Breeding methods for gooseberries in autumn and summer
There are several ways to breed gooseberries. The choice depends on how many seedlings you need to get, the age of the mother bush, the growth of one-year and two-year shoots, and their development. It is just as important which variety you want to propagate - an existing one on the site, or a new one growing in another garden.
Layers
Gooseberries are propagated by horizontal, arcuate or vertical layers. This method is effective, because along the entire length of the shoot, near the buds, there are root rudiments. With constant humidity, they easily wake up and start growing.
Desirable age of uterine gooseberries is from 3 to 5 years.
The soil around the bush must be prepared in advance. It is weeded, dug to a depth of 10 cm, humus or rotted manure is added, mixed with the top layer of soil and leveled.
Horizontal layering produces a large number of branches. With this reproduction, the fruiting of the gooseberry does not stop.
Strongly developed one-year and two-year shoots are suitable for layering. Older branches can also be used, but there will be fewer seedlings. To awaken the kidneys, the tip must be pinched.
- grooves 3 cm deep are made perpendicular to the base of the bush;
- the selected shoot is placed on the bottom, slightly pressing it into the ground;
- fixed in several places with long metal brackets or wooden slingshots;
- the ground must be constantly moist;
- after the buds awaken and new shoots grow 15 cm, they are spud to a height of about 5 cm;
- when the growth increases by another 15 cm, re-hilling is carried out. The total height of the land mound should not be higher than 10 cm above the soil level.
It is necessary to keep the soil moist; in the hot summer, the land around the bush is mulched.
In the fall or spring of next year, the shoot is carefully dug up, the grown shoots are separated, leaving a small part of the parent branch on each.
- seedlings with underdeveloped roots are discarded;
- with weak roots planted for growing on a separate bed;
- with a strong growth of roots, they are planted in a permanent place.
Arcuate layering is used if it is necessary to get 2-3 highly developed bushes.
The difference between this method and propagation by horizontal layers is that only one seedling is obtained from one shoot, with a developed root system and lateral branches. This makes it possible to transplant it immediately to a permanent place, and get the harvest already in the second year after transplanting.
Shoots are rooted in spring and summer, and in autumn they are separated from the mother plant. You can root the shoots of the current year. They are pinned in June and planted the next spring.
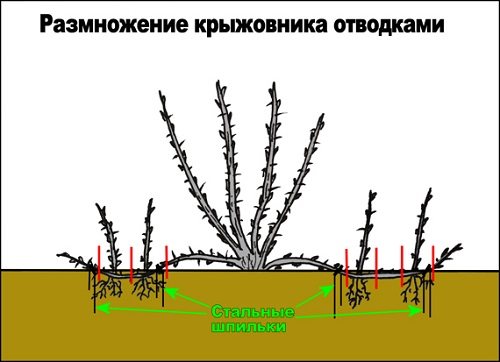
Gooseberry propagation scheme by layering
- dig a hole 10 cm deep;
- the branch is carefully bent and placed in the hole so that the bud, near which the roots will grow, is in the middle of the hole;
- fix with a parenthesis;
- fall asleep with fertile soil, forming a mound of about 10 cm;
- the end of the branch should remain above the ground, 35-40 cm high;
- erect a peg, I tie the shoot so that it is in an upright position;
- pinch the top to enhance the branching.
In September, the shoot is cut off from the mother bush, but transplanted only at the beginning of October.
Gooseberries older than 4-5 years are propagated by vertical layers. Simultaneously with reproduction, the bush is rejuvenated. The gooseberry will not bear fruit this year and next.
Technology:
- small, underdeveloped shoots are cut out completely;
- the remaining branches are cut to a height of 20 cm, this stimulates the growth of shoots from the lower buds;
- when the shoots grow 25 cm, and their base is slightly lignified, hilling young shoots is carried out to a height of 5 cm;
- after three weeks, they huddle again, increasing the height of the mound by 5 cm.
Falling asleep the bushes, you should make sure that the new shoots remain at some distance from each other. This is necessary so that the roots are intertwined as little as possible, and not damaged during transplantation.
In autumn, the soil is carefully raked off, the resulting seedlings are separated and transplanted to a permanent place.
You may also be interested in the following articles about gooseberries:
Cuttings
This method allows you to get a lot of planting material. It is practiced when it becomes necessary to diversify the gooseberry varieties in the garden, or if the species you like grows in another area.
Lignified cuttings are prepared using shoots growing from the base of the bush. You can cut off the top of the branches.
The mother bush should not be more than 8-10 years old, because cuttings cut from an old bush root poorly. The bush must be healthy, not damaged by pests.
The event is held in early autumn.
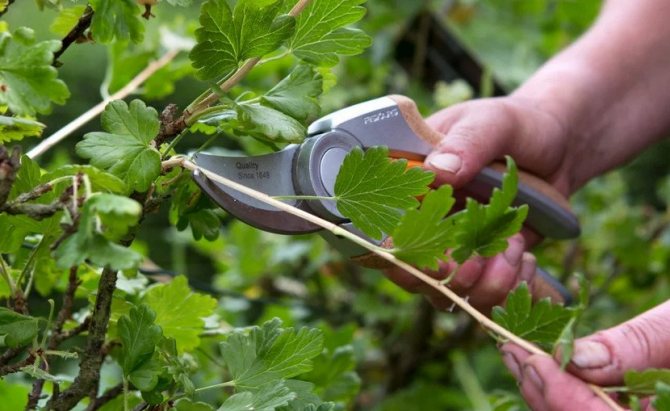
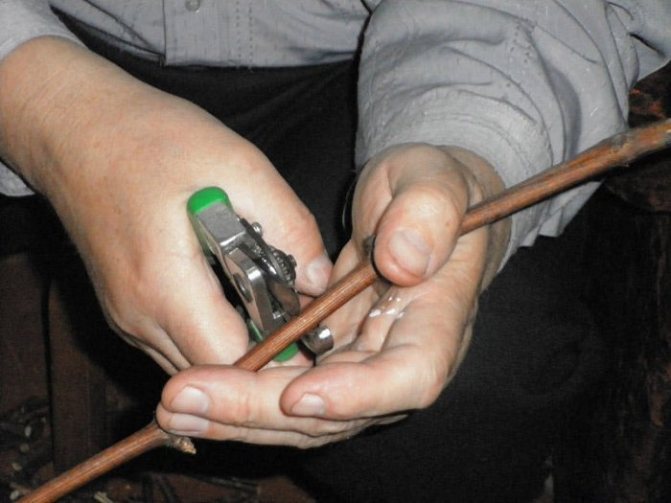
The part of the stem for grafting should be 15-20 cm long and have at least 4 buds. A cut is made under the lower one at a slight angle, retreating 1 cm. The distance from the upper kidney to the cut should also be 1 cm. Cut straight.


