A common strawberry berry is a frequent visitor to summer cottages. It has a fragrant aroma, delicate taste, but pleases with fruits only 1 month a year. To the delight of fans of this culture, breeders have bred varieties that bear fruit until mid-autumn under the general name remontant strawberries. The cultivation and care of these varieties is discussed below.
Repairing strawberries: growing and care
Features of remontant strawberries
It is a berry crop represented by a perennial herb. Suitable for planting in open and closed ground. A distinctive feature of all remontant varieties is long flowering and fruiting from the beginning of summer until the first frost.
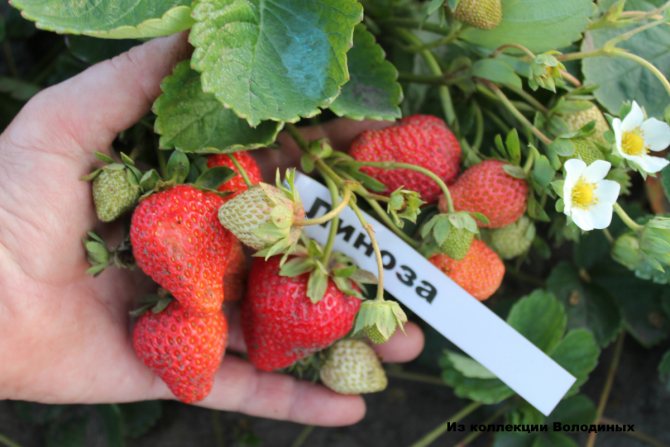
Depending on the size of the berry, it can be large-fruited (strawberry), but small-fruited varieties are more common. Popular varieties:
- Queen Elizabeth;
- Temptation;
- Diamond;
- Moscow delicacy;
- Albin;
- Maestro.
Bushes that do not form a mustache are very popular, which simplifies the process of leaving. When choosing a planting material, one should pay attention to the resistance to diseases typical for the culture, frost resistance and the ripening period of berries.

Preparing for winter
It is important not only to learn how to transplant strawberries correctly, but also to be able to save them until spring. Young bushes, even those that have managed to take root, require insulation.
On the eve of autumn frosts, mulch is applied between the bushes and in the aisles. Usually peat or last year's manure is used. In the Urals, in Siberia, in the central zone, the optimal cut of shelters is at the end of September, in the south - in the second half of October.
In severe frosts, when the winter turned out to be snowless, the bed is covered with agrofibre or film. But immediately after the low temperatures drop, the covering material is removed to prevent the bushes from drying out.
Choosing a place on the site
Garden strawberries are a thermophilic and light-loving culture. Even a slight darkening leads to a slowdown in the growth of the vegetative parts of the bush, and a decrease in yield.
The landing site should be well lit, protected from strong gusts of wind. This culture can be grown on a balcony, loggia, and also as a container plant on the site.
It is recommended to choose beds with loose, breathable and fertile soil. Sandy or loamy areas with a neutral acid reaction are best suited.
It is not recommended to plant strawberries in places with high humidity, lowlands and next to a pond. The best predecessors for this crop are cereal grasses and cereals, ornamental plants (except bulbs), cabbage and all members of the umbrella family.


