A simple and familiar vegetable zucchini has its own nuances of planting and care. Experienced gardeners have known them for a long time, and novice farmers have many questions. How to plant zucchini, where they grow better, what varieties to choose - these problems have to be solved before planting dates. An unpretentious vegetable gives good germination and a bountiful harvest. You can plant it with seeds or seedlings, the main thing is to do it on time and properly prepare the garden bed.

Botanical features
Zucchini is a herbaceous annual plant belonging to a variety of hard-bore pumpkin. The plant can be bushy, semi-bushy and long-growing.
Bush squash has an erect, thick stem with hard pubescence. The leaves are arranged on long petioles. They are large enough with pointed blades. The color is light or dark green. Some varieties - with white spots, have a rough, prickly pubescence.
The root system of zucchini, located in the arable layer, is quite powerful, and consists of tap, lateral, and adventitious roots.
The flowers of the plant are dioecious - on the same bush there are both female and male flowers of yellow color, large, bell-shaped.


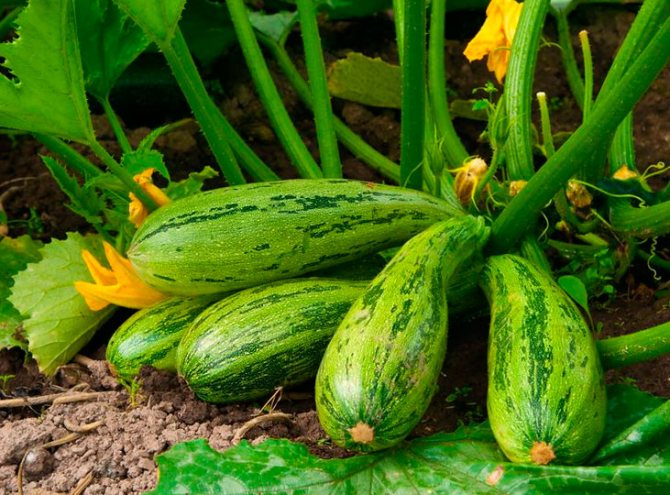
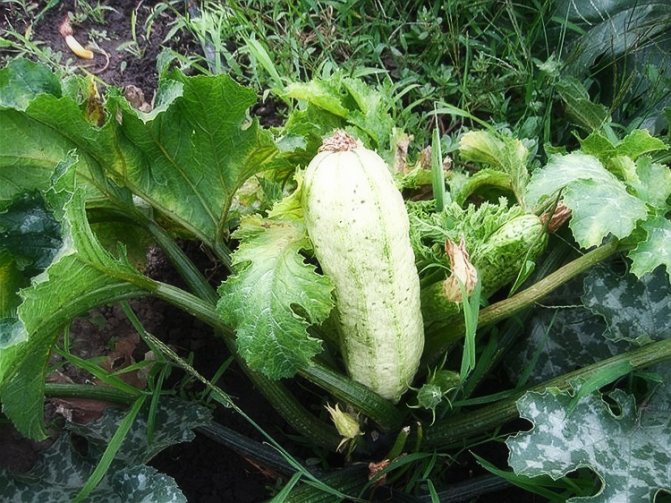
The fruits have an elongated cylindrical shape, sometimes slightly curved. The color can be white, light green, dark green. There are varieties with bright yellow fruit color.
Vegetable care
In order for the squash to grow into a strong plant and produce a rich harvest, a number of standard procedures must be followed, such as loosening and weeding the soil, watering the plant, and controlling diseases and pests.
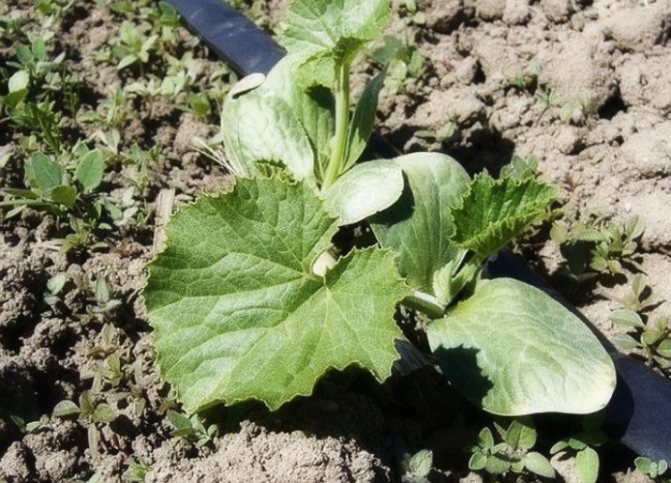
In order for a vegetable to reproduce according to temporary norms, it is necessary to periodically weed the beds. This is done for the first time 7 days after landing. When the seeds / seedlings have germinated so that several young leaves are formed on the sprouts, the zucchini can be hilled.
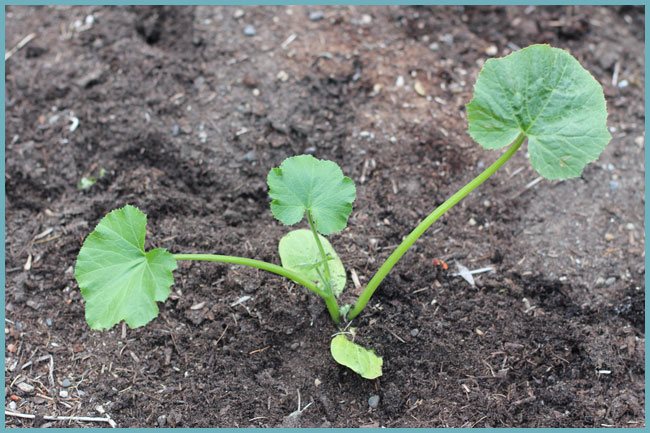