Preparing gooseberry cuttings for propagation
- prepare the bed in advance by introducing compost into it;
- cuttings are planted so that only one upper bud remains above the ground;
- planting is carried out with a line, the distance between seedlings is 15 cm;
- place the cuttings at a slight slope;
- for the winter they are insulated with leaf litter or agrofibre.
Follow-up care consists of maintaining soil moisture, weeding and loosening. By the fall, one shoot grows, the next spring it is cut off, leaving two buds.
Features of cuttings in summer
You can root gooseberry cuttings in summer or September. Green shoots are distinguished by good survival rate and tolerate changes in growing conditions more easily than lignified specimens.
They are covered with a thick cambium (a layer of plant cells), which promotes rapid division and green mass gain.
In addition, combined cuttings, which include lignified branches with green shoots, can also be rooted in the summer.


To propagate gooseberries in the summer, it is important to provide them with the following conditions:
- The optimal concentration of nutrients and cambium in the cuttings. For this, the mother bush is carefully fed with phosphorus and potassium compounds. At the same time, it is better to refuse the use of nitrogen and urea, since they impair rooting. To provide the necessary supply of food, 2 weeks before cutting the shoot, it is pulled with a wire in the lower part.
- Correct temperature range. The soil temperature should be + 4… + 5 ° C higher than the air temperature. In such conditions, the rapid formation of the root system occurs, while the growth of green mass slows down. The air in the greenhouse or greenhouse should be + 25… + 30 ° C.
- Moisture and good soil breathability.
- Introduction of root growth stimulants into the soil. They are intended for better rooting of seedlings.
A greenhouse for summer gooseberry planting is set up in a shaded place.If it is located in a garden, you can choose a shade from a large tree or an area from the north of the house. It is important to isolate the greenhouse from direct sunlight as this will cause moisture to evaporate from the leaves.
The timing of gooseberry cuttings in summer is determined by the end of the shoot growth period. This happens in the middle of summer, when the branches no longer lengthen and lose their elasticity.
2 weeks before the procedure, you need to wrap the shoot in the lower part with wire to retain the supply of nutrients and improve rooting in the future.
Further from the bush, several green branches are cut off, directed to the side, and not up.
Shoots are divided into several cuttings 15-25 cm long. The main thing is that they have from 2 to 4 internodes. The upper elements are not suitable for rooting, as they lack the necessary concentration of nutrients.


Cut specimens are immersed in the growth promoter for ½ the length. If a heteroauxin solution is used, it is important to follow these rules:
- The substance is poorly soluble in water, therefore, before processing, the powder must be diluted with alcohol, and then stirred with water.
- The shank must be kept in a container with the drug for 24 days. In this case, the ambient temperature must not be allowed to drop below + 24 ° C.
- Finally, the cuttings are rinsed with clean liquid to rinse off the growth promoter.
Before planting, the substrate in a greenhouse or greenhouse is watered abundantly. First of all, a manganese solution is used, and then water.
After rooting cuttings in the summer, they need to provide the following care:
- Spraying. Since gooseberries need abundant watering, it is better to organize an aeration system that will automatically spray the area at set intervals. If the cutting is covered with gauze, the frequency of spraying is reduced.
- Watering. Performed as the topsoil dries out. The optimum humidity level is 80-90%.
- On 3-4 days from the moment of planting the seedlings, the beds are watered with succinic acid, which contributes to the formation of the root system.
The roots will begin to grow in 14 days from the moment they are placed in the soil. During this period, you can fertilize the land with complex compounds.
The best time to breed shrubs
When to propagate gooseberries depends on the method chosen.
Reproduction by layering is carried out in early spring, when the earth warms up. It is important to do this before the start of the growing season.
Autumn is suitable for rooting lignified cuttings, and green ones are planted in a greenhouse throughout June and early July. Branch cuttings are carried out in the same period.
The division of the bush or the separation of a perennial branch from it is carried out before the buds swell, or after the end of leaf fall.
High-quality seedlings can only be obtained from a healthy, developed bush. The plant must be prepared in advance: cut out all sick and weak branches, feed it, carry out preventive treatment against diseases and pests. Next season, the gooseberries will be ready and will be able to multiply correctly and quickly.
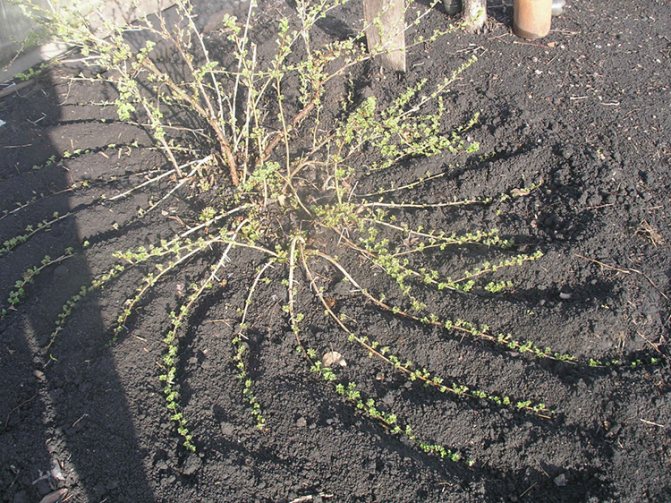


