread by aphids. The signs are the same:
- leaves are irregular, with thicker areas;
- the leaf plate curls, bubbles and turns red;
- the leaves dry up and fall off.
To heal the plant, first get rid of the aphids and remove the damaged leaves. After that, the currants are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid.
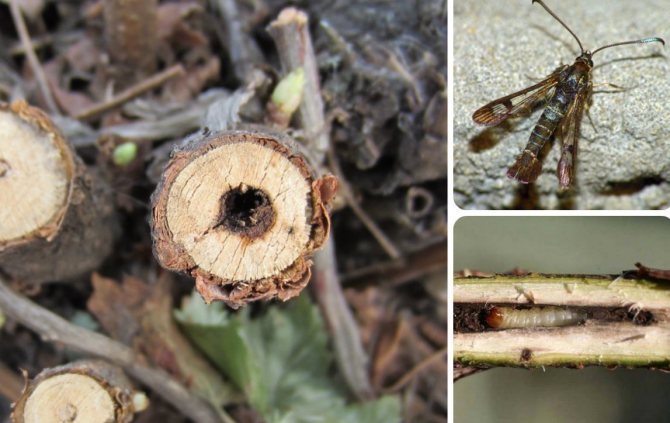
Nectric drying of shoots
Nectric drying affects only red and white currants. The causative agent of the infection is a marsupial fungus. The disease leads to the drying out of young shoots, and then to the death of the entire plant.
Description of the symptoms of the disease:
- orange dots appear on young shoots;
- they grow in size and look bloated;
- the spores of the fungus ripen, and the formations turn black;
- young shoots die off.
To combat the disease, all affected branches are removed. The cut sites are treated with garden varnish, the plants are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid.
Reversal
Reversal, or terry, is a viral disease spread by a kidney mite. The disease leads to mutation of currants and infertility.
Reversal signs:
- leaves become more elongated, asymmetrical and smooth;
- only 3 blades remain on them instead of 5;
- the color of the greens changes to purple;
- flowers become longer and thinner;
- the currant ceases to exude its characteristic aroma;
- the ability to bear fruit is lost.
The disease is not cured. The affected bushes are removed from the site and burned. The site is under quarantine for 5 years.
Chlorosis
Chlorosis is a disease caused by a decrease in the quality of photosynthesis and a lack of chlorophyll in the leaves of a plant. It occurs due to nutritional deficiencies and poor weather conditions. Expressed in:
- pale, yellowish greens;
- premature shedding of foliage;
- chopping shoots;
- dying off of roots.
To remedy the situation, they introduce a complex mineral fertilizer, adjust the care.
Necrosis
Marginal necrosis causes an excess of chlorine in the soil. As a result, the edges of the leaves dry out, the greens become ash gray.
If signs of necrosis are detected, ammonium nitrate is added to the soil. This is done before and after flowering currants.
Anthracnose
Description
Terry black currant: what to do
In the middle of summer, spots of red, brown or black may appear on the currant leaf, which gradually swell and deform the leaves. This fungal infection is called anthracnose. High humidity is the main factor in the occurrence of this disease, which, first of all, affects young branches and reduces the frost resistance of the shrub. The fungus hibernates in fallen leaves, so it can be found on the back of the leaves located on the lower branches.
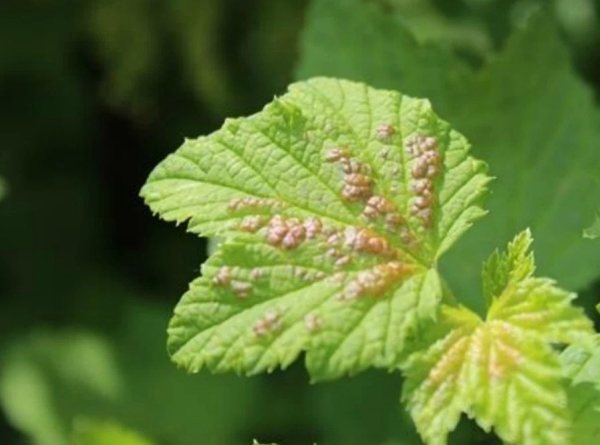


