Propagation by cuttings
Plant propagation by cuttings is one of the methods of vegetative propagation of indoor plants. Before you get acquainted with this method of reproduction, you should understand its advantages. The main factor in the propagation of plants by cuttings is the preservation of all the characteristics of the mother plant. There are indoor plants that are difficult to cut at home, despite this, flower growers often propagate indoor plants by cuttings. Plants are usually propagated by cuttings: stem, root and leaf.
Propagation by root cuttings
Propagation by root cuttings is performed with plants capable of producing root suckers. The mother plant, intended for propagation by root cuttings, is dug out during the dormant period. Aerial shoots are removed, and the roots are washed in water. With a sharp knife at the root collar, carefully cut off the root cuttings.
Attention! The cut at the points of contact with the mother plant should be straight.
After such a procedure, the mother plant is usually returned to its original place, where the plant takes root well, recovering during development. The resulting root cuttings are freed from lateral fibrous appendages and cut into the desired parts. When cutting cuttings of the desired size, an oblique cut is made.

Sections are processed with crushed charcoal. Root cuttings of plants that do not form new roots well are treated with a fungicide.
For germination of root cuttings, ordinary, washed and disinfected sand is used. They fill a flower pot with it, make vertical holes in which the cuttings are placed. Cuttings are placed at a distance of two to four centimeters from each other.
For a quick result, put a plastic bag on the pot. It creates greenhouse conditions for the plant and increases humidity. Watering is not done, but cuttings are sprayed regularly. You should also ventilate the cuttings pot from time to time.
Rooting conditions depend directly on the type of plant. Plants from regions with temperate climates do not require elevated temperatures, which cannot be said about tropical flora.
After rooting the cuttings, it is important to plant them in a permanent place as soon as possible, having prepared containers with the substrate for this in advance.
Cuttings
What are we cutting? This method is most often propagated by: ground cover perennials and shrubs (arabis, periwinkle, saxifrage, lavender, stonecrop, sunflower, thyme, subulate phlox); plants that were kept indoors before planting (dahlias, chrysanthemums, petunias, fuchsias), as well as those that managed to grow too much or do not propagate at all by cuttings of basal shoots (carnations, bells, paniculate phlox, sage).
When? From mid-May to late June.
How? Water the plants you will be taking cuttings from the night before. In the morning, cut off a few stems from them (no more than a third, so as not to weaken). Using a sharp (important!) Knife, cut them into pieces no more than 10-15 cm long, each of which will have at least 3 leaves or 2 pairs of leaves. The lower and upper cuts should be located close to the bases of the leaves and buds (at a distance of 2–5 mm), but not injure them.In most plants, cuttings taken from the middle part of the stem root best, although the tops can be taken from smaller species. Remove the lower leaves that fall into the soil. Cut the top ones, if they are large, in half. Dip the prepared cuttings into the rooting stimulator with the lower part and plant them in the cuttings. Then proceed in exactly the same way as in the case of basal shoots.

Propagation by leaf cuttings
There is a small group of plants that are capable of producing new offspring from a small part of the leaf, that is, propagating by leaf cuttings. Others, for the creation of a new plant, need to use not only leaf plates, but also part of the petiole.
Such plants include:
- aloe;
- Kalanchoe;
- begonia rex;
- zamiocalcas;
- uzumbar violet;
- crassula.
There are plants that can be propagated with a whole leaf. Such plants include:
- gloxinia;
- saintpaulia;
- begonias;
- piperomias.
In order for the leaf of the plant to behave correctly as a successor and parent of a new flower, a healthy leaf with a petiole three or five centimeters long is cut off at the base of the plant. Then place the sheet in a glass of water. Those who do not want to wait two or three weeks resort to phyto-hormones.
In floriculture, there is also a way to propagate a plant using a piece of a leaf. In this case, a healthy adult leaf is picked up, cut off and cut into several separate pieces so that each piece has clearly visible veins.


After that, parts of the leaf are treated with a solution of phyto-hormones and planted in clean and disinfected sand, one third of the height of a piece of the leaf. Cover the pot with cellophane, while making sure that the bag does not come into contact with the edges of the planted leaves.