This undersized prickly shrub is found in almost every garden where berry crops are grown. In order to increase the gooseberry planting area or acquire a good variety, it is not necessary to purchase a seedling in the store. With a healthy plant, getting a new bush is easy.
Generations of gardeners have developed a lot of effective and simple methods for breeding gooseberries at home:
- seeds;
- dividing the bush;
- undergrowth;
- green and woody cuttings;
- horizontal and arcuate layering.
Each owner chooses a suitable method for himself based on the season, the age of the bush, suitable for dividing and his own skills.


The most reliable technologies are those that do not require the separation of the planting material from the bush before root formation.Because, in this way, the future seedling, in addition to its own strength, receives nutrition from the mother plant.
Disembarkation to a permanent place
Regardless of the time of harvesting cuttings, around the beginning of May, the optimal period for rooting of seedlings begins. By this time, not only a dense root mesh should appear on the shoots, but also several young leaves. Rooted cuttings are planted in the early morning or late evening, in dry and cloudy weather. Best suited for this is a well-lit part of the site, protected from drafts, with moderately moisture-absorbing sandy loam soil.
Also find out what to plant next to gooseberries.
Gooseberries should be planted in a row or hole way, to a depth of 10-15 cm. For compact varieties, the distance between neighboring plants should be about 1 m, for spreading plants it is increased to 2-2.5 m.
Before planting cuttings, the soil on the site should be well fertilized. To do this, add 10 kg of humus, 100 g of wood ash, 50 g of superphosphate and 40 g of potassium sulfate to 1 m² of beds, and then mix everything thoroughly with the top layer of soil.
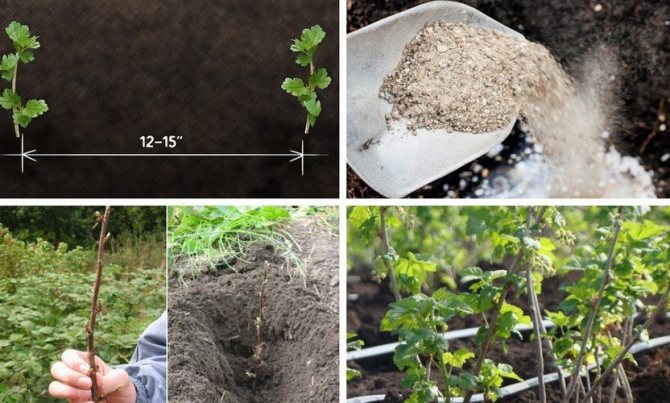