Planting zucchini in the ground
To make the side shoots grow more actively, you can pinch the main stem. When the propagation of lateral roots begins and the leaves gradually close up, the soil can be loosened and weeded again thoroughly.
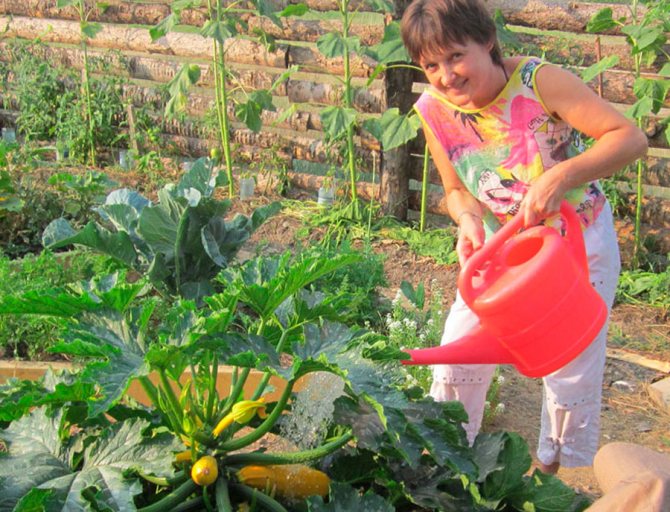
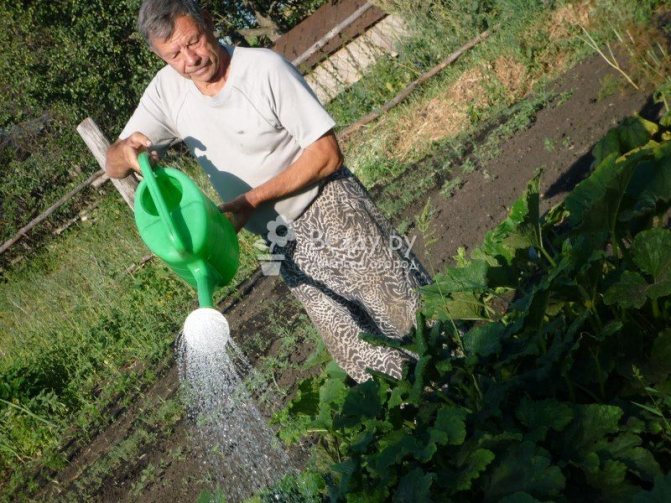
It is better to water zucchini after sunset with water warmed up by the sun. In hot weather, watering should be daily, and when the leaves close and cover the ground, the soil can be moistened less often - a couple of times a week.
Advice. Pour water only at the root, in no case should it get on ripening fruits or leaves, otherwise they will simply rot. If the leaves begin to wither from hot weather, you can moisten them using a special nozzle with small holes.
Fertilizing and feeding zucchini
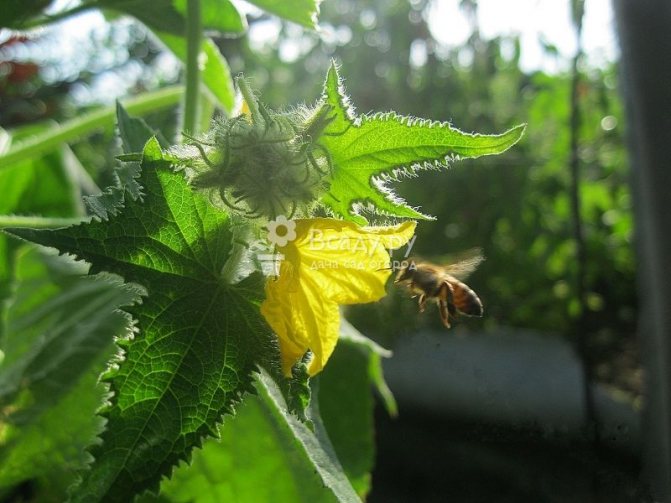
In order for the zucchini to give a good harvest, it is necessary (if necessary) to help it pollinate. To do this, the pollen from the male flower is transferred to the female pistil (you can find the corresponding photos with a detailed description of the process on the Internet). You can also use "heavy artillery" - pollinating insects. To lure them in, spray the plants with honey / sugar water every day.
Zucchini is very fond of organic fertilizers, so do not regret this good. You can prepare an excellent herbal infusion for young seedlings.To do this, put the weeds remaining after weeding into a barrel and fill it with water (be sure to stir the infusion periodically). After a week of infusion, the fertilizer can be drained, mixed with water in a ratio of 1: 8 and water the soil. This must be done very carefully so as not to catch the sprouts.
Secondary feeding must be carried out in a week (with the same infusion). The third time - when the first ovaries appear. Be sure to add double superphosphate (1 tablespoon) and 250 g of wood ash to the fertilizer.
Advice. Before each feeding the plant, it is advisable to water it.
We fight pests and diseases
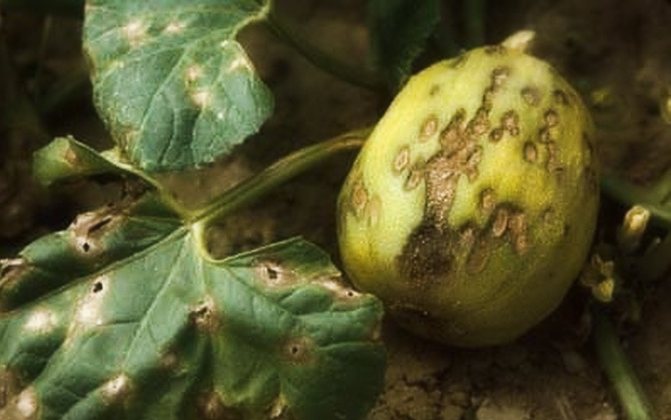
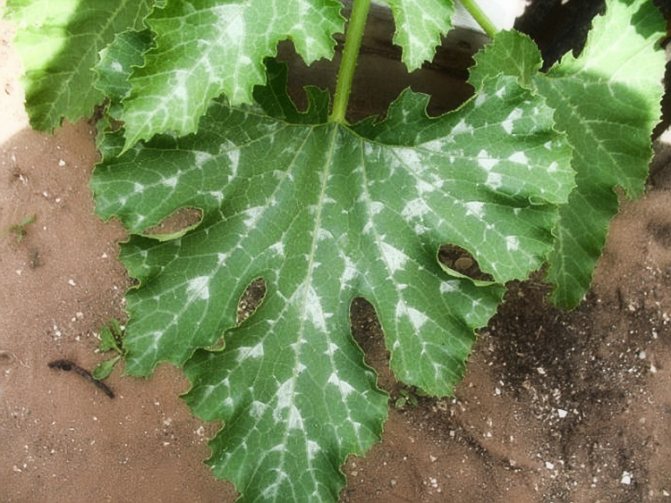
Even with excellent care, squash sometimes suffers from disease. Most often, this representative of the squash family affects several pests and diseases, such as slugs, whiteflies, melon aphids, powdery mildew, etc.
Whitefly is a very big problem for squash gardeners. The main sign of their presence is white sticky discharge that forms on the leaves from the underside. This provokes the development of sooty fungi, destroying the leaves of the plant over time. The easiest way to get rid of the pest is to rinse the leaves with water. If this does not help, then use a special insecticide.
Slugs must be collected by hand. If their number is too large, you can make a kind of bait - pour dark beer into small cans and place them on the site. The slugs will surely react and "run away".
Aphids take the juices from the plant, thereby damaging all its parts. An excellent method of dealing with it is to treat the plant with a soap solution (300 g per bucket of water).
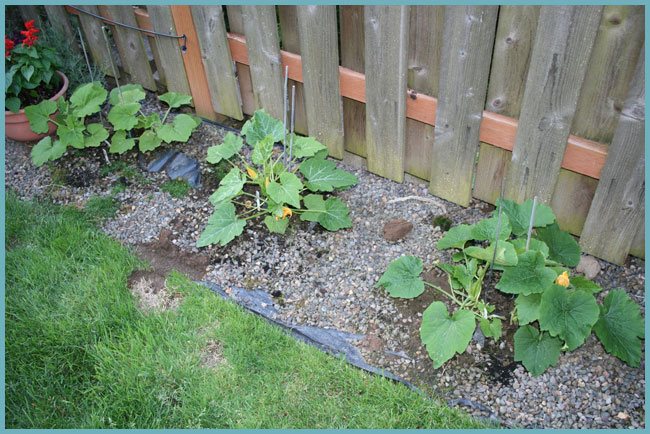


