This article could be called: "Tested on my own experience" or "How I destroyed mold fungus." Perhaps most summer residents once faced with fungus or mold, which are formed on various wooden surfaces, and not only wooden ones. The main reason for the emergence and spread of the fungus is favorable conditions for this. Thanks to the development of chemistry, today on the market it is quite easy to find a lot of funds and preparations that will help in the fight against the spreading fungus. For faster and more reliable removal of fungus or mold, it is necessary to find out exactly which group they belong to. Once removed, steps will need to be taken to guard against future fungal attacks.
Mold in a greenhouse on the basis of how to get rid of
Nov 15 • Uncategorized • 5 Views • No Comments on Mold in the greenhouse on the basis of how to get rid of
Content
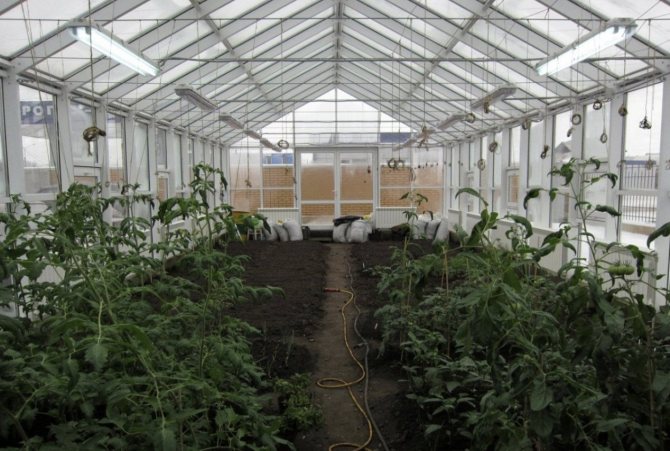
A greenhouse is a closed space in which the land is in special conditions. The greenhouse soil is deprived of the possibility of self-healing, negative fauna and flora accumulate in it more intensively, and bioprocesses pass faster. High temperatures and changes in humidity can provoke the growth of molds, which destroy the wooden frames of greenhouses and greenhouses, infect living plants and negatively affect human health.
Why is it dangerous
When the fungus enters vegetable crops, it clogs the vessels of the plant and starts the process of releasing toxic substances. In the closed space of the greenhouse, they accumulate in the soil, leaves and fruits of vegetable crops, as well as in the air.
- Therefore, the appearance of mold in a greenhouse is always accompanied by such negative consequences:
- damage to the wooden frame of the greenhouse - fungal spores multiplying in the wood provoke rotting of the material;
- contamination of all wooden surfaces inside the structure (tables, boxes, shelves) - they become unsuitable for further use, since they are covered with a layer of mold;
- plant death and loss of yield - a microscopic fungus destroys plantings and makes the fruits unfit for human consumption;
- the appearance of diseases of the respiratory tract and skin in humans - when inhaling spores or eating vegetables contaminated with mold, asthma, a cough or an allergic reaction may develop, accompanied by reddening of the skin and the appearance of itching.

