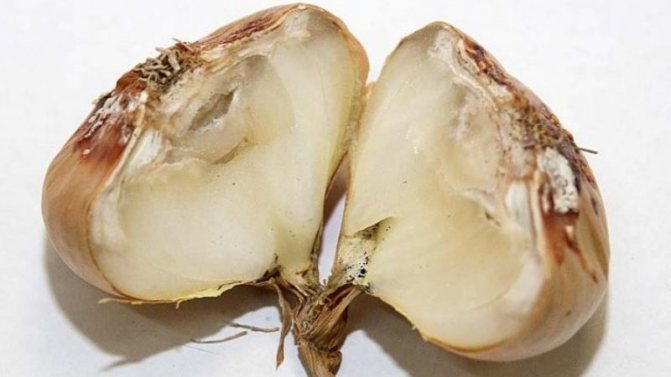
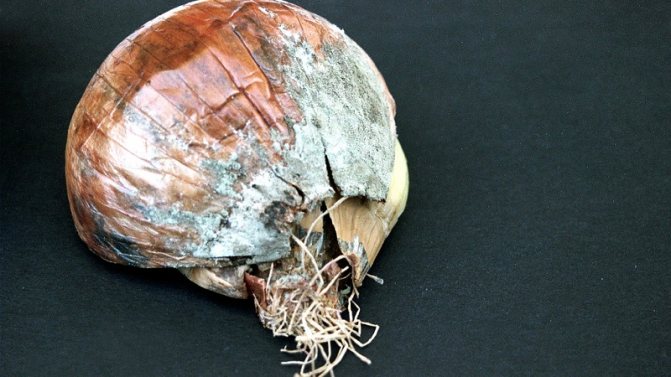
Onion neck rot
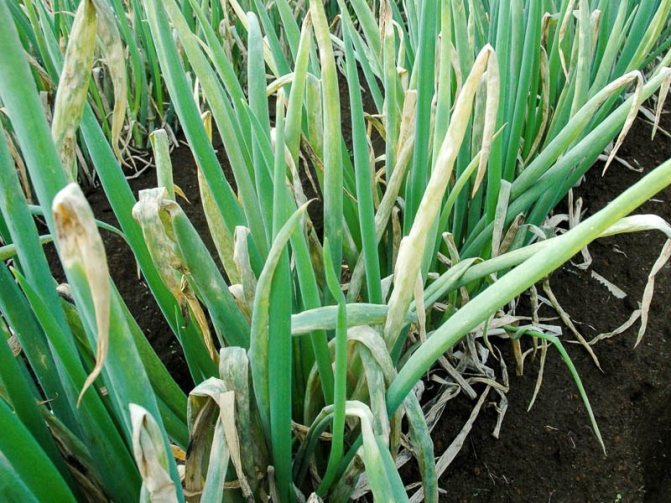
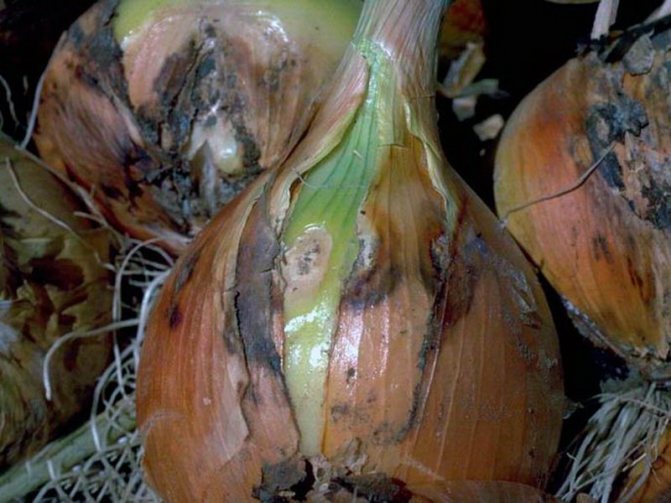
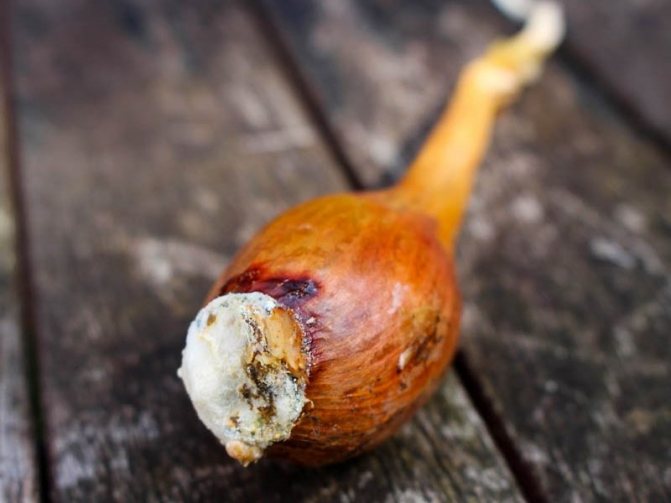
The causative agent of cervical rot is a fungal infection. Often, the disease affects unripe bulbs or crops that have been in moist soil for a long time.
A characteristic feature is the softening of the neck of the bulb, its thinning and rotting. A gray fluffy bloom and an unpleasant odor appear. Gradually, the plaque turns into small black grains, which merge with each other. If you do not start fighting the disease, plaque will cover the entire bulb.
If infected bulbs are planted, feathers will grow weak, pale green in the future. The inflorescences do not reach the ripening stage, become covered with mold and lower their heads down.
The main agrotechnical measures to combat the disease are:

- for planting, you need to choose varieties resistant to fungus;
- after harvesting, the site is freed from all waste;
- weeding, watering the beds is carried out carefully, without damaging the feathers;
- do not overdo it with nitrogen fertilizers;
- you need to harvest in dry weather, drying the harvested bulbs for at least two weeks;
- the leaves of the harvested onion do not need to be cut too short, it is recommended to leave a stump of 3-4 cm.
- only whole, large and dense heads are selected for storage, without damage;
- it is advisable to process the planting material with special solutions.
If onion neck rot has already appeared, chemical control measures will help. Treatment with fungicides such as Tigam, Benlat, Fundazol helps. During the formation of the heads, the beds are watered using the Effekton preparation. For foliar treatment, you can use a solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid.
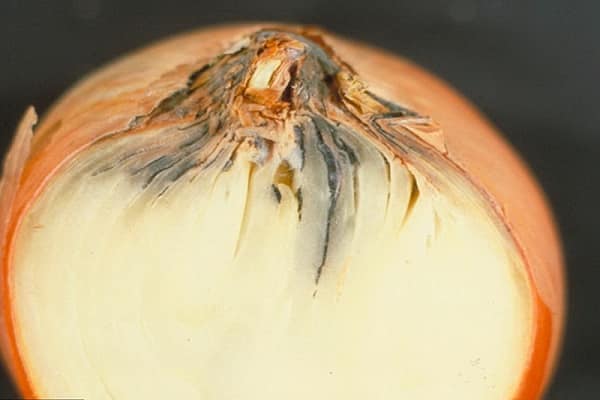


Onion moth
Symptoms
The onion moth is ubiquitous and loves warm, dry weather. It is at this time that its activity increases. The moth larvae are about 11 mm long, are very voracious, they eat the feather from the inside, leaving the outside untouched.


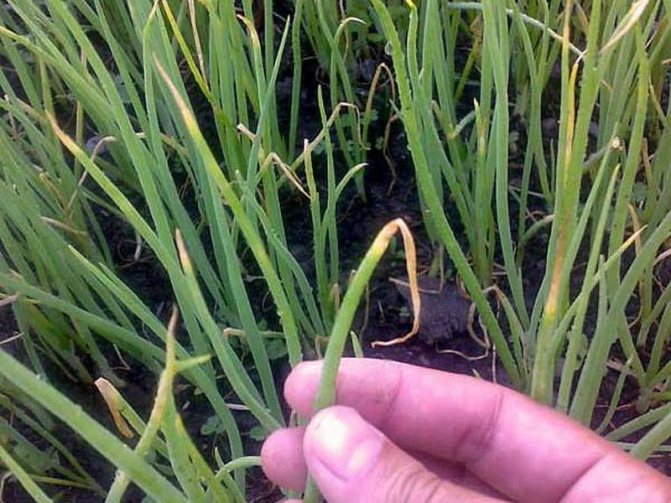
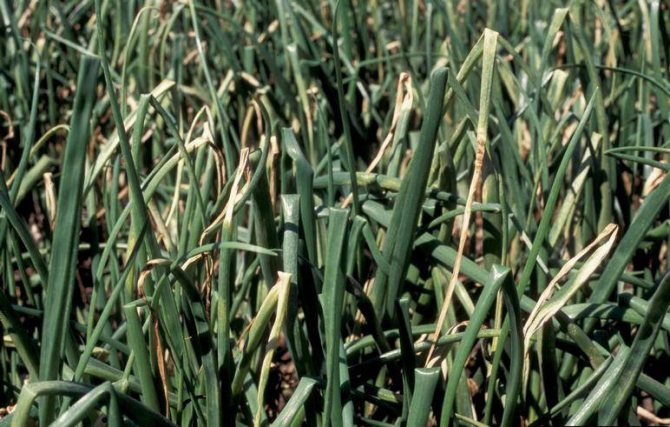
The leaves begin to turn yellow quickly from the end, and then dry out completely. You can immediately see the damaged feather: it will have longitudinal uneven light stripes.
The moth starts flying quite early, in April and May, at night, laying 50–75 eggs each! And after a week, caterpillars appear, which live for about two weeks, then turning into pupae directly on the leaves of onions or on weeds. Within two or three weeks, a new generation appears. The horror is that during the season three generations are formed in the middle lane!
Treatment and prevention
Treatment and prevention consists in proper care of the beds, and then the plantings.
- Obligatory deep digging of the earth in autumn and early spring.
- Cleaning of all residues from the beds, burning of diseased and damaged plants by pests.
- Crop rotation helps to eliminate many problems with pests and diseases, and this gives a significant increase in yield.
Advice! Crop rotation is a whole science. Once you figure it out, then it will be easy to understand what to plant behind the previous crop. Garlic will feel great after potatoes, cucumbers, squash, squash, pumpkin, peas or beans. The soil can improve its health after sowing siderates, which include: oats, barley, rye, vetch, mustard, amaranth, buckwheat and beans.
- Control weeds throughout the season.
- Preventive watering with folk remedies for pests. A solution of ammonia has proven itself well: 3 tbsp. spoons per 10 liters of water, as well as infusions of herbs such as tansy, wormwood, red pepper and tomato tops.
- If you find more than two caterpillars on one lane, then urgently apply some kind of insecticide. But after such processing, do not eat the feather!