Choosing a place
Before replanting strawberries in a new place in the fall, you must select a site. Strawberries are a fairly unpretentious crop and will grow well in almost any soil. But in order for it to give really decent harvests, the gardener needs to take care of top dressing - to fertilize the soil with nutrients and enrich it with minerals important for culture.
On a note! The ideal strawberry bed is an area where the soil contains 2% humus!
Crop rotation
Good precursors for strawberries are:
- legumes;
- onion;
- garlic;
- leaf salad;
- parsley;
- dill;
- radish;
- carrot;
- beet.
Advice! For an autumn transplant, it is best to fill the selected bed in front of the strawberries with onions or garlic, or siderates - lupines, cereals.
But we should not forget about those crops after which it is highly discouraged to plant strawberries. These include:
- nightshades, in particular potatoes;
- cabbage;
- cucumbers.
Landing dates
You can plant seedlings or grown strawberry bushes from early spring to the second half of summer. The earlier you plant, the faster the plant will begin to develop and bear fruit. The recommended period for the southern regions of Russia is the end of April, in the northern regions it is advisable to wait until the first half of May.
The air and ground temperature must warm up by at least 10 ° C. Sowing seeds for seedlings is rarely used. Planting at home is carried out starting in February. A dive into open ground with this method can be carried out as early as April.
What kind of care does she need in the summer?
After the first harvest, the plants are prepared for the next fruiting.
Preparatory work includes:
- regular feeding;
- sufficient watering;
- loosening the soil around each bush;
- cutting leaves to enhance flowering.
Feature! You need to trim the leaves carefully so as not to catch the apical bud. If inflorescences appear, including on the rosettes of the antennae, you should not touch the leaves, otherwise there will be fewer fruits.
Usually bushes live and bear fruit for up to three years, but some do not withstand the load, dying off after the second fruiting. Then, at the end of summer, new seedlings are planted instead.
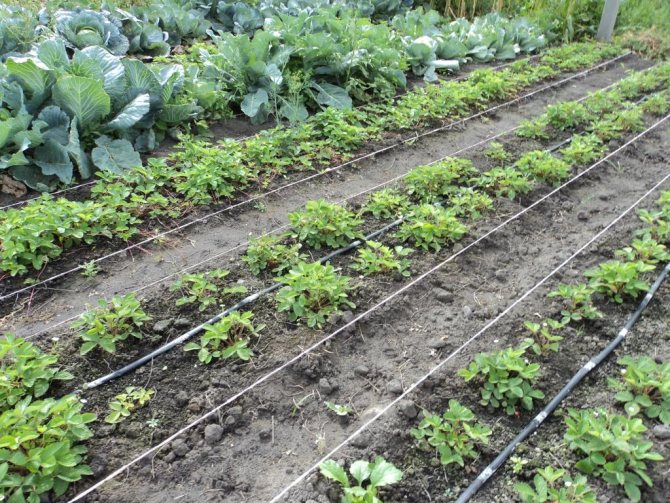
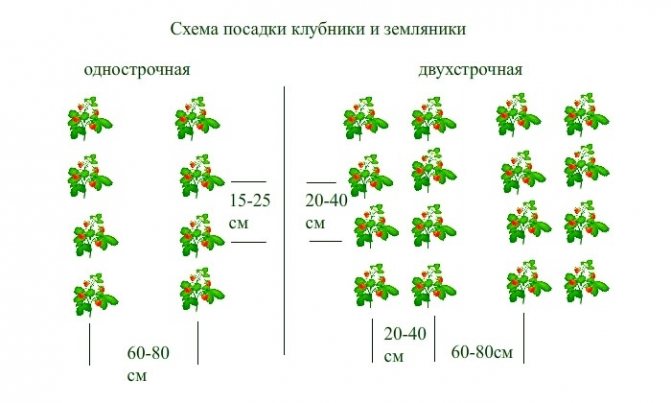
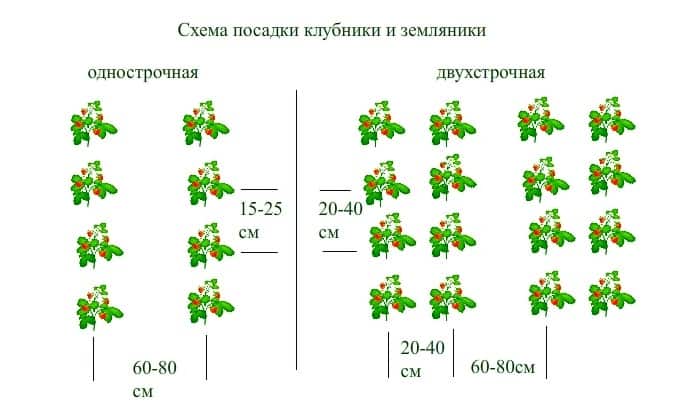
Schemes for the arrangement of bushes in the garden
Garden strawberry bushes can be planted in different ways. The choice of a planting scheme depends on the characteristics of the variety, free space on the site and the required volume of plants. The most popular methods are pipe, greenhouse, container, or line planting. The latter method is used most often. Varieties of line landing:
- One line. The maximum spacing between the bushes is 20 cm, the distance between the lines is 70 cm. At the edges of the garden, the bushes can be planted in two rows;
- Two-line. Bushes are planted every 15-20 cm, the interval between rows is 60-70 cm, and between lines is 20-40 cm.
In addition, the three-line planting of strawberries is known and is used only on large industrial farms. For ease of maintenance, the bed is covered with agrofibre or a dark film with a slot for bushes. This reduces the rate of development of weeds, simplifies harvesting.

How to grow seedlings?
There are two options - buy ready-made seedlings or grow seedlings from seeds yourself. The second method requires the creation of special conditions - soil moisture from 70 to 80%.
This requires:
- Prepare 1 kg of substrate. Light humus or universal soil will do.
- Pour 0.7-0.8 liters of water into the substrate.
- Stir gently until the lumps are completely dissolved.
- Fill molds with a radius of 5-7 cm with the resulting earth.
- Spread the seeds on top.
- Sprinkle with a thin layer of potting soil.
- Spray them with water from a spray bottle.
- Cover with glass or transparent film.
- Place in a warm place with good lighting.
It is recommended to start sowing in late winter or early spring. In warm climates, you can sow a couple of weeks earlier. Until seedlings appear, the soil is kept moist.
The optimum room temperature is 18-20 degrees. The first shoots appear after 10-15 days. After that, they require regular ventilation and additional light.
Landing technology
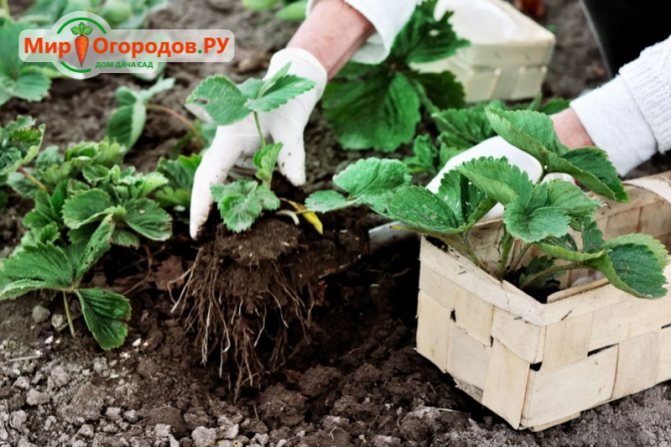
The seed method of growing strawberries is practically not used in practice. Planting material needs stratification, requires long and laborious care. Plants develop slowly.It is recommended to buy already grown seedlings, planting directly into the open ground.
Step by step algorithm:
- Carefully dig up the bed to the depth of the shovel bayonet. Remove plant residues, level the surface.
- Prepare planting holes up to 30 cm deep, the distance between the bushes depends on the growing scheme. Lay a layer of broken brick on the bottom, add 200 g of wood ash.
- Transplant the bushes together with a lump of earth, supplement the voids with a fertile substrate. In this case, the root collar should be flush with the surface. Tamp the soil around the plant.
Immediately after planting, garden strawberries should be watered abundantly with warm water. Mulch the soil or lay a shelter (film, agrofibre). The first top dressing should be applied no earlier than after 10-12 days. If there is a possibility of recurrent frosts, then the bushes are closed at night with a plastic container with a cut off bottom or spruce branches.


