The author of the article
Daria Vorontsova
Reading time: 11 minutes
AA
We are all used to buying a fragrant seasoning in sachets - rosemary. The herb goes well with meat and fish dishes.
Rosemary sprigs give the dish a piney aroma with hints of citrus and camphor. Literal translation from Latin means "sea freshness".
Common rosemary has beneficial properties: relieves stress, tones, and aids digestion.
The plant contains rare essential oils and tannins. Few know how to grow rosemary at home.
Description of the plant
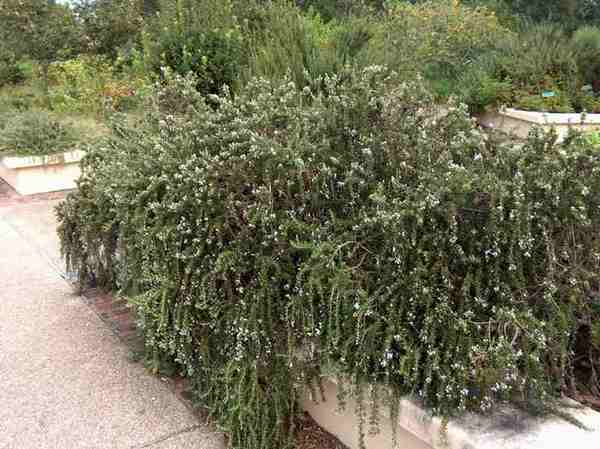
Rosemary (lat.Rosmarinus officinalis) is a shrub plant originating from the Mediterranean. In many countries, it is grown on an industrial scale. In Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, it is grown as an ornamental, medicinal, spicy plant.
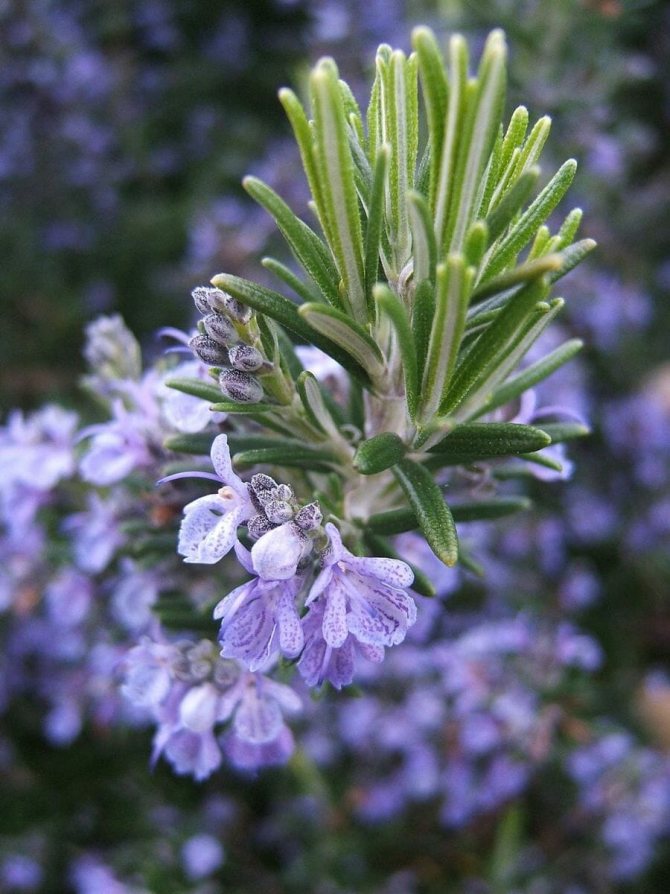
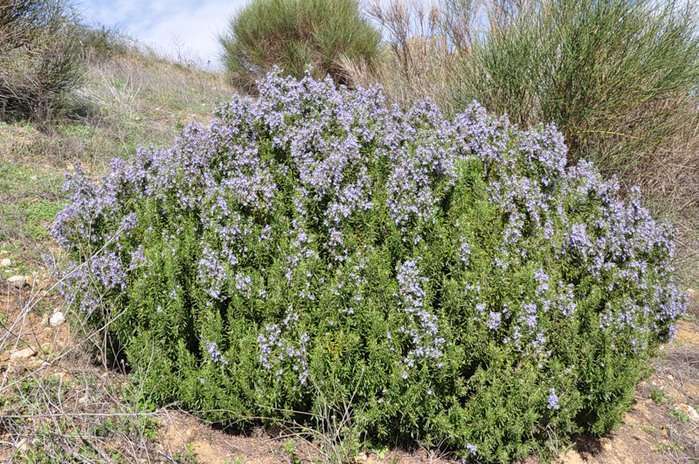
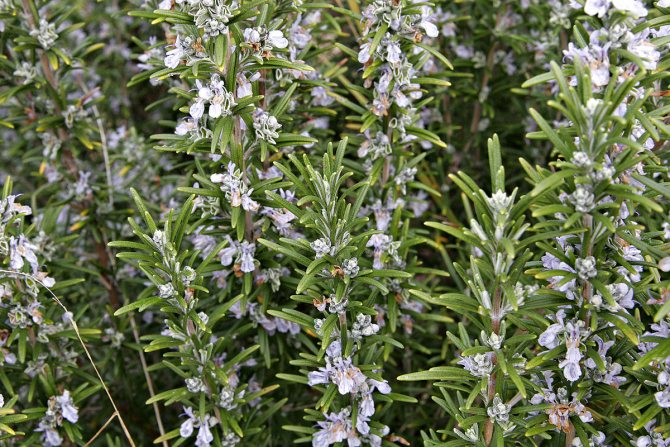
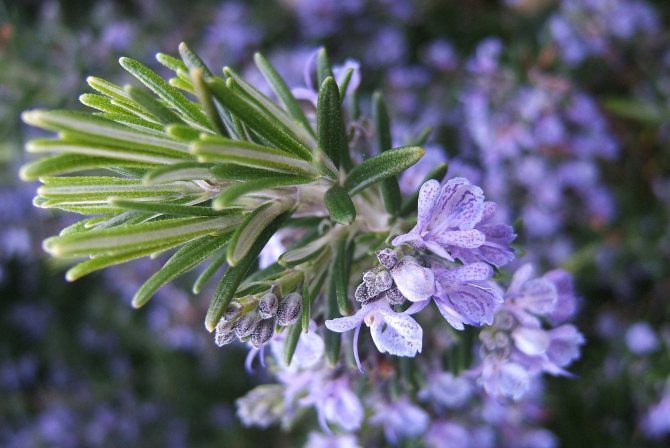
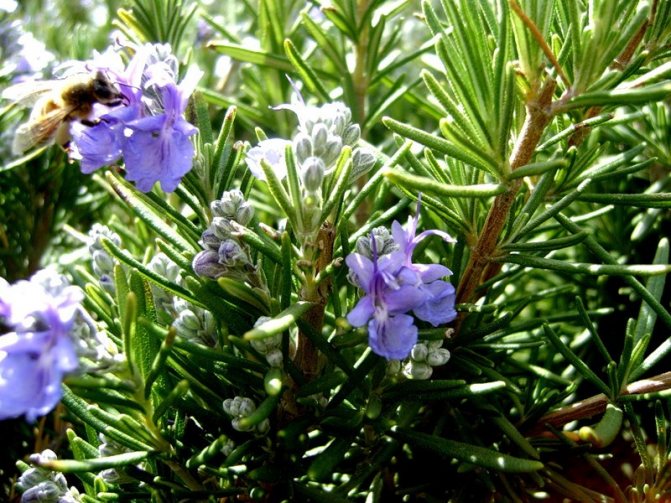
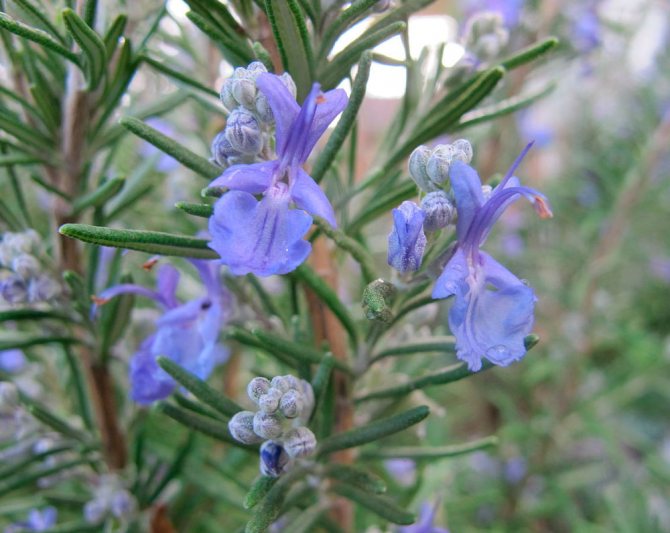
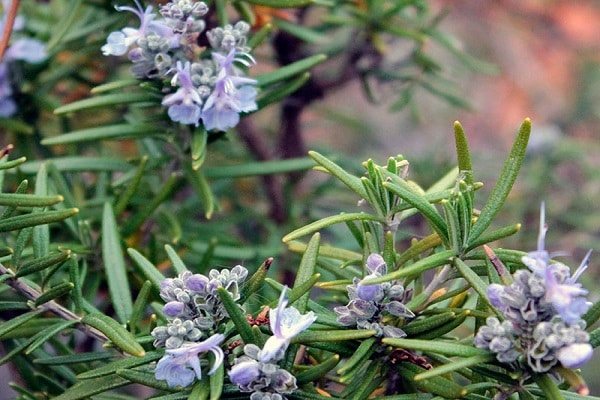
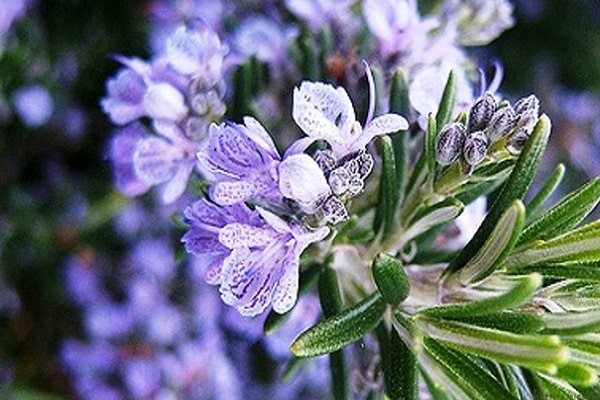
The plant represents in our climatic conditions small shrubs with lignified shoots. The extremely fragrant leaves of the plant are narrow, greenish-gray, reminiscent of lavender leaves. The flowers of the plant are blue or slightly purple.

