Apricot is a deciduous fruit tree from the plum genus, the rose family. It is quite common in our latitudes and is loved by both adults and children. With a little effort, you can plant and grow this fruit tree in the garden yourself and enjoy the delicious and aromatic fruits of apricot every year.

Growing features
The life expectancy of apricot in the Ural region is rather short and is no more than 20 years. Of these, a maximum of half of this period falls on the period of productive fruiting. Therefore, in order to ensure the annual supply of these sunny fruits, it is necessary to periodically plant new trees in the area where apricots are grown. Not all varieties are able to withstand the winter cold when frosts reach 30-40 degrees.
A place for planting should be chosen for this thermophilic culture, sunny, out of reach of cold northerly winds. Then, with good care, apricots in the Urals can give a good harvest.


Their varieties should be selected according to the climatic characteristics of this region. Apricot does not pretend to be soils with high fertility. It can also grow in clayey areas. Only light sandy soils are not suitable for him.
When to plant an apricot?
Like other horticultural crops, apricot trees are best planted in the ground in the spring, before the buds swell, around April. If you choose autumn time for planting, then there is a high probability of freezing of the plant. The risk increases during winters with little snow, which is due to insufficient development of the root system for overwintering.
Features of planting in spring
It is important for spring planting to do early watering and fertilize the seedling as quickly as possible. You cannot plant a plant if its buds are already swollen - this is destructive for it. Basic tips for planting in spring:
- Prepare a hole for planting a tree in the spring in the fall.
- To protect the apricot from excess moisture, make a drainage pad at the bottom of the pit.
- The dimensions of the pit for planting a tree in spring should be at least 70x70 cm.
Features of planting in the fall
Planting apricot seedlings in autumn will harden the plant. If about a month passes between planting and the first frosts, then the root system will be able to firmly and successfully take root in a new place. Basic tips for planting apricots in the fall:
- Plant the apricot on the sunny side and in a low elevation.
- Dig up the soil before planting a tree, to a depth of at least 20 cm.
- Fertilize the soil before planting with mineral fertilizers.
- The depth of the planting pit must be at least 70 cm.
Selection of seedlings
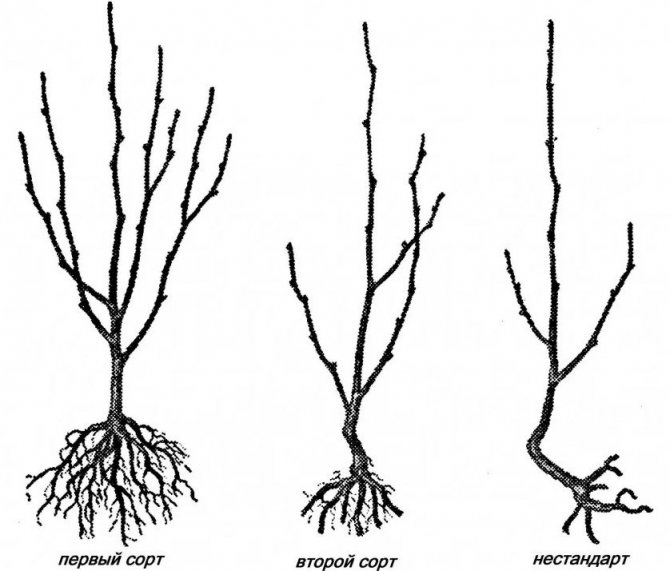
The choice of quality planting material is of great importance for the future harvest. It is best to take well-developed seedlings of the first year of growth. When purchasing them, you should pay attention to the absence of thorns, which are characteristic only of wild-growing varieties.
Branches of cultivated species must be necessarily thick, with a small thorn that forms at the site of grafting. You should not take seedlings with signs of freezing of the root system or a dried aerial part. The likelihood that such plants will take root is practically nonexistent.
How to choose the right stock
The basis for grafting and the future tree is the stock. From it, the plant inherits fertility, resistance to difficult environmental conditions, and longevity.