Anthracnose on leaves
Treatment
You can cure the disease with the help of Bordeaux liquid: you need to thoroughly spray all the bushes when you find the first signs of infection and after removing the berries. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to avoid planting a young bush in the place where the affected specimen grew, and also to burn all the fallen leaves on the site.
Classification of currant diseases
There are a great many varieties of pathological microorganisms that can damage the crop. Often, pathogens attack a crop, regardless of its variety. There are also those who are selective in choosing a donor plant.
There are red currant diseases that are common to white varieties, but never touch plants with black berries.
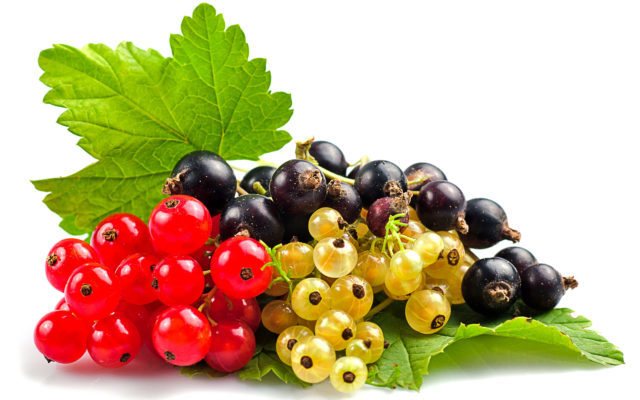


Tasteful qualities delight gardeners with colorful fruits of currant bushes
It is possible to repel the attack of pathogenic bacteria and spores if you know the main signs indicating the onset of the development of the disease. In the following sections, you can find a description of the various diseases to which the currant shrub berry culture is susceptible. Consider currant diseases, a description of symptomatic manifestations, treatment methods.
Rust
Growing black currant in summer cottages
This disease can take two forms:
- Columnar rust covers the leaf with bright red oblong spots. Spores of the fungus appear on conifers and are carried by the wind. The peak of reproduction is in July, when the mushrooms begin to multiply on the leaves, forming growths in the form of columns;
- Goblet rust appears on the back of the leaf as pale or bright orange spots. The defeat occurs by air, spores appear on last year's sedge and are carried by the wind in the spring. By the beginning of June, the spore ripening phase begins, depressions appear on the lower part of the leaves.


Left - goblet, right - columnar rust
How to treat rust-affected currants:
- Four times fungicidal treatment with an interval of 1.5 weeks. The first spraying is carried out before the active growth of the leaves begins. The drug Previkur and Bordeaux mixture is highly effective;
- The folk method of combating the disease is spraying with a garlic-tobacco solution. A mixture of 1 cup of garlic cloves, 200 g of tobacco dust and 2 liters of water to insist for 3 days. Then add soapy water and a pinch of hot pepper. Process the bare branches with the resulting solution before blooming the sheets;
- Preventive measures: complete destruction of infected branches, mowing and disposal of sedge in the area adjacent to the garden, autumn harvesting of dry grass and leaves, selection of disease-resistant varieties.
Disease control measures
So that the fight against diseases is easier or pathologies do not arise at all, it is tedious to properly process the bushes in early spring and autumn. For example, immediately after the snow melts and before the buds bloom on the branches, the bushes can be treated with boiling water. This simple method will help eliminate the larvae of pests and causative agents of major diseases (Figure 6).
In addition, protecting currants from diseases involves a number of other mandatory measures:
- The soil around the bushes should be dug up every fall. This will help destroy some of the pests that serve as carriers of pathologies.
- When preparing shrubs for winter, it is imperative to collect and burn old leaves and branches on which pathogens may remain.
- All old and damaged branches must be removed.
In addition, it is advisable to carry out regular preventive spraying, which will help prevent the development of major diseases.
Colloidal sulfur
Spraying bushes with colloidal sulfur is considered an effective method of combating fungal diseases and some pests.
To properly process the culture, you need to prepare a working solution of a certain concentration. For this, 100 grams of the substance is dissolved in 10 liters of water and the resulting solution is used for the prevention and treatment of the plant.