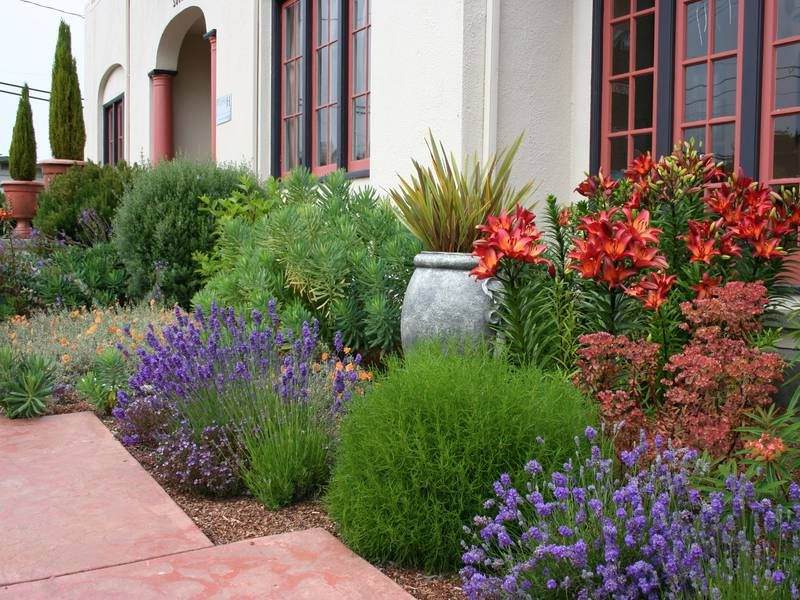
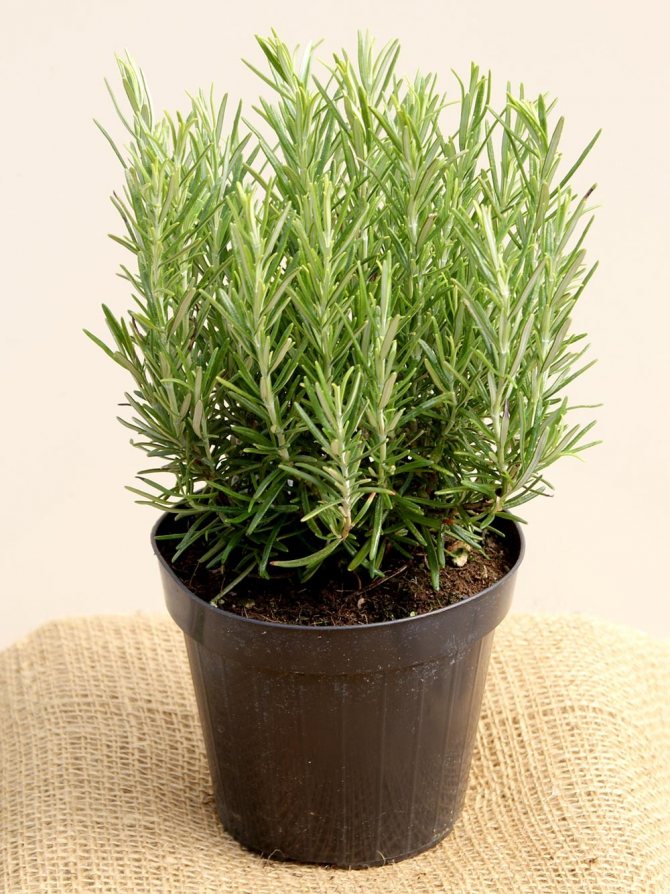
In cold climates, rosemary should be planted in pots so that it can be moved indoors in case of severe frosts. The shrub is suitable for creating a low decorative hedge - you can freely shape it by pruning. Feels great planted in pots on terraces and balconies along with other plants that love the sun in quiet areas of the garden.


It is interesting! In Mediterranean countries, it was believed that in gardens where rosemary grows well, a woman rules the house. In order not to expose themselves to ridicule, the men uprooted the plants. So in the 16th century, rosemary began to disappear from home gardens.
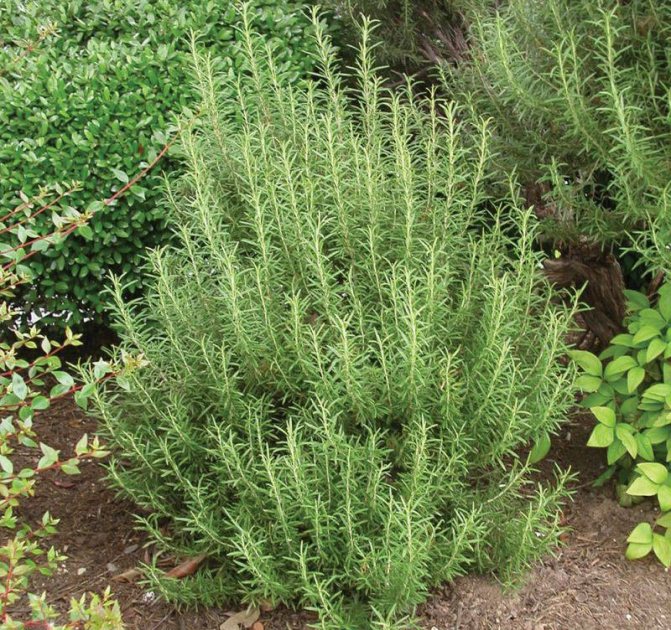
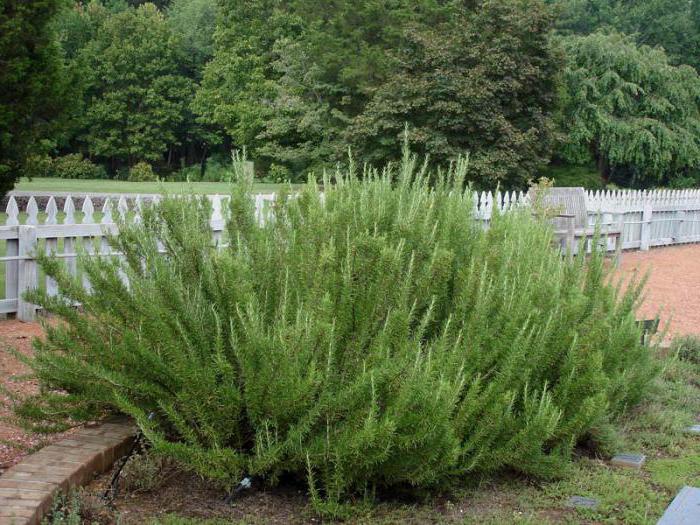
In its natural environment, the plant forms dense, fragrant, evergreen shrubs that grow up to 2-3 m in height. In our climatic conditions, the bush reaches a height and width of up to 70 cm.
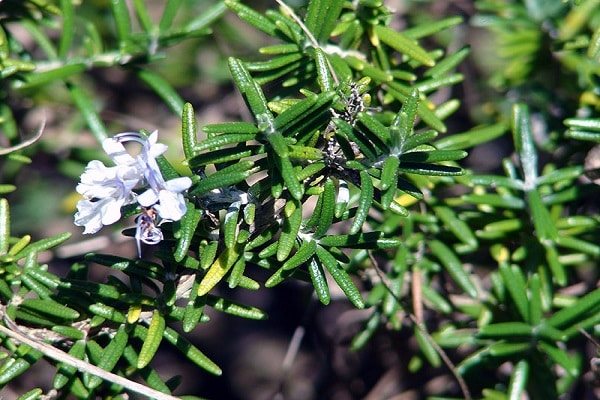
The plant produces tough, erect, tetrahedral shoots. The leaves are lanceolate, with folded edges, dark green above, covered with a silvery bloom below, very fragrant.
A deep (up to 2 m) highly branched root system provides the plant with access to moisture even on dry days from deeper soil layers, which leads to a relatively high plant resistance to drought.
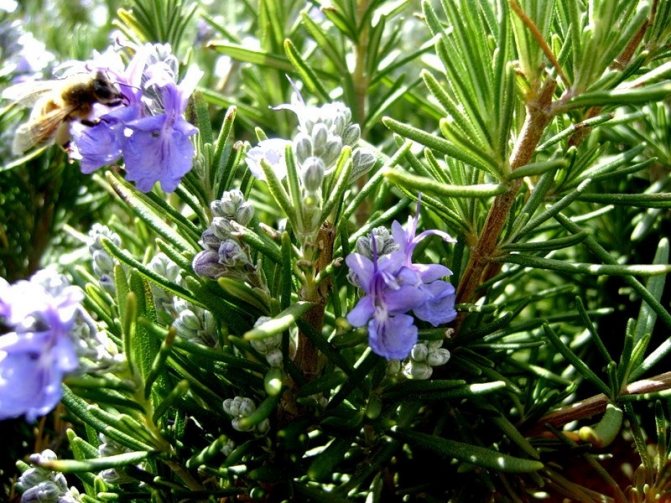
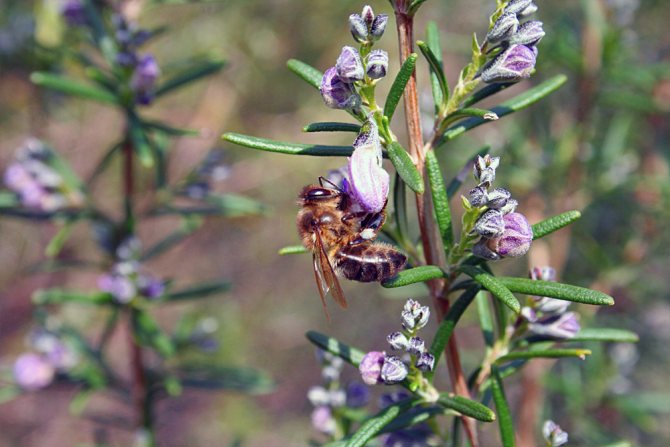
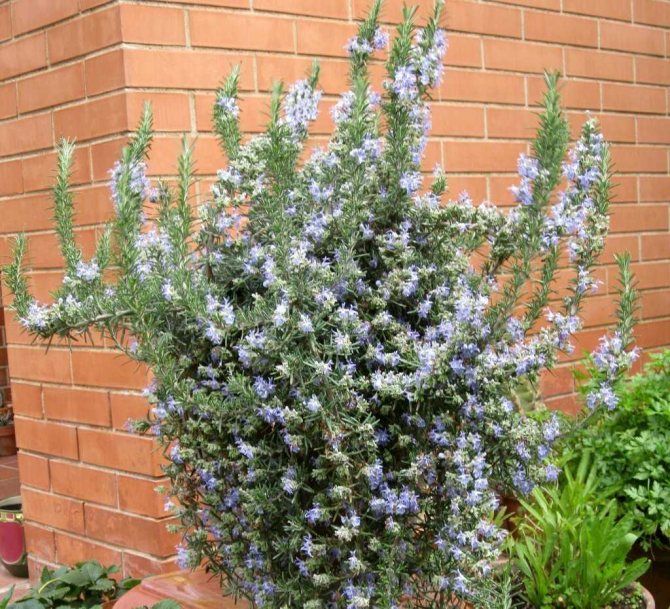
Rosemary blooms in early spring. From April to July, and sometimes longer, the bush is covered with blue or pink flowers. The strong, fragrant flowers attract bees, which convert the nectar into valuable rosemary honey. The fruit of the plant is a nut.