Grafting apricot for the bark
Therefore, it is important to choose a stock for apricot cutting.:
- compatible with a scion, resistant to cold;
- undemanding to soil moisture conditions;
- adapted to local climatic features;
- possessing a powerful developed root system,
- not weakened and not infected pests or microorganisms, only a healthy plant.
There are rootstocks cultivated, wild, weak and vigorous, vegetative and seed.
For the stock, a specially grown tree, wild growth, a broken tree, or just an unsuccessful variety / specimen are chosen.
Planting seedlings
Usually, apricots are planted in the Urals in the spring, then during the summer period the tree will get stronger and better prepare for winter. It is recommended to dig a planting hole in the fall so that the soil settles. Its dimensions should be such that the root system of the seedling fits easily, usually they make a depth of about half a meter, and a diameter of at least 70 centimeters.


It is necessary to plant apricots in the Urals (it is recommended to cultivate it with the obligatory consideration of all requirements), observing the distance between the seedlings of at least five meters. The potting mix should be composed of several components. These are, as a rule, peat, clay, sand with a small addition of manure and lime flour. It's a good idea to add a mixture of superphosphate and ash (500 g and 2 kg, respectively).
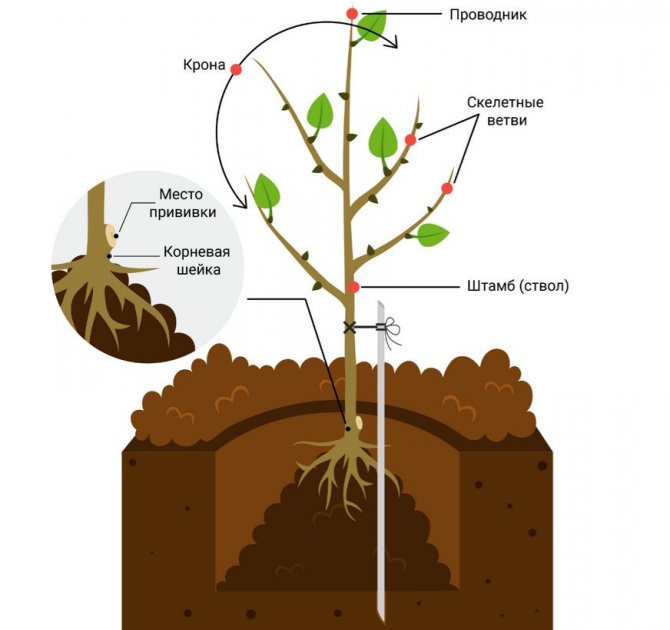
In the center of the planting pit, a peg is driven in, necessary for the future garter of a tree, around which a hill of soil mixture is poured. Before this, a drainage layer must be laid, which can be gravel or small pebbles. Then the seedling is placed in a hole, while its roots are gently straightened and covered with earth. Before planting, they are dipped in a soil mash. The root collar should not be deeply buried; it should be about 4 centimeters above the soil level. The plant is tied up and properly watered around the periphery with water.
Tree propagation methods
Propagation of apricot by cuttings helps to get a new seedling at no extra cost. The main thing is to adhere to the basic recommendations. This will help you get a zoned seedling.
Undergrowth
The growth around a common or bush apricot is usually the result of animal damage to the tree. Also, severe frost or improper pruning may be the cause.
It is required to dig up a one-year shoot. It should grow as far away from the mother tree as possible. It is planted separately. Propagation by shoots is possible only if the apricot is own-rooted.
Growing from a bone
The plantings obtained from the seed have a stable immunity to local conditions. The drupes are washed under running water and planted to a depth of 6 cm. It is better to do this in early or mid-autumn. From above you need to sprinkle the soil with humus.
You can also land in the spring. In this case, the bones are placed in a box with wet sand for the whole winter. After warming, they are transplanted.
A young sprout is covered with a plastic bottle for the winter.
Apricot care
In the Urals, it has significant differences. You have to start taking care of a young seedling from the very first days of planting. The spring thaw is the most dangerous period for plants. When a large amount of snow melts, the root collar may be flooded, which can cause its podoprevanie and eventually lead to the death of the tree. Therefore, care includes the obligatory mulching of the soil and the removal of excess water.
In the future, the apricot needs timely watering, feeding and pruning. This drought tolerant plant does not require much water.More frequent watering is required only during the period of fruit setting and ripening.
Covering apricot trees for the winter
This culture is naturally thermophilic. Until recently, it did not grow at all in Russia due to unfavorable climatic conditions. Thanks to the breeders, new winter-hardy varieties have been developed - "Lel", "Alyosha", Nikitsky ". Nevertheless, the seedlings are still covered for the winter.
We cover the apricot for the winter with a cloth
Shelter is the most important stage of preventive autumn procedures and is carried out as follows:
- the soil around the tree trunk circle is mulched - with straw, hay, sawdust (optional);
- the root collar is wrapped in an airtight material - burlap.
If you live in the northern regions of the country, then you will need to completely cover the tree with a film with fixation on stakes. As a rule, young trees are covered - not older than 5 years, adult trees do not need this procedure.
Top dressing
Depending on age, apricots are fertilized in the Urals. Cultivation without top dressing in this climatic zone is impossible, but their excess can negatively affect the development of the plant. Disease resistance decreases, the process of fruit ripening slows down, and shoots grow rapidly.
Upon reaching the age of two, plants need up to 15 kg of organic fertilizers with the addition of superphosphate (130 g), ammonium nitrate (50 g) and potassium chloride (50 g). For a plant whose age is 4-5 years, the amount of these components should be doubled, for an 8-year-old - 3 times, etc. Potassium has a very beneficial effect on apricot, increasing yields, improving the taste of fruits and affecting their size.
Useful properties and uses of apricots
Why are summer residents so eager to grow at least one apricot tree on their site? What is so special about these fruits? The first and one of the most important reasons that comes to mind is the very special and incomparable taste of apricots. What could be more pleasant than aromatic jam from apricots grown on your site? In addition to their high taste, apricot fruits contain:
- carotene;
- vitamins B1, B2, B6;
- vitamin C;
- vitamins P, PP;
- potassium;
- iron;
- magnesium;
- phosphorus;
- iodine;
- calcium;
- lemon acid;
- tartaric and malic acids;
- inulin;
- tannins;
- dextrin;
- starch;
- pectin.