Reproduction methods
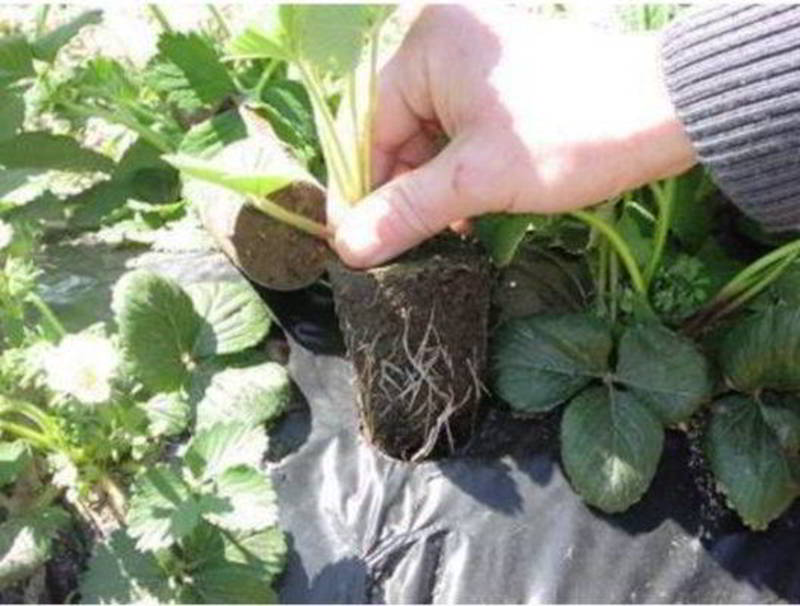
To preserve all the characteristics and qualities of the variety, you can breed with a mustache... It must be remembered that only the first generation mustache is allowed for reproduction. The process does not require special skills from the gardener. When growing strawberry bushes on a healthy plant, about five whiskers are retained, the rest are eliminated. For planting, healthier and stronger sockets are used.
Another way to propagate a plant is to divide a healthy bush into separate parts so that each crop has the right number of roots. It is necessary to divide the plant at the end of the summer season - by the beginning of September, all planting material should be planted, otherwise young crops will not have time to take root until the first frost.
Care features
Remnant strawberry is an unpretentious plant. Even a novice gardener can handle the planting care process. Basic requirements for caring for this crop:
- throughout the summer, the bushes need regular and abundant watering. It should be done at least 2 times a week. For large beds, it is advisable to organize an irrigation system in order to maintain constant soil moisture. You can not water the bushes with cold water, which leads to the development of diseases;
- soil work is a basic part of strawberry care. It is necessary to periodically loosen the soil, which is convenient to do after the next watering. It is important to replenish the layer of mulch that retains moisture on the surface and prevents hypothermia of the roots. Weeding should be carried out at least once a month;
- top dressing is started from early spring. Before flowering, nitrogen-containing compounds or organics are used, for example, water mullein in a ratio of 1:10. The second mandatory feeding is carried out during the period of bud formation, for which phosphorus-potassium compositions are suitable. The term of the last fertilization is the end of autumn, when organic matter, for example, humus or dry mullein, is introduced into the soil for the winter;
- all whisker buds should be trimmed or pinched as they appear. This avoids the spread of strawberries on the site, gives the planting a well-groomed appearance. The cut mustache can be used for further planting.
The remnant strawberry forms berries throughout the summer. Fruits should be removed immediately after ripening to ensure the development of new ovaries. Harvesting can be done by hand or with scissors. Mechanical harvesting is not recommended for all small-fruited varieties.
Preparing for winter
Garden strawberries are grown as a perennial crop. Preparing the wintering site is an important part of care. Fundamental rules:
- as the air temperature decreases in autumn, watering is gradually reduced to a minimum. Starting from the second half of October, you can cut off all deformed, diseased and weak leaves, as well as whiskers;
- you need to remove all plant residues from the garden (roots, buds, leaves and other parts of the bush), and then pour abundantly with warm water;
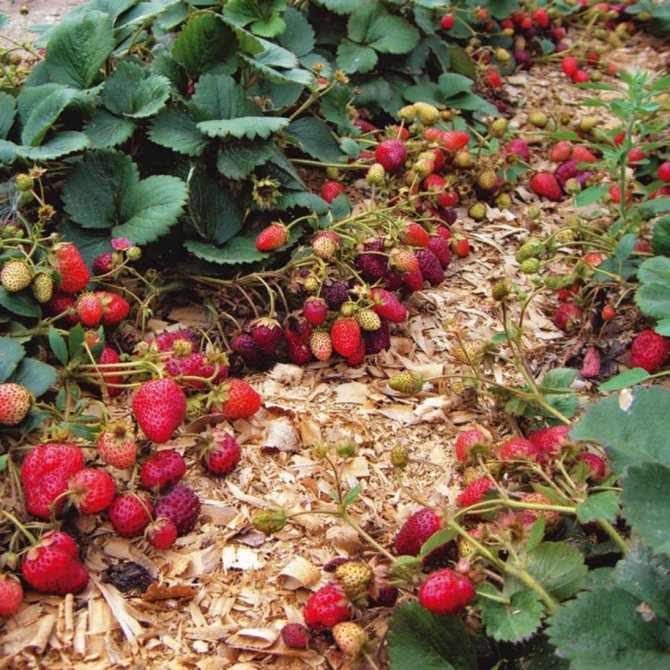
- mulch the soil with peat, sawdust or humus with a layer of 10 cm or more. In cold regions, it is recommended to additionally cover the planting with spruce branches.
If you are growing only a few strawberry bushes, you can dig them up and then place them in a container along with a clod of earth. It is recommended to store the plant in a container in a dark and cool place at a temperature not lower than 10 ° C.
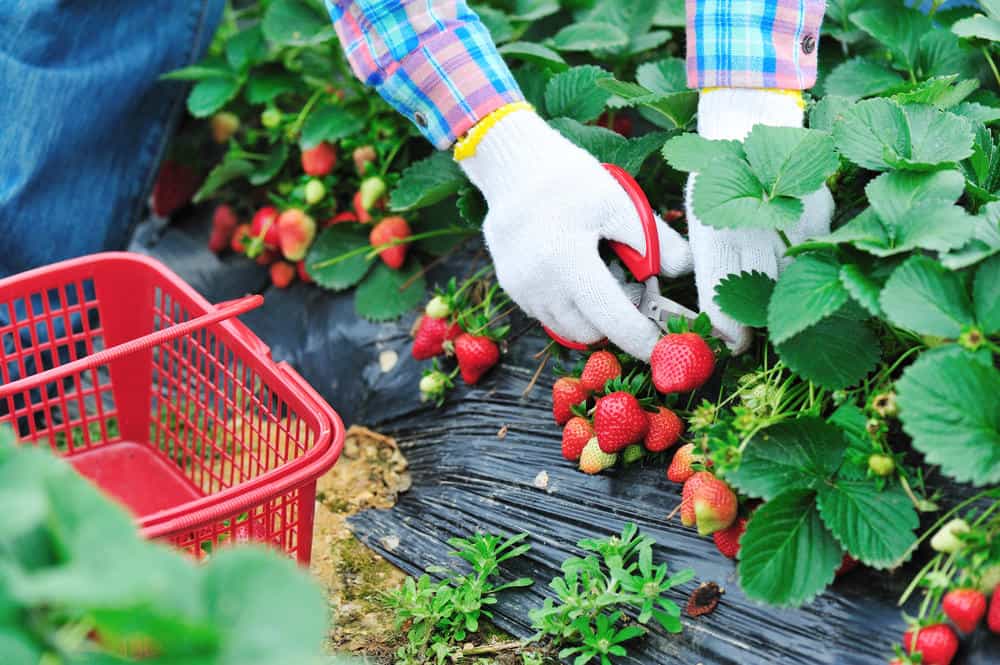