It is interesting! In Europe, since the Middle Ages, rosemary was considered the plant of lovers. The costumes of the future spouses were decorated with twigs. After the ceremony, the newlyweds planted a branch - if it began to grow, the plant promised them a long and happy life. The stems, tied with a multi-colored ribbon, were handed to the wedding guests as thanks for accepting the invitation.
Description and varieties of culture
Rosemary is an evergreen shrub with a height of 50 cm to 2 m and a powerful root system that goes into the ground to a depth of 4 meters. Narrow leathery leaves 3-4 cm long resemble coniferous needles.
Graceful twigs are framed by needle-like leaves, forming spherical bushes, which are covered with delicate flowers in early spring. Their color ranges from snow-white to purple-violet.
The aroma of the plant is complex, with notes of pine needles, camphor, lemon, eucalyptus. Shoots are used in cooking, cosmetology, perfumery, aromatherapy.
There are several types of plants in nature, but only medicinal rosemary (ordinary) is cultivated, suitable for growing in horticultural plots.
One of the most famous varieties is Rosinka. Undersized, with branches up to 40 cm long, does not cause problems when grown outdoors.
A small plant is transplanted into a pot and kept at home - rosemary winters well in a cool, bright room. Fragrant greens can be used all year round.
View this post on Instagram
Publication from blagikh.tetyanka (@vesnianochka_) Oct 10, 2019 11:13 am PDT
Other common varieties suitable for growing in the country:
- "White" - a decorative fragrant bush is used not only for culinary purposes, but also to decorate the site.
- "Biryusa" - blooms twice a year, in spring and autumn. The flowers are blue or purple and attract bees. Honey plant.
- Blue Winter - tolerates a cold snap down to -17 degrees. An ornamental plant that gives a persistent spicy aroma, reaching 80 cm, is applicable in landscape design.
- "Crimean" - originated from the wild type of rosemary. It was planted in the Crimea about 200 years ago.
- "Horizon" - height 1 meter, bush diameter 90 cm, winter hardiness up to -15 degrees. Practically unaffected by diseases and pests.
Another well-known type of culture is prostratus (prostratus), or prostrate rosemary, its cultivation is often aimed at obtaining a ground cover.
With a bush height of only 50 cm, its creeping shoots grow with a diameter of 1.5 meters. Bright green leathery leaves-needles resemble spruce needles. Famous varieties - "Venzano", "Lavender", "Corsica".
In winter gardens, on loggias, the variety "Tenderness" is often found - growing from seeds through seedlings, after the end of frost, planting in open ground for the summer. With sufficient heat, lighting and watering, it reaches a height of 1 meter.
Thanks to the varietal variety of rosemary, you can choose the right shape for the climate. In the southern regions, tall species grow well, and in colder climates, it is worth giving preference to undersized, creeping varieties.
Complete the topic with a bush review from the gardener:
Landing
Growing rosemary in the garden is preceded by planting. It is important to choose the right place and soil.
Optimal position in the garden
Rosemary is an extremely light-loving plant. To maintain optimal growing conditions close to those of his family, he needs to be provided with a warm place in the sun. Even hot sun rays at noon will not harm the plant.
The shrub should not be planted in partial shade.
Compatibility with other plants
Rosemary in the garden can be part of a Mediterranean-style arrangement or part of a herbal garden. You shouldn't be limited to one type.
Sage, belonging to the same plant family, will make a good neighborhood to the shrub. However, the shrub does not tolerate horseradish and mustard growing nearby.


Soil requirements
The ideal soil for the plant is a permeable, sandy soil rich in nutrients. Rosemary does not like acidic substrates, preferring well-drained soil with a pH of 6-7. The permeable structure is very important for this shrub, the plant reacts negatively to excess water.
It is better to refuse to buy land for flowers - it is too fertile.It is better to compose the soil by mixing 2 parts of compost, 1 part of lime sand, 1 part of very small stones. Alternatively, you can use other sand, but then you need to add dolomite in the amount of 1-2 tablespoons to 5 liters of the resulting mixture.
A cactus substrate is also suitable, but due to the lack of minerals, a little compost will be required. Add 2-3 tablespoons of dolomite to this mixture.
If the shrub is to be transplanted into a pot, the flower soil should be mixed in half with sand. Such soil is more permeable. Be sure to cover the bottom of the container with pieces of ceramic to allow excess water to flow out.
Before planting, you can fertilize the soil with slow-release fertilizer and repeat fertilizing every spring. The soil should be relatively moist.
Landing
When planting rosemary, it is helpful to prepare a small mound and cover the surface with stones. The stones heated in the sun give the plants extra warmth and protect the soil from being washed out by heavy rains.
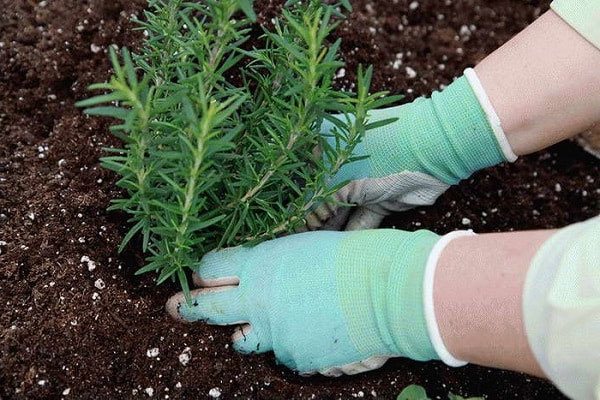


Transplanting or planting rosemary should be carried out in the spring, in autumn only in regions with a warm climate. The plant grows slowly, but in the second year the growth rate increases markedly.
The shrub is very sensitive to root damage and takes a long time to restore the root system, so it is best to avoid replanting.


Briefly about the history of appearance
So what is rosemary and what are its uses? This plant became famous many centuries ago. According to some legends, it owes the sky-blue color of its flowers to the Virgin Mary, who put her cloak on the bush to protect the baby Jesus from the heat of the sun. According to other legends, the reason for the appearance of rosemary flowers was drops of sea foam, in which the goddess of love and beauty was born - Aphrodite from the Greeks and Venus from the Romans.
Medlar Caucasian - growing in the garden in the open field
Since ancient times, rosemary sprigs have been put into the hands of the dead to brighten their way to the kingdom of shadows - in Egypt. It was also added to the bridal bouquet, they decorated the wedding dresses of the newlyweds and gave small bouquets of rosemary branches to guests in medieval Europe.
Interesting to know: at different times, in different cities and countries, rosemary was considered a plant of lovers. And if after the wedding the rosemary branch planted by the young spouses began to grow - this promised a long and happy life for the couple, full of love and harmony.


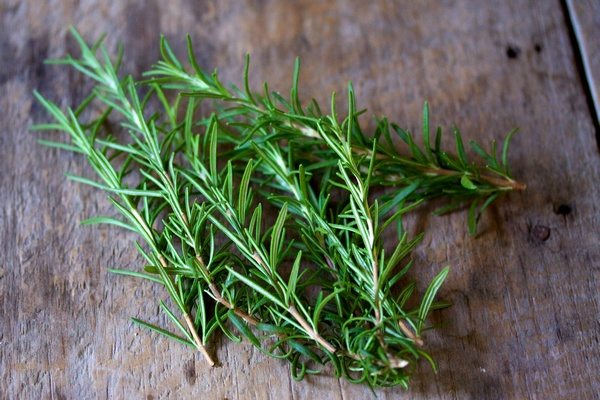
Dried spice leaves and fresh shoots are used in cooking
Growing and caring for the garden
Since rosemary is not a very demanding plant (except for the lack of frost resistance), planting and care is carried out in the open field - in the garden, in the country and in pots. With its help, a garden, balcony or terrace can be filled with a festive mood, suitable for the warm Mediterranean.
Watering
Watering rosemary is carried out in moderation. At home, the shrub can extract most of the moisture it needs from the air. The rest is provided by an extensive, deep root system. Only during the summer heat should you give the shrub a little more water.
It is necessary to inspect the shrub, if the leaves wither - there is a moisture deficit. Excess moisture is much more dangerous for this plant than lack of moisture.
Watering is carried out using the "once, but well" method - then they wait until the soil in the container is almost completely dry. Then water again abundantly so that the water begins to flow out through the drainage holes in the pot. After 15 minutes, drain the water from the pan.
If the plant grows in the ground, it is better not to use the "services" of rain. During rainstorms, it is best to cover the plant, for example, with a large plastic bottle. Why such measures are desirable can be read in the description of diseases and pests below.
Top dressing
Fertilize the rosemary in moderation. In the spring, it is necessary to provide the shrub with some nutrients, preferably organic (compost). In the summer, the shrubs do not need feeding. For the last time before winter, you can feed the plant in August. If the bush grows in a pot, it can be fed every 2-3 weeks with small doses of fertilizer.
Fertilizers with a high nitrogen content should be avoided. Fertilizer is suitable for flowering plants.
When and how to prune rosemary?
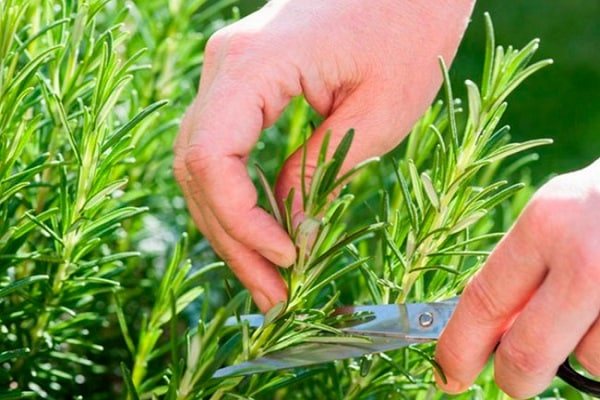
Rosemary is rarely subjected to this operation. In the fall or spring, pruning of rosemary is carried out, which allows the shrub to release new shoots. You need to prune carefully so as not to cut the old shoots. The secateurs must be clean and sharp.
After flowering, the plant is cut by 1/3.
Wintering
There are specially bred rosemary varieties that are resistant to low temperatures: Veitshöchheimer Rosmarin, Blue Winter, Madeleines Hill.
Rosemary is resistant to short-term frosts down to -15 ° C.
It is possible to grow rosemary in open (unprotected) ground in the suburbs of Moscow and the Leningrad region only near the southern walls and under cover in winter. However, the plant often freezes out. In our climatic conditions, temperature drops are observed, so the Mediterranean shrub may not survive the winter.
In unfavorable climates, it is safer to plant rosemary in pots. After the spring frosts, he can calmly decorate the garden until the autumn cold weather. The plant can remain outside until the temperature drops below freezing during the day. Light frosts at night should not harm the shrub.
In the rest of the period, it is necessary to provide the plant with wintering conditions.
- In a warm room... You can grow rosemary in an apartment - a place on the southern windowsill, away from heating radiators, is suitable. When wintering in a warm room, the plant is watered as the soil dries, and occasionally fed.
- In the greenhouse... It is advisable to provide wintering at low temperatures. The room should be bright, with a positive temperature up to 10 ºC, preferably 2-8 degrees C. An unheated room or greenhouse where the temperature does not exceed 5 degrees Celsius is preferable for wintering rosemary. During wintering, the bush should occasionally be watered moderately. Fertilizers are not applied, watering is aimed only at maintaining a slightly moist root system. It is worth paying attention to whether the shrub is suffering from any damage.
Watering is the most difficult art in wintering, it often happens that it is because of this that the rosemary does not survive.