Downy mildew
The fungal disease downy mildew spreads favorably after prolonged rains or if watering rules are not followed. The affected feathers of the vegetable look lethargic, drooping, lose color saturation. Gradually, the leaves become covered with brown-yellow spots, dry out and the plant dies.
The spread of infection is facilitated by onion pests, for example, aphids, whiteflies. They spread spores to healthy plants, and the disease is rapidly gaining traction.
Preventive measures to combat the disease are:
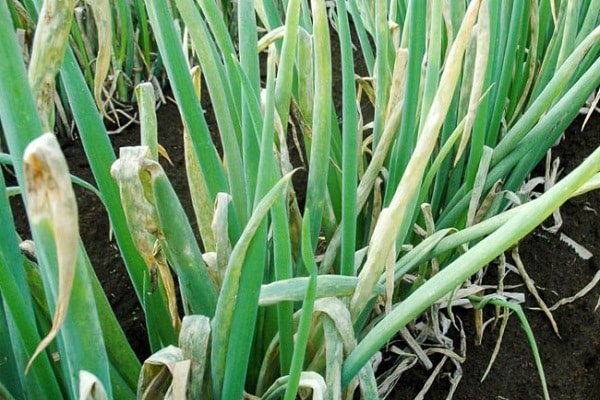


- vegetable beds need to be weeded out;
- since autumn, they begin to prepare the land allotted for planting onions: they dig up, apply fertilizers, disinfect;
- seedlings can be sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid;
- in a rainy, cool summer, it is useful to process vegetable beds with such biological products as Fitosporin, Planriz, Gamair.
To disinfect the soil, you can use a solution of copper sulfate, Fitosporin, Alirin, Gamair, Baikal-Em. You can process the onion from the powdery mildew that has appeared with such means as Thanos, Ridomil, Vectra, Topaz.
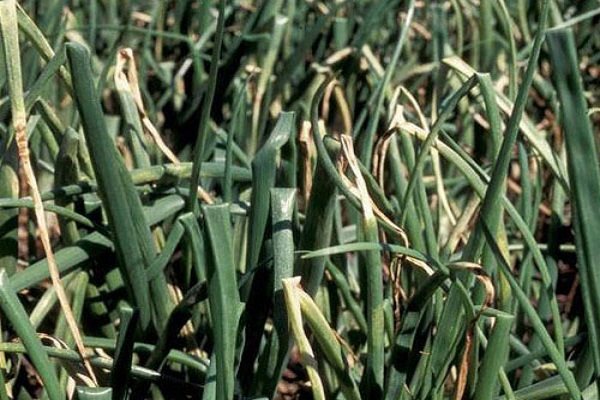


Tobacco thrips
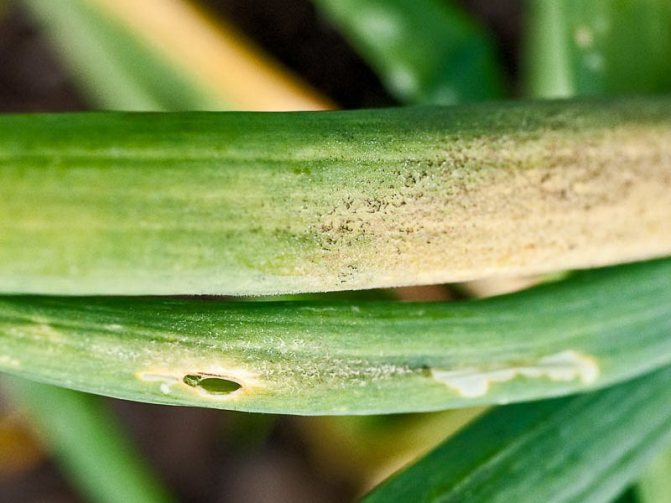
Onion thrips damages the aboveground and underground parts of plants. You can determine the invasion of pests by the following criteria:
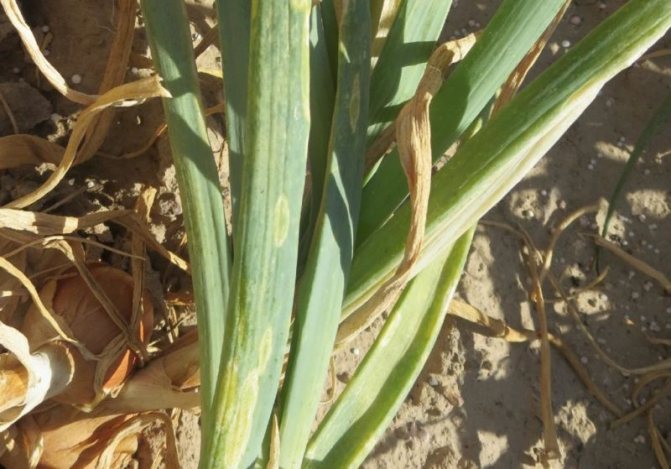
- the juicy scales of the bulb begin to fade, gradually dry out;
- the affected leaves are covered with white stripes, black dots are visible - insect feces;
- growth stops, the seeds become unsuitable for further sowing;
- heavily affected feathers turn pale, bent and dry.


