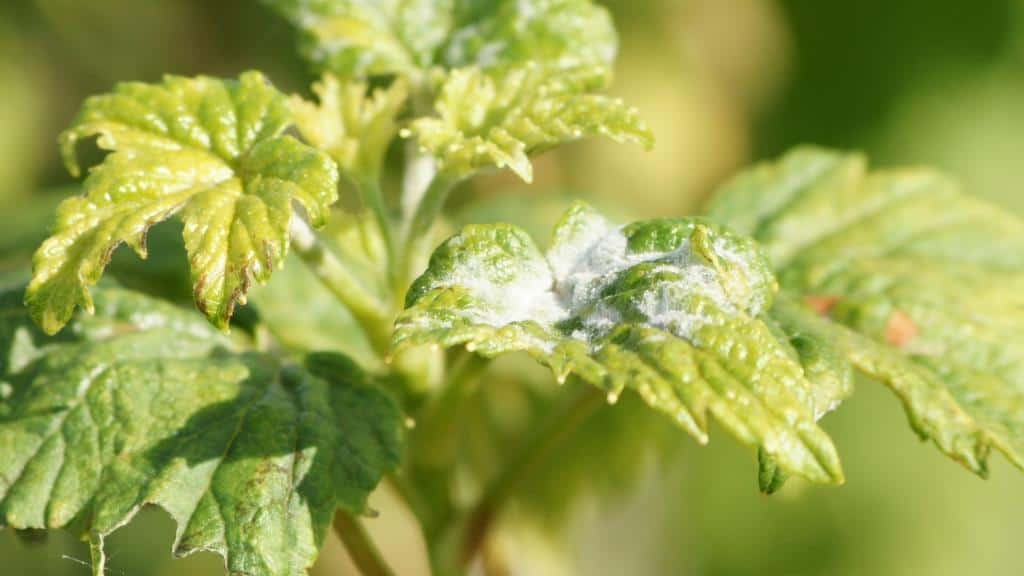
In almost every household plot, black currant grows, which gives tasty and healthy berries. Like other horticultural crops, this shrub is attacked by all kinds of pests. Kidney mite is one of the most dangerous parasites that infect such plantations, along with powdery mildews, aphids and scabies. To save the crop, you need to know how to quickly and effectively destroy these arachnids.
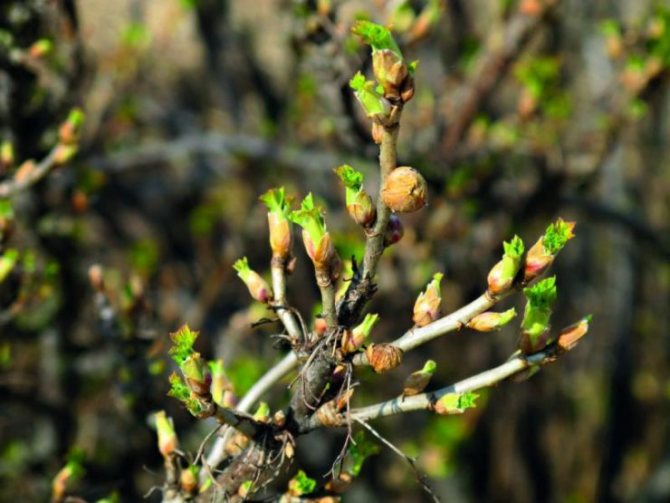

Photo and description of currant kidney mite
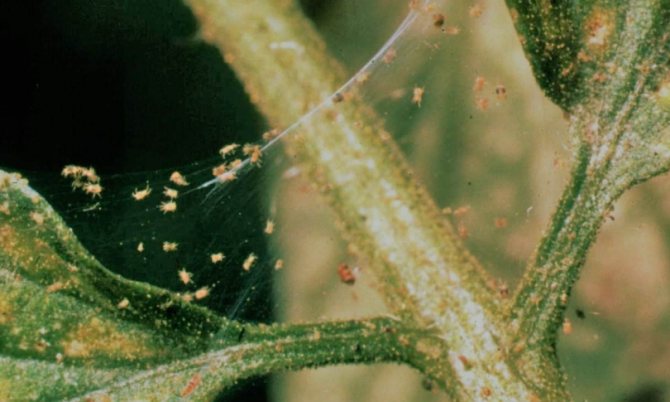
The biology of the currant kidney mite has been little studied, which is due to the difficulty of observing such tiny creatures. However, scientists managed to establish some features of the appearance of this pest:
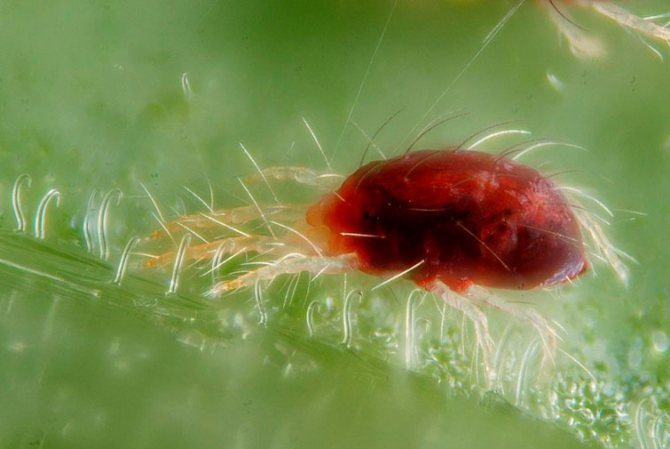
- Worm-shaped elongated body. Its color is not colored, but plain light. These arthropods are very small, so it is impossible to see them with the naked eye. Females grow up to 0.21 mm in length, males - 0.15 mm.
- Two pairs of legs, consisting of several segments.
- The abdomen consists of several dozen rings. Their number depends on the sex of the individual. Females have 70 rings, on each of the rims of which there are spines, in males - from 28 to 62.
- The oral apparatus is a piercing-sucking type.
- The chest is shortened.
- Dorsal setae absent on scutellum. What this arthropod looks like can be seen in the photo.


Treatment of the disease during the ripening of berries
After the ovary of berries on currants, the treatment of the plant with chemical preparations is unacceptable. Therefore, it is better to resort to gentle measures to combat the disease. For example, spraying with water followed by covering the bushes with a film, arranging containers with pungent-smelling liquids near the growing crop.