Ripe apricot fruits can contain up to 27% natural sugars, thanks to which apricots perfectly satisfy hunger and are widely used in dessert dishes. Due to their rich composition, apricots are especially useful for people if they want to:
- improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- activate metabolism;
- have a beneficial effect on the work of the cardiovascular system;
- to carry out the prevention of anemia;
- activate the brain and improve memorization processes;
- relieve overstrain, have a beneficial effect on the work of the nervous system;
- reduce high blood pressure;
- antioxidants contained in apricot fruits, according to some reports, can reduce the risk of developing cancer of the lungs, stomach, esophagus;
- balance hormones and saturate the body with some vitamins for pregnant women;
- get a daily dose of vitamin A for an adult by drinking 150 grams of fresh apricot juice;
- assist in the treatment of bronchitis, laryngitis with apricot oil;
- dried apricots are a valuable food product for pregnant women, children and the elderly.
Apricots, as you can see, can be of great benefit to the human body. Traditional healers have long taken note of this "fruit of longevity" and are often used in the preparation of recipes for traditional medicine. For example, apricot fruits have shown their good effect in the treatment of bronchitis, bronchial asthma, laryngitis and other respiratory diseases.A recipe based on apricot kernels in the fight against similar ailments has become very popular. You will need to grind 20 grams of nucleoli into powder and take it in 1 tsp. during the day with tea or water.
Apricots are used not only as food products, but also:
- in pharmacology. Many medicines contain apricot oil, which has a low viscosity and is perfect for dissolving many medicines;
- in cosmetology. Cosmetology successfully uses both apricot oil and the seeds of these fruits, which, when crushed, act as an excellent natural scrub;
- in the manufacture of musical instruments. Apricot wood is a valuable species for the creation of wind instruments;
- in the production of alcoholic beverages. For this purpose, even an apricot kernel is often used, the extract of which is used to flavor wines and liqueurs;
- in cooking. This is perhaps the widest range of applications for apricot fruit. Housewives have long learned from it to make amazing jams, preserves, marmalade, they are often used for baking, etc.


Contraindications to the use of apricots
Despite the fact that the composition of apricot fruits is rich in valuable trace elements and vitamins, some categories of people should partially, or even completely, refuse to eat these fruits. It is worth taking apricots with caution if you have:
- gastritis with increased acidity of the stomach;
- gastrointestinal ulcer;
- if you have diabetes mellitus, then it is worth giving up apricots due to the excessive sugar content in their composition;
- if you have liver disease or pancreatitis;
- if you suffer from a lack of vitamin A, while simultaneously having problems with the thyroid gland, then using only fresh apricots to replenish the reserves of this vitamin is ineffective;
- if you eat a large enough amount of fresh apricot at a time, then this can provoke diarrhea;
- it is better not to eat fresh apricots on an empty stomach, because digestion problems may appear;
- if you suffer from low blood pressure, then eat dried apricots with caution, because it can lower blood pressure even more, slow down the heartbeat.