Inspect zucchini regularly for pests
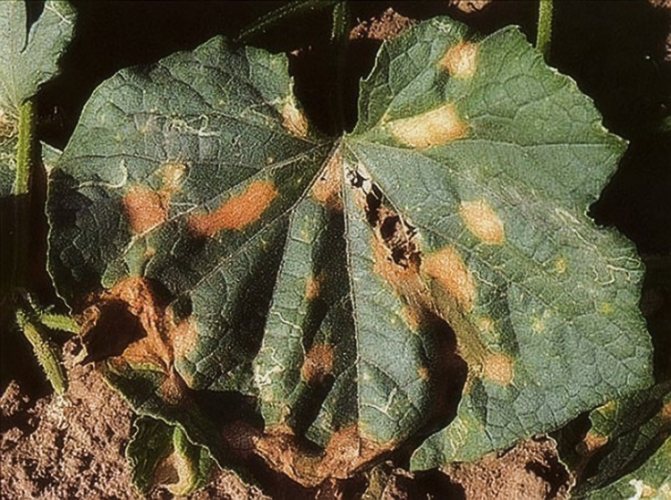
Powdery mildew damages squash leaves with a loose bloom. They dry out over time, and the fruits simply stop growing. At the first signs of this disease, the plant is treated with a 10% solution of fungicides.
Biological features
Zucchini (planting and care in the open field is quite simple) are early maturing and capable of continuous fruiting plant species. For better development and the formation of a larger number of ovaries, it is recommended to collect grown greens as often as possible, not to wait for them to fully ripen. Fruiting of zucchini begins about 60 days after the shoots appear. Flowering and the formation of ovaries continues until late autumn (if good care is taken of zucchini in the open field). Diseases of the plant - powdery mildew, white rot and various spots. Of the pests, it is most often annoyed by ticks, melon aphids, slugs, etc.
How to properly collect and prepare your zucchini seeds


To collect seeds, you should select healthy and strong plants in advance. This is done 2 months after the appearance of the ovaries. On such bushes, no more than two fruits are left, each of which must fully comply with the characteristics of the variety, have a healthy and beautiful appearance.
Plants are cared for as usual, with the exception of top dressing. For these specimens, the dose of nitrogen fertilizers is reduced by 1.5-2 times.
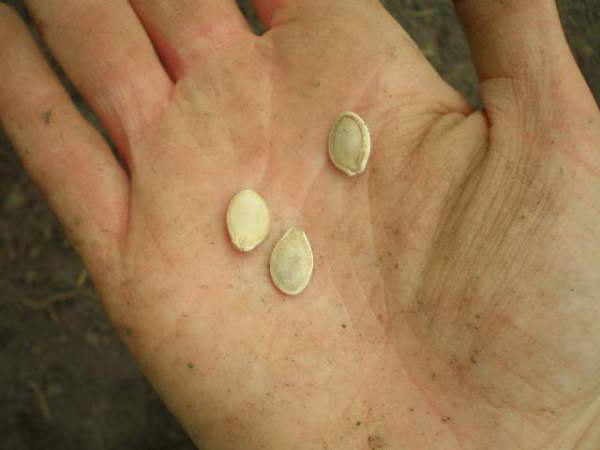
The seeds can be harvested after the crust has completely hardened, this stage can be easily determined by running your fingernail over the zucchini. There should be no trace left on the skin of the fruit. The color of a fully ripe vegetable marrow becomes bright. The fruit is removed and allowed to lie for 2-3 weeks in a dry ventilated room.
If you use seeds from not fully ripe zucchini for planting, they will have poor germination. After waiting for the allotted time, the fruit is cut into pieces and the seeds are taken out by hand. You cannot rinse them. Drying seeds is best done outdoors, but not in direct sunlight.
Experienced summer residents recommend removing seeds from fruits in winter, and then drying them at home at room temperature.
On a note! Seeds should not be overheated, as well as left damp, so that they do not lose germination.
Growing zucchini in the open field: varieties
Zucchini varieties are quite diverse, and when choosing them, you must focus, first of all, on what their origin is: domestic ones are more frost-resistant, and foreign ones have a long growing season.
The most popular varieties of zucchini are:
- Masha F1 is a variety resistant to diseases, pests and unpredictability of the climate, capable of ripening well even in dry and rainy weather. Zucchini bushes are low. Fruits are elongated, glossy, light green. The weight of one zucchini can reach 3 kg.
- Apollo F1 is the guarantor of an excellent harvest in absolutely any weather. The plant bears fruit amicably, even if planted in dense shade. The fruits are large (weight up to 3 kg), white-green.
- Kveta - refers to medium early varieties that ripen in 6-7 weeks. Fruits are cylindrical in shape, with a ribbed surface, weight - up to 1.9 kg.
- White - differs in medium-sized, rather tasty fruits, the weight of which is up to 1 kg. Vegetable growers have noted an increased resistance of the variety to diseases such as powdery mildew, gray rot, etc.
- Gribovsky-37 is a fairly high-yielding variety with white smooth fruits. Maturation occurs 40 days after planting. The pulp of the fruit is milky white, with a delicate taste, and the plants of this variety themselves tolerate transportation and long shelf life well. The only caveat: planting, care and agricultural techniques of zucchini in the open field require a little more space than for other varieties, because the bushes are quite large in size.
- Belogor F1 is a hybrid, early maturing variety. Zucchini are predominantly single-stemmed with a short shoot. Fruits are medium-sized (weight - up to 1 kg), cylindrical, greenish-white. The flesh is white and quite firm.
- Hybrid Nemchinovsky - is an early ripening variety of high yields. Fruits are light green, weighing 0.6-0.8 kg.
- Anchor is a very productive variety that bears abundant fruit with small yellow fruits, the average weight of which is 0.5 kg.
- Spaghetti - this variety got this name because the flesh of the zucchini, after heat treatment, begins to break down into fibers that resemble pasta. The weight of the fetus reaches 2.5 kg. Zucchini of this variety are able to "capture" the entire garden, if their lashes are not directed in the right direction in a timely manner.
- Aeronaut is an early maturing variety with good keeping quality. The fruits are green in color and have yellow flesh. Weight - up to 1.5 kg.
- The roller is an early ripe variety with a large number of ovaries. The fruits have a salad color, delicate taste and a long shelf life.
- Diamond is a mid-season variety, fruit weight - 2 kg.
- White-fruited VIR - refers to an early-maturing high-yielding variety that allows you to collect from one square. m up to 18-20 kg.
- Tsukesha is a zucchini variety that has long, thin-skinned fruits, on the surface of which there is a pattern in the form of light dots. The fruit weighs 0.7-0.8 kg.
How to determine the maturity of zucchini, when to remove it from the garden


