Root zone processing
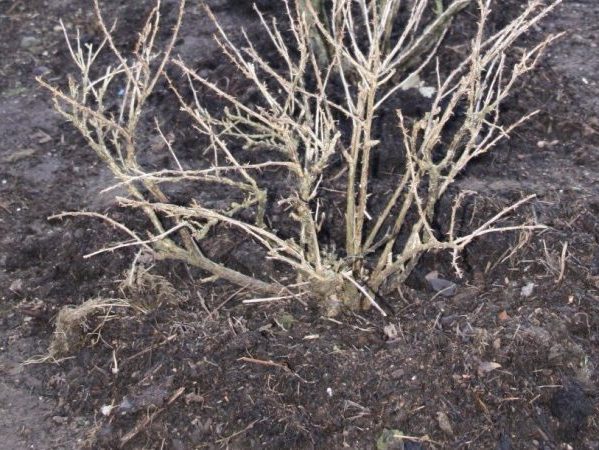

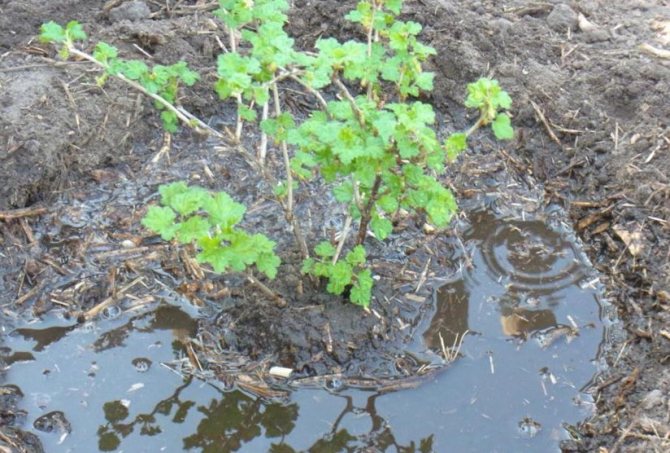
Gooseberries in the fall. Mulching the trunk circle
From spring to autumn, the gardener monitors the purity of the near-stem circle of berry bushes: removes weeds, loosens, mulches. After all, the hygiene of cultivation of fruit crops is a third of success. But, despite this, after harvesting under the gooseberry bushes in the fall, there is no end of work:
- The first step is to rake out the fallen berries and foliage. If traditionally prickly varieties grow, then, protecting your hands with thick gloves and armed with a convenient tool, up to tweezers, they put things in order between the stems of the gooseberry, leaving no plant residues before winter.
- If sick, mummified fruits remain on the branches, they must be removed. Not a single berry should remain on the gooseberry before winter. This will deprive mushroom spores or pest larvae of comfortable wintering conditions.
- Weeds that have managed to appear are weeded out. The upcoming feeding will provide them with a rich nutritional base: the weed will grow, taking away food from the gooseberry.
- When the near-stem circle and the space between the stems are completely cleared, the earth is gently loosened. The closer to the center of the circle, the shallower the depth: there the soil was not so trampled while the harvest was in progress. To the outer circle of the projection of the crown - deeper: during the removal of fruits around the bush, the ground was compacted with feet, so air access to the roots is limited.
- Outside the projection of the crown, where the roots of the gooseberry are gone, the earth is dug up. Depending on the distance between the bushes and the spread of the roots of adjacent plantings, digging from half to full bayonet depth.
- The trunk circle is sprinkled with a continuous layer of wood ash. The double effect of this measure is the additional feeding of gooseberries and the impact on pests and their larvae.
- The last stage is mulching the trunk circle. A thick, at least 10 cm, layer of mulch will cover the roots from freezing, create more comfortable conditions in winter.
If you use compost, humus, then two tasks are solved at once - insulation + feeding. Important! You can fill the ground with peat, rotted sawdust, straw. But in the last two variants, mice often settle. Small rodents like to eat gooseberry trunks in winter. For protection, rubber hoses, car tires or camera trimmings are laid out around the stems.