The nature of molds
When organizing plants in living nature, fungi are isolated into a separate kingdom. There are more than 250 types of fungal organisms, which are combined into orders and groups according to biological characteristics. In the international modern classification, mold fungi occupy the sixth order and are mainly represented by unicellular organisms, and in rare cases - multicellular. Due to the microscopic size of individual groups of fungi, they are called micromycetes.
Basically, mold accumulates and grows in large colonies, the appearance of which is represented by windy mycelium without large fruit bodies. Many molds are facultative or obligate parasites. In other words, they are able to live independently or in the environment of the owner.Spores of such fungi are able to survive in conditions of increased radiation, in permafrost and even in space. Only individual groups die if they are exposed to temperatures above 100 degrees for at least three hours.
Sphere of distribution
Mold fungi can live and spread on soil and in water. Large colonies spread throughout in humid, warm places with a suitable nutrient medium. The soil in the greenhouse is just such an environment. The health of plants directly depends on the quality of the substrate in which they were grown. If the quality of the greenhouse soil has changed, then this will not have a very good effect on the growth and development of seedlings. The very first sign that white mold has appeared in the greenhouse will be a whitish coating on the soil surface, which is a harmful fungus.
The reasons why white mold can appear in the greenhouse are:
- Violation of agrotechnical rules when growing seedlings and crops in protected soil conditions. This can lead to the predominant development of pathogenic microflora.
- Contamination of the room. Mostly mold spreads in dirty conditions. It is because of this that the greenhouse must be systematically treated with antifungal drugs (dyed, whitened, washed) and cleaned.
Types of mold, their nature
Mold in the greenhouse manifests itself in the form of a characteristic plaque on the surface of the soil, plants and the structure itself. This plaque is formed by colonies of unicellular and multicellular microscopic fungi, which are grouped into a separate kingdom according to the international biological classification. They are parasites that can exist both independently and inside the host, and also have an increased ability to survive even in the most extreme environmental conditions.
Did you know? In France, special types of blue cheese are made that can be eaten.
The main types of mold that can appear in the greenhouse:
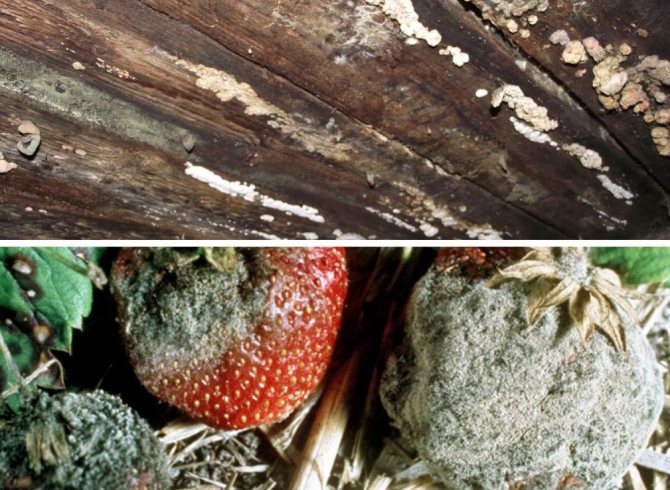
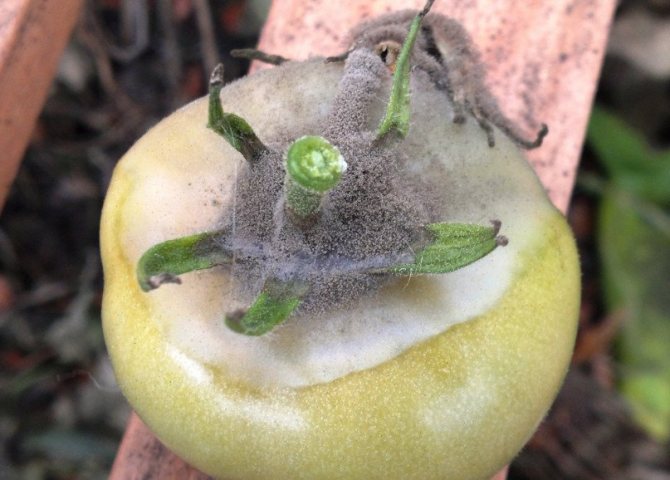
- White mold. Visually, it resembles small lumps of cotton wool, covering with a thin layer some areas of plants and the soil in the beds. The cause of the appearance of the disease is a sharp change in the conditions of the microclimate in the structure, associated with insufficient air circulation or non-compliance with watering rules. As the infection spreads, the spores of the fungus form small, dense patches that are dark in color. The affected plant dries up, the fruits cannot ripen and sometimes begin to rot, which leads to loss of yield.
- Black mold. Spores of this type of fungus form a dark coating with a slight purple tint on the stem. The ideal conditions for the spread of infection are high air temperature and humidity. At the initial stage, the disease attacks the lower leaves of plants, covering them with small red spots that resemble burns. In the future, the lesions spread to the entire leaf, the stem turns black and the plant dies.
- Gray mold. This infection is characterized by the appearance of a grayish coating and moist dark spots on the surface of the stem, leaves and fruits. The disease often occurs in greenhouses with high soil density and improper ventilation systems. Fungal spores first attack the root of the vegetable and then spread throughout the plant. As a result, the culture withers, the entire ground part of the bush is covered with a light or pink coating, and the fruits are deformed and become unusable.






Conditions for development
Microscopic spores are easily carried by air currents and can be dormant for several decades. When conditions are right, they begin to grow and multiply rapidly. In this case, live plants with soft tissues are captured (cucumbers, tomatoes, vegetable seedlings and others like them).
Conditions most suitable for the spread of mold:
- Insufficient illumination (a small amount of ultraviolet rays that fall into thickened stands, as well as cloudy weather without additional lighting);
- Increased soil moisture and stagnant water after irrigation at the root system. This may be due to water leakage in damaged parts of the hose or due to improper watering;
- Poor ventilation or lack of ventilation;
- The temperature regime in the greenhouse is 20-22 degrees above zero;
- Indoors the humidity is 95%.
Where does the greenery come from inside the polycarbonate honeycomb
Cellular polycarbonate is a material consisting of several layers in which there are long longitudinal channels, or stiffening ribs, called honeycombs. These honeycombs contain air, due to which the weight of the material is reduced, and the thermal conductivity and insulation properties are improved. However, sometimes, if the greenhouse is incorrectly installed, condensation accumulates in the honeycomb and a green plaque forms - mossy mold. The reasons for its appearance are the same as for black mold - poor ventilation and high humidity. In addition to contaminating soil and plants, plaque reduces the light transmission of polycarbonate (the walls become opaque due to greenery), which again contributes to the appearance of various types of mold.
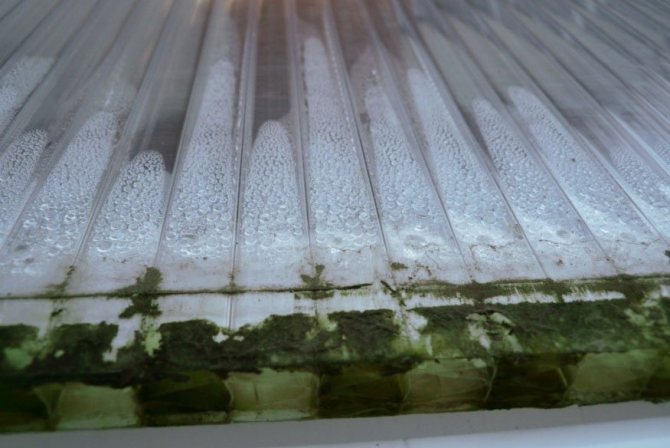