First of all, pay attention to the ripening time of the vegetable, due to the variety. This information can be found on the seed package. Typically, the grower characterizes the ripe fruit.
In addition, the fact that the zucchini is ripe can be determined visually. Its peduncle becomes very tough, partly stiff. If you are going to remove the fruit for long-term storage, wait until the crust becomes firm. Taking a ripe zucchini in hand, and knocking on it, you can hear a dull sound.
No one will prevent you from picking young zucchini 15-20 cm long for eating in the middle of summer.If you are going to keep the fruits until winter or use them for cooking canned vegetables, you need to plant late varieties and harvest in 100-120 days from the moment the shoots appear ...
Soil preparation
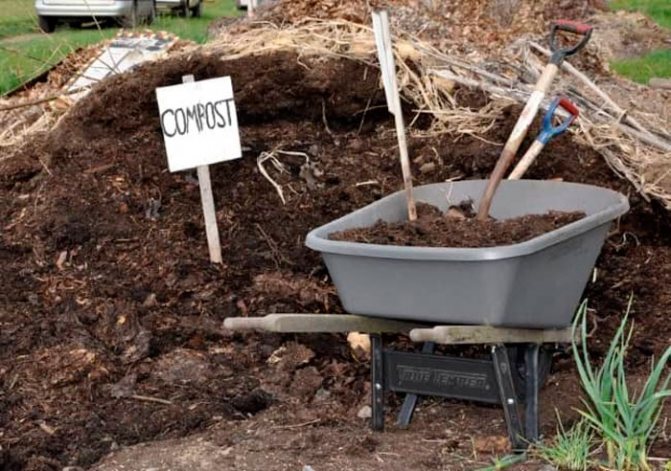
Summer residents and experienced vegetable growers argue that zucchini do not need special beds, as they feel great in the aisles of cabbage, potatoes or along the fence. This culture is very fond of chernozem and loamy soil, rich in humus, therefore it grows quite well on compost heaps. The main thing is that the landing site is not too wet. Areas where groundwater is high are not suitable for such a vegetable crop.
Zucchini refuse to grow in wet clay and peat soil, and they react well to sandy soil, only it should be pre-prepared by adding magnesium fertilizers. Acidic soil needs fertilization with dolomite flour or ash.
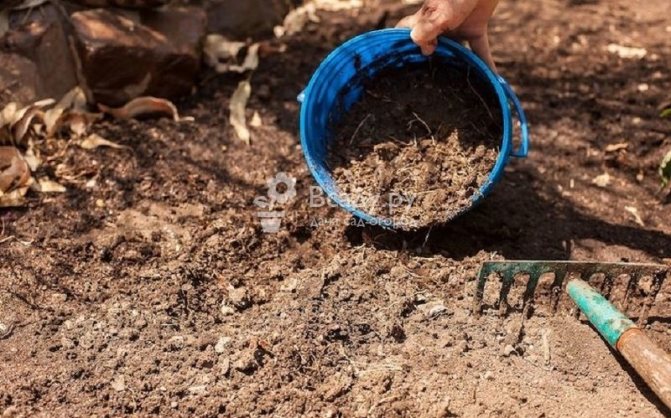
It is better to prepare the beds for zucchini in the fall. The plot is dug up, the soil is enriched with manure or compost, potash fertilizers and superphosphate. In the spring, the beds are dug up again, watered with hot water. The soil is warmed up under plastic wrap. If fertilizers were not applied in the fall, in the spring the soil must be fertilized: for each square meter, add wood ash, 15 kg of compost and 50 g of superphosphate.