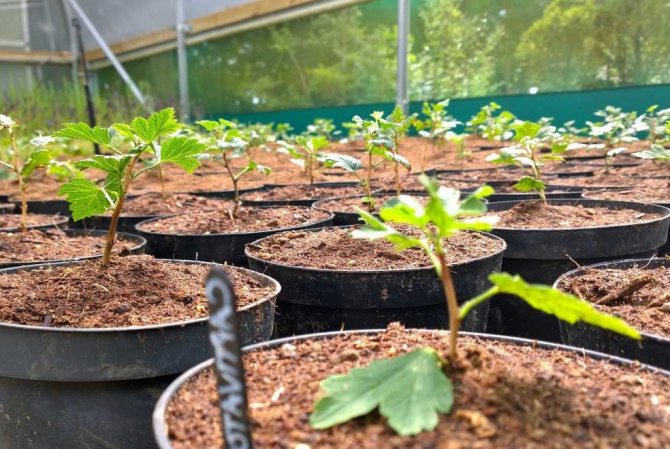
Growing gooseberries by cuttings is an effective, simple and low-cost way to create a highly productive garden on a site. Just one adult bush makes it possible to plant up to 10 young plants, while retaining all the original varietal and production characteristics of the maternal form. However, not many succeed in using effectively cuttings, so often inexperienced gardeners have to be content with purchased planting material.
Reproduction by layering
A simple and effective way that does not require a lot of gardening skills. Its big plus is that it does not injure plants during the growing season. It is produced directly on the bush without taking up much space.
Reproduction by layering is more popular in the southern regions. Sap flow in this climatic zone begins early, young stems grow to the required length by the end of May - beginning of June, root easily and can be used already for the autumn planting of the current year.
How to grow new gooseberries with horizontal layers
This method is used when you need to get a large number of young gooseberry seedlings in one season. For example, for sale.
Reproduction by horizontal layers is carried out in the following order:
- on the gooseberry bush, healthy, strong shoots are chosen, which have formed in the current year;
- depending on the size of the bush, layering can be rejected up to 5-7 pieces;
- it is important not to damage the plant during manipulations, an injured cut in the ground can rot or get sick;
- grooves are dug under the shoots with a depth of no more than 10 centimeters so that the branches can be laid in them, bending to the ground;
- shoots are lowered into grooves and pinned to the ground with wire or wooden hooks;
- the grooves are periodically moistened, making sure that the layers do not rot;
- then the shoots will take root and vertical branches will sprout from them;
- when they rise above the depressions, the grooves are covered with humus;
- after 10-14 days, when the branches rise above the ground again, the places of the layering are sprinkled, sprinkling with an additional layer of fertile soil;
- watering to rooted cuttings should be supplied as needed;
- when the leaves fall off, the cut is cut from the bush, the sprouted vertical branches are separated and planted in permanent places.
How gooseberries reproduce
Gooseberry is a very popular horticultural crop. With proper care, the shrub yields abundant tasty fruits, multiplies very easily, so usually gardeners densely plant the plant on the site using proven propagation methods.
There are several ways to propagate gooseberries.
- By seed method - it is not difficult to propagate a plant from seeds, but the method is not very popular. The fact is that the characteristics of the parent variety in the new bush are not preserved.
- By cuttings - both green and lignified cuttings are used for rooting. The method is most popular among gardeners, since it practically guarantees the successful rooting of a new plant.
- By dividing the bush - this method makes it possible to propagate overgrown shrubs over the site.
- Layers - long flexible gooseberry shoots are well suited for horizontal or apical rooting in the ground near the mother bush.
Gooseberries can be propagated by offspring at the roots and by grafting. The choice of a particular method depends only on one's own preferences and some external conditions.
Gooseberry propagation by cuttings
The method is as time consuming as it is interesting. It is associated with mechanical damage to the aerial parts of plants, therefore it is important to take care of a high-quality instrument and its proper disinfection.
General rules for grafting:
- the handle should have at least two dormant buds and two leaves above them;
- the lower cut of the cutting is made obliquely, the upper one - horizontally;
- effectively treat cuttings with a growth stimulator;
- it takes an average of one month for root formation.
Propagation by green cuttings
For this method, young shoots of the current season, which have not yet had time to overgrow with tree bark, are suitable.
Cuttings of gooseberries with young shoots are carried out in the following sequence:
- in early July, cuttings 12-15 centimeters long are cut from the upper branches of the plant;
- there should be 6-8 leaves on a cut branch;
- the lower third of the cutting is immersed in a solution of any growth stimulant (you can use a solution of heteroauxin in a ratio of 150 g per liter of water) and incubated for up to twelve hours;
- having stimulated young cuttings are planted under a greenhouse in fertile soil, deepening three centimeters;
- the distance between the branches is kept at 5-7 centimeters;
- the greenhouse is watered, maintaining a high temperature in it, but not higher than 30-35 C;
- it is good if there is a place for planting cuttings in the greenhouse;
- two weeks later, they are fed with liquid nitrogen fertilizers to stimulate root formation;
- the greenhouse is not removed until the end of the growing season;
- if cuttings were planted in open ground, they are covered for the winter, like all berry ones;
- grafting ends in spring, when young branches are planted in new places;
- when planting, they need to be buried so that only three buds remain above the surface.