The pot is placed in a shaded, warm place with a constant temperature of 20-22 degrees. After about 4-5 weeks, the roots will appear on the parts of the leaves and the bag is then removed. In the future, if desired, parts of the leaf are seated in various containers. Flowers such as streptocarpus, begonia, sansevieria are propagated with part of the leaf.
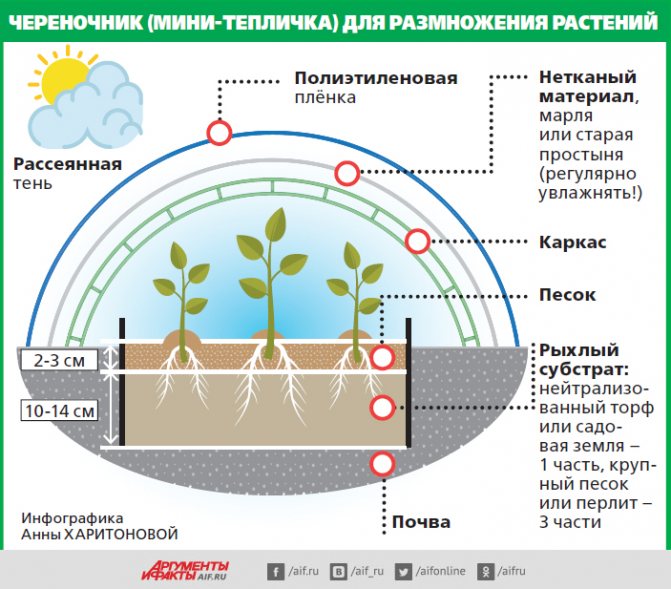
Preparing the cutter
The cutter is a small shaded greenhouse in which the cuttings will be located. Every gardener can create it, because for this you do not need to have special skills. This also does not require expensive materials. The main thing in this matter is to select a site and soil.
The place for the cuttings should be well lit. As for the soil, loose, air and moisture impermeable soil is preferable. Ideally, use black soil for this. When its layer is insufficient, additional peat and sand can be added. The surface of the ridge should not have slopes, otherwise the water will fill the furrows. A few centimeters of river sand should be laid on top of the black soil layer. Cuttings parameters depend on how many cuttings are planned to be rooted. As a rule, a ridge is enough, the length of which is 2.5-3 m, width 70-100 cm. For the construction, you need to prepare:
- 4-6 metal arches for greenhouses (the exact number depends on how long the ridge is);
- greenhouse film (thickness 150-200 microns);
- garden stakes (length 2 m);
- branches of deciduous trees (you do not need to pluck the foliage);
- wire or twine.
Propagation by stem cuttings
There are plants that can recreate new shoots only from a part of the stem, that is, plants propagate by stem cuttings, but at the same time they must have one or two buds. For example, this is how they reproduce:
- hibiscus,
- ficus,
- abutilone,
- citrus plants,
- myrtle.
For propagation by stem cuttings, an annual shoot of the plant is taken with the condition that it is absolutely healthy, and it is cut into several cuttings, up to about eight centimeters long. Each cut piece must have two internodes and two or three leaves.
The lower part of the cutting should be leafless. With a sharply sharpened knife, cut off the shoot 2-1.5 centimeters below the leaf nodule. The lower part of the shoot is immersed in a plant growth solution called heteroauxin for several hours.
Drainage is placed in a dish prepared in advance with a layer of up to about three centimeters, and a substrate is poured on top. The substrate with a layer of 5 cm should consist of leafy earth with an admixture of peat and coarse sand. The stalk is placed in the soil to a depth of 1.5-2 cm and the substrate is carefully tamped.
The planted stalk is watered with warm, settled water and covered with a plastic bag for a week. The best time for cuttings is spring, it is desirable to carry out cuttings in March, the last date may be May.
Rooted cuttings, such as indoor flowers: pelargonium, abutilon, begonia, fuchsia, do not keep themselves waiting long and bloom in the summer, delighting with their beauty. Propagation by stem cuttings is a vegetative method, which is the most affordable and easiest way to propagate indoor plants.