Figure 6. You can fight diseases both by chemical and folk remedies
It is important to remember that colloidal sulfur is a dangerous chemical, therefore, both when preparing a solution and when using it, you must adhere to the rules of personal protection.
Bordeaux liquid
Bordeaux liquid is considered another effective and relatively safe method of dealing with various pathologies. It can be used to treat currants in early spring against fungal diseases, and in the future, it is advisable to spray it periodically for prevention.
It is worth noting that in order to cure an already infected bush, a more concentrated solution of the drug is required than for prophylaxis. Therefore, in order to fight the pathologies of currants correctly, it is important to carefully read the instructions for preparing the solution.
Effective methods of combating currant diseases are discussed in the video.
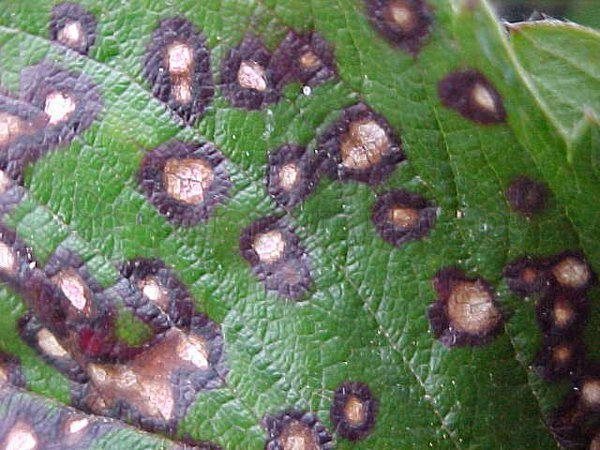
Septoria
Black currant processing in spring
This is the most common disease of black currant, appears in conditions of high humidity on heavily thickened bushes.
Symptoms
The leaves are densely covered with gray dots, framed by a dark brown thick border. When the spores mature, convex round growths appear. This fungus also affects the berries, so the disease destroys the crop, the bush dries out.
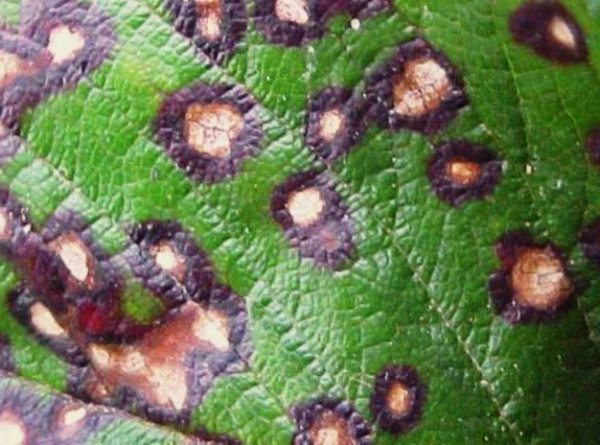