It is required to regularly inspect currant bushes and remove damaged foliage. In an extreme case, when there is a threat of losing a significant part of the crop or the death of plants, it is allowed to spray the garden culture with decoctions and infusions of herbs, biological products.
It is better to start the fight against a spider mite from the moment it is found on the foliage, without waiting for the development of the colony. Because in this case, getting rid of the parasite will be fraught with difficulties. Preventive measures should not be neglected, restraining the reproduction of the pest.
Parasite lifestyle
Knowledge about the lifestyle of the kidney mite, how they reproduce, how much and in what conditions these parasites live, will help to quickly and effectively get rid of them. This information will also allow taking effective measures aimed at preventing the appearance of these dangerous representatives of arachnids in the personal plot.
Reproduction, life cycle, lifespan
Females hibernate inside the buds. In early spring, when the buds of black currants begin to swell and a green cone appears, and the air warms up steadily to 5 ° C, females begin to lay. Duration of reproduction in last year's buds is 75 days. During this period, several generations of ticks are born.
In young buds, parasites move when the temperature rises to 12 ° C. This process takes 1–2 months, but most of the arthropods migrate within the first 14–21 days. With a cold snap, migratory individuals hide under the scales of the buds and in cracks in the bark.Young adults who did not have time to hide perish. Pests feed on the surface of plants until the end of June - mid-July.


Ticks develop along the path of incomplete transformation, i.e., the larval phase is immediately followed by the imaginal one. Fertilization in them, like in all representatives of this family, is spermatophore. Males leave sperm capsules on the surface of the leaves. Females capture them by crushing them with a genital valve and sending the contents of the spermatophore into the spermatheca.