Zucchini can be planted in two ways: seedlings and seeds. Which one to choose? It depends, first of all, on the climatic characteristics and how quickly after planting you want to get the harvest. Planting seeds directly into the soil is performed in the case when there is no need to rush to harvest the crop, or if there is simply no desire to tinker with the seedlings. After the emergence of seedlings or planting seedlings in the soil, caring for zucchini in the open field consists in timely watering, weeding, loosening and feeding.
What can be planted next to zucchini - a favorable neighborhood


To protect from the wind, you can plant corn next to the zucchini, and it will be appropriate to plant greens, various types of salad, and early cabbage directly on the same garden bed. When these crops are harvested, the squash will continue to develop and grow freely. This vegetable can also be combined with legumes, onions, beets.
It is recommended to plant nasturtium, calendula, marigolds in the aisles. These flowers are repellent, repelling pests with the scent of essential oils.
On a note! Do not plant squash, pumpkins, cucumbers, melons at close range - these plants can get dusty with zucchini and then the crop will be spoiled.
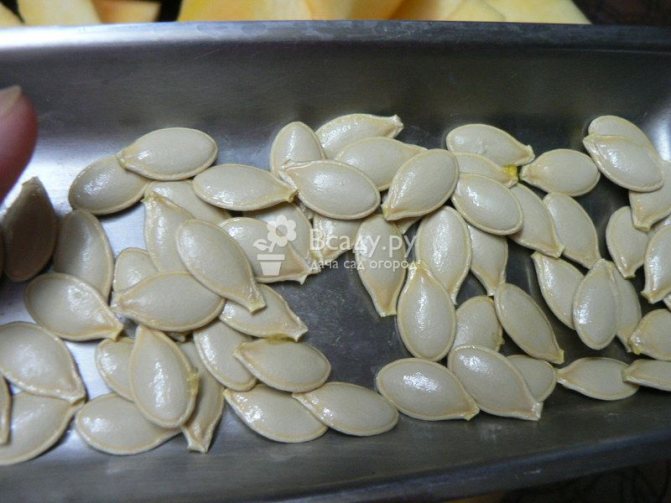
Seed preparation and planting
If unprepared seeds are planted in the soil, they will germinate very slowly. This process can be accelerated in several ways:
- soak seeds for a day in a solution of a growth stimulator;
- germinate in a warm place before pecking;
- soak the seeds for 5-6 hours in warm water (at a temperature of +50).
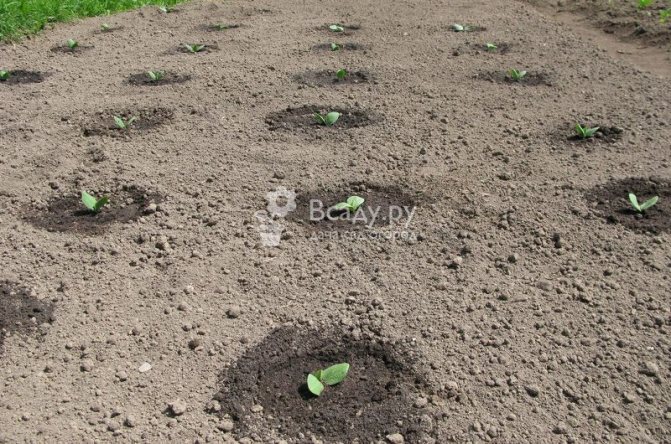
Planting seeds is performed as follows:
- holes are dug on the prepared bed (about 3 per square meter, the plants should be placed according to the 50x70 cm scheme;
- beforehand, each hole must be fertilized with a handful of ash and humus;
- seeds thrown into the hole should be at least 3-4 pcs. (later only one of the most developed sprout is left of them);
- on light soil, the seeds are buried by 5-7 cm, and on heavy soil - by 4-5 cm.
Interesting ways to plant zucchini
When every meter of the plot is registered, you can use unusual methods of growing pumpkin crops. The craftsmen adapted old bags and barrels for them. Dense plastic bags with a volume of 100 liters or more replace the frame of warm beds. They are filled with organic residues, compost, treated sawdust. Waste wood before use is laid out on a film and poured with urea dissolved in hot water (5 tablespoons per bucket of water). After 5 days, the sawdust can be used to fill the bag.
Attention. Remember to make holes in the bottom of the structure to drain excess water when watering.
The top layer of 25-30 cm consists of garden soil. One plant is planted in each bag. If planting is early (mid-May), the leaves are covered with a cut plastic bottle. Plant care is the same as in the soil. It needs to be watered, weeds removed. The bag can be placed anywhere where the sun is shining brightly.
A similar method is used to grow vegetables in a barrel. A drainage layer of brushwood is arranged at the bottom of the container. Further, compost, humus, sawdust, turf soil are applied in layers. A plastic pipe with fine holes along the entire surface is installed in the middle of the barrel. Moisturization of deep soil layers will occur through it. 2-3 plants are placed in a large iron container. Seeds are planted in holes around the pipe in 3-4 pieces. Of the seedlings, the strongest is left. The bushes quickly give a green mass, then begin to bloom. The time of appearance of fruits depends on the variety of zucchini. An iron barrel with vegetables will become not just a garden bed, but an original decoration of the site.