Fertilizer selection
For the normal growth and development of gooseberries, a lot of substances are required, including:
- Nitrogen.
- Phosphorus.
- Potassium.
Nitrogen is used to gain green mass and is an indispensable link in photosynthesis. The lack of a component is accompanied by loss of yield and wilting of green parts. In the absence of radical measures, the growth of gooseberries slows down, and the berries ripen unevenly or crumble. Oxygen starvation occurs when:
- Excessively high soil acidity.
- An overabundance of organic fertilizing, due to which nitrogen takes on a form that is difficult for a shrub.
- An abundance of weeds that absorb matter from the soil.
However, an excess of nitrogen also negatively affects gooseberries and manifests itself in an accelerated set of green mass. This worsens the frost resistance of the bush and causes freezing of young growth in the cold season.
The soil is saturated with a substance in the following ways:
- Vital activity of microorganisms.
- Introduction of organic and mineral compounds.
The main sources of nitrogen include the following compositions:
- Ammonium sulfate. It is intended for the formation of aboveground elements and affects the fruiting of crops. The fertilizer granules dissolve quickly and are not washed out of the soil by precipitation. The disadvantage of the composition is the increase in acidity.
- Ammonium nitrate. Strengthens the gooseberry immune system and has a healing effect on the soil. The substance is distinguished by its rapid dissolution, but in excess, it causes burns.
- Urea. It also strengthens the immune system and is used to prevent dangerous diseases and pests. The composition is introduced into the soil during spring digging. It dissolves quickly and is well absorbed by the shrub. At the same time, there is practically no negative impact on the ground or green parts.


The next important element is phosphorus. It is necessary for most of the life processes in the berry bush: respiration, water absorption, berry formation, etc. Lack of phosphorus results in purple or dark green spots on foliage. In addition, this problem reduces the number of ovaries and makes the shrub stunted.
The excess of the substance does not cause negative consequences, since the plant consumes only the required amount of phosphorus and no more. Deficiency of a chemical element is especially dangerous for young bushes. It is impossible to eliminate the symptoms of phosphorus starvation even with enhanced feeding in the future.
Phosphorus is found in the following mineral formulations:
- Simple superphosphate. It is necessary for a shrub at the stage of fruit formation. Affects the taste and aroma of berries.
- Double superphosphate. Used to strengthen the gooseberry root system.
- Phosphate flour. It is used for processing soil with high acidity.
Potassium is also required for the development of gooseberries. It participates in photosynthesis and metabolic processes, and also determines the sugar content in berries and affects flowering.
Lack of potassium leads to the fact that the shrub ceases to form lateral processes, and the leaves curl and die off. The size of the fruit is reduced and the quality is low. Excess calcium causes the ovaries, leaves and berries to fall off.


To saturate the gooseberry with potassium, the following dressings are used:
- Potassium sulfate. It is introduced under the bush in the fall and is intended to improve the frost resistance of the crop.
- Potassium chloride. It is the most demanded component in the cultivation of berry bushes. It is the main top dressing for the normal course of vegetation processes.
- Potassium salt. Differs in efficiency during soil digging in autumn and spring.
In addition to the listed fertilizers, complex formulations are used for gooseberries. Among them:
- Nitroammofosk. It is a balanced triple fat containing nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Top dressing is used in the autumn period in the amount of 100 g per bush or in the summer in a liquid state (50-60 per sq. M).
- Nitrofoska. Contains 3 important components (nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus). The composition is suitable for autumn-spring processing of bushes and is consumed at the rate of 70-80 g per sq. m.
- Ammophos. It is a combination of 12% nitrogen and 40-50% phosphorus. Applied to gooseberry bushes in autumn.