Eggs are laid irregularly. One female, whose lifespan is 20–45 days, is capable of laying from 5 to 10 dozen eggs in 3–6 weeks. The first nymphs hatch in late spring - early summer. During the season, 5 generations of parasites develop: 2 spring (appear in spring) and 3 summer-autumn (appear in summer and autumn).
Tick characteristics at different stages of metamorphosis:
| Ontogenesis phase | Dimensions, mm | Cycle duration, days | |
| Egg | 0.05x0.04 | 3–7 | |
| Nymph | 0,1–0,13 | 10–14 | |
| Imago | Male | 0,15 | 20–45 |
| Female | 0,21 | ||
Optimal living conditions
They are extremely tenacious creatures. For a comfortable existence, the currant mite requires relative warmth and food supply. Parasites thrive at temperatures up to minus 5 ° C.
With the onset of the cold season, females hibernate, hiding in the buds of red, white or black currants. As for the eggs, they tolerate warm winters well.
Why is a spider mite on currants dangerous?
The spider mite is dangerous at all stages of its development. The pest pierces the leaf plate and feeds on plant sap. In this case, chlorophyll grains are lost. As a result, the leaves lose their color, and their cells die off. Gradually, the lesion spreads over the entire surface.
Under the influence of insects, currants lose their decorative appearance. Its leaves dry out and fall off. The bush does not receive the required development, and its growth slows down. In case of serious damage, the plant may die from a lack of moisture.
Spider mites cause serious damage to yields. If the pest appeared before the formation of ovaries, then fruiting may decrease by 30 - 70%. If it is found during the ripening of berries, then there are chances to save the crop.
Attention! Spider mites reproduce and develop most rapidly at a humidity of 35 - 55% and a temperature of +30 ° C.
The distribution area of the pest includes Europe, Asia, America and Australia. It is also found in the High North. If measures are not taken in time, the tick will move to other plants. In the risk zone, not only currants, but also other crops: apple, gooseberry, strawberry, all stone fruit trees.
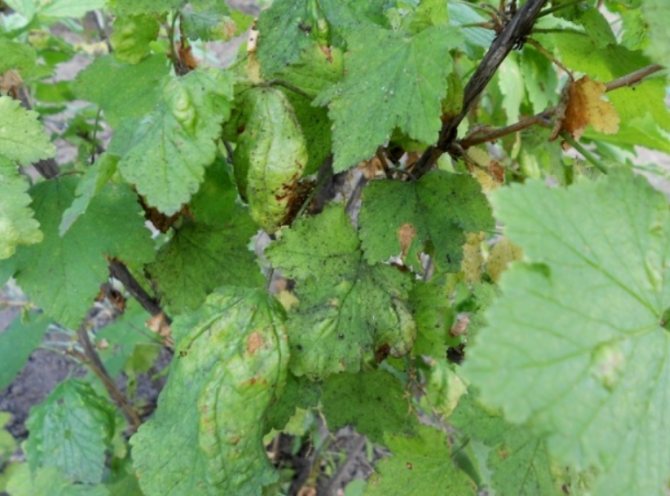
How to understand that a bush is affected by a kidney mite?
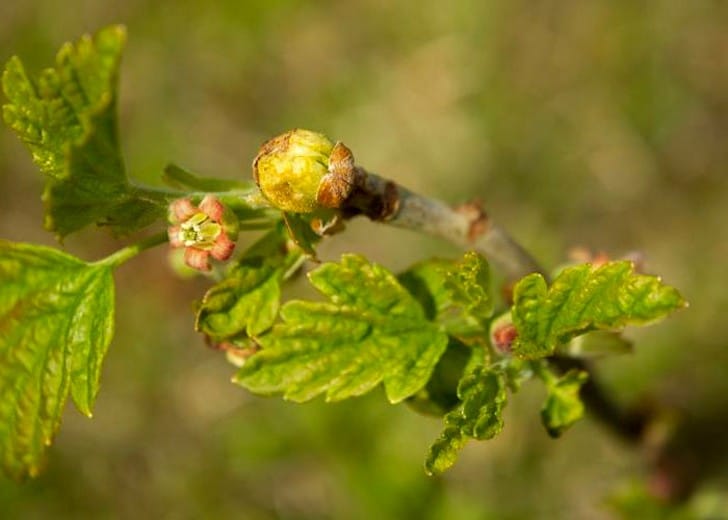
Before proceeding with the destruction of parasites, you need to make sure that the plant is infected with the kidney arthropod. The food supply for these arachnids is black currant, less often red and white, gooseberries. Pests usually infect the buds of these plants, which, after colonization with ticks, acquire a round shape, increasing in size by autumn.