Zucchini on a trellis
Vertical cultivation of vegetables does not take up free space. For this method, climbing varieties "Profit F1", "Ambassador" are selected. Curly shoots are fixed on vertical structures - trellises, walls of buildings, fences. At the initial stage, the lashes are tied up, then they spread themselves. The method has several advantages:
- Vegetables are well ventilated and less likely to become infected with fungal diseases.
- Care is simplified (watering, feeding, harvesting).
- The fruits do not touch the ground, therefore they are dry and clean.
One of the original varieties of "Spaghetti", the pulp of which becomes brittle during cooking, also belongs to the climbing species. Its branches reach 5-7 m, entangling everything around. By directing them to prepared racks, you will get tasty fruits without any problems.
The listed methods of growing pumpkin crops not only save space, but also give a bountiful harvest. Plants inside the bags and barrels rot and produce heat. In comfortable conditions, more fruits are set.
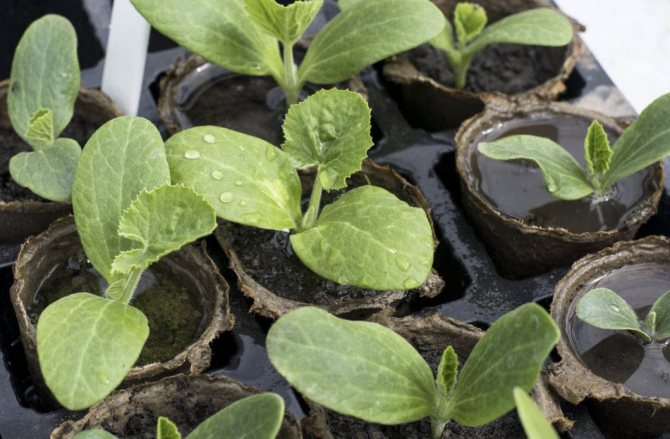
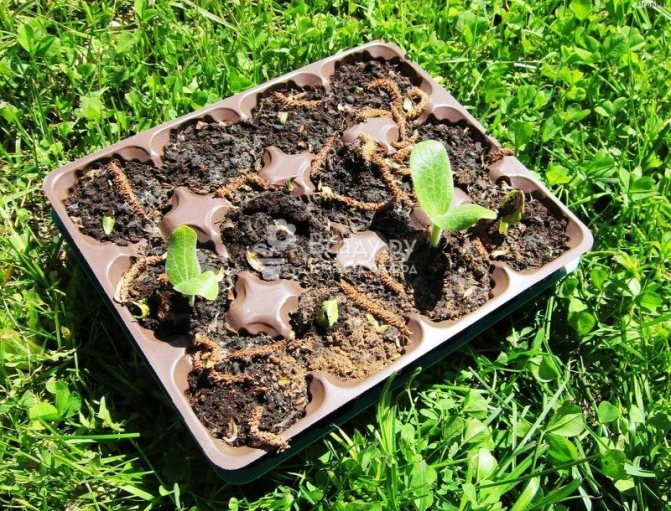
Growing and planting seedlings
The seedling method of growing zucchini allows you to bring the time of the first fruits closer and increase the yield. Seedlings are usually difficult to take root, so they are most often grown in cut-bottom plastic cups or in peat pots.
In a room with seedlings, the temperature should be maintained at + 20-22 degrees. After the plants sprout, it needs to be lowered a little, and then raised again to the previous level. This is necessary so that the zucchini seedlings do not stretch out.
1-2 seeds are planted in plastic cups. As the soil dries, the seedlings are watered with warm water at the rate of 1 liter per 10 glasses.
Seedlings are planted on the garden bed together with containers.
Where to plant zucchini
A sunny and wind-protected area, this is the best choice for a garden where zucchini grows best. Farmers are advised to plant vegetables on the south side, it is good if they are covered by high crops. The optimal protective strip is corn or sunflower stalks. When choosing where to plant zucchini, do not forget about crop rotation. Places occupied by pumpkin crops, exclude immediately. Related crops are planted after 5 years. For planting 1-2 bushes, you can prepare an area on the edge of a bed of beans or cabbage.
Pollination
Caring for zucchini in the open field requires special attention to pollination of the female flowers of the plant. To attract bees and bumblebees, in the morning they are sprayed with a solution of honey (1 teaspoon per glass of water). Another solution is also prepared: for 24 hours, the male flowers are infused in sugar syrup and the female flowers are sprayed.
If, due to unfavorable weather conditions or other reasons, insects are in no hurry to pollinate a flowering plant, you can do this yourself. To do this, the petals of the male flowers are cut off and the female flowers are pollinated with their pollen.
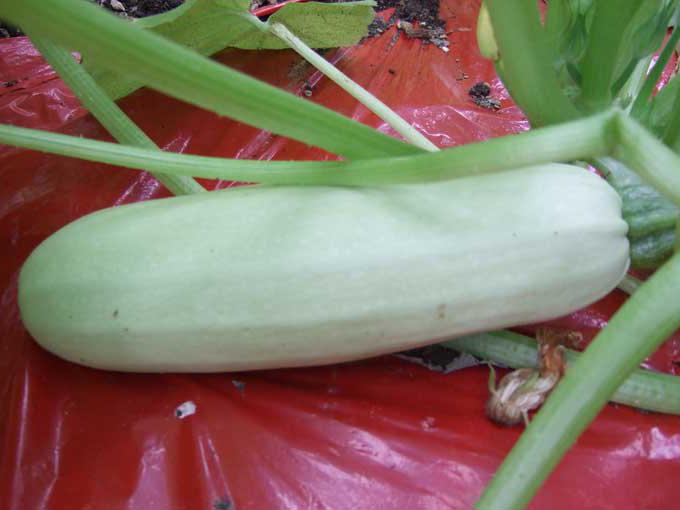