Horizontal layering
In April - May, annual branches are bent to the ground and laid on the bottom of grooves 5–20 cm deep, made in the previously loosened soil under the bush. Secure with wire pins, but do not drop in. The grooves are filled with loose soil after a while, when lateral shoots 10-15 cm high appear on the lying branches: only tops should remain on the surface. As the shoots grow further, the soil is raked up to them additionally (1 or 2 times in the first half of summer). The soil should be constantly moderately moist.
Readiness
Layers are ready for transplanting in the fall, by early October. It is necessary to carefully shake off the soil, separate the resulting plants with a pruning shears and plant them. You can do this in the spring.
When to cut a stalk
The best breeding season for plants by cuttings is spring and autumn (for most indoor plants) - the time of active growing season. The stalk is usually taken from a healthy, disease-resistant and indoor plant. You can not take a cutting from plants that have undergone stress.
Cuttings taken from a recently purchased imported plant take root especially poorly. The secret of these flowers is that for a quick and effective presentation, they are saturated with special preparations that promote flowering, fruiting and growth, which negatively affects the root system.
Know! It is recommended to take a cutting from such a plant no earlier than in a year.
The cuttings must be semi-lignified, that is, the bark on the upper part of the cutting should be still green, but at the cut level it must be recently lignified. It is better to take cuttings from fresh growth, which appeared this year. Cuttings from plants rooted poorly, the substrate of which is oversaturated with fertilizers, especially nitrogen. As a result, these cuttings rot.
Most indoor plants develop in waves. At first, young shoots grow quite actively, then they freeze for a while, and then continue their growth again. It is advisable to carry out cuttings of indoor plants precisely during the freezing period.
In beautifully flowering plants, cuttings should be trimmed immediately after flowering (clerodendrum, plumbago, bougainvillea).
In citrus, cuttings should be taken only when the shoots from the ribbed ones become rounded. Typically, the stalk should have from three to five buds (large-leaved plants - ficus, hibiscus, abutilon).
Cuttings of small-leaved plants should contain more buds and be up to ten centimeters long. Here, cuttings can be both apical and stem cuttings, that is, cut from intermediate shoots. A twig of passionflower can be cut into pieces from five to ten centimeters long (each stalk has 3-4 buds) - this will be the propagation of the plant by stem cuttings.
How to properly cut a stalk
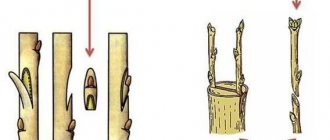
On a plant that is planned to be propagated by cuttings, the desired branch is cut off. For a cut branch, an oblique cut must be made immediately under the lower bud, and the leaf is removed.
When grafting houseplants with milky sap, such as ficus, it is imperative to place the cut cuttings under running water until the sap stops flowing.
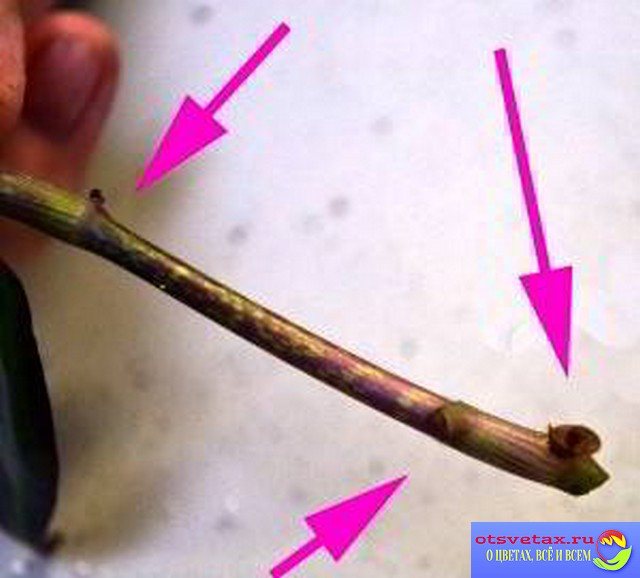


The cut cutting should have at least one or two buds, from which a new young plant will grow in the future. It is not advisable to dwell on the question of the number of buds on the handle. Ficus can be propagated by cutting with one single bud, but in this case the chances of getting a new plant will be much less than that of a cutting with two buds.