Why transplant strawberries?
To begin with, you should talk about why a strawberry transplant is carried out. This process is carried out in order to rejuvenate the plantings. This culture is not recommended to be grown in one place for more than 3-4 years, since during this time a fairly large number of pathogenic bacteria and fungi accumulate in the soil, which pose a serious threat to strawberry bushes. And if the transplant is not carried out in a timely manner, then the yield of the plants will begin to fall, and the berry will noticeably become smaller.
Important! It makes no sense to simply transplant whole bushes to a new place, since three- or four-year-old plants are considered old - they begin to throw out few inflorescences, bear poor fruit and over time their yield dwindles. Therefore, it is imperative to plant strawberries: either by dividing the bushes, or with the help of a mustache!
Transplant timing
When to transplant strawberries to a new location? This can be done in spring, late summer, or fall. But most gardeners carry out this procedure in the fall. And that's why.
In the spring - the culture transplanted at this time of the year takes root well and begins to develop very quickly, especially if the work was planned and carried out in early spring. But there is also a significant disadvantage - this year, the transplanted plants will not please with the harvest, since the first flowering will begin only next season.
In summer, transplanting can be done immediately after harvest, that is, at the end of July. Indeed, many specialized publications for transplanting strawberries recommend this particular period, since August is quite enough for plants to root well, and sometimes you can even observe young flowering. However, this can only happen if the air temperature in August is not too high and there is enough rainfall. But unfortunately, it is impossible to predict the weather and it is far from always favorable for gardeners.
As for the autumn dates, it is September for transplanting strawberries that is most favorable. And there are several reasons for this.
- First, the ground is sufficiently moist.
- Secondly, the air temperature dropped to the optimal level, but the ground was still warm.
- Thirdly, the plants have time to gain sufficient deciduous mass, with which they hide, leaving before winter.
Therefore, by transplanting strawberries in September, we give them the opportunity to take root normally before the onset of cold weather.
As practice shows, strawberries transplanted to a new place in the fall easily survive the winter and in the spring they necessarily begin to bloom. Of course, the first harvest will not be as plentiful as in biennial bushes, but the berries will still be able to be picked.
On a note! It is impossible to keep track of the weather, and the early onset of cold weather can destroy young strawberry bushes. The same situation can arise with a snowless winter! But you should not be upset, since most of the seedlings often manage to survive, and the dead young growth can be replaced with new plants in the spring!
Growing difficulties
Garden strawberries can be affected by a large number of diseases and pests. Infection is most often observed when planting in excessively humid places, if the irrigation and feeding regime is not followed. Typical diseases:
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
- late blight;
- brown and white spotting;
- leaf mottling and wrinkling virus.
If any signs of infection are found, all diseased parts of the bush should be cut off, and then the planting and soil should be treated with a chemical fungicide. Spraying is carried out in two stages with an interval of 10-12 days.
Among pests, nematodes and slugs are dangerous (especially for undersized varieties). To combat them, folk methods are used - spraying with onion or soapy water, dusting with wood ash. Chemical preparations show great efficiency.
When choosing a specific insecticide or molluscicide, one should take into account the characteristics of the lesion, the scope of the agent.
Problems often arise when growing strawberries in unfavorable conditions. These include waterlogging and drying out of the soil, insufficient illumination, a deficiency of minerals in the substrate.
The plant changes the color and elasticity of the leaves, slows down growth and stops fruiting. The problem can only be solved by correcting care.
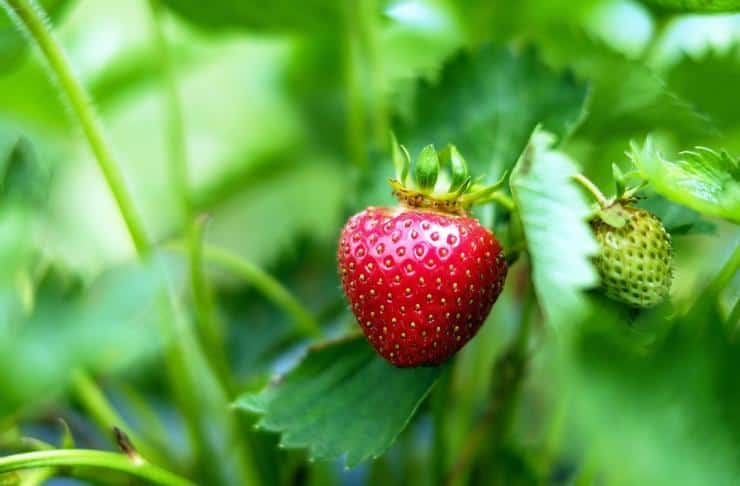