Green plaque on polycarbonate appears inside the honeycomb
Another option for the further occurrence of such a green plaque on the walls may be the absence of a foundation under the greenhouse.
Strashnov
Preventive actions
The appearance of mold is associated with the processes of decomposition of vegetation and biocorrosion. It is because of this that mold grows most strongly in the fall. But with a one-time use of mold preparations, the desired result will not be. To create optimal conditions for the growth and development of plants on protected soil, a number of measures must be taken.
It is imperative to disinfect the greenhouse after harvesting in the autumn before the next season of growing vegetable crops in a seedless way. To get rid of mold on the soil in a greenhouse, you can do several things:
- Treat the room with a sulfuric checker FAS;
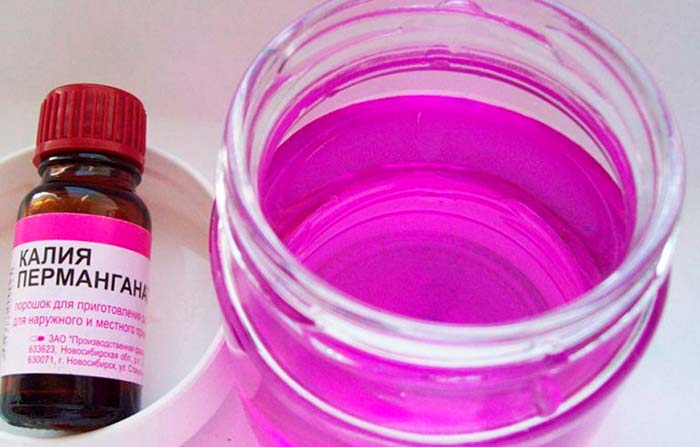
- In the spring, it is necessary to repeat the procedure for treating the premises with a solution of potassium permanganate and adhesives (soap and the like), if mold was detected in the greenhouse in the previous year;
- Constantly monitor the indicators of soil and air moisture during the cultivation of crops and seedlings;
- The irrigation system must be kept in good working order. Waterlogging should not be allowed. One of the indicators of waterlogging is the appearance of a black leg in seedlings. In this case, the soil must be sprinkled with dry sand under the plants. It is necessary to check the greenhouse well, but avoid drafts;
- Mold doesn't like alkaline environments. It is because of this that greenhouse soil with an interval of 3-4 weeks should be powdered 3 times per season under all plants with a mixture of charcoal and ash, ground into powder (the proportion of the mixture is 1: 1).
If mold appears on the soil (especially on compacted one), you can process it with peat, represented by dry briquettes of high-moor peat. Peat contains a synthetic polymer that serves as a soil loosening agent. When it is soaked, it increases several times in volume. In order to neutralize the acidity in the soil, it is necessary to carry out the treatment with a peat copper solution. Mineral water-soluble fertilizers are also added there.
In order to prevent damage and save plants and seedlings from fungal diseases (root and root rot, fusarium wilting, black leg and others), 8-10 days after the plants sprout, they need to be treated with biofungicides using drugs according to the recommendations ( Fundazol, Planriz-Zh, Gamair-SP, Alirin-B,Fitosporin-M).
The same biofungicides can be used to treat the soil under the plants. It is possible to re-treat the soil with biological products (plant and soil) after 15–20 days, unless otherwise specified in the recommendations.
If the seedlings are grown at home, then it is best to use specialized soils. This is especially true for beginners in the gardening business. Such soil is specially treated against pests and diseases and fertilized according to all agrotechnical requirements.
Growing seedless crops and seedlings in home and greenhouse conditions requires unquestioning compliance with all agrotechnical measures. Otherwise, all the measures that were applied will not have the desired result.
It should be remembered that mold is not harmless to human health. If a person is in a room that is infected with mold, he can get bronchial asthma, otitis media, allergic rhinitis, bronchitis. When mold spores settle on the lungs, they can cause lung diseases up to oncology. It is strictly forbidden to eat foods, including fruits and vegetables, that are affected by mold.
The problem of mold in the greenhouse is not very common. Usually such rooms are well ventilated, and transparent walls and ceilings let in enough sunlight to prevent fungus from developing.
If we talk about what to do when such a problem appears, then there are several options (from budget to expensive).
house mushroom
signs of defeat: a snow-white fluff that suddenly appeared on wooden floors and walls. Gradually, it changes color to yellowish gray or lilac pink. The fluff settles and the fungus forms a thick gray film with a silvery sheen on the surface of the tree. Over time, the stain darkens, turns brown and begins to fall apart. The fungus is absolutely ruthless to any wood species, but soft wood suffers most from it. The mushroom house loves dampness, and therefore most often settles in basements, cellars or rooms where poorly dried building materials or firewood are stacked. Run:
raw building materials, especially those already in use, must be carefully inspected for the presence of a mushroom house. If suddenly suspicious spots appear on the boards, then it is best to destroy these boards, and treat the surviving remains with a special preventive solution. As such a solution, you can use a mixture of salicylic acid and denatured alcohol in a ratio of 1 to 10. When processing, do not forget that this mixture is flammable. Also for processing, you can use a mixture of copper sulfate with wood vinegar. In this case, the proportion will be slightly different: 1 to 20. With such solutions, not only is it possible, but even new boards must be processed, which are intended for wall decoration or flooring. Sodium fluoride is also perfect for these purposes. If the irreparable nevertheless happened, then you can fight the house mushroom with the help of 950 grams of sodium chloride diluted in boiling water with 50 grams of boric acid. Then it is necessary to lubricate the sore spots five or six times, the more - the better. Those places where the tree is constantly in contact with the ground or water pipes can be treated from time to time with a 10% solution of copper sulfate or 15% steel sulfate. You can hold the places affected by the fungus on the boards over a fire or some other source of heat, or it is best to replace the damaged wood with a new one, not forgetting to pre-treat it with a preventive antiseptic composition.
Why does mold appear in the greenhouse?
There is no universal answer to the question of why mold occurs in a greenhouse.
It develops due to several reasons at once:
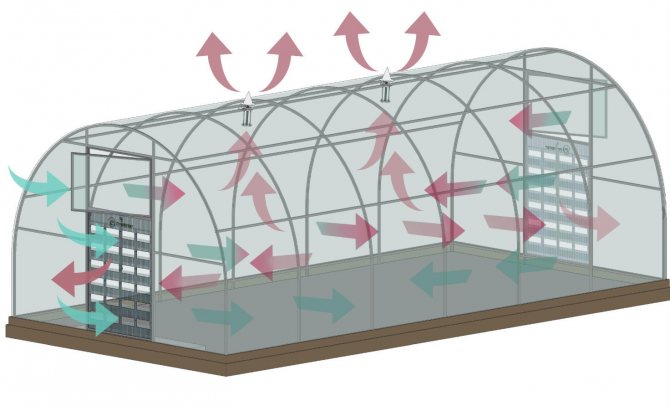
There is no normal ventilation (insufficient air exchange). Problems with ventilation can affect both the entire room and its individual sections (for example, some corner is not ventilated - and then mold can develop there).
High humidity is maintained. This can occur due to stagnant water on the ground and on plants. Congestion is caused by over-watering or leaking water hoses (if cracked).
There are a large number of wooden surfaces (and if they are not already painted, this will accelerate the development of mold).
Insufficient lighting. This is an unlikely factor, since there are usually no problems with lighting in greenhouses - otherwise the plants simply could not grow normally.
The main reason is precisely the first reason - the absence of a normal ventilation system. If the air stagnates and other negative factors are present (humidity, lack of lighting), mold will appear sooner or later.
Where exactly does the fungus appear?
There are several "favorite" places where fungus appears in the greenhouse:
wooden structures: beams, furniture, racks, boxes;
on the soil and on the plants themselves (especially tomatoes, cucumbers);
areas with stagnant air and / or lack of lighting: usually these are corners on the floor, the space under the racks (if the greenhouse has racks on which boxes with plants stand).
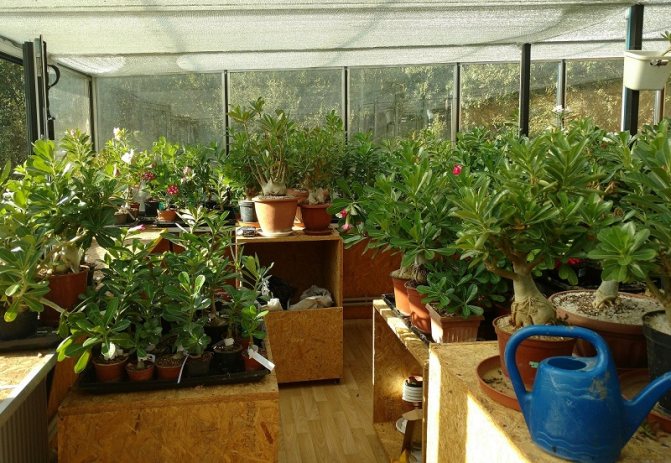