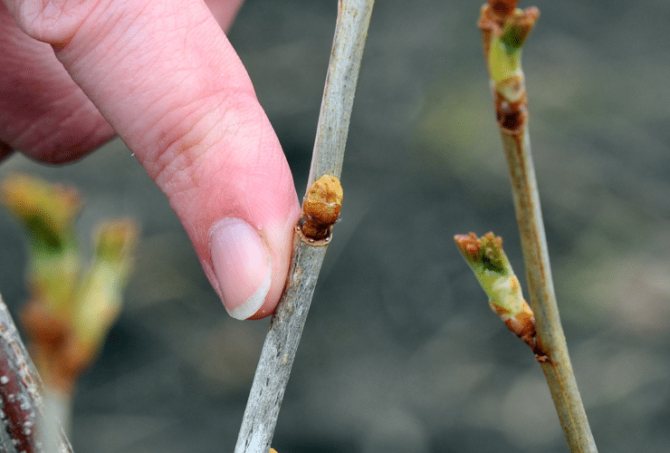


Preventive actions
Annual prevention will help protect currants from spider mites. This includes adherence to agricultural practices and preventive treatments. In the fall, fallen leaves are removed from the site, in which the pest hibernates. The soil under the bush is dug up so that the females of the parasite are on the surface. When cold weather sets in, they die.
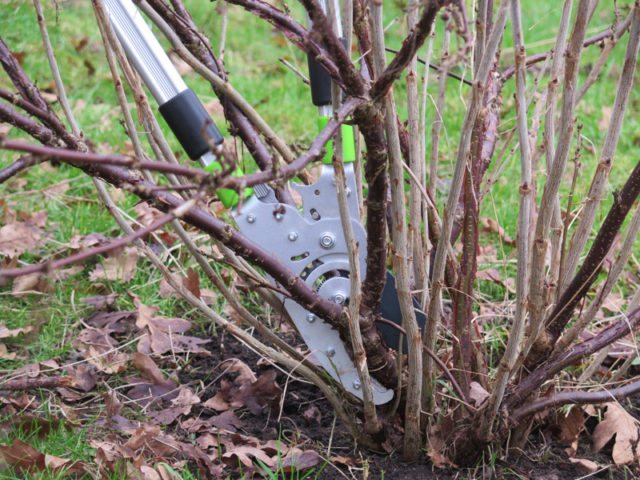


Spring prevention includes spraying. Use drugs Fitoverm or Bitoxibacillin. Treatment begins in early spring to eradicate the pest before larvae appear.
In spring or autumn, currants are cut to avoid thickening of the bush. Nitrogen fertilizers are applied before flowering, after which they switch to phosphorus and potash compositions.In the near-trunk circle, weeds are regularly weeded.
What harm does a mite do to plants?
This parasite is a carrier of one of the most dangerous diseases of viral etiology that currants suffer from - terry (reversion). This is a poorly understood disease, most often it leads to the degeneration and sterility of currant bushes. The yield of shrubs affected by the mite is reduced by about 20%. In case of severe damage, losses can reach 70%. In some cases, a gardener or gardener faced with such a problem has no choice but to uproot currants that are infected with a tick.
Reviews of gardeners
Olga, Moscow
The bushes must be doused with boiling water before the buds begin to swell on the plant. Plus the treatment with chemistry before the blooming of flowers has not been canceled. And then our people are used to being stuck in the ground and hope for huge harvests.