Seasonal work
Planting apricots in the Urals requires certain work related to caring for the plant, which depends on the season. In autumn, this thermophilic tree must be prepared for frost by creating conditions suitable for wintering. If this is not done, the plant may die. Roofing material or roofing felt is wrapped around the tree, securing with wire or rope. Such a "fur coat" will protect the plant in winter from temperature extremes and severe frosts.
After harvesting, the lower part of the trunk must be whitewashed so that the tree does not turn into a wintering place for insect pests. Pre-winter whitewashing ensures that various insects do not settle in the bark.
How to grow an apricot in the middle lane?
There will be no particular trouble in such latitudes with this fruit tree. If the spring is very rainy, then in order to maintain flowering, you need to spray twice. Potassium must be added to the soil under the apricot. Spring pollination with sweet water will help improve pollination of different varieties of apricot.
On the video - growing in the middle lane6
Harvesting takes place when the apricot is fully ripe. So that they can then be canned, they must be harvested in dry weather. But how to grow an apricot from a stone, and what you should pay attention to, is described in great detail here.
Pruning
The cultivation of apricots in the Urals, the varieties of which give a high yield under these conditions, is impossible without pruning. This procedure is carried out in the spring. The branches growing inside the crown are removed.


Pruning well stimulates the growth of new shoots, which are distinguished by higher fertility. It is on them that the bulk of the apricots is formed.In addition, the risk of overloading the tree is eliminated. Trimming the crown allows you to adjust and shape it in the right direction so that a huge tree does not grow with a handful of fruits at the very top.
Usually, the crown is formed in a sparse-tiered type, when the branches are located at intervals of 35-40 cm. The most abundant fruiting occurs on shoots that are 2-3 years old. It is recommended to remove old branches in time. But too intensive pruning should not be carried away. This can lead to lower yields.
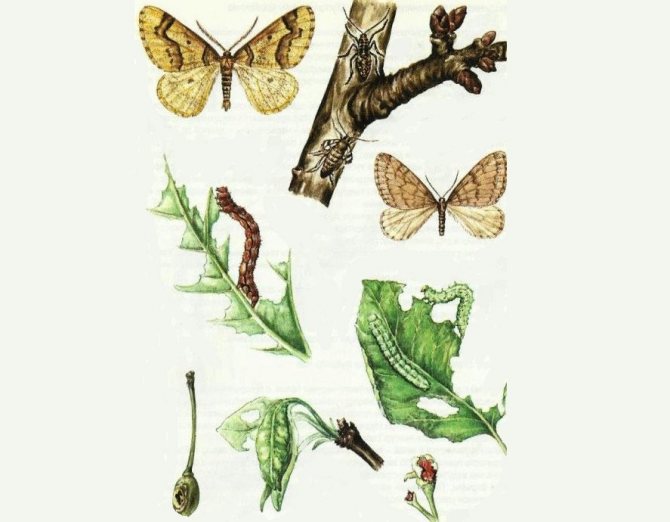
Pests
There are many insect pests that can infect apricots. In the Urals, the cultivation of this tree is also not complete without their participation. The main one is aphid, which can weaken the plant and destroy the crop. To combat this pest, spraying the tree with infusion of tobacco, dandelion and ash is used. But mechanical cleaning will be much more effective.


The hawthorn butterfly caterpillar is another of the pests that often inhabit the apricot.
The most dangerous thing is the appearance of a black goldfish on a plant. Only one larva of this insect, which manages to penetrate the root system, is capable of destroying the entire tree. The main method of dealing with it is spraying the plant with Bordeaux liquid. The procedure is performed in the fall, when the leaves fall.
Protection from pests and diseases
There are many diseases and pests that can harm the apricot. How to carry out prevention correctly?
In early spring, until the buds swell, a urea solution is used to treat the plant (700 g of substance per 10 l of water). If you do not have time before the swelling of the kidneys, then you can no longer use urea. In this case, copper sulfate, Bordeaux liquid or the previously listed drugs are used. In parallel with this, you can use a solution of "Zircon" or "Ekoberin". They will increase the apricot's resistance to weather conditions and pathogens.