- Nitrophosphate. The composition is composed of 23% nitrogen and 17% phosphorus. Designed for both summer and autumn use.
Gooseberries respond well to organic fertilization. They saturate it with useful substances, strengthen the immune system and increase resistance to diseases and pests.


Introduce under the bushes:
- Slurry.
- Bird droppings.
- Mullein.
- Compost.
It is better to provide organics in a liquid state by diluting the components in a bucket of water. The proportions of substances are determined according to the following scheme:
- Slurry - 1:10.
- Compost - 1: 4.
- Mullein - 1: 6.
- Bird droppings - 1:13.
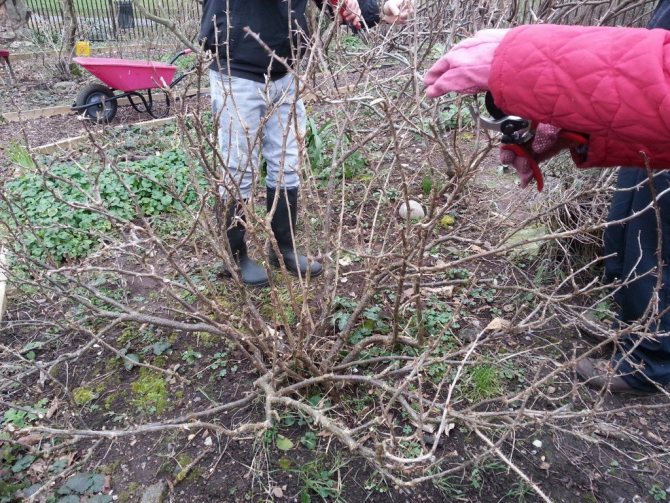
Pruning gooseberries in the fall
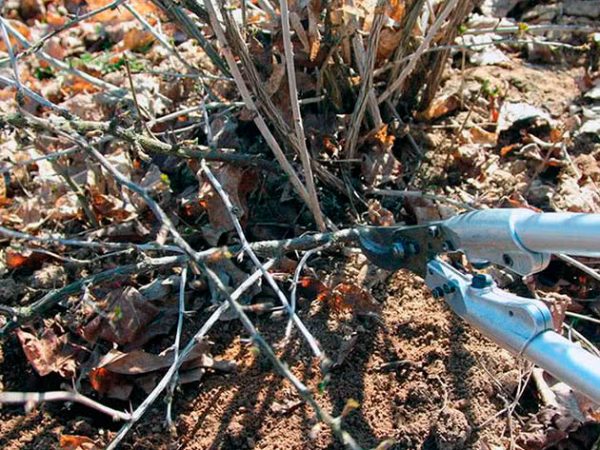


Pruning gooseberry bushes in the fall
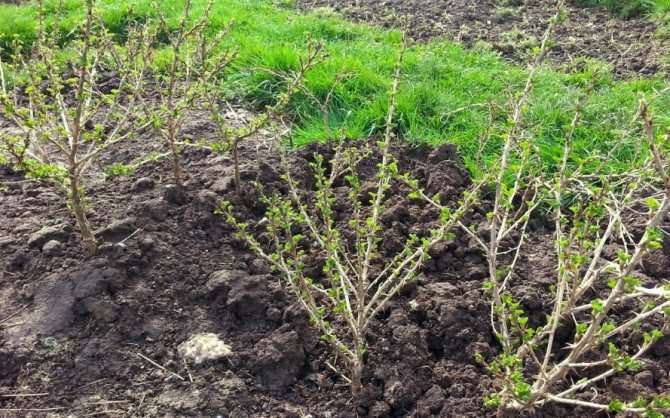
Preparation of gooseberries for the coming winter begins in early autumn, when all the fruits have already been removed, the foliage dries up and falls off. As the shoots are exposed, problem areas become visible:
- broken, shriveled branches;
- stems showing signs of infection: darkened bark, spots, fungus or mold;
- root growth, horizontally growing branches along the ground;
- thickened areas with shoots growing inward;
- duplicate branches (or competitors) grow side by side, in parallel, interfering with each other and thickening the bush.