The thrips larva has 2 developmental stages: during the first stage, it actively feeds, while you can see a yellowish intestine on its belly, with the onset of the second stage it hides in the ground or hides in the dried onion husk.
It is simple to recognize a defeat, it is much more difficult to deal with thrips, since not all means can have a destructive effect on it. The following drugs have proven themselves:
- VDG, Aktara.
- ISS, Karate Zeon - 200-300 liters per hectare.
It is necessary to process with solutions twice with an interval of a week. Such a small gap is due to the high resistance of the larvae and eggs to the constituents of the preparations, as well as the fact that the used solution might not touch them.
Onion rust
Signs of fungal rust infection are wilting, drying and yellowing of the leaves. The bulb is small and poorly stored. On the leaves affected by the disease, tubercles of an orange-yellow or brown-reddish color appear. Gradually, the feathers begin to die off.
See also
The correct timing when to remove onions from the garden in SiberiaRead
Spores of a fungal infection tolerate cold well and hibernate on plant debris. That is why it is recommended to remove the remaining tops from the garden at the end of the growing season. Rust development is also facilitated by cool, rainy summers, too dense plantings and an excess of nitrogen in the soil.
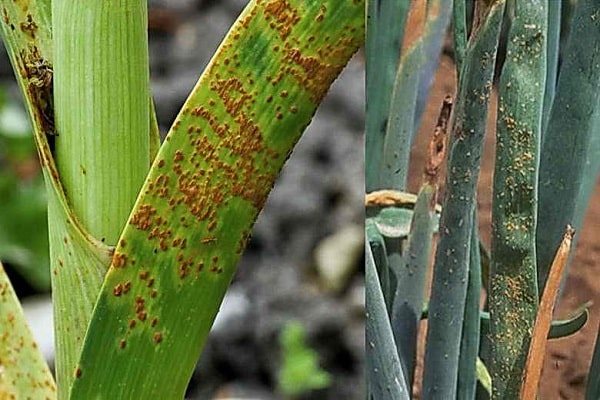


What if the feathers are coated and other signs of rust appear? Most often, the disease develops at the end of summer, so it is important to inspect your plantings daily. If a problem arises, you need to stop watering the beds and applying nitrogenous fertilizers. Damaged stems are cut and removed further from the site.
If signs of the disease were found, the vegetable crop should be treated with fungicides. Folikur, Ordan, Topaz are considered effective.The drug Hom, Tilt or simple Furacilin copes well with the disease.


How to get rid of pests without chemicals?
Those who adamantly refuse to work with chemicals can try neem seed oil. It is a powerful natural insecticide capable of disrupting the life cycle of insects at all stages. The oil is biodegradable and non-toxic to pets, birds, people. It is also a natural fungicide that fights mold and fungal infections.
You can buy the drug at many garden or organic stores. In order to use neem oil as an insecticide, you must mix 2 teaspoons of oil, 1 teaspoon of mild liquid soap with 1 liter of water. Pour the resulting solution into a bottle and spray on the green arrows. It is necessary to process onions every day for a week, then take a break. If new larvae appear on the stems, water the plants again.


Garlic is another natural insecticide. Its strong smell is unpleasant not only for people, but also for garden pests. In fact, the garlic spray will not kill the pests, but it will quite successfully prevent them from further reproduction.
In order to prepare a natural insecticidal solution, you need to take two heads of garlic, grind them in a food processor with a little water. Insist the resulting mixture overnight, and then mix with 1/2 cup vegetable oil, 1 teaspoon of mild liquid soap and a liter of water. Spray the resulting solution onto the infected onion. Chili pepper spray has a similar effect.