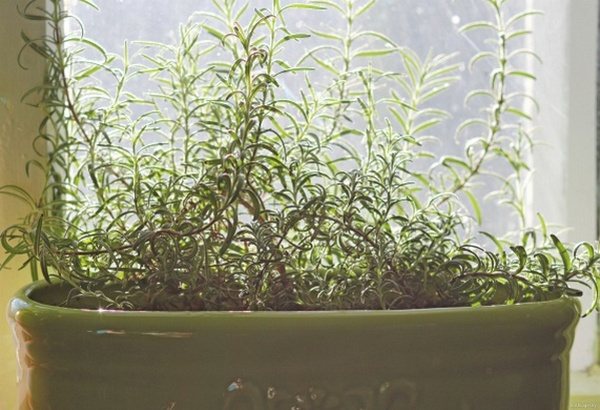
Photo. Rosemary on the balcony and in the room in winter at rest.
Preparing to plant rosemary
Seeds germinate for a long time, the plant has its own requirements for the soil, so you should prepare for planting in advance.
Cultivation of a culture is possible:
- in the country or in the garden in a seedling way;
- at home or in a greenhouse - reckless.
When to plant seeds
Planting rosemary seeds in open ground in spring is possible only in southern regions with long warm summers and no frost.
In colder areas, seed propagation can only take place through seedlings grown at home or in heated greenhouses.
Planting in open ground is carried out at the end of return frosts, when the seedlings reach a height of 7-10 cm.
Place and soil for planting
To grow rosemary, you need to choose the place that best meets the requirements of the crop. On the site, preference should be given to the southern, southeastern or eastern side of the house, fence or other building, where there will be no drafts and cold air currents.
High groundwater levels are highly undesirable. There should be no tall plants nearby that will give shade.
How to prepare the soil for growing rosemary:
- add sand - 1 bucket per 1 m2;
- crushed stone - 1 kg per 1 m2;
- phosphate-potassium fertilizers - 1 handful per 1 m2;
- dig up the soil, removing the roots of the weeds.
Seed preparation
The essential oils in rosemary seeds inhibit germination. It is important to carry out pre-sowing treatment. For germination, the seeds are soaked in gauze or between two cotton pads for 2-3 days.
To speed up the process, not water is used, but a solution of "Epin" - a growth stimulator.
To view an overview of growing a crop:
How to propagate rosemary?
There are 2 ways to propagate a plant:
- The easiest way to reproduce is to buy the first plant, and then propagate it vegetatively.
- A more sophisticated method is to grow rosemary seedlings from seeds and then transplant them into soil, pots.
Growing from seeds
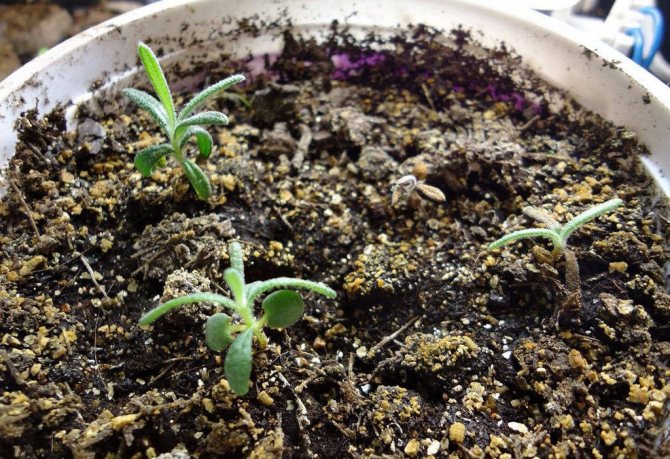
Rosemary seeds are sown in March-April. Seed germination is average, it is more convenient to sow more seeds, and then thin out the seedlings. The seeds are not covered with soil; they need light to germinate. Crops are placed in a warm, sunny place, covered with a film until germination, then the film is removed. The optimum soil is slightly alkaline or neutral.
Germination can take a long time - 3-4 weeks. Germination is uneven, requires a temperature of at least 20 ° C. When the seedlings are producing their first pair of true leaves, the seedlings must be carefully transplanted into small pots.
Note - a plant planted from seed grows very slowly in the first year.


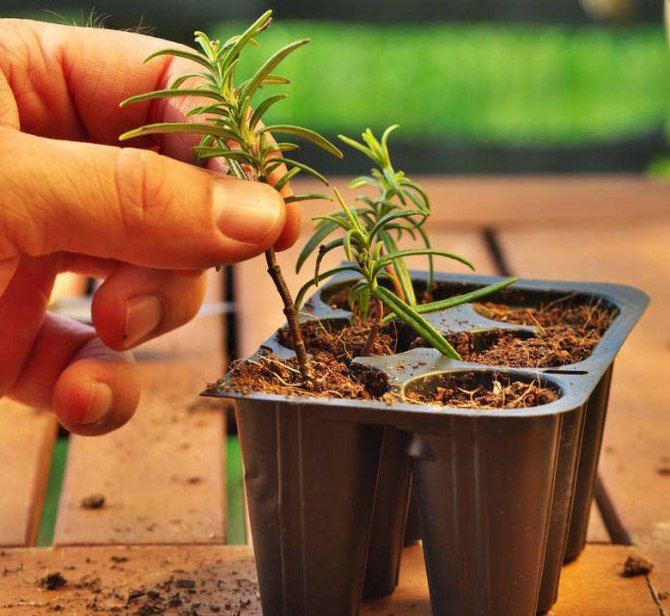
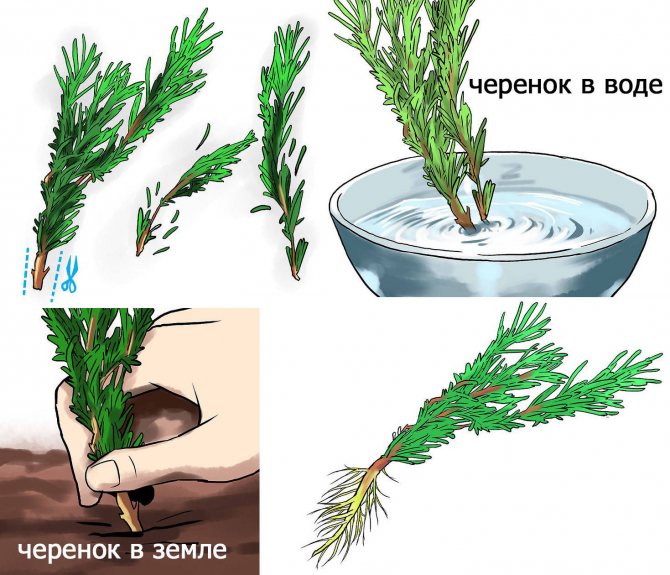
Propagation by cuttings
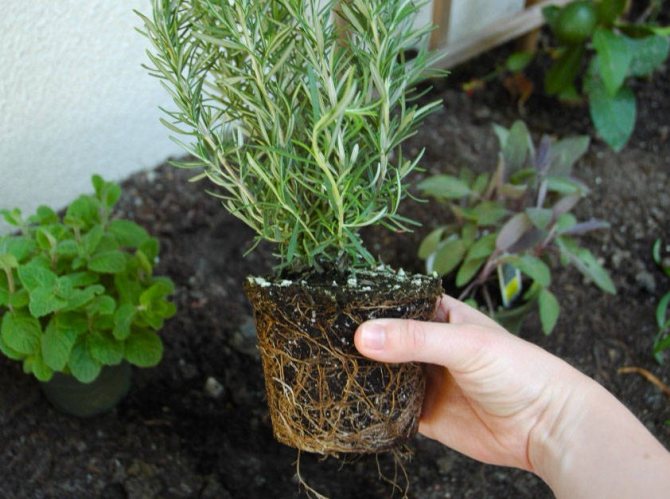
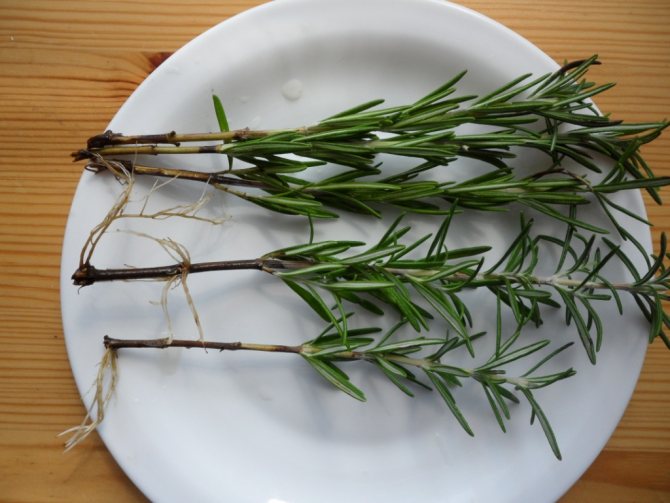
It is much easier to propagate rosemary by cuttings. For this, a 10-15 cm long stalk with several pairs of leaves from the tops of young shoots or from lateral shoots is cut from the plant.
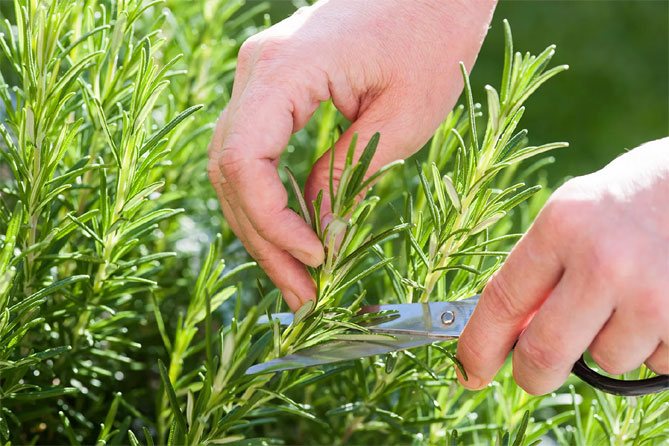


After placing the cuttings in the soil, after a few weeks (usually 3) roots appear. Removing the tip of the shoot will cause the plant to branch out and create a beautifully formed shrub.
Cuttings can be cut for almost the entire growing season (except for hot and dry summer days and the flowering season). The use of preparations - rooting for plants increases the efficiency of rooting cuttings. Herbaceous cuttings can be rooted in water.
After rooting, young plants are planted in a mixture of garden soil and peat. In open ground, seedlings should be planted when the probability of frost passes (May).


Features of growing rosemary on the window
Growing a fragrant spice in an apartment is not difficult with proper care. The plant reproduces both by cuttings and seeds. Before planting the seed, it is pre-germinated in wet gauze for at least 3 days. Growing cuttings is much easier and faster. To do this, it is enough to plant the shoot with roots in the prepared soil.
On the windowsill, rosemary grows to a maximum of 1.5 meters in height. To keep the plant lush, it is pruned during the warm season. A healthy shrub at home usually reaches 60 centimeters, which is the norm.
Home care
Unfortunately, rosemary is not a potted plant like dracaena or ficus. You can grow it in pots, but in the summer it should be taken out into fresh air, in sunny places. At home, the plant is too dark (even on the southern window), too hot in winter. Growing in a pot will make it easier for the bushes to winter by moving them from the garden to the appropriate room. In any case, rosemary should not be left at home all year long.
It is very practical to have herbal flower pots on the windowsill in the kitchen. However, with a few exceptions, many kitchen herbs are not suitable for indoor cultivation - so is rosemary.
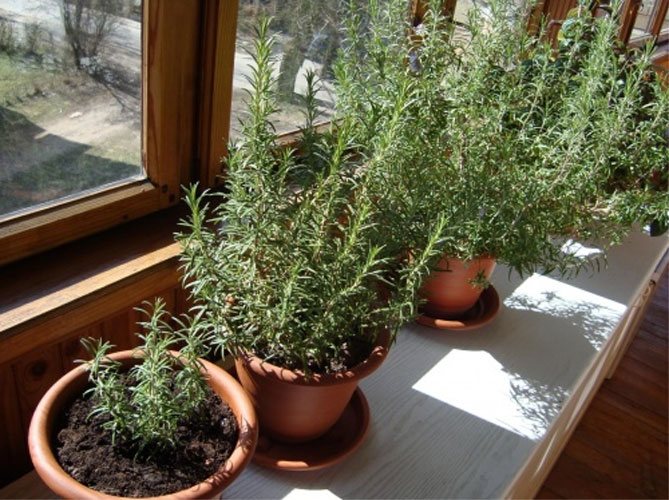


What you need to grow rosemary
A plant from warm countries perfectly tolerates the cold of central Russia. Rosemary is transplanted for the winter in flower pots, or germinated from seeds.
To grow rosemary on a windowsill you will need:
- Drainage filler;
- Fertile soil;
- Ceramic pot or other container;
- Good lighting;
- Regular airing;
- A little patience.
Frankincense herb needs regular air circulation in the apartment, but does not tolerate sudden temperature jumps.
Choosing the best place in the house


Rosemary is grown at home on a balcony, loggia or windowsill. These are the most favorable places for evergreen perennials. However, some tips for choosing a place will come in handy for novice plant lovers.
Warmth and long daylight hours are the main conditions for the successful cultivation of a shrub. Therefore, it is preferable to choose windows in the apartment from the south or east side. In winter, when daylight hours are short, an electric lamp compensates for the lack of lighting. If the rosemary is in the shade most of the time, the leaves will dry out quickly. The plant will die.
In no case should bush pots be placed near heating appliances. Dry warm air has a detrimental effect on the soil, the root system suffers from drought.
Selection and preparation of containers
The root system of rosemary is branched, so it is better to choose a container for planting a plant that is wide and deep. A clay or ceramic pot is ideal. Why is it undesirable to choose plastic containers or wooden boxes? In the first case, plastic disrupts the natural thermoregulation of the soil. Wooden boxes will not cope with excess moisture: mold and decay are possible troubles.