In order to destroy the ticks living in the bark of a tree, colloidal sulfur or "Neoron" is used. Decis or Kinmiks help well against weevils and leafworms. It is important to do the treatment when the air is already warm (+18 ° C), but the tree has not yet bloomed. After flowering, it is desirable to carry out preventive treatment with "Oxyhom" or "Ridomil". These drugs are an excellent remedy for moniliosis.
While the fruits are ripening (no later than a couple of weeks before the start of the harvest), it is allowed to process the tree with "Horus" or colloidal sulfur. This will help with coccomycosis.
After the apricot has shed its leaves, the tree must be treated with urea again. It is also very important to remove all the leaves and burn them, as they are an excellent breeding ground for pests. The owners who know how to care for their apricots always get a good harvest.
Diseases
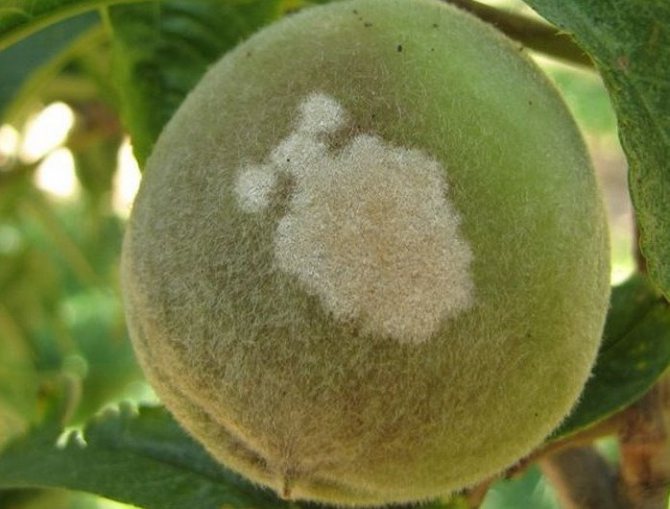
It is worthwhile to thoroughly study all possible plant diseases and preventive measures before planting an apricot. In the spring in the Urals, there are sharp fluctuations in temperature, which makes trees too susceptible to various diseases caused by fungi and bacteria. The most common of these is moniliosis. The causative agents of this disease caught on the flowers lead to its drying out and, moving inside the branch, affect all the shoots. If you do not take action on time, you can lose up to 80% of the crop. All infected fruits and other parts of the plant should be removed immediately and the tree should be sprayed with Bordeaux liquid.
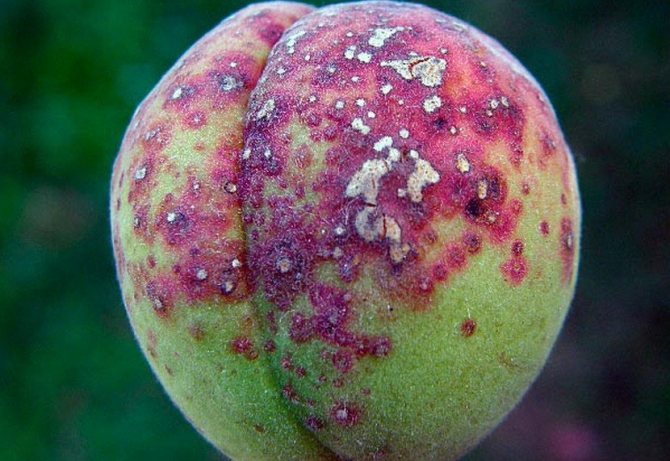
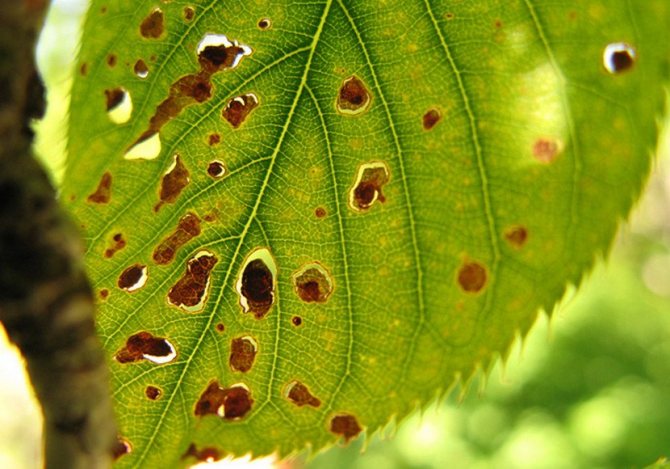
No less dangerous disease is clotterosporiosis (perforated spot). First, small specks appear on the leaves with a purple border around the edges, which gradually turn into holes. On fruits, similar spots form scabs. Bordeaux liquid is also used for treatment, spraying swelling buds in spring and tree branches after foliage falls in autumn.