Division of rhizomes
The most common method of vegetative propagation is division of rhizomes... Rhizome is an elongated underground part of a plant that bears the remains of leaves, buds and adventitious roots. For propagation of plants by rhizome, cuttings ** obtained from the periphery of the old bush are used. To obtain high-quality planting material for irises, peonies, daylilies, etc., it is better to propagate plants at the age of 3-4 years. With age, a large number of renewal buds develop on the rhizome, which over time begin to compete for living space. As a result, in the center of the bush, the buds are weak, and on the periphery, they are stronger and more viable. Therefore, when dividing old bushes, it is better to use the material from the outer part of the rhizome, and remove the central one. Some gardeners grow the central part of the old bush and re-divide after a while.
Most rhizome plants have a loose rhizome, which is divided by hand or with a sharp knife. A very old plant or plant with a dense root system is cut with a shovel.
If the task is not to get as much planting material as possible, it is better to divide the bush into 3-5 divisions. Plants from such plots can bloom in the first year, from the second year they form powerful, well-developed and normally flowering bushes. If you need to get many plants from one mother bush, then it can be divided into smaller divisions (with one bud), but in this case, in the first two years after division, the plants will develop slowly and bloom only in the second or third year. In order for such a plant to grow better, it is not allowed to bloom in the second year, breaking off the peduncles. With fine division, a complete renewal of the root system occurs, and in the future this plant will be stronger and more durable than the one propagated by the standard division.
Dividing plants is best done in a cool, shaded area.... To stimulate the growth of young lateral roots in the resulting cuttings, the roots are cut to about 1/3 of their length. Long, uncut roots are difficult to distribute evenly in the planting hole when planting, which can lead to kinking, decay and death of the entire plant.
The division and transplantation of perennials is carried out in early spring (April-early May) or at the end of summer (late August - early September). In the spring periods of division, while the buds have not yet started to grow, it is enough only to trim the roots. For summer-autumn transplants, it is necessary to cut off the aerial part of the plants, leaving about 15-20 cm, because the roots will not yet be able to provide the plants with everything they need, which can lead to disease and delay in flowering.
The division of certain cultures often has its own characteristics. So, for example, when propagating a peony, you should not use large delenki with a large number of buds and many long roots, as it will hurt for a long time and bloom weakly. To quickly form a large iris bush, delenki are planted in a circle or in rows, taking into account the area required for an adult plant, etc.
When dividing the daylily, the old roots are pruned, leaving no more than 7-8 cm, the places of the cuts are sprinkled with ash.
Before planting the delenok, it is advisable to dip the root system in a clay mash. For its preparation, a small amount of clay is added to 10 liters of water (so that after dipping in a chatterbox, a thin layer of clay remains on the hand), 1 tablet of heteroauxin or a bag of root (any other root stimulator can be used, according to the instructions) and 1 kg of fresh manure. Add components in the specified order. Roots treated with a chatterbox must be dried in the open air for 30 minutes, and then the cuttings should be planted in prepared, moistened pits.
Reproduction conditions by cuttings
Lighting
Light is needed to root the cuttings. In this case, it is not advisable to expose the greenhouse to the sun, since internal overheating of the container is possible. Light deficiency is achieved with additional lighting.
Here you can use special phytolamps (LED), as well as simpler and cheaper fluorescent lamps. Daylight hours for rooting cuttings should consist of twelve hours, and the day should be replaced by night.
Temperature
The optimum temperature for rooting cuttings of indoor plants is a temperature of plus twenty-five degrees, if the temperature is lower, the formation of the root system is very slow.
There are some indoor plants that need lower heating, for example bougainvillea, in which case the lower temperature should be higher than the air temperature.