Attention! Chili solution also affects people, so be sure to wear gloves on your hands and a face shield.
Fusarium
Common onion ailments include the fungal disease Fusarium. The appearance of the first signs is indicated by yellowing and wilting of the leaves. Initially, the tops of the feathers are affected, gradually rotting spreads to the entire length of the leaves. Often, the bulb itself also rots. It becomes watery, softened and smells unpleasant. A pinkish fungal bloom forms at the bottom of the bulb.
The provoking factors are an excess of moisture in the soil, untimely harvesting, poor-quality planting material, too dense planting.
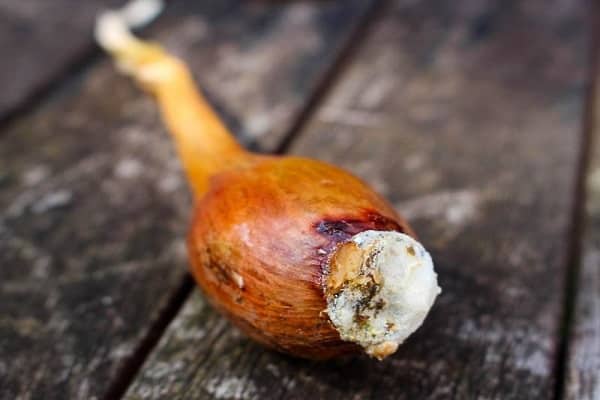


Preventive control measures are considered to be the correct preparation of the soil and seed material. It is recommended to treat the soil with copper sulfate or a preparation such as Iprodion. Disinfection of planting material is carried out with a solution of the drug Fitosporin, Quadris or Fundazol, it can be soaked in a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
If signs of illness are found, it is necessary to remove the affected plants from the garden and burn them, and process the remaining vegetables, for example, with Fitosporin.


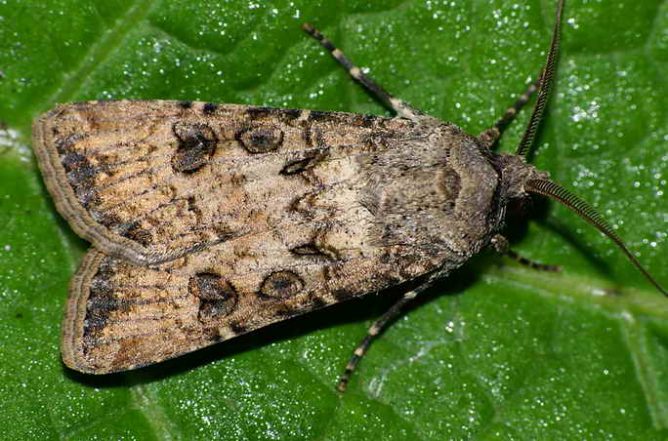
Gnawing (cotton) scoop
The gnawing scoop is dangerous only in the form of a caterpillar. The adult scoop looks like a large, light brown moth. When the wings are folded, a V-shaped speck forms on the back. The butterfly lays single cream-white eggs. From them, larvae appear, which are reborn into caterpillars of brown or greenish color. It is at this stage of life that the gnawing scoop gives gardeners the most problems.
The larvae are usually located inside the stem, but subsequently (during the transition to the next stage of life), they begin to move closer to the soil. The caterpillar buries itself in the soil and begins to gnaw the white pulp of the onion. As a result, the green stems completely dry out, and the vegetable itself becomes unfit for human consumption. To get rid of the gnawing scoop, you can use the same insecticides that are used against thrips.