Vertical wilt can cause the entire tree to dry out.The lower leaves turn yellow, fall off and, once in the ground, infect the roots of the plant.
Any disease is easier to prevent, so it is worth paying more attention to prevention. To do this, it is necessary to burn all infected parts of the plant, apply a sufficient amount of nitrogen fertilizers and prevent waterlogging of the soil.
Observing all the rules of agricultural technology and carefully looking at the trees in order to provide assistance in time, in general, it is not difficult to get a healthy apricot in the Urals. Cultivation, photos of damaged plants and methods of treatment, correct pruning - all this must be carefully studied so that in the future harvesting can only bring positive emotions.
Possible problems when growing apricots
It happens that an agrarian who grows an apricot in the middle lane is faced with a problem when a magnificently flowering tree suddenly does not give ovaries, or does not bloom in the spring.
Why apricot does not bloom
First, it should be noted that most varieties of apricot yield irregularly. This means that one year the tree is completely covered with fruits, and the next season only a few fruits hang on it.
Possible reasons why the apricot in the middle lane does not bloom on time:
- some varieties zoned in the middle lane begin to bloom not at 3, but at 6–8 years (you just have to wait);
- instead of a varietal seedling, a seedling of unknown nature was purchased;
- the climate of the middle zone is not suitable for this variety;
- the seedling was planted in the ground at the wrong time, in the wrong place or at the wrong time;
- the tree is frozen, sick or severely damaged by pests;
- improper care of apricot (incorrect pruning, excess fertilizer).
A warning! The correct choice of varieties, seedlings and adherence to the rules of agricultural technology developed for the climate of the middle zone will help to avoid most of the listed problems.


Why apricot does not bear fruit
In the event that there were a lot of flowers, but the fruits did not wait, you should figure out why the apricot does not bear fruit and what to do:
| External manifestations | Cause | Solution to the problem |
| Apricot sheds ovaries | Lack of nutrients | Regular watering and feeding |
| The tree sheds flowers without even forming ovaries | Lack of pollination | Planting a number of pollinator varieties or attracting beneficial insects |
| Inflorescences fell off after a night cold snap | The flowers are frozen | Next year, you need to postpone flowering 2 weeks later, in June, half cutting off young shoots |
| Apricot bears fruit well after a year | Perhaps a feature of the variety | No need to do anything |


Root collar heating
With the arrival of spring, the water that appears on the soil surface, sometimes freezing, then thawing again, causes the death of cambial cells. A tree with a podoprevaya root collar can actively bloom, but after a few weeks it slowly dies. This is the most common cause of the death of apricots in the Urals.
In order to prevent podoprevaniya, after the appearance of the first snow, carry out the necessary work. To do this, snow is shoveled from the root collar by 20-30 cm so that the ground is frozen. The root system of the apricot is quite resistant to frost. In March, this procedure is repeated, additionally digging grooves to drain the melt water.
Reproduction
There are several ways to plant an apricot orchard. The main thing is to know the characteristics of each.
Shoots or root suckers
This breeding method is the most popular and simplest. In this case, one-year-old shoots are chosen that are as far as possible from the mother plant. Dig it out carefully so as not to injure the underground part. This method is more relevant for apricots with their own root system; in grafted plants, shoots are obtained from the stock, and not from the varietal scion.
Growing from a bone
Several seeds are planted on the site designated for planting, of which, after germination, it will be necessary to select the highest quality ones. The apricot grown in this way is characterized by sufficient resistance to temperature extremes, high humidity and good acclimatization.
It is recommended to plant the seeds in October, having previously kept them in a container with water for 24 hours. Instances that have surfaced are not used. The selected material is deepened into the ground by 6-8 cm, maintaining an interval between them of 8-10 cm. For greater efficiency, humus, dry grass, and sand are placed on the bottom of the hole in layers. The appearance of apricot sprouts should be expected in the spring.
Apricot grafting
This method of reproduction allows you to quickly get a young plant. The rootstock is selected from a two-year-old tree of homemade plum, cherry plum, apricot, bitter almond, or peach. The barrel thickness must be 8 mm or more. The time of the operation is April or May. It is optimal to graft the apricot by copulation. The stock is trimmed at a height of 7 cm from the top, after which oblique cuts are made and applied to each other. The docking area is disinfected and isolated.
Recommended varieties of apricots
In the conditions of the Urals, it is better to use varieties specially bred for this region for planting. When planting, some of them require the presence of a tree of a different variety on the site for pollination. Kichiginsky, Piquant, Snezhinsky are the most famous apricots in the South Urals. In addition to these, there are other varieties suitable for growing in cold climates.