It is important to distribute the drainage to the bottom of the vessel. It can be expanded clay, aquarium soil or medium-sized pebbles. To avoid stagnation of moisture, small holes are made at the bottom of the pot.
Soil selection
The successful cultivation of rosemary at home in a pot depends on the quality of the soil. Although the perennial plant is not demanding on the soil, it is worth choosing a neutral and slightly alkaline soil. In order for the soil to pass air well, sand can be added to it. You can buy a ready-made base in the store or prepare it yourself from a mixture of humus and garden soil.


The soil from the garden can contain pests, therefore, before planting rosemary, it is disinfected with special preparations. The heat treatment method suppresses the vital activity of pathogens. For this, the soil is calcined in the oven for at least an hour. Another method is freezing. The earth in the bag is left for 3-5 days in the cold.


The drainage base is evenly distributed over the bottom of the container. To create favorable conditions, the earth is poured into pots at least a week before planting. In order for the soil to absorb more oxygen, it is enough to distribute it on a horizontal paper surface.
Preparing seeds or cuttings for planting
The container and soil have been prepared. The crucial moment comes for the preparation of seeds and cuttings. These are the 2 main methods of potted breeding for home care. You can buy rosemary seeds at your gardening store. However, this is the most time-consuming process, in addition, perennial seeds are distinguished by poor germination.
Preliminary preparation of seeds for sowing:
- Before sowing in the ground, the seeds are spread in damp gauze, for about 3-4 days;
- Every day the gauze is moistened, but not under the tap, but with a spray bottle;
- On day 4-5, the seeds are ready for planting. Depressions up to 1 centimeter are made in the soil and sprouted seeds are sown;
- The surface is sprinkled with a thin layer of earth, then covered with a plastic bag. Ventilation holes are required;
- The container is placed in a warm place with a constant temperature of + 15-20 ° C. After the mass emergence, the seedlings are placed on the windowsill.
Sowing many seeds in one vessel is not worth it, otherwise the root system of plants will compete with each other.


The grafting method is the most successful and simple at home. To do this, you need to rip off the top of the shrub, or buy a branch of fresh rosemary.
Preparing cuttings:
- Remove the lower leaves from the branch, place in clean water. It will take 4 to 14 days for the shoot to take root. It is important to change the water every couple of days;
- When the first roots appear, plant the cutting in the soil. Depressions are pre-formed. Moisten the ground after disembarkation;
- Cut off the top of the plant for intensive root development. This step is optional though.
April is the most suitable month for transplanting cuttings.
Propagation by cuttings is faster than by seeds. Usually, transplanting or growing seeds is planned for the spring - early fall.
Creation of the necessary conditions: temperature, humidity, lighting
After the shoots have taken root and the seeds have sprouted, it is important to maintain favorable conditions in the apartment. It is important for rosemary that the moisture is below average. The plant begins to dry out when the air stagnates. The room or loggia is ventilated twice a day, while the plant is removed from the draft.
In winter, the perennial shrub goes into hibernation, so the optimum air temperature is + 7-15 ° C. Plant pots are placed closer to the glass on the windowsill and loggia. During the growing season, a constant temperature of + 20-25 ° C is maintained.
Rosemary is a hardy shrub. His immunity weakens only in winter.
Lighting for rosemary should be intense and last at least 7-10 hours a day. In this case, it is important that the shrub receives light evenly from all directions. It is useful to rotate the perennial pot 180 degrees every 3 days. In winter, phytolamps or artificial light sources are additionally used.
Diseases and pests
The following problems can arise when growing rosemary:
- powdery mildew;
- spider mite;
- coccids;
- mealybugs, or felt insects;
- whiteflies can attack weakened plants, especially in winter;
- rotting roots in too wet soil.
To prevent root rot, wilting of the tops of the shoots, rotting of leaves, it is necessary to provide sufficient drainage in the soil, adequate air circulation.
Yellow leaves most often indicate excess water - when rosemary leaves turn yellow, this is the most common symptom of poor watering.
White spots on leaves can have different causes:
- if the leaves are covered with a thin white layer, it is probably a fungal disease - powdery mildew. The affected leaves must be removed immediately.
- Mites can also be responsible for white spots.
White, relatively light spots may indicate the presence of thrips, which feed on plant sap. Diseased plants should be treated with a suitable preparation.
In many regions (Siberia, Ural), frosts destroy the aboveground part of the plant. To prevent this, the plant is planted in pots against the south wall to protect it from cold winds. Using mulch to protect the roots won't hurt either. In warm regions (Crimea, Krasnodar and Krasnodar Territory), rosemary does not need additional protection.
Popular varieties of ordinary rosemary
Domestic varieties of medicinal rosemary (ordinary) are quite few:
- Dewdrop;
- Tenderness;
- Vishnyakovsky Semko.


They are so similar that it is not possible for a novice gardener to distinguish them: all these varieties reach a height of 1–1.5 m, have densely leafy leathery (textured) shoots and small purple or blue flowers.
A foreign alternative to the fragrant shrub is presented in a more diverse range:
- Severn Sea - has a short stature (up to 50 cm) and a particularly "fresh" taste;
- Prostratus - its branches do not straighten up, but bend to the ground, so its height can be called completely "dwarf" - no more than 15 cm;
- Prostratus Hill’s Hardy is an upright growing analogue of the previous cultivar with intense green leaves;
- Taurentius is a dense, non-sprawling dwarf shrub with bright, dark purple flowers;
- Barbecue - the earliest variety, distinguished by a lilac shade of flowers and highly aromatic greens;
- Arp is a very unpretentious plant with pale blue flowers;
- Roseus and Albiflorus - a characteristic feature of these species is fully revealed during the flowering period - their flowers are distinguished by their large size and color that is not standard for rosemary (in 1 they are pale pink, and in 2 they are completely white);
- Miss Jessopp's Variety is a very tall-stemmed variety (up to 2 m) with blue-lilac flowers;
- Majorca Pink is an erect shrub with lavender or pinkish flowers;
- Salem is a tall variety, its leaves have the most delicate and delicate aroma of any “edible” rosemary.


Obviously, there are much more imported varieties, and they also have more tempting characteristics, but most of the inhabitants of Russia do not have to choose: it is worth experimenting with planting heat-loving "foreigners" only in the south of the country, while in the middle lane it makes sense to dwell on the domestic variety , because these plants are more frost-resistant.
Collection and storage
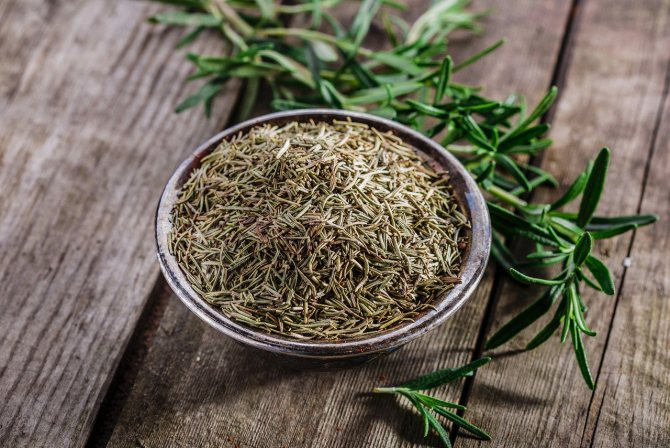
Rosemary can be harvested by pruning. As a spice, rosemary is best used fresh regularly. It can be dried. For drying, it is best to harvest just before the flowering of the plant.
Rosemary can be hung dry by tying bundles of several stems together. The room should be warm and well ventilated. For "forced" drying in tumble dryers, remember that the temperature should not exceed 35 ° C.
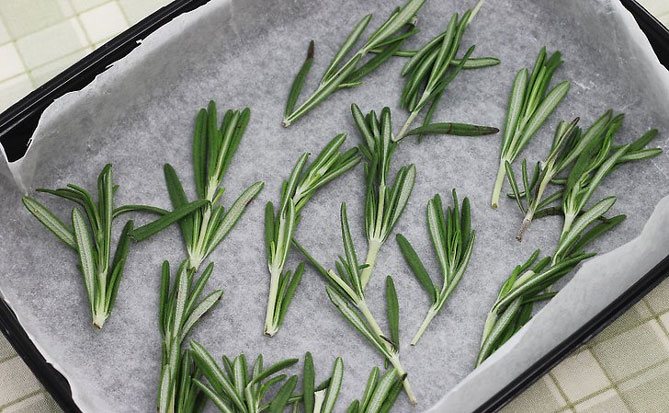


When the stems are dry, the leaves are separated.
There are also other ways to preserve rosemary:
- freezing (sliced in a bag or filled with water to form herbal ice cubes),
- canning in vinegar, oil.
Store dried herb in a dry place, such as a paper bag.
Pinching rosemary
Both in pots and in the garden, rosemary needs pinching to help it grow faster. Usually only young shoots are pinched (from 5 to 15 cm of the apical part). Plucked or cut rosemary sprigs can be used as a seasoning in food preparation, or for growing a new bush.


Timely pinching is the key to good growth
Using
Although our cuisine is dynamically developing (pepper and salt are no longer enough), rosemary is not yet as popular as in French or Mediterranean cooking. While he loses many other spices, such as marjoram, basil, bay leaf, turmeric.
Rosemary is a spice with a specific, spicy-bitter taste and a characteristic strong aroma reminiscent of pine needles. The spice belongs to a group of natural additives used to season foods in very small quantities. For seasoning, use whole or ground leaves (fresh, dried, frozen). It is better to add the leaves at the end of cooking, they increase the clarity of the taste and aroma of the dish (so you cannot overdo it).
Rosemary works well with other herbs, but it can also be used on its own when preparing dishes from:
- lamb,
- pork,
- birds,
- veal,
- beef.
Pork chops marinated in a small amount of chopped rosemary leaves are delicious. The spice enhances the flavor of the dishes, adding a forest aroma to them.
In addition, rosemary works well as an addition to eggplant, potatoes, soups, meat, vegetables, sauces.