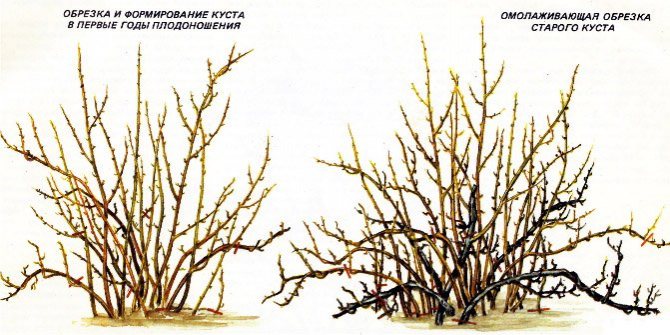
The first two points - healthier gooseberries - sanitary haircut. This procedure is carried out in the first place, after which the front of further work is more clearly visible. The next three problems on the list are the main pruning task for the formation of gooseberry bushes in the fall.
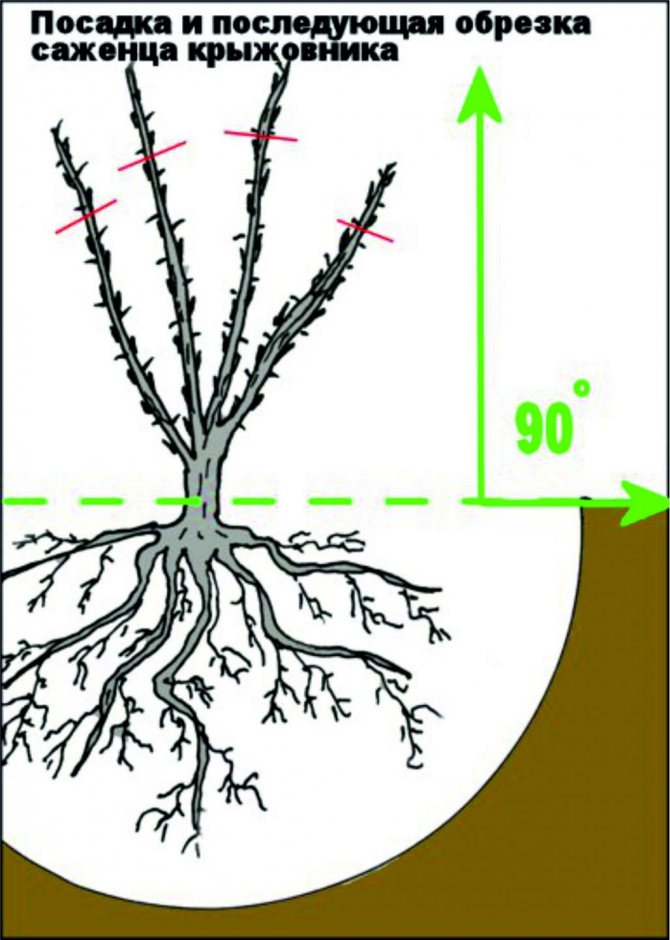
It is important not only to see what to prune, but also to know how to prune gooseberries correctly in the fall. And this already depends on the age of the berry. Only the planted bushes are shortened so that at least 4 buds remain on each shoot. Each next year of the gooseberry's life according to the scheme:
- Leave 3-4 zero (this year) stems. They are shortened to 20-30 cm.
- All sterile shoots are removed under the root.
- The central shoots (depending on the age of the bush 1-4 pcs) are shortened by a third, the side shoots are removed from them.
- Cut out all large and small branches growing in the center of the bush.
- Of the backup branches, the one that is stronger is left, which bears fruit more abundantly. It, like the rest of the shoots, is shortened by a third, and the competitor is cut out.