In such a greenhouse, mold can appear under and between boxes, behind boxes and inside them.
If glass and polycarbonate are covered with mold, then it is already with a serious infection, when the fungus has struck the wooden surfaces nearby.
Why is it dangerous?
What exactly is the greenhouse affected by: black, white or gray (sooty) mold - there is no difference. Any mold is dangerous for humans, plants, and the building itself.
Damage to the structure (building) itself, if it is made of wooden materials.
Damage to wooden products inside the greenhouse (racks, boards, boxes).
Harm to plants (decrease in the intensity of growth, decrease in metabolic processes in plant tissues, weakening in front of other diseases).
Harm to people who will work inside the greenhouse. Inhalation of mold spores can aggravate or cause problems such as bronchial asthma, dermatitis, cough, and itchy skin. Allergic reactions can also occur.
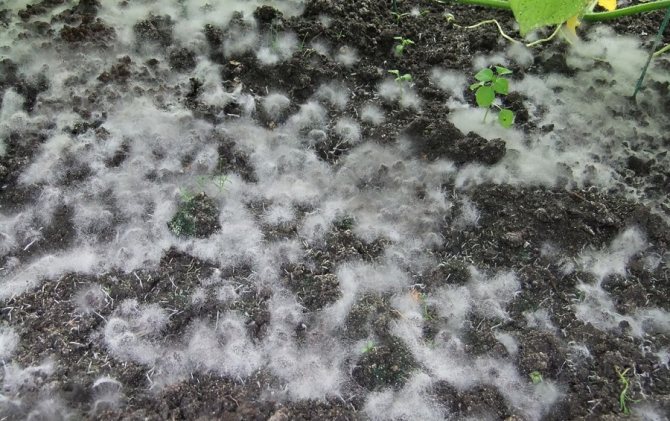