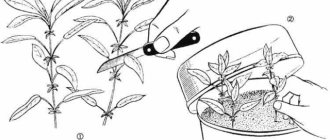
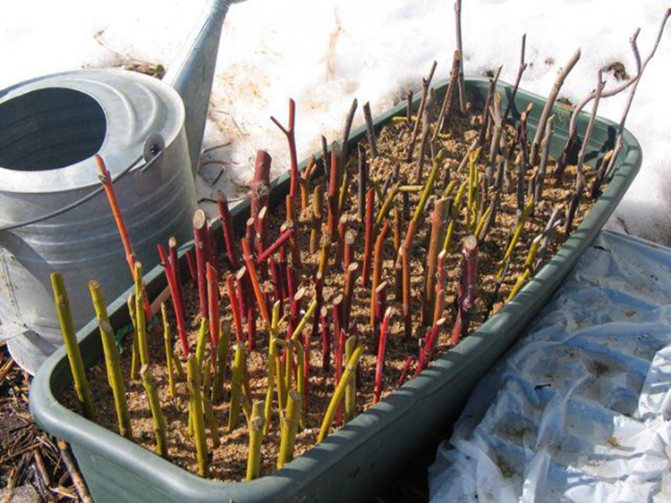
Propagation by lignified cuttings
Less reliable compared to cuttings with greens - the older the shoot, the less likely it is to take root. In the middle lane or in the south of Siberia, this breeding method will be more effective than in the southern regions.
Reproduction begins at the end of the garden season. The plant is not injured, in the season of greatest danger of infection with viral and fungal diseases.
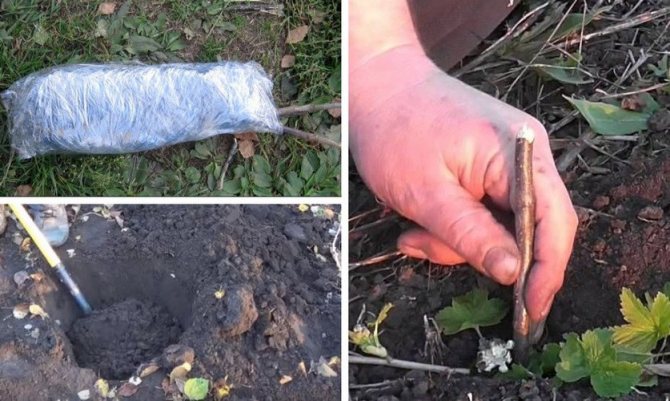
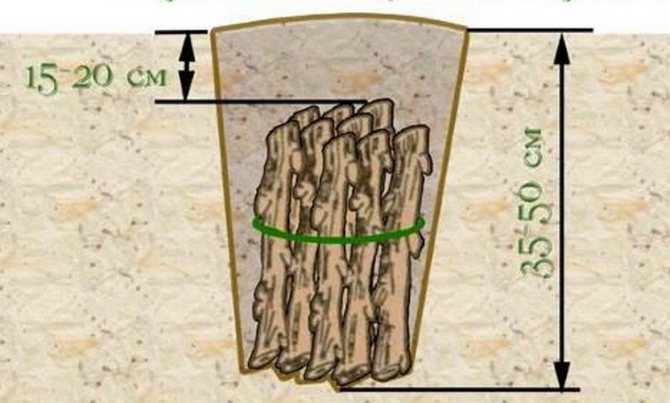
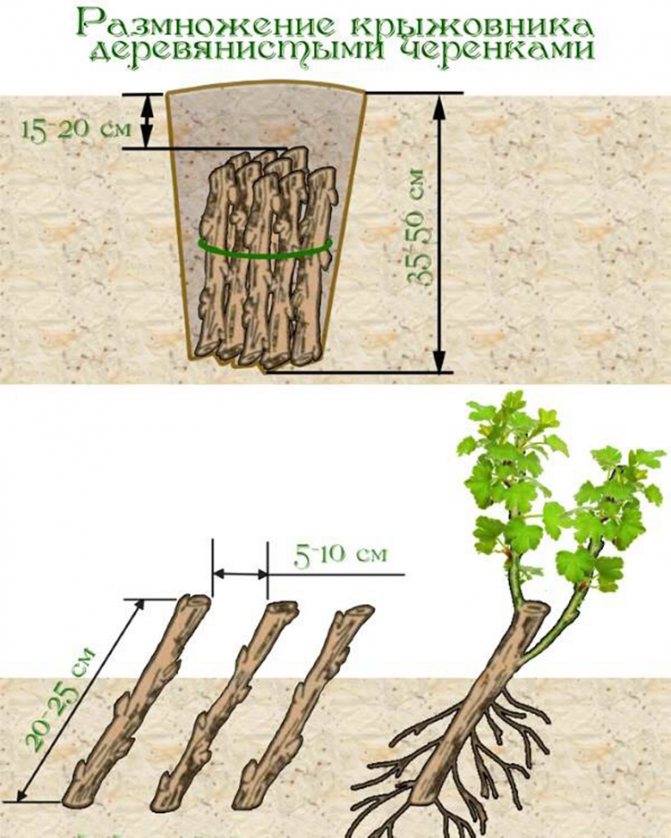
Reproduction by lignified cuttings is carried out in mid-September (in the south, this can be done in "Indian summer" - until October):
- Cuttings are cut from woody shoots of the current season, 15-20 centimeters long;
- Then they are tied into a bundle with a piece of fabric, without pulling it over;
- For one bundle, from 10 to 20 branches are harvested;
- A bunch of cuttings is placed vertically in a container with a moistened mixture of sand and peat and covered with a layer of 20-25 centimeters on top;
- A bucket with cuttings is stored for about one month indoors at above-zero temperatures, periodically moistening;
- A kind of influx is formed at the ends of the cuttings;
- A month later, the cuttings are separated and, having shifted with wet sawdust, are stored until spring;
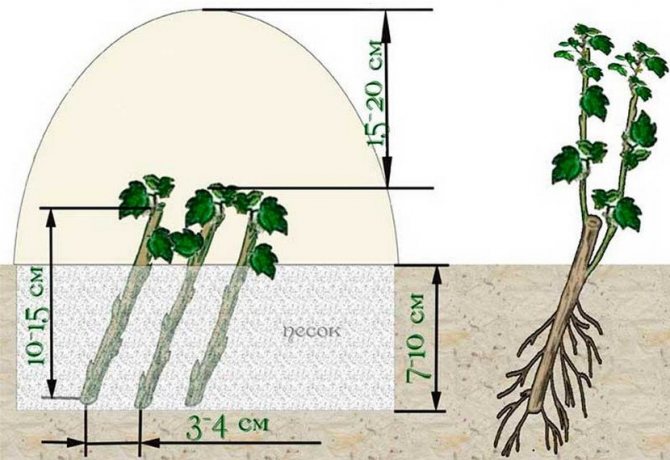
- In spring, cuttings are planted at an angle, keeping a distance of 5-10 centimeters;
- Two or three kidneys are released above the ground;
- In the fall, already rooted gooseberry twigs are planted in permanent places.

Using combined cuttings for propagation of gooseberries
This method is used in the spring, when the shoots of the current year have grown by 10-15 centimeters.
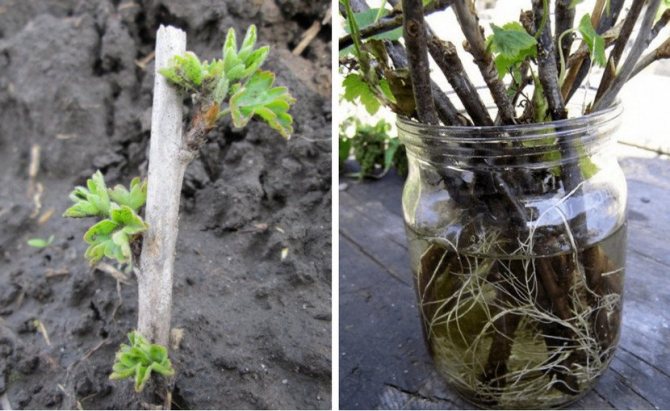
- They are cut with a small section of last year's ligneous shoot (3-5 centimeters) and placed in water;
- In a low concentration, a preparation for stimulating growth can be dissolved in a container for germination (approximately 1 to 10 of the dosage for soaking);
- When new roots are formed, the cuttings are planted in a permanent place - the planting is autumn.
The method is good in that it allows you to immediately judge the degree of development of the cuttings, observing the formation of the root.