Oleg, Kursk
Fitoverm in three approaches was removed for some time, sufficient for the plants to grow and get stronger.
How to deal with a pest of currants?
This representative of the arachnids belongs to the group of very dangerous pests of fruit-bearing fruit crops. In a year, one tick can produce from 15 to 40 thousand parasites, which are able to withstand almost any climatic cataclysm, which greatly complicates the fight against them. If you do not take drastic measures to destroy pests, they can destroy the entire crop in one season.
When and how are plants treated?
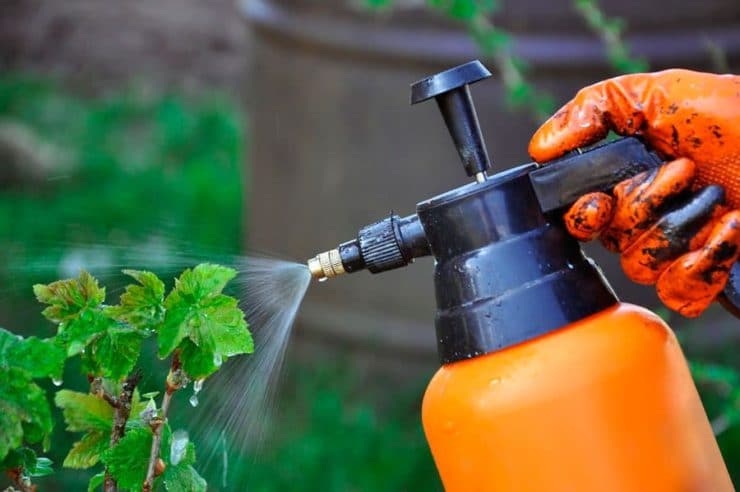


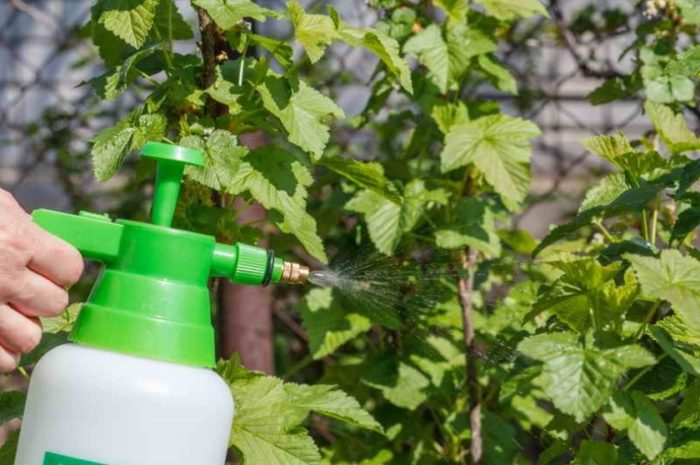
When using chemical pest control methods, it is not enough to choose an effective product. In order for the treatment of plantations affected by the parasite to bring good results, the procedure must be carried out not when you want, but at a strictly defined time. Shrubs infected with kidney arthropods can be sprayed with acaricidal agents or biological products.
Acaricidal treatments
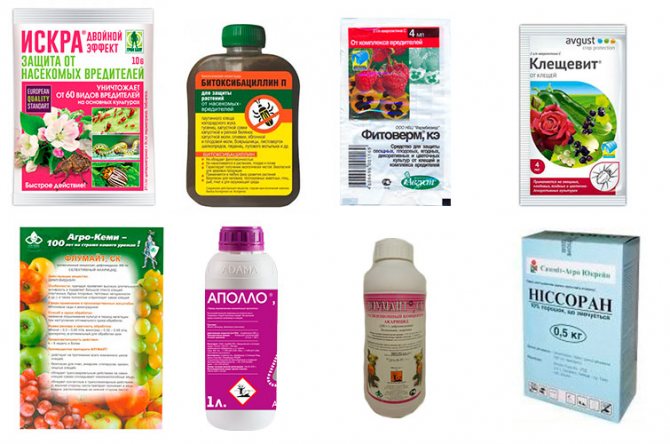
Having decided to resort to this method of pest control, one must take into account that the use of acaricides ("Kleschevit", "Karbofos", "Aktellik") in a limited area is unsafe for people and living organisms. Before using them, you need to carefully study the manufacturer's recommendations and safety precautions for working with potent drugs. It is necessary to process the affected plantings taking into account the life cycle of the parasite. If the sequence of stages and the frequency of processing is violated, it is unlikely that the desired result will be achieved.