Currant leaf septoria
Treatment
- Copper sulfate treatment at intervals of 1 time per 2 weeks. The procedure must be carried out three times, the first - after the foliage has completely bloomed;
- Destruction of infected plant parts;
- Thinning branches to avoid excessive thickening of the bush;
- A preventive measure of control is digging up the earth around the bushes, harvesting grass and leaves.
Prevention of diseases and pests
Insect control, disease treatment and follow-up care for beginners is not as easy as it might seem. Therefore, it is much easier to prevent problems:
- Compliance with the rules of care (watering, loosening, mulching) is the basis of prevention. It is improper irrigation and the lack of loosening that become the main reason for the defeat of fungal infections.
- All old and diseased branches must be removed.
- When the snow melts, experienced gardeners "burn" the currants. To do this, the bush itself and the soil around it are watered with boiling water.
- Leaves and other vegetation around the bush are harvested and burned in the fall. As the culture grows, the land around is weeded.
- In spring, currants, gooseberries and other fruit and berry bushes are treated with copper sulfate.
- It is advisable to choose varieties that are resistant to viral and fungal diseases.
- When planting currants, it is important not to thicken the planting.
- The soil, planting material and garden tools must be disinfected.
Terry
Description
Terry is a viral disease that completely destroys the bush. To date, it is not known how to treat currants for viral diseases. The causative agent is a kidney mite. On the infected bush, ugly inflorescences appear that do not yield a crop. Then the branches begin to ache, this is expressed in the fact that they become thin. The infection gradually captures the entire plant, begins to rot it, as a result, the currant dies. After which it remains to dig up and destroy. Preventive measures can be taken to avoid currant diseases. First of all, this is the protection of the bush from the tick. The treatment of bushes should be carried out only with sterile tools, since the virus hibernates in the tissues of a diseased bush, and is not spread by wind or rain.
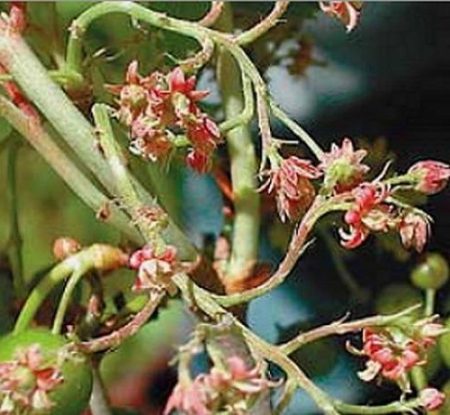


Terry on berries
How to process currants - prevention
Currant processing in spring
Work with currant bushes begins in early spring, until the buds woke up and sap flow began. First of all, you should carry out "hot" processing of currants. It is carried out in order to prevent pests and diseases and to ensure full development and subsequent abundant fruiting. Heat the water to 80 ºC and pour it over the currant bushes from a watering can. Ten liters of hot water should be enough for three bushes.


After a hot shower, it is very advisable to prune the currants - remove damaged and weakened shoots, slightly trim the tips of the branches that have frozen over the winter, thin out the bush, if for some reason you did not do this in the fall. When pruning, remove those branches or buds that are affected by the bud mite. All scraps must be burned, and cuts with a diameter exceeding 8 mm must be treated with garden varnish. After that, you need to clean the area with currants from last year's foliage, in which the larvae of insect pests and pathogens must have wintered.
Treatment of currants from diseases
In early spring, before the buds bloom, spray the currant bushes and the soil under them with a 2% solution of nitrophene or karbofos - this will protect the plants from almost all diseases. After a while, for fidelity, process the currants with Bordeaux liquid, and when the real spring begins and the currants grow, from time to time you can spray the currants with a foundation for preventive purposes.


Pest control of currants
How to spray currants so that pests do not affect it? Yes, all the same karbofos or nitrofen, which perfectly cope with their preventive function and protect currants not only from diseases, but also from pests. The fight against kidney mites can be carried out at a temperature of at least 20 ºC, otherwise, after spraying, the bushes must be wrapped in plastic. Do not be lazy, otherwise you will not escape problems with a kidney mite. So that the moth does not harm the currant bushes, with the beginning of the growing season, lay roofing material around the bushes, sprinkling its edges with earth. When the flowering is over and the fruits appear, the roofing material can be removed.


Processing currants in autumn
In the fall, you will need to do an annual pruning of currants. All branches older than five years are deleted, since they are no longer very productive, but take up too much space. In addition, you need to cut off to a healthy part or completely all the shoots in which the glass pot has settled - they are easy to identify, they are withered and dry. If possible, remove all bud mite infested shoots covered with powdery mildew, all weak and too thin zero shoots to the base of the bush.
- White American Butterfly: Wrestling
If you have an old bush, rejuvenate it, just do not overdo it with pruning: if you need to remove too many old branches, do it in three stages, that is, within three years - prune a third of the branches every year. And do not forget to process the cuts of thick branches with garden pitch, and burn the cuttings.