Gooseberry propagation by perennial branches
Perennial branches that remain after spring pruning are also suitable for germination:
- three-year-old shoots are cut in half of the growth;
- grooves are prepared with a depth of 20-30 centimeters, strewing their bottom with fertile soil, well-rotted compost or a mixture of sand and peat;
- the cuttings are placed in the grooves obliquely, leaving a one-year growth at the top;
- covered with mulch soil on top and watered abundantly;
- moisture is covered on top with another layer of soil and slightly compacted the planting site;
- two weeks later, a liquid top dressing is introduced from azofoska or nitroammofoska;
- cuttings are moved to the place of permanent planting in the fall, when they have formed their own root system.
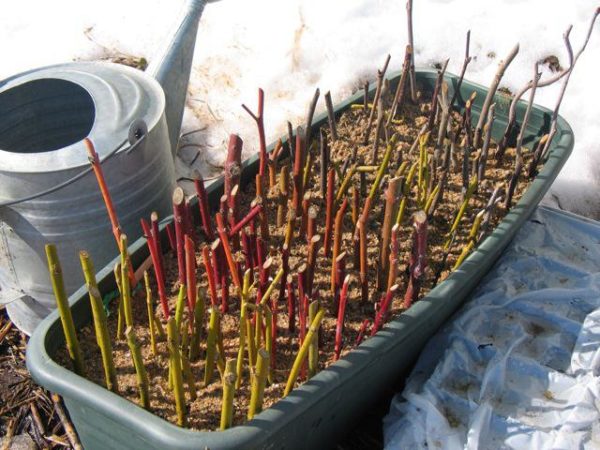
Features of cuttings in spring
Breeding gooseberries with cuttings in spring is suitable for those gardeners who do not have time to prepare and care for shoots during the winter. If you adhere to all the rules, you can plant a highly productive shrub that will delight you with a good harvest for a long time. Cuttings are carried out in early spring before budding.


When selecting planting specimens, it is worth considering a number of nuances and carefully assessing their condition. If there are traces of disease or parasite activity on the surface of the branches, it is better to exclude them. Otherwise, the cuttings will not be able to form a stable immunity.
It is also important to study the structure of the bush. For cuttings in the spring, you can use green or semi-lignified shoots, the age of which does not exceed 1 year. The healthy material has a brownish green tint and elastic fabrics.
Cuttings can be cut from the tops of the branches. The main thing is that they have a length of 25 cm and contain from 4 to 6 healthy kidneys.
Having decided on the specimens for planting, you need to move them to the refrigerator for 24 hours. Then you should cut at an angle of 45 ° and put the cuttings in a container with clean liquid for 4-6 hours.
The rooting procedure is carried out according to the same principles as when germinating autumn material. When several healthy roots appear on the seedlings, they can be dived into separate pots or plastic cups of a suitable size.
If you are going to transplant cuttings into open ground, you should provide them with abundant care. The substrate should be watered regularly, but in small portions, in order to exclude a sharp change in soil moisture.
After 14 days from the moment of moving into the soil, the seedlings are fed. For these purposes, complex formulations based on mineral and organic components are suitable. You can buy top dressing at a gardening store or prepare it yourself.


If green cuttings are used, the propagation principle will be as follows:
- Cutting young shoots is started in the morning or afternoon with cool and humid weather.
- With a sharp knife, the branch is divided into cuttings of 8-15 cm.
- Then the cuttings are placed in a manganese solution or container with a growth stimulator. The optimum processing time is 24 hours.
- Cuttings are washed with water and kept in pots.To speed up the formation of the root system, they can be covered with a plastic bag or cling film. The shelter is periodically removed to allow the plant to ventilate.
- After rooting, the cuttings are moved to open soil.
During the first days, the seedlings are fed with urea. The substance promotes the rapid growth of roots and the adaptation of gooseberries to new conditions. Subsequent dressings are carried out with a composition based on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, observing the proportions of 1: 3: 3.
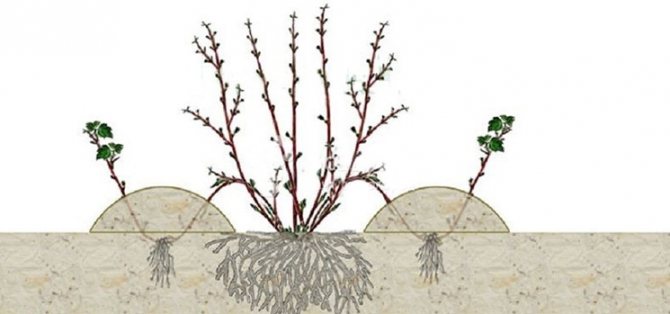
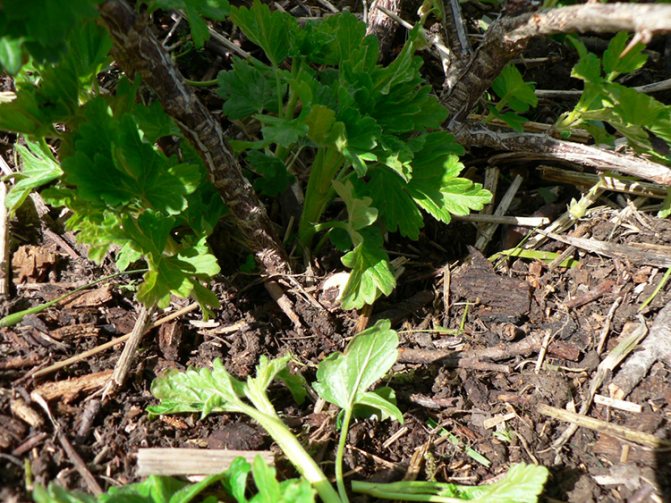
Reproduction by shoots
This is the most "humane" and non-traumatic way of breeding gooseberries. It consists in the timely planting of young growth naturally formed around the bush.
It is best carried out in the fall at the end of seasonal work. Young shoots are carefully separated from the mother plant and transferred to a new location. The area from which the growth was dug is best covered with well-rotted compost in order to improve the composition of the soil under the old bush.
Important: if large berries are expected from the bush, it is necessary to systematically remove young shoots. An overgrown bush is degenerating and sick, and harvesting from it is a real torture. When the owner is not going to plant the growth, it can simply be destroyed or donated.