Growing in a greenhouse all year round
Repair strawberries are often used when grown in greenhouses, in conditions of regular maintenance and timely replacement of old bushes with young ones, you can get a harvest all year round. When choosing the most suitable varieties, you should pay attention to the possibility of their self-pollination, otherwise the process of pollination of inflorescences will have to be done independently, either with a brush or by installing a small hive right in the greenhouse.
Did you know? The largest strawberry was grown in the United States in the 80s of the last century, and its weight was 231 g.
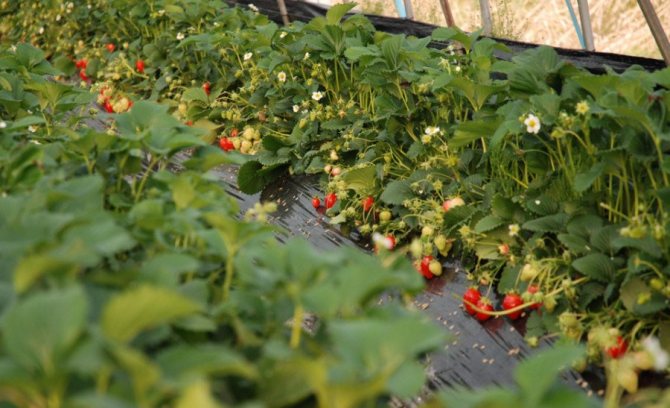
Today, there are several main technologies for growing remontant strawberries in a greenhouse, which have proven to be the most effective:
- Growing in soil - one of the simplest methods that does not require additional investments, however, it has several drawbacks - you will need to regularly and thoroughly inspect the bushes for the first signs of pests, as well as berries that can rot when in contact with wet soil.


- In pots - a frequently used method when grown in greenhouse conditions, which, however, cannot provide a year-round harvest. This is due to the rapid depletion of the soil, which is in small volumes, and therefore frequent replanting of plants will be required.