The periods of development of an arthropod depend on the air temperature. The larvae demonstrate their first activity at 10–12 ° С, emerge and migrate at 18 ° С. The more intense the warming, the faster the parasites will develop.
The development rate of nymphs sharply increases at 20–30 ° C. During this period, it is necessary to have time to carry out 3 treatments for destruction:
- overwintered ticks and calves that emerged earlier than all;
- pests of the second wave emerging with the onset of stable heat;
- surviving individuals.
The third procedure is a safety one and is aimed at preventing the laying of new eggs. It is important to spray at the time of the first larval migration. These arthropods belong to the class of arachnids, therefore, not insecticides are used to combat them, but acaricides or insectoacaricides. The names and brief information about some of the most effective ready-made preparations against this type of ticks:

| Drug name | Active substance | General application information | Safety measures when working with chemistry |
| Contos | Spirotetramat | During budding and relocation of larvae, plants should be treated with a chemical 2 times within 8-12 days. |
|
| Actellic | Pyrimiphos-methyl | ||
| Vertimek | Abamectin | ||
| Nissoran | Hexythiazox | ||
| Envidor | Spirodeclofen | ||
| BI-58 | Dimethoate | Spray the affected shrubs with the solution after harvest, i.e. in the fall. | |
| Rogor-S | |||
| Phosphamide | Dimethyl 8- (H-methylcarba-moylmethyl) dithiophosphate | ||
| Sunmight | Pyridaben | ||
| Nitrafen | Sodium salt of alkylphenol nitration products |
You can also spray currants with "Fufanon", "Kleschevit", "Karbofos", "Akarin". These drugs have a wide spectrum of action, therefore they are able to destroy not only the kidney parasite, but also other pests, such as aphids.
Many gardeners and gardeners prefer to fight the mite with a solution of colloidal sulfur. To prepare it, you need to dissolve 10 g of sulfur in 10 liters of water, and then let the mixture brew for 10-15 minutes.
Biological products against pests
These preparations for protecting plants from various insects are living objects or natural biologically highly active chemical compounds that are synthesized by living organisms. In the production of bioacaricides, strains of fungi and bacteria are used. Biologics are completely safe for humans, but destructive against many parasites (aphids, ticks, worms, leaf rollers).
Biological pesticides (Fitoverm, Akarin, Bicol, Boverin), unlike chemical ones (Kleschevit, Aktellik, Omite), are activated only at an air temperature of at least 15 degrees. Such conditions do not always occur in early spring, so if it is long and cold, there is no point in using them. "Fitoverm", "Bitoksibatsillin", "Akarin" and other biological products should be sprayed before the end of flowering and after harvesting. When using this method of dealing with the pest of currant bushes, it is recommended to alternate bioacaricides, otherwise the pest will become addicted to the same composition.