Thorough cultivation of the topsoil is also recommended.Regular loosening of chernozem creates unfavorable conditions for laying and normal development of eggs. If some root crops are planted in the summer cottage, then you can hang several feeders on the surrounding trees. This is the most natural and inexpensive pest control method. The scoop caterpillars are the best treat for birds.
Bacterial onion rot
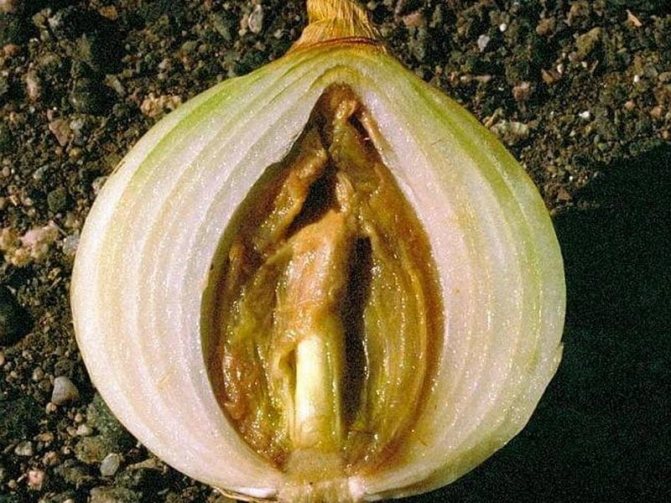
Bacterial rot penetrates the wounds that form on the leaves during weeding or watering. The first signs of rot infection are visible on the leaves. Light spots first appear on them, then they increase in size and reach the neck. After rain, watering or dew, bacteria penetrate deep into the soil to the head of the onion.
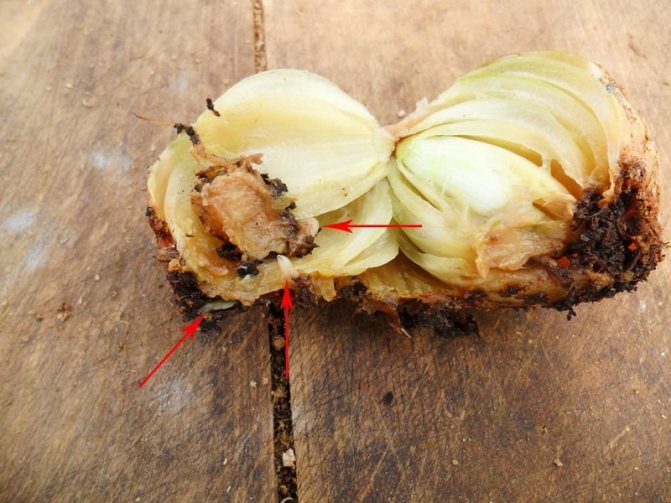
In contrast to the bulbs, which are affected by rot of the bottom of the onion (fusarium), the heads with this disease may look healthy in appearance. But when you cut it, you can see that the core is completely rotten. Rotting gradually spreads from the center to the edges of the head.
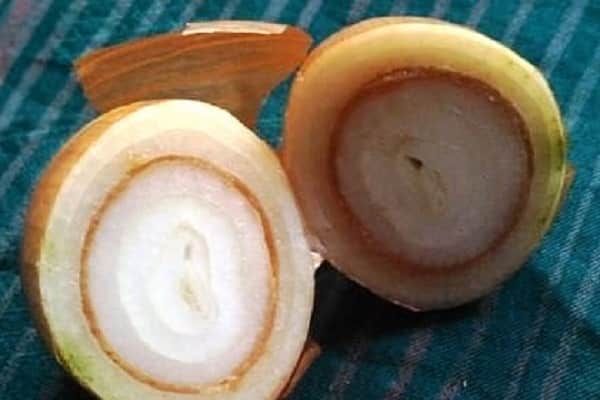


Prevention and control of the disease consists in observing the following rules:
- it is not recommended to plant onions in the same place for several years in a row;
- after harvesting from the garden, you need to remove all plant residues;
- all work on the garden must be carried out carefully, without injuring the feathers of the onion;
- monitor the regularity of watering, from the moment the bulb forms, they should be moderate;
- loosening the soil slows down the spread of the disease;
- apply fertilizers in accordance with the norms (an excess of nitrogen becomes the cause of the activity of the infection).
See also
Description of the Hercules onion variety, its characteristics and productivityRead


Pests such as onion flies and spider mites are carriers of the infection. Therefore, preventive measures should also be aimed at pest control.
So that bacterial rot does not appear in the planting material, it is kept for several hours in a solution of formalin or potassium permanganate. Then dry well in the sun. Suspicious bulbs are treated with antibiotics. A mixture of tetracycline with streptomycin is suitable.


Content:
- Onion diseases and control measures
- Leaf spot
- Onion bacteriosis
- White rot
- Peronosporosis
- Onion mosaic
- Rot of the bottom
- Video "Onion diseases and their treatment"
The causative agents of diseases that have settled in your garden can negate all the efforts made and ruin the harvest. To prevent this from happening, you need to know the "enemy" by sight and try to prevent possible infection of plants. Well, if you notice characteristic signs of the disease on onion shoots, then advice on how to cope with the misfortune will come in handy.
Before talking directly about onion diseases, it is worth noting that one of the basic rules of cultivation is observance of crop rotation: onions and other crops of the lily family can be returned to their previous beds only after 4-5 years, not earlier. In addition, the room in which the harvested onions will be stored is treated with a solution of bleach one and a half to two months before harvesting. And onion sets for planting are recommended to be kept at a temperature of about 40 degrees for 10-12 hours.
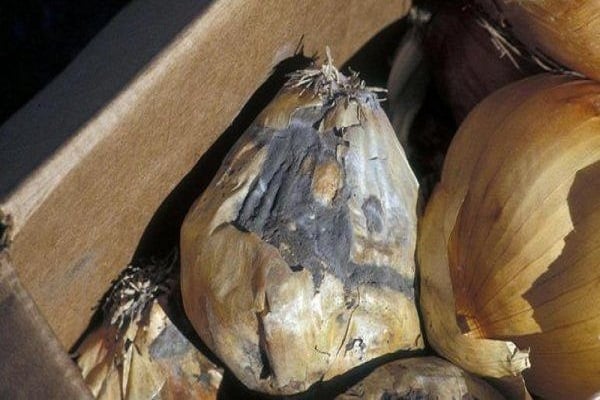
Green mold rot
Green mold rot affects already harvested crops during storage. The onion shell dries up and becomes covered with green mold. The main reasons are: damage to the bulbs during harvest and high humidity in the room where the crop is stored (more than 70%).
Onion pests are often the cause of the development of the disease. They still carry infection into the plant in the beds, and under favorable conditions, pathogens begin to actively develop, leading to rotting of the crop.
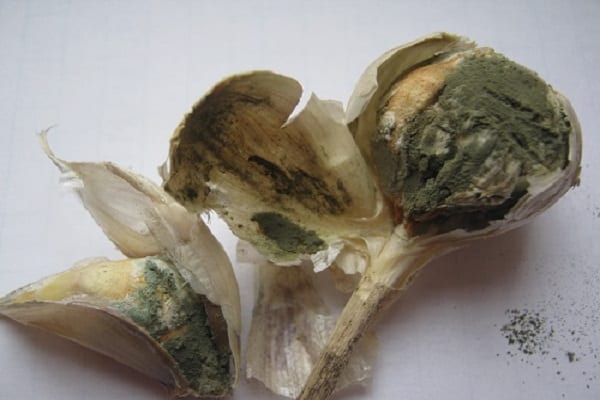