Dishes
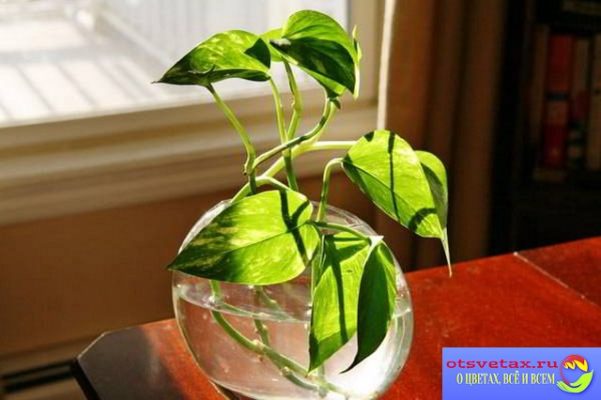
One of the important factors for propagation by cuttings at home is the substrate and the choice of containers. Most plants take root in water without any problems. In order for the water not to deteriorate, it is advisable to add activated carbon to the water.
Attention! It is advisable to choose utensils for keeping cuttings not transparent.
It is better to choose a vessel made of opaque plastic or dark glass. It is imperative to monitor the condition of the water and, if necessary, change it.
Cuttings in water are easily rooted by indoor plants such as:
- epipremnum;
- monstera;
- syngonium;
- scindaptus.
Plants such as: hibiscus, myrtle, ficus can also give roots in water, but with further planting of young plants in the ground, the regrown roots change to new ones, which causes the plants to get used to new growth conditions for a long time.


For these indoor plants, it is desirable to perform rooting immediately in the earthen substrate. Rooting successfully with such a planting of ninety percent cuttings of such plants as:
- olive,
- eugene,
- myrtle,
- callistemon,
- plumbago,
- Garnet,
- hibiscus, etc.
Priming
It is recommended to take a substrate depleted in organic matter for growing cuttings (organic matter is useless here and can cause decay). The most optimal solution would be a substrate consisting of fifty percent peat and fifty percent sand mixed with a small amount of sphagnum moss.
Moss is added to make the soil lighter, increase moisture resistance and bond the substrate. The bunch of the substrate is very important when further transplanting the rooted cuttings to a permanent place.
It is very important to sterilize the substrate. This is done quite easily in the microwave. In its absence, you can steam the soil in a saucepan.
At the bottom of the pan, lay a layer of washed and sifted sand two to three centimeters high, settle the peat upstairs and steam it on fire for about thirty to forty minutes. This method will help you get rid of all pathogenic micro and macro organisms and weeds.
For soil disinfection without steaming, microbiological agents such as "Vostok - EM1" and "Shining" can be used. You will read the instructions for use on the label, the process is quite simple.But, using these tools, you will need more than two weeks of time.
Before propagating plants at home, it is necessary to mix sphagnum, sand and peat, and fill disposable cups with the prepared soil. Transparent glasses make it quite easy to observe the process of root formation without disturbing the plant. It is imperative to pre-make drainage holes in the walls and bottom of the glasses.
When planting large-leaved cuttings, we take a two hundred gram glass, and for small-leaved, one hundred gram. After distributing the substrate, it should be slightly wetted, it is not recommended to allow the soil to become too wet.
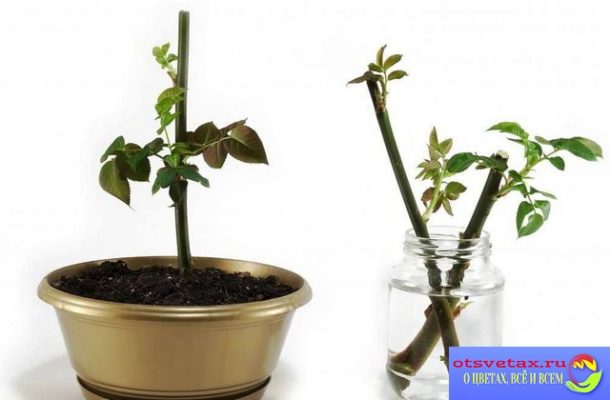
Planting cuttings
It is advisable to dip the lower part of the cutting into a root solution and place it vertically in a glass with a substrate, so that the second bud from the bottom is at the level of the ground. It is necessary to provide the cutting with a dense, stable position in the substrate. To achieve this, you can not remove the leaf under the lower bud, but slightly deepen it into the substrate.