Caring for zucchini in the open field does not provide for pinching the tops, since the plant does not need it.
Prevention of diseases and pests
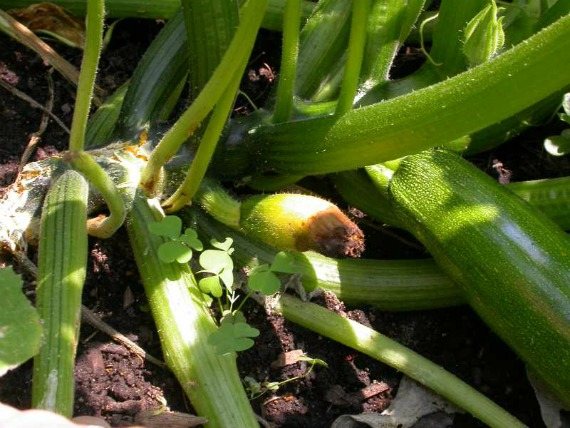


Due to improper care, zucchini can be sick with bacterial and fungal diseases. Most often they are affected by powdery mildew, bacteriosis of fruits, root rot.
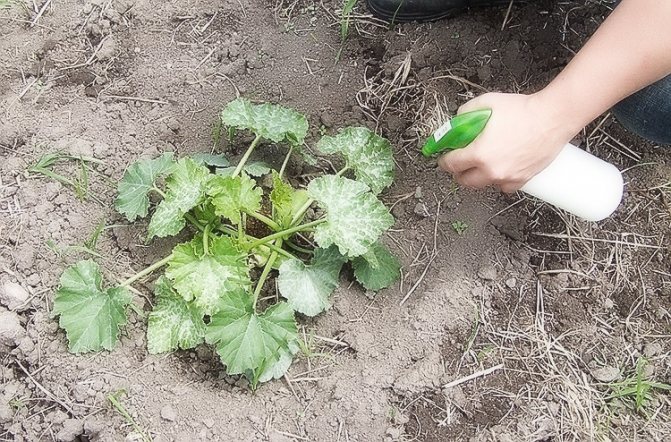
To reduce the risk of diseases, it is necessary to pickle the seeds before sowing, plant zucchini according to the recommended scheme, process the bushes at the initial stages of growth with a 1% Bordeaux mixture, and fight pests in a timely manner.
To scare off whiteflies, spider mites and aphids, squash is sprayed with a solution of laundry soap with the addition of copper sulfate. It is undesirable to use chemical insecticides at the fruiting stage, during this period biological preparations are used (Fitoverm, Bitoxibacillin, Trichodermin, Alirin B).
Description of the plant
The birthplace of the plant is Central America.... Like many plants in the Western Hemisphere, it came to Europe about 500 years ago, and for quite a long time it was grown there exclusively as an ornamental greenhouse plant.
More than two hundred years passed before the gastronomic features of the vegetable were appreciated and it took its place in the composition of more than one hundred dishes. First of all, these are dietary and baby food, as well as numerous pickles and canned food.
The varietal variety of zucchini is quite large. There are several hundred varieties and intervarietal hybrids. Currently, there are zucchini that can be grown in almost any conditions, with a wide variety of colors and pulp consistency. We can say that any gardener will be able, among all this variety, to choose the variety that will satisfy all his needs.
Zucchini is a herbaceous annual plant of the pumpkin family. It has a branched root system spreading within a radius of 0.8-1 m from the central stem. The penetration depth of the root system is about one and a half meters, although in the overwhelming majority of cases, the roots do not sink deeper than 40 cm.
The stalks of the squash bear large leaves of a characteristic five-lobed shape. Both the stems and leaf stalks of zucchini have noticeable pubescence. The growing season for zucchini is relatively short - no more than one and a half months. After it, the plant begins to form flowers and forms them until late autumn.
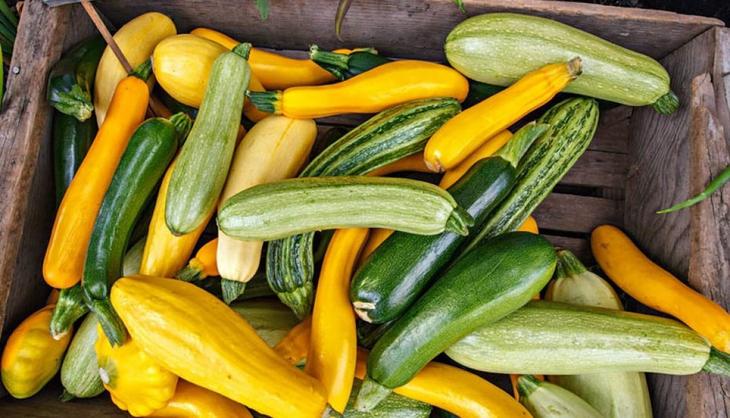


Different varieties of zucchini
The plant is monoecious. Typically, each plant produces approximately the same number of male and female flowers. It is not recommended to plant different varieties of zucchini in the same area, as well as other pumpkin plants in order to avoid cross-pollination.
Zucchini contains a lot of potassium, vitamins C and B. The calorie content of zucchini is low, about 27 Kcal per 100 g of mass, which makes this plant an excellent dietary dish.
Unusual cultivation methods
This method can be conditionally called "portable". Zucchini seedlings are grown in the usual way, and then transplanted into containers of at least 5 liters, where they grow to the end.
Zucchini in bags and tubs
The advantages of this method are that you can compactly place zucchini in a greenhouse or even in a living room. Then, with the onset of a steady heat - 18-25 degrees during the day, they can be taken out into the street, freeing up the valuable area of the greenhouse for other crops.
The disadvantage of this method is that zucchini with this method cannot develop in full force. In natural conditions, their root system is located wide and shallow from the surface. In a limited container, they go through to form the root system in an unnatural form - to the bottom of the container in depth and limited by the diameter of the container. The soil in a container dries up much faster than in a solid massif of a vegetable garden. Therefore, you have to water almost every day.In the garden, the roots of the squash themselves find the most nutritious and favorable layer of the earth. In a closed container, they completely depend on how fertile and suitable soil they have prepared.


They look somewhat depressed
For comparison, what can look like zucchini bushes "on the loose":
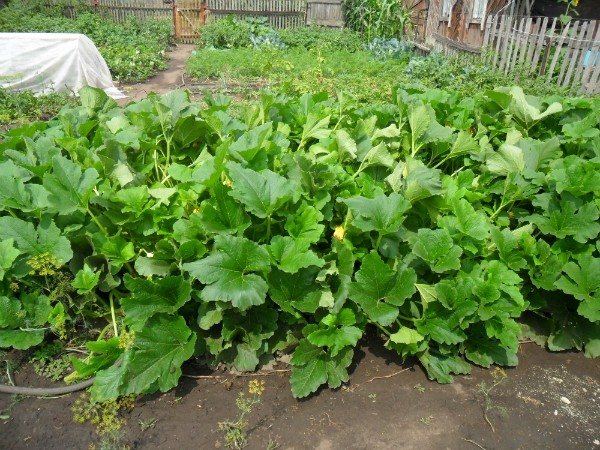


This is how normal zucchini bushes look from the middle of summer.
The most suitable soil for zucchini in closed containers:
- 1 part of garden land, black soil, loam or sandy loam, rich in humus.
- 1 part of mature manure, compost or forest humus.
- 0.5 liter can of wood ash for 10 liters of mixture.
If the garden soil is too heavy, the composition is made looser by adding no more than 10% (one tenth) of sand, 20% (one fifth) of peat.
Despite the disadvantages, this method allows you to grow zucchini in a warm place until the end or before the onset of heat. Therefore, for the northern regions, it may be the only way to grow zucchini.
Zucchini in barrels
Sometimes squash is planted in 200-liter iron barrels.