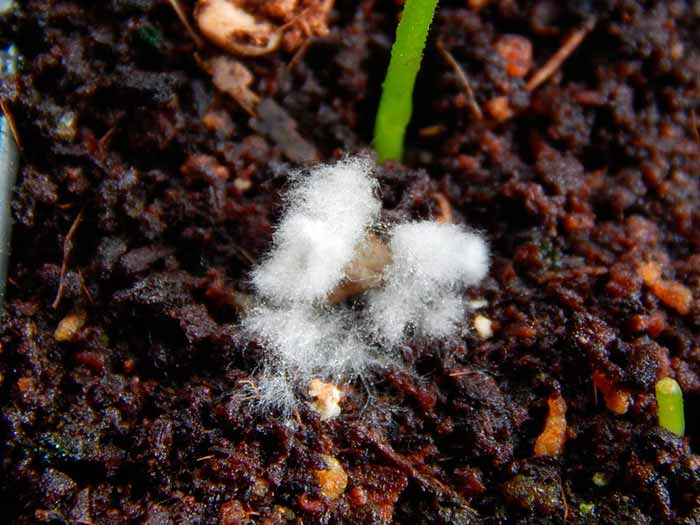
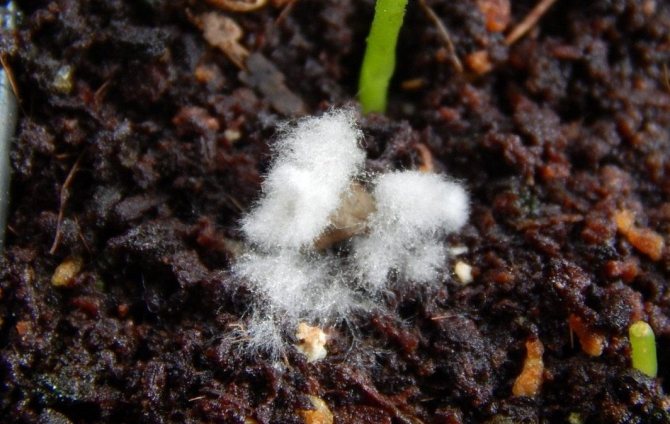
Mold in a greenhouse on the ground often looks like light whitish fluff
At first, mold contamination may not manifest itself in any way (while the concentration of spores in the air is still small).
Green bloom on the ground in a pot. White mold (Mucor)


Molds grow and multiply on the soil surface, food, organic waste.
Some Mucor species are capable of causing human disease. And certain types are used for the production of antibiotics.
White mold on the ground in a pot does not bring any benefit, rather, on the contrary, it can be dangerous. In appearance, it resembles a white fluff that gradually fills the soil surface. To the touch, the structure is soft, easily wrinkled with your fingers.