Watery brownish spots appear on the infested bulbs in the area of the bottom. After a while, an unpleasant mold smell appears from them, and a greenish bloom is observed under the scales.
Preventive measures are considered to be thorough drying of the crop and compliance with all requirements for its storage. The room should be dark, cool (about +3 degrees) and not damp. Pre-disinfection of the storage space for onions.

It is recommended to select bulbs in advance for planting next year. Tip: Take seed material for storage in another place. Review it periodically and get rid of diseased and damaged bulbs in time.
Onion fly
Symptoms
If you suddenly notice yellowed tips of feathers, drooping arrows or twisting them while planting onions, it means that the onion fly has settled in the beds - the most frequent pest.


The onion fly is similar to a common fly, only it is gray in color and 1 cm in length. When the lilac blooms, the fly begins to actively fly and look for a place to lay eggs. The best place for this is dry onion scales at the very base. The larvae bite into the bulbs and for three weeks "gobble up" with juicy pulp, eating up extensive passages.
The leaves of the plant wither, turn yellow and then dry out completely, and the bulb gives off an unpleasant odor. The larvae go to the ground, where by July they turn into flies, fly out and damage all crops with renewed vigor. In the southern regions, where onions are grown in large quantities, three generations of flies grow per season.
Treatment and prevention
If you have already been infected with a fly onion, then, most likely, the soil is already infected with pupae of this pest. Therefore, digging the soil in early spring will give a good result: the pupae will fall into the cold air and most of them will disappear.
What other means are there?
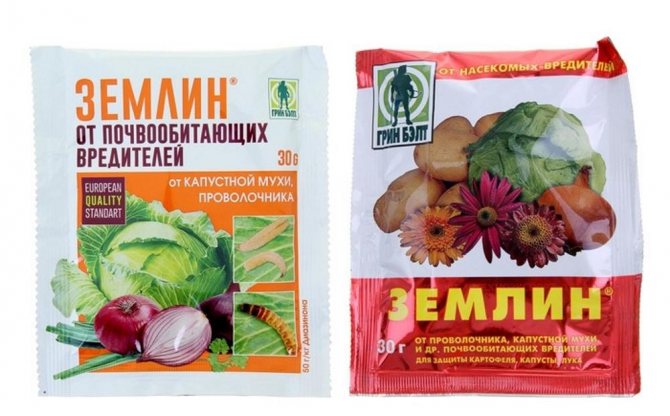
A good proven drug "Zemlin", which fights against many soil pests. It is simply scattered over the soil surface. It has long been known that the onion fly avoids laying eggs in carrot plantings, so this fact must be used.
Advice! Plant two crops close to each other, at an optimal distance, remembering that when growing, carrots become spreading. Good experience: line method, alternating onions and carrots.
When planting, you can reduce the likelihood of a fly laying eggs in the onion scales by deepening the sevok during planting by 3 cm, hiding the neck in the ground.


Folk methods of struggle:
- From the moment the feather grows 3–5 cm, watering with saline is used: 200 g of salt per 10 liters of water, watering once every 10 days.
- Ammonia solution: 3 tablespoons per 10 liters of water.
Water so that the solutions do not fall on the leaves! If you find damaged bulbs, remove them mercilessly!
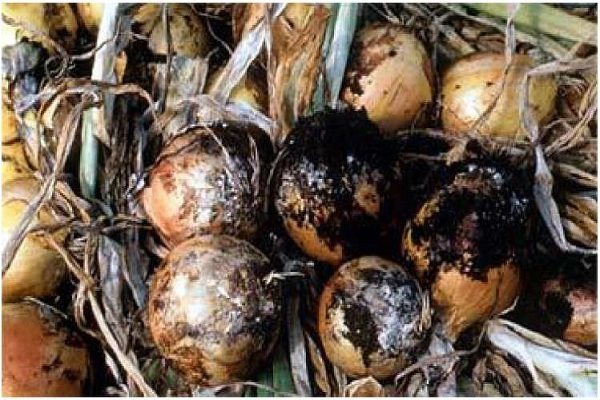
Black mold rot
Fungal disease black mold rot is a problem mainly in harvested crops that have been stored. Diseased bulbs become soft, rot, deform, the scales dry out and become covered with black bloom. But you can see signs in the garden. Fungal spores infect leaves when they are wet for more than 7 hours.
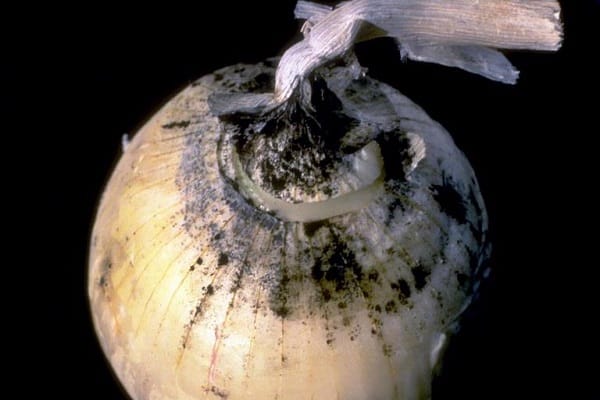