If the gooseberry grows reluctantly, the growth of young shoots for reproduction can be provoked with simple agronomic techniques:
- in spring, the land around the bush is well loosened, fluffed and enriched with mulch;
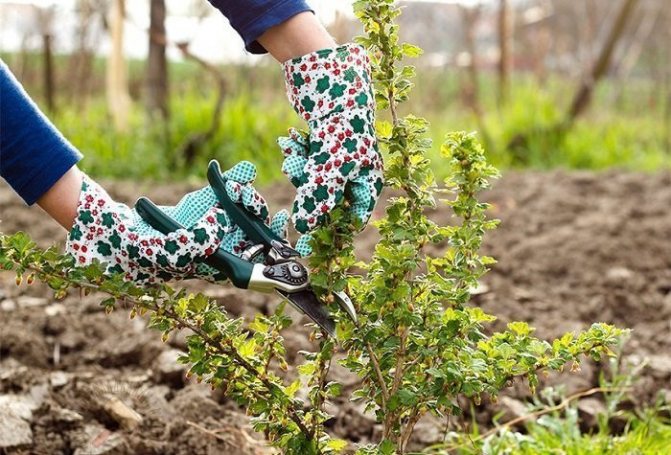
- cut the gooseberries;
- aryk is dug around the bush and plentiful watering is established;
- when the young shoots grow the bush, they spud, covering them with a third layer of soil (you can add the brought compost on top);
- the shoots are pinched for better branching, removing three to five leaves from above;
- the root system of young shoots will be formed in the fall;
- at the discretion of the owner, the shoots can be planted in the winter, or you can wait for the next spring.
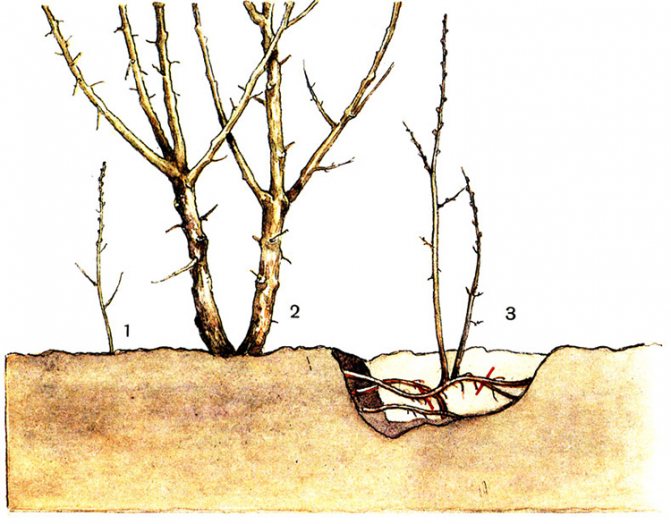

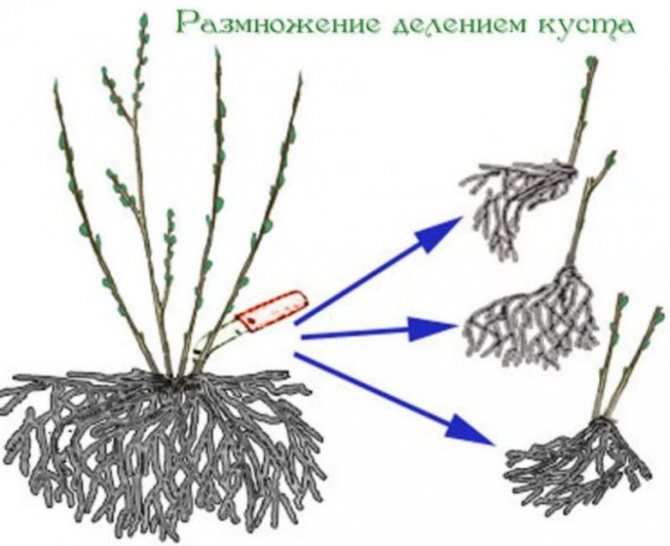
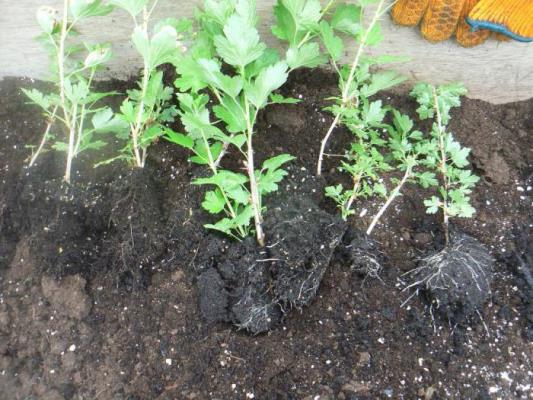
Reproduction by dividing the bush
A simple method is used when the owner decides to transplant the plant to another place. Or in the case when the bush has grown.
In the place of germination of young shoots, additional roots are always formed, which are able to support the life of the branch if it separates from the mother plant.
You can divide a bush of any age if it has young shoots. But for plants that have been growing in one place for five or more years, such a procedure is indicated to increase the yield and size of berries, as well as to renew the soil and rejuvenate the root system.
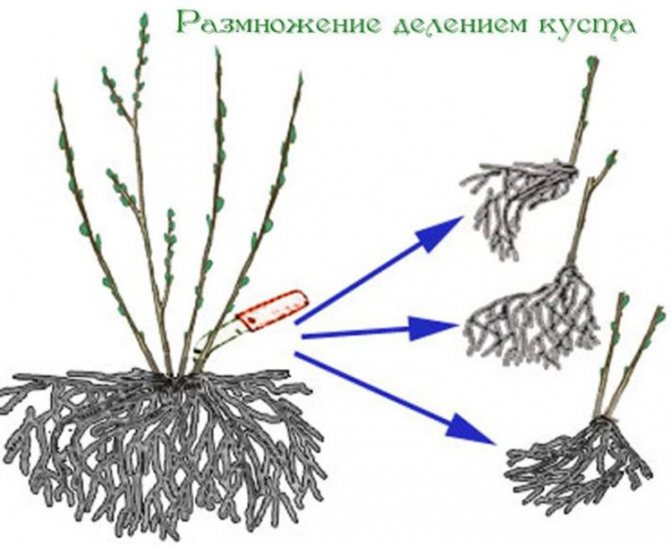