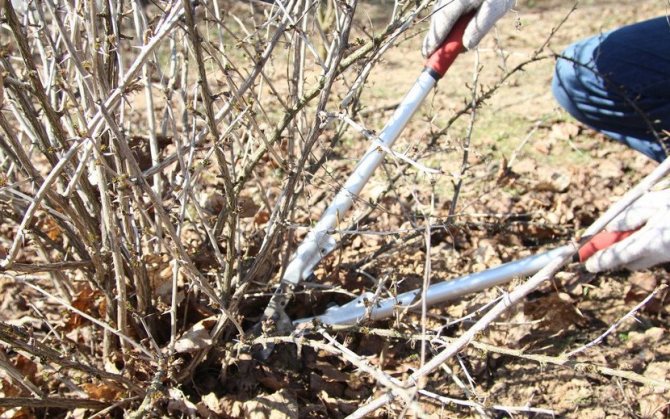
- On bushes over five years old, the removal of 5-year-old stems is added to the listed items.
If the gardener does not set the goal of forming a bush in a special way - with a stem or under a trellis, then these classical pruning measures are sufficient for long-term fruiting of gooseberries.
They carry out sanitary and formative pruning of gooseberries, when the foliage has already fallen, the bush is bare, the average daily temperatures are not higher than 10-15 ° C, but the first frosts are not expected for another couple of weeks.
Important! Cut the shoot obliquely and so that there is a kidney 3-5 mm from the cut on the outside. Slices are covered with pitch.
The importance of autumn gooseberry care
After fruiting has ended and all the berries are collected, it's time to take care of the gooseberries. During fruiting, the strength of the bush has depleted, all nutrients have been selected from the soil, and flower buds of the future harvest must still be laid on the bushes, so in the fall the gooseberry needs special care.
In addition, it is important to carry out preventive measures against pests and pathogenic microorganisms in the care process, which can hide in the soil and vegetation debris for the winter.
In particular, it is important to care for varietal gooseberry species. In its absence or with poor care (including in the fall), varietal traits can be lost irretrievably. As a result, the berries become small, their taste deteriorates, and the yield decreases sharply.
The main activities for caring for gooseberries in the fall are pruning and feeding.
Top dressing for gooseberries in the fall is very important - the shrub receives nutrients, recovers its strength after fruiting, thus preparing for the onset of the winter season.
Correct pruning during autumn care allows you to remove excess, dried and damaged shoots, thereby improving the appearance of the gooseberry. Also, rejuvenating pruning is carried out, in the process of which old branches are removed, which take food from fruiting shoots, and cannot bear fruit themselves.
Moisture-charging gooseberry watering in autumn
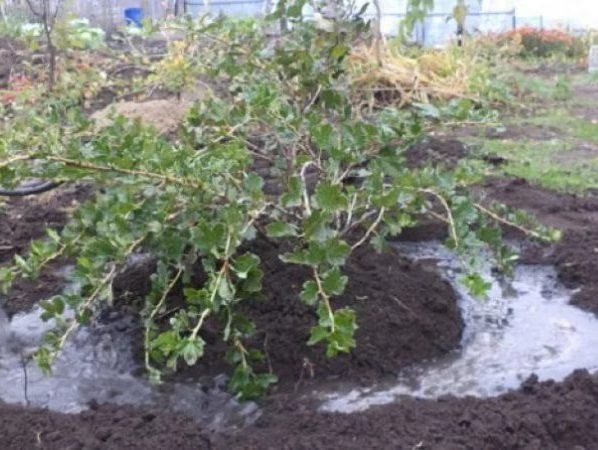


Preparing gooseberries for winter
This is the name of the last watering of the season, podzimny. For berry bushes, it is important if the autumn is dry or with occasional rains. Moisture-charged irrigation will nourish the roots, shoots, the bush will leave before winter with a sufficient charge of moisture, which prevents it from freezing.