The development of the disease is provoked by improper storage conditions. Black mold on onions develops in musty, damp rooms where humidity is high, temperature fluctuations are high, and air ventilation is poor. An insufficiently dried crop after digging out of the soil provokes the disease.
Protection measures are:
- during loosening and weeding of the soil, care must be taken so as not to damage the leaves, otherwise the wound can become a site of infection;
- the harvested crop should be protected from damage;
- the room maintains low air humidity and low temperature;
- remove old tops of plants from the garden;
- since onion pests become the cause of the disease, it is not necessary to allow them to appear in the garden.
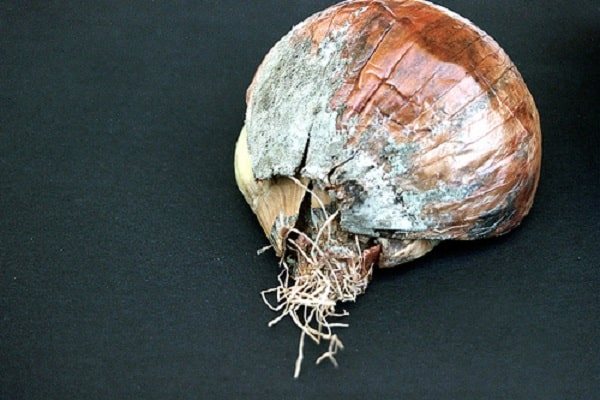


Harvesting must be done in a timely manner. Do not remove unripe or overripe onions. It will be poorly stored and a high risk of developing various diseases.


Root bulb mite
The root bulb mite, despite its name, attacks garlic more often than onions. Ticks are translucent, cigar-shaped, microscopic in size (adults do not grow more than 1 mm in length), and are almost invisible to the naked eye. The eggs are attached with a thin adhesive tape to the stem of the plant, and after ripening, they are moved into the soil.
Signs of damage to onions by microscopic mites are not too obvious. Pests grind off the roots and pulp of the bulbs very slowly. This leads to stunted plant growth, twisting and discoloration of the stems. But small yellow specks appear mainly at the very edge of the arrows, which means that not every gardener will be able to notice such an important sign in time. Mites can damage already dug healthy bulbs.
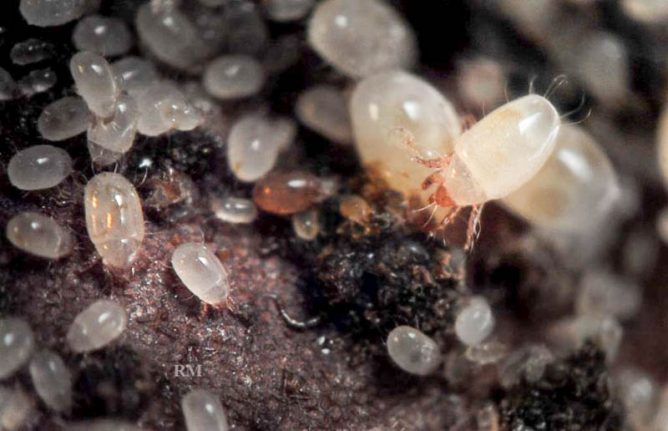


To prevent the occurrence of bulb mites, it is necessary to avoid sequential planting of onions and garlic on the same bed for several years. Before the start of the summer cottage season, it is necessary to treat the soil with a solution of sulfur (0.3%) and dimethoate (0.03%) or dicofol (0.05%) in an amount of 2 ml. for 1 liter of water. As a post-sowing soil prophylaxis, it is recommended to use preparations based on clofentezin.
Remember
- Properly care for onions... This will reduce the risk of pests.
- Inspect the plants periodically... If you notice the appearance of pests immediately, it will be easier to exterminate them.
- Get rid of pests right away. As soon as you notice insects, start treating the plant, then it may be too late.
- Use folk methods. They will not harm you or the plants. Use insecticides only in difficult cases when pest colonies have spread throughout the garden.
- Carry out prevention. To avoid the appearance of pests, take preventive measures.