The spice is characterized by excellent taste as an additive in baked goods, marinades with the addition of olive oil, wine, garlic.
Lignified shoots without side branches and leaves are sometimes used instead of skewers.
The use of rosemary in cooking
Figs - care and cultivation in the open field, pruning
Today, this spice is confidently winning the hearts of gourmets from all over the world: the question of where to add rosemary gets a lot of answers. The dried leaves go well with fish and meat, as well as many stewed or baked vegetables. Ready meals are also garnished with fresh leaves and shoots.
Important! Due to the high content of essential oils and a fairly bright aroma, this spice requires very careful and extremely dosed use.
Most often, the herb is added a few minutes before the end of cooking to create an interesting accent in the dish. Otherwise, there is a risk of interrupting the aroma and taste of the ingredients themselves.
Composition and medicinal properties
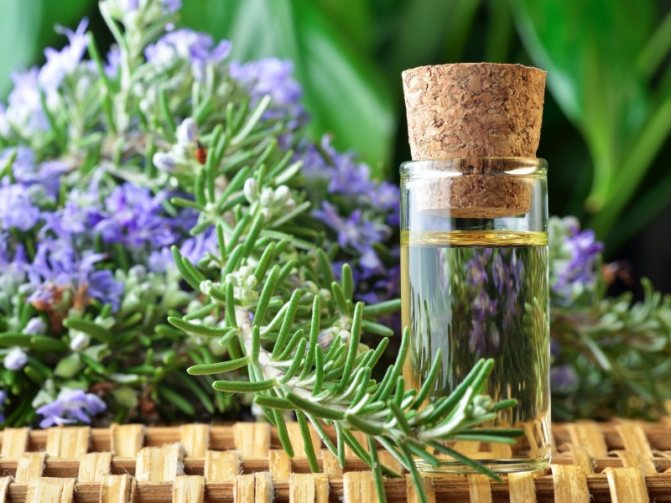
Medicinal raw materials - rosemary leaf contains 1.5-2.5% essential oil. It consists of borneol, cineole, limonene, pinene and camphor. Also, rosemary leaves are a source of flavonoids, tannins, resins, saponins, phytosterols, rosemary acid, vitamins (A, C, B) and mineral salts (calcium, iron, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc).
Attention! Pure rosemary officinalis oil has a narcotic effect and a strong poisonous effect. Pregnant women should stop using it.
Rosemary has the following effects:
- antispasmodic,
- choleretic
- diuretic,
- carminative,
- antiseptic,
- sedative,
- astringent,
- bactericidal,
- strengthens the nervous system,
- stimulates appetite,
- dilates blood vessels.
Rosemary infusion improves mood, relieves mental fatigue, soothes and relieves stress. The infusion is used as a rinse for hair, strengthens it, prevents hair loss, removes dandruff.
Rosemary is used for:
- digestive disorders, digestive system problems;
- liver problems;
- intestinal cramps;
- states of mental stress, depression;
- for general strengthening of the body;
- to lower blood sugar levels;
- with muscle pain, neuralgia (externally);
- from dandruff and premature hair loss (applied externally).
Benefits of rosemary
Rosemary is a source of a large number of useful substances, therefore in many countries it is cultivated as a raw material for the production of medicines.
Medicinal properties of the plant:


increased secretion of gastric juice;- normalization of digestion;
- stimulation of the heart muscle;
- increased blood pressure;
- improvement of cerebral circulation, memory and vision;
- removal of nervous tension, stress;
- an increase in the amount of bile;
- reducing pain;
- air disinfection (efficiency about 80%);
- destruction of harmful microorganisms.
People knew about the ability of rosemary to stimulate the nervous system for a long time: in Ancient Rome, Greece, Egypt, and later in Europe, wreaths of its leaves and flowers were worn not only from superstition (it was believed that they ward off evil spirits), but also from quite practical considerations - for concentration and memory improvement.
Nutritional value of rosemary (per 100 g):
| Energy composition | type of product | |
| dried | fresh | |
| Proteins, g | 4,9 | 3,3 |
| Fat, g | 15,2 | 5,9 |
| Carbohydrates, g | 64,1 | 20,7 |
| Calorie content, kcal | 331,0 | 131,0 |
Content of vitamins and minerals (per 100 g):
| Vitamin composition, mg | type of product | Mineral composition, mg | type of product | ||
| dried | fresh | dried | fresh | ||
| Retinol (A) | 0,16 | 0,146 | Sodium (Na) | 50,0 | 26,0 |
| Thiamin (B1) | 0,51 | 0,036 | Potassium (K) | 955,0 | 668,0 |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 0,43 | 0,152 | Calcium (Ca) | 1 280,0 | 317,0 |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | 1,46 | 0,804 | Magnesium (Mg) | 220,0 | 91,0 |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | 0,863 | 0,336 | Phosphorus (Ph) | 70,0 | 66,0 |
| Folic acid (B9) | 0,19 | 0,109 | Iron (Fe) | 29,25 | 6,65 |
| Nicotinic acid (PP) | 1,0 | 0,912 | Manganese (Mn) | 2,93 | 0,96 |
| Ascorbic acid (C) | 61,20 | 21,8 | Copper (Cu) | 469,0 | 301,0 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 2,62 | 0,93 | |||
The leaves, tops of the shoots and flowers of rosemary contain a valuable essential oil (0.3-1.2%), which is widely used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. The oil contains α-pinene (30%), camphene (20%), cineole (10%), borneol, bornyl acetate, limonene, caryophyllene, L-camphor, and various resins.
Propagation of rosemary
Can be used:
- seeds;
- layering;
- cuttings;
- division of the bush.
Cuttings remain after spring pruning - they are rooted in a mini-greenhouse in well-loosened soil. The length of the cuttings for planting is about 10 cm. Root them at an angle.
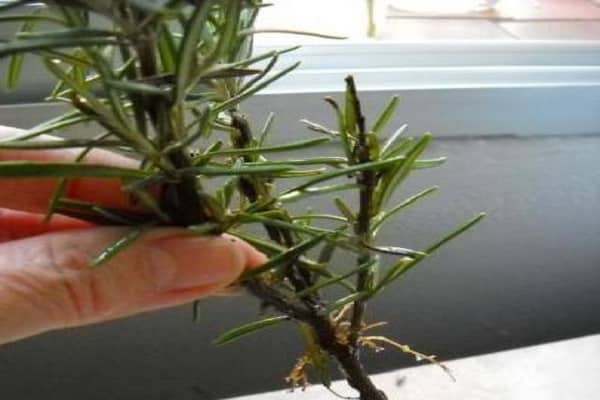


The cuttings should have been small in length
The seeds are usually commercially available - they are sown around February or March, 2-3 months before warming.
On a note! Germination occurs at temperatures above 11-12 degrees.
For disembarkation, it is convenient to use food containers with a lid - it is convenient to ventilate them, it is necessary to leave access for air. The lid is completely removed when the plants have emerged.


Food containers are well suited for disembarkation
Fertilization is required only for those plants that survive the winter in the open field. Complex universal fertilizers with the addition of nitrogen or phosphorus are required. It is enough to carry out top dressing once a month.
On a note! If the plant hibernates indoors, no feeding is required.
Top dressing rosemary
In warm climates, where frost is rare in winter, rosemary overwinters well. The lowest temperature limit for rosemary is 5 degrees below zero, at this temperature the plant may die. Therefore, a good shelter is required if such temperatures can be in winter.


It is necessary to maintain a warm climate in the house
Features of rosemary


Rosemary is a shrub that can vary in height from 0.5 to 2 meters. Its root system is very powerful and developed, it penetrates into the soil to a depth of 3-4 meters. On the surface of grayish obtuse-tetrahedral young shoots there is pubescence. Perennial woody stems with peeling bark are colored dark gray. Seated linear leaf plates, leathery to the touch, have downward curved edges. The leaves reach about 0.4 cm in width, and up to 3.5 cm in length, their front surface is glossy, and pubescence is on the back. Lush panicle inflorescences consist of pale purple, dark purple or white flowers. This plant is a relative of the following crops: hyssop, basil, lavender, mint, motherwort, thyme (thyme), oregano and lemon balm. The tops of annual shoots, along with foliage and flowers, are used fresh, adding to dishes from legumes, cabbage, eggplant and meat.
Selection and preparation of a flower pot
The rhizomes of rosemary are highly branched and a deep and wide container is better. It is good when the bush pot is made of ceramic or clay. Plastic or wooden ones are not suitable for it, since in the first case, the thermoregulation of the soil will be unnatural, and excess moisture will negatively affect the tree. This can lead to rotting of the root system or damage to it by a fungus.
When choosing a pot for a fragrant shrub, it must be borne in mind that the plant must necessarily drain. Therefore, the depth of the flower container must be calculated "with a margin". This will allow enough room for the rosemary and not run out of space in the pot for its roots. But you do not need to take an excessively large flower pot - for the first time, a capacity of 1-2 liters will be enough to grow medicinal rosemary from seeds at home.
Reproduction methods and rules
Propagated by seed or cuttings, rosemary. You can use the methods of layering and dividing the bush, but, given the high efficiency of the first two methods, there is no particular need for this.
To grow this spicy crop from seeds, you will need containers, sheet soil mixed with sand and expanded clay. The seed can be purchased at flower shops. If you grow rosemary exclusively as a spice, choose undersized, early maturing varieties, for example, Tenderness, the leaves of which become usable after 3 months.


They begin to sow seedlings in March:
- Containers ½ are filled with drainage, soil is laid on top, watered abundantly.
- Spread the seeds at a distance of 1.5-2 cm, cover them with a thin layer of sand, lightly tamp them.
- The containers are placed in greenhouse conditions. Ventilate frequently, avoiding condensation.
- If necessary, moisten from a spray bottle, preventing overdrying of the top layer of the soil.
Seedlings appear by the end of the month. They are gradually weaned from greenhouses, placed on southern windowsills to prevent stretching. After 3-4 true leaves dive into separate containers, pinch. They are planted in the ground when the threat of recurrent frosts has passed. Before disembarking, at least a week is taught to new conditions, gradually increasing the time spent on the street. Rosemary seedlings can be grown in greenhouses, and in regions with warm spring, sown with seeds directly into the ground.
Rosemary and cuttings propagate well. Cuttings of young shoots 5-10 cm long are suitable. The lower part of the shoots is freed from the leaves and dipped for half an hour in a solution of any root formation stimulant (Epin, Kornevin, succinic acid). It is better to use sand for rooting cuttings. You can also put them in a glass of water. To prevent souring of the liquid, a small amount of charcoal is added to it, for example, a burnt match.
The containers are placed in a warm, not lower than 20 degrees, well-lit place, protected from direct sunlight. Cover them with a jar or plastic bag. The greenhouses are ventilated several times a day to prevent condensation from getting on the cuttings. If roots sprout in the water, keep it constant. If necessary, moisten the sand, preventing it from drying out.
The roots appear after 3 weeks, and after 4, when they get stronger, the cuttings are ready to be transplanted into pots - on the street the immature seedlings will die. Use a mixture of sheet soil and sand, lightened with coconut fiber. After another 2 weeks, pinch the tops to stimulate the growth of lateral shoots. Further, the seedlings are looked after as adult plants. After a month, they can be planted in open ground.
How to properly provide wintering?
The first frosts in the middle lane are usually expected by the second half of October - at this time, rosemary is placed in a warm room, where the temperature will not drop below +7 degrees.
On a note! Carefully move the rosemary from the garden or flower bed into a tub or container without damaging the roots.


You need to move the rosemary very carefully.
Something to remember for those who grow rosemary at home.
- The volume of the pot must be at least a liter.
- The soil should be well prepared or purchased from a garden store. Components - sod land, leaf humus, sand.
- Lay expanded clay or pebble drainage at the bottom of the pot.
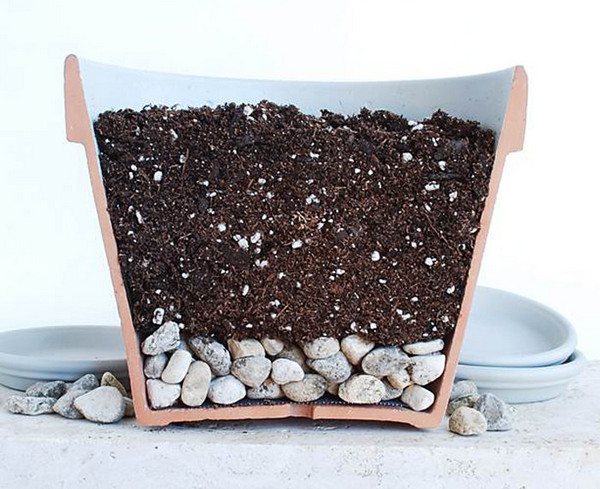


Expanded clay or pebbles need to fill the bottom of the pot - When sowing seeds, they are not covered with earth, but only leveled over its surface.
- The first watering of seeds is carried out using a spray bottle.
When the first shoots appear, carefully remove the film in order to accustom the plant to indoor air. You can winterize rosemary in pots in a cool room, and when grown in a room on an ongoing basis, transplant it every two years as the root system grows.