After pruning, it is time to carry out an autumn preventive spraying of currants with a 2% solution of karbofos or a 1% solution of colloidal sulfur. Spray generously on the soil under the bushes. Spraying should be done in warm, windless dry weather.
Striped mosaic
If the veins of the leaf turn yellow, and their number is growing all the time, then this is a sign of infection with a viral disease. Fighting with striped mosaics is useless, just like with terry. The virus is spread by insects and remains in the tissues of the bush. Therefore, the only measure is to burn the bush. The soil at the site of the affected plant can be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate.


Leaf appearance with striped mosaic disease
Nectric drying of the shoot, marginal necrosis, gray rot are also common diseases of black currant, the fight against them consists in treating the bushes with fungicides, cleaning the area from grass and leaves and destroying diseased branches.
The reasons for the development of septoria on currant bushes


The cause of the development of currant septoria disease is the Septoria mushroom. This fungal disease can affect even indoor plants. The main reason for the development of the disease is the active spread of the fungus, which is capable of infecting many cultures. A favorable environment for the development of the disease are: temperature from 15 * C to 20 * C, rainy weather. The active spread of fungal spores is favored by moist soil, warm and little snowy winters
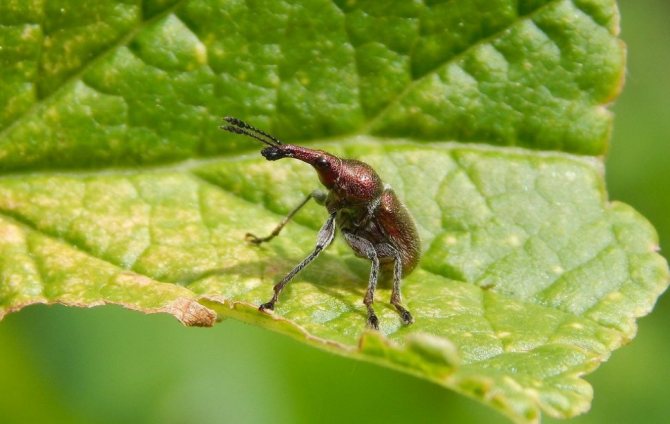
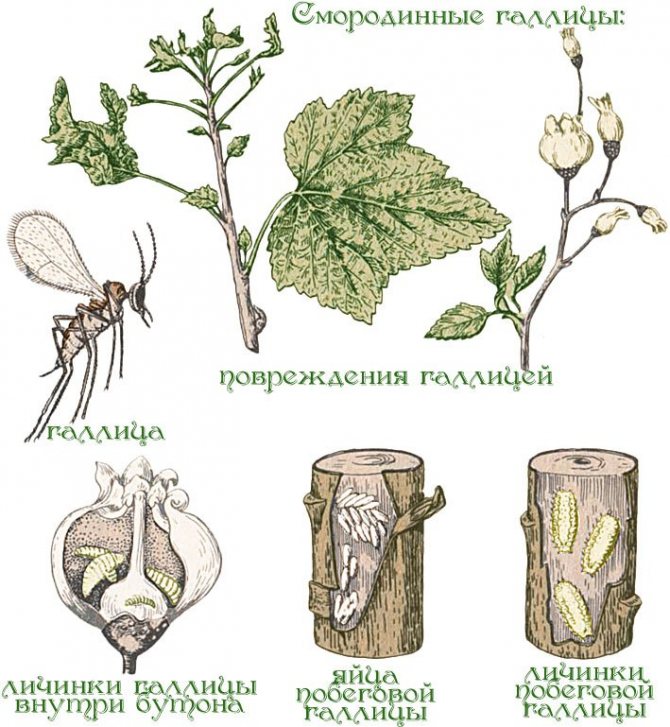
Kidney mite
Characteristic
A very small insect 0.3 mm long that settles in the buds of a plant and lays eggs there. Each kidney can hide a thousandth colony. The kidney grows to an unnatural size. Since the bud mite feeds on the sap of the plant, the buds quickly dry out and fall off. Therefore, the yield of the bush is greatly reduced. Also, the tick is the causative agent of viral terry, which completely degenerates the bush. In view of the small size of this insect, it is almost impossible to take a photo, but by the appearance of the kidney, you can accurately determine the presence of this pest.