- On film or agrofibre - a new technology that implies planting seedlings in small holes made in the canvas, which completely covers the garden bed. The climate formed under the film is optimal for the growth and development of strawberries, and therefore the yield indicators with this method of cultivation increase significantly.


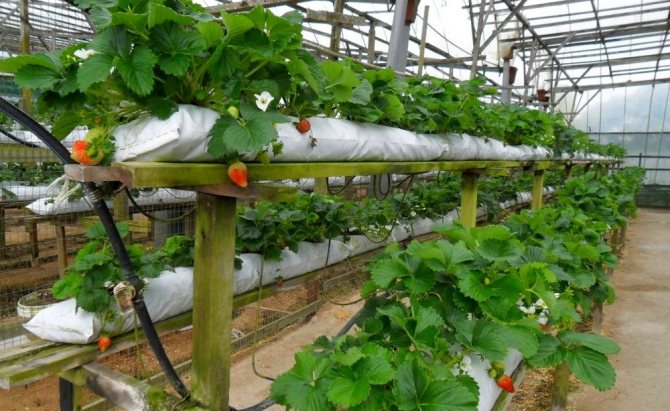
- Dutch technology - strawberries are grown in bags filled with a substrate (it has a certain similarity to growing on a film). The advantages of the Dutch technology are the ease of replacing the bags located on the racks.


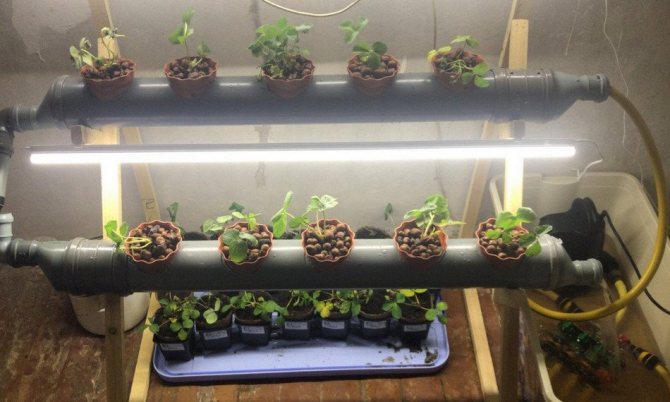
- Hydroponic growing method - implies the rejection of soil, instead of which an aqueous solution with the addition of fertilizers circulates in containers with plants.


The process of growing remontant strawberries cannot be called simple - this culture constantly needs courting and knowledge of the features of agrotechnical measures, and ignoring this immediately affects the harvest. However, the result is worth it - the opportunity to enjoy large, juicy and sweet fresh strawberries, regardless of the season and the price of this product.
conclusions
- Remnant strawberries (strawberries) are distinguished by continuous flowering, active fruiting throughout the summer.
- The plant can be grown in a greenhouse, on a balcony or in a pot. The garden bed in the open field should be located in a bright and wind-protected place.
- Planting is permissible by seed, but it is recommended to plant strawberries with already grown seedlings. The bushes are arranged in rows of 1-3 lines.
- Caring for garden strawberries includes systematic watering and feeding, trimming the mustache, mulching, as well as preparing the garden for winter.
Possible problems and solutions
Remaining strawberry varieties have the same diseases as ordinary ones, for example:
- late blight;
- powdery mildew;
- leaf spot;
- gray rot.
At the same time, modern varieties are highly resistant to most diseases, so ordinary summer residents rarely face the need to use powerful drugs for their treatment. Preventive measures are as follows:
- treatment of the beds before planting strawberries with a 1-2% solution of copper sulfate;
- disinfection of seedlings and adult plants (before flowering) with a pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- periodic spraying of plants with Fitosporin (relatively safe biofungicide);
- elimination of plant thickening and overgrowing with weeds;
- timely pruning of bushes.
Video: strawberry diseases
Of the pests, the strawberry mite remains the most dangerous. To prevent its appearance at the very beginning of May, strawberries are treated with special preparations, for example, Neoron. During fruiting, you can use the relatively safe Fitoverm: after processing, after a few days you can eat berries.


The tick is not easy to see, but spoiled young leaves indicate its presence.
How to plant small-fruited strawberries. How to grow small-fruited strawberries from seeds? Main secrets
- miscellanea
- Admin
Small-fruited garden strawberries in aroma are not inferior to wild berries. Like a large variety of this berry, it can be used to make fruit salads, jams. You can just eat it fresh.
Most gardeners grow small-fruited strawberries traditionally, planting young plants that were formed on the mother's mustache. In this case, it is enough to simply divide the plants and plant them. Growing a new plant from seeds is a rather laborious process. However, such efforts make sense.