It negatively affects the well-being of people and plants. For most healthy people, Mucor will not do any tangible harm. But during sporulation, microscopic spores of the fungus, entering the respiratory tract, can cause an allergic reaction.
The home plant is harmed not so much by the mold itself as by the conditions under which it develops. It appeared because the rules for keeping flowers were violated.
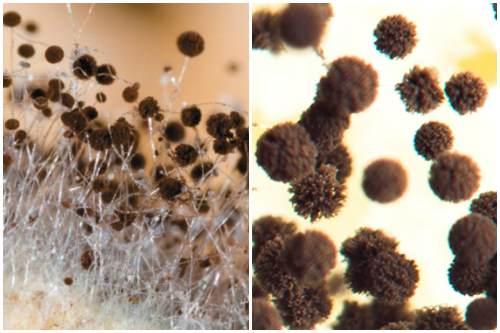

Favorable conditions for spore germination, such as high humidity at low temperatures, heavy soils, negatively affect the development of crops. Therefore, the appearance of Mucor is not the cause of the depressed state of the plant, but the result, signaling the deterioration of conditions.
How to get rid of


In order to eliminate the fungus in flower pots, the following measures must be taken:
- Replace the top soil layer, approximately 2 - 3 cm deep, with fresh soil, lighter texture.
- Reduce the amount of watering.
- Prevent stagnant water.
- Provide drainage.
- Loosening will saturate the soil with oxygen.
- Antifungal drugs are fungicides. For medicinal as well as prophylactic purposes, the earth is periodically watered with Fitosporin solution. It is absolutely safe, as it is a remedy for mold of biological origin.
What to do if mold appears in the greenhouse: ways to fight (+ video)
To get rid of mold in a greenhouse, you need to:
Remove plaque itself.
Understand what caused the mold.
Eliminate the causes of its appearance. If favorable conditions remain for the development of the fungus, it will continue to appear.
What exactly can be used to remove plaque:
Folk remedies. The option is cheap and simple - many of the suitable substances can be found on the farm (you don't have to go to the store). But these are not specialized tools. It is worth using them if the fungus has not grown too much and has not eaten into the tree too much.
Purchased funds. A more effective method of struggle - specialized drugs kill spores more reliably. They are sold in the form of a ready-to-use liquid (that is, you do not need to cook or dilute anything).
Smoke bombs (sulfur or tobacco). They are used both for prophylaxis and for combating mold that has already appeared. Set on fire in the greenhouse. The smoke that forms during combustion kills spores. Compared to purchased liquids, it is a more effective method (smoke will penetrate into each gap), but longer (after using the checker, the greenhouse will have to be aired for 2-3 days).
The optimal control scheme: to remove plaque - use purchased products, and 1-2 times a season - fumigate the room with a saber.
Why mold occurs on the ground and vegetables
A greenhouse is itself a favorable environment for the development of a fungus, since it is warm and humid by default.
The main reasons for the occurrence of mold lie in the creation of the wrong conditions:
- You do not ventilate the greenhouse well, so the air stagnates in it.
- Stagnant air, in turn, is oversaturated with moisture - if you do not monitor the level of humidity, then the fungus will be grateful to you.
- Poorly adjusting the temperature balance. Heat combined with moisture is the ideal formula for the development of disease.
- Do not check the acidity of the soil - the higher it is, the more nutritious it is for the "pest".


However, even if you do everything right, the fungus can start. To prevent contamination of the crop as much as possible, take preventive measures.
Preventing mold in the greenhouse
The main and easiest way of prevention is proper care of plants and a greenhouse. Ventilate the area well, do not create puddles while watering. To maintain sufficient humidity, you can place containers of water around the greenhouse.
Before planting vegetables, prepare the seeds and decontaminate the soil and the greenhouse itself.
Advice on how to prevent the development of mold in the beds:
Remember, timely treatment will help remove mold in your greenhouse and preserve your crop. Watch your vegetables closely and only harvest healthy fruits.
Sequence of work: step by step plan
Action plan:
We find all the places affected by mold. To do this, you will have to turn everything inside the greenhouse: move the racks, boxes, inspect every corner, look under the leaves of plants and behind the plants that grow along the edges close to the walls.
We take out all the items that can be taken out into the street. If the product is severely damaged, it is better to discard it.
We open the vents and doors of the greenhouse.
We put on protective equipment (gloves, a respirator, ideally also glasses so that mold spores do not get into the eyes).
We process the greenhouse with the selected product.Since greenhouses are usually small, mold spores are likely to be found on all surfaces. Therefore, for reliability, it is better to walk everywhere.
We leave the room to ventilate.
If there were large colonies of mold on the walls or ceiling of the greenhouse, the treatment can be repeated after 1-2 days.
If you decide to use a checker, it can be used both instead of liquid products, and in addition to them. In what sequence to do this (first treatment with drugs, then a checker, or vice versa) - it does not matter.
If mold appears on the ground, special sorbent substances must be used to process it. They increase the alkaline level in the soil, which prevents fungus from growing on it.
To prevent mold from reoccurring:
Ensure normal air exchange in the greenhouse - the room must be ventilated at all times. It is also useful for plants that need fresh air and which can be harmed by high humidity. Air vents are often used to ventilate greenhouses.
Periodically (at least once a month) inspect the places where mold may appear - in order to notice it in time.
Do not allow moisture to rise. Do not exceed the watering rates, find and eliminate leaks in hoses and their connections in a timely manner.
Subject to these rules, the fungus will definitely not be able to develop.
One of the most common problems in greenhouse soil is the appearance of white bloom on its surface. White bloom has appeared on greenhouse soil. What are the causes of mold? How can you get rid of it?
Not only the appearance and health of plants cultivated in the greenhouse, but also the yield depends on the quality of the soil substrate. Any change in soil composition, as well as moisture parameters, can negatively affect greenhouse crops. Among the most common problems in greenhouse soil is the appearance of white bloom on its surface.
Effective control methods
If the owners notice that the soil is moldy, then you need to know what to do in such a situation. There are many different ways and methods for the destruction of pathogenic microflora, but various factors will affect their effectiveness.
The first step is to replace the contaminated soil with new greenhouse soil. After that, you need to thoroughly loosen it so that air can easily penetrate into the lower layers of the soil. The frequency of watering is reduced, and a small layer of quartz sand is poured onto the surface of the earth.