Developing unevenly in two adjacent barrels
Zucchini barrels have more food area than sacks. But another problem lurks. The iron or plastic walls of the barrels do not allow air to pass through, and the roots lack oxygen. In the heat of the sun, the surface of barrels, especially iron ones, can heat up above 50 degrees, and all the roots near the walls suffocate and burn out.
Also, with such a planting, daily watering is required. And a simple question arises - why not plant the zucchini just in the ground exactly in the same place where the barrels are. But here, as they say, the master is the master.
Crop rotation and compatibility with other crops
Accelerated growth and large fruit production is facilitated by the selection of suitable precursors. It is better to plant bush squash after cabbage, legumes, tomatoes, onions and potatoes. It is not recommended to grow zucchini after pumpkin and any kind of cucumber.
The rules of agricultural technology for growing zucchini also imply the provision of crop rotation. It is forbidden to grow zucchini on the same land for two seasons in a row. Simultaneously with zucchini, pumpkin culture should not be placed in the garden.
It is allowed to grow zucchini in different parts of the garden, using small unoccupied areas. It is important that such areas are located in a lighted and warm place.
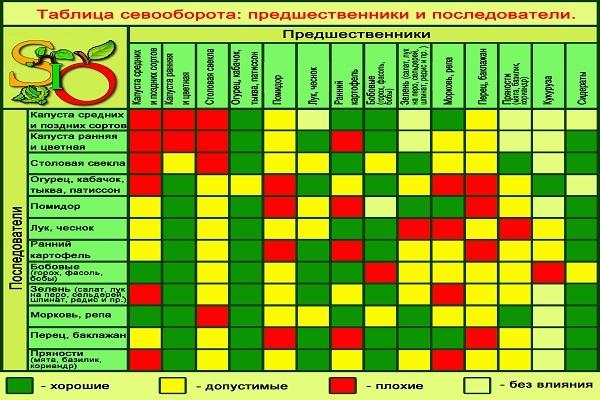

Choosing the most suitable variety for planting
Before you grow zucchini, you need to decide on the variety.
In this case, a number of varietal features should be taken into account:
- ripening terms (early, middle, late);
- yield;
- exactingness to growing conditions;
- pollination (cross or parthenocarp);
- type of growth (bush or climbing plant);
- taste, appearance.
Did you know? Zucchini is a type of pumpkin and was introduced to Europe by the Spaniards in the 16th century from America. Originally, they were cultivated as exotic plants with unusual flowers.
It is best to opt for zoned varieties. In the northern regions, preference should be given to early ripening varieties with resistance to low temperatures (Rolik, Beloplodny, Pharaoh).
For greenhouses, seed material that does not need pollination is well suited - Belogor, Parthenon, Aeronaut, Astoria, Apollo, Suha, Bely, Black Zucchini, Cavili. These are parthenocarpic hybrids, the fruits of which do not form full-fledged seeds.
On balconies and loggias, it is permissible to grow early bush varieties that are resistant to adverse environmental factors. This is Beloplodny, Anchor, Roller, Belogor.


In the southern regions, exotic varieties with a long growing season can be grown. For example, the Spaghetti variety, in which the ripened pulp breaks down into fibers or Lagenaria. You can opt for late-term zucchini that keep well.
Insulated beds
Growing zucchini on insulated beds Is the most effective way to get an early harvest and extend the fruiting season. It is not difficult to make such beds. To do this, you need to dig a small groove no more than 30 cm deep and fill it with compost and all kinds of vegetable debris, and pour about 20 cm of earth on top. Alternatively, you can do insulated holes... This is when there is not enough compost for the whole garden bed. The order of work is the same. Dig a hole about 30 cm deep, pour about 2 buckets of compost into it and cover it with earth on top. The result is a low mound on which the zucchini will grow.
Harvesting and storing zucchini
On the bushes from which fruits will be collected for winter storage, 4-5 fruits are allowed to ripen. Then they are cut off along with the stalk, kept in the sun, constantly turning over for a week for good heating, and put into a room for long-term storage.


Storing zucchini harvest on racks
In a ventilated basement, crops can be stored for up to 5 months. They are placed in nets and hung from the ceiling, or laid out on shelves covered with straw. It is important that the fruits do not touch each other and are inaccessible to the mice.
Top dressing during the growing season of zucchini
In order for the zucchini to bear fruit well, they must be fed, and the first feeding should be done after two or three weeks, when the plant begins to gain color.
To do this, you need to prepare compost from rotted manure and water. It will not be superfluous to add a small dose of mineral fertilizers. The approximate consumption of compost can vary from one liter to two liters per plant. The next top dressing will be aimed at the development of the fruits themselves and include not only organic fertilization, but also superphosphate with potassium. Foliar dressing is also beneficial for squash. You can make a urea solution and spray it on plant leaves during the fruiting period, no more than once a week.


Zucchini grown by the seedling method need two additional dressings. The first is carried out when the plant reaches a height of 7-9 centimeters, with drugs to stimulate growth, bought in specialized stores or the old method using slurry, on chicken droppings. Top dressing should be applied without fail under the root, trying not to get on the leaves of the plant in order to avoid possible burns. The next feeding should be carried out after a two-week break, with mineral fertilizers: potassium and phosphorus.
How to properly prepare seeds for planting?
If the purchased seeds have not been processed, then it is imperative to disinfect them with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate for 20 minutes. Then they should be rinsed and dried on a napkin.


Such seeds are already suitable for sowing, but their germination can be improved by the following procedures:
- Soaking seeds in nutrient fluids or stimulants. For this purpose, use a solution of "Epin", "Zircon", ash, aloe juice or complex fertilizer ("Nitroammofoski"). The seeds are immersed for 8-24 hours, and then they are not washed.
- Sparging. Suitable for aquarium owners. The seeds are placed in water enriched with oxygen by an aquarium compressor for 15-18 minutes.
- Hardening. For three days, the seeds, wrapped in a cloth moistened with water, are placed in a refrigerator for 16 hours, and the rest of the time (8 hours) is kept in a warm room.
- Soaking in warm water for a day, at a temperature of + 25 ° C.
- Germination. The seeds are kept warm in a damp cloth until sprouts appear.
Did you know? Regular consumption of zucchini in food inhibits the appearance of gray hair. This is due to the antioxidants they contain. For maximum preservation of the beneficial properties, this vegetable should be cooked in the microwave.
Which seeds should you choose?
The final result of gardening work largely depends on the quality of the planting material. Seeds can be harvested from last year's own harvest or purchased from agricultural stores.


When choosing seeds, you should pay attention to the following points:
- We choose seeds from a trusted manufacturer, about which we have heard good reviews or have personally used the products.
- Most of the imported seeds are hybrid. Such varieties are not suitable for removing new planting material from ripe fruits. Their growing season is longer, but the presentation of the vegetable lasts longer.
- The seeds of domestic producers are frost-resistant, retain their taste during any processing, have a thin skin and a pleasant aroma.
- The shelf life of squash seeds is 5-7 years.
