Expanded clay or pebbles need to fill the bottom of the pot
Germinating seeds
First of all, the rosemary seeds must be soaked by placing them between 2 cotton pads and dampening with water. After that, it is enough to wait 2-4 days.
Next, the soil is prepared. To do this, you need to mix leafy soil, peat and sand (or purchase ready-made soil for seedlings). This composition must be poured into a prepared container and spilled with water. After that, you need to spread the seeds on the ground and sprinkle them with soil a little. It is best to put a piece of transparent cellophane on top and remove the blank in a warm place.
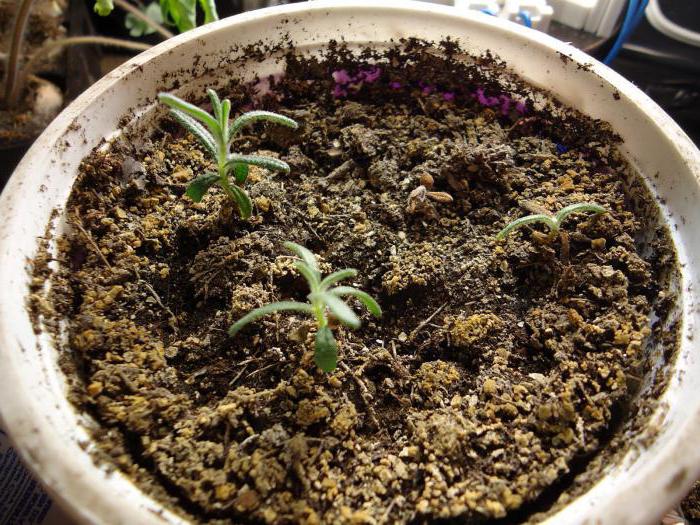


As soon as the first shoots appear, you can transfer the pots to the windowsill.
How to germinate seeds?
Before sowing seedlings, it is best to pre-germinate seeds to improve germination.Before being sent to the ground, the seeds are soaked, spreading them between two clean cloth napkins or cotton pads. Soak for about three or four days, maintaining moisture.
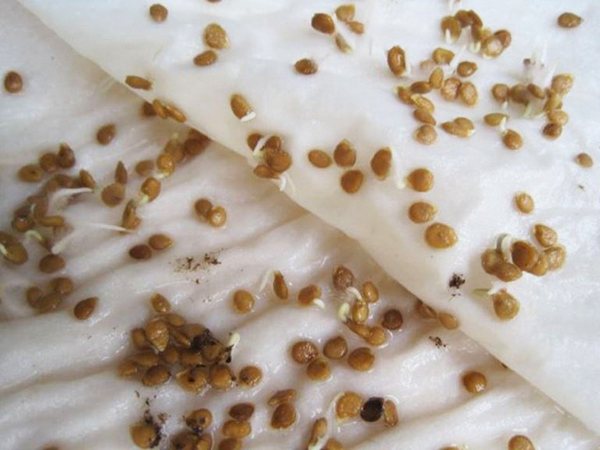


To strengthen the seeds, it is better to soak them first.
For sowing, a substrate is prepared from a mixture of deciduous humus, sand and peat. You can use ready-made seedling potting mix.
On a note! Seeds are laid out in a flat tray with a substrate, without burying in the ground, covered with a film and removed to a warm place until the first shoots appear.


The substrate will be useful for seedlings
Rosemary germination is reduced due to the presence of a large amount of essential oils. This makes it similar to plants such as carrots and basil, so it is recommended to soak the seeds in a growth promoter or just in water.
Seed washing increases germination - for this they are laid out in a deep glass dish and poured with water for about half an hour, then filtered through cheesecloth and the procedure is repeated up to 3-4 times.


Washing the seeds improves their growth
Reproduction by dividing the bush
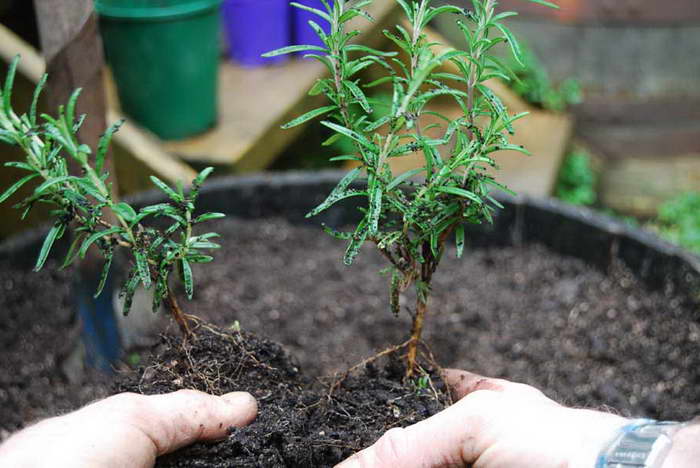


How to split a rosemary bush photo
Indoor rosemary is most often propagated by dividing the bush. Remove the bush from the soil, divide it into several parts: each division should contain a developed rhizome and shoots. Treat the cut sites with a fungicide, plant the cuttings.
Characteristics of rosemary and what it looks like
Rosemary is a genus of perennial plants from the Lamiaceae family. In its natural habitat, it can grow in the form of a shrub or semi-shrub, due to which it is quite often grown as a hedge. The Mediterranean wild plant can be found in the dry sloping mountains of Africa, Turkey, Cyprus, Greece, Israel, Italy, Portugal and Spain.
The shrub has a highly developed root system, which is capable of penetrating 4 m into the depth of the soil, due to which it can grow even in arid areas. Thanks to its beautiful and flexible bark, the plant can be grown in the bonsai style. The height of the bush can reach 1.5-2 m in its natural habitat and up to 1 m indoors.
Sessile leaves in a linear shape are attached to the gray pubescent shoots of rosemary with the help of short petioles. Leathery glossy leaves with curved edges have a two-tone color. Above they are deep green, and below they are gray-green or almost white.
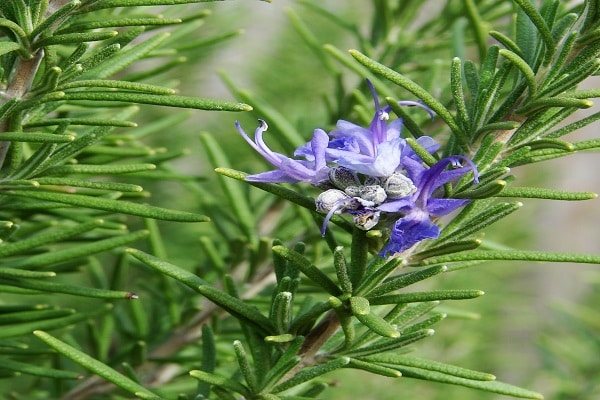
Blue-violet rosemary flowers are collected in dense inflorescences of small size. Flowering under favorable conditions can last about 25 days. The shrub exudes a pleasant refreshing aroma, reminiscent of a mixture of pine needles, eucalyptus and lemon.
What kind of rosemary is found on sale
Specialized stores offer rosemary varieties to gardeners:
- Semko, Tenderness, Vishnyakovsky, Rosinka (developed by Russian breeders);
- Severn Sea (grows to a maximum of half a meter);
- Prostpatus (shoots spread along the ground, carpet height 15 cm);
- Roseus (differs in flowers of a pink hue);
- Albiflorus (decorated with white flowers).
Foreign varieties are particularly decorative.


Trimming and shaping
Cut off some of the shoots to give the rosemary bush the desired shape. As a rule, this occurs in mid-spring, until the plant has entered a phase of active growth.
On a note! Approximately every eight years, the plant is rejuvenated - the bushes are cut to the very root.
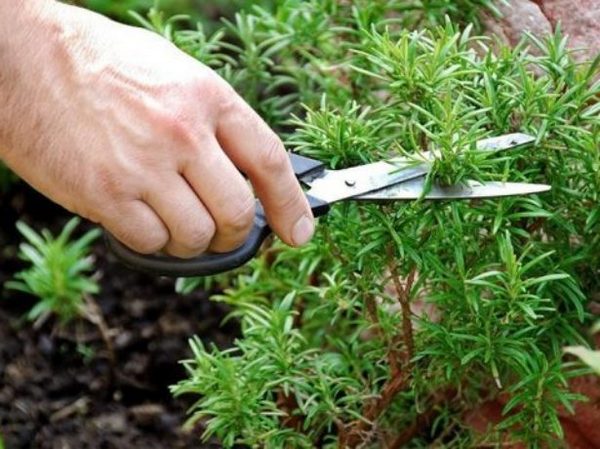


Only part of the shoots needs to be cut
Cut young twigs can be used immediately on the farm - fresh or dried. Greens are also harvested in the fall, before sending the plant for the winter.
Plant application
Essential oil extracted from rosemary is used in the manufacture of medicines from migraines and diabetes mellitus. The plant also helps in the treatment of diseases of the liver, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.
The aroma of rosemary is prized in cookingwith a pleasant pine scent.It is added to meat and fish dishes, and is used to decorate desserts. Drinks containing rosemary have a tonic taste and are good for rejuvenating.
The spice grown in the home purifies the atmosphere and infuses it with soothing fluids.
Possible growing problems and how to solve them
Growing rosemary rarely has any problems. The most important thing here is to adhere to all instructions and take proper care. But you still need to be aware of possible errors:
- if the leaves are dull and wither, protect the rosemary from direct sunlight, create a shade for it;
- if only the lower ones turn yellow, watering should be increased;
- if the aroma of the plant has become weak and the leaves fall off, on the contrary, moderate watering;
- if the leaves are curled up and covered with dots, the bush is affected by a whitefly or aphid, spray the plant with a suitable composition ("Admiral", "Aktara", etc.).
Southern plants are always associated with rest, warmth, sea and relaxation, so almost every gardener seeks to have one or two such green guests on his plot. Recently, rosemary is gaining great popularity. Through trial and error, gardeners have adapted this fragrant shrub to life in different regions of Russia.
Rules for buying a new plant
When buying an adult rosemary, pay attention to its appearance:
- leaves should be rich, dark green;
- they should not have yellowness and black dots;
- look at the bases of the trunks so that there is no white bloom on them;
- bushes should be branched, which indicates a well-developed root system.
If you pluck a leaf of a healthy and strong plant and rub it in your hands, you will feel a characteristic intense smell. In diseased specimens with a damaged root system, it will be weaker.
Transfer
Rosemary, which is constantly growing in a pot, needs annual soil renewal. The transplant procedure is carried out in the spring. If necessary, increase the diameter of the pot by 2 cm.
Choosing the right pot and soil
Soil for rosemary should be light, breathable and moisture-permeable, nutritious. A mixture of leafy, turfy soil and sand will be optimal. For loosening, add agroperlite, vermiculite and coconut substrate. Peat, especially horse peat, like sphagnum moss, is not mixed, since the roots of rosemary do not develop well in an acidic environment.


The branched root system of rosemary needs a wide pot. It can be plastic, but the plant feels more comfortable in ceramic containers, which are less heated in the sun. The size is selected so that 5-7 cm remain from the stems to the side. The presence of drainage holes is mandatory.
Step-by-step transplant process
Planting rosemary in a pot is carried out as follows:
- The plant is removed from an old container.
- The root system is partially freed from the soil and carefully examined for rot. All questionable areas are removed by abundantly sprinkling the sections with charcoal.
- The roots can be trimmed by 1/3 if necessary.
- A layer of drainage and fresh soil is placed in a new pot.
- Place the rosemary bush so that the base of the trunk is not below ground level.
- Pour the substrate on the sides, tamping it slightly.
- Water abundantly.
When transplanting adult rosemary, greenhouse conditions are not needed.
We select the best landing place
Rosemary is a Mediterranean inhabitant. To grow it in other regions, you should create conditions as close as possible to your native ones. You need to take care of planting in advance: only in this case the gardener will get the desired result.