They are resistant to low temperatures, the short summer does not interfere with the ripening of fruits, which taste little different from their southern counterparts.
- Cupid is a winter-hardy and drought-resistant variety with a high yield, which sometimes reaches 40 kg. Fruits weighing 30 g are covered with a yellow ruddy skin. The tree is of medium height, with a rounded shape.
- Khabarovsk is a tree with a spreading crown, the yield is quite high (up to 35 kg). Fruits with a pale yellow skin and the same color pulp ripen in late July and early August.
- Seraphim - gives a regular yield of about 30 kg, ripening at the end of July. This is one of the earliest varieties. The pulp of the fruit is creamy, sweet and sour in taste.
These are the most popular apricots in the Urals. The varieties Minusinsky ruddy and Minusinsky amber are recognized as the most winter-hardy. Sibiryak Baikalova is not inferior to them.
All of the above varieties have passed the necessary tests and are recommended for planting in the Ural region.
The best frost-resistant varieties for the Urals
There are many varieties of apricot that thrive in harsh climatic conditions. In this case, gardeners usually give preference to self-fertile varieties of culture.
Mountain Abakan
This culture is characterized by a spreading crown, reaching a height of 3 meters. It is a frost-resistant variety that has flattened yellow-green fruits. In terms of taste, they are sweet and sour and have a juicy pulp. With prolonged thaw, there is a risk of fruit buds falling off. From 1 tree it is possible to get 15 kilograms of fruit.
Khabarovsk
The crop can be obtained for 4 years. Culture requires systematic care. The tree is characterized by a spreading crown. From an adult plant, it is possible to get 35 kilograms of fruits with excellent taste. The tree tolerates even severe frosts well.


Northern Lights
This is an elite variety of apricots with excellent frost resistance. At the same time, the culture can grow out. The fruit weighs about 30 grams and has a medium density pulp.
East Siberian
It is an early variety that is frost-resistant. With a prolonged thaw, there is a risk of debate on the root collar, which will lead to freezing of the culture. The fruit tastes great.
Sibiryak Baikalova
It is an excellent variety that can withstand even the most severe frosts. An adult crop yields up to 25 kilograms of apricots. They are large in size and sweet in taste.


Manchurian
This variety is characterized by a tall tree reaching 12 meters. The fruits have a sour taste and are well suited for harvesting. At the same time, the plant easily tolerates severe Ural frosts.
Chelyabinsk early
It is a versatile variety that is considered partially self-fertile. The fruits ripen early enough. The tree is medium in size and has an open crown. The fruits weigh 16-22 grams and have a light orange flesh.
Kichiginsky
It is a medium late variety that is considered self-fertile. The culture has excellent frost resistance. It produces small fruits 12-15 grams in size. They are yellow in color and rounded.


Spicy
It is a versatile variety that is considered medium late. The culture is partially self-fertile. The tree is medium in size and has a spreading crown. The fruits are round in shape and weigh 16 grams. Inside there is a yellow fragrant pulp.
Snezhinsky
It is a mid-early variety that is considered to be partially self-fertile. The plant is characterized by high resistance to frost. The tree reaches 3 meters in height. The fruits are round in shape and weigh 17-22 grams. The pulp is moderately firm and has a sweet taste.
See also
How can you propagate an apricot, cuttings and planting at home
To read
Uralets
The variety is considered medium early. The fruits have a universal purpose. The tree is medium in size and has a spreading crown. The fruits are round and yellow in color. Inside there is a delicate sweet pulp.