Benefits of growing sprouts from seeds
Two important points provide the benefits of this method of growing strawberries:
- Diseases of the mother plant are not transmitted to new shoots. They are more resistant to pests;
- In addition, strawberries are not reborn, thus ensuring a stable harvest.
Yield
Fruiting of remontant strawberries depends on the length of the day, temperature and climatic zone. The formation of flower buds begins at a day length of 12 hours or more. Bushes give 3 harvests:
● early spring; ● in the middle of summer; ● at the beginning of autumn.
The peculiarity of growing strawberries is protection from strong sun and drought. In the heat, the bushes stop bearing fruit and die. Renovated strawberries are suitable for cool, mild climates.
Harvesting and Seed
The crop is harvested regularly, allowing the berries to fully ripen on the mother plant. But if this is not possible, then the strawberries are harvested and unripe. For harvesting seed, ripe berries should be selected and dried in the sun. Before sowing, the fruits are placed in a glass of water and kneaded. This technique causes the seeds to settle to the bottom of the container. Next, you need to dry the seed or pour it onto the prepared soil. You can also buy seeds at the garden center. Thanks to their high yields and easy care, remontant strawberry varieties are increasingly found in gardens and summer cottages. The taste and useful properties of berries cannot be replaced by anything. In addition, it is remontant strawberries that will allow you to enjoy berries from spring to autumn.
Content
- Listen to the article
- Description
- Growing seedlings of remontant strawberries Sowing
- Seedling care
- Picking
- When to plant
- Spring care
- Pruning in the fall
- Mustache reproduction
Secrets of growing delicious strawberries
To grow strawberries with pleasure, the harvest is high and tasty, it is worth knowing some of the subtleties. Below are a few secrets to help you succeed.
- Purchase of certified virus-free strawberry seedlings. Healthy plants are the key to successful strawberry cultivation.
- Predecessors. Avoid planting strawberries in areas where potatoes, tomatoes, and strawberries have been recently grown.
- You need to provide plenty of sunlight. Find a sunny spot. The warmth and light helps to produce sweet and tasty berries.
- Fertile and permeable soil. It is better to plant strawberries in slightly acidic soil 6-6.5 pH. Mix the soil with compost or manure about a month before planting. Granular manure (easy to use, natural, safe and odorless) is also a great solution.
- Agrotextile against weeds. Don't let weeds compete with strawberries. Black agrotextiles naturally prevent the development of weeds, while allowing water and air to pass through, retaining moisture in the soil. Strengthens the root system and speeds up the growing season. An additional advantage of using agrotextile is the collection of pure and unsorted berries. It is worth additionally spreading straws under the plant during the flowering season, which will reflect the sun's rays and the fruits will not ripen so quickly.
- Space. Plant the seedlings about 30 centimeters apart, with a row spacing of 50 centimeters. Strawberry roots should not curl. Be careful not to plant the strawberries too shallow, so that the roots do not dry out or too deeply.
- Pick ripe berries on a sunny day. To keep your strawberries fresh and firm for longer, pick the fruit with a stem at least 1 cm long.
- Replace old plants every 3-4 years. Strawberries will become unproductive after this time. It is best to replace them with new ones, free from diseases and pests.
When growing strawberries with repeated fruiting, it is imperative to take into account the peculiarities of its development, the plants must be properly cared for. It is possible to hope for high yields only if these conditions are met.


Open ground landing rules
Sowing of remontant strawberries begins early - at the end of February, or in the first week of March. It is carried out as follows:
- Pour into seedling container loose earth and pour water on it.
- Spread the seeds evenly on the surface and lightly press your fingers into the ground. It is not necessary to cover with earth.
- Cover the container with glass to create a greenhouse effect and place on a windowsill.
- Moisten the ground periodically from the spray bottle and lift the glass for ventilation.


Growing seedlings of remontant strawberries: temperature - 20-22 degrees, bright lighting - 12-15 hours a day, regularly ventilate containers
Strawberry seeds hatch long enough - from 20 to 30 days... When the sprouts hatch, and 3 leaves appear on them, the seedlings need to be dived.
You can plant strawberries on open ground as soon as the night frosts stop.
The plant is capricious about the planting site. If cucumbers, tomatoes, cabbage or potatoes were previously grown in this place, then the berry will not grow there. It is better to choose an area where beans, garlic, dill or parsley grew before. The soil will also contribute to a rich harvest of berries after bulbous flowers - tulips, hyacinths, crocuses.
The most optimal planting method is considered to be a two-line bush. It will relieve thickening and protect the plant from fungal infections.... With this method, a distance of 30 cm is left between two lines in the tape, and 70 cm between the tapes themselves. In the rows, the bushes are seated at a distance of 25-30 cm from each other.
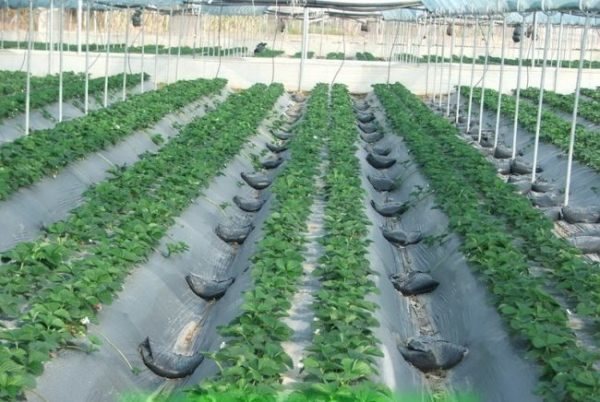