To provide a culture with a deep root system with a sufficient amount of moisture, like that of a gooseberry, 3-4 buckets are poured under an adult, from 3-4 years old. 1-2 is enough for the young. How to water properly so that the water goes deep and does not spread:
- A groove is dug along the border of the crown projection, the width and depth of which is up to 10 cm. The required volume is gradually poured into this groove under the root and into this groove (from a hose or watering can).
- In the same place, they do not make a groove, but an earthen roller that will keep water inside the trunk circle.
Important! In a rainy autumn, this point of care is excluded, since excess moisture for the berry is harmful.
Folk ways to feed gooseberries
Some gardeners prefer the use of natural, environmentally friendly fertilizers for feeding garden and horticultural crops.
Fixed assets used by gardeners for a long time include:
- Infusions of herbs, vegetable tops, weeds. To prepare a solution, grass (5 kg) is mixed with ash and onion husks, taken in 1 glass. The mixture is diluted with a bucket of water, leaving to ferment for 7-8 days. Before use, the infusion is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10 and applied under the root or sprayed with a bush.
- Eggshells are used to reduce the acidity of the soil. 50 g of ground powder is added under each bush.
- Feeding with yeast. Yeast (1 kg) is added to warm water (5 liters), after which the mixture should ferment for several hours. Before watering, dilute with water (1:10). The disadvantage of this method is the absorption of significant reserves of potassium by yeast starter culture, which requires adding wood ash to the soil to replenish it.
- Potato waste - stimulates the awakening of the buds and the development of young shoots. Pour boiling water (10 liters) of cleaning (1 kg), leave the infusion to cool, having previously wrapped the container. After cooling, add ash (250 g) and water the bushes.
- How to properly use potato peelings in the country as fertilizer.
- Useful properties of eggshells for horticultural crops.
- Feeding with yeast.
- What are the benefits of feeding with yeast for various plants and how to use it.
- Fertilization with onion husks.
Organic substances, which form the basis of natural dressings, have a beneficial effect on the development and fruiting of gooseberries.
Top dressing gooseberries in the fall
Mandatory item in the autumn work schedule. Everything that has borne fruit must be fed. After all, the plant spent so much energy on the harvest, and winter is ahead - it needs to be restored. Choosing what - organic or mineral water - to feed the gooseberries in the fall, the gardener proceeds from personal preferences. But feeding with organic matter has a triple effect:
- Having mulched the near-trunk circle with a layer of humus or compost, the shrubs simultaneously feed, without fear of an overdose, and shelter the roots from frost.
- Organic mulching improves the structure of the soil, which is difficult to loosen under the bushes, and cannot be dug up.
- After sprinkling the mulch with ash, they provide an additional dose of potassium, while protecting the plant from pests, their larvae.
If there are no fertilizers of natural origin at hand, ready-made phosphorus-potassium complexes (without or with a minimum percentage of nitrogen!), Or separately phosphorus / potassium-containing agricultural chemistry products, are added. A large selection of specially equipped formulations for autumn feeding: from Kemir "Autumn" to those intended specifically for berry bushes. Bring in strictly the amount indicated by the manufacturer.
Important! Top dressing is carried out soon after harvesting, without waiting for the end of the summer season. The culture must have time to assimilate the necessary amount of nutrition in order to lay the buds for the next year, to prepare for wintering.