The removed fungus and old land must be taken out of the apartment or garden (greenhouse).
The owners must remember that drying out the soil does not guarantee an absolute result of getting rid of the fungus. If mold has appeared, then it is not easy to destroy it. Drying may give a little time, since during this period the microflora colony will stop spreading.
The introduction of carbon fertilizers - charcoal - can give a certain positive effect. If you grind this coal into dust and sprinkle on the plant, it can absorb excess moisture, stopping the growth of mold.
To combat yellow mold, activated charcoal is used in flower pots. To do this, even in the process of planting the plant, pieces of sphagnum moss and several tablets of ground activated or charcoal are added to the ground. They can also be added to the ground, with which you will replace the top layer. When, along with the appearance of mold on the ground, indoor flowers begin to fade, you should use "Fundazol".
How to remove mold from a flower pot or vegetable garden so that it no longer appears on seedlings? The emerging fungus must be treated with special chemical preparations of targeted antiseptic and antibacterial action.
It is possible to effectively get rid of the fungal infection with the help of such drugs: "HOM", "Oksikhom", "Fitosporin-M", "Fundazol". These products are dissolved in water, adhering to the dosage indicated by the manufacturer. The solution is poured over the beds in which the development of mold is observed. After watering with medicinal preparations, the soil must be loosened, allowing it to dry out faster.
When preparing seedlings in greenhouses, care must be taken to ensure that good, clean soil is taken for cultivation. The room should be periodically ventilated. It is advisable to provide sunlight for the seedlings, since this measure prevents the formation of colonies of any kind of fungus. To prevent the soil in the flower from becoming moldy, it is recommended to use a solution of lemon juice or acid for watering once every two weeks instead of plain water. In a glass of water, either a pinch of citric acid or a teaspoon of juice are diluted.


If mold appears in the garden on the bark of trees or shrubs, then you can cover it with a limestone solution. Not only the focus of the spread of the fungus is covered, but also the adjacent area so that it does not undergo disease after treatment.
The main causes of mold
Greenhouse soil is not an abstract dead substrate, but a complex system inhabited by a variety of microorganisms that must be in optimal balance.
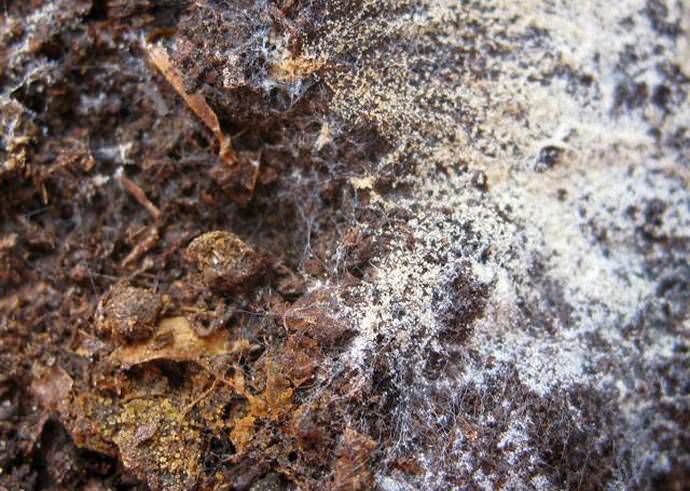


First of all, the appearance of mold on the surface of the soil indicates high humidity.
Illiterate care and gross non-observance of the rules of cultivation upsets the natural balance, and harmful microflora takes the place of beneficial microorganisms. First of all, the appearance of mold on the surface of the soil indicates the following errors in care:
- Too high temperature indicators in the greenhouse, combined with rare ventilation;
- high humidity of air and greenhouse soil;
- insufficient amount of ultraviolet radiation;
- weakness or lack of ventilation in the greenhouse;
- violation of the seal in the irrigation system: water leaking from the hose is an excellent medium for fungal infection in indoor conditions.