Accommodation at home
“Urban summer residents” also successfully grow rosemary. At home, it is realistic to create suitable conditions:
- put rosemary on the southern, southwestern or southeastern windowsill (if there are none, the western or eastern ones will do);
- the bush requires additional lighting (agrolamp is suitable);
- to ensure the required air humidity, it is recommended to pour a layer of expanded clay 2-3 cm thick over the ground of the pot (when it is moistened, the water evaporates, and the air around the rosemary becomes comfortable);
- plant roots need air access: rosemary should be planted in a clay container;
- the shrub should be replanted once a year (the pot should be 2/3 larger than the previous one);
- a guest from the Mediterranean is afraid of drafts: when airing, it is required to protect him with a plastic screen.


Subject to all the rules, the plant will delight the gardener with aroma and original flowers. But the British argue that at home rosemary grows only with good owners.
Landing in the country
Before planting on the site, the gardener should carry out preparatory work. In its homeland, rosemary is an unpretentious plant. But in regions with excellent climatic conditions, you need to carefully prepare. The shrub feels great in the place:


- the sunniest and warmest;
- sheltered from cold northerly winds;
- with deep groundwater;
- with alkaline, light soils.
Placement on the south side of the house is ideal. The wall will cover the rosemary from the northerly winds. It heats up during the day and gives off heat to the plant at night.
Rosemary does not tolerate shading. In insufficient light, it withers and sheds leaves.


On flooded areas, drainage should be poured into the planting pit. Crushed stone, broken red brick, gravel, expanded clay are suitable. Layer thickness - 5-10 cm.
Rosemary placed in the garden does not tolerate weeds in the neighborhood: the soil around must be clean. In dry summers, mulching of the earth with a layer of 5-7 cm is allowed.
If the soils do not meet the required characteristics, it is necessary to carry out structuring in the intended planting site..
See also
Types and varieties of rosemary with names, cultivation and careRead


In the greenhouse
Some gardeners have enough space to accommodate a plant in a greenhouse. In regions with harsh climates, gardeners try to grow rosemary in heated greenhouses. Subject to the rules of cultivation, summer residents have spicy herbs on the farm all year round. Some sell cut shoots: the demand for an exotic spice is great.
What the plant needs:


- light calcareous soils with an admixture of rubble;
- lack of neighbors-weeds or cultivated plants;
- moist warm air;
- lack of drafts;
- temperature in summer is 25-26 degrees Celsius, in winter 5-15;
- daylight hours 16-18 hours.
Summer residents often plant rosemary in an unheated room. In this case, the plant is ready for cutting 2-3 months earlier than planted outdoors. Leave a bush in such a greenhouse for the winter only during relatively warm winters: the temperature should not fall below zero. Otherwise, the guest from the south will freeze.


What problems can you face?
Usually rosemary does not tolerate high soil moisture - this leads to the formation of a whitish coating on the leaves. The frequency of watering should be reduced and the plant provided with plenty of sunlight. Fungicide helps some plants, but after using it, rosemary leaves will become unusable and even poisonous.


Fungicides make rosemary poisonous
On a note! The enemy of rosemary is the spider mite. It starts in dry air, and you can get rid of it by spraying it with insecticide and clean water.
Large rosemary bushes form a huge number of shoots, therefore, require transplanting.
Growing your own rosemary is a great way to get a lovely and always fresh seasoning and beautiful plant at home.
Errors in indoor growing
Rosemary in a container can suffer from some accidental mistakes - the leaves will begin to turn yellow, dry out or lose color saturation.Problems with indoor cultivation, if you follow agricultural techniques exactly, rarely arise. But, when the bush began to feel worse and looks lethargic, before treatment with drugs, you need to check for the presence of such signs:
- yellowing and falling foliage - lack of watering;
- wilting and drying of the lower leaves - waterlogging;
- spotting - lack of copper, fertilizing with copper-containing fertilizers is needed;
- darkening of leaves - lack of light or hypothermia.
Even an inexperienced grower can take care of rosemary indoors. The shrub is not particularly capricious, but immediately reacts to the deteriorating conditions of detention. Overflows should not be allowed, and in winter it is imperative to protect the plant from drafts and cold, reducing the lack of daylight hours with the help of a phyto-lamp. Rosemary, if agrotechnical standards are met, will develop well and yield crops even on the windowsill.
How to trim?
After the plant has grown, crown formation can be performed. To do this, pinching the ends of the branches to slow down the growth of shoots.
| Step | Description |
| Lumber branches are cut. It is important to leave enough green matter for the plant to retain its vigor. |
| Prune again after the plant has faded |
| Remove no more than 1/3 of one shoot, starting from the tips of the leaves. In no case should you chop down the bush at the base. |
| When pruning, you need to leave bearing old shoots. |
Important! Pruning is carried out either in winter or early spring.
Growing problems
As always, problems arise where care is misplaced. Rosemary was poured, and its leaves turned yellow, and there it was not far before the appearance of powdery mildew.
The plant lacked moisture - it sheds leaves. Low humidity can cause spider mite infestation.
The lack of light and nutrients affects the state of the shoots: they weaken and stretch out strongly. Restore competent care, and all these problems will not affect you.
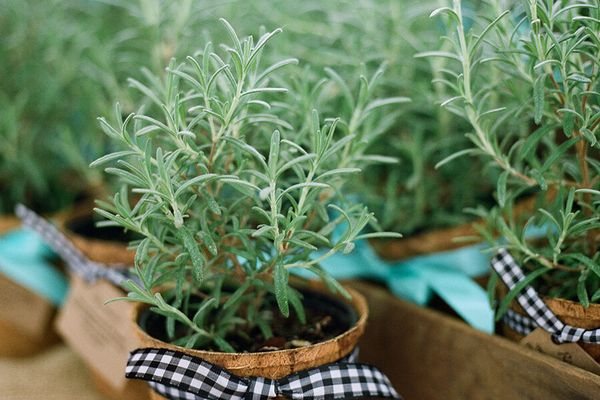


How to plant rosemary outdoors?
In the second half of May, after the complete end of frosts, the seedlings are moved to a permanent planting site. There are no special requirements for the soil, rosemary can easily grow on nutrient-poor soils. However, it is important that the soil is loose enough to allow air to pass through.
Important! Plant the rosemary in a sunny spot, preferably against a wall that will keep out the wind.


It is necessary to loosen the soil on which the rosemary grows
Rosemary does not require frequent watering, just water it as the soil dries. During the flowering period, the inflorescences are cut off and used for culinary or medicinal purposes, as well as for drying. Upright rosemary requires pruning, but widespread varieties do not. At the same time, the second type of rosemary tolerates pruning well - this way you can collect young shoots.

Not all rosemary varieties require pruning.
Important! In no case, do not cut the shoots to the woody old sections of the plant - this leads to damage, it is necessary that a quarter or a third of the length remain.
Cuttings
If vegetative propagation of rosemary is necessary, the grafting method is used - fresh shoots are cut about 5-10 centimeters long, a nutritious soil mixture is prepared into which the planting material is planted. Leave in a place shaded from sunlight or on a northern windowsill. The root system will begin to develop in about two months.
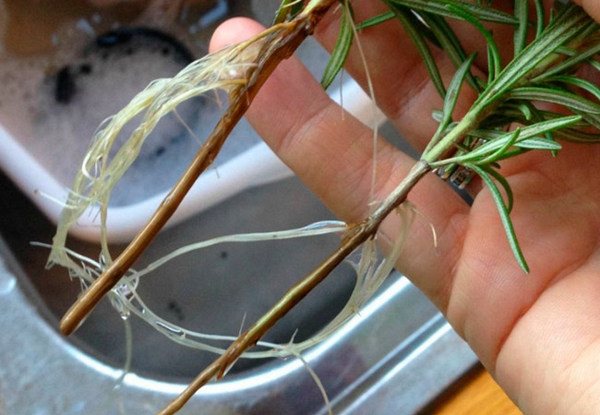


Roots after cuttings appear after two months
On a note! When planting cuttings, keep a distance of two meters from each other - the bushes of open rosemary can reach more than a meter in length.
Priming
The soil for planting rosemary is selected loose so that air and water can flow well to the roots.In the wild, rosemary grows on soils with a high content of sand and gravel. Its root system allows it to stay well in the ground.
On a note! Acidic and waterlogged, swampy soils are unacceptable.


Do not plant rosemary on acidic soil.
What varieties of rosemary can be grown in the apartment?
Translated from Latin the name of the plant sounds like "sea dew"... It comes from the Mediterranean coast, where its lush bushes (pictured) grow in the warm southern sun.
However, not all types of rosemary are suitable for home keeping. Experts recommend certain varieties:
- fragrant or aromatic;
- drug;
- Tenderness;
- Richard;
- Dewdrop.


Care conditions
Correct care sometimes turns out to be much more important than taking into account the nuances of planting. There are some general rules.
Watering
Watering will depend on many conditions, including the region in which the shrub was planted. Rosemary bushes are usually watered sparingly. If the weather is hot outside, then you need to water every other day. If it is still cool enough, then watering should be repeated every 3-4 days. It is important to ensure that the soil does not retain moisture and has good drainage, so you will have to periodically pad the beds.
Top dressing
Active fertilization should be started closer to flowering. Once a month, between April and August, the shrub should be fertilized. At the beginning of autumn and throughout the winter, this is needed no more than once a month.
Wintering
The most difficult period for rosemary is winter, since frost resistance is not at all inherent in it. In order to minimize the risk of plant death, you need to build a greenhouse for it, the roots need to be covered with sawdust. Watering for the winter is reduced to 1 time in 7 days. If the spice lives at home, then watering should be done more often - 2 times every 7 days.
Of course, wintering depends entirely on climatic conditions. In the south, the plant most often does not need any manipulations at all and winters well by itself in the same garden or garden.
Diseases
Rosemary has excellent immunity. It is not susceptible to diseases, and its pungent smell repels almost all pests.
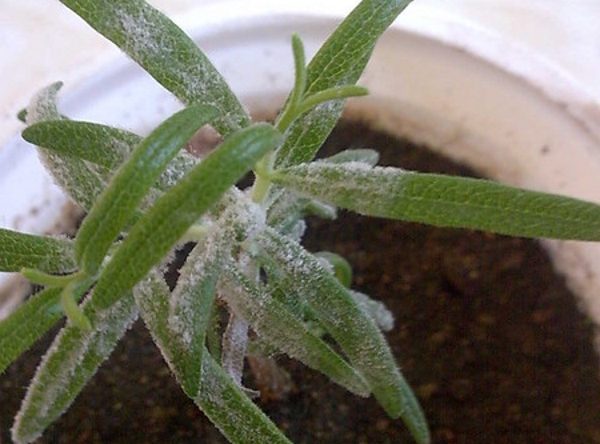


If, nevertheless, you notice a white coating on the leaves and stems, which subsequently turned brown, the plant is affected by powdery mildew. This is not scary - it is necessary to remove the damaged areas, transplant into uninfected soil and treat with special means (for example, Baikal-M or Fitosporin-M)
For those unfamiliar with rosemary
Rosemary is widely used in cooking:
- is part of fruit salads;
- in the form of sauces and additives to fillings of stuffed eggplants, tomatoes, zucchini;
- added to bean and pea dishes;
- is a part of dishes from all types of cabbage;
- used in hot dishes of meat and poultry;
- lovers drink tea with rosemary.
Dear Readers! A magnificent new plant may appear in your indoor flower garden, which will not only decorate the room, but also serve as a good healer. Try to grow and you will not regret the time spent.