For cuttings of small-leaved plants, the number of buds both inside the substrate and on the surface should be greater than that of large-leaved indoor plants. For plants such as citrus fruits, hibiscus, it is recommended to lightly wound the cuttings. A light scratching of the bark of the cuttings is performed with a clean needle in the area that will be immersed in the substrate.


After planting the cuttings, it is advisable to spray them with "Zircon" and arrange the cups in the greenhouse. You can make a greenhouse yourself by taking a sufficient capacity or with a margin for the required height of cuttings planted in cups, and cover it with foil.
Know! Usually a glass aquarium, plastic bowl or container is used for these purposes.
If you want to create a mini-greenhouse, then you need to take a plastic water bottle and cut it across. It is imperative that the cuttings be in conditions of high humidity until they form roots, which will provide the new young plants with the process of supplying moisture.
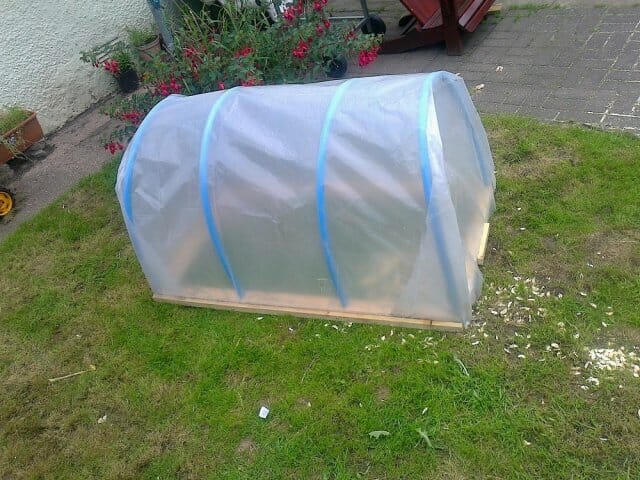
Shelter and shading plantings
When planting is over, the cuttings need to be covered. It is important for planting to provide a deaf shelter, without drafts. Thus, it will be possible to achieve ideal air humidity. Place the greenhouse arcs on the ridge. You will need to stretch the film over them. From each edge it must be sprinkled with earth (with the exception of the north side). Next, build a tyn from stakes (on 3 sides of the ridge). Dig the stakes into the ground and create shading from the branches. Thus, the landings will be protected from direct sunlight.
When the tyn is ready, deepen the film into the ground from the north side, and then carry out the same manipulations on the other sides. Water the furrow around the resulting structure. All-round protection, completely blocking out the sun's rays, significantly reduces the percentage of rooted cuttings. Therefore, it is not advisable to use burlap or cardboard for this.


The results of plant propagation by cuttings
The very first results of rooting during cuttings appear, as a rule, after 2-3 weeks for plants such as:
- abutilone;
- figs;
- callistemon;
- myrtle;
- melaleuca;
- ficus.
Indoor plants such as:
- hibiscus;
- eugene;
- psidium;
- olive;
rooting results appear in about a month. Their new, formed roots are very clearly visible through the walls of the cups.
It's time to transfer the rooted cuttings from the greenhouse to room conditions. With a sharp movement of plants, leaf wilting may occur. To avoid such undesirable results, it is better to allow the plants to gradually acclimate at home. There are no general rules here, everything is individual.
It is desirable to spray some plants often, while others gradually accustom them to external conditions, placing them for a while in loosely closed greenhouses.Still others are often ventilated, accustoming them to the dry air of the apartment.
When young plants are acclimatized after transplanting into new pots (after about two weeks), they are fed with fertilizer - this helps the plants grow more actively.
P.S. From a young age I have been interested in fine arts. I especially like landscapes, oil paintings and painting flowers. I always try to find free time and visit exhibitions of artists and art galleries.