Fertilizers when planting gooseberries
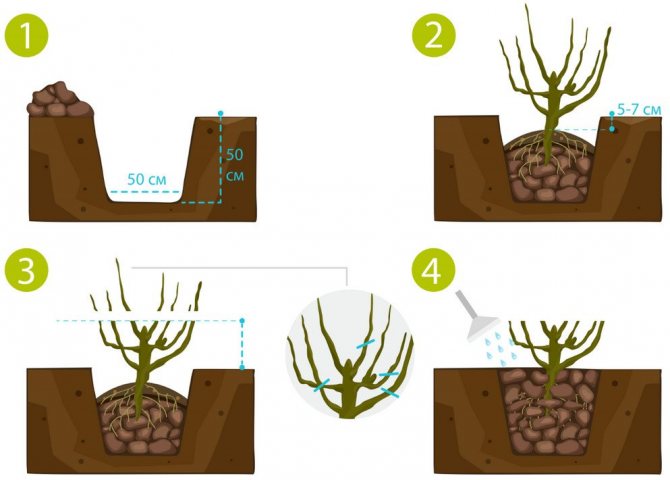
If you are going to plant gooseberries on your site, you need to abundantly feed the hole where the seedling will be placed.The planting process is considered a stressful situation for the crop, therefore, nutrient deficiencies reduce the chances of survival in new conditions. At the stage of preparing the planting pit, the following should be added to the soil:
- Compost (rotted foliage or manure) - 1 bucket.
- Wood ash - 1 glass.
- Double superphosphate - 2 tbsp. l.
- Fertilizers based on nitrogen.
Ash and organic matter can be replaced with complex triple fat. Mineral compositions are mixed with the soil to exclude burns that occur when the roots interact with fertilizing. With a high acidity of the soil, it is treated with dolomite flour at the rate of 200-300 g per m² or lime (400-500 g per sq. M).


After preparing the soil mixture, you can start planting the shrub. During the first year of life, the plant is mulched with compost and humus. If the substrate is poor, periodic application of organic complexes and folk remedies is allowed.
Treatment against diseases and pests
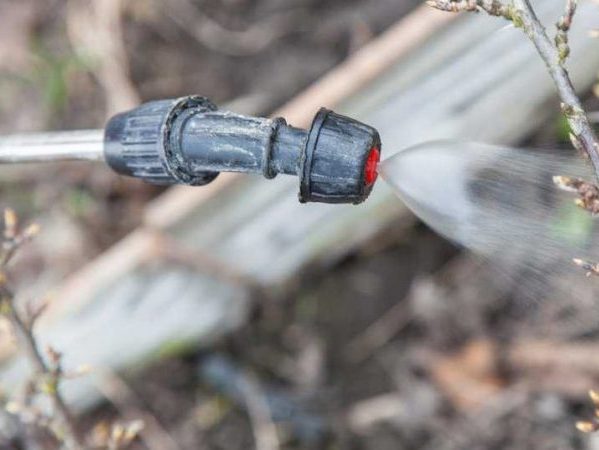


Gooseberry processing in autumn
Autumn is the time when not only plants are prepared for wintering, but also pests that parasitize them. They settle in the top layer of soil, fallen leaves, spoiled berries. If the gardener puts in order the earth in the near-trunk circle in time, loosens it, then these pests will not find a place for wintering.
But there are those that winter in the cracks of the trunks, the axils of the leaves, on the shoots. It is impossible to consider the threat with the naked eye - processing gooseberries in the fall will protect the shrub by destroying insects and ticks.
There are no problems of choosing how and how to process gooseberries in the fall: folk remedies are effective, and in stores - the range of drugs at an adequate price is almost unlimited. But still the most popular are:
- Bordeaux mixture (late autumn processing 3%);
- soap-ash solution;
- onion and garlic infusion;
- inkstone.
Each shoot is processed so that the liquid gets to all areas. The earth under the bush is also shed to destroy the remaining pests.
Spring make-up
In spring, the berry shrub needs strength for the development of shoots, foliage growth, and the formation of ovaries. At this time, the gooseberries are fed twice:
- in March-April - before the buds begin to bloom;
- in May - before flowering.
The first spring top dressing provides for the saturation of the soil with nitrogen-containing fertilizers. To do this, carbamide (15 grams) and nitrate (20-25 grams) are included in the nutritional mixture.
Features of safe storage and use of urea B.