Two-line system for growing remontant strawberries in a film greenhouse
It is popular with gardeners and a combined planting method, when strawberries are alternated with other crops. Most often, garlic acts as its neighbor, which protects the strawberries from the invasion of slugs.
The technology of direct planting of bushes in the ground includes the following stages:
- Loosen the soil on the bed and form holes in it 25 cm wide, long and deep.
- Thoroughly pour the holes water.
- Add top dressing to the soil... Take a bucket of compost mixed with vermicompost in the amount of 2 liters on a bucket of earth. You can also add 2 glasses of ash there.
- Plant seedlings... Spread out the roots, they sink vertically. In this case, the apical kidney is located strictly above the surface.
- Water the planted bushes water.
- Mulch the ground in a thin layer... To do this, use dried grass, needles, compost, but not straw, it is too tough for young plants.
That's it, most of the work is done. Now it remains only with the help of proper care to create conditions for strawberries for active fruiting.
Diseases and pests


The most common diseases of garden strawberries:
- Powdery mildew;
- Black rot;
- Gray and white rot;
- Root rot;
- Withering;
- Mottling;
- Mosaic.
Insects are another problem:


Aphid;- Ants;
- Strawberry nematode;
- Pennitsa;
- Strawberry weevil;
- Spider mite;
- Slugs;
- Ants.
Timely prevention becomes the best measure of control.
It includes replanting shrubs regularly and planting plants that smell unpleasant to insects next to beds. Also, severely affected plants are removed to avoid spreading the problem.
Remaining strawberry varieties
Most of them grow in the form of bushes, although hanging berries are also found. It can be planted in hanging pots.
Among the popular varieties are:
- Mice Nova is distinguished by its very sweet fruits.
- White dream - with a pineapple flavor.
- Arapaho - gives a high yield.
- Lyubasha is frost-resistant.
If you provide proper care for remontant strawberries, they will delight you with a good harvest twice a year and large, juicy berries.
5 / 5 ( 3 votes)
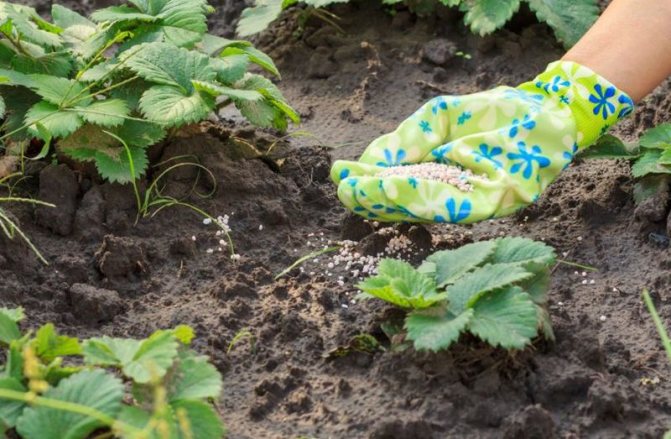
How to fertilize correctly?
Top dressing of remontant varieties provides a high yield and at the same time prolongs the life of plants. They regularly need potassium and nitrogen. If enough phosphorus was added before planting seedlings, it will not have to be added again during growth and fruiting.
To fertilize properly, you must:
- mulch the beds with humus at the rate of 2-3 kg per sq.m. or with manure - consumption 5-6 kg per sq.m .;
- at the end of spring, fertilize with a 1-2% urea solution;
- in mid-June, add chicken droppings - 8-10 parts of water per bucket of droppings;
- make 10-15 dressings throughout the season;
- use mineral fertilizers.
You need to feed it until late autumn so that the plant does not enter weakened and exhausted during the period of calm.
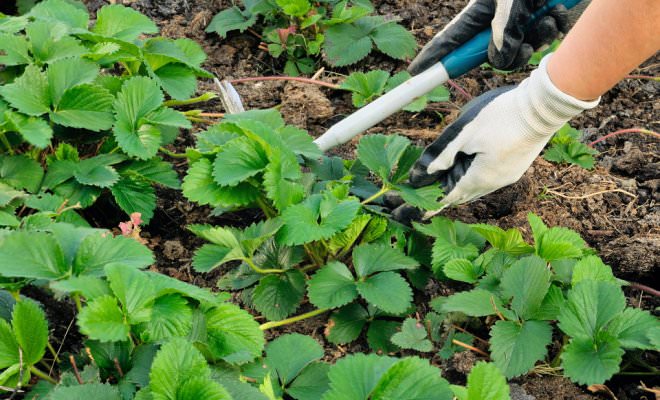


Pruning
Excess or unhealthy leaves and whiskers can be removed twice a year - with the onset of autumn or spring. In the first case, preparations are underway for wintering, and in the second, for the first harvest.
What you need to know about autumn?
After harvesting the autumn harvest of berries, the leaves are carefully removed from the bushes. This avoids infection and pest exposure.
Cropping is done as follows:
- for the winter, only full-fledged shoots that are ripe are left;
- the sinuses of the upper leaves should remain intact - this is the basis for fruit buds for the next year;
- sharp garden shears are used - you cannot tear it off with your hands so as not to damage the plant;
- after removing the leaves, the site is treated with drugs for parasites and diseases;
- The antennae can be trimmed throughout the season, but this is not necessary.
Attention! If the leaves are removed before the onset of winter, then the mustache is removed along with them.
Spring
During the removal of leaves in spring, the following rules are followed:
- Bushes get rid of old, yellow leaves.
- Leaves are removed that have not been cut from the last season.
- Next, you need to process the beds from pests and infections.
New and healthy greens grow back faster.