Water leaking from a hose is an excellent medium for fungal infections in indoor conditions
The soil in the pot turned green. Why is the soil in pots covered with a white coating?
I think many people understand that most of these problems in the same home floriculture usually reflect our mistakes in caring for plants. A similar "white shroud" is an ordinary salt crust. It can be white, and sometimes white and yellowish. In such a crust arises in pots simply - when the physical evaporation of water from the soil significantly prevails over the evaporation of the same water of the plant itself. Again, there are several reasons for this, as always:
Perhaps the texture of the mixture in the flower pot is too heavy. That is why there is a high (sometimes even excessive) its capillarity and because of such capillarity, water is more intensively pulled up to the soil surface.
- Again, errors are not excluded when watering the plant. Perhaps you water immediately with water that you just poured directly from your tap. You do not need to do this, let it at least settle down a little.
- Drainage at the bottom of the pot can be difficult. If this is the case, then again evaporation from the very surface of the soil in the pot will be the main way of spending moisture.
- Perhaps you have simply over-fertilized the mixture or you have already purchased such a mixture. Indeed, many manufacturers of such soil mixtures are guilty of this, especially if they make this mixture for vegetables.
- We "went too far" with top dressing.
- And a simple reason that immediately occurs to many is the banal dryness of the air itself. It is because of the dryness that evaporation increases many times over and the salts are thus “drawn out” to the surface.
In addition to all these points, white plaque can easily appear due to fungal microflora. This microflora is again created by our diligence, which we excessively show when watering. Therefore, to get rid of such plaque, water your flowers correctly. That is, when the top layer of earth in the pot is already dry.
What to do and how to get rid of it?
In order for such a white (and any other) plaque to be less, you just need to cover the soil from above with expanded clay. Of course, such a raid may appear on expanded clay after some time. Then they just remove it, wash it well and put it back in place.
- Another option is to sprinkle the soil in the pot with river sand. After that, the top layer, together with the sand, should be loosened. The very addition of sand and the subsequent loosening of the soil is very beneficial for the roots of your plant. Also, you can remove the top layer itself and simply add good leafy earth or no less good humus in its place.
- The easiest way is to remove all this "whiteness" along with the earth, and then add new ones there.
- If the water in your home is hard (and it is for the most part), then filters should be used. You can also water for irrigation and soften. To do this, simply put a rag bag in the jar, where you need to put a little peat.
Mold control methods
If microscopic molds appear on the surface of the soil, anti-mold measures should be taken as soon as possible. Subsequently, regular preventive soil cultivation is required. The following mold control methods are recommended:
- treatment of greenhouse soil with carbon-mineral mixtures twice with an interval of a month: an increase in the alkaline parameters of the soil prevents the development of mold;
- dusting the greenhouse soil with a powdery mixture of equal parts of ash and crushed charcoal;
- treatment with a copper solution of peat, which, after soaking, is poured under all the plants in the greenhouse;
- treatment with fungicides "Fitosporin-M" or "Fundazol".
It should be remembered: even the most effective means are powerless in the fight against mold without adherence to agricultural technology and preventive measures.


It is recommended to dust the greenhouse soil with a powdery mixture of equal parts of ash and crushed charcoal.
Preventing mold
The following measures will minimize the risk of mold in the greenhouse soil:
- compliance with the ventilation regime of greenhouses and greenhouses or the use of high-quality ventilation;
- control of indicators of humidity of air and soil;
- compliance with the irrigation regime and prevention of stagnation of moisture under the plants;
- maintenance of irrigation equipment in good condition;
- providing access to the greenhouse with active ultraviolet radiation in the form of sunlight;
- competent and timely disinfection of greenhouses in the fall with the help of a sulfur checker "FAS";
- spring pre-planting treatment of the walls and frame of the greenhouse with soap and manganese solution.
What to do when the ground in the greenhouse turns green
Initially, in order to remove green plaque, it is necessary not only to process the surface of the earth, but also to carry out the so-called cleaning. If the reason for the appearance of green plaque is groundwater and round-the-clock watering, then you need to stop it until the soil dries out.
It is imperative to establish ventilation.
If the soil in the greenhouse began to be covered with moss, then you need to remove it by means of sunlight. If algae have formed, then it is necessary, on the contrary, to block any access to light, which is done by sprinkling with sawdust or sand. Removing the top layer of soil is considered a more effective way to combat greenery on the ground.
Airing in a greenhouse and a greenhouse is the most important stage in growing crops, which will exclude not only the covering of the earth with a green bloom in the form of moss, but also the formation of pathogenic bacteria.


If the ground is too acidic, then you need:
- Spread with a classic deoxidizer such as ash, dolomite flour or lime;
- Sow green manure, the species does not matter at all;
- A month after the green manure sprouts, you can safely plant seedlings of crops such as tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants or peppers;
- After the seedlings begin to grow stronger, cut the green manure, which can be used in the future for mulching.
Horticultural experts strongly discourage the use of copper sulfate to combat moss or algae, as this radical method will remove not only pests, but also some crops, including those soil inhabitants that benefit the plants. As soon as the earth is saturated with fine vitriol, you can safely remove the soil and throw it away. This is a tough method that allows you to overcome greens in greenhouse soil, but it is better to push these options to the farthest box, otherwise you can lose your crop for several years in advance.