Kidney with kidney mite
Control measures
- Removal of infected buds or whole branches;
- Pouring boiling water over before the start of sap flow. Ticks die instantly. The procedure is best done several times;
- Pouring garlic solution. The mite does not tolerate the bright garlic odor and remains in a place where it is easy to find and remove;
- Decis treatment before flowering.
Water currants regularly, loosen and remove weeds
| Watering Stages:
|
| Pruning Stages:
|
| Weeding Stages:
|
Spider mite
Description
On the back of the plant, spider mites can appear - sucking insects up to 0.6 mm in length. They live in colonies, suck out juice from currants, from which dry yellow spots appear on the leaves.A sure sign of infection is the massive appearance of a thin cobweb around leaves and thin stems.


Spider mite photo
Control measures
Before the growing season, the bushes should be treated with Trichlormetaphos or other acaricides, it is important that there is no sulfur in the composition. In late July - early August, you can repeat the treatment, since this is the period of active reproduction of the pest. A good result is given by a folk remedy consisting of mustard powder (200 g) and water (10 l), which you need to spray the bush.
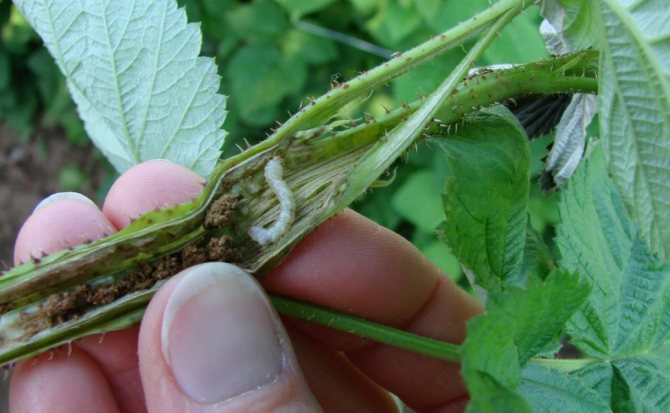
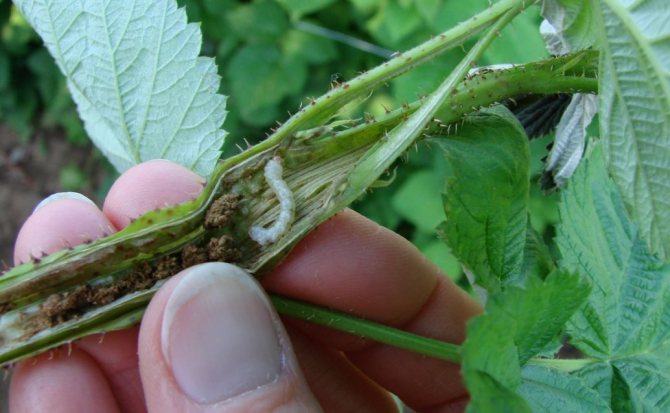
Berry sawfly
It is a flying insect 4 mm long, yellow-orange in color with transparent wings. Lays the larvae in the currant ovary. Subsequently, the berries acquire an angular shape, ripen ahead of time. To destroy this pest, currants need to provide proper care:
- Digging up the earth around the bush with careful removal of weeds and dry leaves;
- Hilling and mulching with peat in a thick layer up to 10 cm;
- Spraying with insecticides before flowering. If the insect reappears after flowering, then the procedure must be repeated, but the crop cannot be eaten;
- Destruction of the contaminated crop.