An adult bush is divided in the fall after the termination of the growing season, or in the spring before it begins. The plant is dug up and disassembled into separate shoots, which have their own root, which are immediately planted in the garden. The division must be made at least three or four parts.
If you carry out this procedure in the fall, then the chances that young bushes will begin to bear fruit as early as the next season will be greater.
All breeding methods for gooseberries are very simple. To master them, you just need to start working in sequence. The knowledge gained from reading this article will allow you to regularly rejuvenate plants and share good varieties with other gardeners.
The propagation of gooseberries by cuttings (and not only by them) in the fall is explained by the vegetative processes of the plant. It is hardly possible to get a viable seedling with a developed root system and able to easily survive the first winter in a couple of weeks. Despite the fact that the berry culture itself is unpretentious and takes root quickly.
Content:


Benefits of breeding gooseberries in the fall
There are several reasons to propagate and immediately transplant gooseberries to a new place in the fall.
- Early onset of gooseberry vegetation in the spring.You may simply not have time to cut the cuttings before flowering. Shoots during flowering and fruiting are not suitable for reproduction, since the rooting process will take a long time, and the cuttings themselves will require careful maintenance, which is difficult to organize in the midst of sowing work.
- When the gooseberry is propagated by layering, it is by autumn that seedlings will be ready for transplantation.
- It is also better to divide the gooseberry bushes in the fall, when they are in the dormant stage.
In autumn, as a rule, there is enough moisture and there is no sweltering heat. Therefore, the seedlings have every chance of successful engraftment.
So, to summarize
Gooseberries take root easily. Summer rooting with green cuttings produces many good seedlings. It is necessary to build a greenhouse in a shady place, pour sand and light soil into it, put an automatic sprayer.
Cut the cuttings, after preliminary ringing, from the middle and lower parts of the shoot growing out of the bush to the side. It is imperative to keep the cuttings in a root growth stimulator. Plant them in the ground at an angle, cover with gauze. Spray and water frequently. When the first leaves from the buds appear, reduce watering.
Breeding methods for gooseberries in autumn
It is difficult to say that any breeding method is exactly autumn. As a rule, in autumn there are either the initial or final stages of work.
- When the gooseberry is propagated by layering in the fall, the prepared seedlings are separated from the mother bush, examined and planted on separate ridges for growing or in a permanent place. It depends on the degree of development of the root system and the method that was used to obtain layering.
- If you want to breed gooseberries with cuttings, then autumn is the time for harvesting them, as well as for planting already prepared seedlings in open ground.
- Dividing the gooseberry bushes is probably the only method that is performed in the fall, although some work will still have to be done during the year preceding the planting of the bushes.
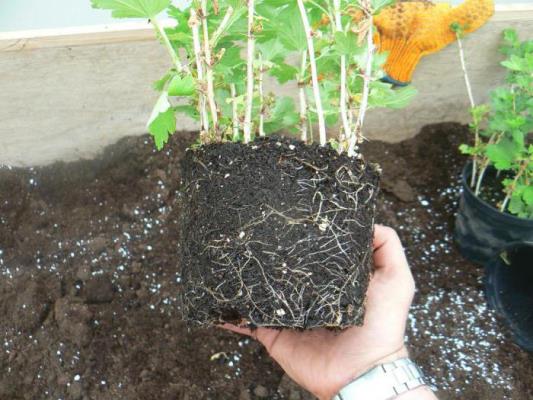


It is worth taking a closer look at how to properly propagate gooseberries in the fall, and what preparatory measures need to be taken to get healthy seedlings.
How can you propagate gooseberries without thorns?
Selective varieties of gooseberries without thorns are very popular; it is easier to harvest from such a bush. You can propagate gooseberries without thorns by all standard methods, but cuttings bring the best results. In the process of breeding a plant without thorns, it is especially important to monitor the fertility of the soil and often feed the shrub with organic matter and mineral fertilizers.
Advice! Since the gooseberry without thorns has low self-pollination, it is not recommended to plant it alone, it is better to place the bush near other plants.