During the formation of flowers, the most effective will be mixtures with a predominance of potassium and phosphorus (superphosphate, potassium salt, ash).
Potassium salt.
On acidic soils, the use of superphosphate is recommended only after limestone treatment, since superphosphate can increase the acidity of the soil.
To saturate the soil, 2 methods are used:
- dry top dressing, when the granules are scattered half a meter from the base of the bushes and embedded 30 cm deep;
- a liquid mixture, for the preparation of which minerals are diluted in water and filled with grooves dug around the plant.
After the introduction of nutrients, the bushes are watered abundantly and the earth is mulched.
What is soil mulching.
How to prepare gooseberries for winter in the fall in different regions
The schedule of autumn work on the plots depends on the region, climate characteristics, soil structure:
- Siberians prepare gooseberries for winter until mid-September, since by October 14, on Pokrov, snow is not uncommon in those parts.
- The central regions, the middle lane are managed until mid-October, when there is still time before frost.
- Southerners, where the longest season, have time to finish preparing for winter before the beginning of November.
- The southern regions with high temperatures and low rainfall are especially concerned about irrigation and organic fertilization (saline soils are more common there), introducing mineral complexes to a minimum.
- Summer residents in areas blown by the winds (where the flat terrain is flat), take measures to keep snow. After all, a snowdrift is the gooseberry's best protection from frost.
- The further north the gooseberry grows, the more reliable protection from frost is required.The harsh climate makes it necessary to postpone formative pruning for the spring, to do only sanitary before winter. This decision is due to the fact that it is easier to tie long flexible shoots, wrap them with covering material, lay them on the ground, pin them and fill them with peat, fallen leaves, sawdust for the winter. Wherever there is a plot with gooseberries, the main principle is to be in time before the first frost.
Replenishment of nutrients in summer
After the berry has faded, the formation and ripening of fruits begins. During this period, the feeding of the bushes is carried out at intervals of 2 weeks with a predominance of potassium and phosphorus in nutrient solutions. From organic fertilizers, slurry is used, dissolving 2 kg of mullein in 10 liters. water and insisting day. Before adding the mixture, the gooseberries must be watered abundantly.
Of the mineral fertilizers, the most effective are superphosphate and potassium sulfate.
Foliar feeding is carried out with complex formulations or ash.
Summer gooseberry support with beneficial additives helps the plant to bear fruit better, increases fruit size and improves berry flavor.
Pruning errors
Improper pruning will worsen the condition of the gooseberries, reduce yields:
- Radical pruning in the fall - over 50%. A haircut is always stress, after which the plant needs to recover, gain strength for wintering. If such a voluminous work is needed, then it is divided into autumn-spring.
- Cutting on the first frost is too late. The bush will not cope with the load.
- Removing one-year-old shoots - the main sources of fruiting - reduces yields. Only non-fertile old ones (from 5 years old) are completely removed.
Not paying attention to the recommendations to cut the gooseberry shoot at an angle above the bud outside the trunk, an inexperienced gardener is surprised in the spring: the shrub very quickly overgrown "inside".
Outcome
High-quality and timely feeding is a guarantee of a generous harvest and berry taste. Gooseberry is an unpretentious plant to care for, but it constantly needs nutrients. With proper care, one adult bush can bring up to ten kilograms of juicy and healthy berries. Gooseberry feeding begins immediately after the snow melts. At this time, the soil is wet, it will accept mineral and organic fertilizers well. Dry agrochemicals are scattered right under the bush, sprinkling a little with earth. Humus is spread around the roots.
Gooseberries respond well to urea (carbonate) and nitrate. Superphosphates are also needed by the plant, like nitrogen. It is advisable to apply organic fertilizers in autumn, and agricultural chemistry goes well in spring and summer. Also, gardeners use mixed organic-chemical fertilizers to provide gooseberries with everything they need as much as possible. However, do not forget about the treatment of diseases in plants, otherwise no additional feeding will bring results.