Adult sawfly
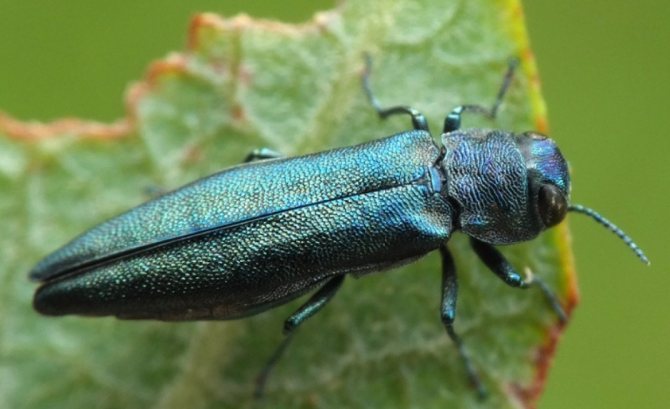
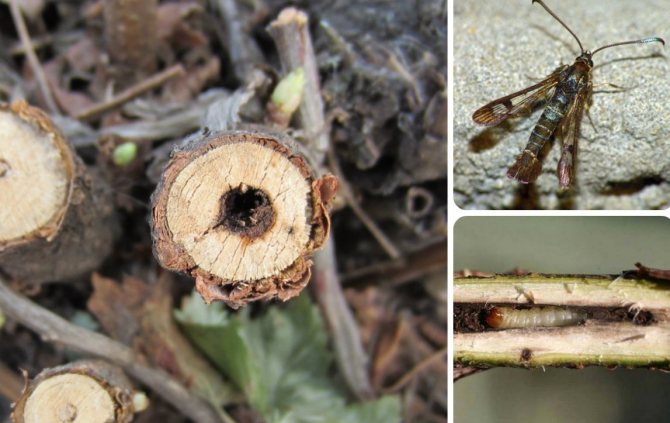
There are several more types of pests that infect currant bushes, the most common of which are firewood, glassworm, gall midge, moth. Outwardly, they are all small butterflies, no more than 2 cm long. They lay eggs in the bark or currant flowers, then the larvae eat the plant, which leads to the death of the bush. To protect plants from these pests, the bushes need to be constantly inspected; if found, the branches are removed and burned.
Resistant black currant varieties
Every summer resident who has had a chance to treat a plant knows how much time and effort needs to be invested in healing, sometimes efforts are in vain, and the currant dies. What to do with sick currants? Breeders recommend that you approach the issue thoroughly and start by choosing the right variety. There are many varieties with high immunity against diseases and pests:
- Russia: Selechenskaya, Klussonovskaya, In memory of Vavilov, Zoya, Kipiana, In memory of Pavlova (Binar);
- Belarus: Katyusha, Kupalinka, Minsk;
- Europe: Titania.
Black currant is not a picky plant. In conditions of high humidity, black currant diseases occur, and their treatment is reduced to the timely detection of the problem and the adoption of immediate measures.
Non-communicable diseases
There is an ailment that develops in the absence of fungal or bacterial pathogens. Marginal necrosis is nothing more than the dying off of the marginal line of the leaf. An excess of chlorine in the soil layers provokes the development of the disease. At the end of August, a grayish strip forms along the edge of the foliage, which subsequently dries up. Sometimes the symptomatic manifestations of the disease can be confused with potassium deficiency.
A significant difference is a clearly defined line between healthy tissue and areas affected by necrosis. The varieties of white and red currants are susceptible to ailment. When the first signs of an illness appear, an urgent introduction of an ammonium nitrate solution is required. Visual signs of this currant disease, photo:
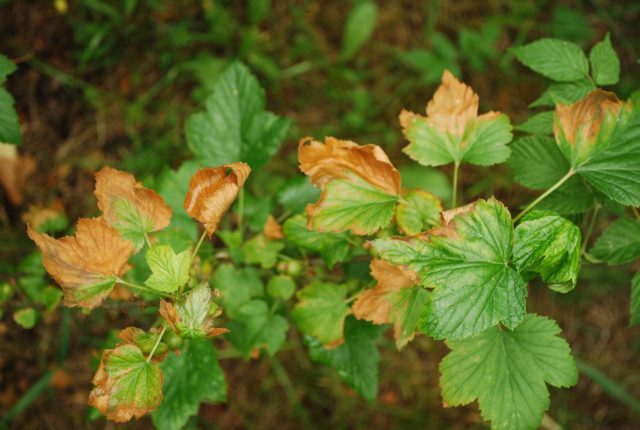


Marginal necrosis affects both white and black currants.