Means prepared according to folk recipes
To cure a plant affected by currant arachnids and protect it from further encroachments, you can resort to the help of a poison prepared according to folk recipes. These funds are usually used in cold spring, replacing biological products with them. Information on how and from what to prepare homemade poison, as well as how to properly treat a sick bush with it, is presented in the table:


Use folk methods
Folk remedies help get rid of pests without chemicals:
| Garlic Use minced cloves... You need about 200 g, which are filled with 3 liters of hot water. The liquid is infused for at least a day, then filtered. Dilute the concentrate with water in a ratio of 1: 5... Carefully handle the plants, trying to get to the bottom of the sheets. Repeat the procedure every 5-7 days |
| Onion peel Waste from onion peeling will do, as in the photo... You need about a half-liter jar of husks. It must be filled with a bucket of warm water. Leave for 3-4 days to infuse. Process currants with a strained composition... Try to carry out work in dry, calm weather without the bright sun. Before processing, make sure that there will be no rain in the next day, this rule applies to all folk methods |
| Laundry or tar soap Grate about 100 g of soap... Dilute it with 3 liters of water and mix well. Use a sponge or small brush to apply. Apply to all leaves and branches... You can also cultivate the soil under the bushes. This option is suitable both as a fight against a mite on a fruiting tap, and as a prophylaxis |
| Tobacco dust Dilute 400 g of tobacco dust in a bucket of water and mix well... Bring the composition to a boil and leave to infuse for 24 hours. Strain before use. Spray plants as thoroughly as possible... Cover leaves and twigs on all sides to prevent pests from finding a clean place to feed |
| Potato tops Pick up about a kilogram of tops and chop it a little... Pour boiling water over and leave for a day. Strain before use. Handle in calm dry weather... Repeat spraying about once a week until the spider mite disappears |
How to prevent the infection of shrubs with currant mites?


This is a dangerous parasite, and in order not to have to fight with it, using such potent drugs as "Kleschevit", "Actellik", "Bi-58" and others, it is necessary to take measures to prevent its appearance on the personal plot:
- use varieties resistant to pests ("Minx", "Mystery", "Sevchanka", "Nightingale Night", "Memory Michurin", etc.);
- take into account the type of soil when planting;
- carry out crop rotation at the prescribed frequency;
- reject suspicious planting material;
- carry out spring and autumn sanitary pruning;
- disinfect seedlings and cuttings before planting;
- inspect shrubs during pruning for pests;
- treat bushes with signs of the disease, preventing the spread of parasites to neighboring plantations;
- keep the site clean, promptly removing fallen leaves and carrion from it, as well as removing weeds.
Loading ...
Observe preventive measures
- Remove weeds from the soil... From them, the tick often gets on the currant, so the soil must be clean. It is also very important to remove all plant debris in the autumn, since most of the tick larvae overwinter in them.
- Thin plants and prune branches... Avoid thickening of the bushes, when they are well ventilated, they are less affected by the tick. It is important that all diseased shoots are removed.
- Maintain normal humidity... If the air is very dry, then the pests multiply much faster.
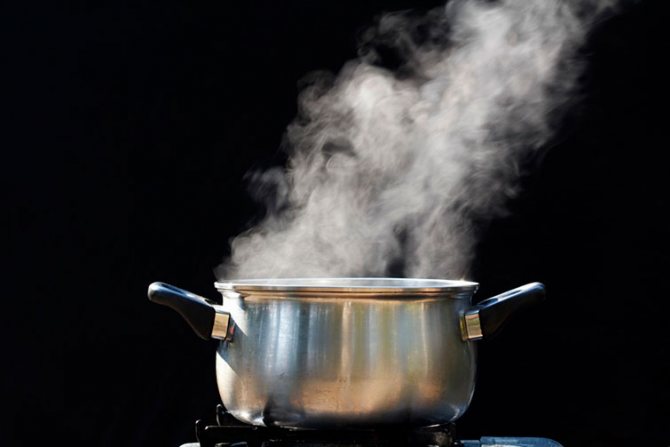
- Scald currants with hot water in early spring... This simple manipulation kills the spores of many diseases and pest eggs.
Application of chemicals
Chemicals can be used before flowering, in extreme cases, during it. During fruiting, the chemicals are absorbed into the fruit, causing poisoning in humans. Processing during fruiting is justified only with a strong defeat of the bush, you cannot eat berries.
It is noteworthy that acaricidal agents act only on adult ticks and larvae, without harming the eggs. Therefore, the treatment of the bush with chemicals is carried out in several stages in order to destroy all generations of the pest.
Such drugs as Sunmite, Oberon, Nissoran and Envidor have proven themselves well. The drugs are recommended to be used alternately so that the parasite does not develop addiction to them.





































